Abstract
The IrrigaSys decision support system (DSS) has supported farmers’ decision-making regarding irrigation scheduling in the Sorraia Valley irrigation district in Southern Portugal over a span of six years (2017–2022). This study aims to conduct a postevaluation of farmers’ adherence to the DSS, employing a multicriteria analysis (MCA) approach with data from the 2019 (driest year) and 2020 (average year) growing seasons. Two distinct scenarios were taken into consideration: the first focused on water conservation, and the second centered on farmers’ economic returns. The outcomes of the first scenario revealed that farmers exhibited a reasonable level of expertise, particularly during the driest season. They achieved water-saving indicators comparable to those obtained when adhering to optimized irrigation schedules generated weekly by the DSS. In the wetter season, discrepancies emerged between farmers’ and model indicators, primarily attributed to challenges in integrating reliable information from precipitation forecasts into the decision-making process. In the second scenario, both farmers’ and model results exhibited close economic indicators throughout both seasons. While IrrigaSys requires further developments, these results show that the DSS has effectively contributed to supporting irrigation water management in the study region.
1. Introduction
In water-scarce regions, irrigation is essential for meeting crop water requirements, enhancing food production with higher yields, addressing the growing demand for food, ensuring food stability, and promoting the prosperity of rural areas [1]. On the other hand, irrigation is also responsible for building-up the pressure on water resources, representing 70% of all freshwater withdrawals in the world and 90% in the least developed regions [2]. Irrigation is also associated with land degradation, primarily through its contribution to the contamination or depletion of water resources, the promotion of soil erosion and soil salinization, as well as biodiversity loss [3]. Therefore, the imperative need to ensure the sustainability of agricultural systems has driven the development of decision support systems (DSSs) focused on improving irrigation water management at both the field and irrigation district scales.
DSSs are interactive software-based tools employed to gather valuable information from various raw data sources (e.g., soil moisture sensors, proximal and remote sensing platforms, soil water balance models) and deliver optimized solutions (e.g., irrigation scheduling), aiding farmers in the decision-making process [4]. DSSs are now widespread throughout the most important agricultural regions in the world as reviewed by Pereira et al. [5] and Pôças et al. [6]. These systems benefit from the advancing field of information and communication technology (ICT), including the Internet of things (IoT), satellites, drones, robotics, and artificial intelligence, providing limitless possibilities to improve farming operations and the management of soil and water resources. Examples of web-based irrigation DSSs are CIMIS [7], AIS [8], and TOPS-SIMS [9] in use in the United States; IrriSatSMS [10] in Australia; IRRINET-IRRIFRAME [11,12] and IRRISAT [13] in Italy; and SPIDER [14] in Spain. All of these DSSs employ tipping-based approaches for computing the soil water balance, relying on FAO 56 procedures [15] for estimating crop irrigation needs. Those incorporating remote sensing data further make use of preestablished relationships between canopy reflectance and crop transpiration for the accurate assessment of crop water requirements.
The IrrigaSys [16], in use in Portugal, exhibits important differences from the aforementioned systems due to its increased complexity. The core engine of this system, the MOHID-Land model [17], adopts a mechanistic approach wherein the Richards’ equation is used for computing soil water storage and fluxes in the root zone, meaning that a full description of soil hydraulic functions is required, i.e., the soil water retention and soil hydraulic conductivity curves from saturation to oven dryness. Moreover, the model includes the simulation of crop growth, considering factors such as intercepted light, the conversion of intercepted light into biomass, crop stress, and the number of heat units defining the crop season [18,19]. The model further includes a system-dependent boundary condition based on soil pressure heads for irrigation scheduling [17].
Despite the complexity of the model, the DSS requires only a limited set of inputs from farmers, which include the location of the agricultural field, crop type, sowing and harvest dates, soil texture, and characteristics of the irrigation system [16]. As the DSS is not remotely connected to sensors, data regarding daily or weekly applied irrigation depths are collected through weekly surveys conducted by the technical staff of the local water board, which oversees the system. This information is critical for the reliability of outputs. Furthermore, a series of demonstrative case studies have been implemented over the years to gain farmers’ confidence in the DSS outputs [17,20,21,22]. However, there is still uncertainty regarding the willingness of farmers to adhere to the recommended irrigation schedules generated by IrrigaSys. A multicriteria analysis (MCA) may provide insights into the extent to which farmers follow the IrrigaSys recommendations by comparing their performance with irrigation schedules generated by the DSS using a range of environmental and economic indicators.
The MCA emerged in the 1960s as a decision-making tool, facilitating a comparative evaluation of diverse alternatives or heterogeneous scenarios, considering multiple criteria simultaneously within complex situations. Its structure is designed to yield conclusions based on the preferences and priorities of multiple decision-makers, or to generate single synthetic conclusions at the end of the evaluation [23]. This method aids the integration of various options, incorporating the perspectives of involved decision-makers within a prospective or retrospective framework. Additionally, the MCA aims to organize and merge diverse evaluations considered by decision-makers to find conclusions based on multiple choices. Ultimately, this process provides operational suggestions or recommendations for future activities [24,25]. The MCA finds applications across various fields such as hydrology, the environment, and agronomy. In irrigation agriculture, the MCA improves the understanding of impacts, allowing for a satisfactory compromise between conflicting decision-maker objectives [26,27,28,29]. The MCA is further considered as a valuable tool for addressing water management issues, highlighting social, economic, environmental, and water-related aspects that require careful consideration to meet sustainability objectives in the irrigated agriculture sector. As such, the MCA has been extensively applied in irrigation scheduling, design, and management, aiding in finding suitable solutions for specific environmental conditions [30,31,32,33,34].
Therefore, the primary objective of this study is to gain insights into farmers’ adherence to IrrigaSys recommendations using the MCA. The specific aim is to compare different sets of farmers’ and model applications from both water-saving and economic perspectives. The ultimate goal is to assess how closely farmers’ performance aligns with an optimized irrigation schedule provided by IrrigaSys.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Area
From 2017 to 2022, IrrigaSys annually supported 30 farmers in managing about 103 plots, varying in size from 0.03 to 75 hectares, covering a total area of 2080 ha. These plots were situated within the Sorraia Valley irrigation district (Figure 1), in southern Portugal. The district is overseen by a local water board, the Associação de Regantes e Beneficiários do Vale do Sorraia (ARBVS). Water access is on demand. The region experiences a semiarid to dry subhumid climate characterized by hot, dry summers and mild winters with irregular rainfall. The mean annual rainfall is around 500 mm, varying from 200 to 900 mm over the years. Annual surface air temperature averages 15 °C, ranging from approximately 9 °C in January to around 22 °C in July. The mean annual reference evapotranspiration (ETo), calculated using the FAO56 Penman–Monteith (PM) equation [15], is close to 900 mm. The most representative soil types include Fluvisols, Planosols, Cambisols, Luvisols, and Regosols [35]. Rice (Oryza sativa L.) and maize (Zea mays L.) were the main crops in the region, constituting approximately 33.4–36.0% and 23.2–20.2%, respectively, of the total irrigated area (16,661–19,173 ha) during the operational period of IrrigaSys (2017–2022). Olive (Olea europaea L.), tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.), and other vegetable crops were also grown in the region. Surface irrigation and center pivots were used in 36.7–39.9% and 30.0–36.1% of the total irrigated area during the same period (2017–2022). IrrigaSys only supported irrigation management of plots equipped with pressurized systems.
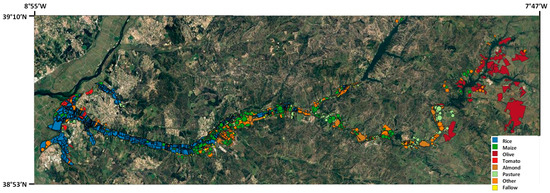
Figure 1.
Location of the study area.
2.2. Computation of Soil Water Balance and Crop Yields
The MOHID-Land model [17] was used as the core in IrrigaSys to compute the soil water balance and crop yields. The soil water balance equation was solved in a vertical soil column using a finite-volume approach, as follows:
where ΔS is the change in soil water storage (mm), ETa is the actual evapotranspiration (mm), RO is the surface runoff (mm), DP is the deep percolation (mm), I is the irrigation depth (mm), P is the precipitation amount (mm), and CR is the capillary rise (mm), all computed between time steps. Because the model is solved using a one-dimensional domain, RO was neglected. CR was also not considered due to difficulties in considering the upward fluxes from the groundwater using such simplified approach. As explained later, this is one major limitation of IrrigaSys.
In the grid domain, a variable saturated flow was computed using the Richards equation. The unsaturated soil hydraulic properties were described using the Mualem–van Genuchten functional relationships [36,37]. The sink term in the Richards equation was computed following the macroscopic approach proposed by Feddes et al. [38]. In this approach, the potential transpiration (Tp, L T−1) is linearly distributed over the root zone, resulting in the function Tp(z), which is diminished as a function of the soil pressure head. The piecewise linear model proposed by Feddes et al. [38] was adopted for computing actual transpiration rates (Ta, L T−1). The water uptake was assumed to be equal to the potential rate when the pressure head was between h2 and h3, to drop off linearly when h > h2 or h < h3, and to become zero when h < h4 or h > h1 (subscripts 1 to 4 denote different threshold pressure heads). Actual soil evaporation (Ea, L T−1) was obtained by limiting Ep values using a threshold pressure head [39].
The atmosphere and irrigation data provided the necessary data for imposing surface boundary conditions. Crop evapotranspiration rates (ETc, L T−1) were also given as the product of the single crop coefficient (Kc) and the reference evapotranspiration (ETo, L T−1) computed by the FAO PM equation [15]. ETc values were then partitioned into potential Ep and Tp as a function of simulated leaf area index (LAI, m2 m−2) following Ritchie [40]. The LAI, as well as other crop growth state variables (total biomass, root depth, crop height, crop yield), were simulated using a modified version of the EPIC model [18,19]. This model is based on the heat unit theory, which assumes that all heat above the base temperature accelerates crop growth and development.
2.3. Data Selection
For each plot, IrrigaSys generated weekly reports with the irrigation schedule for the upcoming week. During its operation, the system retrieved daily weather data from the closest weather station in the local network and a weather forecast model, which was subsequently used to compute the ETo using the FAO-PM equation. ETc rates were then determined following the single Kc approach [15] and were used for defining the atmospheric boundary conditions in MOHID-Land. Following this, the model calculated the soil water balance for both the preceding and forthcoming week using irrigation data provided by farmers through ARBVS technicians. In some instances where irrigation data from farmers were not input promptly, the system incorporated a set of procedures, as elaborated in Simionesei et al. [16]. Most of these procedures assumed that farmers had adhered to the irrigation schedule outlined in the previous report. Upon receiving the delayed data, the system proceeded to update the soil water balance, incorporating all information from the time of sowing up to the provided date using farmers’ data. When providing recommendations, a full irrigation strategy was adopted with the goal of maximizing crop yields by aligning actual evapotranspiration (ETa) rates with their potential values. IrrigaSys solely provided recommendations, allowing farmers to decide whether to follow the irrigation advice. Consequently, farmers’ schedules naturally exhibited varying degrees of deviation from the optimized model outputs, which this study aimed to analyze.
Twenty plots were selected for conducting the MCA based on the following criteria: (i) maize was chosen as the most representative crop in the region (excluding rice) and in IrrigaSys, and (ii) the center pivot was selected as the most represented pressurized irrigation system in the region. The selected plots included the same crop grown in both the driest year (2019) and the average year (2022) served by IrrigaSys for seasonal comparison. For each plot, data extracted included the seasonal gross irrigation amount (IWU), the seasonal ETa, and crop yield (Y). The data from farmers were compared to the corresponding optimized values generated by the MOHID-Land model. Model estimates of gross irrigation amounts assumed an application efficiency of the center pivot of 85% [41]. Farmers’ data on ETa and crop yields were estimated using farmers’ irrigation data as model input instead of the optimized schedules. In both scenarios (farmers vs. model), ETa values were computed from the soil water balance by summing Ea and Ta rates. Yields were obtained as the product of the aboveground biomass and a harvest index [17]. This procedure can be found in many different modeling applications [42,43,44].
2.4. Multicriteria Analysis
The MCA was organized into five phases, as depicted in Figure 2. Phase 1 involved defining the study objectives, specifically comparing farmers’ performance in each plot against irrigation schedules recommended by the model using a set of water-saving and economic indicators.
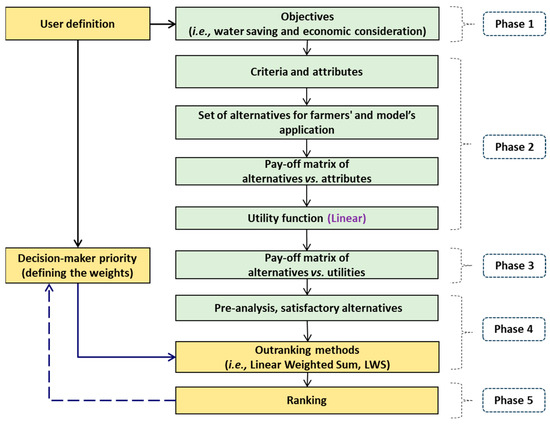
Figure 2.
Functional diagram of the multicriteria analysis model.
Phase 2 involved a sequence of steps. The first step referred to the definition of the criteria attributes, which were applicable to two scenarios: Scenario 1 (S1), focusing on environmental and water-saving assessment in relation to irrigation performance, and Scenario 2 (S2), addressing the benefit and economic assessment associated with farmers’ economic perspectives. For S1, the following criteria attributes were considered [45,46]:
- Irrigation water use (IWU, m3 ha−1), representing the total or gross irrigation applied each season.
- Water-use efficiency (WUE, dimensionless), calculated as the ratio of ETa to the sum of IWU and precipitation (P).
- Crop water productivity (WPc, kg m−3), given by the ratio of the actual marketable yield (Y) to ETa.
- Irrigation water productivity (WPi, kg m−3), calculated as the ratio of Y to IWU.
- For S2, the criteria attributes were the following [45,46]:
- Land productivity (LP, kg ha−1), corresponding to Y.
- Economic land productivity (ELP, EUR ha−1), representing the value of Y in current prices. In this study, maize yield was 0.26 EUR kg−1 following market prices in 2022.
- Economic crop water productivity (EWPc, EUR m−3), given by the ratio of ELP and Eta.
- Economic irrigation water productivity (EWPi, EUR m−3), calculated by the ratio between the ELP and IWU.
The second and third steps in Phase 2 involved creating a payoff matrix that put together alternatives (a total of 40 results from both farmers and models for each season) against attributes (water-saving and economic indicators). The last step in Phase 2 involved defining the utility function (Uj) for each attribute value (xj) considered in criterion j using a linear model [32,47,48], as follows:
where α is the slope’s function, and β is the utility value of Uj(xj) for a null value of the attribute. In this function, Uj is normalized from 0 to 1; 0 corresponds to the most adverse condition, while 1 signifies the most advantageous result. As commonly observed in irrigation studies [34,49], the slope α is negative (Figure 3B) for criteria associated with water savings (IWU) and positive (Figure 3A) for the water productivity, WUE, and economic criteria.
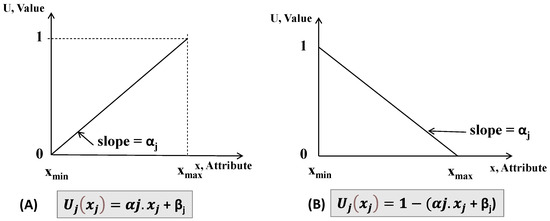
Figure 3.
Linear utility functions relating two points of type (A) “more is better” and (B) “more is worst”; βj in this figure is 0.
In Phase 3, a pay-off matrix of the alternatives versus utilities of each criterion (normalized water-saving and economic indicators) was established. Phase 4 started by pre-analyzing all sets of alternatives to eliminate unsatisfactory results. The viable alternatives were then subjected to outranking. Outranking methods are based on multiple comparisons of the type: “does Measure A outrank Measure B from the point of view of the environmental or economic criterion?” [50,51,52,53]. Among various available methods [54,55,56,57], the linear weighted sum (LWS) [58] was used. The LWS has the advantage of simplicity, facilitating a clearer understanding of the procedures and results. However, a drawback lies in the full compensatory assumption of the LWS method, meaning any criterion with lower results can be compensated by another one with better results.
In this method, a global utility value (U) is computed for each alternative by integrating the utilities of the different criteria attributes using weights that are assigned to reflect users’ priorities [32,33,34,47,48,59], as follows:
where U is the global utility (scaled from 0 to 1), n is the number of criteria attributes (n = 8), and λj is the corresponding attribute weight. In this study, criterion weights aimed to emphasize the environmental and economic perspectives. Table 1 presents the weights assigned to attributes for water-saving and economic result priorities. These were used in Phase 5 to compare global utilities and rank alternatives by building the prioritization scenarios. S1 assumed a 90% weight for water-saving results and 10% for farm economic results. S2 was the opposite, assuming 10% weight for water-saving results and 90% for farm economic results.

Table 1.
Criteria attributes, utility functions, and criteria weights.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Environmental and Economic Indicators
Figure 4 presents the environmental and economic indicators computed for each plot based on the outputs derived from the irrigation schedules adopted by farmers or recommended by the MOHID-Land model for the 2019 and 2022 growing seasons. Plots are designated from P1 to P20 to ensure anonymity, with the letters F and M representing results from farmers and the model, respectively. The results inherently depict both individual management practices and the spatial distribution of plots throughout the Sorraia Valley district.
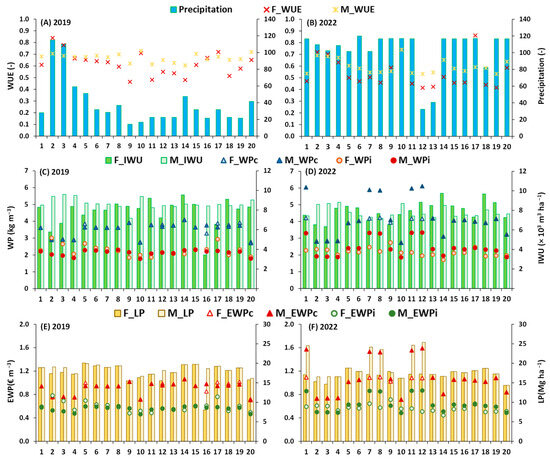
Figure 4.
Farmers (F) versus model (M) alternatives during the growing seasons of 2019 and 2022 relative to: (A,B) water-use efficiency (WUE, ratio); (C,D) gross irrigation water use (IWU, m3 ha−1) and crop and irrigation water productivities (WPc, WPi, kg m−3); and (E,F) land productivity (LP, EUR∙ha−1), economic crop, and irrigation water productivities (EWPc, EWPi, EUR m−3).
Figure 4A,B show model alternatives for WUE, calculated as the ratio of ETa to the sum of IWU and P, ranging from 0.60 to 0.73 in 2019 and 0.53 to 0.74 in 2022. The variation in P values among plots can be attributed to the spatial variability of precipitation, as well as temporal differences in sowing date and the duration of the crop season throughout the year. Correspondingly, WUE results from farmers showed a wider dispersion in both seasons, varying from 0.46 to 0.84 in 2019 and 0.42 to 0.86 in 2022. Moreover, except for a few plots (F_P2, F_P3, and F_P17), WUE values computed from farmers’ results were generally lower during the average (wetter) season of 2022 than the drier season of 2019. They were also generally lower than the WUE values computed from model results. Therefore, despite relatively high and comparable WUE values during the dry season, Figure 4A highlights some challenges farmers faced in incorporating precipitation forecasts, whether provided by IrrigaSys or other sources, into their irrigation scheduling during the wetter season.
Figure 4C,D indicate that IWU values from both farmers and the model were relatively close, averaging 7800 and 8650 m3 ha−1 in 2019 and 7940 and 7800 m3 ha−1 in 2022, respectively. IWU values from farmers being higher than those recommended by the model during the average (wetter) season align with the earlier observation regarding the challenges of assimilating weather forecasts into irrigation schedules. Larger differences between IWU values from farmers’ schedules and those recommended by the model were noticed in F_P2, F_P3 and F_P16 in 2019 and F_P2 and F_P3 in 2022. Because WUE values in these plots are comparable to others, these differences may be explained by the contribution of upward water fluxes from a shallow groundwater table to the soil water balance. As reported in Cameira et al. [60] and Ramos et al. [17], capillary fluxes may constitute a significant component of the soil water balance in certain locations of the Vale Sorraia irrigation district, contributing up to 45% of crop evapotranspiration. However, IrrigaSys does not consider such fluxes because modelling the groundwater table requires a regional approach, while the service uses a one-dimensional plot-scale model for computation of the soil water balance. Therefore, farmers’ performance, for example in plots F_P2 and F_P16, appear to outperform the IrrigaSys service.
Figure 4C,D further show the WPc and WPi values computed from farmers and model results. It should be noted that yields were estimated in both cases using the MOHID-Land model while assuming the irrigation schedules defined by farmers or those recommended by the model. Therefore, farmers’ results reflect solely the impact of irrigation scheduling on crop yields and do not account for the effect of pests and diseases that eventually occurred during the two studied seasons. Farmers’ consumptive WPc values ranged from 2.75 to 4.08 kg m−3 in 2019 and 2.47 to 4.22 kg m−3 in 2022. These values are comparable to those reported in Ramos et al. [17] for maize grown in the same region (2.71–2.73 kg m−3). The model’s optimized schedules returned similar values, ranging from 2.71 to 4.08 kg m−3 in 2019 and 2.74 to 6.12 kg m−3 in 2022. However, average WPc values notably differed in the average (wetter) season, with farmers’ results averaging 3.66 kg m−3, while the model reached an average of 4.19 kg m−3. Similar findings were observed for WPi (1.71–3.34 kg m−3), despite yielding smaller values than WPc. Nonetheless, values were within the WPi range reported by Paredes et al. [61] for the same crop and region. While the WPc and WPi values for both farmers and the model’s results exhibited relatively close ranges, notable disparities emerged in plots P1, P7, P8, P11, and P12 during the 2022 season. Although IWU values were relatively close in these plots, it appears that farmers’ less efficient irrigation schedules may have induced some stress (reflected in lower ETa) in the plants, leading to diminished yields. In contrast, the model-generated irrigation schedules resulted in optimal crop growth, translating into higher performance indicators.
Lastly, Figure 4E,F present the land productivity and economic indicators computed for the study plots. In 2019, LP values in farmers’ results varied from 8 to 20 Mg ha−1. However, only results from F_P16 stand out from the others, being abnormally low. As previously hypothesized, this low LP may have resulted from not considering the contribution of groundwater flows to the root zone when computing the soil water balance, with actual yield values being substantially higher than estimated here. In this case, model parametrization in this plot should be reevaluated. Alternatively, the lower LP value could reflect some mismanagement of irrigation water during that season, as the same was not observed in 2022. In that year, farmers’ LP values were found to be within the 16 to 20 Mg ha−1 range. The same was observed for the model’s LP values in both seasons, despite some high values (>23.5 Mg ha−1) estimated in five plots for 2022. These higher yields can be attributed to farmers choosing a longer crop cycle and more productive varieties of maize in that year, which required making some adjustments to the model estimates.
EWPc and EWPi trends naturally aligned with the yield variations observed between plots and seasons (Figure 4E,F). EWPc values computed from farmers’ results ranged from 0.72 to 1.06 EUR m−3 in 2019 and 0.64 to 1.10 EUR m−3 in 2022. The corresponding values computed from model results were similar for 2019, and again higher for 2022 (0.71–1.59 EUR m−3). Similar findings and interpretations can be applied to the EWPi values, with farmers’ values ranging from 0.48 to 0.78 EUR m−3 in 2019 and 0.44 EUR m−3 to 0.71 in 2022. Nonetheless, all reported values were found to be higher than the EWPc (0.29–0.51 EUR m−3) and EWPi (0.31–0.69 EUR m−3) values reported in Paredes et al. [61] for the same crop and region, which can be explained by the lower commodity price of maize (0.21 EUR m−3) at the time of that study compared to today’s prices (0.26 EUR m−3).
3.2. Ranking Farmers’ Performance
The global utilities (U) characterizing farmer and model alternatives when priorities were assigned to water saving (S1) or farm economic returns (S2) during 2019 and 2022 are presented in Figure 5. In the water-saving S1 scenario, farmers’ U values varied from 0.21 to 0.55 in 2019 and from 0.16 to 0.45 in 2022. The corresponding model U values ranged from 0.23 to 0.38 in 2019 and from 0.26 to 0.55 in 2022. The results clearly indicate that farmers’ performance during the dry season (2019) approached or even surpassed model performance in most fields. This means that during the dry season, in general, farmers adopted irrigation schedules deemed comparable to those optimized by the physically based model. The reasons for surpassing model results in some plots were previously discussed and refer to challenges associated with incorporating upward fluxes from the groundwater table in the one-dimensional modeling of the soil water balance, as implemented in IrrigaSys.
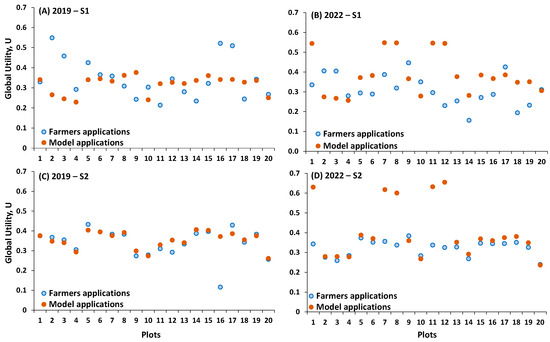
Figure 5.
Global utilities, U, for farmers versus model alternatives when prioritizing water conservation (A,B) or economic returns (C,D) during the growing seasons of 2019 and 2022.
During the wetter season of 2022, farmers’ U values consistently fell below those of the model, highlighting the difficulties in integrating dependable information from precipitation forecasts into decision-making processes. Several cases were identified where farmers’ irrigation schedules led to substantially lower water productivity values than those computed from model recommendations. The relevance of precipitation forecast for computing the soil water balance increased for the earlier sowing dates, which, depending on the farmer and season, may vary in the region from April to July. Hence, it appears that the most crucial factor for increasing the efficient use of water in the region is reliable precipitation forecast information. Regarding other factors considered in this analysis, most farmers demonstrated an acceptable level of knowledge in terms of irrigation scheduling and irrigation water management. However, as demonstrated by Linker et al. [62], who assessed the quality of current weather forecasts, including those for the Sorraia Valley region, precipitation forecasts exhibited significant shortcomings at the locations studied by those authors. This inadequacy was observed not only in terms of predicting rain amounts but also in predicting rain/no rain events.
Relative to farmers’ economic returns S2 scenario, farmers’ U values varied from 0.12 to 0.43 in 2019 and from 0.24 to 0.38 in 2022. The corresponding model U values ranged from 0.26 to 0.41 in 2019 and from 0.24 to 0.65 in 2022. The results were highly consistent in both years, indicating that farmers achieved economic returns comparable to those obtained by following the model’s recommendations. It is crucial to reiterate that yield estimates in farmers’ applications do not incorporate the impacts of pests, diseases, or other transient stresses. These estimates solely reflect the effects of water stresses resulting from nonoptimal irrigation schedules on crop transpiration rates and consequently, on yields. The actual yield values undoubtedly varied from the estimates considered here, which are contingent solely upon irrigation schedules. Economic indicators also did not account for variable costs (e.g., operation, maintenance, labor, energy) that certainly differed from one plot to the other. However, from a water management perspective, both farmers and the model exhibited equivalent performance.
Lastly, Table 2 ranks the first 20 best alternatives based on water-saving and economic returns priorities. The table confirms that in the dry year of 2019, farmers’ applications proved to be feasible and effective solutions concerning water conservation and economic considerations. Additionally, model solutions exhibited progress in ranking, securing the sixth and third positions for S1 and S2, respectively. The top common applications for farmers in both S1 and S2, ranked among the best 10, were F_P17, F_P5, and F_P6. Conversely, for model applications, M_P15 emerged as the best common choice.

Table 2.
Ranking of the 20 best alternative solutions for water saving and economic priorities in 2019 and 2022.
In 2022, model solutions took the lead in the rankings showing superiority in both scenarios S1 and S2, having M_P1, M_P7, M_P8, M_P11, and M_P12 in the first top rank order when the priority was assigned to water saving, while the set of plots of M_P1, M_P5, M_P7, M_P8, M_P11, and M_P12 showed a high ranking order when the priority was assigned to economic return. Some of these best common applications showed up as good options for both S1 and S2. However, farmers also presented viable and satisfactory solutions, such as F_P9, which was applicable in both scenarios. In general, in S2, without including the unusual high values of yield (>23.5 Mg ha−1) simulated in five plots in 2022, farmers and models’ applications showed very similar results for both seasons and the differences in ranking were very small. In S1, the difference was larger, with farmers’ solutions showing superiority compared to model applications in some plots. However, as discussed earlier, these differences might stem from challenges in accurately configuring the DSS in those specific plots rather than representing an actual enhancement in farmers’ performance. Nevertheless, the farmers’ rankings in 2022 undeniably highlight the challenges arising from inaccurate precipitation forecasts in the decision-making process.
The results underscore the overall good performance of farmers in irrigation management. It is important to note that farmer results cannot be expected to match the model performance that simulates optimized conditions not present in the real world. While the general performance of farmers was deemed satisfactory, several cases were identified where their decisions on irrigation scheduling yielded significantly weaker indicators compared to the model outputs. In light of these findings, technicians from ARBVS, the local water board overseeing the Sorraia Valley district, can now pay closer attention to supporting these farmers, especially during rainier seasons. Furthermore, the results have shed light on system weaknesses that necessitate improvement in future developments.
4. Conclusions
This study aimed to conduct a postevaluation of IrrigaSys, a DSS that facilitated farmers’ decision-making regarding irrigation scheduling in the Sorraia Valley irrigation district in Southern Portugal from 2017 to 2022. This postevaluation primarily focused on comparing farmers’ performance with recommendations generated by the model running the DSS. Periodic assessments of this nature are crucial for the continual enhancement of the system. The comparison was conducted using a set of water-saving and economic indicators, employing a multicriteria analysis approach.
In general, a more comprehensive characterization of the problem in multicriteria analysis applications tends to yield better solutions. However, in this case, the MCA approach employed was somewhat constrained by the available data provided by farmers and the model. The analysis relied solely on irrigation scheduling data. Achieving a more reliable solution could be possible by incorporating additional criteria dependent on various factors such as irrigation timing, energy costs, agricultural service costs, and other relevant factors. It is also worth noting that various MCA methods could be explored for analyzing the study area, although the primary focus of this paper was not to compare different MCA methods. Nevertheless, although it cannot be directly concluded that farmers strictly adhered to the system, the results of the MCA unequivocally demonstrate that farmers demonstrated a commendable level of expertise in irrigation scheduling, closely aligning with the water-saving and economic indicators derived from the model’s recommendations, particularly during the dry season. However, in a wetter season, a noticeable disparity emerged between farmers’ and model indicators, primarily due to the difficulties associated with incorporating reliable information from precipitation forecasts into the decision-making process. Addressing this challenge appears to be the key factor for enhancing the future utilization of IrrigaSys and improving water-use efficiency in the region.
IrrigaSys requires further developments for reimplementation in the Sorraia Valley region, specifically targeting the resolution of the outdated requirement for acquiring information on irrigation applications in various plots through surveys. This demanded excessive effort from the water board technicians responsible for this task. Numerous solutions, particularly those using remote sensing data, are today available for automatically obtaining this information. The primary objective of subsequent developments should be to test, validate, and incorporate data derived from these methods into the system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.D. and T.B.R.; methodology, H.D.; software, L.S. and A.R.O.; validation, H.D., L.S. and T.B.R.; formal analysis, H.D.; writing—original draft preparation, H.D.; writing—review and editing, H.D. and T.B.R.; supervision, R.N. and T.B.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by national funds through FCT—Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, I.P., under projects UIDB/04129/2020 of LEAF-Linking Landscape, Environment, Agriculture and Food Research Unit; and UIDP/EEA/50009/2020 of LARSyS. The support of FCT through grants attributed to H.D. (CEECIND/01153/2017) and T.B.R. (CEECIND/01152/2017) is also acknowledged.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Pereira, L.S.; Cordery, I.; Iacovides, I. Coping with Water Scarcity. Addressing the Challenges; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Berlin, Germany, 2009; p. 382. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO. United Nations World Water Development Report 2020. Water and Climate Change; United Nations: Paris, France, 2020; p. 234. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Status of the World’s Soil Resources; Main Report; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and Intergovernmental Technical Panel on Soils: Rome, Italy, 2015; p. 650. [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi, M.; He, Z. Decision Support Systems to manage irrigation in agriculture. Adv. Agron. 2014, 123, 229–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.S.; Paredes, P.; Jovanovic, N. Soil water balance models for determining crop water and irrigation requirements and irrigation scheduling focusing on the FAO56 method and the dual Kc approach. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 241, 106357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pôças, I.; Calera, A.; Campos, I.; Cunha, M. Remote sensing for estimating and mapping single and basal crop coefficients: A review on spectral vegetation indices approaches. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 233, 106081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eching, S. Role of technology in irrigation advisory services: The CIMIS experience. In Proceedings of the Workshop “Irrigation Advisory Services and Participatory Extension in Irrigation Management”, Montreal, QC, Canada, 24 July 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Vories, E.; Tacker, P.; Hall, S. The Arkansas irrigation scheduler. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2009: Great Rivers, Kansas City, MO, USA, 17–21 May 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.F.; Trout, T.J. Satellite NDVI Assisted Monitoring of Vegetable Crop Evapotranspiration in California’s San Joaquin Valley. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornbuckle, J.W.; Car, N.J.; Christen, E.W.; Stein, T.M.; Williamson, B. IrriSatSMS—Irrigation Water Management by Satellite and SMS—A Utilisation Framework; CRC for Irrigation Futures Technical Report No. 01/09; CSIRO Land and Water Science Report No. 04/09; CSIRO: Canberra, Australia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Giannerini, G.; Genovesi, R. The water saving with Irriframe platform for thousands of Italian farms. J. Agric. Inform. 2015, 6, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannini, P.; Genovesi, R.; Letterio, T. IRRINET: Large scale DSS application for on farm irrigation scheduling. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2013, 19, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfiore, O.R.; Castagna, A.; Longo-Minnolo, G.; Ippolito, M.; Bavieri, A.; Comegna, A.; D’Urso, G. Monitoring of irrigation water use in Italy by using IRRISAT methodology: The INCIPIT project. In AIIA 2002: Biosystems Engineering Towards the Green Deal, Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering; Ferro, V., Giordano, G., Orlando, S., Vallone, M., Cascone, G., Porto, S.M.C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2023; Volume 337, pp. 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calera, A.; Campos, I.; Osann, A.; D’Urso, G.; Menenti, M. Remote Sensing for Crop Water Management: From ET Modelling to Services for the End Users. Sensors 2017, 17, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; Irrigation & Drainage Paper 56; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Simionesei, L.; Ramos, T.B.; Palma, J.; Oliveira, A.R.; Neves, R. IrrigaSys: A web-based irrigation decision support system based on open source data and technology. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 178, 105822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, T.B.; Simionesei, L.; Jauch, E.; Almeida, C.; Neves, R. Modelling soil water and maize growth dynamics influenced by shallow groundwater conditions in the Sorraia Valley region, Portugal. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 185, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neitsch, S.L.; Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Williams, J.R. Soil and Water Assessment Tool; Theoretical Documentation; Version 2009; Texas Water Resources Institute; Technical Report No. 406; Texas A&M University System: College Station, TX, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.R.; Jones, C.A.; Kiniry, J.R.; Spanel, D.A. The EPIC crop growth model. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Biol. Eng. 1989, 32, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, T.B.; Simionesei, L.; Oliveira, A.R.; Darouich, H.; Neves, R. Assessing the Impact of LAI Data Assimilation on Simulations of the SoilWater Balance and Maize Development Using MOHID-Land. Water 2018, 10, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, T.B.; Simionesei, L.; Oliveira, A.R.; Neves, R.; Darouich, H. Exploring the Use of Vegetation Indices for Validating Crop Transpiration Fluxes Computed with the MOHID-Land Model. Application to Vineyard. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simionesei, L.; Ramos, T.B.; Oliveira, A.R.; Jongen, M.; Darouich, H.; Weber, K.; Proença, V.; Domingos, T.; Neves, R. Modeling Soil Water Dynamics and Pasture Growth in the Montado Ecosystem Using MOHID Land. Water 2018, 10, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bana e Costa, C.A. Readings in Multiple Criteria Decision Aid; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; p. 660. [Google Scholar]
- Linkov, I.; Satterstrom, F.K.; Kiker, G.; Batchelor, C.; Bridges, T.; Ferguson, E. From comparative risk assessment to multi-criteria decision analysis and adaptive management: Recent developments and applications. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 1072–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keen, P.G.; Scott Morton, M.S. Decision Support Systems: An Organizational Perspective; Addison-Wesley Publishing Company: Boston, MA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Hajkowicz, S.; Collins, K. A review of multiple criteria analysis for water resource planning and management. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 1553–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, I.B.; Keisler, J.; Linkov, I. Multi-criteria decision analysis in environmental sciences: Ten years of applications and trends. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3578–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.C.; Chen, C.-H. Using the ELECTRE II method to apply and analyze the differentiation theory. Proc. East. Asia Soc. Transp. Stud. 2005, 5, 2237–2249. [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka, A.; Nemery, P. Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis: Methods and Software; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; p. 296. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, J.M.; Pereira, L.S. Decision support system for surface irrigation design. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2009, 135, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedras, C.M.G.; Pereira, L.S. Multicriteria analysis for design of microirrigation systems. Application and sensitivity analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darouich, H.; Gonçalves, J.M.; Muga, A.; Pereira, L.S. Water saving vs. farm economics in cotton surface irrigation: An application of multicriteria analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 115, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darouich, H.; Pedras, C.M.G.; Gonçalves, J.M.; Pereira, L.S. Drip vs. surface irrigation: A comparison focusing water saving and economic returns using multicriteria analysis applied to cotton. Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 122, 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darouich, H.; Cameira, R.M.; Gonçalves, J.M.; Paredes, P.; Pereira, L.S. Comparing sprinkler and surface irrigation for wheat using multi-criteria analysis: Water saving vs. economic returns. Water 2017, 9, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014: International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; World Soil Resources Reports No. 106; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mualem, Y. A new model for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated porous media. Water Resour. Res. 1976, 12, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Genuchten, M.T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feddes, R.A.; Kowalik, P.J.; Zaradny, H. Simulation of Field Water Use and Crop Yield; Simulation Monographs Pudoc: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE). Hydrology Handbook Task Committee on Hydrology Handbook; II Series, GB 661.2. H93; ASCE: Reston, VA, USA, 1996; pp. 96–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie, J.T. Model for predicting evaporation from a row crop with incomplete cover. Water Resour. Res. 1972, 8, 1204–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.; Bliesner, R.D. Sprinkle and Trickle Irrigation; Van Nostrand Reinhold: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, D.; Xu, X.; Hao, Y.; Huang, G. Modeling and assessing field irrigation water use in a canal system of Hetao, upper Yellow River basin: Application to maize, sunflower and watermelon. J. Hydrol. 2016, 532, 122–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanuytrecht, E.; Raes, D.; Steduto, P.; Hsiao, T.C.; Fereres, E.; Heng, L.K.; Vila, M.G.; Moreno, P.M. AquaCrop: FAO’s crop water productivity and yield assessment model. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 62, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Zhao, C.; Šimůnek, J.; Feng, G. Evaluating the impact of groundwater on cotton growth and root zone water balance using HYDRUS-1D coupled with a crop growth model. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 160, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.S.; Cordery, I.; Iacovides, I. Improved indicators of water use performance and productivity for sustainable water conservation and saving. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 108, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.E.; Alcon, F.; Diaz-Espejo, A.; Hernandez-Santana, V.; Cuevas, M.V. Water use indicators and economic analysis for on-farm irrigation decision: A case study of a super high density olive tree orchard. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 237, 106074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, J.M.; Muga, A.P.; Horst, M.G.; Pereira, L.S. Furrow irrigation design with multicriteria analysis. Biosyst. Eng. 2011, 109, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. A scaling method for priorities in hierarchical structures. J. Math. Psychol. 1977, 15, 234–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Q.; Shi, H.; Gonçalves, J.M.; Pereira, L.S. Basin irrigation design with multi-criteria analysis focusing on water saving and economic returns: Application to wheat in Hetao, Yellow River Basin. Water 2018, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.; Vincke, P. Multicriteria analysis: Survey and new directions. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1981, 8, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetschera, R. Sensitivity analysis for the ELECTRE multicriteria method. Zeitschrift für Oper. Res. 1986, 30, B99–B117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincke, P. Multicriteria Ddecision-Aid; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1992; p. 174. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, L. Do decision makers know what they prefer? MAVT and ELECTRE II. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 1996, 47, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, M.; Arora, M.; Malano, H.; Sharma, A.; Moglia, M. Integrated Evaluation of Hybrid Water Supply Systems Using a PROMETHEE–GAIA Approach. Water 2018, 10, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazar, A.; Gheidari, O.N.; Snyder, R. A fuzzy analytical hierarchy methodology for the performance assessment of irrigation projects. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 121, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, S.; Hao, X. An Improved Analytic Hierarchy Process Method for the evaluation of agricultural water management in irrigation districts of north China. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 179, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karleuša, B.; Hajdinger, A.; Tadić, L. The application of multi-criteria analysis methods for the determination of priorities in the implementation of irrigation plans. Water 2019, 11, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomerol, J.C.; Romero, S.B. Multicriterion Decision in Management: Principles and Practice; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Alphen aan den Rijn, The Netherlands, 2000; Volume 25. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, J.M.; Muga, A.P.; Pereira, L.S. A Web-based decision support system for surface irrigation design. Efficient Decision Support Systems-Practice and Challenges in Multidisciplinary Domains. In Proceedings of the 7th World Congress on Computers in Agriculture Conference, Reno, NV, USA, 22–24 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cameira, M.R.; Fernando, R.M.; Pereira, L.S. Monitoring water and NO3-N in irrigated maize fields in the Sorraia Watershed, Portugal. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 60, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes, P.; Rodrigues, G.C.; Alves, I.; Pereira, L.S. Partitioning evapotranspiration, yield prediction and economic returns of maize under various irrigation management strategies. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 135, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linker, R.; Sylaios, G.; Tsakmakis, I.; Ramos, T.B.; Simionesei, L.; Plauborg, F.; Battilani, A. Sub-optimal model-based deficit irrigation scheduling with realistic weather forecasts. Irrig. Sci. 2018, 36, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).