Long-Term Organic Substitution Promotes Carbon and Nitrogen Sequestration and Benefit Crop Production in Upland Field
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Descriptions
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Cropping and Management Practices
2.4. Sampling and Analyses
2.5. Calculations
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
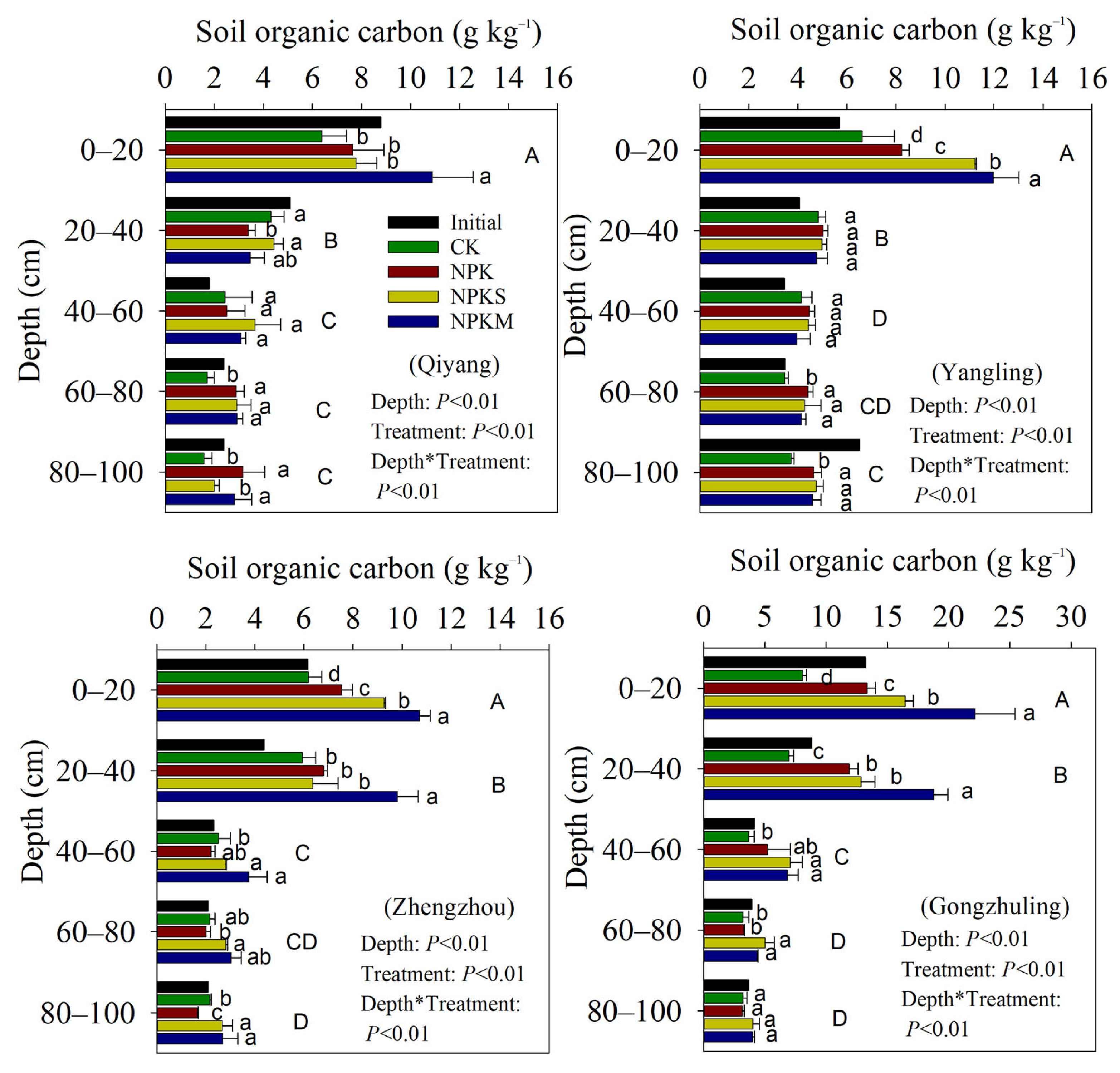
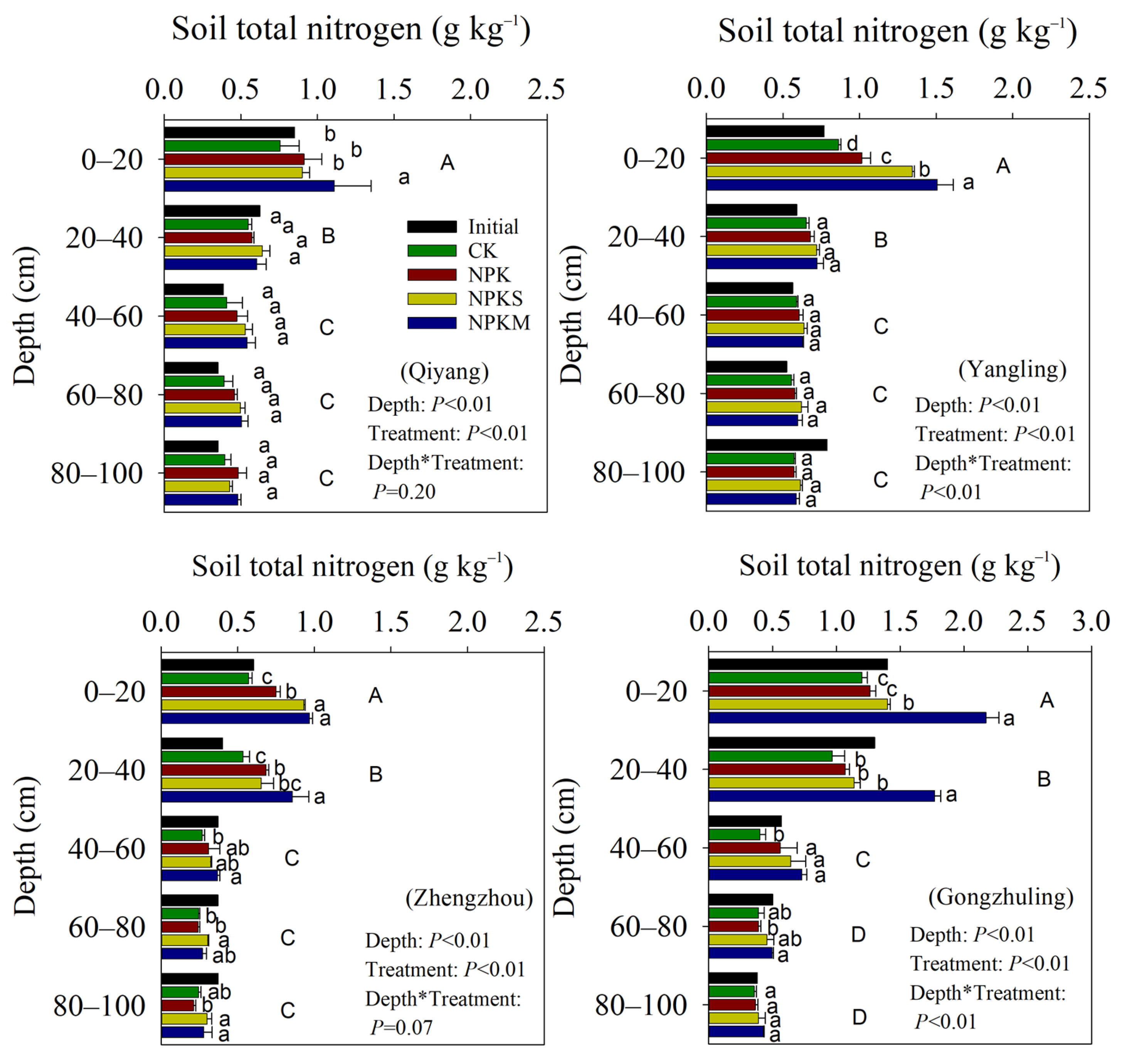
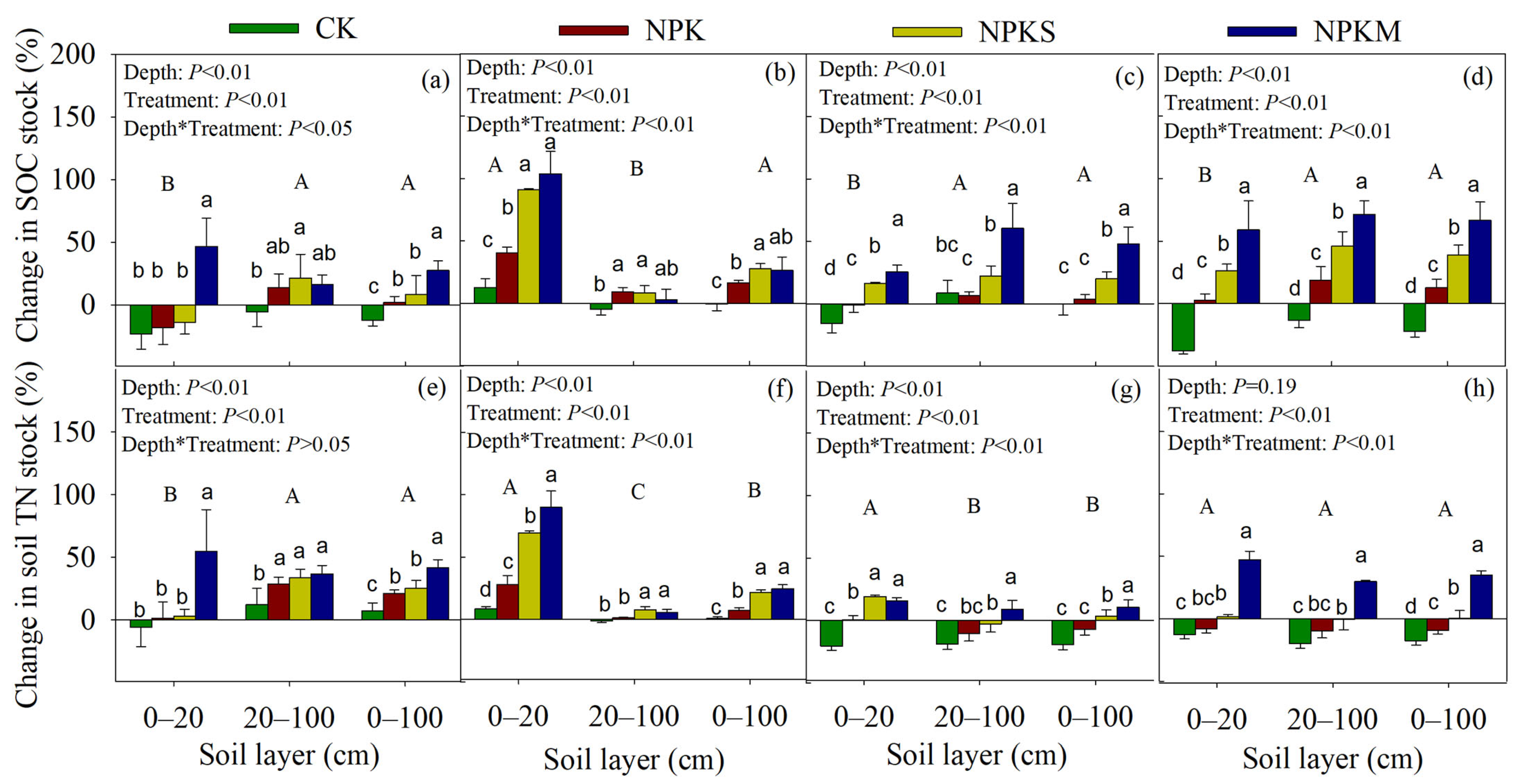
3.1. Soil OC and TN Concentrations and Their Stocks Change in Soil Profile
3.2. OC Input and SOC Sequestration Efficiency in the Entire 100 cm Soil Profile
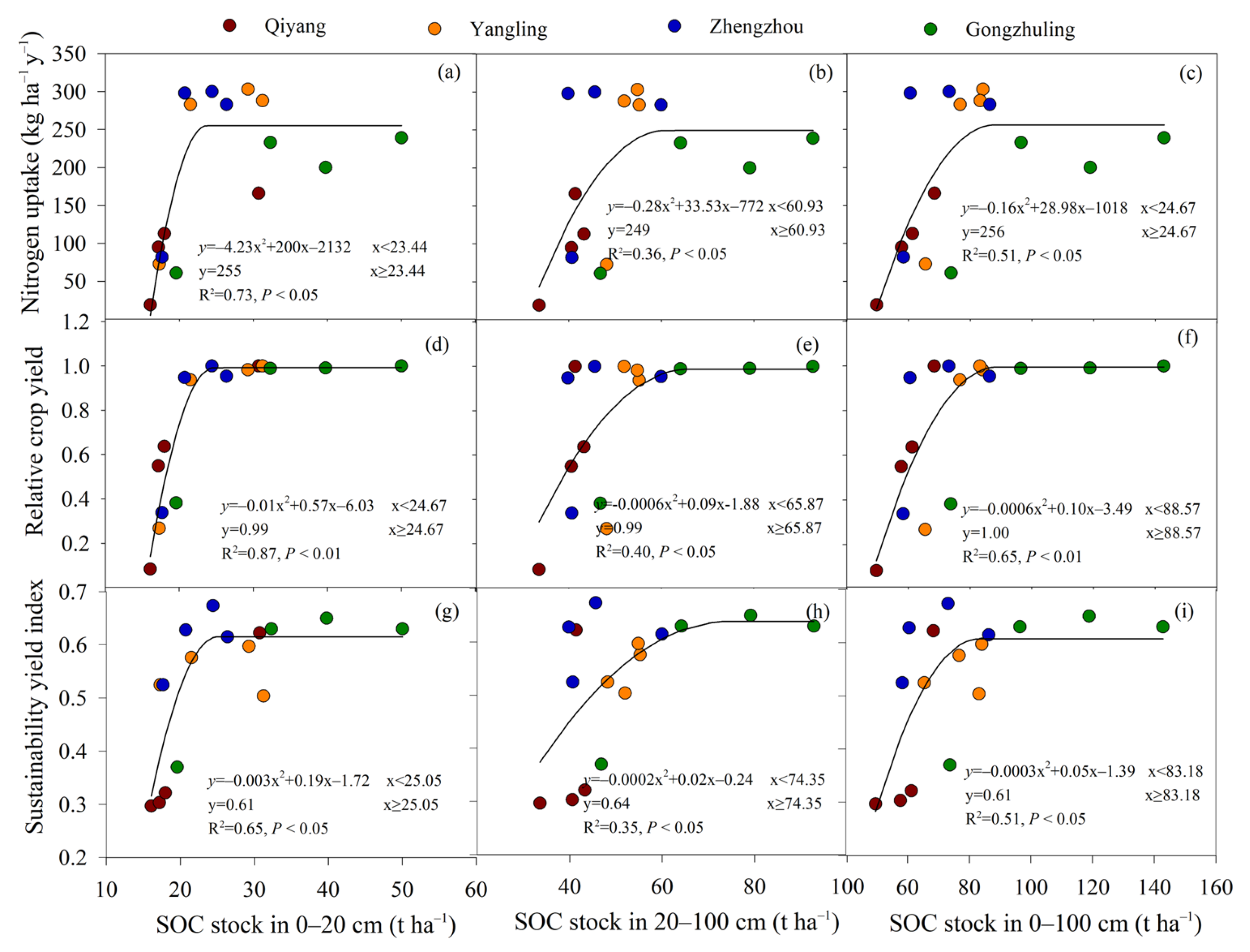
3.3. Crop Productivity and Its Relationship with Soil OC and TN Stocks in Soil Profile
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Fertilization and Cropping on SOC and TN
4.2. Relationships between Changes in OC and TN Stocks in Different Soil Layers
4.3. Responses of Crop Productivity to OC Accumulation in Soil Profile
4.4. Limitations and Implications of This Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, Q.; Rengel, Z.; Rose, T. The Effectiveness of Deep Placement of Fertilisers Is Determined by Crop Species and Edaphic Conditions in Mediterranean-Type Environments: A Review. Soil. Res. 2009, 47, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelung, W.; Bossio, D.; de Vries, W.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Lehmann, J.; Amundson, R.; Bol, R.; Collins, C.; Lal, R.; Leifeld, J.; et al. Towards a Global-Scale Soil Climate Mitigation Strategy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumpel, C.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Deep Soil Organic Matter—A Key but Poorly Understood Component of Terrestrial C Cycle. Plant Soil 2011, 338, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gami, S.K.; Lauren, J.G.; Duxbury, J.M. Influence of Soil Texture and Cultivation on Carbon and Nitrogen Levels in Soils of the Eastern Indo-Gangetic Plains. Geoderma 2009, 153, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Wilson, B.; Ghoshal, S.; Senapati, N.; Mandal, B. Organic Amendments Influence Soil Quality and Carbon Sequestration in the Indo-Gangetic Plains of India. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 156, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Nayak, A.K.; Puree, C.; Tripathi, R.; Lal, B.; Gautam, P.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Mohanty, S.; Kumar, A.; Panda, B.B.; et al. Carbon and Nitrogen Fractions and Stocks under 41 Years of Chemical and Organic Fertilization in a Sub-Humid Tropical Rice Soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 170, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.L.; Han, W.X.; Zhang, W.F.; Christie, P.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Vitousek, P.M.; Zhang, F.S. Significant Acidification in Major Chinese Croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.T.; Zhang, C. Nitrogen Cycling and Environmental Impacts in Upland Agricultural Soils in North China: A Review. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 2848–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Sun, Q.; Yuan, H.; Lian, B. A practical soil management to improve soil quality by applying mineral organic fertilizer. Acta Geochim. 2017, 36, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Hou, Y.; Meng, T.; Ma, Y.; Tan, M.; Zhang, F.; Oenema, O. Replacing Synthetic Fertilizer by Manure Requires Adjusted Technology and Incentives: A Farm Survey across China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 168, 105301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Pan, J.; Zhai, L.; Khoshnevisan, B.; Wu, S.; Wang, H.; Yang, B.; Liu, H.; Lei, B. The Reactive Nitrogen Loss and GHG Emissions from a Maize System after a Long-Term Livestock Manure Incorporation in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Song, D.; Zhou, W.; Liu, G.; Liang, G.; He, P.; Sun, G.; Yuan, F.; Liu, Z.; Yao, Y.; et al. Partial Substitution of Chemical Nitrogen with Organic Nitrogen Improves Rice Yield, Soil Biochemical Indictors and Microbial Composition in a Double Rice Cropping System in South China. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 205, 104753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Ni, K.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yi, X.; Yang, X.; Ling, N.; You, Z.; Guo, S.; Ruan, J. Effect of Organic Substitution Rates on Soil Quality and Fungal Community Composition in a Tea Plantation with Long-Term Fertilization. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2020, 56, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Feng, W.T.; He, X.H.; Zhu, P.; Gao, H.J.; Sun, N.; Xu, M.G. Chemical Fertilizers Could Be Completely Replaced by Manure to Maintain High Maize Yield and Soil Organic Carbon (SOC) When SOC Reaches a Threshold in the Northeast China Plain. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobbagy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B. The Vertical Distribution of Soil Organic Carbon and Its Relation to Climate and Vegetation. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tautges, N.E.; Chiartas, J.L.; Gaudin, A.C.M.; O’Geen, A.T.; Herrera, I.; Scow, K.M. Deep Soil Inventories Reveal That Impacts of Cover Crops and Compost on Soil Carbon Sequestration Differ in Surface and Subsurface Soils. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 3753–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Dwivedi, B.S.; Biswas, D.R.; Meena, M.C.; Sarkar, A.; Agarwal, B.K.; Mahapatra, P.; Shahi, D.K.; Agnihorti, R.; et al. Depth Dynamics of Soil N Contents and Natural Abundances of 15N after 43 Years of Long-Term Fertilization and Liming in Sub-Tropical Alfisol. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2018, 64, 1290–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Meena, M.C.; Dwivedi, B.S.; Singh, G.; Agnihotri, R.; Sharma, C. Long-Term Fertilization Effects on Soil Organic Carbon Sequestration in an Inceptisol. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 177, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.A.T.; Giacomini, S.J.; Aita, C.; Lourenzi, C.R.; Brunetto, G.; Bacca, A.; Ceretta, C.A. Short- and Long-Term Effects of Animal Manures and Mineral Fertilizer on Carbon Stocks in Subtropical Soil under No-Tillage. Geoderma 2021, 386, 114913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ji, H.; Wang, R.; Hu, Y.; Guo, S. Synthetic Fertilizer Increases Denitrifier Abundance and Depletes Subsoil Total N in a Long-Term Fertilization Experiment. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, M.C.; Swarup, A.; Wanjari, R.H.; Ravankar, H.N.; Mishra, B.; Saha, M.N.; Singh, Y.V.; Sahi, D.K.; Sarap, P.A. Long-Term Effect of Fertilizer and Manure Application on Soil Organic Carbon Storage, Soil Quality and Yield Sustainability under Sub-Humid and Semi-Arid Tropical India. Field Crops Res. 2005, 93, 264–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldfield, E.E.; Bradford, M.A.; Wood, S.A. Global Meta-Analysis of the Relationship between Soil Organic Matter and Crop Yields. Soil 2019, 5, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Zhang, A.; Chao, Y.; Wang, H.; Pan, H.; Lou, Y.; Zhuge, Y. Long-Term Effect of Fertilizer and Manure Application on the Balance of Soil Organic Carbon and Yield Sustainability in Fluvo-Aquic Soil. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2020, 66, 1520–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, S.; Barot, S.; Barré, P.; Bdioui, N.; Mary, B.; Rumpel, C. Stability of Organic Carbon in Deep Soil Layers Controlled by Fresh Carbon Supply. Nature 2007, 450, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Zhu, J.; Liu, G.; Cadisch, G.; Hasegawa, T.; Chen, C.; Sun, H.; Tang, H.; Zeng, Q. Soil Organic Carbon Stocks in China and Changes from 1980s to 2000s. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2007, 13, 1989–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil Carbon Sequestration Impacts on Global Climate Change and Food Security. Science 2004, 304, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhang, W.; Huang, S. Soil Fertility Evolution in China, 2nd ed.; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.; Xu, M.; Wang, B.; Yang, X.; Huang, S.; Gao, S. Long-Term Evaluation of Manure Application on Maize Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in China. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 1562–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, M.; Wang, B.; Wang, X. Soil Organic Carbon, Total Nitrogen and Grain Yields under Long-Term Fertilizations in the Upland Red Soil of Southern China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2009, 84, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaswar, M.; Jing, H.; Ahmed, W.; Dongchu, L.; Shujun, L.; Lu, Z.; Cai, A.; Lisheng, L.; Yongmei, X.; Jusheng, G.; et al. Yield Sustainability, Soil Organic Carbon Sequestration and Nutrients Balance under Long-Term Combined Application of Manure and Inorganic Fertilizers in Acidic Paddy Soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 198, 104569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, N.; Wu, L.; Xu, M.; Bingham, I.J.; Li, Z. Effects of Enhancing Soil Organic Carbon Sequestration in the Topsoil by Fertilization on Crop Productivity and Stability: Evidence from Long-Term Experiments with Wheat-Maize Cropping Systems in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, M.; Wang, X.; Huang, Q.; Nie, J.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Hwang, S.W.; Lee, K.B. Effects of Organic Amendments on Soil Carbon Sequestration in Paddy Fields of Subtropical China. J. Soils Sediments 2012, 12, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Li, H.; Yang, X.; Zhou, B.; Shi, X.; Wang, B.; Li, D.; Shen, J.; Chen, Q.; Qin, W.; et al. The Critical Soil P Levels for Crop Yield, Soil Fertility and Environmental Safety in Different Soil Types. Plant Soil 2013, 372, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Wang, X.J.; Xu, M.G.; Huang, S.M.; Liu, H.; Peng, C. Soil Organic Carbon Dynamics under Long-Term Fertilizations in Arable Land of Northern China. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Wang, E.; Sun, O.J. Can No-Tillage Stimulate Carbon Sequestration in Agricultural Soils? A Meta-Analysis of Paired Experiments. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 139, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nave, L.E.; Vance, E.D.; Swanston, C.W.; Curtis, P.S. Impacts of Elevated N Inputs on North Temperate Forest Soil C Storage, C/N, and Net N-Mineralization. Geoderma 2009, 153, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, L.J.T.; Hinckley, E.-L.S.; Robertson, G.P.; Matson, P.A. Rainfall Intensification Increases Nitrate Leaching from Tilled but Not No-till Cropping Systems in the U.S. Midwest. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 290, 106747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriyagoda, L.; De Costa, W.A.J.M.; Lambers, H. Growth and Phosphorus Nutrition of Rice When Inorganic Fertiliser Application Is Partly Replaced by Straw under Varying Moisture Availability in Sandy and Clay Soils. Plant Soil 2014, 384, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menichetti, L.; Ekblad, A.; Kätterer, T. Contribution of Roots and Amendments to Soil Carbon Accumulation within the Soil Profile in a Long-Term Field Experiment in Sweden. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 200, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutser, R.; Ebertseder, T.; Weber, A.; Schraml, M.; Schmidhalter, U. Short-Term and Residual Availability of Nitrogen after Long-Term Application of Organic Fertilizers on Arable Land. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2005, 168, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Conant, R.T.; Paul, E.A.; Paustian, K. Stabilization Mechanisms of Soil Organic Matter: Implications for C-Saturation of Soils. Plant Soil 2002, 241, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liu, K.; Zhang, W.; Rui, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, L.; Colinet, G.; Huang, Q.; Chen, X.; Xu, M. Long-Term Fertilization and Intensive Cropping Enhance Carbon and Nitrogen Accumulated in Soil Clay-Sized Particles of Red Soil in South China. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 1824–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Wang, B.; Xu, M.; Zhang, H.; He, X.; Zhang, L.; Gao, S. Intensified Soil Acidification from Chemical N Fertilization and Prevention by Manure in an 18-Year Field Experiment in the Red Soil of Southern China. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, W.L.; Miya, R.K. Global Patterns in Root Decomposition: Comparisons of Climate and Litter Quality Effects. Oecologia 2001, 129, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinweg, J.M.; Plante, A.F.; Conant, R.T.; Paul, E.A.; Tanaka, D.L. Patterns of Substrate Utilization during Long-Term Incubations at Different Temperatures. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 2722–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Su, B.; Currie, W.S.; Dukes, J.S.; Finzi, A.; Hartwig, U.; Hungate, B.; McMurtrie, R.E.; Oren, R.; Parton, W.J.; et al. Progressive Nitrogen Limitation of Ecosystem Responses to Rising Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide. Bioscience 2004, 54, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; He, T.; Chen, H.; Peng, W.; Song, T.; Wang, K.; Li, D. Impacts of Vegetation Restoration Strategies on Soil Organic Carbon and Nitrogen Dynamics in a Karst Area, Southwest China. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 101, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.L.; Wu, J.S.; Dang, T.H.; Liu, W.Z.; Li, Y.; Wei, W.X.; Keith, S.J. Impacts of Fertilizer Practices on Environmental Risk of Nitrate in Semiarid Farmlands in the Loess Plateau of China. Plant Soil 2010, 330, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas, M.A.; Kaya, C.; Riaz, A.; Farooq, M.; Nawaz, I.; Wilkes, A.; Li, Y. Potential Mechanisms of Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Crop Plants Induced by Thiourea. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Cai, Z.; Wang, X.; Liang, W.; Zhou, S.; Xu, M. Integrated Analysis of Liming for Increasing Crop Yield in Acidic Soils. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2017, 50, 2519–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Luan, L.; Hu, K.; Liu, M.; Chen, Z.; Geisen, S.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Xu, Q.; Bonkowski, M.; et al. Trophic Interactions as Determinants of the Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungal Community with Cascading Plant-Promoting Consequences. Microbiome 2020, 8, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, C.; Gao, P.; Wang, B.; Lin, W.; Jiang, N.; Cai, K. Impacts of Chemical Fertilizer Reduction and Organic Amendments Supplementation on Soil Nutrient, Enzyme Activity and Heavy Metal Content. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 1819–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, L.; Carswell, A.; Misselbrook, T.; Shen, J.; Han, J. Fate and Transfer of Heavy Metals Following Repeated Biogas Slurry Application in a Rice-Wheat Crop Rotation. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Qiyang | Yangling | Zhengzhou | Gongzhuling | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start year | 1990 | 1990 | 1990 | 1990 |
| Climate type a | ST-H | WT-SH | WT-SH | MT-SH |
| MAT(°C) b | 18.0 | 13.8 | 14.3 | 4.5 |
| MAP (mm) c | 1255 | 525 | 632 | 525 |
| MAE (mm) d | 1470 | 993 | 1450 | 1400 |
| Cropping e | DC-WM | DC-WM | DC-WM | MC-M |
| Tillage (times, depth) | 2, 20 cm | 2, 20 cm | 2, 20 cm | 1, 25 cm |
| Plot size (m2) | 196 | 196 | 43 | 400 |
| Initial physical and chemical characteristics, 0–20 cm | ||||
| FAO/UNESCO Soil classification | Ferralic Cambisol | Cumulic Anthroso | Calcaric Cambisol | Luvic Phaeozems |
| Texture (USDA) | light loam | silt loam | silt loam | clay loam |
| Sand (%) | 3.7 | 31.6 | 26.5 | 38.3 |
| Silt (%) | 34.9 | 51.6 | 60.7 | 29.9 |
| Clay (%) | 61.4 | 16.8 | 12.8 | 31.8 |
| SOC (g kg−1) f | 8.79 | 5.68 | 6.15 | 13.23 |
| TN (g kg−1) g | 0.85 | 0.77 | 0.60 | 1.40 |
| BD (g cm−3) h | 1.19 | 1.35 | 1.70 | 1.19 |
| pH i | 5.7 | 8.6 | 8.3 | 7.6 |
| Treatments | Qiyang | Yangling | Zhengzhou | Gongzhuling | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat | Maize | Wheat | Maize | Wheat | Maize | Maize | |
| Nitrogen (synthetic + manure/straw) (kg ha−1) | |||||||
| Control | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| NPK | 90 | 210 | 165 | 188 | 165 | 188 | 165 |
| NPKS | 90 + 9 | 210 + 9 | 165 + 42 | 188 + 0 | 123 + 42 | 188 + 0 | 112 + 53 |
| NPKM | 27 + 63 | 63 + 147 | 50 + 115 | 188 + 0 | 50 + 115 | 188 + 0 | 50 + 115 |
| Phosphorus (in synthetic + manure/straw) (kg ha−1) | |||||||
| Control | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| NPK | 16 | 37 | 58 | 25 | 36 | 41 | 36 |
| NPKS | 16 + 1 | 37 + 1 | 58 + 4 | 25 + 0 | 36 + 8 | 41 + 0 | 36 + 6 |
| NPKM | 16 + 13 | 37 + 31 | 58 + 95 | 25 + 0 | 36 + 66 | 41 + 0 | 36 + 39 |
| Potassium (in synthetic + manure/straw) (kg ha−1) | |||||||
| Control | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| NPK | 30 | 70 | 69 | 78 | 68 | 78 | 68 |
| NPKS | 30 + 17 | 70 + 17 | 69 + 57 | 78 + 0 | 68 + 86 | 78 + 0 | 68 + 58 |
| NPKM | 30 + 30 | 70 + 70 | 69 + 180 | 78 + 0 | 68 + 92 | 78 + 0 | 68 + 77 |
| Treatments | Experimental Sites | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qiyang | Yangling | Zhengzhou | Gongzhuling | ||
| Cinput (t ha−1 yr−1) | Control | 0.4 cB | 1.2 cA | 1.4 dA | 1.1 cA |
| NPK | 1.4 bB | 3.8 bA | 4.1 cA | 2.8 bA | |
| NPKS | 2.1 bC | 5.7 aB | 9.8 aA | 5.7 aB | |
| NPKM | 7.1 aA | 6.1 aAB | 6.1 bAB | 4.7 aB | |
| CSE (%) a | Control | −71.1 bB | −1.2 bA | −0.1 bA | −67.6 cB |
| NPK | 3.9 aB | 12.6 aA | 2.3 bB | 16.7 bA | |
| NPKS | 10.1 aAB | 14.0 aAB | 5.4 bB | 25.4 bA | |
| NPKM | 9.5 aB | 12.4 aB | 20.0 aB | 53.4 aA | |
| Sites | Treatments | Mean Yield (t ha−1) | SYI | Crop N Uptake (kg ha−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maize | Wheat | Maize | Wheat | |||
| Qiyang | Control | 0.27 ± 0.21 c | 0.36 ± 0.13 c | 0.08 | 0.38 | 19 ± 4.0 c |
| NPK | 2.88 ± 1.53 b | 1.06 ± 0.61 b | 0.24 | 0.19 | 95 ± 39 b | |
| NPKS | 3.37 ± 1.67 b | 1.19 ± 0.63 b | 0.26 | 0.21 | 113 ± 44 b | |
| NPKM | 5.11 ± 1.09 a | 1.77 ± 0.75 a | 0.56 | 0.22 | 166 ± 16 a | |
| Yangling | Control | 2.25 ± 0.49 b | 1.08 ± 0.53 b | 0.50 | 0.19 | 73 ± 10 b |
| NPK | 6.11 ± 1.00 a | 5.56 ± 1.38 a | 0.60 | 0.48 | 283 ± 33 a | |
| NPKS | 6.51 ± 1.02 a | 5.73 ± 1.44 a | 0.62 | 0.45 | 303 ± 39 a | |
| NPKM | 6.63 ± 1.15 a | 5.82 ± 1.66 a | 0.56 | 0.41 | 288 ± 38 a | |
| Zhengzhou | Control | 1.75 ± 0.42 b | 3.02 ± 0.98 b | 0.41 | 0.51 | 82 ± 11 b |
| NPK | 6.44 ± 1.02 a | 6.96 ± 1.95 a | 0.45 | 0.62 | 298 ± 34 a | |
| NPKS | 6.33 ± 0.92 a | 7.55 ± 1.90 a | 0.49 | 0.64 | 300 ± 30 a | |
| NPKM | 6.04 ± 0.96 a | 7.21 ± 1.86 a | 0.49 | 0.64 | 283 ± 35 a | |
| Gongzhuling | Control | 3.53 ± 1.10 b | - | 0.37 | - | 61 ± 12 c |
| NPK | 9.13 ± 1.63 a | - | 0.63 | - | 233 ± 36 a | |
| NPKS | 9.15 ± 1.37 a | - | 0.65 | - | 200 ± 25 b | |
| NPKM | 9.23 ± 1.76 a | - | 0.63 | - | 239 ± 39 a | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, H.; Cai, A.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S.; Huang, S.; Wang, B.; Zhu, P.; Colinet, G.; Sun, N.; Xu, M.; et al. Long-Term Organic Substitution Promotes Carbon and Nitrogen Sequestration and Benefit Crop Production in Upland Field. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2381. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092381
Xu H, Cai A, Yang X, Zhang S, Huang S, Wang B, Zhu P, Colinet G, Sun N, Xu M, et al. Long-Term Organic Substitution Promotes Carbon and Nitrogen Sequestration and Benefit Crop Production in Upland Field. Agronomy. 2023; 13(9):2381. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092381
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Hu, Andong Cai, Xueyun Yang, Shulan Zhang, Shaomin Huang, Boren Wang, Ping Zhu, Gilles Colinet, Nan Sun, Minggang Xu, and et al. 2023. "Long-Term Organic Substitution Promotes Carbon and Nitrogen Sequestration and Benefit Crop Production in Upland Field" Agronomy 13, no. 9: 2381. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092381
APA StyleXu, H., Cai, A., Yang, X., Zhang, S., Huang, S., Wang, B., Zhu, P., Colinet, G., Sun, N., Xu, M., & Zhang, W. (2023). Long-Term Organic Substitution Promotes Carbon and Nitrogen Sequestration and Benefit Crop Production in Upland Field. Agronomy, 13(9), 2381. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092381









