Will Climate Change Affect the Disease Progression of Septoria Tritici Blotch in Northern Europe?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Surveyed Area and Survey Strategy
2.2. Sampling and Disease Assessment
2.3. Data Analyses
k = number of neighbouring time intervals
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
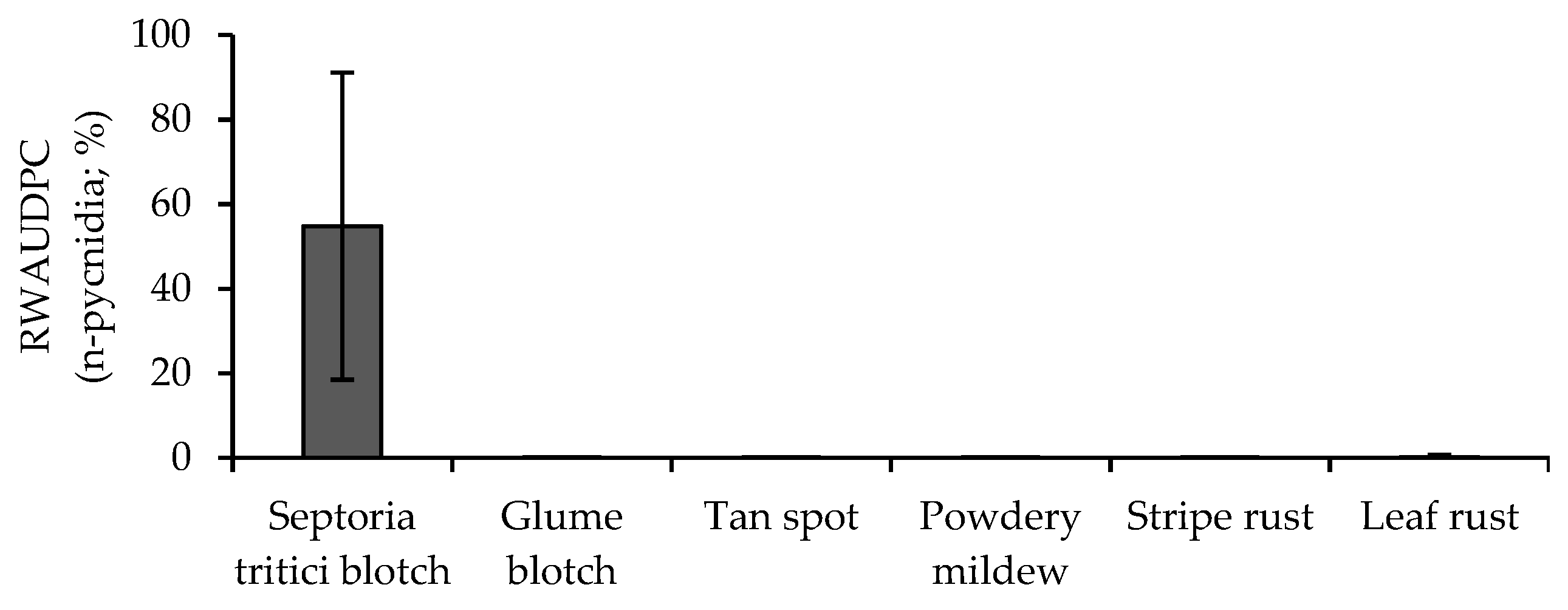
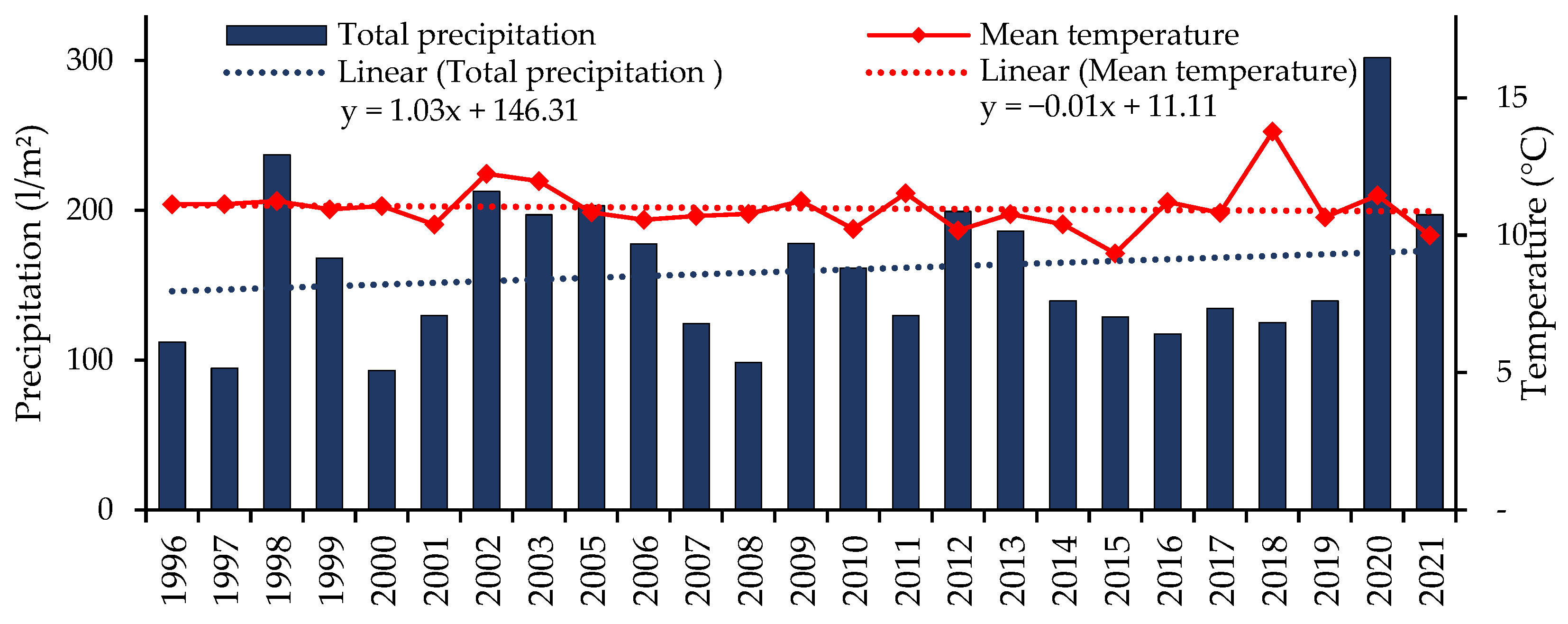
3.1. Occurrence of Foliar Diseases from 1996 to 2021
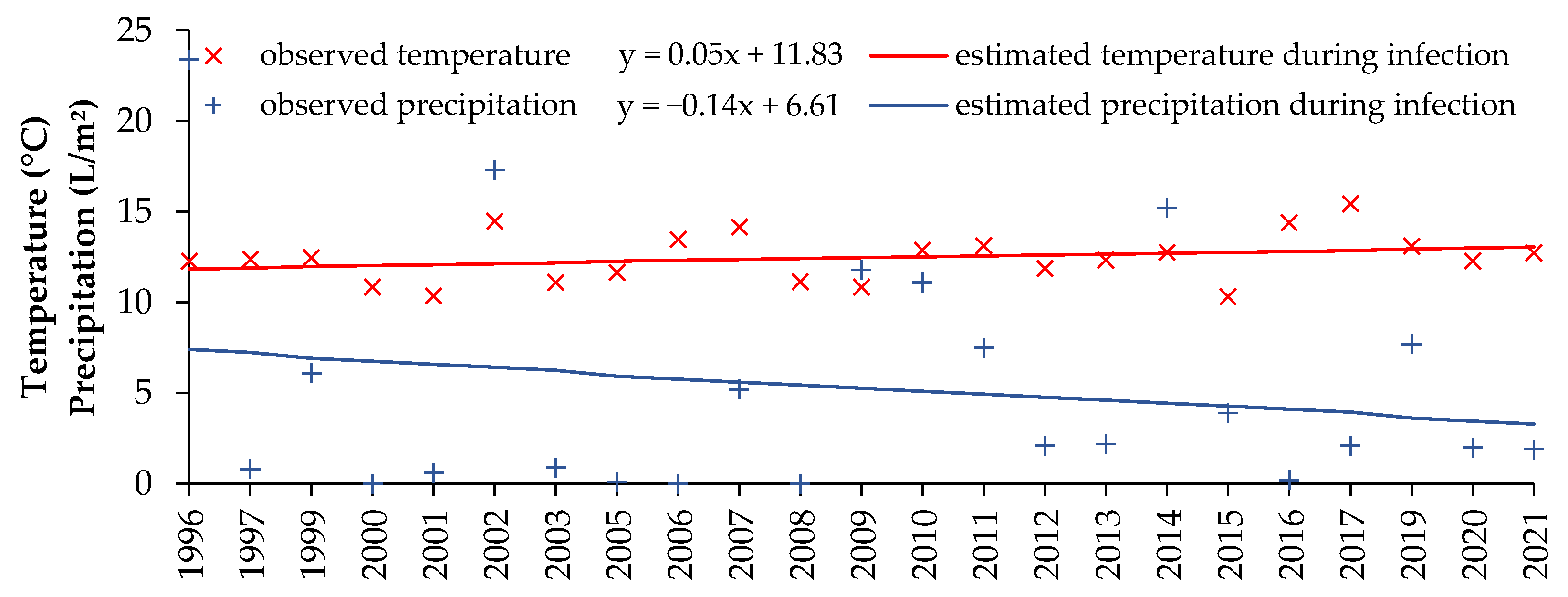
3.2. Prevailing Weather Conditions and Occurrence of Septoria tritici blotch
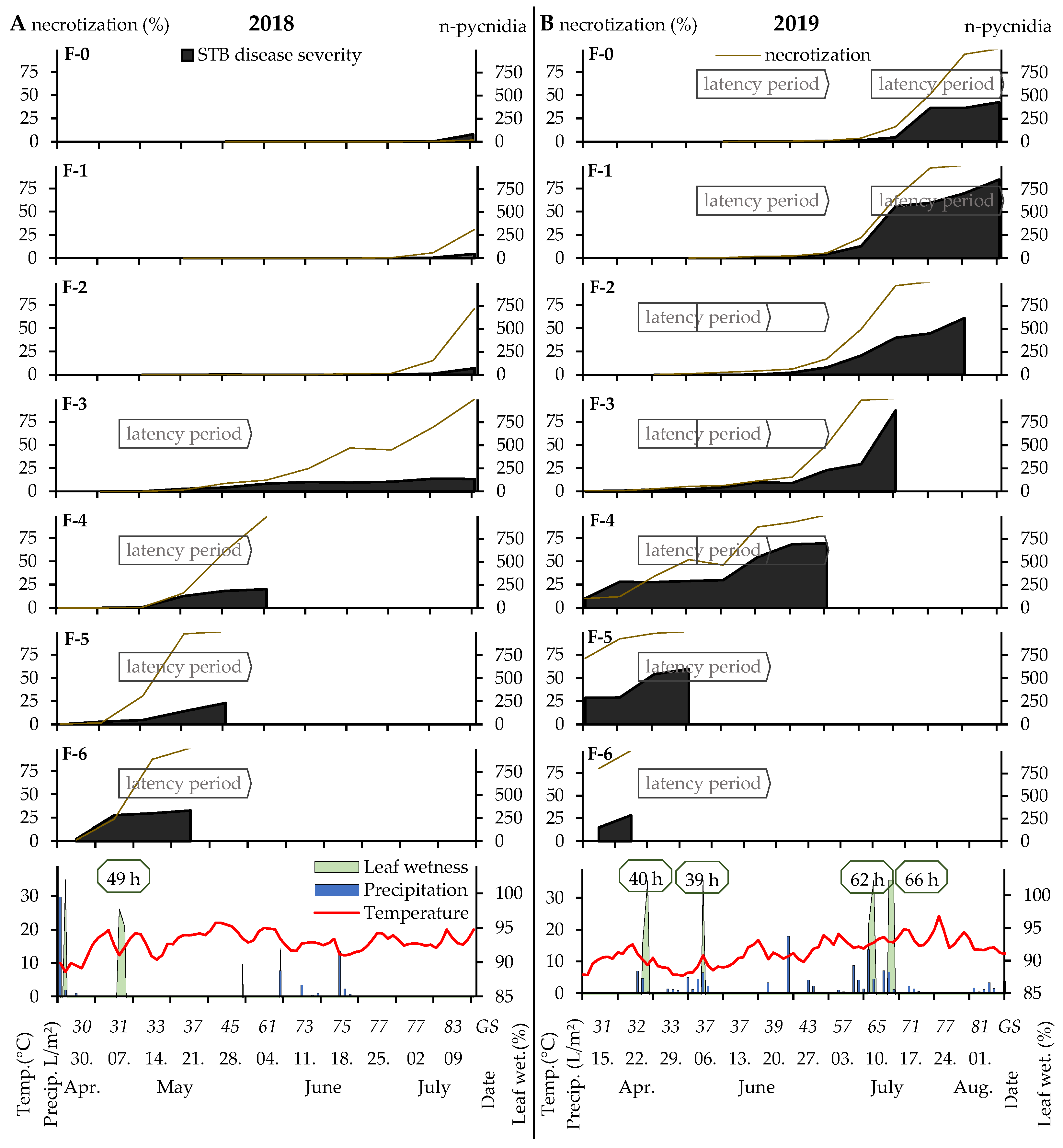
3.3. Case Study of Septoria Tritici Blotch
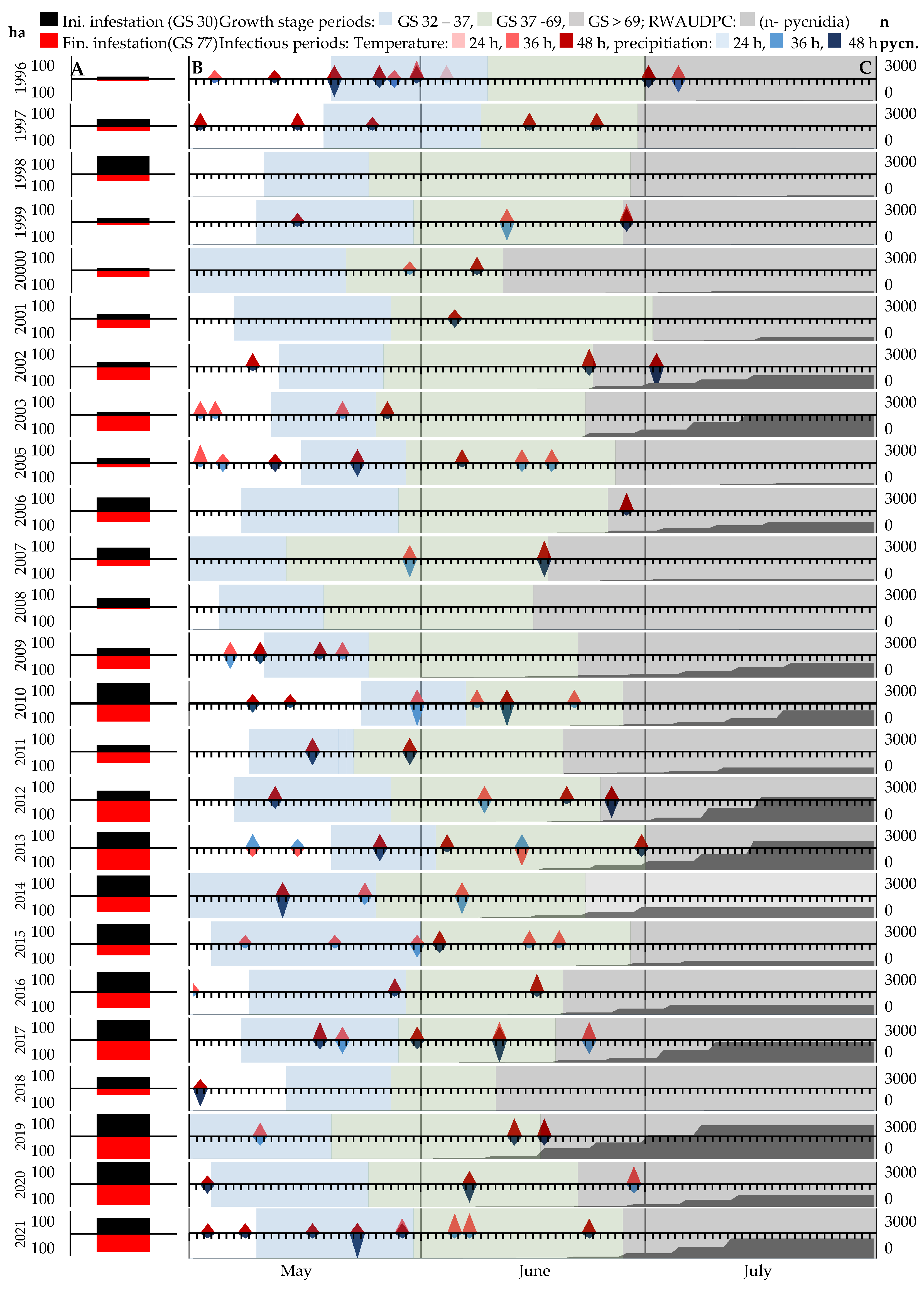
3.4. Conducive Conditions of Septoria Tritici Blotch during the Survey Period
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fones, H.; Gurr, S.J. The impact of Septoria tritici Blotch disease on wheat: An EU perspective. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2015, 79, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouma, E. Development of comparable agro-climatic zones for the international exchange of data on the efficacy and crop safety of plant protection products. Bull. OEPP 2005, 35, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klink, H.; Prahl, K.C.; Hasler, M.; Verreet, J.-A.; Birr, T. Efficiency and Effectivity of a Biological–Epidemiological Fungal Disease Management System in Wheat—A Study of 26 Years. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verreet, J.-A.; Klink, H.; Hoffmann, G.M. Regional Monitoring for Disease Prediction and Optimization of Plant Protection Measuares: The IPM Wheat Model. Plant Dis. 2000, 84, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henze, M.; Beyer, M.; Klink, H.; Verreet, J.-A. Characterizing Meteorological Scenarios Favorable for Septoria tritici Infections in Wheat and Estimation of Latent Periods. Plant Dis. 2007, 91, 1445–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Miedaner, T.; Juroszek, P. Climate change will influence disease resistance breeding in wheat in Northwestern Europe. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 1771–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IPCC. Global Warming of 1.5 °C. An IPCC Special Report on the impacts of global warming of 1.5 °C above pre-industrial levels and related global greenhouse gas emission pathways. In The Context of Strengthening the Global Response to the Threat of Climate Change, Sustainable Development, and Efforts to Eradicate Poverty; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC (Ed.) Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC (Ed.) Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin, S.B. Diseases affecting wheat: Septoria tritici blotch. In Integrated Disease Management of Wheat and Barley; Oliver, R., Ed.; Burleigh Dodds Science Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 47–68. ISBN 9781786762160. [Google Scholar]
- Chungu, C.; Gilbert, J.; Townley-Smith, F. Septoria tritici Blotch Development as Affected by Temperature, Duration of Leaf Wetness, Inoculum Concentration, and Host. Plant Dis. 2001, 85, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesus Junior, W.C.; Paula Júnior, T.J.; Lehner, M.S.; Hau, B. Interactions between foliar diseases: Concepts and epidemiological approaches. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2014, 39, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Statistisches Amt für Hamburg und Schleswig-Holstein. Kreisergebnisse Schleswig-Holstein 2020—Endgültiges Ergebnis der Landwirtschaftszählung 2020–: Kennziffer: C IV—LZ 2020 SH, SK Sonderbericht Kreisdaten; Statistisches Amt für Hamburg und Schleswig-Holstein: Hamburg, Germany, 2021.
- DWD Climate Data Center. Vieljährige Stationsmittelwerte für die Klimareferenzperiode 1991–2020, für Aktuellen Standort und Bezugsstandort. Available online: https://www.dwd.de/DE/leistungen/klimadatendeutschland/vielj_mittelwerte.html (accessed on 18 May 2021).
- Hamer, W.B.; Birr, T.; Verreet, J.-A.; Duttmann, R.; Klink, H. Spatio-Temporal Prediction of the Epidemic Spread of Dangerous Pathogens Using Machine Learning Methods. Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundessortenamt. Beschreibende Sortenliste Getreide, Mais, Ölfrüchte, Leguminosen (Großkörnig), Hackfrüchte (außer Kartoffeln) 2007; Deutscher Landwirtschaftsverlag: Hannover, Germany, 2007; ISBN 0948-4167. [Google Scholar]
- Zadoks, J.C.; Chang, T.T.; Konzak, C.F. A decimal code for the growth stages of cereals. Weed Res. 1974, 14, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, L.V.; Hughes, G.; van den Bosch, F. (Eds.) CHAPTER 4: Temporal Analysis I: Quantifying and Comparing Epidemics. In The Study of Plant Disease Epidemics; The American Phytopathological Society: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-0-89054-505-8. [Google Scholar]
- Avci Birsin, M. Effects of Removal of Some Photosynthetic Structures on Some Yield Components in Wheat. Tarim Bilim. Derg. 2005, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.; Alam, K.; Salam, A.; Iqbal, S. Effect of flag leaf removal on grain yield, its components and quality of hexaploid wheat. Cereal Res. Commun. 1991, 19, 305–310. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; Statistical Computing; R Foundation: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Klöhn, H. Populationsgenetische Erhebungen von Weizenpathogenen zur Entwicklung Eines Lernfähigen, Telemetriefähigen Gerätesystems zur Pflanzenschutzoptimierung Anhand des Modellpathogens Septoria Tritici. Ph.D. Thesis, Christian-Albrechts-Universiät, Kiel, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ponomarenko, A.; Goodwin, S.B.; Kema, K. Septoria tritici blotch (STB) of wheat. Plant Health Instr. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garin, G.; Pradal, C.; Fournier, C.; Claessen, D.; Houlès, V.; Robert, C. Modelling interaction dynamics between two foliar pathogens in wheat: A multi-scale approach. Ann. Bot. 2018, 121, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willocquet, L.; Aubertot, J.N.; Lebard, S.; Robert, C.; Lannou, C.; Savary, S. Simulating multiple pest damage in varying winter wheat production situations. Field Crops Res. 2008, 107, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, B.A.; Mundt, C.C. How Knowledge of Pathogen Population Biology Informs Management of Septoria Tritici Blotch. Phytopathology 2016, 106, 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prahl, K.C.; Klink, H.; Hasler, M.; Hagen, S.; Verreet, J.-A.; Birr, T. Can Decision Support Systems Help Improve the Sustainable Use of Fungicides in Wheat? Sustainability 2022, 14, 15599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, T.; Epke, K.; Gerstner, V.; Leuthner, C.; Rotterdam, A.; Johnen, A.; von Richthofen, S. Klimawandel in Nordrhein-Westfalen—Auswirkungen auf Schädlinge und Pilzkrankheiten Wichtiger Ackerbaukulturen. Available online: https://www.lanuv.nrw.de/fileadmin/lanuv/klimaanpassung/dokumente/bericht_klimawandel_schaedlinge.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2023).
- Gouache, D.; Bensadoun, A.; Brun, F.; Pagé, C.; Makowski, D.; Wallach, D. Modelling climate change impact on Septoria tritici blotch (STB) in France: Accounting for climate model and disease model uncertainty. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 170, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, D.J.; Hunter, T.; Powers, S.J.; Parker, S.R.; van den Bosch, F. Effect of temperature on latent period of septoria leaf blotch on winter wheat under outdoor conditions. Plant Pathol. 2004, 53, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaloner, T.M.; Fones, H.N.; Varma, V.; Bebber, D.P.; Gurr, S.J. A new mechanistic model of weather-dependent Septoria tritici blotch disease risk. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 374, 20180266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klink, H. Geoepidemiologische Erhebungen von Weizenpathogenen in Schleswig-Holstein unter Anwendung und Entwicklung des Integrierten Pflanzenschutzsystems (IPS-Modell Weizen) für Einen Minimierten, Bedarfsgerechten Fungizideinsatz (1993–1996). Ph.D. Thesis, Christian-Albrechts-Universität, Kiel, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Beyer, M.; Pallez-Barthel, M.; Dam, D.; Hoffmann, L.; El Jarroudi, M. Enhancing septoria leaf blotch forecasts in winter wheat I: The effect of temperature on the temporal distance between critical rainfall periods and the breaking of the control threshold. J. Plant. Dis. Prot. 2022, 129, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magboul, A.M. Environmental Influence on the Infection of Wheat by Mycosphaerella graminicola. Phytopathology 1992, 82, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, M.; Marozsak, B.; Dam, D.; Parisot, O.; Pallez-Barthel, M.; Hoffmann, L. Enhancing septoria leaf blotch forecasts in winter wheat II: Model architecture and validation results. J. Plant. Dis. Prot. 2022, 129, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DWD Deutscher Wetterdienst. Time Series and Trends for the Parameters Temperature, Precipitation, Sunshine Duration and Various Climate Indices. Available online: https://www.dwd.de/EN/ourservices/zeitreihen/zeitreihen.html?nn=24778 (accessed on 28 January 2023).
- Jacob, D.; Petersen, J.; Eggert, B.; Alias, A.; Christensen, O.B.; Bouwer, L.M.; Braun, A.; Colette, A.; Déqué, M.; Georgievski, G.; et al. EURO-CORDEX: New high-resolution climate change projections for European impact research. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2014, 14, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; World Meteorological Organization (WMO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; ISBN 978-92-9169-143-2. [Google Scholar]
- DWD Deutscher Wetterdienst. Klimavorhersagen der Nächsten Wochen bis Jahre. Available online: https://www.dwd.de/DE/leistungen/kvhs_de/0_main/start_main.html (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- Gladders, P.; Paveley, N.D.; Barrie, I.A.; Hardwick, N.V.; HIMS, M.J.; Langdon, S.; Taylor, M.C. Agronomic and meteorological factors affecting the severity of leaf blotch caused by Mycosphaerella graminicola in commercial wheat crops in England. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2001, 138, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietravalle, S.; Shaw, M.W.; Parker, S.R.; van den Bosch, F. Modeling of Relationships Between Weather and Septoria tritici Epidemics on Winter Wheat: A Critical Approach. Phytopathology 2003, 93, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iturbide, M.; Fernández, J.; Guitérrez, J.M.; Bedia, J.; Cimadevilla, E.; Díez-Sierra, J.; Manzanas, R.; Casanueva, A.; Baño-Medina, J.; Milovac, J.; et al. Repository supporting the implementation of FAIR principles in the IPCC-WGI Atlas. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guitérrez, J.M.; Jones, R.G.; Narisma, G.T.; Alves, L.M.; Amjad, M.; Gorodetskaya, I.V.; Grose, M.; Klutse, N.; Krakovska, S.; Li, J.; et al. Atlas. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC, Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Fealy, R.; Bruyère, C.; Duffy, C. Regional Climate Model Simulations for Ireland for the 21st Century: (2011-CCRP-MS-2.2); Online Version; Environmental Protection Agency; Johnstown Castle, Co.: Wexford, Ireland, 2018; ISBN 978-1-84095-770-9. [Google Scholar]
- Birr, T.; Hasler, M.; Verreet, J.-A.; Klink, H. Temporal Changes in Sensitivity of Zymoseptoria tritici Field Populations to Different Fungicidal Modes of Action. Agriculture 2021, 11, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klink, H.; Verreet, J.-A.; Hasler, M.; Birr, T. Will Triazoles Still Be of Importance in Disease Control of Zymoseptoria tritici in the Future? Agronomy 2021, 11, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2015/408 of 11 March 2015 on implementing Article 80(7) of Regulation (EC) No 1107/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the placing of plant protection products on the market and establishing a list of candidates for substitution. Off. J. Eur. Union 2015, 2015, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission; Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety. Proposal for a Regulation of the European Parliament and of the Council on the sustainable use of plant protection products and amending Regulation (EU) 2021/2115. Off. J. Eur. Union 2022, 2022, 1–71. [Google Scholar]
- Tidd, H.; Rudd, J.J.; Ray, R.V.; Bryant, R.; Kanyuka, K. A large bioassay identifies Stb resistance genes that provide broad resistance against Septoria tritici blotch disease in the UK. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1070986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saintenac, C.; Lee, W.-S.; Cambon, F.; Rudd, J.J.; King, R.C.; Marande, W.; Powers, S.J.; Bergès, H.; Phillips, A.L.; Uauy, C.; et al. Wheat receptor-kinase-like protein Stb6 controls gene-for-gene resistance to fungal pathogen Zymoseptoria tritici. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stam, R.; McDonald, B.A. When resistance gene pyramids are not durable-the role of pathogen diversity. Mol. Plant. Pathol. 2018, 19, 521–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana-Torrejon, C.; Vidal, T.; Saint-Jean, S.; Suffert, F. The impact of wheat cultivar mixtures on virulence dynamics in Zymoseptoria tritici populations persists after interseason sexual reproduction. Plant Pathol. 2022, 71, 1537–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana-Torrejon, C.; Vidal, T.; Boixel, A.-L.; Gélisse, S.; Saint-Jean, S.; Suffert, F. Annual dynamics of Zymoseptoria tritici populations in wheat cultivar mixtures: A compromise between the efficacy and durability of a recently broken-down resistance gene? Plant Pathol. 2022, 71, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prahl, K.C.; Klink, H.; Hasler, M.; Verreet, J.-A.; Birr, T. Will Climate Change Affect the Disease Progression of Septoria Tritici Blotch in Northern Europe? Agronomy 2023, 13, 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13041005
Prahl KC, Klink H, Hasler M, Verreet J-A, Birr T. Will Climate Change Affect the Disease Progression of Septoria Tritici Blotch in Northern Europe? Agronomy. 2023; 13(4):1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13041005
Chicago/Turabian StylePrahl, Ketel Christian, Holger Klink, Mario Hasler, Joseph-Alexander Verreet, and Tim Birr. 2023. "Will Climate Change Affect the Disease Progression of Septoria Tritici Blotch in Northern Europe?" Agronomy 13, no. 4: 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13041005
APA StylePrahl, K. C., Klink, H., Hasler, M., Verreet, J.-A., & Birr, T. (2023). Will Climate Change Affect the Disease Progression of Septoria Tritici Blotch in Northern Europe? Agronomy, 13(4), 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13041005


_Asaduzzaman.jpg)


