Abstract
The continuous cropping of cabbage or kidney bean results in a decrease in yield by influencing the soil environment. To decrease the damage caused by continuous cropping, ten treatments of cabbage–maize–cabbage (CMC), kidney bean–maize–cabbage (BMC), cabbage–cabbage–cabbage (CCC), cabbage–maize–kidney bean (CMB), kidney bean–maize–kidney bean (BMB), kidney bean–kidney bean–kidney bean (BBB), cabbage–cabbage–maize (CCM), cabbage–kidney bean–maize (CBM), kidney bean–kidney bean–maize (BBM) and kidney bean–cabbage–maize (BCM) rotation combinations were set up. The changes in soil nutrients, fungal community structure, composition and diversity in topsoil under the ten crop rotation combinations were analyzed using Illumina NovaSeq high-throughput sequencing technology and chemical technology. Fungal species were abundant in the ten treatments. The OTUs (operational taxonomic units) showed no significant differences. The richness index values of each treatment had significant differences. The diversity index value of the CCC treatment was significantly lower than those of the other treatments. The dominant soil fungal phylum was Ascomycota, and the subordinate soil fungal phylum was Basidiomycota. No significant differences were observed in Ascomycota between the treatments. Basidiomycota in the BBM treatment was significantly higher than that in the CCM treatment. Kickxellomycota was not found in the CCM and CCC treatments. The BBM treatment had no Entorrhizomycota. The dominant soil fungal class belonged to Ascomycota. The common distinction between continuous cropping and crop rotation was Diaporthales, which might be the main fungal order causing continuous cropping disorders. As the best choice, the BBM treatment could prevent soil-borne fungal diseases and provide the basis for the rational crop rotation of cabbage, kidney bean, and maize.
1. Introduction
Soil is the carrier for crops and microorganisms to live together. Soil, crops, and microorganisms interact with each other. Soil microorganisms actively affect the growth and reproduction of crops. They are often used as the indicators to reflect soil quality and health, and dominate soil formation and evolution [1], because they are sensitive to changes in the surrounding environment [2]. Soil microorganisms can be divided into biological control microorganisms and rhizosphere growth-promoting microorganisms according to their different mechanisms of action [3]. Fungi are abundant components of biomass and one of the important components of soil microorganisms. The numbers of fungi are second only to those of bacteria, but they can better degrade complex compounds [4], participate in soil nutrient cycling, and widely exist in soil. Soil bacteria have been widely studied, but the study of fungi is also essential [5]. The large numbers of soil fungi make it easier for them to cause diseases [6]. The chemical properties of soil directly affect the composition of the fungal community structure, and different tillage systems affect the soil’s chemical properties [7]. The available nutrients in a soil can reflect the soil’s fertility level. Available nitrogen (AN), available phosphorus (AP) and available potassium (AK), reflecting the supply of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in soil fertility, are soil nutrients that can be absorbed and utilized by crops directly or after simple transformation [8]. Research has shown that in the semi-arid region of the Loess Plateau in China, soil health problems are particularly prominent due to long-term intensive cultivation [9]. Ascomycota can resist the impact of environmental change [10], and Basidiomycota has a strong ability to decompose lignocellulose [11]. Both play an important role in soil nutrient cycling. Crops such as legumes and crucifers are more prone to continuous cropping barriers [12]. In crop rotations of different families, the roots absorb nutrients in different soil layers because of the different root depths, which is beneficial to the balance of the soil nutrients [13] and reduces the incidence of soil-borne diseases [14].
The dry land area in China accounts for 42% of the national land area, with the dry land area in western region accounting for 83% of the western land area, which has been continuously expanding in recent years [15]. This means that the development of dryland agriculture has great potential. Cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata) is an annual or biennial herb originating in Europe. Its yield is easily affected by the tillage system and can reflect the suitability of the system in the time interval. Kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris Linn.), with well-developed root nodules that can fix nitrogen, is a leguminous annual herb native to America. Its pods are highly nutritious, and it can be used as a vegetable when young and as a grain on maturity [16]. Chinese kidney bean output is ranked first in the world [17]. Continuous cropping has a great effect on kidney bean yields, and can cause large areas of wilting and death in Phaseolus vulgaris, resulting in serious yield reduction [18]. The previous crops from different families produce different root exudates, thereby altering the community structure of the microorganisms in the field [19]. This results in smaller differences in comparison between the same treatments of the previous crops. The effect on kidney bean is better when the current stubble crops are Gramineae species and leafy vegetables [20,21]. Maize (Zea mays L. sinensis Kulesh), a gramineous herb originating in China, is one of the important food crops in China. Maize is used for fresh food and canning, and has a high starch content [22]. Cabbage [23], kidney bean [24], and maize [25,26] are often planted in large areas in semi-arid areas of China for successive years, resulting in changes in the soil fungal diversity and community structure, a decrease in the soil’s available nutrients [27], and finally leading to continuous cropping obstacles. Therefore, it is crucial that three types of crop rotation should be used to improve the agricultural production patterns dominated by monocultures. It was recognized that continuous cropping of cabbage and kidney bean leads to increased pressure from soil-borne pathogens. This study focuses on a three-year continuous cropping and rotation experiment, using a combination of chemical technology and Illumina NovaSeq high-throughput sequencing technology to analyze the effects of different continuous cropping and rotation combinations on crop yield, soil available nutrients, and fungal community structure. The aim is to provide a theoretical basis for the rational selection of rotation combinations in semi-arid areas.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Summary of the Natural Conditions of the Test Area and Test Site
The experiment was performed at Hecun base, Yangqu county, Taiyuan city, Shanxi Organic Dry Farming Research Institute, Shanxi Agricultural University (38°04′ N and 112°89′ E), with an altitude of 1248.5 m and an average annual precipitation of 450 mm. Most rainfall is in summer, whereas the other three seasons have little rainfall and high evaporation. It is a typical semi-arid area with a temperate continental monsoon climate, with a mean annual temperature of 6–7 °C and large day–night temperature variation. The ≥10 °C accumulated active temperature is about 2600 °C, annual sunshine duration is 2662 h, and the frost-free period is about 120 d [28]. The terrain is flat and the soil is Loess light brown soil. The basic physicochemical properties of the 0–20 cm soil layer: organic matter (OM) 14.41 g/kg, total nitrogen (TN) 1.19 g/kg, total phosphorus (TP) 0.7 g/kg, total potassium (TK) 20.7 g/kg, available nitrogen (AN) 54.63 mg/kg, available phosphorus (AP) 9.57 mg/kg, available potassium (AK) 103.8 mg/kg and pH value 7.72. This area mainly depends on natural precipitation for agricultural cultivation. Maize, cabbage, kidney bean, and other crops are those mainly cultivated.
2.2. Experimental Design
The experiment was performed for three consecutive years from 2018 to 2020, and a single-factor random block design was used to form the cabbage–kidney bean–maize rotation system. As shown in Table 1, ten combination treatments were conducted. Each treatment had three repetitions. The cultivation area of each plot was 30 m2. According to the local field conditions, the application rate of compound fertilizer was N 108 kg ha−1, P 77.58 kg ha−1, K 89.62 kg ha−1 for cabbage, and N 216 kg ha−1, P 94.32 kg ha−1, K 179.24 kg ha−1 for maize and kidney bean. The cabbage, kidney bean, and maize varieties were Shinong 307, Red Pearl, and Jingkenuo 2000, respectively. The planting densities of cabbage, kidney bean, and maize were 33,333, 64,000, and 60,000 plants per hectare, respectively. During the three years, maize and kidney bean in the experimental field were sown in mid-May, and the cabbage in mid-June. All crops were harvested in mid-September. The experimental field was without irrigation. Adopting a rotation fallow cultivation method, only one crop was planted annually, and seasonal rotation fallow cultivation was carried out in spring and winter.

Table 1.
Treatments in the experiment.
2.3. Determination of Items and Methods
Before sowing crops in 2021, a small soil drill was used to collect 0–20 cm soil from each treatment plot, and the five-point sampling method was used. There were 30 plots, and 5 points in each plot were selected for sampling; this method was used in each plot, resulting in a total of 30 soil samples. The following procedure was repeated for each of the 30 soil samples. After the soil was mixed, it was divided into quarters to remove the impurities such as stones and roots, and then ¼ of the soil was sifted through a 2 mm mesh sieve and put into a sealed packet for cryopreservation at −80 °C. TGuide S96 magnetic bead-based soil genomic DNA extraction kit was used to complete the extraction of nucleic acid. The nucleic acid protein analyzer was used to determine the DNA content and the ratios of A260/A280 and A260/A230. After the content and purity of DNA were determined, the qualified samples were used to construct the target region PCR system. Fungi were subjected to PCR amplification of the fungal ITS1rRNA gene using primers ITS1F (5′-CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA-3′) and ITS2 (5′-GCTGCGTTCTTCATCGATGC-3′). After that, the product was purified, and then the gel was cut and recovered. Fungal genes were sequenced by Illumina NovaSeq high-throughput sequencing platform. Reads were clustered at 97.0% similarity level by USEARCH software. The species abundance table was generated by QIIME software. The dilution curve, community structure map, and species clustering heatmap were drawn by R language tools. The relationship between fungal community structure and soil available nutrients was studied by correlation analysis. The remaining ¾ of the soil sample was air-dried and ground in a cool place, sifted through a 1 mm mesh sieve, and stored in a self-sealed bag at room temperature. The AN, AP, and AK content were determined by the alkaline diffusion method, molybdenum–antimony anti-colorimetric method, and flame spectrophotometry, respectively [8].
2.4. Data Processing and Calculation Methods
Excel 2003 software was used to process nutrient data. SPSS 18.0 software was used for statistical analysis. The significant difference was p ≤ 0.05. R language tools were used to draw Venn diagrams.
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Soil Chemical Properties
The analysis of the soil available nutrients in the different rotation combinations (Table 2) showed that there was no significant difference in the contents of the soil AN among the seven treatments in which cabbage and maize were planted in the third year of the experiment. Significant differences were observed in the AP and AK content. The AP and AK contents in the CMC treatment were significantly higher than those in the CCC treatment. The AP and AK contents in the BMB treatment were significantly higher than those in the BBB treatment. The AK content in the CMB treatment was significantly lower than that in the BBB treatment. The content of AN in the CMB treatment group decreased by 7.73% compared with the BBB treatment group, but there was no significant difference. When the previous crop was maize, only the AP content was significantly different in the CCM, CBM, BBM and BCM treatments. The AP content in the CBM treatment was significantly higher than it was in the other treatments. The AP content in the BBM treatment was significantly higher than it was in the BCM treatment. When the previous crop was kidney bean, the AN content was higher than it was with cabbage and maize. Compared with the CCC treatment, the BBB treatment significantly increased the AN and AK content by 19.99 and 39.83%, respectively. Different crop rotation sequences had different effects on soil available nutrients. No significant differences were observed in the soil available nutrients between the CMC and CCM treatments. The AN and AK contents in the BMB treatment were significantly higher than those in the BBM treatment. No significant differences were observed in the AN content between the BMC, CMB, CBM, and BCM treatments. The AP content in the CBM treatment was significantly higher than in the other treatments. The AK content in the BMB and CCM treatments was also significantly higher than in the other treatments.

Table 2.
Effects of different treatments on soil available nutrients in 0–20 cm soil.
The effect of crop rotation sequence on soil available nutrients was different. On comparing treatments with the same previous crop, the treatments with higher soil available nutrients were CMC, BMB, and CBM.
3.2. Data Analysis of Fungal Sequencing
The sequencing of 30 samples produced 2,018,919 clean reads. Each sample produced at least 153,483 clean reads, and the sequence lengths ranged from 160 bp to 460. Table S1 shows the effective reads, average sequence length, feature OTU numbers, and coverage of each process. The results showed that the average sequence length of each treatment ranged from 243 bp to 248 bp. The number of OTUs from large to small was CCM > BBM > CMC > BBB > CMB > CBM > BMC > BCM > CCC > BMB. A total of 1711 fungal OTUs were obtained, belonging to 12 phyla, 36 classes, 84 orders, 187 families, 386 genera, and 494 species. The number of OTUs could reflect the diversity of the soil fungi to some extent. The coverage of each processing library was >98.80%. Combined with the analysis of the sample dilution curve in Figure 1, the OTUs increased with the increase in sequencing quantity. When it exceeded a certain value, the curve tended to be smooth and the sequencing was deeply saturated, covering all species among the treatments and truly reflecting the composition of the soil fungal communities in each treatment.
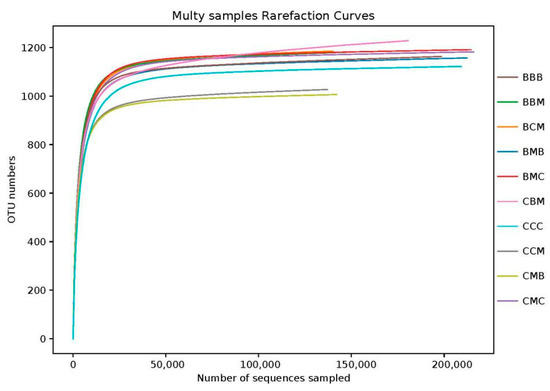
Figure 1.
Each sample’s rarefaction curves.
3.3. Distribution of Fungal OTUs
The OTU Venn diagram of the soil fungi showed the common and unique OTUs in different treatments. Figure 2 shows that when the previous crop was cabbage, the common OTUs in the CMC, BMC, and CCC treatments were 116, 126, and 116, respectively, with 729 OTUs. When the previous crop was kidney bean, the common OTUs in the CMB, BMB, and BBB treatments were 79, 147, and 188, respectively, and the total number of OTUs was 644. When the previous crop was maize, the common OTUs in the CCM, CBM, BBM, and BCM treatments were 39, 64, 74, and 70, respectively, with 594 OTUs. The ten treatments had 374 unique OTUs. The number of unique OTUs in each treatment was low, and only the CMC treatment had no unique OTUs. As shown in Table S2, the BMB, BBB, and BCM treatments had one unique OTU, and the CCC, CMB, and BBM treatments had two unique OTUs. The CMC, BMC, and CBM treatments had three unique OTUs. The specific OTUs in each treatment were Ascomycota, Basidiomycota, and Mortierellomycota. The unique OTUs in the CMC treatment were OTU885, OTU1337, and OTU1462. The unique OTUs in the BMC treatment were OTU1075, OTU574, and OTU1094. The unique OTUs in the CCC treatment were OTU4139 and OTU822. The unique OTUs in the CMB treatment were OTU1987 and OTU996. The unique OTU in the BMB treatment was OTU986. The unique OTU in the BBB treatment was OTU620. The unique OTUs in the CBM treatment were OTU1113, OTU1419, and OTU922. The unique OTUs in the BBM treatment were OTU819 and OTU851. The unique OTU in the BCM treatment was OTU1004. Thus, the differences in soil fungi in each treatment were large. Specific OTUs decreased with the increase in the number of treatments.
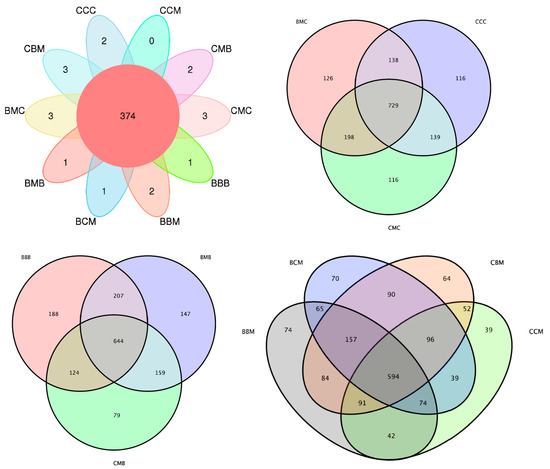
Figure 2.
Venn diagram of characteristics of each sample.
3.4. Analysis of Fungal Diversity
The alpha diversity indices of all treatments are shown in Table 3. The significant changes in the Simpson and Shannon diversity indices were the same. When the previous crop was the same, the richness and diversity of CCC were lower than those of CMC and BMC; the richness and diversity of BBB were higher than those of CMB and BMB; the richness of CBM was significantly higher than that of CCM, BBM, and BCM; and the diversity of BBM was higher than that of the other treatments. These results showed that continuous cropping with different crops had different effects on the diversity and richness of the soil fungal community. Compared with the rotation treatment of the previous crop, cabbage continuous cropping reduced the diversity and richness of the soil fungal community, whereas kidney bean continuous cropping was the opposite. When the previous crop was cabbage, the change rules of the richness and diversity index were the same, which was BMC > CMC > CCC. When the previous crop was kidney bean, the change rule of the richness index was the same as that of the Shannon index, which was BBB > CMB > BMB. When the previous crop was maize, the change rules of the richness and diversity index were different. In the first year, the richness of cabbage was higher than that of kidney bean, but the diversity was opposite.

Table 3.
Alpha diversity indices of soil fungi under different rotation treatments.
Of the ten treatments, the richness and diversity were the lowest in the CCC treatment, and the diversity of the soil fungal community was significantly different between the CCC treatment and the other nine treatments, indicating that continuous cropping of cabbage had the greatest negative effect on the richness and diversity of the soil fungal community between the ten treatments. The richness index of the CBM treatment was significantly higher than that of the other treatments. No significant difference was observed in the diversity index between the CBM and the other treatments (except CCC), indicating that the richness of the soil fungal community in the CBM treatment was the highest. On comparing the same crop rotation combination with a different planting sequence, no significant differences were observed between the CMC and CCM treatments, the BMB and BBM treatments, the richness and diversity indices, or between these four treatments. The richness index of the soil fungal community in the CBM treatment was significantly higher than that in the BMC, CMB, and BCM treatments, but the diversity index showed no significant difference, indicating that the two crop rotations had little effect on the richness and diversity of the soil fungal community. The cabbage, kidney bean, and maize rotation had no significant changes, whereas the three crop rotations had significant differences in the richness of the soil fungal community.
3.5. Analysis of Community Composition at the Phylum Level
The relative abundance of soil fungi with each treatment is shown in Figure 3. The relative abundance of soil fungi from high to low was Ascomycota (71.80–78.15%), Basidiomycota (9.27–13.13%), Mortierellomycota (5.42–9.21%), Chytridiomycota (0.41–2.05%), Rozellomycota (0.76–1.30%), Neocallimastigomycota (0.26–1.06%), Olpidiomycota (0.07–0.68%), Glomeromycota (0.02–0.20%), Kickxellomycota (0.00–0.04%), and Entorrhizomycota (0.00–0.03%). The relative abundance of these ten fungal phyla accounted for >95.00% of the total number of fungi. The relative abundance of the CCM and CCC treatments had no Kickxellomycota. The relative abundance of the BBM treatment had no Entorrhizomycota. The ranks of Kickxellomycota and Entorrhizomycota were BMB > CBM > CMC > BMC > CMB > BBM > BBB > BCM and BMB > BCM > CMC > CMB > BBB > CCM > CCC > BMC > CBM, respectively.
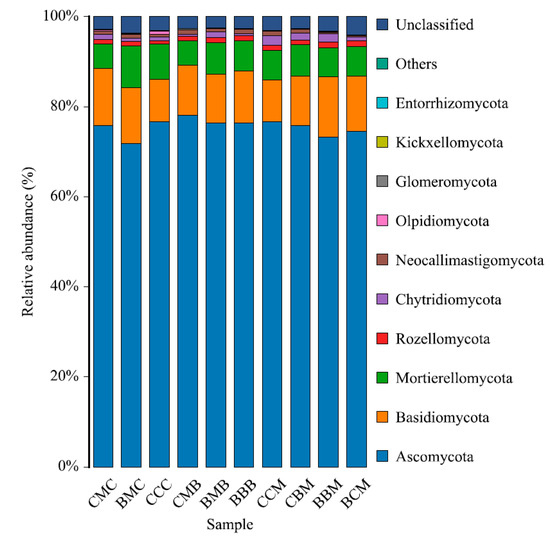
Figure 3.
Community composition of fungi at the phylum level in different treatment soils.
Table 4 shows the relative abundance of phyla among the treatments. Combined with Figure 3, Ascomycota was the dominant fungal phylum, dominant in each treatment, and no significant differences were observed in its relative abundance. This showed that Ascomycota had a strong ability to adapt to the environment and could maintain its own changes in a small range. Basidiomycota was a subdominant fungal phylum, except that its relative abundance in the BBM treatment was significantly higher than that in the CCM treatment. Compared with the treatments with the same previous crops, the relative abundance of Ascomycota in the CCC treatment was 1.15 and 6.82% higher than in the CMC and BMC treatments, respectively; whereas the relative abundance of Basidiomycota in the CMC and BMC treatments decreased by 25.40 and 24.62%, respectively. The relative abundance of Ascomycota in the BBB treatment was lower than that in the CMB and BMB treatments, whereas the relative abundance of Basidiomycota in the BBB treatment was higher than that in the CMB and BMB treatments. The relative abundance of Ascomycota was CCM > CBM > BCM > BBM, whereas that of Basidiomycota was the opposite. Thus, the change rules of Ascomycota and Basidiomycota were roughly opposite in the treatments with the same previous crop. According to the comprehensive comparison, the relative abundance of Ascomycota and Basidiomycota was highest in the CMB and BBM treatments, and lowest in the BMC and CCM treatments. The CCM treatment was significantly higher than the BMC, CMB and BBB treatments in the relative abundance of Chytridiomycota. The BMB, BBB, CCM, BBM, and BCM treatments were significantly higher than the CCC treatment in the relative abundance of Rozellomycota. The CCM, BBB, and CMB treatments were significantly higher than the BBM and BCM treatments in the relative abundance of Neocallimastigomycota, and the BMC treatment was significantly higher than the BCM treatment.

Table 4.
Differences in relative abundance of soil fungal phyla under different rotation treatments.
3.6. Analysis of Characteristics at the Order Level
Because characteristics could not be explained specifically by OTU distribution and the unclassified families, genera, and species below the order level were many, items were selected to explain the specific differences in fungal species between the different treatments at the order level. There was no feature order in the comprehensive comparison between treatments. The common distinction between continuous cropping and crop rotation was Diaporthales, which might be one of the main fungal orders leading to continuous cropping obstacles (Table 5).

Table 5.
Feature order of soil fungi.
3.7. Distribution Heatmap at the Genus Level
The sum of the dominant genera of the top ten relative abundance of fungi was 31.64–42.23%, comprising Aspergillus (6.42–10.74%), Mortierella (5.06–8.97%), Fusarium (5.03–6.82%), Botryotrichum (1.65–3.33%), Cladosporium (2.02–2.93%), Podospora (1.17–4.19%), Chaetomidium (1.11–3.55%), Tetracladium (0.78–9.70%), Penicillium (1.06–2.39%), and Paecilomyces (0.98–2.15%). Cluster analysis was performed according to species or sample abundance similarity. Heatmaps were drawn, and the findings are shown in Figure 4. Horizontal and vertical clustering represented the abundance of various species in different samples and the similarity of the abundances of different species between different samples. The dominant genus in the CCC treatment was Tetracladium, and the secondary dominant genus was Mortierella. The relative abundance of the other genera in the CCC treatment was low. The dominant genera in the BMC treatment was Mortierella and Fusarium. The dominant genus in the CCM treatment was Podospora. These four genera were concentrated in each treatment.
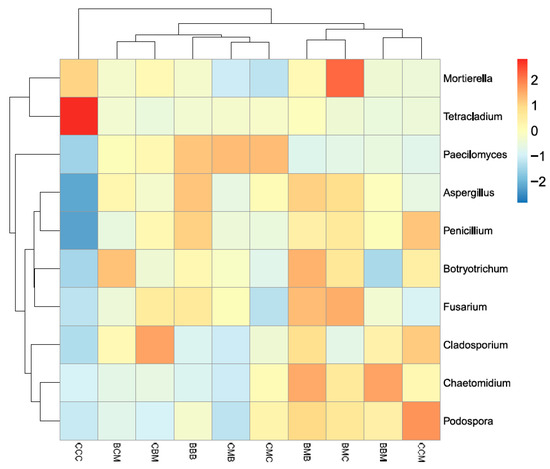
Figure 4.
Abundance cluster heatmap of fungi at genus level in the different treatment soils.
The ten treatments were divided into two categories. The CCC continuous cropping treatment was one group, whereas the other treatments were clustered into another group, indicating that the community structure of the CCC treatment was significantly different from those of the other treatments at the level of soil fungi, and the adverse effect of cabbage continuous cropping was much greater than that of kidney bean continuous cropping. Except for the CCC treatment, the other nine treatments could be divided into two groups. The community structures of the BCM and CBM treatments were similar, while those of the BBB, CMB, and CMC treatments were similar. The BCM, CBM, BBB, CMB, and CMC treatments were clustered into one group. In the second group, the community structures of the BMB and BMC treatments were more similar, while those of the BBM and CCM treatments were more similar. The final planting crop, planting sequence during rotation, and continuous cropping species all affected the soil fungal community structure.
4. Discussion
The study of soil fungal diversity mainly includes community diversity, genetic diversity, and functional and structural diversity. Species diversity in the community varies significantly because of the different external environments [1]. Crop diversity is closely related to soil fungal diversity. The diversity of soil fungi in crop rotation was higher than that in continuous cropping [29]. The study of the soil fungal community diversity mainly analyzed the alpha diversity index changes in each treatment, and can reflect the degree of environmental changes by comparing each treatment. The alpha diversity index includes the species richness index and the species diversity index, and is a comprehensive index to reflect the richness and evenness of each treatment. The richness index includes the Ace and Chao1 indices, and the higher the values of these, the higher the richness of the community. The diversity index includes the Simpson and Shannon indices, and the community diversity increases with the increase in their values [30].
The OTUs and alpha diversity index were higher after crop rotation than after continuous cropping of cowpea and other leafy vegetables [31], and were similar to the continuous cropping of millet [32], Cyperus esculentus [29], and other single crops. Different crop types can lead to changes in the soil microbial environment, but most studies have shown that the soil microenvironment after rotation planting is better than that in a continuous cropping soil environment. Crop rotation can increase the richness and diversity of fungal OTUs and the fungal community, thereby affecting the fungal community structure. Single crop continuous cropping consumes soil, water, and nutrients in the same soil layer for a long time, and the nutrient utilization components are the same [33]. A soil acid–base imbalance promotes the accumulation of harmful microorganisms in the soil and destroys the soil microbial environment [34], reducing the number of fungal species. Compared with the rotation and continuous cropping combinations in this study, cabbage continuous cropping accords with this change law, whereas kidney bean continuous cropping does not. The Ace and Chao1 indices of the CCC treatment were lower than those of the other treatments, and the Simpson and Shannon indices were significantly lower than those of the other treatments; the soil fungal richness and diversity were decreased, and the number of OTUs was only higher than that of the BMB treatment. The Ace and Chao1 indices of the CBM treatment were significantly higher than those of the other treatments, and the index value of the BBB treatment was second only to the CBM treatment, which improved the richness of soil fungi. The richness and diversity indices of CMB and BMB rotation treatments were significantly lower than those of BBB continuous cropping. In this study, according to the different crops planted in the previous cropping, the number of common OTUs in the group with maize and without maize continuous cropping was lower than those in the two groups with control. It could be concluded that the more treatments compared in the rotation pattern, the less the specific OTUs, and continuous cropping had a greater effect on the community structure of the soil fungi. In the treatments with the same previous crop, the order common to continuous cropping and crop rotation was Diaporthales, which might cause continuous cropping obstacles.
The difference in crop species is one of the main factors that promotes the change in the soil fungal community composition. Different crops affect the proportion of beneficial and harmful fungi by the type and number of root exudates, and then affect the community composition [35]. As decomposers, extracellular enzymes secreted by fungi can degrade complex compounds to produce nutrients easily absorbed by microbes [36], thus maintaining the stability of the agro-ecosystem. The dominant groups of soil fungi were affected by many factors. This study showed that the dominant phyla of soil fungi were Ascomycota, Basidiomycota, and Mortierellomycota. The dominant fungal classes were Sordariomycetes, Eurotiomycetes, and Dothideomycetes, all of which belong to Ascomycota. The dominant fungal genera were Aspergillus, Mortierella, and Fusarium. These results were similar to the results of Sun et al. [32] and Liu et al. [37], for the dominant phyla. The large difference in the dominant genera was similar to that of Ni et al. [31]. The results showed that planting crops, planting patterns, rotation years and other factors changed the composition of the soil’s fungal communities by changing the ratio of bacteria to fungi, and the ratio of beneficial bacteria to harmful bacteria to regulate the soil rhizosphere microecosystem.
The relative abundance of Ascomycota was the highest in the CMB treatment and the lowest in the BMC treatment. In contrast to Mortierellomycota, the relative abundance of Basidiomycota in the BBM treatment was significantly higher than that in the CCM treatment. The relative abundances of Kickxellomycota and Entorrhizomycota were the lowest among the dominant fungi, and the relative abundance of the BMB treatment was the highest. The CCM and CCC treatments had no Kickxellomycota, and the BBM treatment had no Entorrhizomycota. The specific role of Kickxellomycota remains unstudied. Root swelling disease is a soil-borne disease caused by the specific parasitism of Entorrhizomycota, which seriously affects the growth of cruciferous crops [38]. Rotation with legumes can prevent and control root swelling disease to some extent [39]. The fungal genera in the top ten of relative abundance belong to Ascomycota, except Mortierella (Mortierellomycota). Penicillium, Fusarium, and Aspergillus can degrade lignin in soil lignocellulose and increase the rate of carbon cycling [40]. Fusarium is the main pathogen causing root rot of leguminous crops and the main factor limiting continuous cropping of leguminous crops [41]. The relative abundance of Mortierella in the BMC and BMB treatments was the highest. The relative abundance of Mortierella was low in the CCC, CMC and CCM treatments without a legume crop in the three-year rotation. Compared with Yan’s [42] study on the specific type of Fusarium vegetables, the Mortierella identified in this study was highly likely to be F.solani f. sp. glycines, which is only pathogenic to legumes but not to other crops. The fungal community structure of the CCC treatment was significantly different from that of the other treatments, and the relative abundance of the other fungi, except Tetracladium, was lower. The contents of the available nutrients in the CCC treatment (except that AN was higher than in the BMC treatment) were lower than those in the other nine treatments. This is consistent with the results of Zheng et al. [43]. It is possible that continuous cropping destroys soil aggregate structure and increases soil nutrient loss. Therefore, different rotation combinations affect fungal growth and change the composition of the soil fungal community and soil nutrient content to different degrees.
5. Conclusions
There were significant differences in the soil available nutrient content between the different crop rotations, the main environmental factor affecting the structure and composition of soil fungal community. The unique OTUs of the BBB treatment were Ascomycota, Sordariomycetes, Sordariales, and unclassified; the unique OTUs of the CCC treatment were Mortierellomycota, Mortierella, Mortierella calciphila, and the unique OTUs of the treatment were Ascomycota, Dothideomycetes, Pleosporales, Leptosphaeriaceae, Leptosphaeria, and Leptosphaeria maculans. Under different crop rotation patterns, the contents of soil available nitrogen and soil available potassium in the BMB treatment were significantly higher than those in the other nine treatments, while soil feature OTUs were significantly lower than those in the other nine treatments, with the highest OTUs in Entorrhizomycota and Kickxellomycota. The BBM treatment had the highest Simpson index and Shannon index, and the relative abundance of the subdominant phylum Basidiomycota was the highest, while Entorrhizomycota was absent in the BBM treatment. The BBM treatment not only ensured high yield but also increased the soil available nutrient content, reduced the harmful fungal species in the soil, and increased the beneficial fungal species. These results could facilitate the selection of scientific rotation patterns to improve the soil microbial community structure and soil productivity.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy13071883/s1, Table S1: Original data of soil fungal sequencing under different treatments; Table S2: Soil fungal specific OTU under different treatments.
Author Contributions
Investigation, T.W.; writing—original draft preparation, T.W.; writing—review and editing, X.W. and L.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Science and Technology Major Project of Shanxi Province, China (Grant No. 202101140601026-4-4); National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2021YFD1901101-4-4); the Youth Top-Notch Talent Support Program of Shanxi Province (Grant No. HNZXBJ001); Key research plan of Shanxi Province, China (Grant No. 201703D211002-7-1).
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request on request due to privacy restrictions. The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yu, W.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Ding, Y.; Huang, S. Research progress of soil microorganisms in alpine ecosystem. J. Southwest Minzu Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2021, 47, 455–461. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Yao, T.; Yang, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, C.; Li, Q.; Feng, Y. Soil nutrients, enzyme activities and ecological stoichiometric characteristics in degraded alpine grasslands. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 32, 287–295. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Fan, J. Research and prospect of plant root exudates and microenvironment. Rural. Sci. Technol. 2021, 12, 96–98. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, A.; Ngouajio, M. Soil microbial biomass, functional microbial diversity, and nematode community structure as affected by cover crops and compost in an organic vegetable production system. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2012, 58, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zeng, R.; Gao, S.; Dai, M. Review on the effect of soil fungal communities on soil-borne diseases. Acta Agric. Shanghai 2017, 33, 161–165. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, J.; Tan, J.; Guo, Q. Effects of Bacillus megaterium and Bacillus subtilis on growth physiology of Solanum tuberosum L. and microbial biomass in rhizosphere soil. J. Hunan Agric. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2017, 43, 377–381. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Y.; Cui, Y.; Li, H.; Kuang, A.; Li, X.; Wei, Y.; Ji, X. Rhizospheric soil and root endogenous fungal diversity and composition in response to continuous Panax notoginseng cropping practices. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 194, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S. Soil Agrochemical Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Nan, L.; Tan, J.; Guo, Q. Effects of fallow rotation modes on soil fungal communities in semi-arid area of the Loess Plateau, northwest China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 8582–8592. [Google Scholar]
- Egidi, E.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Plett, J.M.; Wang, J.; Eldridge, D.J.; Bardgett, R.D.; Maestre, F.T.; Singh, B.K. A few Ascomycota taxa dominate soil fungal communities worldwide. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taina, K.L.; Miia, R.M.; Kristiina, H. Lignin-modifying enzymes in filamentous basidiomycetes—Ecological, functional and phylogenetic review. J. Basic Microbiol. 2010, 50, 5–20. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, M.; Zhong, W.; Ouyang, L.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Z. Research status of continuous cropping obstacles in China from 1989 to 2018: Based on bibiometric analysis and knowledge mapping of CNKI. J. Agric. 2021, 11, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Zhu, W. Effect of soil chemical properties on cucumber seedlings grow in different rotation system soils. J. Northeast Agric. Univ. 2020, 51, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, G. Green prevention and control technology of root swelling disease of cruciferous vegetables in Shanghai. Shanghai Veg. 2016, 6, 31–32. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Y.; Wang, R.; Cai, Z. Climate change and its impacts in arid and semi-arid areas of China. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2009, 23, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Feng, T.; Gao, H.; Liu, F. A brief report on Bean Germplasm Resources in Jilin Province. China Seed Ind. 2009, 11, 26–27. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, G. Research on High-Quality Kidney Bean Germplasm Resources and Breeding Strategies in Heilongjiang Province. Ph.D. Thesis, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, China, 2008; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, A.; Yang, H.; Li, X.; Shi, Y.; Xie, X.; Li, L.; Fan, T.; Li, B. Identification of pathogen causing Common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) wilt in Inner Mongolia Tengfei1, LI Baoju1. Acta Phytopathol. Sin. 2023, 53, 33–136. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Tang, L.; Huang, X.; Yang, X.; Wu, W.; Xiang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y. Effects of soybean as pre-cropping plant on occurrence of clubroot in oilseed rape. Chin. J. Oil Crop. Sci. 2020, 42, 480–485. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Discussion on high-yield cultivation techniques of Phaseolus vulgaris in greenhouse in early spring. Contemp. Hortic. 2021, 44, 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, D.; Sun, Y.; Xiao, W.; Zhou, X.; Xia, X.; Ren, H. Grey correlation analysis of pod weight related agronomic traits of common bean. Heilongjiang Agric. Sci. 2021, 9, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D. Production and cultivation techniques of fresh waxy Corn. Farmers Consult. 2021, 20, 44–45. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Liao, L. Pathogenicity variation and genetic structure differentiation of Fusarium oxysporum f.sp.conglutinans in soil under successive cultivation of Brassica oleracea. Acta Phytopathol. Sin. 2013, 43, 58–68. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Li, M.; Wang, F. A preliminary survey of diversities of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal fungi on greenhouse vegetables. J. Laiyang Agric. Coll. 2001, 18, 280–283. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Song, X.; He, B.; Chen, X. Effects of different cropping patterns on soil fertility and physical and chemical properties of continuous cropping maize. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2021, 12, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Hao, M.; Wang, L.; Li, S. Effects of cropping systems on soil water, organic N and mineral N in dryland soil on the loess plateau. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2008, 41, 2686–2692. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, H.; Xiao, Z.; Yan, J.; Ma, J.; Meng, Y. Effects of continuous cropping of maize on soil microbes and main soil nutrients. Pratacultural Sci. 2011, 28, 1777–1780. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W. Construction of the high-density genetic linkage map and QTL analysis for main agronomic traits in cabbage. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2013; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wei, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, F.; Wang, Z.; Mou, Z. The effects of rotational cropping with Phaseolus vulgaris L. on the growth of oily beans Cyperus esculentus L. and field soil microorganisms. J. Shanxi Agric. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2021, 41, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z. Study on the Characteristics of Microbial Community and Response of Environmental Factors in Bahe River (Chanba eco-Region). Master’s Thesis, Xi’an University of Technology, Xi’an, China, 2021; pp. 39–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, M.; Cheng, S.; Han, X.; Wang, L.; Lei, X.; Ju, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, P. Effect of rotating different leafy vegetables on soil fertility and soil microbial characteristics of cowpea. China Veg. 2019, 5, 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Wu, H.; Chen, F.; Kang, J. Characteristics of soil nutrients and fungal community composition in crop rhizosphere under different rotation patterns. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 4682–4689. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B.; Sun, L.; Wang, C.; Gao, Y.; Wang, H. Effect of continuous vegetable cropping on soil nutrient variation in plastic greenhouse. J. Northeast. Agric. Univ. 2014, 45, 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Kintché, K.; Guibert, H.; Sogbedji, J.; Levêque, J.; Bonfoh, B.; Tittonell, P. Long-term mineral fertiliser use and maize residue incorporation do not compensate for carbon and nutrient losses from a Ferralsol under continuous maize–cotton cropping. Field Crop. Res. 2015, 184, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Lv, D.; Qin, S. Research Progress on the interaction between plants and Rhizosphere microorganisms. J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 2016, 38, 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi, N.; Matsuda, Y.; Sakai, A.; Fujita, K. A large amount of biogenic surface dust (Cryoconite) on a glacier in the Oilian Mountains, China. Bull. Glaciol. Res. 2005, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Luo, X.; Wu, M.; Trang, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J. Comparison of cassava yield and soil microbial characteristics under continuous cropping and rotation. Chin. J. Trop. Crop. 2019, 40, 1468–1473. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Hu, C.; Cheng, Q.; Jia, W.; Zhao, X. Research progress on the interaction between rhizobium androot system and its influencing factors. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2019, 35, 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhan, Z.; Piao, Z.; Zhang, C. Progresses and prospects of germplasms innovation for clubroot resistance and genetic improvement in Brassica napus. Acta Agron. Sin. 2018, 44, 592–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zeng, G.; Huang, G.; Hu, T.; Chen, Y. Screening of lignin-degrading fungi and their enzyme production. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2004, 5, 639–642. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, L.; Fan, X.; Jie, W.; Cai, B.; Yu, W. Research progress of AM fungi on root rot of leguminosae. China Sci. Technol. Inf. 2004, 13, 33–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, W. Identification of Fusarium formae speciales on three vegetablesand the discovery of new diseases in China. Chin. Acad. Agric. Sci. 2019, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y. Soil properties and microbial diversity in the muskmelon fields after continuous cropping for different years. Microbiol. China 2022, 49, 101–114. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).