Drought Characteristics during Spring Sowing along the Great Wall Based on the MCI
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
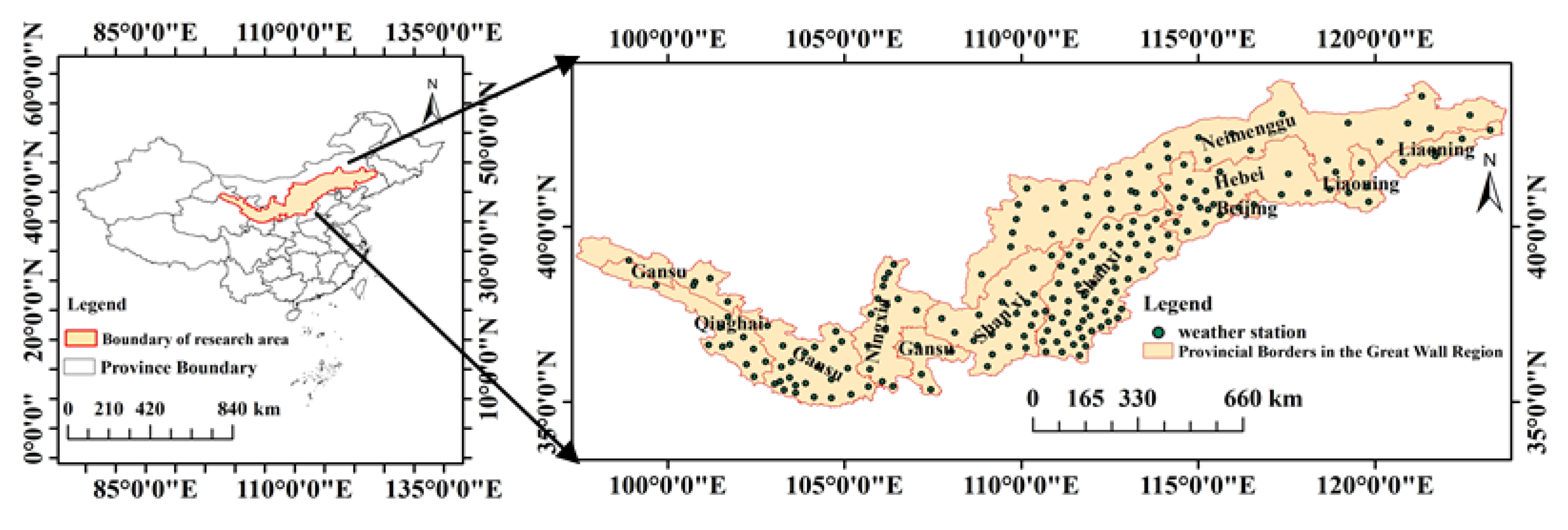
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Research Method
2.3.1. Meteorological Drought Composite Index (MCI)
- Step 1:
- Calculate the daily potential evapotranspiration (PET), using the FAO Penman–Monteith method for this study [25].
- Step 2:
- Calculate the relative humidity index (MI) [33]
- Step 3:
- Calculate the SPI [33]. Since the distribution of precipitation is generally not normal, a Gamma distribution is used to describe the variation in precipitation. After calculating the Gamma distribution probability of precipitation, a normal standardization process is carried out. Finally, the cumulative frequency of the standardized precipitation is used as the Standardized Precipitation Index.
- (1)
- Calculate the Gamma distribution probability density function of precipitation.
- (2)
- Calculate the probability F(x) of precipitation.
- (3)
- Perform normalization on the probability of distribution, that is, substitute the probability value obtained from the second step into the standardized normal distribution function:
- Step 4:
- Calculate the Standardized Weighted Precipitation Index (SPIW)
- Step 5:
- Calculate the MCI [33]
2.3.2. Drought Characterization Indicators
- (1)
- Drought Intensity
- (2)
- Drought Frequency
- (3)
- Station Ratio
2.3.3. The Mann–Kendall Test
2.3.4. Wavelet Analysis
2.3.5. Center of Gravity Migration
3. Results
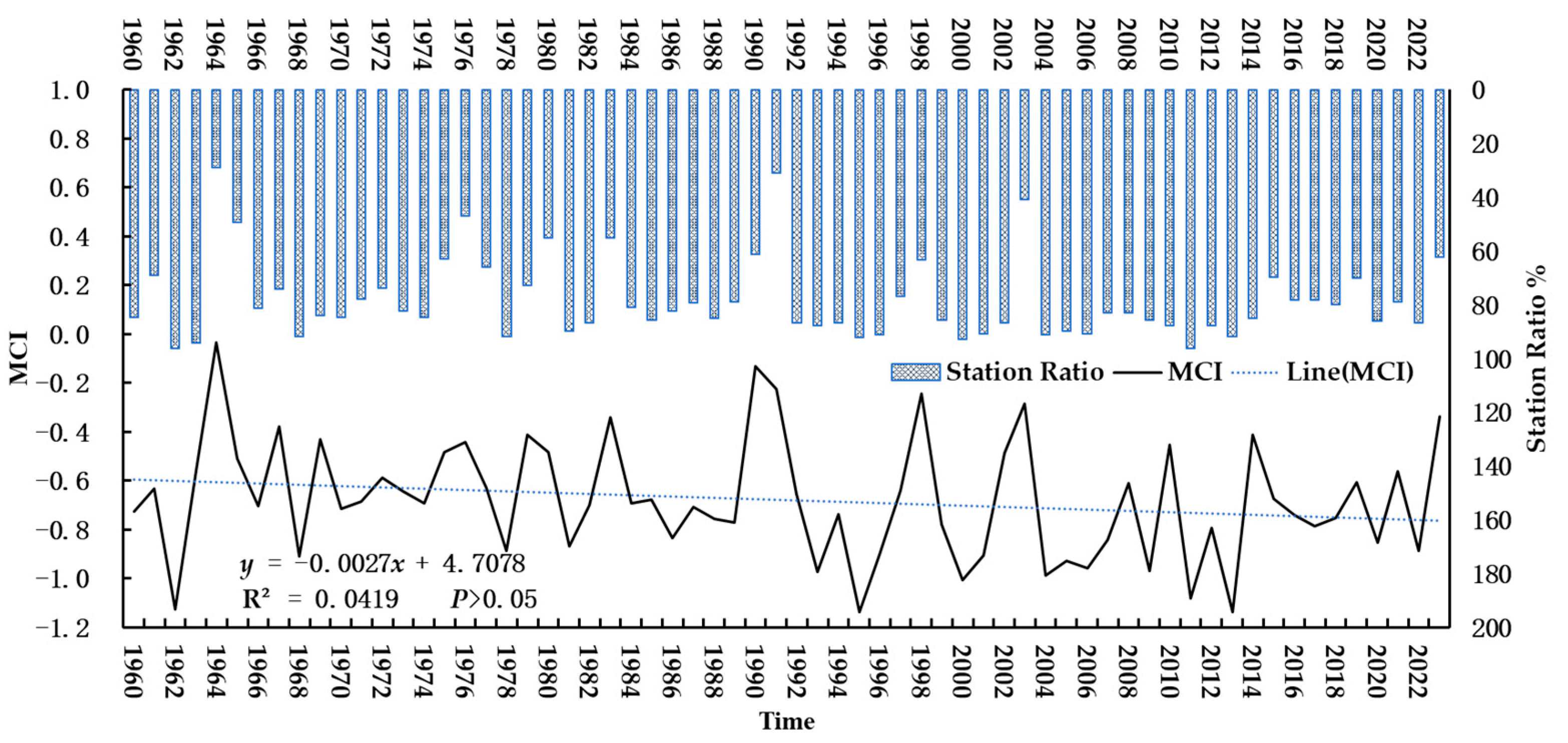
3.1. Drought Intensity
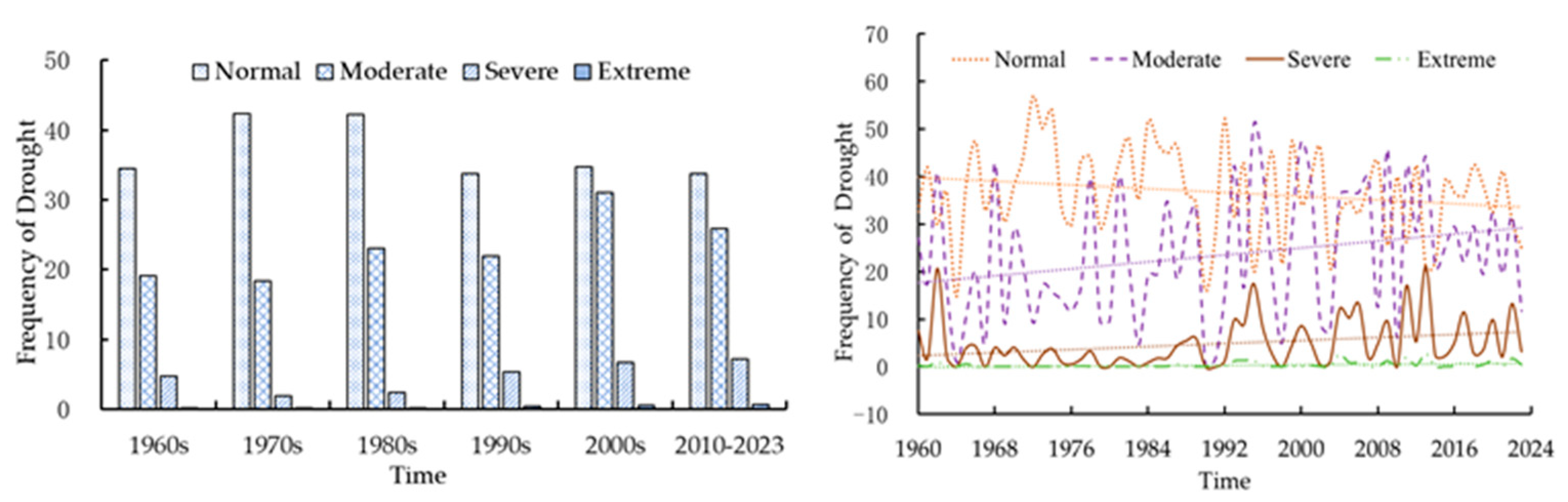
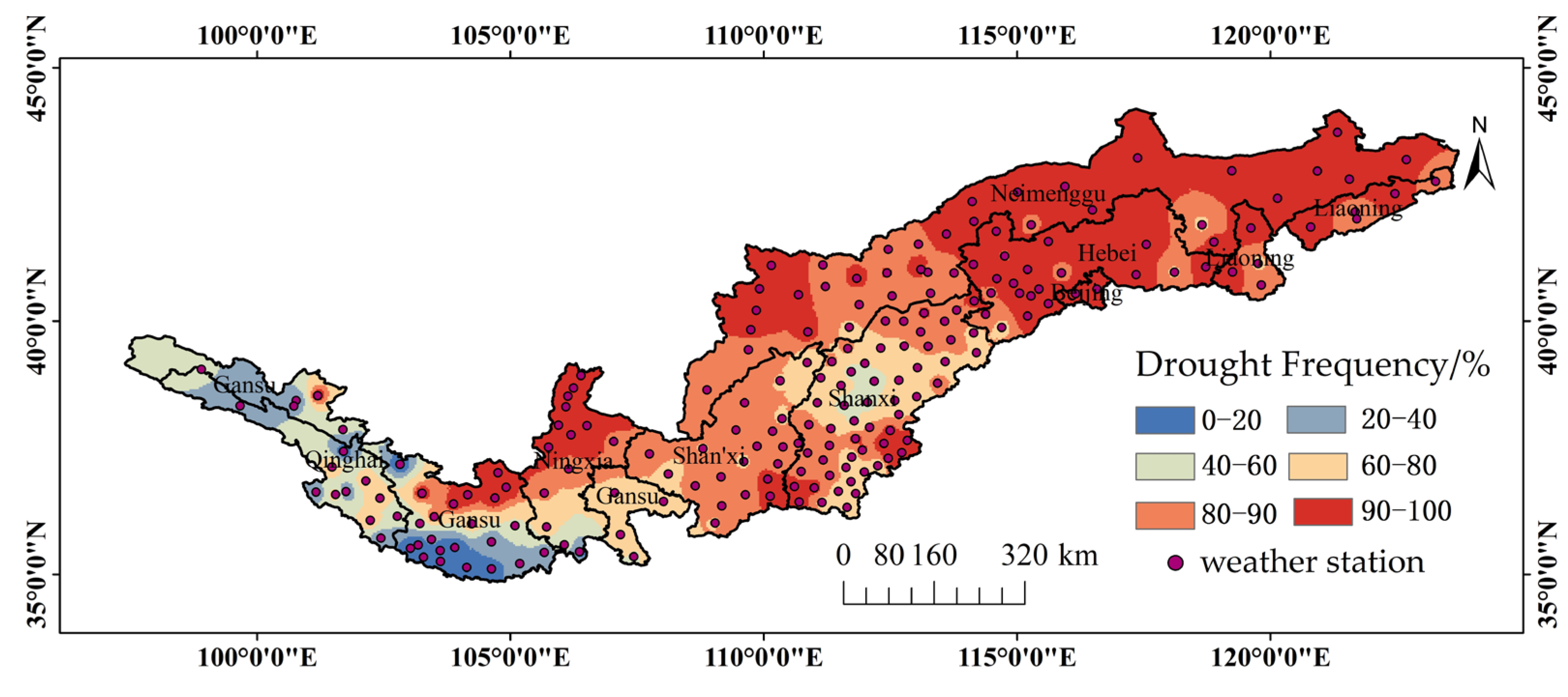
3.2. Drought Frequency
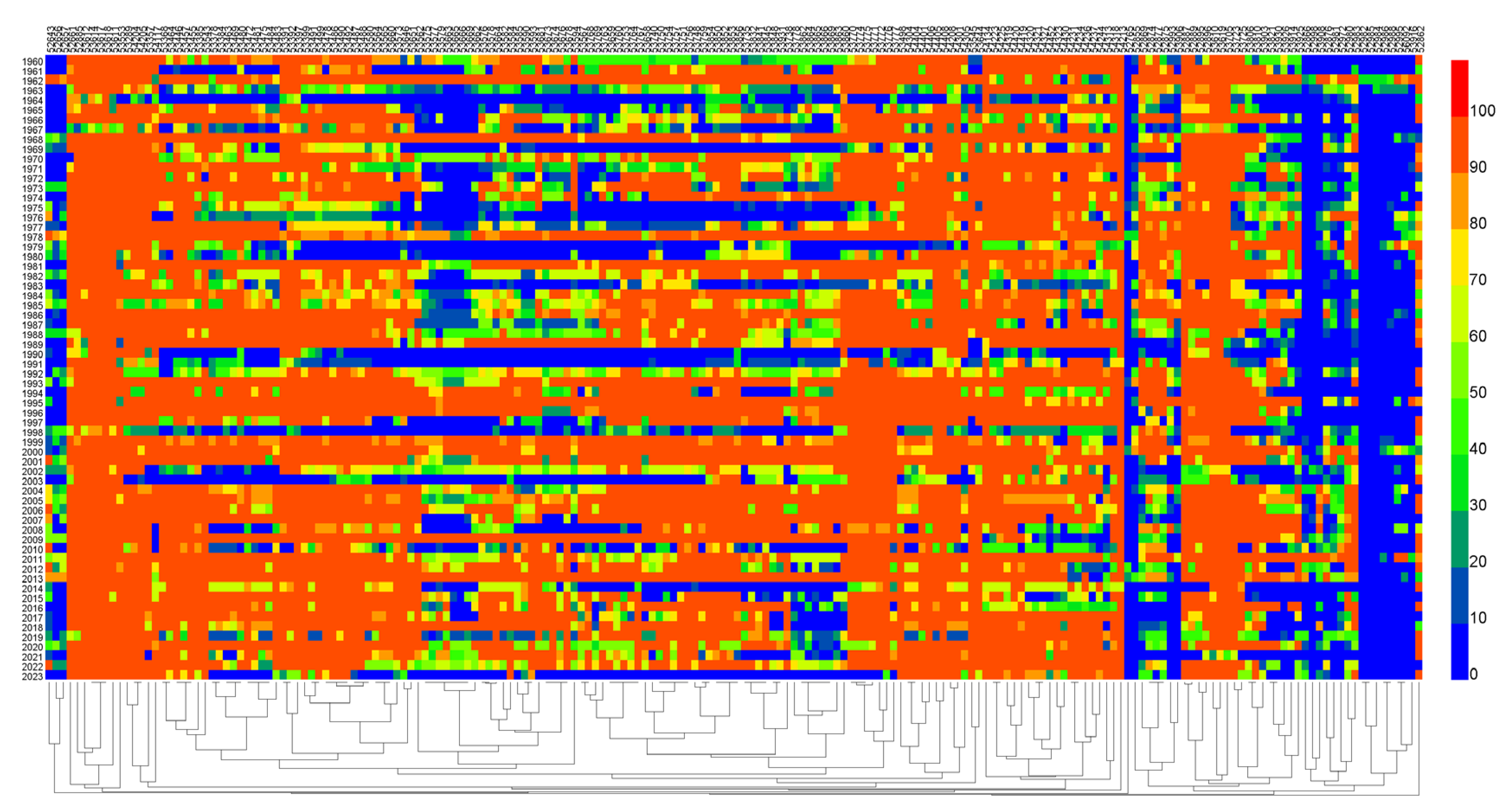
3.2.1. Temporal Analysis
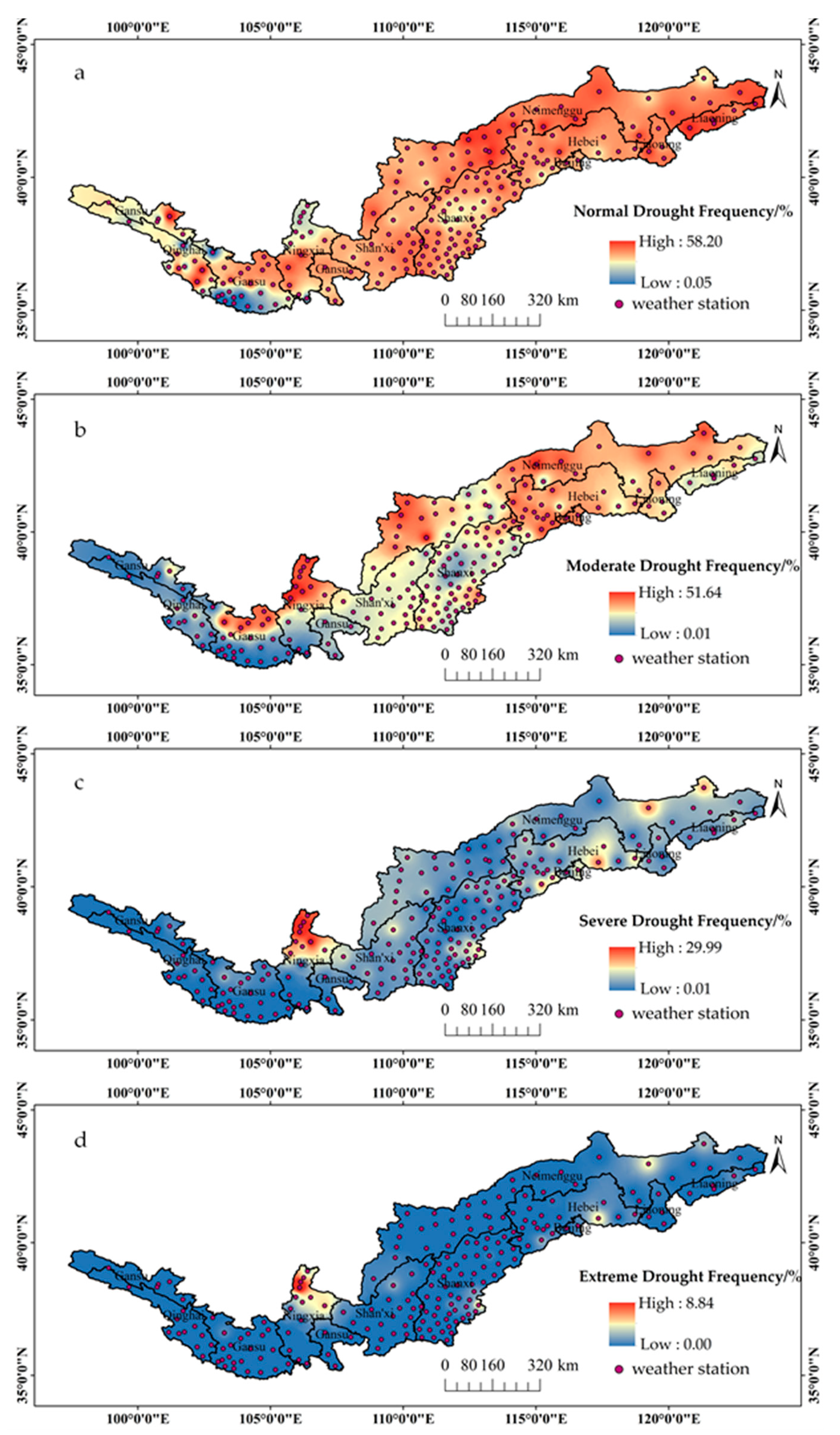
3.2.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics
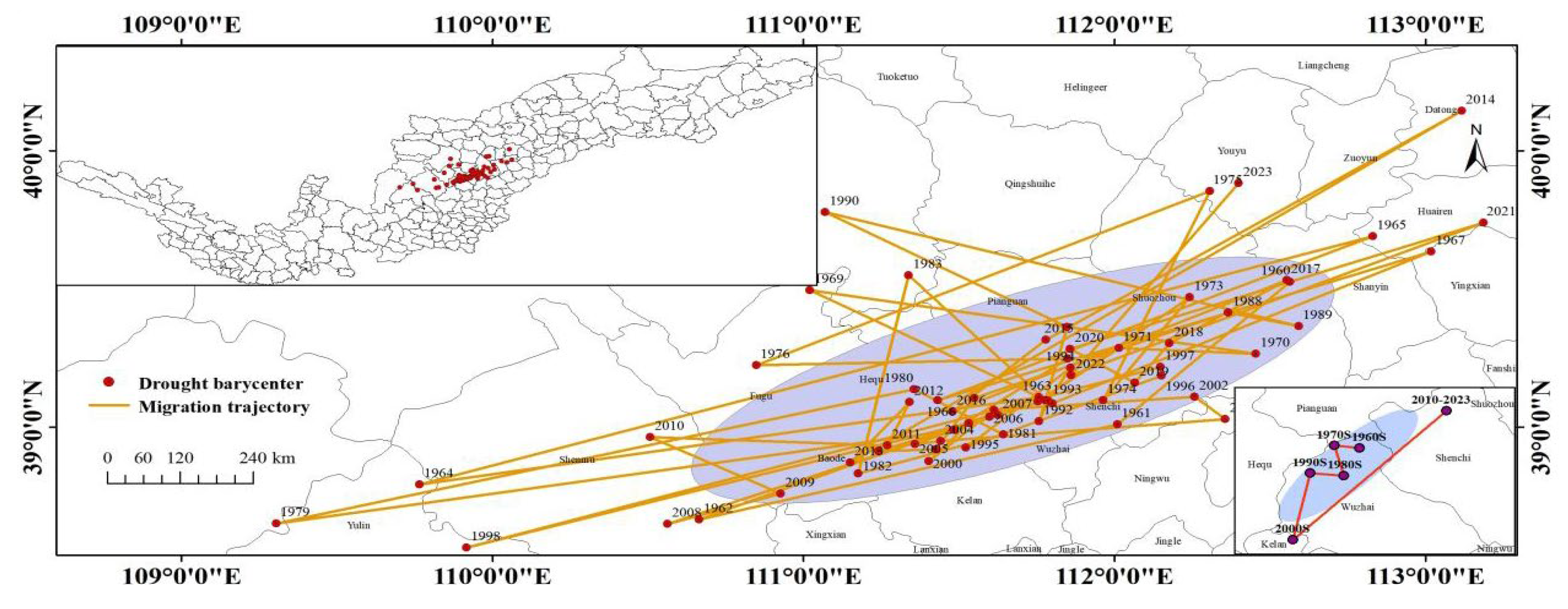
3.3. Drought Center Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tye, M.R.; Dagon, K.; Molina, M.J.; Jadwiga, H. Indices of extremes: Geographic patterns of change in extremes and associated vegetation impacts under climate intervention. Earth Syst. Dyn. Discuss. 2022, 13, 1233–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Yang, D.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Tang, X. Research on Drought Characteristics in the Lijiang River Basin Based on Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index from 1980 to 2019. Water Sav. Irrig. 2024, 1, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Chen, J.J.; Lou, P. Temporal and spatial changes of drought in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region based on remote sensing technology. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, 10, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yan, R.; Luo, P.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, S.; Wei, Z.; Zha, X. Analysis of the Ongoing Effects of Disasters in Urbanization Process and Climate Change: China’s Floods and Droughts. Sustainability 2023, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilky; Patra, S.; Ekka, P.; Kumar, A.; Saikia, P.; Khan, M.L. Climate Change: A Major Challenge to Biodiversity Conservation, Ecological Services, and Sustainable Development. Biodivers. Conserv. 2023, 9, 577–592. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Ruan, T.; Luo, G.; Gao, C. Response of winter wheat drought to meteorological drought above the Bengbu Sluice in the Huaihe River. J. Nat. Disasters 2019, 28, 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, D.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Q.; Yang, J. Applicability of Drought Severity Index (DSI) in Remote Sensing Monitoring of Drought in Shandong Province. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2020, 41, 102–112. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, R.; Deng, B. Characteristics of the extreme high temperature and drought and their main impacts in southwestern China of 2022. J. Arid Meteorol. 2022, 40, 764–770. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Liao, L.; Gan, R.; Wang, W.; Wang, T.; Liang, L. The regional characteristics of meteorological drought event and its multidimensional factors measurement by daily SPEI in Guangxi, China. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2022, 14, 117–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, S.; Dixon, R.D. Long-Term Seasonal Drought Trends in the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor. Climate 2023, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, P.; Chen, B.; Yuan, D.; Hong, M.; Liu, H. Dynamic risk assessment of drought disaster: A case study of Jiangxi Province, China. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2020, 12, 1761–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meitner, J.; Bálek, J.; Bláhová, M.; Semerádová, D.; Hlavinka, P.; Lukas, V.; Jurečka, F.; Žalud, Z.; Klem, K.; Anderson, M.C.; et al. Estimating Drought-Induced Crop Yield Losses at the Cadastral Area Level in the Czech Republic. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Tao, H. Assessing drought disaster hazard in Xinjiang of China using MCI and Gumbel-Copula function. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2023, 39, 133–141. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Gan, C.; Zhou, K.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, D. Spatiotemporal distribution of drought and hazard assessment of highland barley in Tibet. Arid Land Geogr. 2023, 46, 1098–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrimore, J.H.; Heim, R.R.; Svoboda, M.D.; Swail, V.R.; Englehart, P.J. Beginning a new era of drought monitoring across North America. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 83, 1191–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, R.R., Jr. A Review of Twentieth-Century Drought Indices Used in the United States. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 83, 1149–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Hernández, K.A.; Corzo Perez, G.A. A Comparative Analysis of Spatiotemporal Drought Events from Remote Sensing and Standardized Precipitation Indexes in Central America Dry Corridor. Water Sci. Technol. Libr. 2022, 105, 77–103. [Google Scholar]
- Dukat, P.; Bednorz, E.; Ziemblińska, K.; Urbaniak, M. Trends in drought occurrence and severity at mid-latitude European stations (1951–2015) estimated using standardized precipitation (SPI) and precipitation and evapotranspiration (SPEI) indices. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2022, 134, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Begueria, S.; Lopez-Moreno, J.I. A Multiscalar Drought Index Sensitive to Global Warming: The Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagan, B.; Zhang, Z.; Baopeing, F.; Wagan, H.; Si, H.; Ahmad, I.; Kabo-bah, A.T. Using the SPI to Interpret Spatial and Temporal Conditions of Drought in China. Outlook Agric. 2015, 44, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, X.; Pan, Y.; Bai, J.; Li, S. Performance of different drought indices for agriculture drought in the North China Plain. J. Arid Land 2018, 10, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Leng, X.; Sun, G.; Peng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Q. Assessment of Drought Characteristics in Yunnan Province Based on SPI and SPEI from 1961 to 2100. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2018, 49, 236–245+299. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Wang, F.; Lu, X. Spatiotemporal Variation of Drought in Shandong Province Analyzed Using the Standardized Precipitation-evapotranspiration Index. J. Irrig. Drain. 2021, 40, 1672–3317. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.A.; Riaz, S.; Jiang, H.; Qamar, S.; Ali, Z.; Islamil, M.; Nazeer, A.; Faisal, M.; Satti, S.; Zhang, X. Development of an assessment framework for the proposed Multi-Scalar Seasonally Amalgamated Regional Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index (MSARSPEI) for regional drought classifications in global warming context. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 312, 114951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, M.; Han, H.; Hu, X.; Xia, Q.; Guo, X. Drought characteristics and causes during summer maize growth period on Huang-Huai-Hai Plain based on daily scale SPEI. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 280, 108198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Yang, Q.; Wang, H.; Cao, Q.; Lin, C. Characteristics of Meteorological Drought Intensity in Inner Mongolia Based on MCI. Meteorol. Environ. Sci. 2019, 42, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Y.; Zhang, C. Spatio-Temporal distribution characteristics and disaster change of drought in China Based on meteorological drought composite index. Meteorol. Mon. 2017, 43, 1402–1409. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhi, X.; Li, F. Characteristics of spatiotemporal variation of drought in Henan based on meteorological drought composite index. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2020, 20, 3420–3426. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Dou, Y.; Zhan, X.; Xi, F.; Luo, Z.; Gan, C. Analysis on Change Characteristics of Drought Intensity during the Growth Period of Highland Barley in Tibet. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2023, 44, 834–844. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, D.; Huang, G.; Liu, M. Linwangtian—Basic Farmland Construction Model in the Great Wall Area. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 1992, 2, 40–49. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F. Artificial Degradation of Natural Landscapes and Rational Regulation Strategies for Human-Land Systems in Ecologically Fragile Areas—A Case Study of the Great Wall Area in Shanxi, Shaanxi, and Inner Mongolia. Resour. Environ. Arid Reg. 1989, 3, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, D.; Huang, G.; Liu, M. History and Prevention Strategies of Soil Erosion Development in the Great Wall Area of Shaanxi, Mongolia, and Shanxi. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 1986, 3, 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 20481-2017; Meteorological Drought Level. National Climate Center. Lanzhou Institute of Arid Meteorology. National Meteorological Administration. Forecasting and Network Department of China Meteorological Administration. Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2017; p. 32.
- Wang, D.; Chen, X.; Sun, Z.; Xin, Y.; Wang, H.; Chai, H.; Wang, H. Long-Term Monitoring of Remote Sensing Ecological Index Changes in Golmud. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 5922–5933. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, W.; Yang, L.; Pan, J.-Y.; Wang, S.; Lai, X.; Long, A. A Study of Drought and Flood Cycles in Xinyang, China, Using the Wavelet Transform and M-K Test. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; E, C.; Li, X.; Qi, D.; Zhou, L. Characteristics of Winter Precipitation Changes and Centroid Migration in the Qinghai Plateau from 1960 to 2019. J. Nat. Disasters 2023, 32, 118–130. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Lai, H.; Men, R.; Wang, F.; Feng, K.; Qi, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Quan, Q.; Huang, S. Dynamic Characteristics of Meteorological Drought and Its Impact on Vegetation in an Arid and Semi-Arid Region. Water 2023, 15, 3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Si, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Wulan, Y.; Peng, Y.; Gao, J. A seasonal forecast scheme for the Inner Mongolia spring drought. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 135, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Qian, H.; Chen, J.; Han, X. Characteristics of Spatial-Temporal Evolution of Meteorological Drought in the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region of Northwest China. Water 2018, 10, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Qin, D.; Huang, B.; Chen, H. Drought disaster risks under CMIP5 RCP scenarios in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China. Nat. Hazards 2020, 100, 909–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Jiaxuan, W.; Cheng, W. Drought in Shanxi Province Based on Remote Sensing Drought Index Analysis of Spatial and Temporal Variation Characteristics. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Li, Y.; You, L.; Zhai, D. Analysis of the Trends in Extreme Temperature and Precipitation Changes in Shanxi over the Past 53 Years. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2014, 30, 120–126. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Causes and Changes of Drought in China: Research Progress and Prospects. J. Meteorol. Res. 2020, 34, 460–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Dai, A.; Huang, J.; Zhang, L. Preface to the Special Issue on Causes, Impacts, and Predictability of Droughts for the Past, Present, and Future. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2023, 41, 191–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Level | Type | MCI | Drought Impact Degree |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | No Drought | −0.5 < MCI | Surface is moist, crop water supply is sufficient |
| 2 | Normal Drought | −1.0 < MCI ≤ −0.5 | Surface air is dry, soil has slight moisture deficiency |
| 3 | Moderate Drought | −1.5 < MCI ≤ −1.0 | Soil surface is dry, soil has moisture deficiency |
| 4 | Severe Drought | −2.0 < MCI ≤ −1.5 | Soil moisture is severely deficient, surface has dry soil, crops are wilting |
| 5 | Extreme Drought | MCI ≤ −2.0 | Soil moisture is severely deficient, thick dry soil layer appears, crops are dying on a large scale |
| Type | 1960s | 1970s | 1980s | 1990s | 2000s | 2000–2023 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Migratory direction | - | West | Southeast | West | Southwest | Northeast |
| Migration distance (km) | - | 5.570 | 9.865 | 7.529 | 21.708 | 53.691 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, G.; Wang, J.; Sun, W.; Huang, M.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Zhang, W. Drought Characteristics during Spring Sowing along the Great Wall Based on the MCI. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14102195
Wang G, Wang J, Sun W, Huang M, Zhang J, Huang X, Zhang W. Drought Characteristics during Spring Sowing along the Great Wall Based on the MCI. Agronomy. 2024; 14(10):2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14102195
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Guofang, Juanling Wang, Wei Sun, Mingjing Huang, Jiancheng Zhang, Xuefang Huang, and Wuping Zhang. 2024. "Drought Characteristics during Spring Sowing along the Great Wall Based on the MCI" Agronomy 14, no. 10: 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14102195
APA StyleWang, G., Wang, J., Sun, W., Huang, M., Zhang, J., Huang, X., & Zhang, W. (2024). Drought Characteristics during Spring Sowing along the Great Wall Based on the MCI. Agronomy, 14(10), 2195. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14102195





