Regulation of Fumonisin B1 Production and Pathogenicity in Fusarium verticillioides by Histone Deacetylases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.2. Strains and Growth Condition
2.3. Generation of Deletion Mutants and Complementary Stains
2.4. Generation of Overexpression Mutants, Fluorescence Fusion Strains, and Fluorescence Microscopy
2.5. RNA Extraction and Real-Time qPCR (RT-qPCR)
2.6. RNA-Seq Analysis
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Yeast Two-Hybrid Experiment
2.9. Pathogenicity Assays and Detection of Fumonisin FB1
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Subcellular Localization of Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) in F. verticillioides
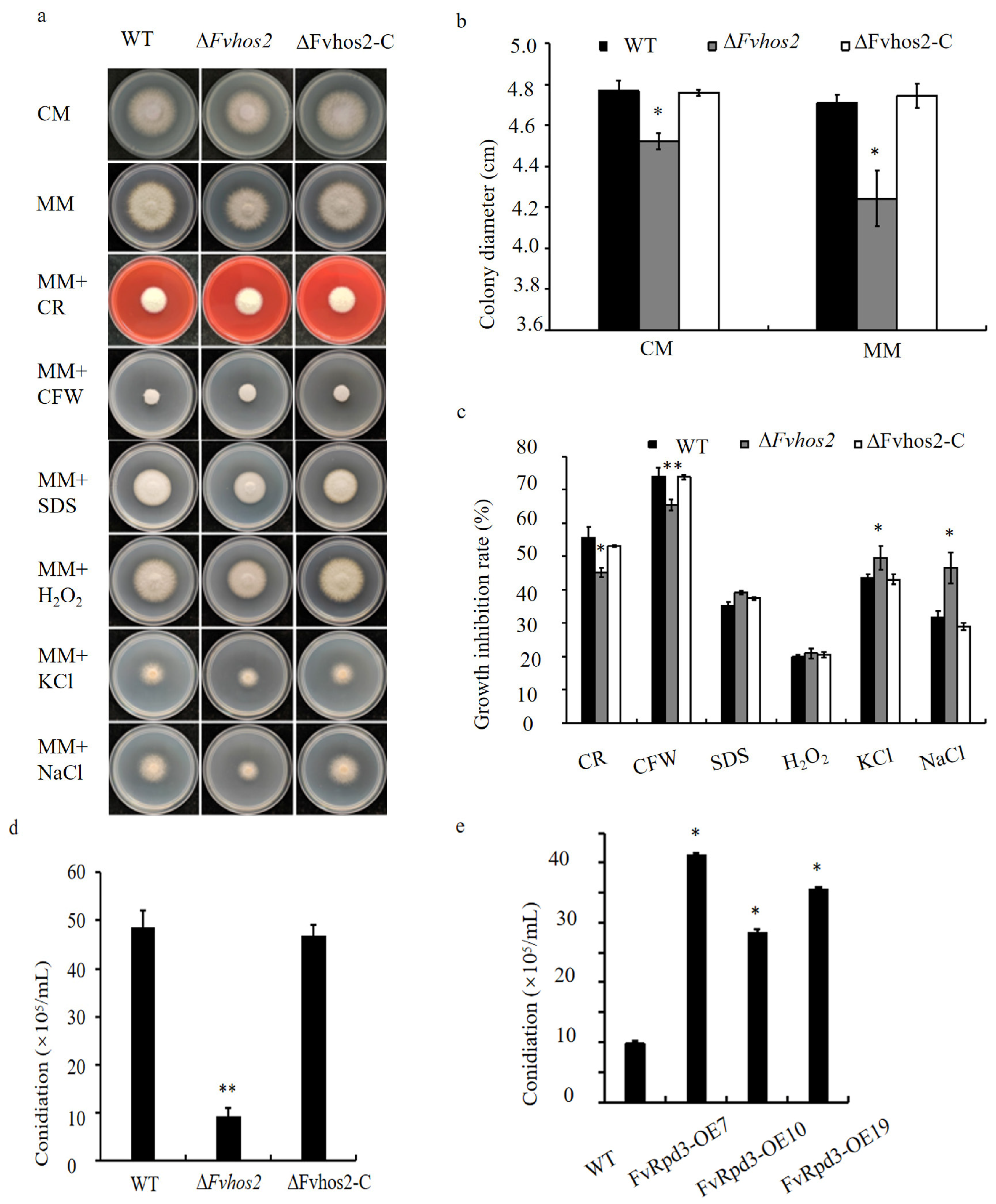
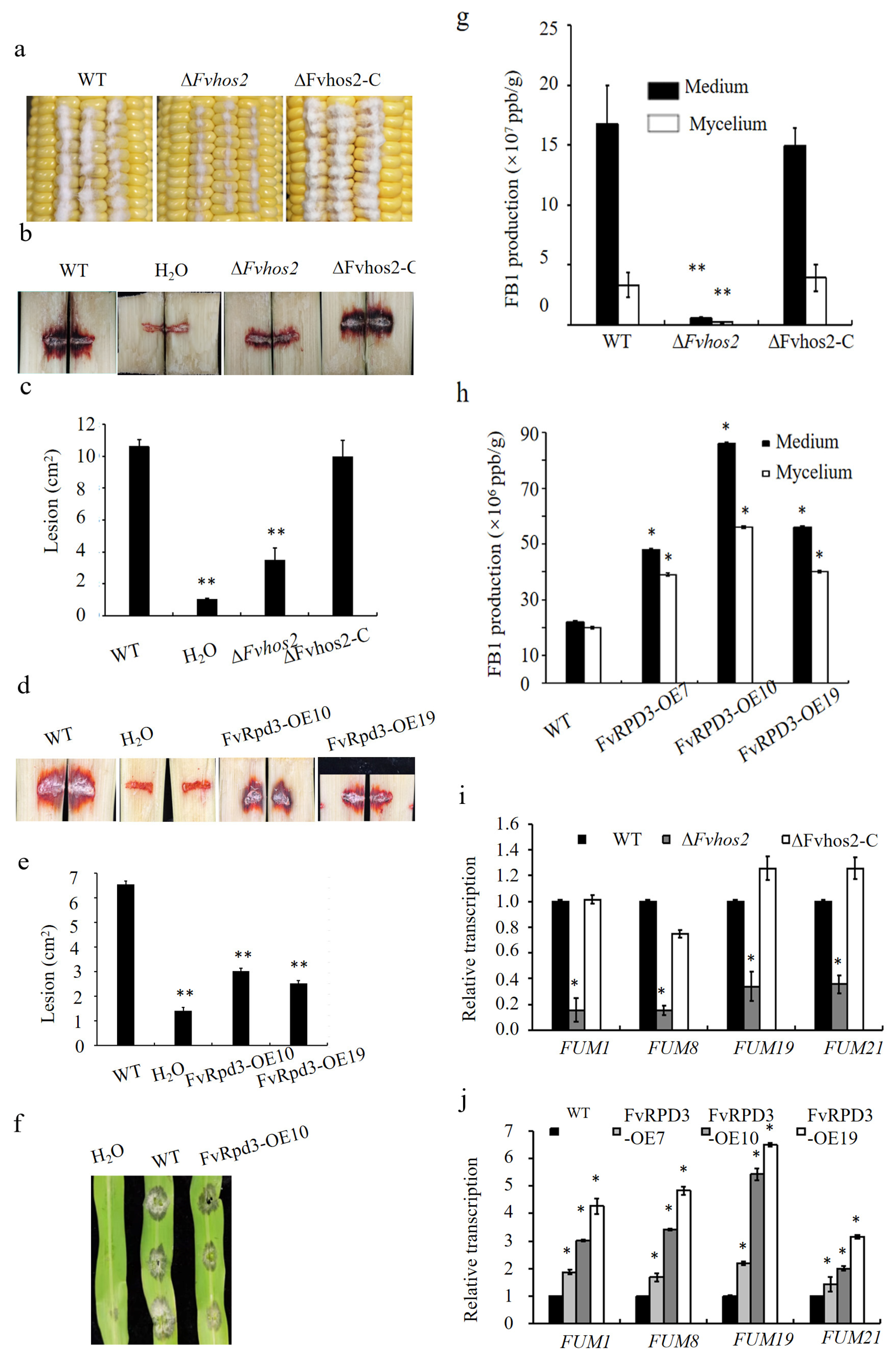
3.2. The Class I HDACs FvHos2 and FvRpd3 Were Crucial for the Vegetative Growth, Conidiation, Osmotic Stress Response, Pathogenicity, and Mycotoxin Production in F. verticillioides
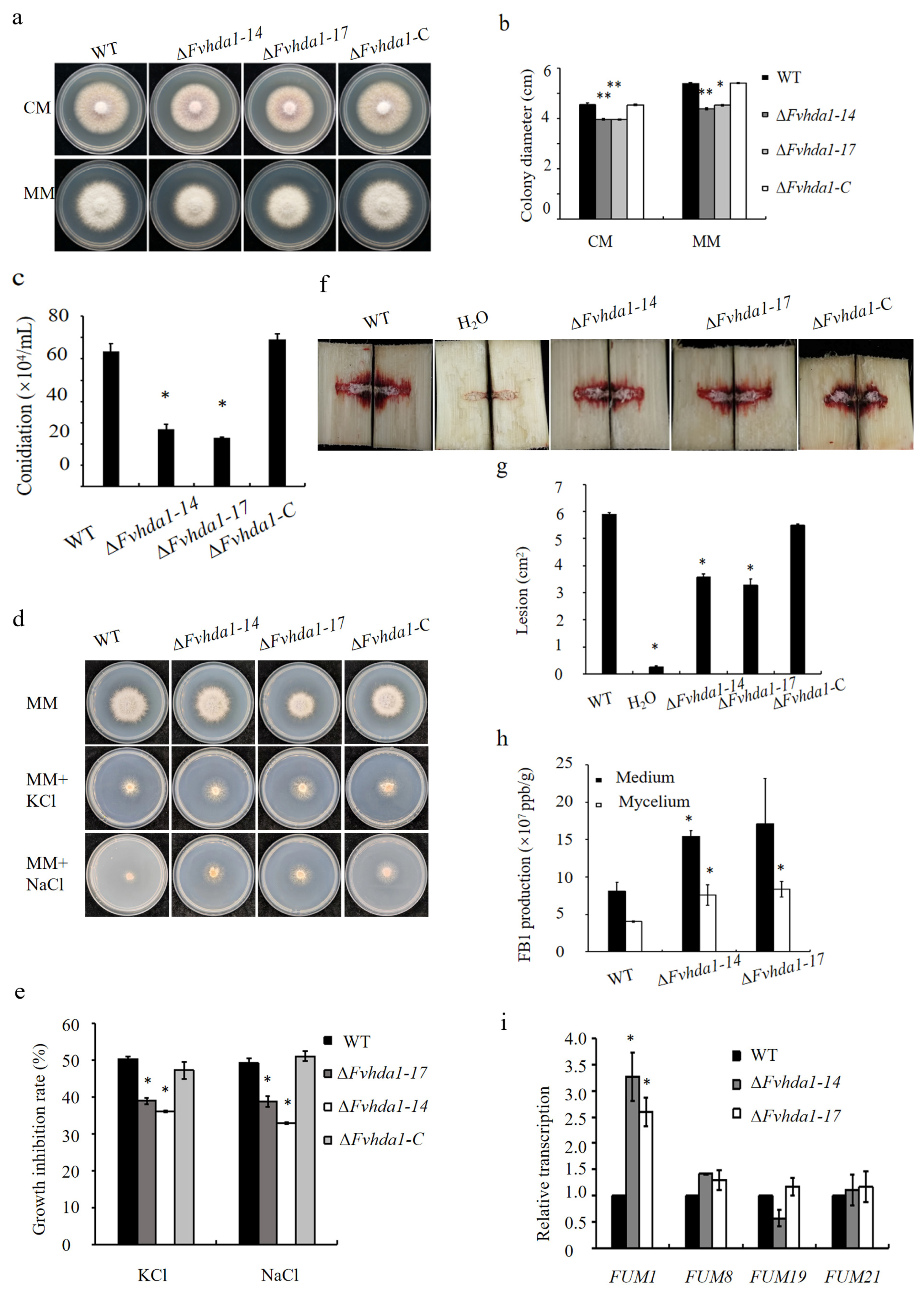
3.3. The Class II HDAC Hda1 Regulated the Growth, Spore Production, Osmotic Stress Sensitivity, Pathogenicity, and FB1 Synthesis in F. verticillioides
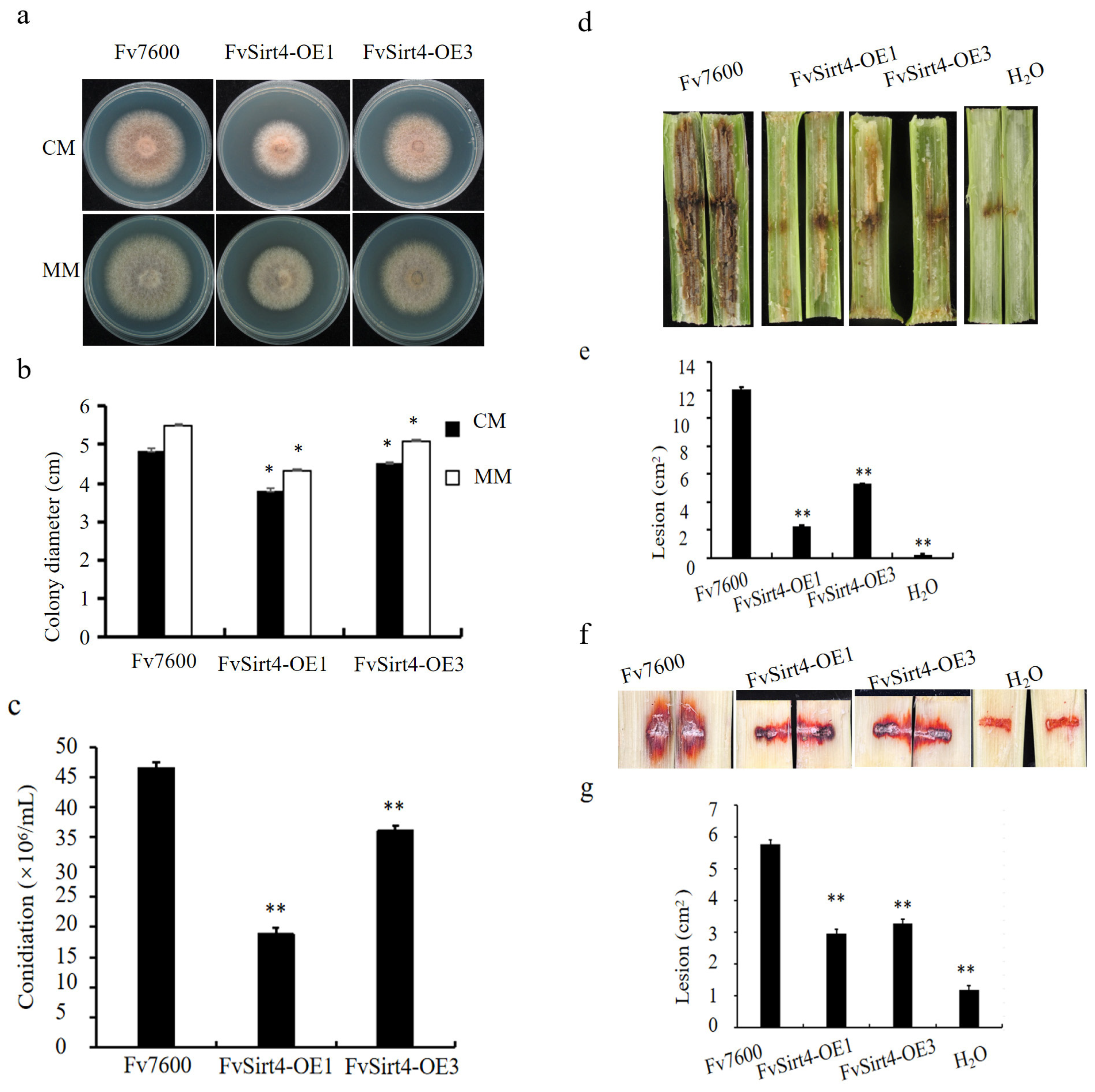
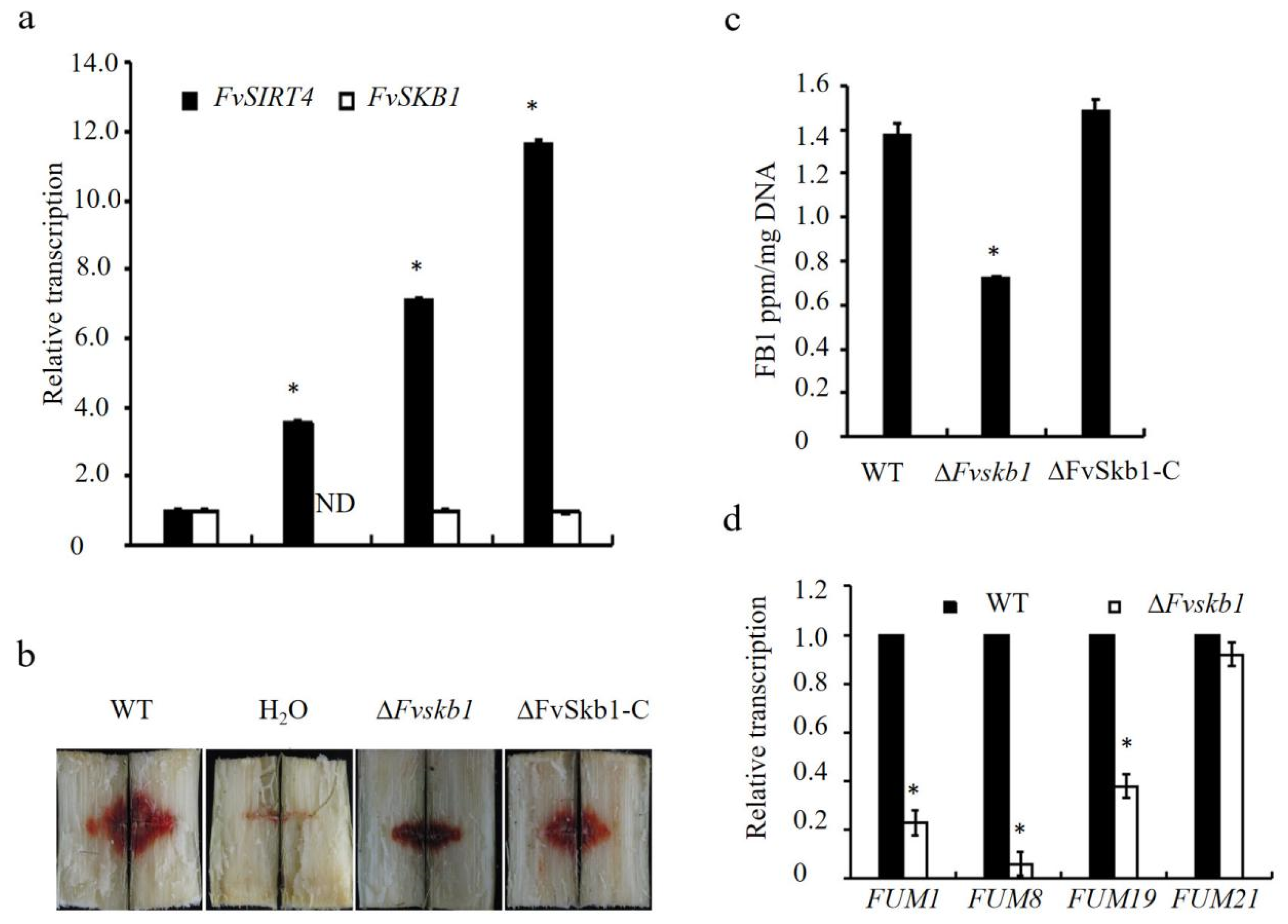
3.4. The Class III HDACs FvSir2, FvHst2, and FvSirt4 Regulated the Growth, Pathogenicity, and FB1 Production in F. verticillioides
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nitsch, S.; Zorro Shahidian, L.; Schneider, R. Histone acylations and chromatin dynamics: Concepts, challenges, and links to metabolism. EMBO Rep. 2021, 22, e52774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdin, E.; Ott, M. 50 years of protein acetylation: From gene regulation to epigenetics, metabolism and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 16, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, M.; Gaber, R.F. RPD3 encodes a second factor required to achieve maximum positive and negative transcriptional states in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1991, 11, 6317–6327. [Google Scholar]
- Taunton, J.; Hassig, C.A.; Schreiber, S.L. A mammalian histone deacetylase related to the yeast transcriptional regulator Rpd3p. Science 1996, 272, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Egervari, G.; Wang, Y.; Berger, S.L.; Lu, Z. Regulation of chromatin and gene expression by metabolic enzymes and metabolites. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rundlett, S.E.; Carmen, A.A.; Kobayashi, R.; Bavykin, S.; Turner, B.M.; Grunstein, M. HDA1 and RPD3 are members of distinct yeast histone deacetylase complexes that regulate silencing and transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 14503–14508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frye, R.A. Phylogenetic classification of prokaryotic and eukaryotic Sir2-like proteins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 273, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdistani, S.K.; Grunstein, M. Histone acetylation and deacetylation in yeast. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Faller, D.V. Transcription regulation by Class III histone deacetylases (HDACs)-Sirtuins. Transl. Oncogenomics 2008, 3, 53–65. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, A.B.; Qing, J.; Tam, K.H.; Zaman, S.; Luiso, M.; Radhakrishnan, I.; He, Y. Cryo-EM structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rpd3L histone deacetylase complex. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeheskely-Hayon, D.; Kotler, A.; Stark, M.; Hashimshony, T.; Sagee, S.; Kassir, Y. The roles of the catalytic and noncatalytic activities of Rpd3L and Rpd3S in the regulation of gene transcription in yeast. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e85088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurdistani, S.K.; Robyr, D.; Tavazoie, S.; Grunstein, M. Genome-wide binding map of the histone deacetylase Rpd3 in yeast. Nat. Genet. 2002, 31, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrozza, M.J.; Li, B.; Florens, L.; Suganuma, T.; Swanson, S.K.; Lee, K.K.; Shia, W.J.; Anderson, S.; Yates, J.; Washburn, M.P.; et al. Histone H3 methylation by Set2 directs deacetylation of coding regions by Rpd3S to suppress spurious intragenic transcription. Cell 2005, 123, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Carmen, A.A.; Kobayashi, R.; Suka, N.; Grunstein, M. HDA2 and HDA3 are related proteins that interact with and are essential for the activity of the yeast histone deacetylase HDA1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4391–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Turner, E.L.; Menzel, J.; Malo, M.E.; Harkness, T.A. Antagonistic Gcn5-Hda1 interactions revealed by mutations to the anaphase promoting complex in yeast. Cell Div. 2011, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Suka, N.; Carlson, M.; Grunstein, M. TUP1 utilizes histone H3/H2B-specific HDA1 deacetylase to repress gene activity in yeast. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Kurdistani, S.K.; Grunstein, M. Requirement of Hos2 histone deacetylase for gene activity in yeast. Science 2002, 298, 1412–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirén, M.; Silverstein, R.A.; Sinha, I.; Walfridsson, J.; Lee, H.M.; Laurenson, P.; Pillus, L.; Robyr, D.; Grunstein, M.; Ekwall, K. Genomewide analysis of nucleosome density histone acetylation and HDAC function in fission yeast. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 2906–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, B.J.; Verdin, E. Sirtuins: Sir2-related NAD-dependent protein deacetylases. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarente, L. Sir2 links chromatin silencing, metabolism, and aging. Genes. Dev. 2000, 14, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Horiuchi, T.; Tongaonkar, P.; Vu, L.; Nomura, M. SIR2 regulates recombination between different rDNA repeats, but not recombination within individual rRNA genes in yeast. Cell 2004, 117, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, K.; Xie, W.; Grunstein, M. Sir2 deacetylates histone H3 lysine 56 to regulate telomeric heterochromatin structure in yeast. Mol. Cell 2007, 27, 890–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Fine, R.D.; Dinda, M.; Bekiranov, S.; Smith, J.S. A Sir2-regulated locus control region in the recombination enhancer of Saccharomyces cerevisiae specifies chromosome III structure. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, I.; Misslinger, M.; Shadkchan, Y.; Dietl, A.M.; Petzer, V.; Orasch, T.; Abt, B.; Graessle, S.; Osherov, N.; Haas, H. The lysine deacetylase RpdA is essential for virulence in Aspergillus fumigatus. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, W. BcRPD3-mediated histone deacetylation is involved in growth and pathogenicity of Botrytis cinerea. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Farh, M.E.; Lee, J.; Oh, Y.T.; Cho, E.; Park, J.; Son, H.; Jeon, J. A histone deacetylase, Magnaporthe oryzae RPD3, regulates reproduction and pathogenic development in the rice blast fungus. mBio 2021, 12, e0260021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studt, L.; Schmidt, F.J.; Jahn, L.; Shevchenko, A.; Tekotte, H.; Wilm, M.; Rigaut, G.; Séraphin, B.; Aasland, R.; Stewart, A.F. Two histone deacetylases, FfHda1 and FfHda2, are important for Fusarium fujikuroi secondary metabolism and virulence. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 7719–7734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichmann, M.; Jamnischek, A.; Weinzierl, G. The histone deacetylase Hda1 from Ustilago maydis is essential for teliospore development. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 46, 1169–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijnappel, W.W.; Schaft, D.; Roguev, A.; Ladendorf, O.; Huber, S.; Kahmann, R.; Kämper, J. The S. cerevisiae SET3 complex includes two histone deacetylases, Hos2 and Hst1, and is a meiotic-specific repressor of the sporulation gene program. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 2991–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hnisz, D.; Majer, O.; Frohner, I.E.; Komnenovic, V.; Kuchler, K. The Set3/Hos2 histone deacetylase complex attenuates cAMP/PKA signaling to regulate morphogenesis and virulence of Candida albicans. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Martín, J.; Uría, J.A.; Johnson, A.D. Phenotypic switching in Candida albicans is controlled by a SIR2 gene. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 2580–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, J.; Marroquin-Guzman, M.; Nandakumar, R.; Shijo, S.; Cornwell, K.M.; Li, G.; Wilson, R.A. Plant defence suppression is mediated by a fungal sirtuin during rice infection by Magnaporthe oryzae. Mol. Microbiol. 2014, 94, 70–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Tian, L.; Xie, J.T.; Huang, Q.Y.; Feng, M.G.; Keyhani, N.O. A fungal sirtuin modulates development and virulence in the insect pathogen, Beauveria bassiana. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 5164–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, F.A.; Derengowski, L.S.; Albuquerque, P.; Nicola, A.M.; Silva-Pereira, I.; Poças-Fonseca, M.J. Histone deacetylases inhibitors effects on Cryptococcus neoformans major virulence phenotypes. Virulence 2015, 6, 618–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallegos-García, V.; Pan, S.J.; Juárez-Cepeda, J.; Ramírez-Zavaleta, C.Y.; Martin-del-Campo, M.B.; Martínez-Jiménez, V.; Castaño, I.; Cormack, B.; De Las Peñas, A. A novel downstream regulatory element cooperates with the silencing machinery to repress EPA1 expression in Candida glabrata. Genetics 2012, 190, 1285–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arras, S.D.M.; Chitty, J.L.; Wizrah, M.S.I.; Erpf, P.E.; Schulz, B.L.; Tanurdzic, M.; Fraser, J.A. Sirtuins in the phylum Basidiomycota: A role in virulence in Cryptococcus neoformans. Scientificreports 2017, 7, 46567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Cao, X.; Qu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Naqvi, N.I.; Deng, Y.Z. The histone deacetylases MoRpd3 and MoHst4 regulate growth, conidiation, and pathogenicity in the rice blast gungus Magnaporthe oryzae. mSphere 2021, 6, e0011821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce-García, N.; Serna-Saldivar, S.O.; Garcia-Lara, S. Fumonisins and their analogues in contaminated corn and its processed foods—A review. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2018, 35, 2183–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.Y.; Lin, M.; Peng, M.H.; Yan, H.J.; Wang, J.J.; Zhou, J.; Lu, G.D.; Wang, Z.H.; Shim, W.B. Fusarium verticillioides FvPex8 is a key component of the peroxisomal Docking/Translocation module that serves important roles in fumonisin biosynthesis but not in virulence. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2021, 34, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.Y.; Lin, M.; Yan, H.J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Lu, G.D.; Wang, Z.H.; Shim, W.B. The peroxisomal matrix shuttling receptor Pex5 plays a role of FB1 production and virulence in Fusarium verticillioides. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 2957–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.J.; van der Does, H.C.; Borkovich, K.A.; Coleman, J.J.; Daboussi, M.J.; Di Pietro, A.; Dufresne, M.; Freitag, M.; Grabherr, M.; Henrissat, B.; et al. Comparative genomics reveals mobile pathogenicity chromosomes in Fusarium. Nature 2010, 464, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, H.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, H.; Huang, X.; Li, S.; Zhou, A.; et al. WEGO 2.0: A web tool for analyzing and plotting GO annotations, 2018 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W71–W75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo-Oller, G.; Ordoñez, R.; Dotor, J. A new background subtraction method for Western blot densitometry band quantification through image analysis software. J. Immunol. Methods 2018, 457, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Abubakar, Y.S.; Wei, L.J.; Wang, J.J.; Lu, X.G.; Lu, G.D.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhou, J.; Yu, W.Y. Fusarium verticillioides Pex7/20 mediates peroxisomal PTS2 pathway import, pathogenicity, and fumonisin B1 biosynthesis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 6595–6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, A.; Zhang, H.; Yu, W.; Shim, W.B. Identification and characterization of pathogenic and endophytic fungal species associated with pokkah boeng disease of sugarcane. Plant Pathol. J. 2017, 33, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallan, D.Z.; Henrique, M.O.; Silva-Filho, M.C. The phytopathogen fusarium verticillioides modifies the intestinal morphology of the sugarcane borer. Pathogens 2023, 12, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malapi-Wight, M.; Smith, J.; Campbell, J.; Bluhm, B.H.; Shim, W.B. Sda1, a Cys2-His2 zinc finger transcription factor, is involved in polyol metabolism and fumonisin B1 production in Fusarium verticillioides. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, E.; Yoshida, M. Erasers of histone acetylation: The histone deacetylase enzymes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a018713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Zhang, H.; Yan, H.; Yoon, B.J.; Shim, W.B. Characterizing co-expression networks underpinning maize stalk rot virulence in Fusarium verticillioides through computational subnetwork module analyses. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, S.; Sharma, A.; Raucci, R.; Costantini, M.; Autiero, I.; Colonna, G. Genealogy of an ancient protein family: The Sirtuins, a family of disordered members. BMC Evol. Biol. 2013, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaquero, A.; Scher, M.B.; Lee, D.H.; Sutton, A.; Cheng, H.L.; Alt, F.W.; Serrano, L.; Sternglanz, R.; Reinberg, D. SirT2 is a histone deacetylase with preference for histone H4 Lys 16 during mitosis. Genes. Dev. 2006, 20, 1256–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeulen, M.; Carrozza, M.J.; Lasonder, E.; Workman, J.L.; Logie, C.; Stunnenberg, H.G. In vitro targeting reveals intrinsic histone tail specificity of the Sin3/histone deacetylase and N-CoR/SMRT corepressor complexes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 2364–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suka, N.; Suka, Y.; Carmen, A.A.; Wu, J.; Grunstein, M. Highly specific antibodies determine histone acetylation site usage in yeast heterochromatin and euchromatin. Mol. Cell 2001, 8, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torreblanca, J.; Stumpferl, S.; Basse, C.W. Histone deacetylase Hda1 acts as repressor of the Ustilago maydis biotrophic marker gene mig1. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2003, 38, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwab, E.K.; Bok, J.W.; Tribus, M.; Galehr, J.; Graessle, S.; Keller, N.P. Histone deacetylase activity regulates chemical diversity in Aspergillus. Eukaryot. Cell 2007, 6, 1656–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, W.; Wang, G.; Kang, Z.; Kistler, H.C.; Xu, J.R. The HDF1 histone deacetylase gene is important for conidiation, sexual reproduction, and pathogenesis in Fusarium graminearum. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2011, 24, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trojer, P.; Brandtner, E.M.; Brosch, G.; Loidl, P.; Galehr, J.; Linzmaier, R.; Haas, H.; Mair, K.; Tribus, M.; Graessle, S. Histone deacetylases in fungi: Novel members, new facts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3971–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robyr, D.; Suka, Y.; Xenarios, I.; Kurdistani, S.K.; Wang, A.; Suka, N.; Grunstein, M. Microarray deacetylation maps determine genome-wide functions for yeast histone deacetylases. Cell 2002, 109, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentin, I.; Montis, V.; Döll, K.; Alabouvette, C.; Tamietti, G.; Karlovsky, P.; Cardinale, F. Transcription of genes in the biosynthetic pathway for fumonisin mycotoxins is epigenetically and differentially regulated in the fungal maize pathogen Fusarium verticillioides. Eukaryot. Cell 2012, 11, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roze, L.V.; Arthur, A.E.; Hong, S.Y.; Chanda, A.; Linz, J.E. The initiation and pattern of spread of histone H4 acetylation parallel the order of transcriptional activation of genes in the aflatoxin cluster. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 66, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elías-Villalobos, A.; Fernández-Álvarez, A.; Moreno-Sánchez, I.; Helmlinger, D.; Ibeas, J.I. The Hos2 histone deacetylase controls Ustilago maydis virulence through direct regulation of mating-type genes. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCord, R.; Pierce, M.; Xie, J.; Wonkatal, S.; Mickel, C.; Vershon, A.K. Rfm1, a novel tethering factor required to recruit the Hst1 histone deacetylase for repression of middle sporulation genes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 2009–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Xie, J.; Pierce, M.; Gailus-Durner, V.; Wagner, M.; Winter, E.; Vershon, A.K. Sum1 and Hst1 repress middle sporulation-specific gene expression during mitosis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 6448–6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.D.; Ham, S.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Jang, I.; Lee, B.B.; Lee, M.K.; Hwang, J.T.; Roh, T.Y.; Kim, T. Transcription-dependent targeting of Hda1C to hyperactive genes mediates H4-specific deacetylation in yeast. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
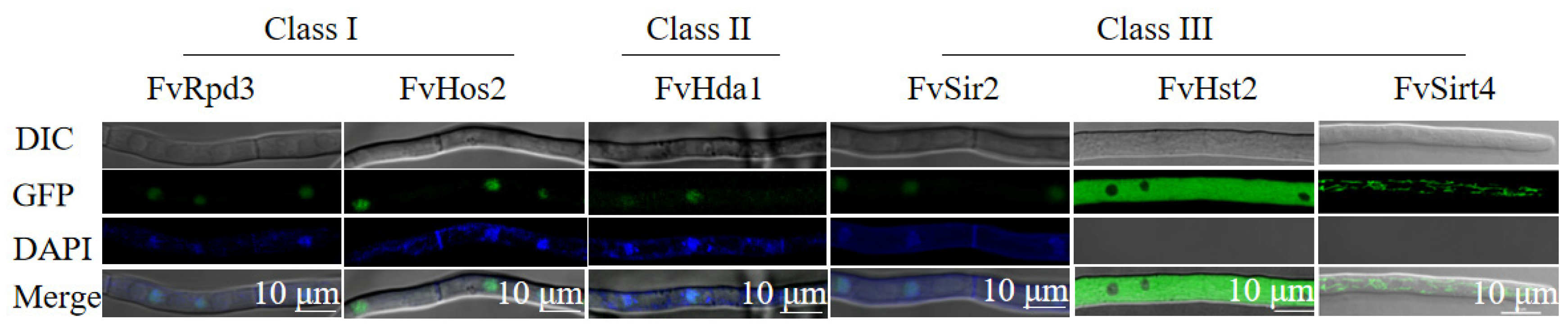


| Class I | Class II | Class III Sirtuins | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identify | Rpd3 | Hos2 | Hda1 | Hos3 | Sir2 | Hst2 | Hst3 | Hst4 | Sirt4 | Sirt5 | Sirt6 |
| Mutants | OE 1 | KO 2 | KO | KO | KO | OE | |||||
| Pathogenic | + 3 | + | + | − 4 | − | + | |||||
| Affect different genes on FB1 | FUM1, 8, 19, 21 | FUMs, FvSda1 5 | FUM1, 8, 19, 21 | FUM19 6 | FUM1, 8, 19, 21 FvSkb1 7 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Wen, G.; Liang, J.; Chen, X.; Lu, G.; Wang, Z.; Huang, J. Regulation of Fumonisin B1 Production and Pathogenicity in Fusarium verticillioides by Histone Deacetylases. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2196. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14102196
Yu W, Wang J, Wang M, Wen G, Liang J, Chen X, Lu G, Wang Z, Huang J. Regulation of Fumonisin B1 Production and Pathogenicity in Fusarium verticillioides by Histone Deacetylases. Agronomy. 2024; 14(10):2196. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14102196
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Wenying, Jiajia Wang, Meiduo Wang, Gaolong Wen, Jiayan Liang, Xiaoting Chen, Guodong Lu, Zonghua Wang, and Jun Huang. 2024. "Regulation of Fumonisin B1 Production and Pathogenicity in Fusarium verticillioides by Histone Deacetylases" Agronomy 14, no. 10: 2196. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14102196
APA StyleYu, W., Wang, J., Wang, M., Wen, G., Liang, J., Chen, X., Lu, G., Wang, Z., & Huang, J. (2024). Regulation of Fumonisin B1 Production and Pathogenicity in Fusarium verticillioides by Histone Deacetylases. Agronomy, 14(10), 2196. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14102196







