Advanced Plant Phenotyping: Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Remote Sensing and CimageA Software Technology for Precision Crop Growth Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Trial and Materials Acquisition
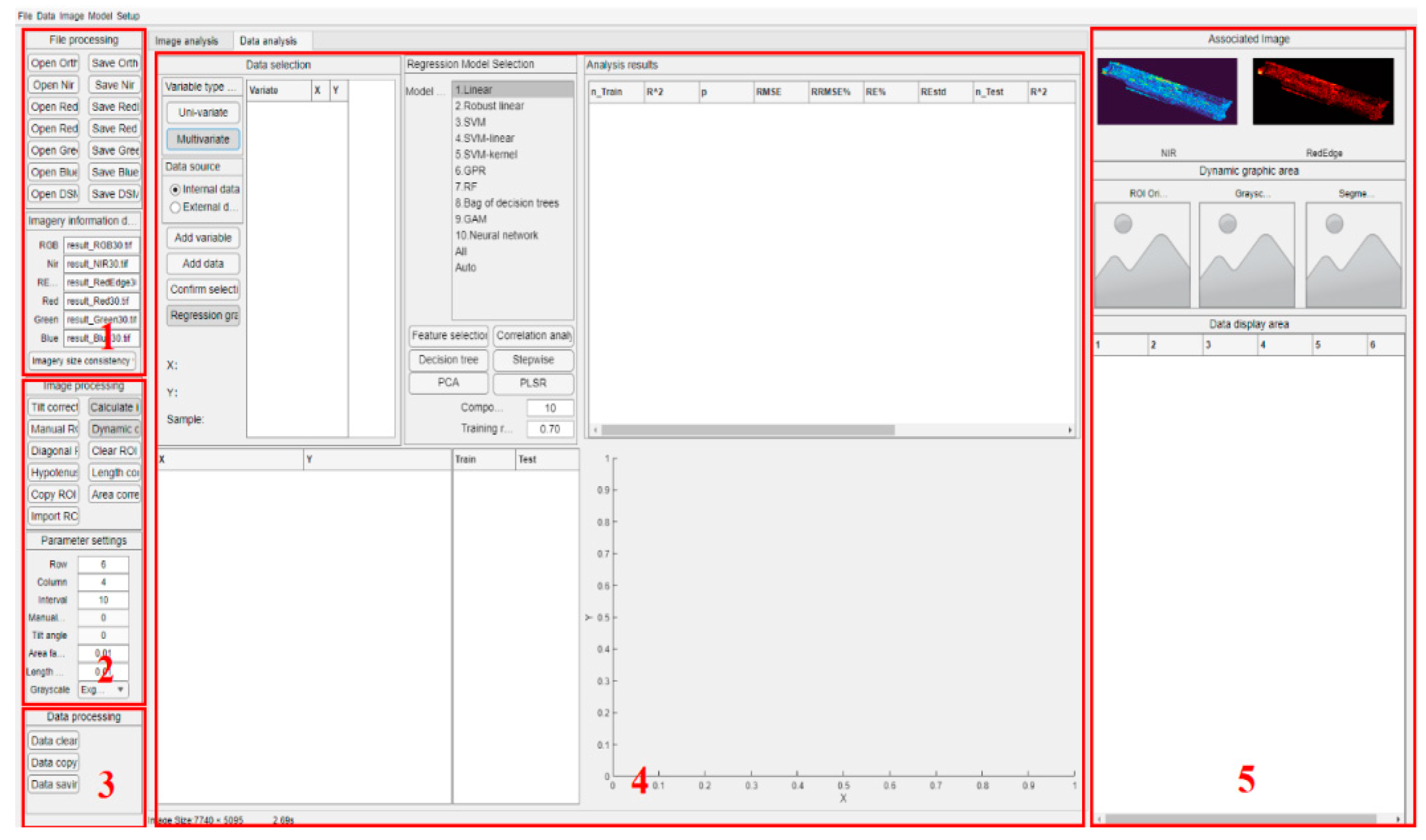
2.2. Overview of CimageA
2.3. Function Realization
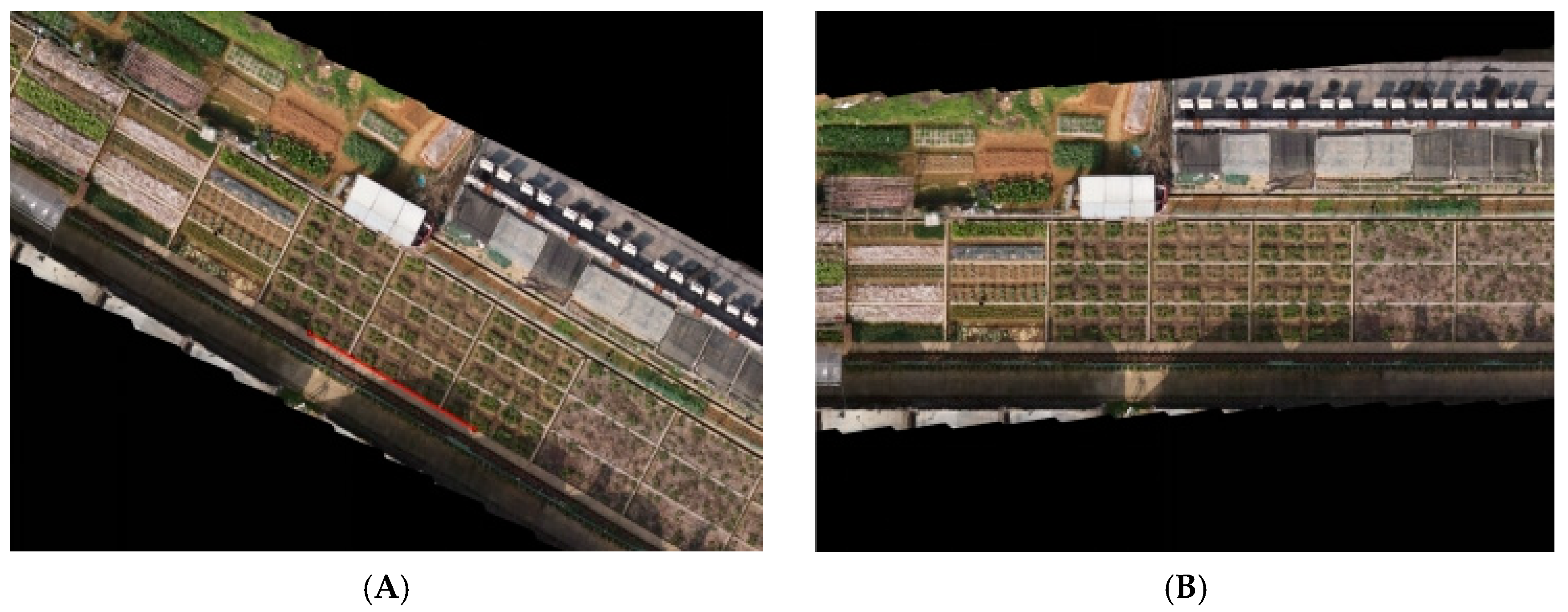
2.3.1. Tilt Correction
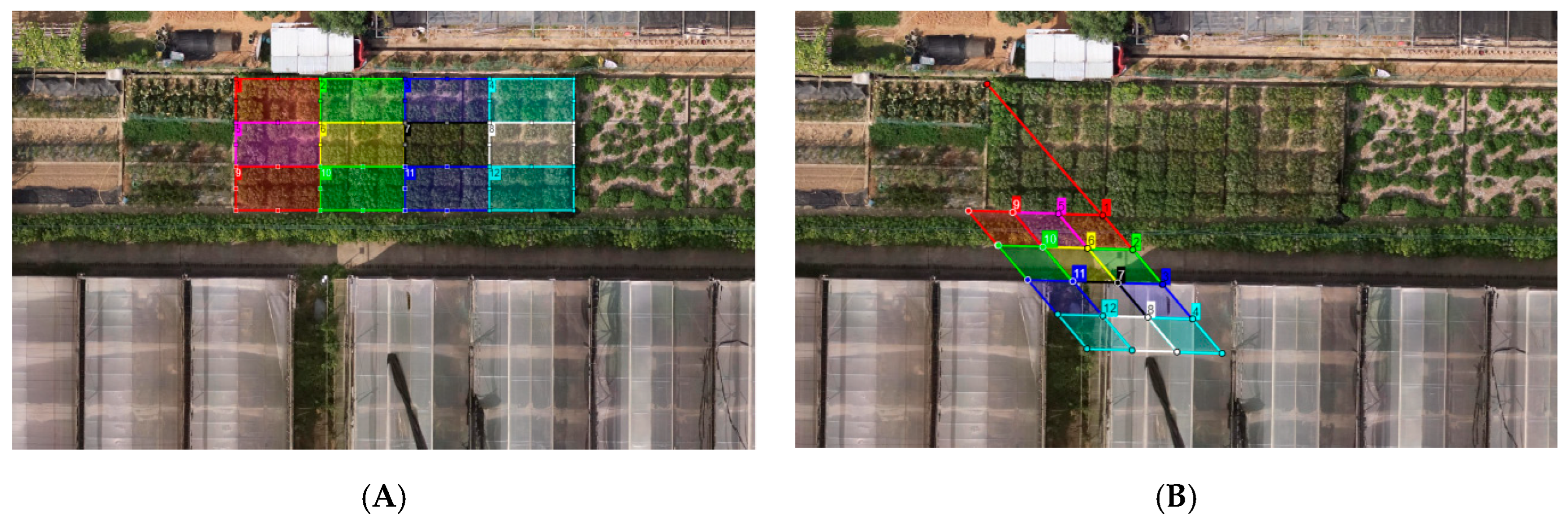
2.3.2. Intelligent Drawing of AOI
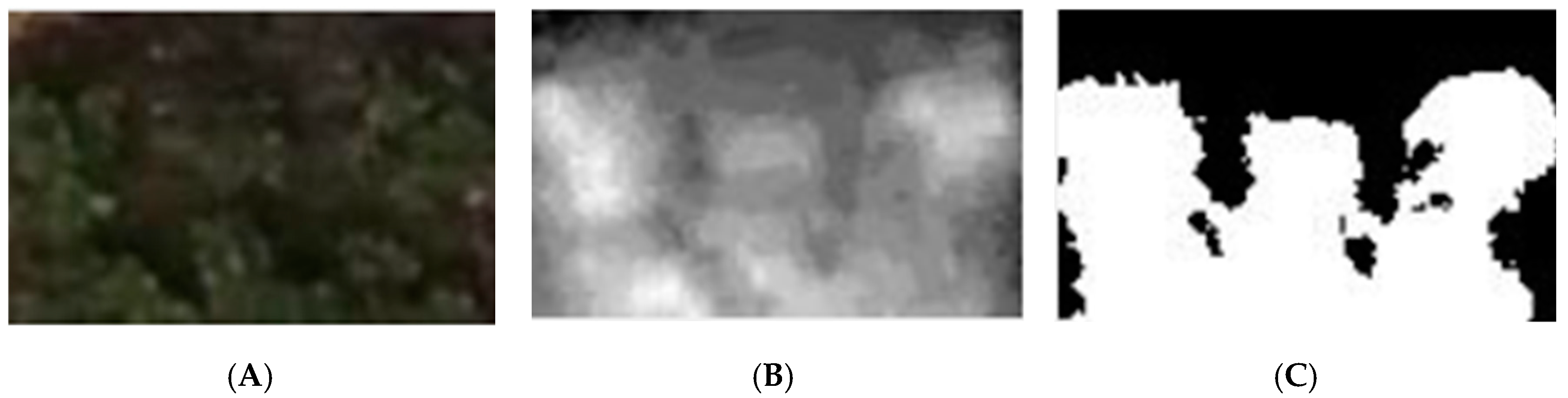
2.3.3. Plant Segmentation
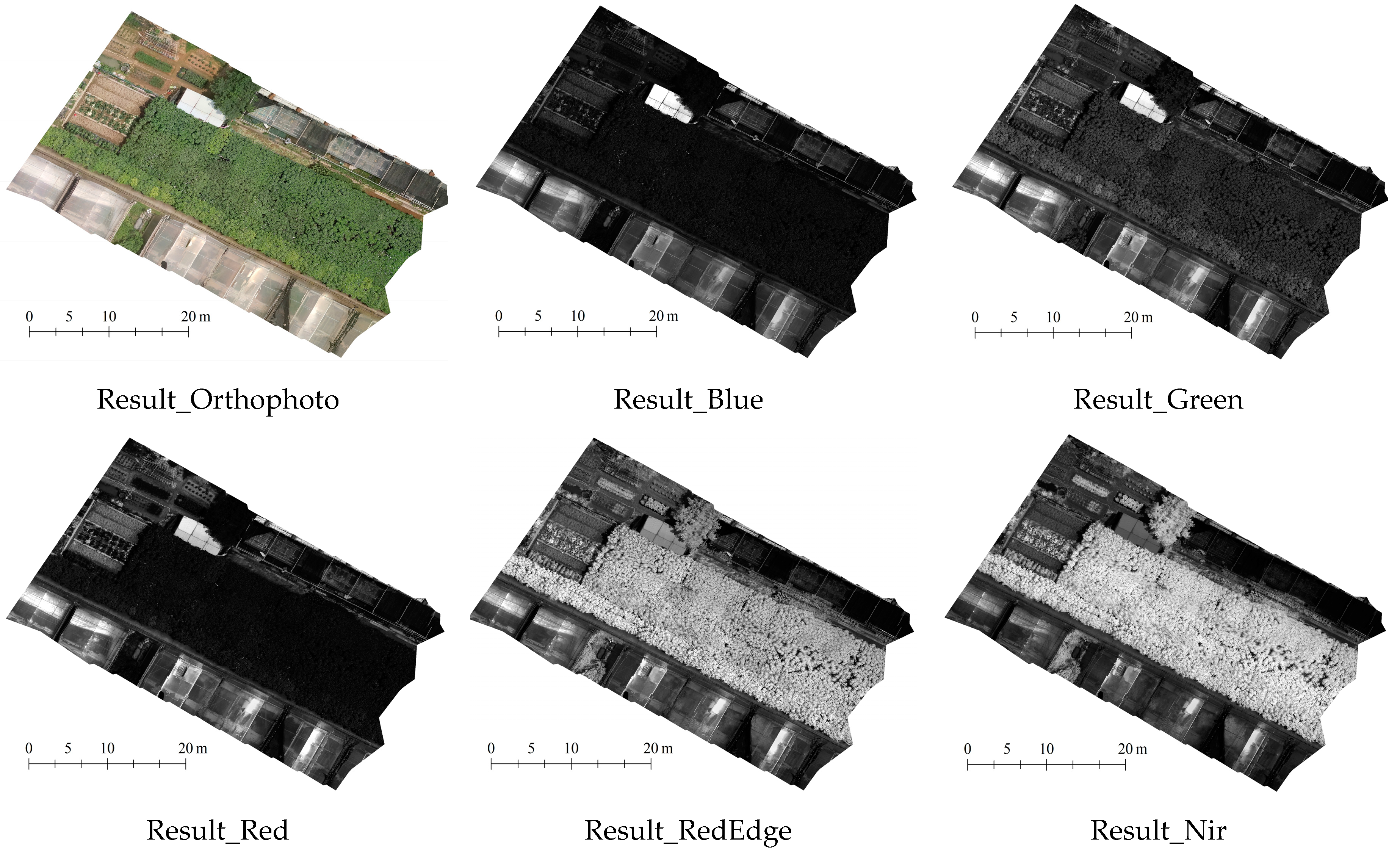
2.3.4. Remote Sensing Eigenvalue Extraction
2.3.5. Model Construction and Evaluation
2.3.6. Large Scale Image Processing
2.3.7. Running Progress Display
2.4. Performance Validation of CimageA
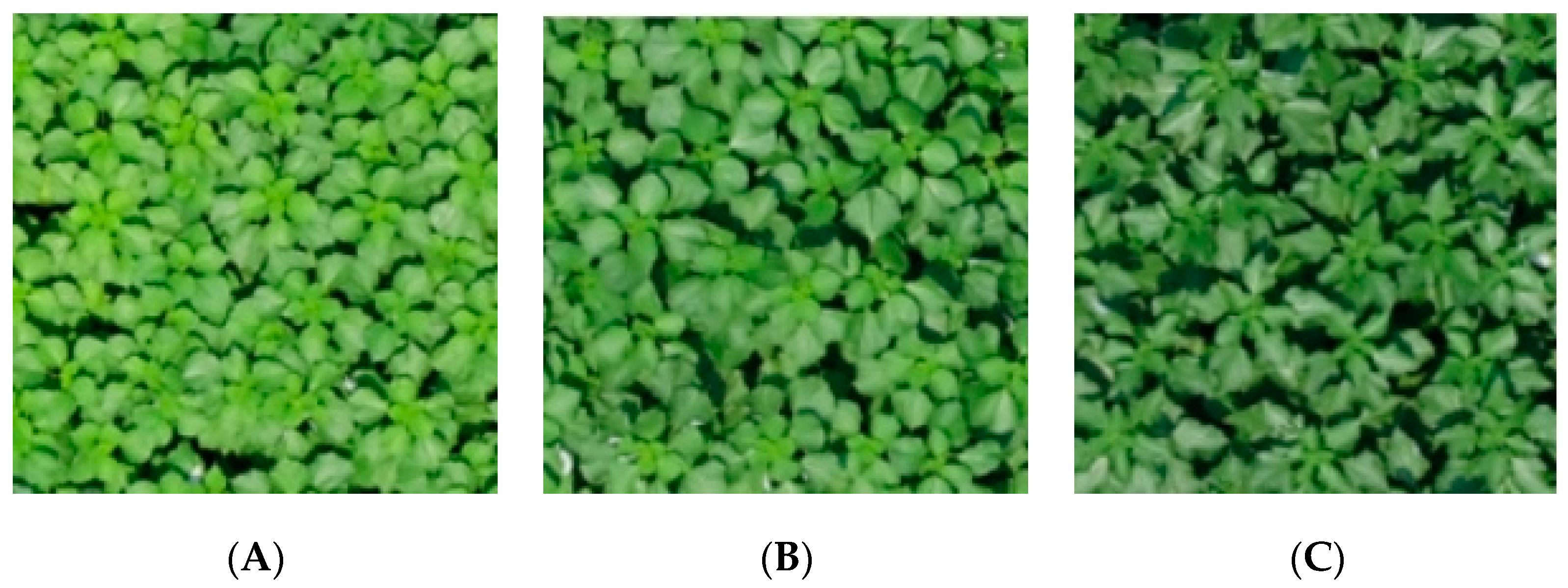
2.4.1. Extraction of Ramie Leaf Color Features
2.4.2. Extraction of Ramie Leaf Area Index
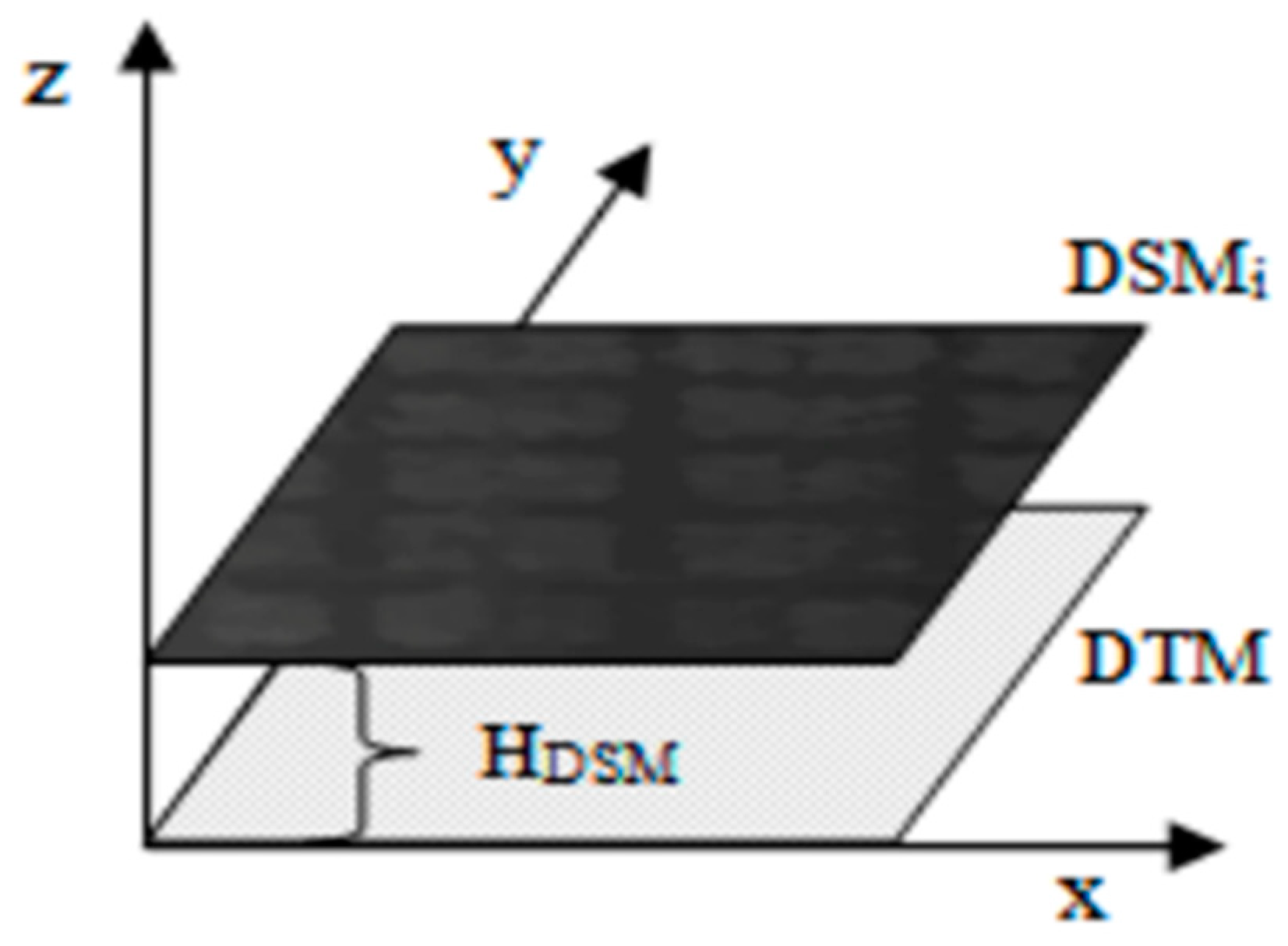
2.4.3. Extraction of Ramie Plant Height
2.4.4. Extraction of Crop Planting Area
3. Results
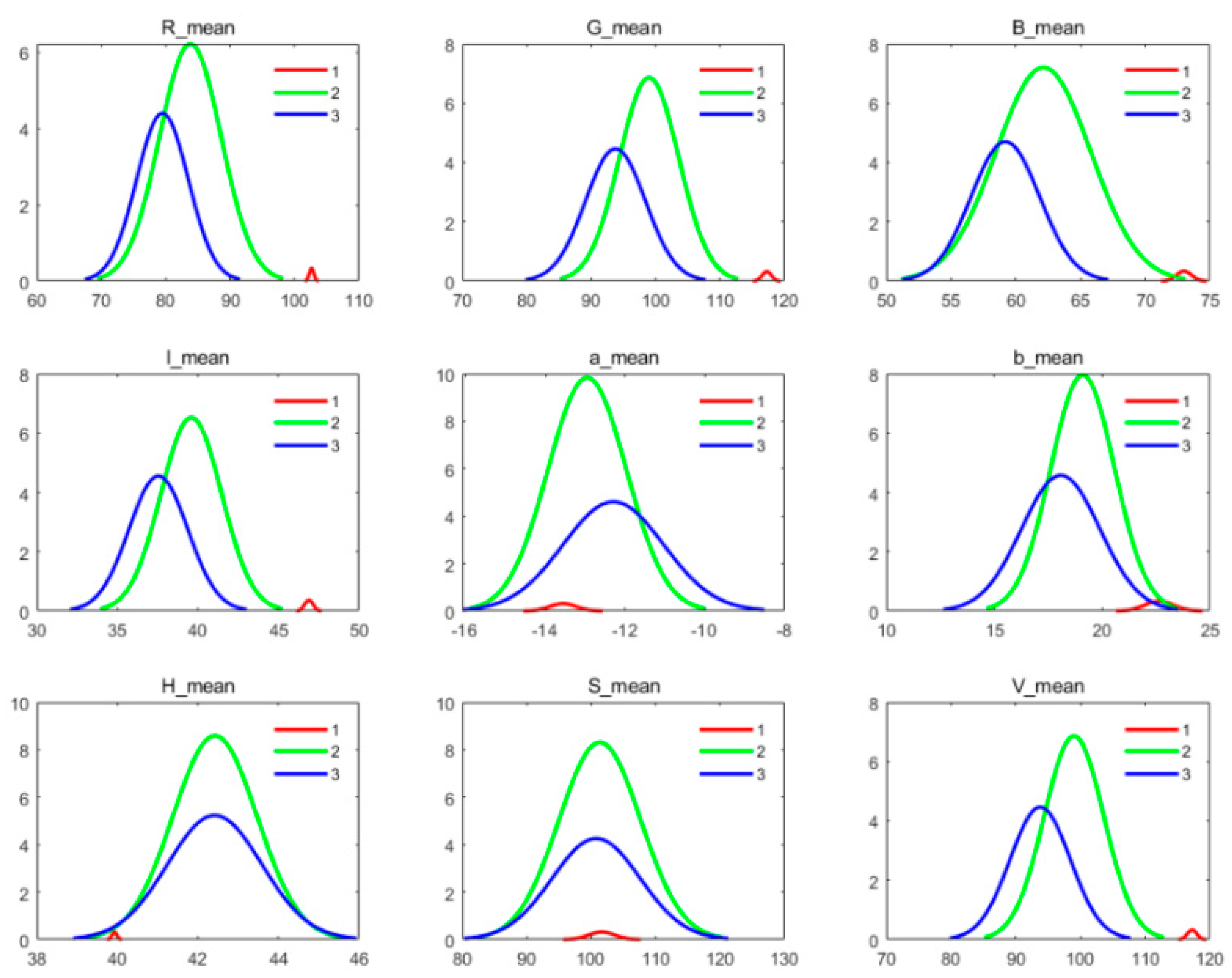
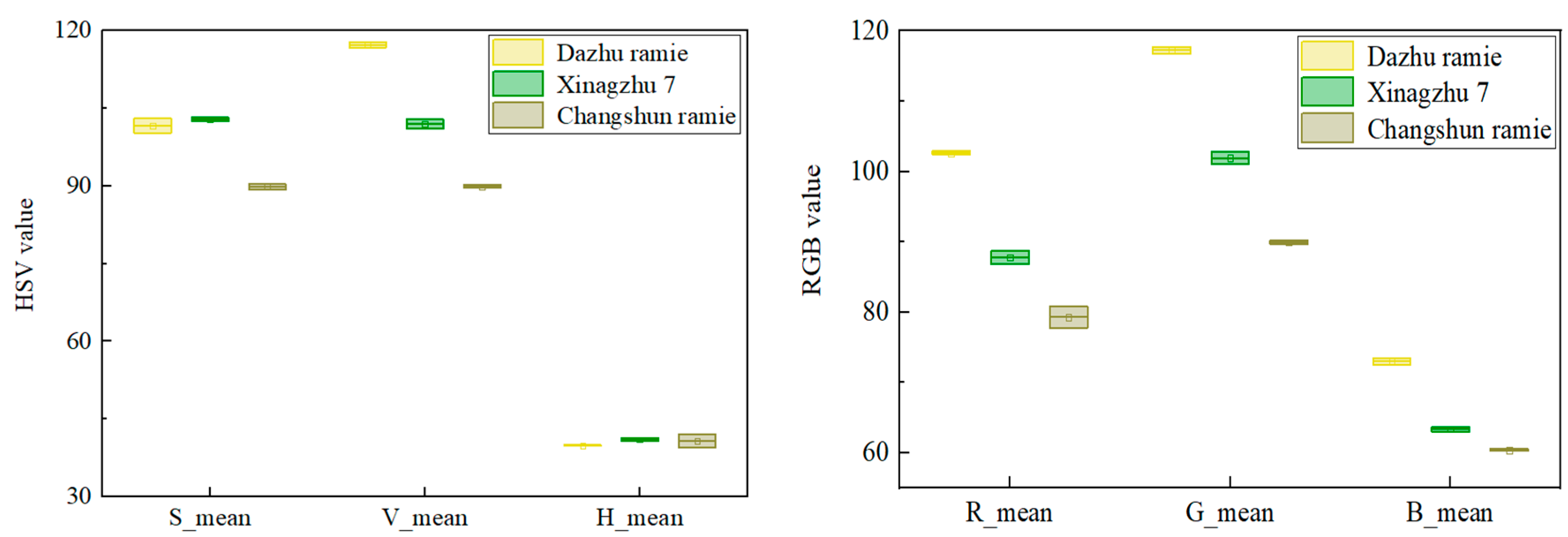
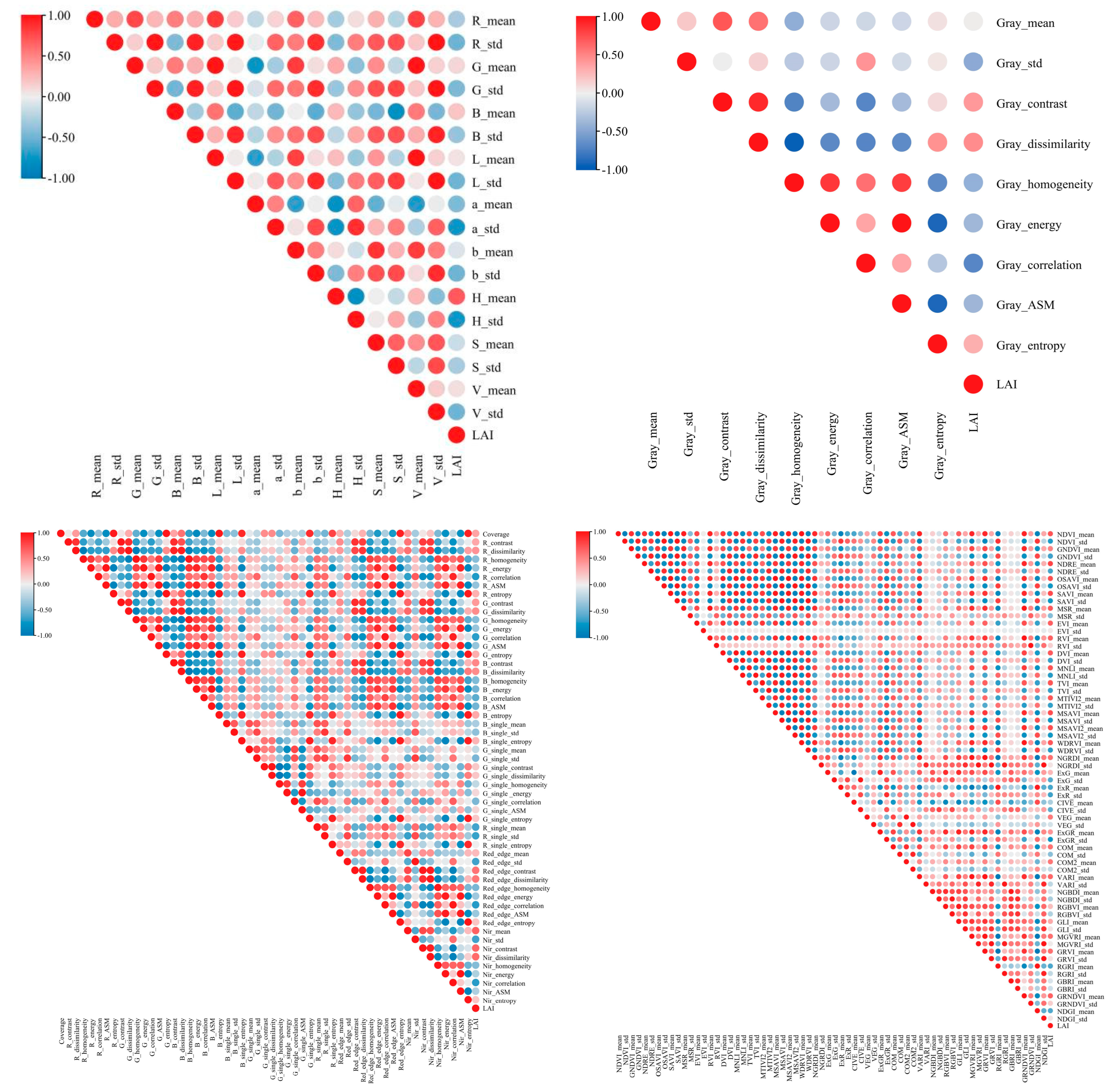
3.1. Verify the Ramie Color Features Extracted by CimageA
3.2. Verify the Phenotype Inversion of CimageA
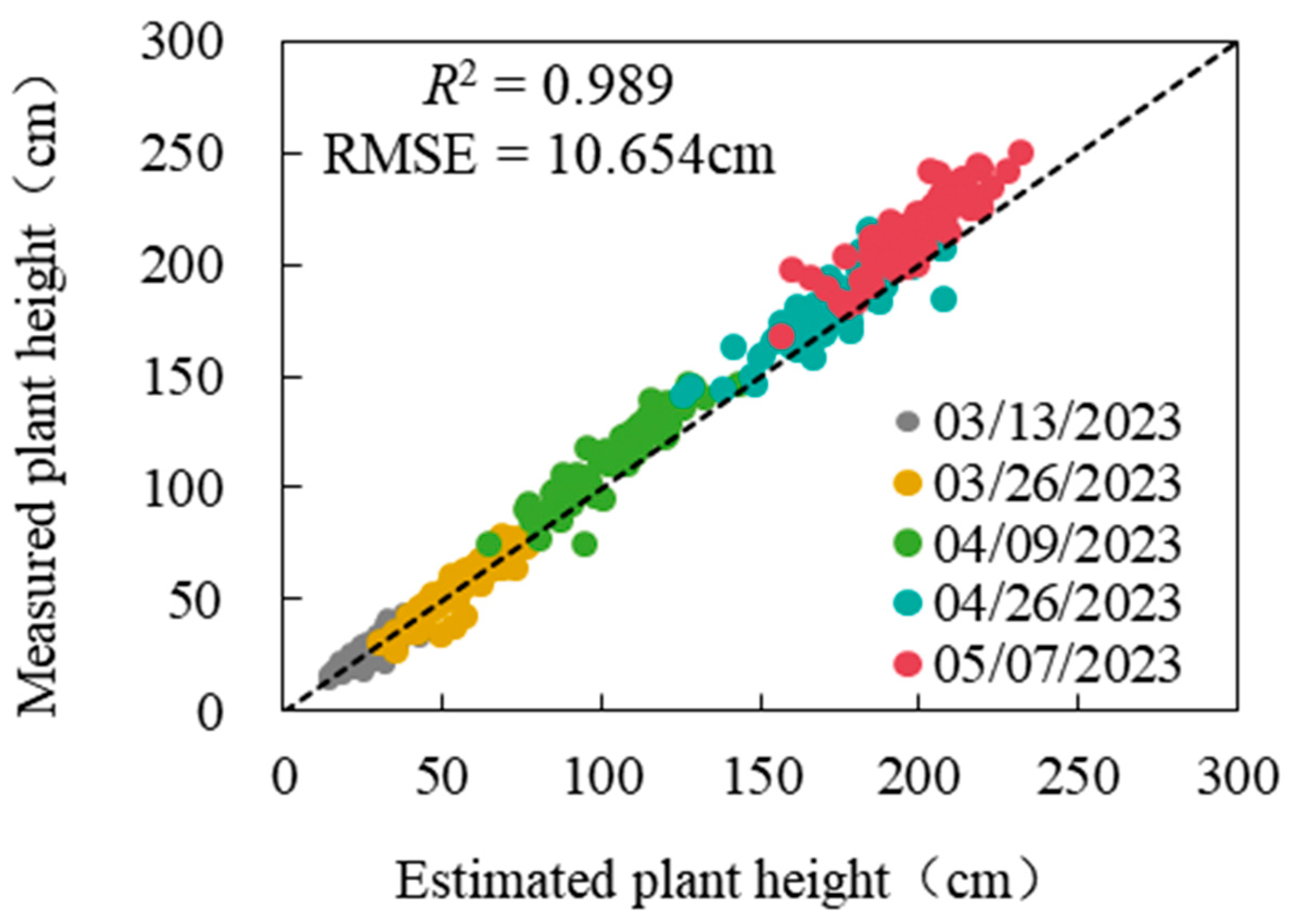
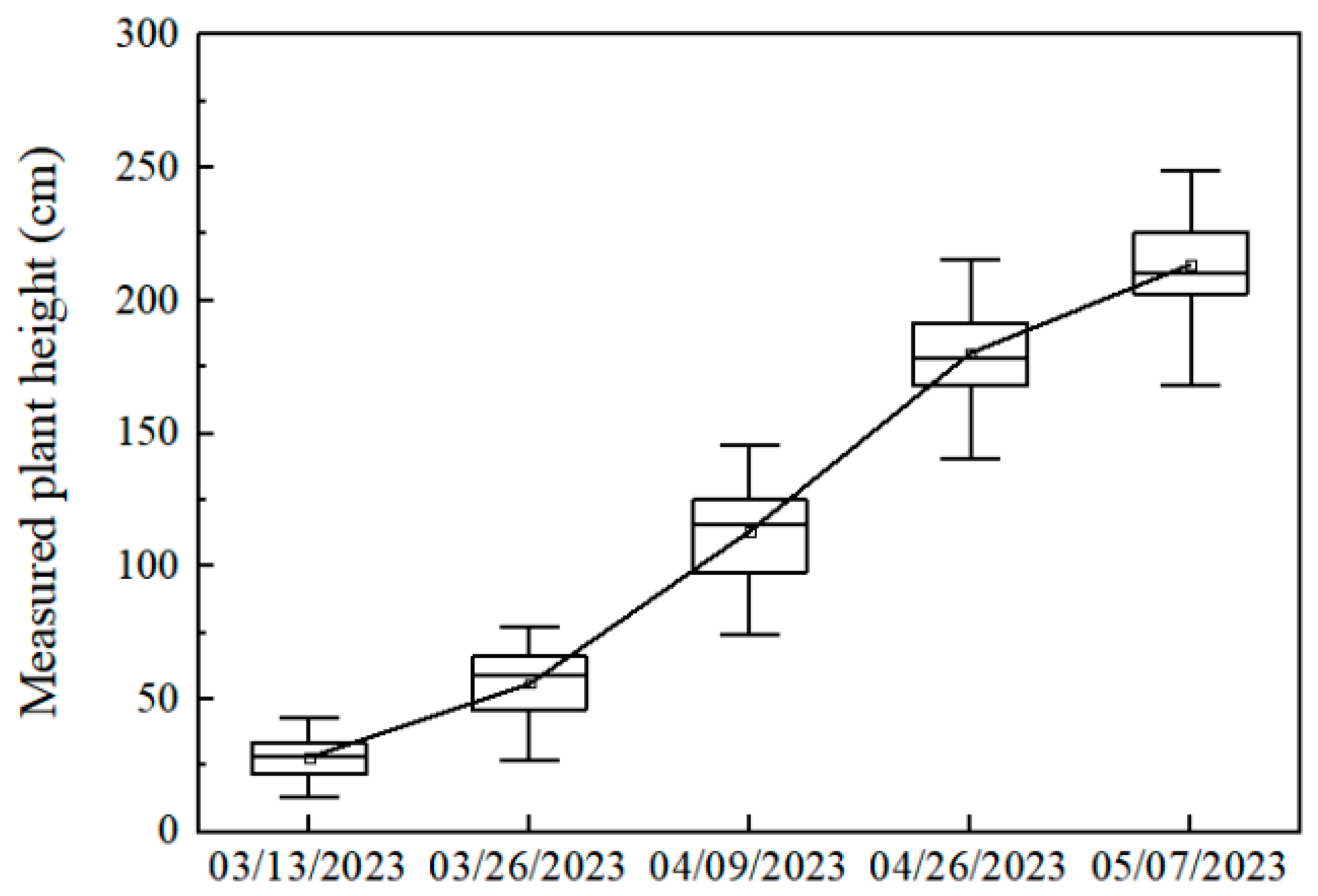
3.3. Verify the Ramie Plant Height Extracted by CimageA
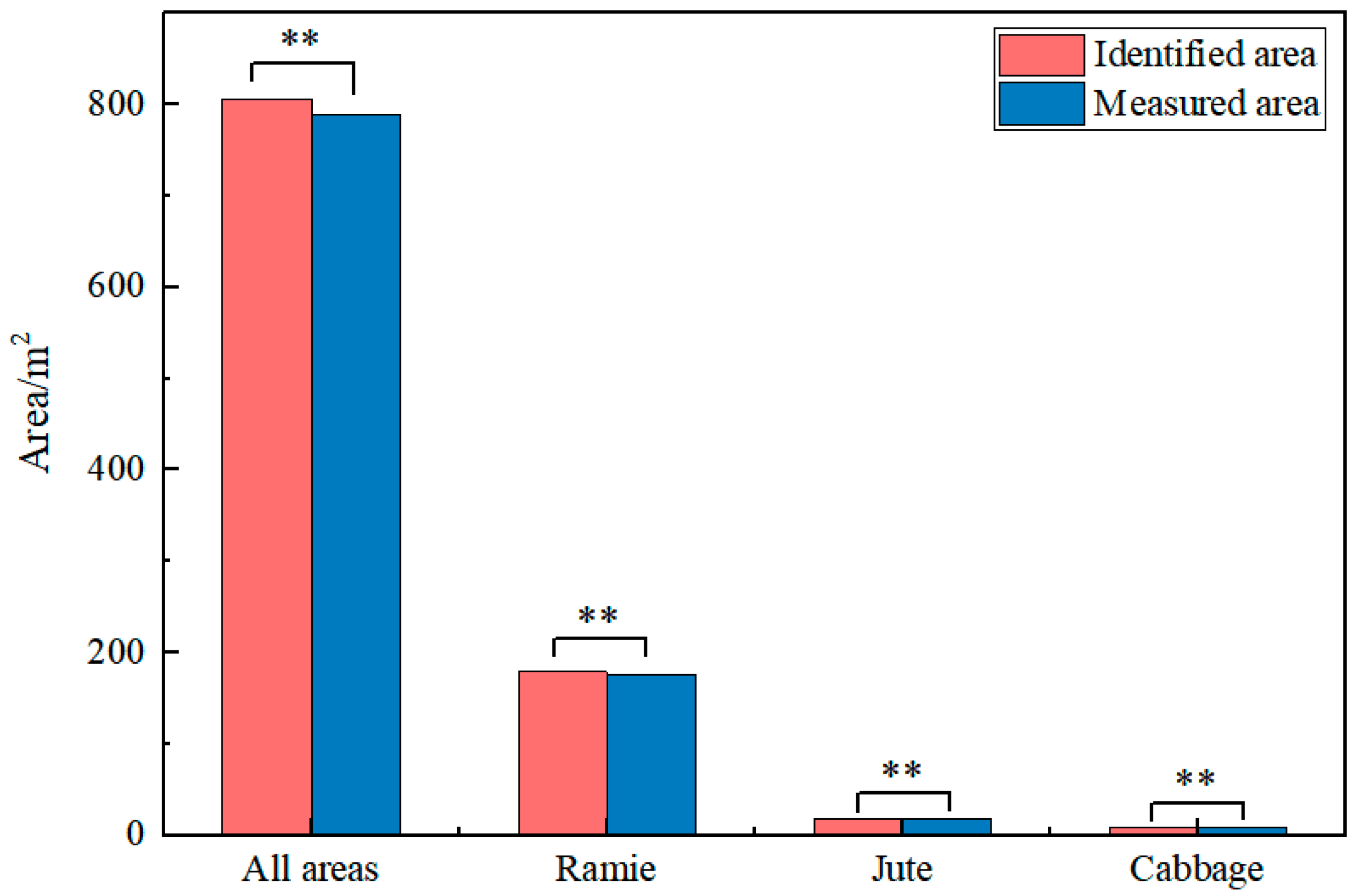
3.4. Verify the Crop Area Extracted by CimageA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tester, M.; Langridge, P. Breeding technologies to increase crop production in a changing world. Science 2010, 327, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furbank, R.T.; Tester, M. Phenomics technologies to relieve the phenotyping bottleneck. Trends Plant Sci. 2011, 16, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Qiu, L.; Jing, R.; Ren, G.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Qin, P.; Gu, Y.; Li, L. Evaluation on phenotypic traits of crop germplasm: Status and development. J. Plant Genet. Resour. 2022, 23, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Persa, R.; Ribeiro, P.; Jarquin, D. The use of high-throughput phenotyping in genomic selection context. Crop Breed. Appl. Biotechnol. 2021, 21, e385921S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Quan, C.; Song, Z.; Li, X.; Yu, G.; Li, C.; Muhammad, A. High- throughput plant phenotyping platform (HT3P) as a novel tool for estimating agronomic traits from the lab to the field. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 8, 623705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, C.; Yang, G.; Yu, H.; Zhao, X.; Xu, B.; Niu, Q. Review of field-based phenotyping by unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing platform. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 98–106. [Google Scholar]
- Cabrera, B.L.; Crossa, J.; Von, Z.J.; Serret, M.D.; Araus, J.L. High-throughput phenotyping and genomic selection: The frontiers of crop breeding converge. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2012, 54, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, D.C.; De Oliveira Cunha, M.P.; Dos Santos, R.G.; Cotrim, M.F.; Teodoro, L.P.R.; Da Silva Junior, C.A.; Baio, F.H.R.; Teodoro, P.E. High-throughput phenotyping allows the selection of soybean genotypes for earliness and high grain yield. Plant Methods 2022, 18, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y. Roadmap to high throughput phenotyping for plant breeding. J. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 45, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, D. A review of imaging techniques for plant phenotyping. Sensors 2014, 14, 20078–20111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangra, S.; Chaudhary, V.; Yadav, R.C.; Yadav, N.R. High-throughput phenotyping: A platform to accelerate crop improvement. Phenomics 2021, 1, 31–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Ling, H.; Fu, X. Development and application of the plant phenomics analysis platform. Genetics 2019, 41, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar]
- Fahlgren, N.; Feldman, M.; Gehan, M.A.; Wilson, M.S.; Shyu, C.; Bryant, D.W.; Hill, S.T.; McEntee, C.J.; Warnasooriya, S.N.; Kumar, I.; et al. A versatile phenotyping system and analytics Platform reveals diverse temporal responses to water availability in setaria. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 1520–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Tassel, D.L.; DeHaan, L.R.; Diaz-Garcia, L.; Hershberger, J.; Rubin, M.J.; Schlautman, B.; Turner, K.; Miller, A.J. Re-imagining crop domestication in the era of high throughput phenomics. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2022, 65, 102150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Doonan, J.H.; Hawkesford, M.J.; Pridmore, T.; Zhou, J. Editorial: State-of-the-art technology and applications in crop phenomics. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Lu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Jackson, R.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L.X.; Wang, A.; Colmer, J.; Ober, E.; et al. AirMeasurer: Open-source software to quantify static and dynamic traits derived from multiseason aerial phenotyping to empower genetic mapping studies in rice. New Phytol. 2022, 236, 1584–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Feng, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Doonan, J.H.; Batchelor, W.D.; Xiong, L.; Yan, J. Crop phenomics and high-throughput phenotyping: Past decades, current challenges, and future perspectives. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 187–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Cunha, M.; Jayavelu, S.; Cammarano, D.; Fu, Y. Machine learning-based approaches for predicting spad values of maize using multi-spectral images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.J.; Guo, J.K.; Miao, J.C.; Xu, H.Y.; Tian, B.Q.; Gong, D.C.; Zhao, J.; Lan, Y.B. Summer maize LAI retrieval based on multi-source remote sensing data. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2023, 16, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccardi, M.; Mele, G.; Pulvento, C.; Lavini, A.; d’Andria, R.; Jacobsen, S.E. Non-destructive evaluation of chlorophyll content in quinoa and amaranth leaves by simple and multiple regression analysis of RGB image components. Photosynth. Res. 2014, 120, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, H.C.; Lawrence, F.A.; Ryan, A.J.; Cameron, D.D. Free and open-source software for object detection, size, and colour determination for use in plant phenotyping. Plant Methods 2023, 19, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; You, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, W. IHUP: An integrated high-throughput universal phenotyping software platform to accelerate unmanned-aerial-vehicle-based field plant phenotypic data extraction and analysis. Plant Phenomics 2024, 6, 0164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, K.; Wu, W.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Dong, X.; Wang, M.; Sun, Q. AIseed: An automated image analysis software for high-throughput phenotyping and quality non-destructive testing of individual plant seeds. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 27, 107740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhaski, R.R.; Chopade, P.B.; Dale, M.P. Determination of ripeness and grading of tomato using image analysis on Raspberry Pi. In Proceedings of the 2015 Communication, Control and Intelligent Systems (CCIS), Mathura, India, 7–8 November 2015; Volume 2016, pp. 214–220. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.M.; Zhang, F.G.; Lu, J.T. Research on recognition of tea tender leaf based on image color information. J. Tea Sci. 2013, 33, 584–589. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, D.D.; Cui, G.X.; Yang, R.F.; She, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Su, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Phenotypic characteristics of ramie (Boehmeria nivea L) germplasm resources based on UAV remote sensing. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2021, 68, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, J.; Edwards, J.; Cai, J.; McDonald, G.; Miklavcic, S.J.; Kuchel, H. High-Throughput field imaging and basic image analysis in a wheat breeding programme data. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, Y.C.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Z.M.; Chen, J.F.; Xing, H.C.; She, W.; Cai, S.W.; Wang, X.F.; Qin, Z.J.; Luo, Z.Q. Description and Data Standard of Ramie Germplasm Resources; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, H.Y.; Lu, J.N.; Chen, J.F.; Wang, W.; Cui, G.; She, W. Influence of structure and texture feature on retrieval of ramie leaf area index. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Han, W.; Liu, Q.; Song, R.; Hou, G. Inversion of summer maize leaf area index based on gradient boosting decision tree algorithm. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2019, 50, 258–266. [Google Scholar]
- Wanga, M.A.; Shimelis, H.; Mashilo, J.; Laing, M.D. Opportunities and challenges of speed breeding: A review. Plant Breed. 2021, 140, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Du, X.; Chen, S.; Yu, F.; Zhu, J.; Xu, T.; He, Y.; Cen, H. Rice panicle phenotyping using UAV-based multi-source spectral image data fusion. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 162–170. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, B.; Wang, C.F.; Yang, C.H.; Xu, B.; Zhou, G.; Li, X.; Xie, J.; Xu, S.; Liu, B.; Xie, T.; et al. Retrieval of rapeseed leaf area index using the PROSAIL model with canopy coverage derived from UAV images as a correction parameter. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102373. [Google Scholar]



| Model | Dataset | RMSE | RRMSE | RE | RESTD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLM | Training set | 0.382 | 7.598 | 6.340 | 5.692 |
| Validation set | 0.924 | 17.678 | 14.654 | 15.972 | |
| RLM | Training set | 0.401 | 7.914 | 6.562 | 6.440 |
| Validation set | 0.841 | 16.344 | 13.979 | 13.472 | |
| SVM | Training set | 0.670 | 13.359 | 10.955 | 8.774 |
| Validation set | 0.786 | 14.931 | 13.526 | 12.450 | |
| SVM-linear | Training set | 1.518 | 29.754 | 24.577 | 12.768 |
| Validation set | 1.484 | 29.306 | 22.145 | 13.245 | |
| SVM-kerne | Training set | 0.754 | 14.785 | 12.705 | 18.913 |
| Validation set | 1.512 | 29.835 | 30.582 | 30.170 | |
| GPM | Training set | 0.579 | 11.236 | 9.752 | 7.628 |
| Validation set | 0.903 | 18.241 | 15.219 | 14.150 | |
| RF | Training set | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Validation set | 1.007 | 19.269 | 16.455 | 15.856 | |
| DT | Training set | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Validation set | 0.977 | 18.514 | 15.396 | 14.828 | |
| GAMS | Training set | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Validation set | 1.196 | 24.201 | 21.448 | 18.793 | |
| NNM | Training set | 0.670 | 13.049 | 11.029 | 9.410 |
| Validation set | 0.684 | 13.722 | 12.458 | 11.499 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, H.; Lu, J.; Cui, G.; Nie, J.; Wang, W.; She, W.; Li, J. Advanced Plant Phenotyping: Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Remote Sensing and CimageA Software Technology for Precision Crop Growth Monitoring. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112534
Fu H, Lu J, Cui G, Nie J, Wang W, She W, Li J. Advanced Plant Phenotyping: Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Remote Sensing and CimageA Software Technology for Precision Crop Growth Monitoring. Agronomy. 2024; 14(11):2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112534
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Hongyu, Jianning Lu, Guoxian Cui, Jihao Nie, Wei Wang, Wei She, and Jinwei Li. 2024. "Advanced Plant Phenotyping: Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Remote Sensing and CimageA Software Technology for Precision Crop Growth Monitoring" Agronomy 14, no. 11: 2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112534
APA StyleFu, H., Lu, J., Cui, G., Nie, J., Wang, W., She, W., & Li, J. (2024). Advanced Plant Phenotyping: Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Remote Sensing and CimageA Software Technology for Precision Crop Growth Monitoring. Agronomy, 14(11), 2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14112534




