Effects of Different Planting Densities of Solanum nigrum L. on the Growth and Cadmium Uptake of Young Grapevines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
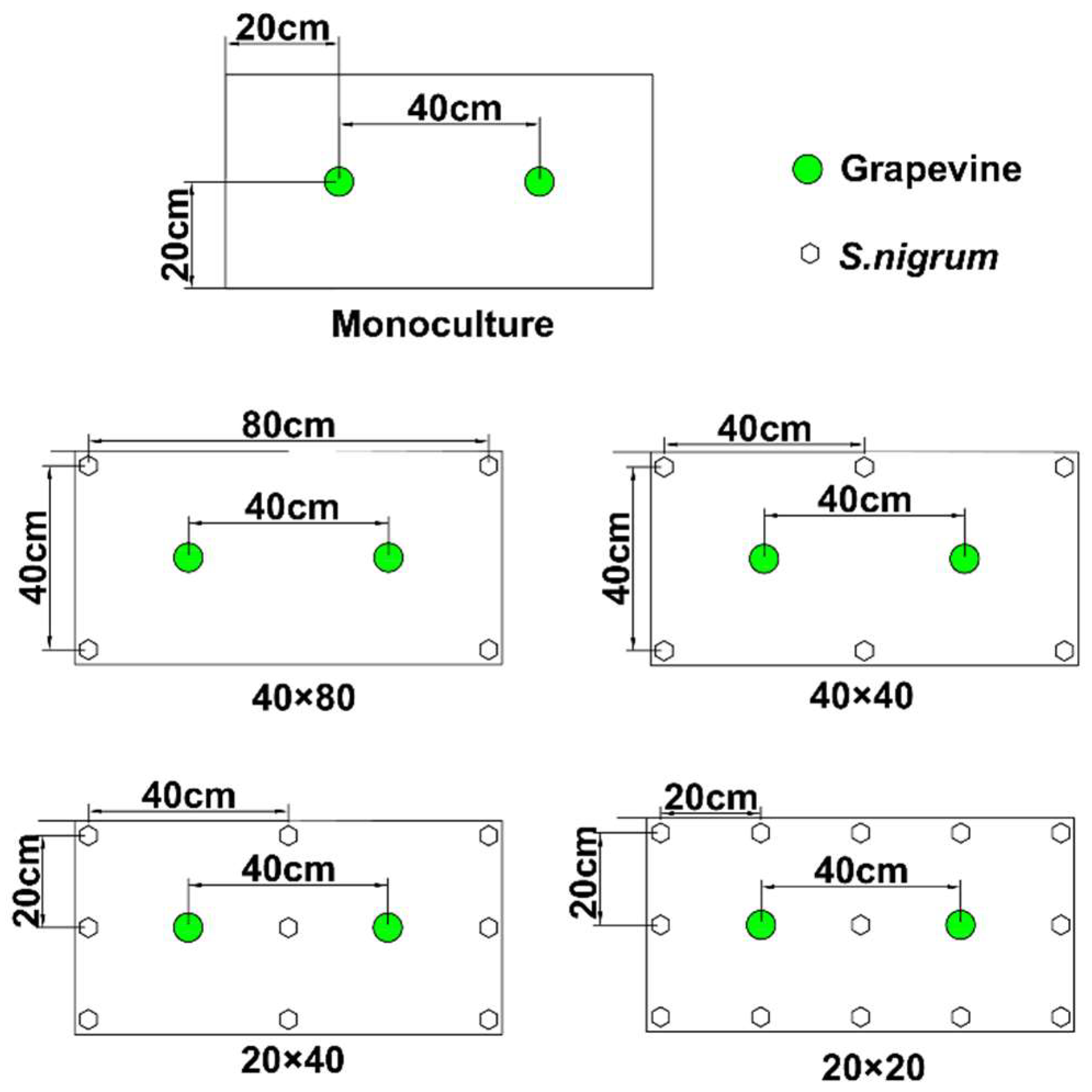
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Biomass
3.2. Photosynthetic Pigment Contents
3.3. Gas Exchange Parameters
3.4. Antioxidant Enzyme Activity
3.5. Cd Content in Plants
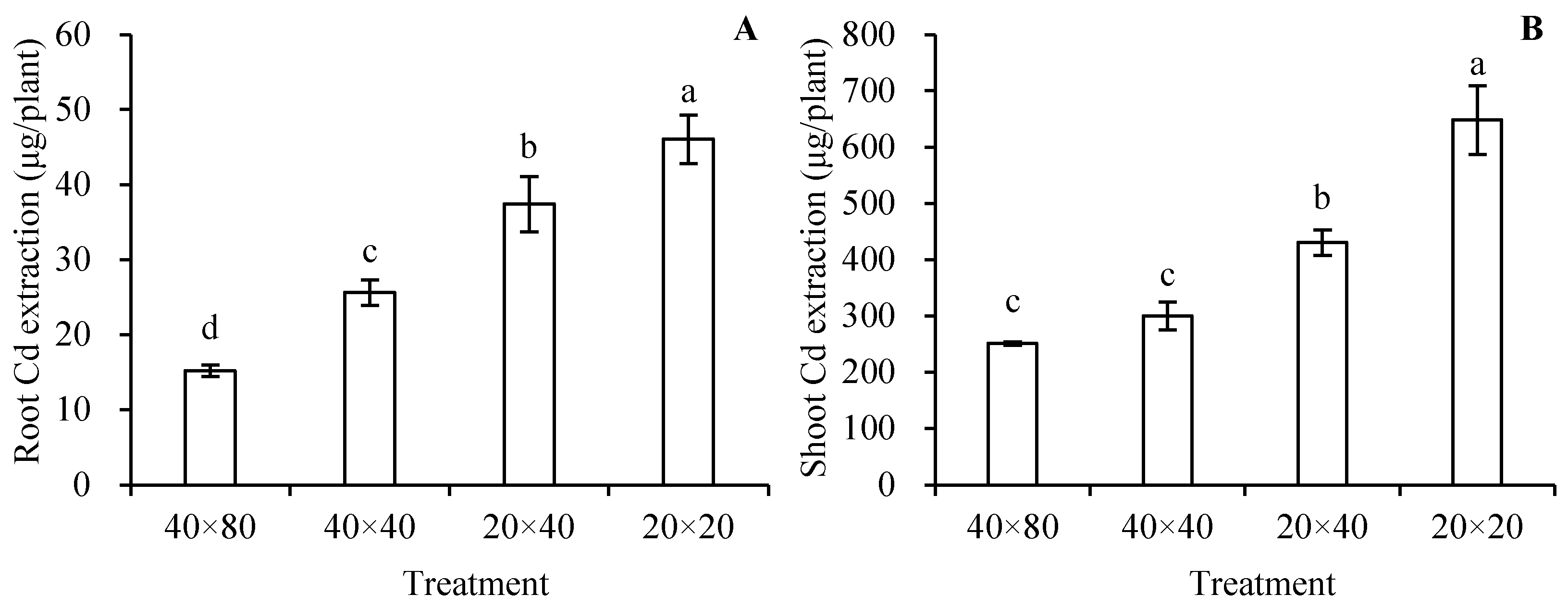
3.6. Cd Extraction in S. nigrum
3.7. Chemical Forms of Soil Cd and Soil pH
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bouida, L.; Rafatullah, M.; Kerrouche, A.; Qutob, M.; Alosaimi, A.M.; Alorfi, H.S.; Hussein, M.A. A review on cadmium and lead contamination: Sources, fate, mechanism, health effects and remediation methods. Water 2022, 14, 3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, P.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kandasamy, J.; Naidu, R. Cadmium sorption and desorption in soils: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 42, 489–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafzadeh, S.; Leung, D.W.M. Development of cadmium-safe crop cultivars: A mini review. J. Crop Improv. 2016, 30, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Lauria, G.; Carocci, A.; Catalano, A. The effects of cadmium toxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasafi, T.E.; Oukarroum, A.; Haddioui, A.; Song, H.; Kwon, E.E.; Bolan, N.; Tack, F.M.G.; Sebastian, A.; Prasad, M.N.V.; Rinklebe, J. Cadmium stress in plants: A critical review of the effects, mechanisms, and tolerance strategies. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 52, 675–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, E.; Cavani, L.; Mazzon, M.; Marzadori, C.; Quartieri, M.; Toselli, M. Fourteen years of compost application in a commercial nectarine orchard: Effect on microelements and potential harmful elements in soil and plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.; Zhuo, H.; Kang, A.; Fang, Z.; Zhu, M.; Dong, M.; Wang, J.; Ren, L. Contamination, risk assessment and source apportionment of the heavy metals in the soils of apple orchard in Qixia City, Shandong Province, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2022, 36, 2581–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, C.; Ashraf, M.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Ahmad, P. Responses of nitric oxide and hydrogen sulfide in regulating oxidative defence system in wheat plants grown under cadmium stress. Physiol. Plant. 2020, 168, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Saleem, M.H.; Alsafran, M.; Jabri, H.A.; Mehwish; Rizwan, M.; Nawaz, M.; Ali, S.; Usman, K. Response of cauliflower (Brassica oleracea L.) to nitric oxide application under cadmium stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 243, 113969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavanya, M.B.; Viswanath, D.S.; Sivapullaiah, P.V. Phytoremediation: An eco-friendly approach for remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soils-A comprehensive review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2024, 22, 100975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitra, S.; Hossain, A.; Brestic, M.; Skalicky, M.; Ondrisik, P.; Gitari, H.; Brahmachari, K.; Shankar, T.; Bhadra, P.; Palai, J.B.; et al. Intercropping—A low input agricultural strategy for food and environmental security. Agronomy 2021, 11, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, J.; Xiao, W.; Luo, X.G.; Shah, S.R.U.; Aslam, M.; Ahmed, I.; Abdullah, S.; Babar, A.; Jakhar, A.M.; Azam, T. Garlic (Allium sativum) based interplanting alters the heavy metals absorption and bacterial diversity in neighboring plants. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.; Pan, J.; Mubeen, S.; Ma, W.; Luo, D.; Cao, S.; Chen, P. Intercropping of kenaf and soybean affects plant growth, antioxidant capacity, and uptake of cadmium and lead in contaminated mining soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 89638–89650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Wang, X.; Lu, M.; Hamid, Y.; Lin, Q.; Liu, X.; Li, T.; Liu, G.; He, Z.; Yang, X. The Cd phytoextraction potential of hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii-oilseed rape intercropping system under different soil types and comprehensive benefits evaluation under field conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.W.W.; So, P.S.; Wong, J.T.F.; Lau, S.Y. Intercropping of Pinellia ternata (herbal plant) with Sedum alfredii (Cd-hyperaccumulator) to reduce soil cadmium (Cd) absorption and improve yield. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 318, 120930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kama, R.; Ma, Q.; Nabi, F.; Aidara, M.; Huang, P.; Li, Z.; He, J.; Diatta, S.; Li, H. Hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum L. intercropping reduced rice cadmium uptake under a high-bed and low-ditch planting system. Plants 2023, 12, 4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zou, R.; Li, Y.C.; Tong, Z.; You, M.; Huo, W.; Chi, K.; Fan, H. Effect of Wheat-Solanum nigrum L. intercropping on Cd accumulation by plants and soil bacterial community under Cd contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 206, 111383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, F.; Qin, L.; Guo, X.; Tan, J.; Liu, N.; Zu, Y.; Li, Y. Cadmium and lead accumulation and low-molecular-weight organic acids secreted by roots in an intercropping of a cadmium accumulator Sonchus asper L. with Vicia faba L. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 33240–33248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; He, M.; Meng, X. Effects of intercropping peaches with Hylotelephium spectabile on Cd uptake, rhizosphere soil properties and phytoremediation efficiency. Ecol. Eng. 2024, 207, 107356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kama, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Hamani, A.K.M.; Song, J.; Cui, B.; Aidara, M.; Liu, C.; Li, Z. Combination of intercropping maize and soybean with root exudate additions reduces metal mobility in soil-plant system under wastewater irrigation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 266, 115549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Han, L.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, D.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, R. Effects of intercropping modes of Zea mays L. and Solanum nigrum L. on plant growth and Cd enrichment characteristics. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2020, 39, 2162–2172. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, P.; Sun, T.; Song, Y.; Ackland, M.L.; Liu, Y. Strategies for enhancing the phytoremediation of cadmium-contaminated agricultural soils by Solanum nigrum L. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, R.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, L.; Liao, M.; Tang, Y.; Liang, D.; Xia, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Lv, X.; et al. Intercropping with hyperaccumulator plants decreases the cadmium accumulation in grape seedlings. Acta Agric. ScandInavica Sect. B—Soil Plant Sci. 2019, 69, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Cang, J.; Xu, Z. Plant Physiology Experiment; Harbin Institute of Technology Press: Harbin, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rastmanesh, F.; Moore, F.; Keshavarzi, B. Speciation and phytoavailability of heavy metals in contaminated soils in Sarcheshmeh area, Kerman Province, Iran. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 85, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Peng, P.; Song, J.; Liu, C.; Peng, J.; Lu, P. Utilization of modified BCR procedure for the chemical speciation of heavy metals in Chinese soil reference material. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2012, 21, 1881–1884. [Google Scholar]
- El-Tohory, S.; Zeng, W.; Huang, J.; Moussa, M.G.; Dong, L.; Mohamed, A.; Khalifa, O.; Saleem, M.H.; Zhran, M.; Salama, M.A.; et al. Effect of intercropping and biochar application on cadmium removal capacity by Corchorus olitorius and Zea mays. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 29, 103033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araghian, S.; Haghighi, R.S.; Ghasemi, M.; Darban, A.S. The effects of intercropping and plant density on the growth and yield characteristics of quinoa and guar. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, F.; van Ittersum, M.K.; Simon, E.; Leffelaar, P.A.; van der Putten, P.E.; Zhang, L.; van der Werf, W. Intercropping wheat and maize increases total radiation interception and wheat RUE but lowers maize RUE. Eur. J. Agron. 2017, 84, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makoi, J.H.J.R.; Chimphango, S.B.M.; Dakora, F.D. Photosynthesis, water-use efficiency and δ13C of five cowpea genotypes grown in mixed culture and at different densities with sorghum. Photosynthetica 2010, 48, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Hussain, J.; Yanwisetpakdee, B.; Iqbal, I.; Chen, X. The effects of monoculture and intercropping on photosynthesis performance correlated with growth of garlic and perennial ryegrass response to different heavy metals. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foyer, C.H.; Noctor, G. Redox homeostasis and antioxidant signaling: A metabolic interface between stress perception and physiological responses. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 1866–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.S.; Dietz, K.J. The relationship between metal toxicity and cellular redox imbalance. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowler, C.; Montagu, M.V.; Inze, D. Superoxide dismutase and stress tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 1992, 43, 83–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, F.; Zhong, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Gu, L.; Huang, Z.; Gai, X.; Huang, Z. Intercropping improves heavy metal phytoremediation efficiency through changing properties of rhizosphere soil in bamboo plantation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Zou, D.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, F.; Wang, A.; Zeng, Q.; Zhang, G.; Li, L. Cadmium accumulation in oilseed rape is promoted by intercropping with faba bean and ryegrass. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 205, 111162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yang, X.; Tong, X.; Peng, Y.; Deng, Y.; Yan, X.; Zhou, Y. Cleaner production of Chinese cabbage by intercropping from Cd contaminated soil: Effects of hyperaccumulator variety and planting strip width. Chemosphere 2023, 341, 139975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, L.; Liang, Z.; Wei, T. Cadmium tolerance mechanism of Solanum nigrum based on subcellular distribution and organic acid content. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, X.; Shokohifard, G.I. Effect of pH on chemical forms and plant availability of cadmium, zinc, and lead in polluted soils. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1989, 45, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ma, W.; Zhang, F. Rhizosphere talk and its impacts on plant growth. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2008, 14, 178–183. [Google Scholar]


| pH | Organic Matter (g/kg) | Total N (g/kg) | Total P (g/kg) | Total K (g/kg) | Available N (mg/kg) | Available P (mg/kg) | Available K (mg/kg) | Total Cd (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.55 | 12.09 | 0.49 | 0.58 | 11.55 | 42.95 | 12.39 | 41.33 | 0.23 |
| Treatment | Chlorophyll a (mg/g) | Chlorophyll b (mg/g) | Carotenoid (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grapevine | |||
| Mon. | 1.313 ± 0.027 b | 0.602 ± 0.039 b | 0.545 ± 0.021 b |
| 40 × 80 | 1.334 ± 0.066 b | 0.622 ± 0.018 b | 0.556 ± 0.023 b |
| 40 × 40 | 2.136 ± 0.107 a | 0.816 ± 0.032 a | 0.784 ± 0.030 a |
| 20 × 40 | 1.157 ± 0.019 c | 0.462 ± 0.020 c | 0.494 ± 0.008 c |
| 20 × 20 | 1.111 ± 0.046 c | 0.457 ± 0.032 c | 0.481 ± 0.024 c |
| S. nigrum | |||
| 40 × 80 | 1.314 ± 0.041 d | 0.451 ± 0.017 c | 0.454 ± 0.012 c |
| 40 × 40 | 1.509 ± 0.040 c | 0.541 ± 0.006 b | 0.520 ± 0.014 b |
| 20 × 40 | 1.702 ± 0.036 a | 0.611 ± 0.032 a | 0.534 ± 0.020 ab |
| 20 × 20 | 1.620 ± 0.041 b | 0.560 ± 0.031 b | 0.558 ± 0.017 a |
| Treatment | Pn (µmol CO2/m2/s) | Gs (mol H2O/m2/s) | Ci (µmol CO2/mol) | Tr (mmol H2O/m2/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grapevine | ||||
| Mon. | 14.51 ± 0.24 b | 0.053 ± 0.003 c | 198.23 ± 9.25 b | 1.49 ± 0.03 c |
| 40 × 80 | 14.64 ± 0.54 b | 0.063 ± 0.004 b | 215.55 ± 8.88 a | 1.75 ± 0.10 b |
| 40 × 40 | 15.51 ± 0.50 a | 0.077 ± 0.005 a | 221.44 ± 11.03 a | 2.10 ± 0.09 a |
| 20 × 40 | 12.92 ± 0.26 c | 0.050 ± 0.003 cd | 191.15 ± 5.66 bc | 1.43 ± 0.03 c |
| 20 × 20 | 12.07 ± 0.16 d | 0.045 ± 0.004 d | 180.55 ± 10.13 c | 1.46 ± 0.08 c |
| S. nigrum | ||||
| 40 × 80 | 18.19 ± 0.80 c | 0.132 ± 0.003 bc | 129.89 ± 2.58 c | 3.78 ± 0.27 ab |
| 40 × 40 | 19.54 ± 1.11 c | 0.126 ± 0.002 c | 133.93 ± 1.41 bc | 3.53 ± 0.24 b |
| 20 × 40 | 24.64 ± 0.70 a | 0.168 ± 0.007 a | 170.71 ± 8.08 a | 4.15 ± 0.21 a |
| 20 × 20 | 21.96 ± 0.60 b | 0.137 ± 0.004 b | 143.94 ± 9.80 b | 4.07 ± 0.10 a |
| Treatment | CAT Activity (mg/g/min) | SOD Activity (U/g) | POD Activity (U/g/min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grapevine | |||
| Mon. | 0.580 ± 0.030 d | 402.6 ± 6.58 d | 13.00 ± 1.00 b |
| 40 × 80 | 0.610 ± 0.020 d | 417.9 ± 8.00 c | 14.63 ± 1.00 b |
| 40 × 40 | 0.827 ± 0.038 c | 453.6 ± 7.24 b | 15.28 ± 0.06 b |
| 20 × 40 | 0.943 ± 0.042 b | 489.2 ± 6.52 a | 23.27 ± 1.90 a |
| 20 × 20 | 1.033 ± 0.040 a | 481.4 ± 1.40 a | 20.97 ± 1.68 a |
| S. nigrum | |||
| 40 × 80 | 5.812 ± 0.066 d | 393.3 ± 0.65 d | 1907 ± 86.63 c |
| 40 × 40 | 6.089 ± 0.115 c | 407.9 ± 9.00 c | 2013 ± 60.01 c |
| 20 × 40 | 6.311 ± 0.052 b | 465.5 ± 2.11 b | 2269 ± 63.89 b |
| 20 × 20 | 6.618 ± 0.110 a | 491.1 ± 2.89 a | 2459 ± 70.11 a |
| Treatment | Root Cd Content (mg/kg) | Shoot Cd Content (mg/kg) | Translocation Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grapevine | |||
| Mon. | 28.60 ± 0.72 a | 0.383 ± 0.015 a | 0.013 ± 0.001 b |
| 40 × 80 | 9.71 ± 0.36 b | 0.303 ± 0.006 b | 0.031 ± 0.002 a |
| 40 × 40 | 8.89 ± 0.37 c | 0.283 ± 0.015 b | 0.032 ± 0.002 a |
| 20 × 40 | 7.74 ± 0.23 d | 0.237 ± 0.012 c | 0.031 ± 0.002 a |
| 20 × 20 | 6.50 ± 0.30 e | 0.207 ± 0.006 d | 0.032 ± 0.002 a |
| S. nigrum | |||
| 40 × 80 | 5.22 ± 0.31 d | 15.03 ± 0.71 d | 2.88 ± 0.05 a |
| 40 × 40 | 7.74 ± 0.28 c | 16.86 ± 0.32 c | 2.18 ± 0.10 b |
| 20 × 40 | 9.30 ± 0.53 b | 18.58 ± 0.52 b | 2.00 ± 0.06 c |
| 20 × 20 | 13.13 ± 0.75 a | 29.55 ± 1.11 a | 2.25 ± 0.05 b |
| Treatment | Acid Extraction Cd Content (mg/kg) | Reducible Cd Content (mg/kg) | Oxidizable Cd Content (mg/kg) | Residue Cd Content (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mon. | 0.639 ± 0.009 a | 1.685 ± 0.023 a | 2.567 ± 0.013 a | 0.068 ± 0.003 a |
| 40 × 80 | 0.489 ± 0.020 d | 1.347 ± 0.088 c | 2.518 ± 0.013 a | 0.069 ± 0.002 a |
| 40 × 40 | 0.549 ± 0.016 c | 1.355 ± 0.068 c | 2.520 ± 0.061 a | 0.064 ± 0.002 b |
| 20 × 40 | 0.584 ± 0.008 b | 1.529 ± 0.016 b | 2.330 ± 0.095 b | 0.053 ± 0.002 c |
| 20 × 20 | 0.599 ± 0.012 b | 1.614 ± 0.060 ab | 2.206 ± 0.106 b | 0.053 ± 0.001 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, J.; Lv, X.; Liang, D.; Liao, R.; Lin, L. Effects of Different Planting Densities of Solanum nigrum L. on the Growth and Cadmium Uptake of Young Grapevines. Agronomy 2024, 14, 3056. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14123056
Yang Y, Zheng Q, Wang J, Lv X, Liang D, Liao R, Lin L. Effects of Different Planting Densities of Solanum nigrum L. on the Growth and Cadmium Uptake of Young Grapevines. Agronomy. 2024; 14(12):3056. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14123056
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yuanxiang, Qinfeng Zheng, Jin Wang, Xiulan Lv, Dong Liang, Renyan Liao, and Lijin Lin. 2024. "Effects of Different Planting Densities of Solanum nigrum L. on the Growth and Cadmium Uptake of Young Grapevines" Agronomy 14, no. 12: 3056. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14123056
APA StyleYang, Y., Zheng, Q., Wang, J., Lv, X., Liang, D., Liao, R., & Lin, L. (2024). Effects of Different Planting Densities of Solanum nigrum L. on the Growth and Cadmium Uptake of Young Grapevines. Agronomy, 14(12), 3056. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14123056






