A Moderate Wetting and Drying Regime Combined with Appropriate Nitrogen Application Increases Grain Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Rice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cultivation Conditions and Materials
2.2. Treatment and Design
2.3. Sampling and Measurement
2.3.1. Leaf Water Potential, Photosynthetic Rate, and N Content
2.3.2. Population Traits and Non-Structural Carbohydrate (NSC) Remobilization
2.3.3. Root Traits and Soil N Content
2.3.4. Final Harvesting
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
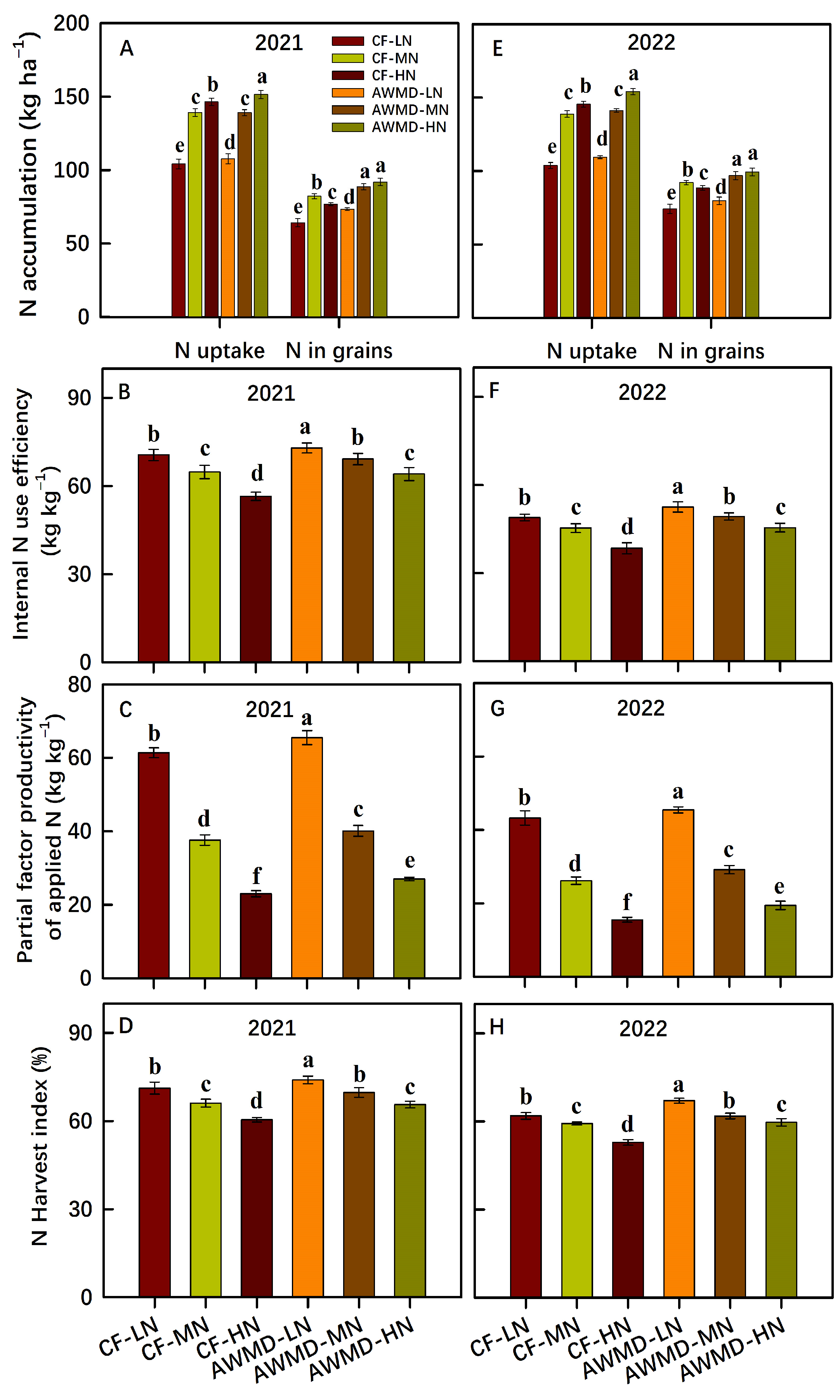
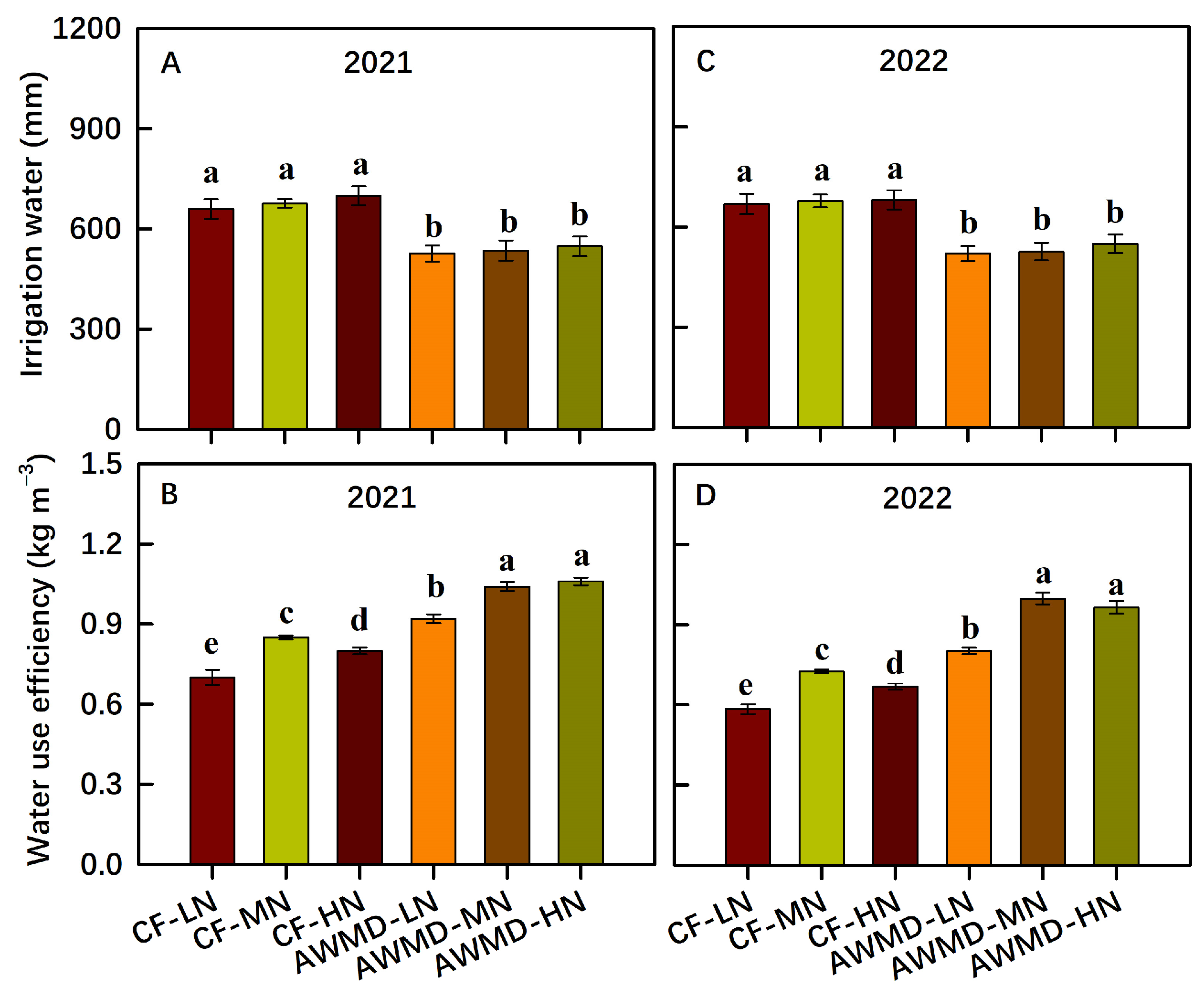
3.1. Grain Yield, NUE and WUE
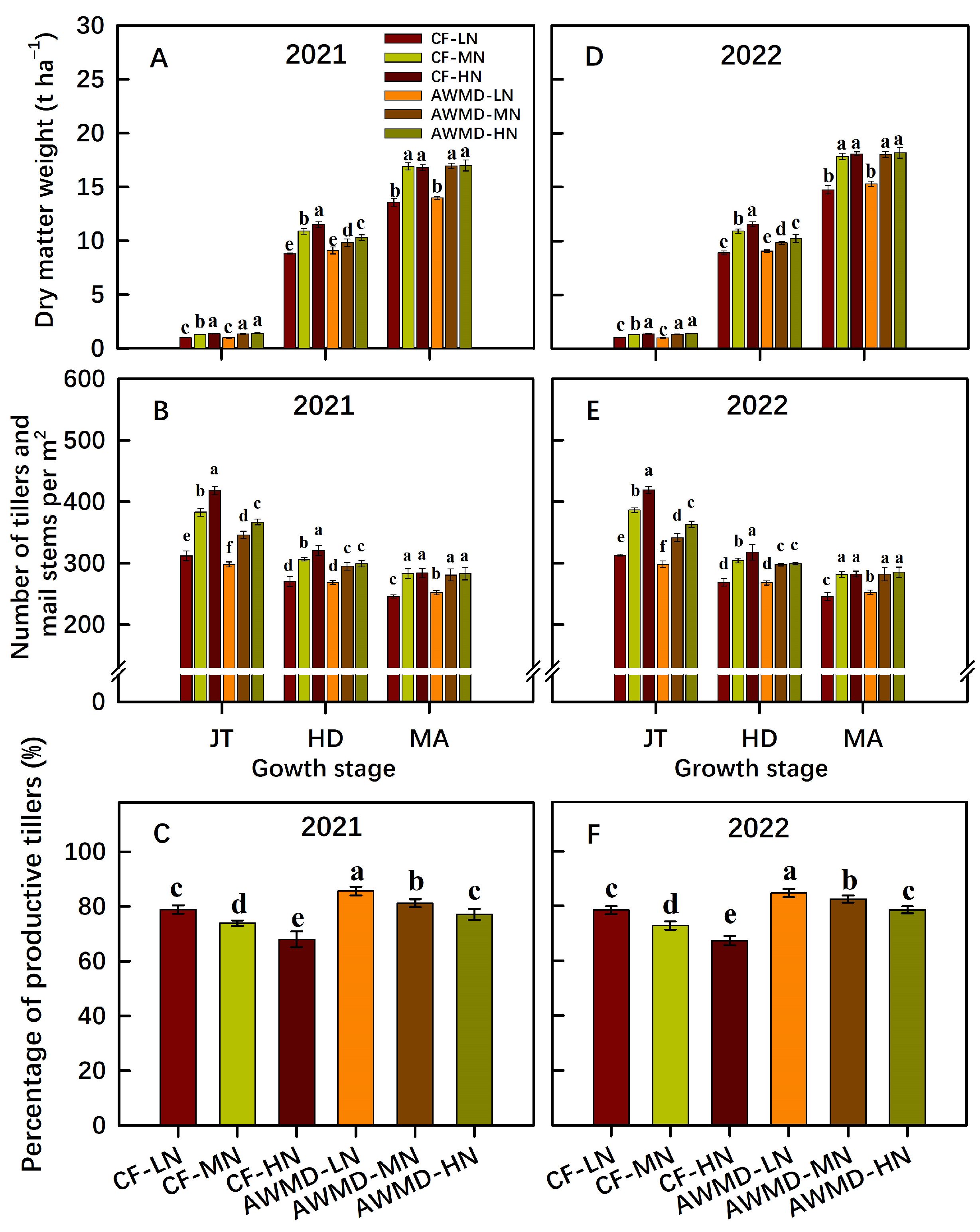
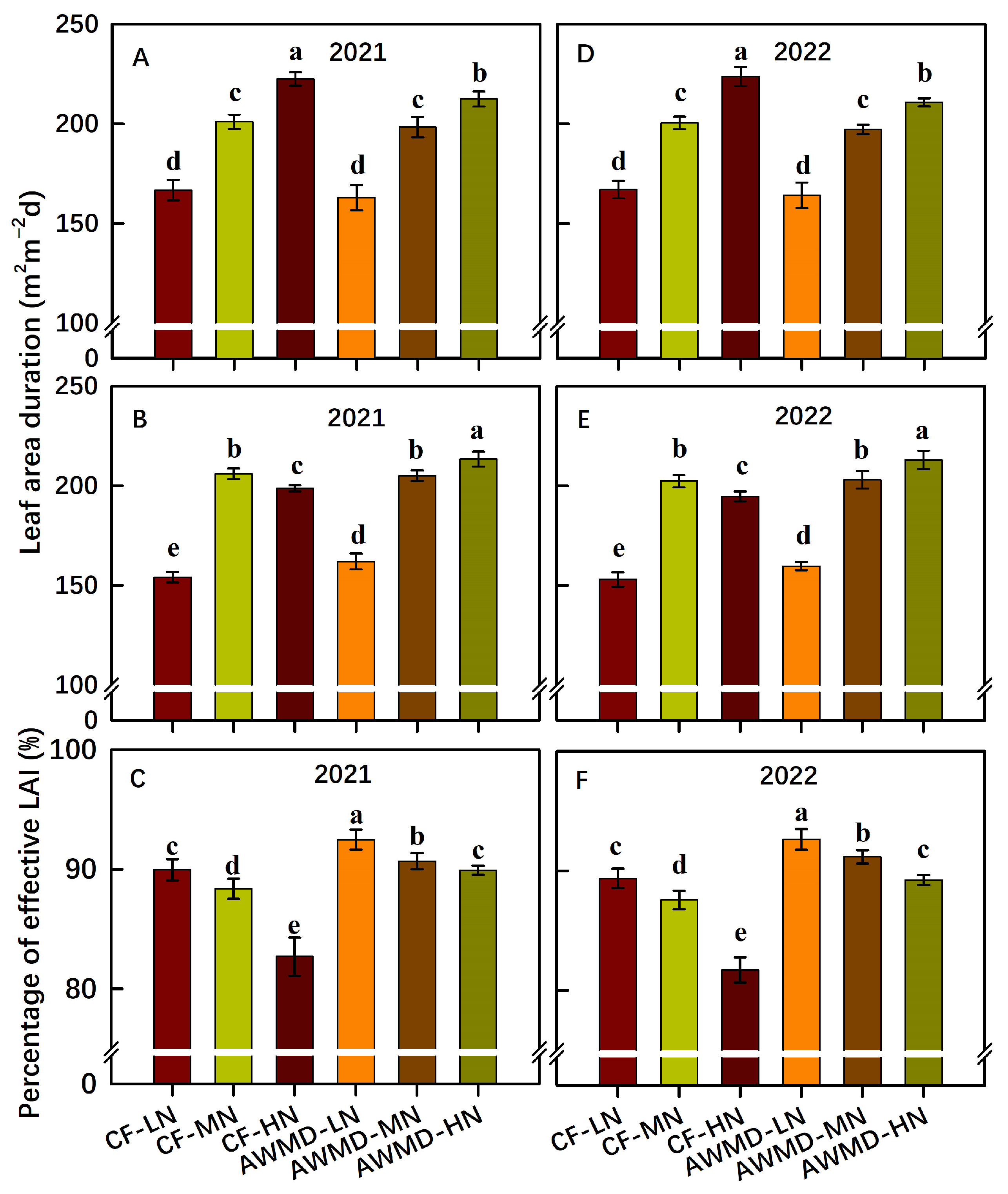
3.2. Leaf Water Potential (LWP), Shoot Dry Weight, Tiller Number, and LAI
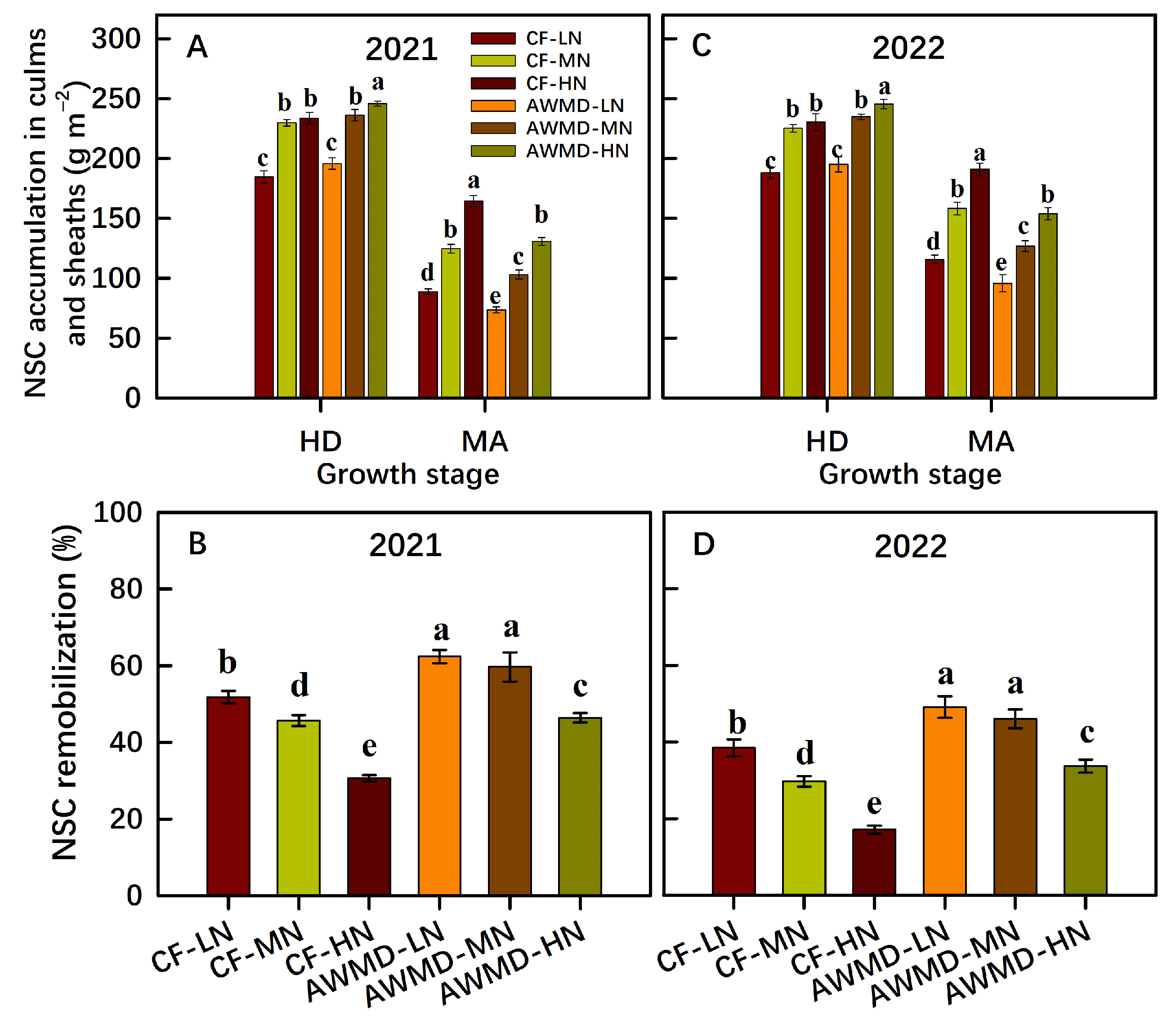
3.3. Non-Structural Carbohydrate (NSC) Remobilization
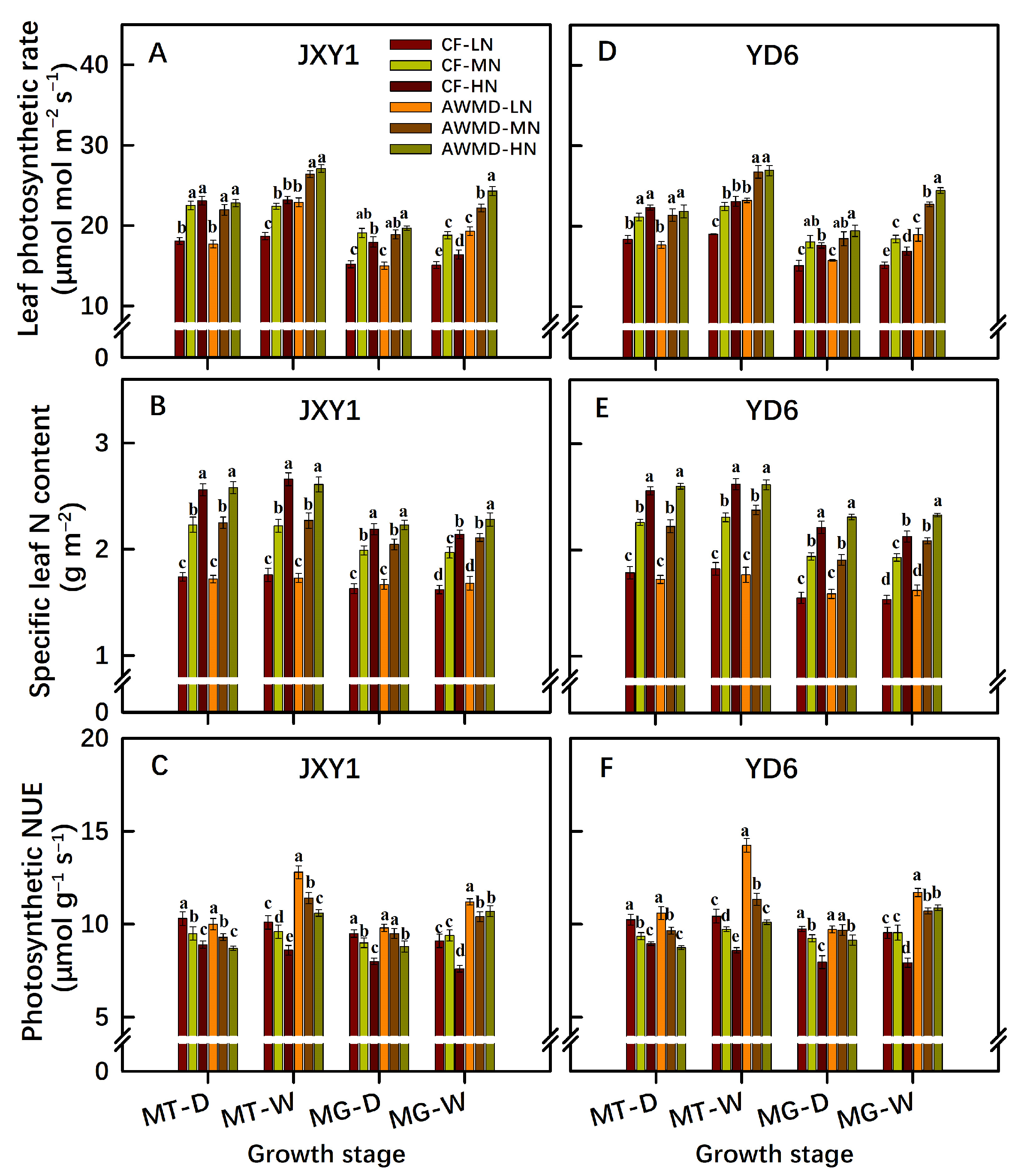
3.4. Leaf N Content, Photosynthesis and PNUE
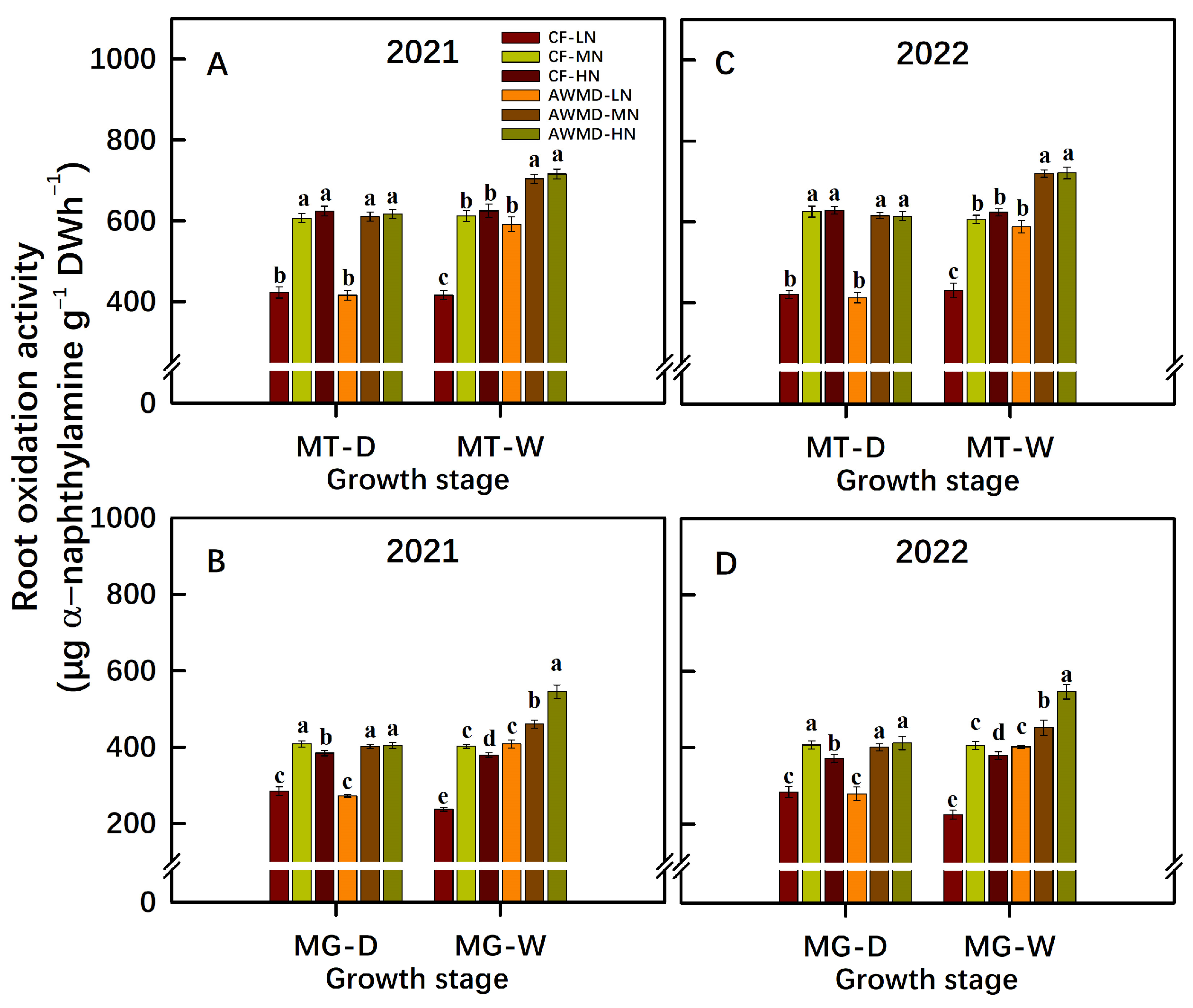
3.5. Root Dry Weight and ROA
3.6. Activities of the Enzymes Related to N Assimilation in Roots
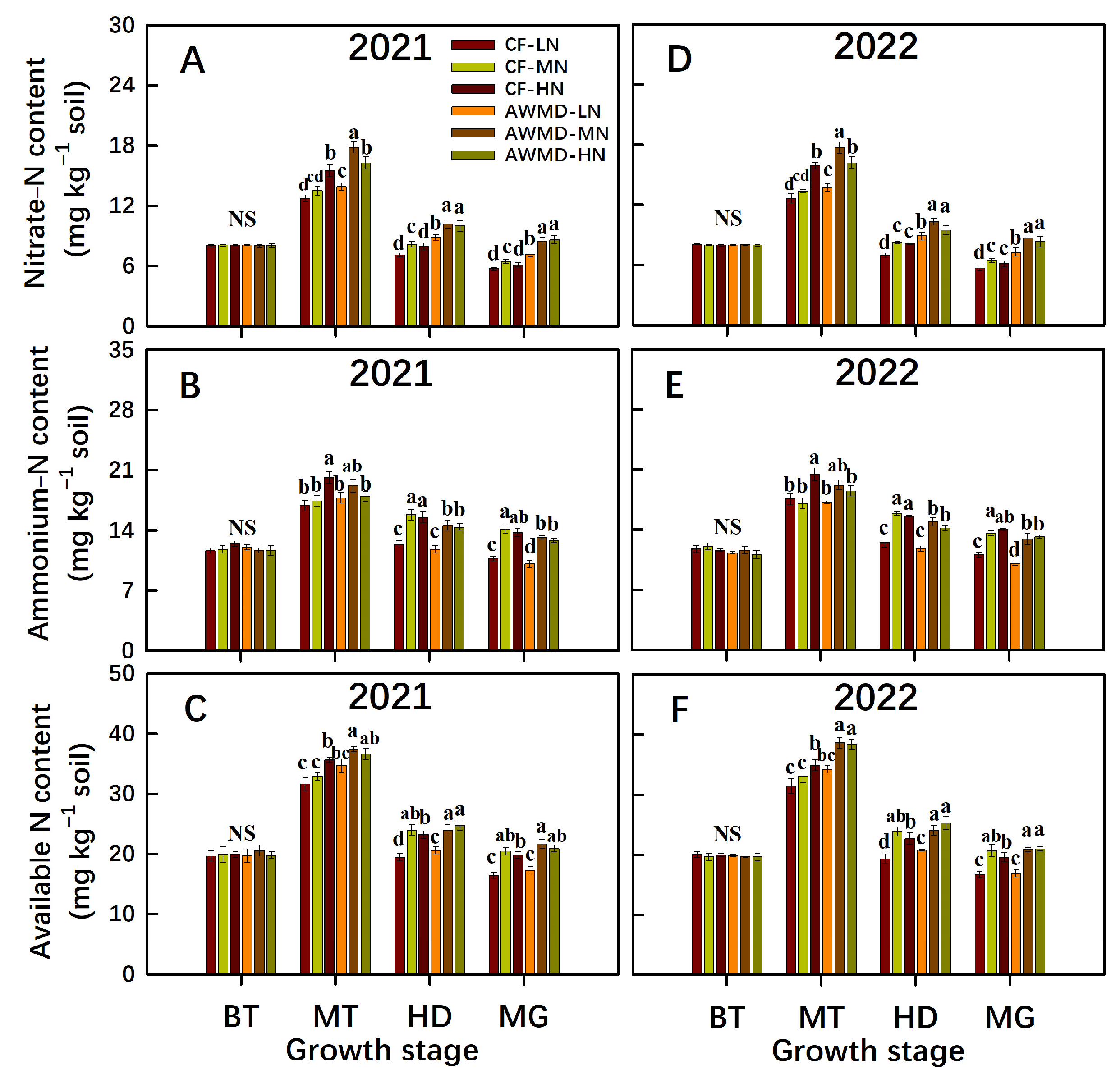
3.7. Soil Available N Content
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Dillard, H.R. Global food and nutrition security: From challenges to solutions: Report of the international congress of plant pathology 2018, Boston, USA, 29th July-3rd August 2018 with the title plant health in a global economy. Food Secur. 2019, 11, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Balzer, C.; Hill, J.; Befort, B.L. Global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20260–20264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouman, B.A.M. A conceptual framework for the improvement of crop water productivity at different spatial scales. Agric. Syst. 2007, 93, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Peng, L.; Gong, J.; Wang, J.; Wu, C.; Sui, X.D.; Tian, Y.F.; Hu, M.M.; Li, C.M.; He, X.M.; et al. Effects of water stress on starch synthesis and accumulation of two rice cultivars at different growth stages. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1133524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekhar, S.; Mailapalli, D.R.; Raghuwanshi, N.S. Effect of Alternate Wetting and Drying Irrigation Practice on Rice Crop Growth and Yield: A Lysimeter Study. ACS Agric. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Pan, Y.; Shi, P. Agricultural irrigation in China. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 68, 147A–154A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouman, B.A.M.; Peng, S.; Castañeda, A.R.; Visperas, R.M. Yield and water use of irrigated tropical aerobic rice systems. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 74, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wu, L.; Li, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhu, D.; Uphoff, N. Influence of the System of Rice Intensification on Rice Yield and Nitrogen and Water Use Efficiency with Different N Application Rates. Exp. Agric. 2009, 45, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Brueck, H.; Dittert, K.; Kreye, C.; Lin, S.; Sattelmacher, B. Growth and yield formation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) in the water-saving ground cover rice production system (GCRPS). Field Crops Res. 2006, 95, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Zhai, L.; Zhou, F.; Ye, Y.; Ruan, S.; Wen, W. Effects and potential of water-saving irrigation for rice production in China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 217, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, P.; Jiang, S.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Cao, C. Evaluation of resource and energy utilization, environmental and economic benefits of rice water-saving irrigation technologies in a rice-wheat rotation system. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H.; McClung, A.M.; Rohila, J.S.; Barnaby, J.Y. Effects of alternate wetting and drying irrigation management and air temperature during grainfill on rice grain physicochemical and functionality traits of US inbred varieties. Cereal Chem. 2021, 98, 980–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.S.; Liang, X.Q.; Chen, Y.X.; Liu, J.; Gu, J.T.; Guo, R.; Li, L. Alternate wetting and drying irrigation and controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer in late-season rice. Effects on dry matter accumulation, yield, water and nitrogen use. Field Crops Res. 2013, 144, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, K.; Wang, Z.; Du, Y.; Zhang, J. Water-Saving and High-Yielding Irrigation for Lowland Rice by Controlling Limiting Values of Soil Water Potential. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2007, 49, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Huang, J.; Cui, K.; Nie, L.; Xiang, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, W.; Chen, M.; Peng, S. Agronomic performance of high-yielding rice variety grown under alternate wetting and drying irrigation. Field Crops Res. 2012, 126, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.Y.; Qin, T.; Du, X.Z.; Sheng, F.; Li, C.F. Effects of irrigation regime and rice variety on greenhouse gas emissions and grain yields from paddy fields in central China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 250, 106830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Chen, T.; Wu, Q.; Yu, J.; Chen, W.; Chen, Y.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Meng, W.; Chi, D.; Xia, G. Effect of zeolite application on phenology, grain yield and grain quality in rice under water stress. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 206, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, J.H. Moderate wetting and drying increases rice yield and reduces water use, grain arsenic level, and methane emission. Crop J. 2017, 5, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.-T.; Xing, G.-X.; Chen, X.-P.; Zhang, S.-L.; Zhang, L.-J.; Liu, X.-J.; Cui, Z.-L.; Yin, B.; Christie, P.; Zhu, Z.-L.; et al. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, C.; Buresh, R.J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J. Root and shoot traits for rice varieties with higher grain yield and higher nitrogen use efficiency at lower nitrogen rates application. Field Crops Res. 2015, 175, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GRiSP (Global Rice Science Partnership). Rice Almanac, 4th ed.; International Rice Research Institute: Los Banos, Philippines, 2013; p. 283. [Google Scholar]
- Muthayya, S.; Sugimoto, J.D.; Montgomery, S.; Maberly, G.F. An overview of global rice production, supply, trade, and consumption. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1324, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.; Buresh, R.J.; Huang, J.; Yang, J.; Zou, Y.; Zhong, X.; Wang, G.; Zhang, F. Strategies for overcoming low agronomic nitrogen use efficiency in irrigated rice systems in China. Field Crops Res. 2006, 96, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; He, P.; Yin, X.; Struik, P.C.; Ding, W.; Liu, K.; Huang, Q. Simultaneously improving yield and nitrogen use efficiency in a double rice cropping system in China. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 137, 126513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, D.; Britto, D.T.; Shi, W.; Kronzucker, H.J. Nitrogen transformations in modern agriculture and the role of biological nitrification inhibition. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 17074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Shi, K.; Li, P.; Sun, Z.; Chang, D.; Shen, X.; Wu, D.; Song, X.; Liu, M.; Li, H.; et al. Assessing of an irrigation and fertilization practice for improving rice production in the Taihu Lake region (China). Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 201, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, A.B.; Kjeldby, M.; Nilsen, S. The effect of intermittent flooding on the growth and yield of wetland rice and nitrogen-loss mechanism with surface applied and deep placed urea. Plant Soil 1985, 84, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Y. Quantifying direct N2O emissions in paddy fields during rice growing season in mainland China: Dependence on water regime. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 8030–8042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, N.; Subedi, S.R.; Yadaw, R.B.; Chaudhary, B.; Prasai, H.; Iftekharuddaula, K.; Thanak, T.; Thun, V.; Battan, K.R.; Ram, M.; et al. Root Traits Enhancing Rice Grain Yield under Alternate Wetting and Drying Condition. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrijo, D.R.; Akbar, N.; Reis, A.F.B.; Li, C.; Gaudin, A.C.M.; Parikh, S.J.; Green, P.G.; Linquist, B.A. Impacts of variable soil drying in alternate wetting and drying rice systems on yields, grain arsenic concentration and soil moisture dynamics. Field Crops Res. 2018, 222, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, T.; Yu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, K.; Zhang, H.; Gu, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, L. Alternate wetting and moderate soil drying irrigation counteracts the negative effects of lower nitrogen levels on rice yield. Plant Soil 2022, 481, 367–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Zhang, W.Y.; Beebout, S.S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.J.; Yang, J.C.; Zhang, J.H. Grain yield, water and nitrogen use efficiencies of rice as influenced by irrigation regimes and their interaction with nitrogen rates. Field Crops Res. 2016, 193, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yu, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Gu, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J. Alternate wetting and drying irrigation combined with the proportion of polymer-coated urea and conventional urea rates increases grain yield, water and nitrogen use efficiencies in rice. Field Crops Res. 2021, 268, 108165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Forno, D.A.; Cock, J.H. Laboratory Manual for Physiological Studies of Rice; International Rice Research Institute: Los Banos, Philippines, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.L.; Gong, Z.T. Analytical Methods of Soil Survey Laboratory; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2012; pp. 60–64. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kimball, B.A.; Mauney, J.R. Response of Cotton to Varying COz, Irrigation, and Nitrogen: Yield and Growth. Agron. J. 1993, 85, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepaskhah, A.R.; Hosseini, S.N. Effects of Alternate Furrow Irrigation and Nitrogen Application Rates on Yield and Water-and Nitrogen-Use Efficiency of Winter Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Prod. Sci. 2015, 11, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Zhang, J.H. High-Yielding and Water-Saving Irrigation in Rice; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2019; pp. 4–5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, C.; Kong, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J. Canopy light and nitrogen distributions are related to grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency in rice. Field Crops Res. 2017, 206, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Yin, X.; Yang, J.; Struik, P.C. Roles of canopy architecture and nitrogen distribution in the better performance of an aerobic than a lowland rice cultivar under water deficit. Field Crops Res. 2021, 271, 108257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Gu, J.; Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J. Brassinosteroids function in spikelet differentiation and degeneration in rice. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2019, 61, 943–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, J. Crop management techniques to enhance harvest index in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 3177–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J. Pre-anthesis non-structural carbohydrate reserve in the stem enhances the sink strength of inferior spikelets during grain filling of rice. Field Crops Res. 2011, 123, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhan, M.; Zhu, K. Physiological bases for the formation of green traits in rice. Chin. Bull. Life Sci. 2018, 10, 1137–1145. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ye, N.; Jia, L.; Zhang, J. ABA signal in rice under stress conditions. Rice 2012, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Tang, W.; Xiong, Z.; Peng, S.; Li, Y. Stomatal conductance in rice leaves and panicles responds differently to abscisic acid and soil drought. J. Exp. Bot. 2023, 74, 1551–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nira, R.; Miura, S. Rice yield and soil fertility of an organic paddy system with winter flooding. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2019, 65, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Nie, T. ‘Preferential’ ammonium uptake by rice does not always turn into higher N recovery of fertilizer sources under water-saving irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 272, 107867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Cui, D.; Shen, H. Effects of nitrogen forms and application rates on nitrogen uptake, photosynthetic characteristics and yield of double-cropping rice in south China. Agronomy 2021, 11, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Tang, J.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, X.; Lu, B.; Yang, W. Improvement of straw decomposition and rice growth through co-application of straw-decomposing inoculants and ammonium nitrogen fertilizer. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nhamo, L.; Magidi, J.; Nyamugama, A.; Clulow, A.D.; Sibanda, M.; Chimonyo, V.G.; Mabhaudhi, T. Prospects of improving agricultural and water productivity through unmanned aerial vehicles. Agriculture 2020, 10, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reavis, C.W.; Suvočarev, K.; Reba, M.L.; Runkle, B.R. Impacts of alternate wetting and drying and delayed flood rice irrigation on growing season evapotranspiration. J. Hydrol. 2021, 596, 126080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakakibara, H. Cytokinin biosynthesis and transport for systemic nitrogen signaling. Plant J. 2021, 105, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Zhou, Q.; Shen, Y.; Yan, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J. Agronomic and physiological performance of an indica–japonica rice variety with a high yield and high nitrogen use efficiency. Crop Sci. 2020, 60, 1556–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. Effect of Moisture and Nitrogen Nutrient on Grain Yield and Quality of Rice and Their Physiological Mechanism; Yangzhou University: Yangzhou, China, 2004. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
| Year/Irrigation Regime | N Rate (kg ha−1) | Grain Yield (t ha−1) | Panicles per m2 | Spikelets per Panicle | 1000-Grain Weight (g) | Filled Grains (%) | HI a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | |||||||
| LN | 7.36 d | 246 b | 129 c | 26.7 a | 89.1 b | 0.542 c | |
| CF | MN | 9.03 b | 283 a | 137 b | 26.8 a | 87.7 c | 0.534 d |
| HN | 8.27 c | 284 a | 141 a | 25.9 b | 81.6 d | 0.522 e | |
| LN | 7.86 d | 252 b | 130 c | 26.7 a | 92.0 a | 0.562 a | |
| AWMD | MN | 9.62 a | 281 a | 142 a | 26.8 a | 91.7 a | 0.559 ab |
| HN | 9.71 a | 283 a | 143 a | 26.8 a | 91.2 b | 0.550 b | |
| 2022 | |||||||
| LN | 4.93 d | 223 b | 122 c | 27.4 a | 67.1 b | 0.372 c | |
| CF | MN | 6.19 b | 278 a | 132 b | 27.5 a | 62.3 c | 0.361 c |
| HN | 5.72 c | 279 a | 135 a | 26.7 b | 57.6 d | 0.338 d | |
| LN | 5.48 d | 229 b | 123 c | 27.6 a | 70.8 a | 0.426 a | |
| AWMD | MN | 7.01 a | 284 a | 136 a | 27.6 a | 69.6 a | 0.418 ab |
| HN | 7.00 a | 290 a | 137 a | 27.7 a | 67.4 b | 0.412 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, H.; Xu, R.; Yu, J.; Zhang, W.; Gu, J.; Zhu, K.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J. A Moderate Wetting and Drying Regime Combined with Appropriate Nitrogen Application Increases Grain Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Rice. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1729. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071729
Huang H, Xu R, Yu J, Zhang W, Gu J, Zhu K, Zhang J, Yang J. A Moderate Wetting and Drying Regime Combined with Appropriate Nitrogen Application Increases Grain Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Rice. Agronomy. 2023; 13(7):1729. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071729
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Hanghang, Rongyue Xu, Jixiang Yu, Weiyang Zhang, Junfei Gu, Kuanyu Zhu, Jianhua Zhang, and Jianchang Yang. 2023. "A Moderate Wetting and Drying Regime Combined with Appropriate Nitrogen Application Increases Grain Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Rice" Agronomy 13, no. 7: 1729. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071729
APA StyleHuang, H., Xu, R., Yu, J., Zhang, W., Gu, J., Zhu, K., Zhang, J., & Yang, J. (2023). A Moderate Wetting and Drying Regime Combined with Appropriate Nitrogen Application Increases Grain Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Rice. Agronomy, 13(7), 1729. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071729







