Chemical and Biological Response of Four Soil Types to Lime Application: An Incubation Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Test Soil Samples
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Soil Sample Collection and Analysis
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
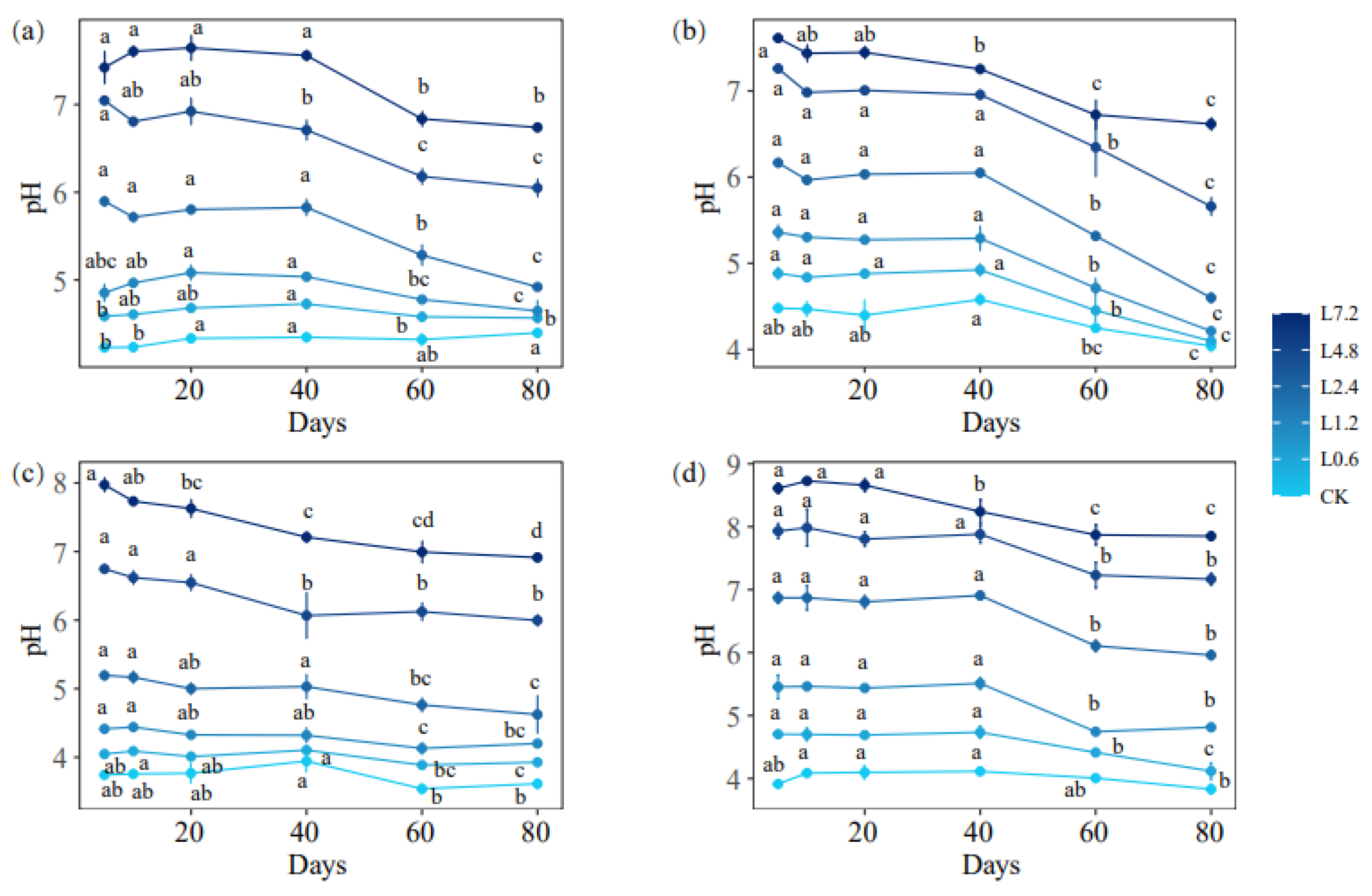
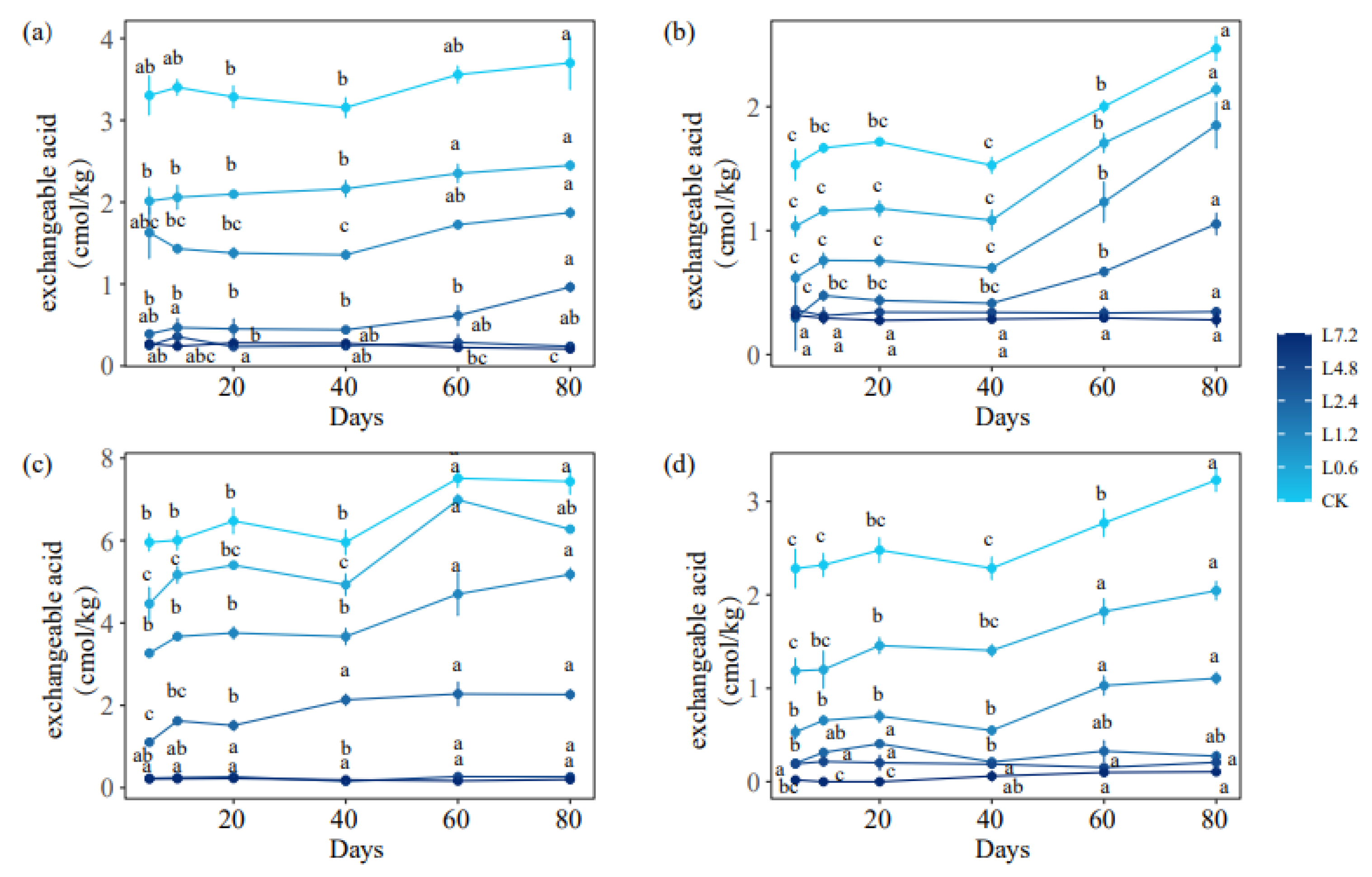
3.1. Effect of Lime on the Dynamics of Soil Acidity
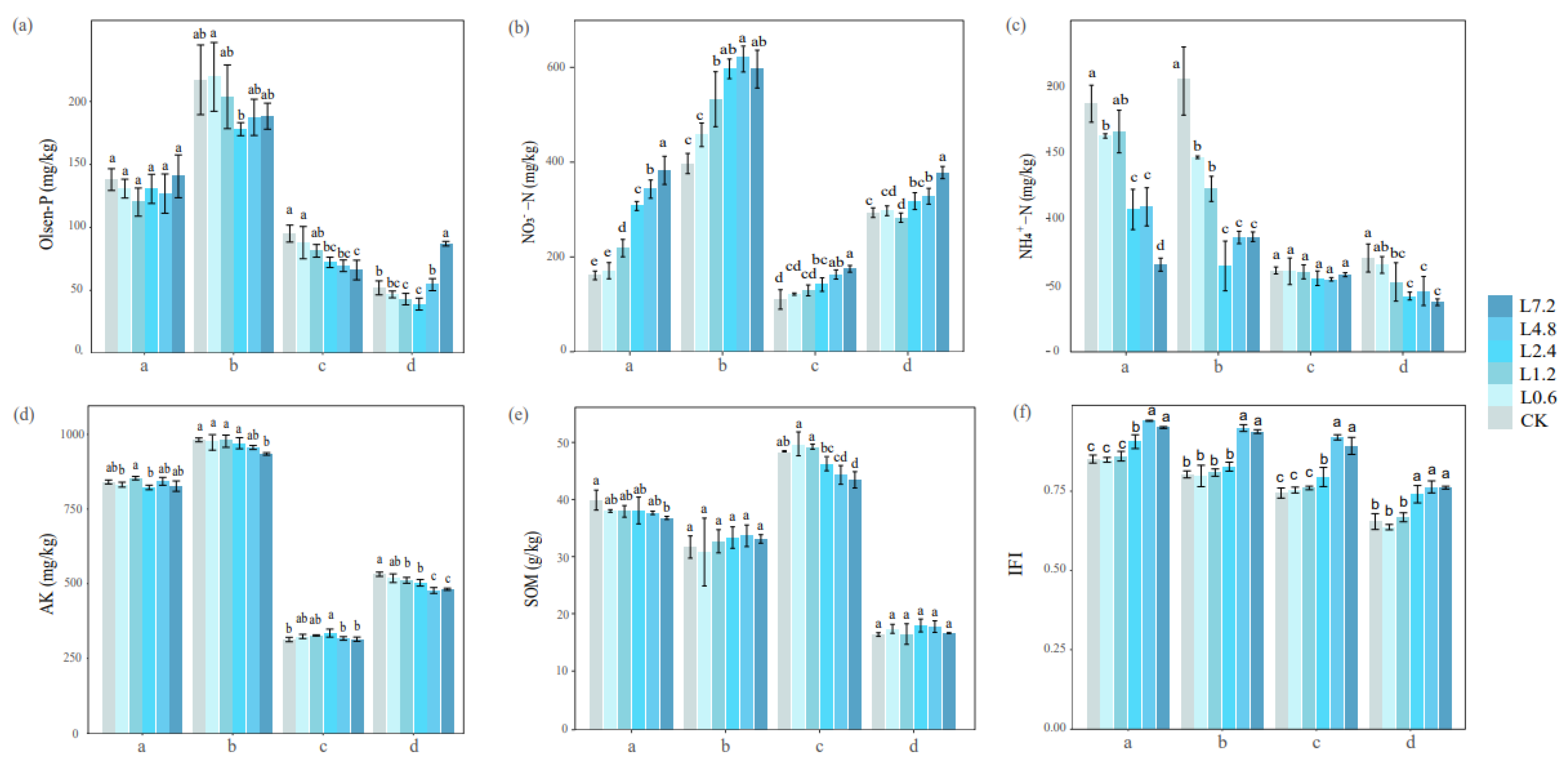
3.2. Effect of Lime on Soil Fertility Status
3.3. Effect of Liming on Soil Bacterial
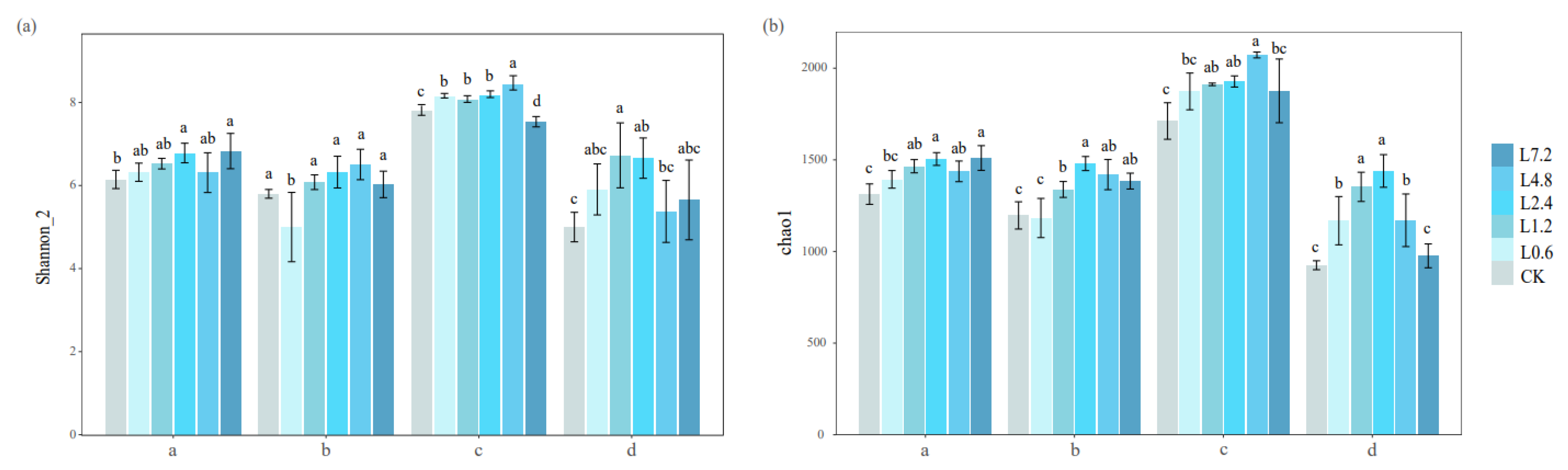
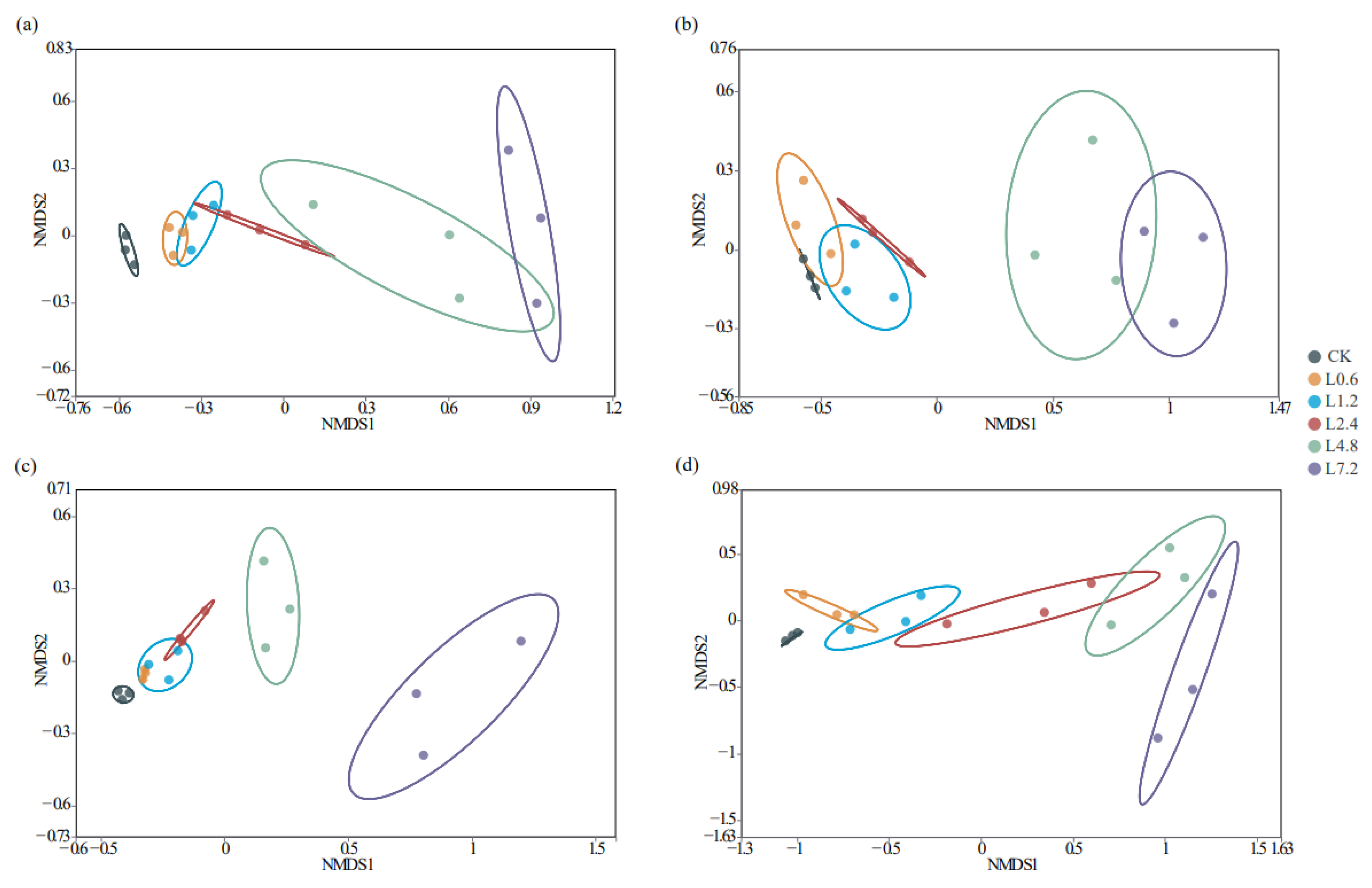
3.3.1. Effect of Different Lime Dosage Treatments on the Diversity of Soil Bacterial Communities
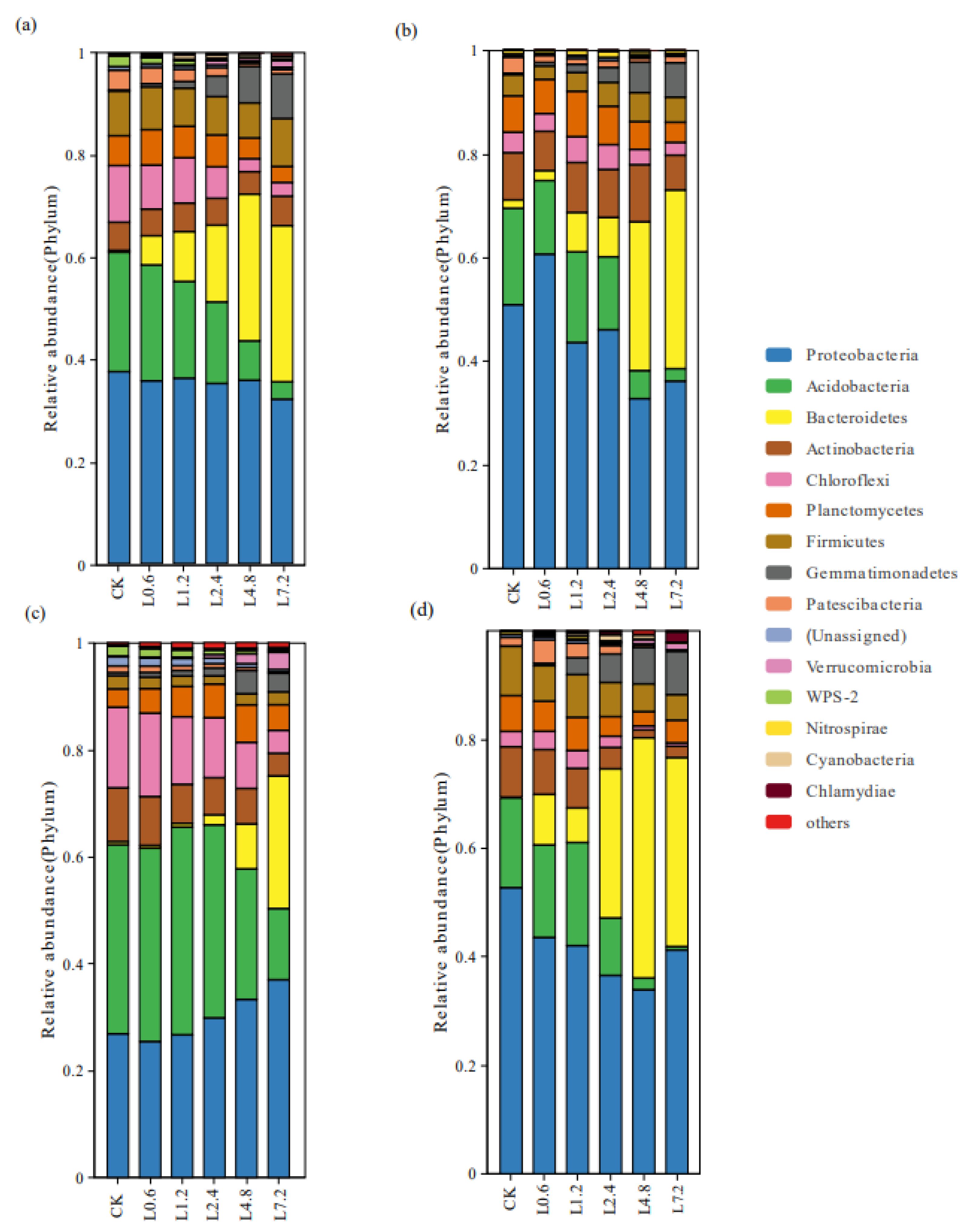
3.3.2. Composition of Soil Bacterial Community under Different Lime Dosage Treatments
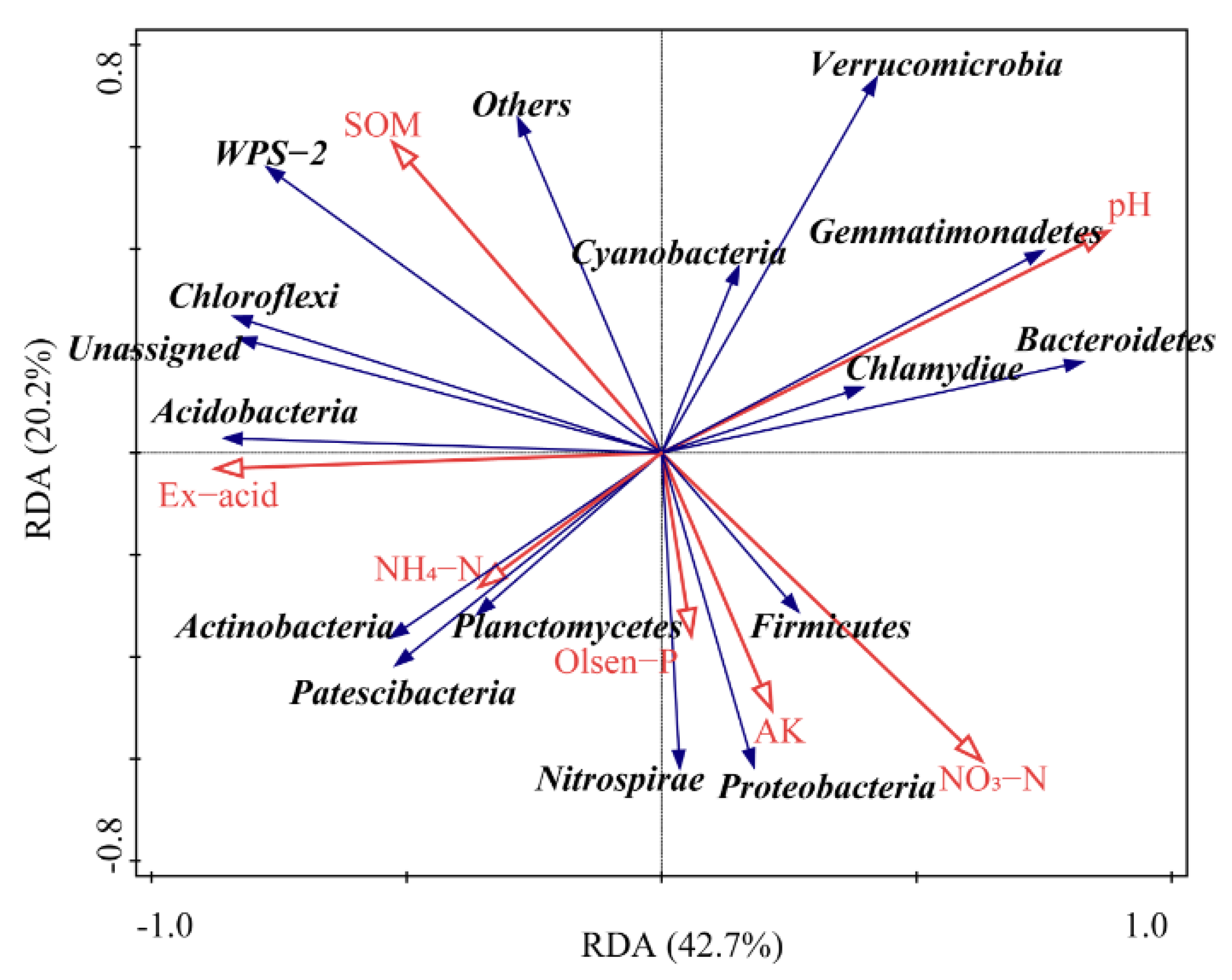
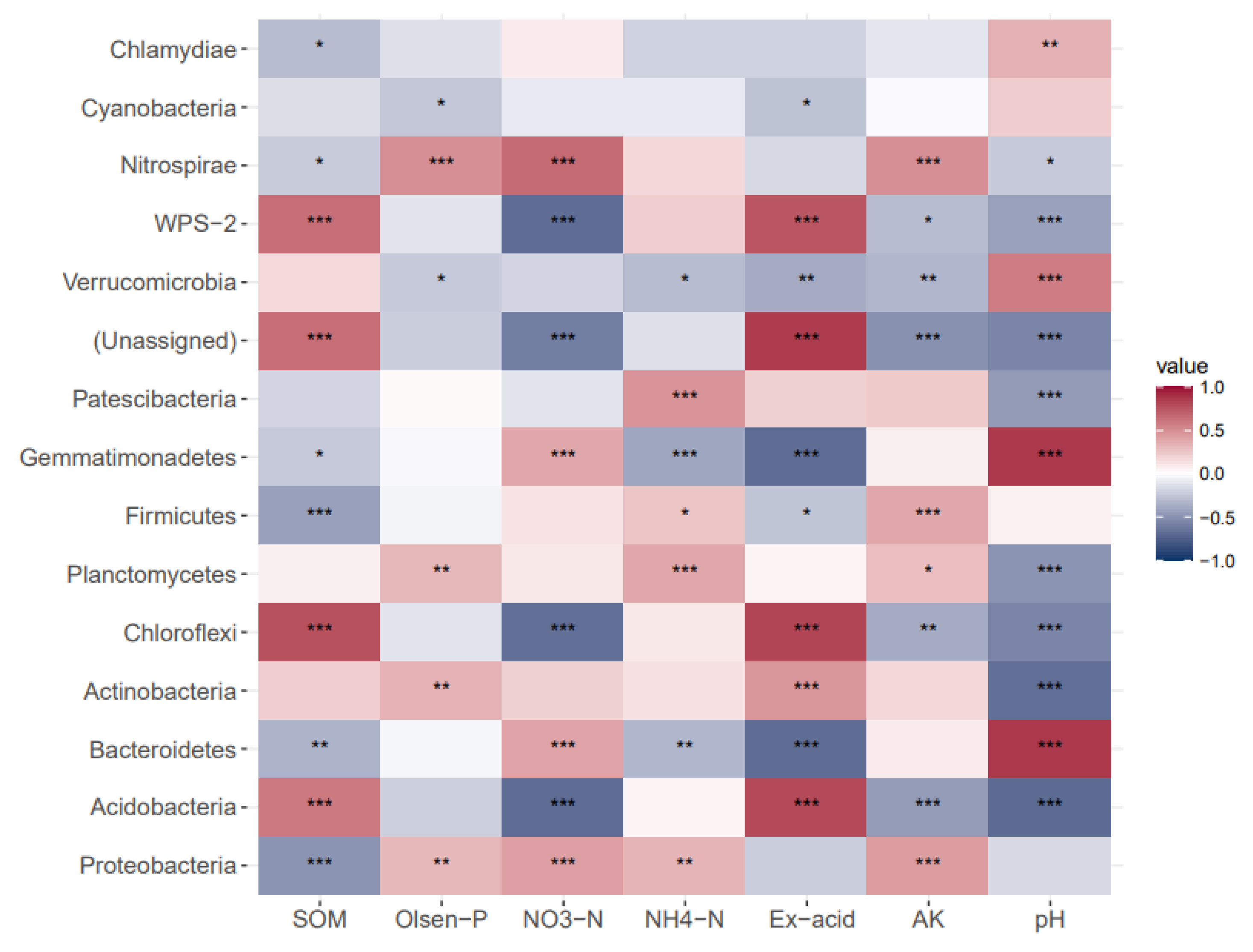
3.3.3. Effect of Soil Chemistry on Bacterial Communities
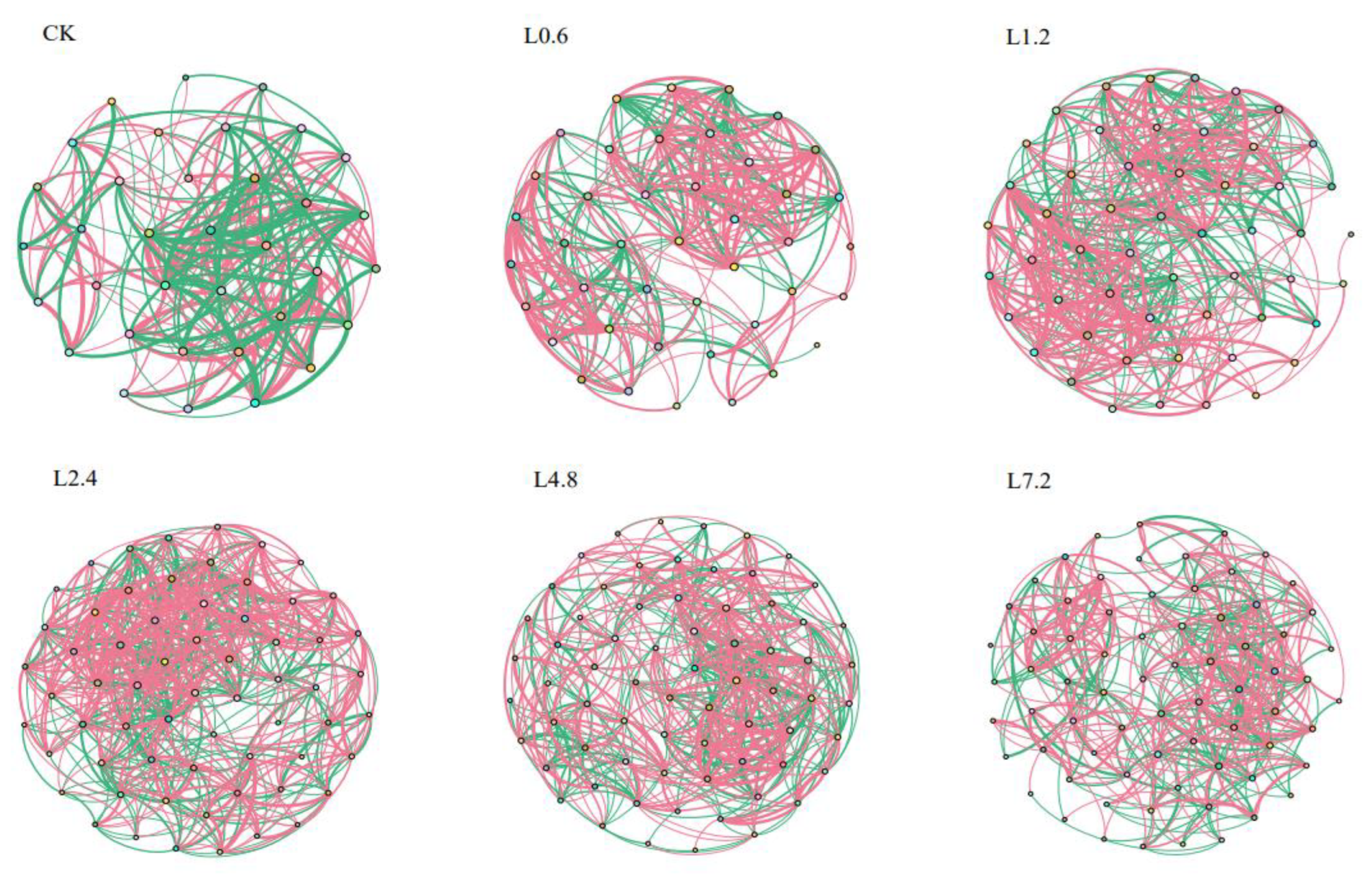
3.3.4. Co-Occurrence Network Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Liming on Acidified Soil
4.2. Effects of Liming on Soil Nutrients
4.3. Changes of Soil Bacterial Community
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wen, M.X.; Lu, L.M.; Wang, P.; Wu, S.H.; Pu, S.X.; Huang, Z.D. Status of soil nutrients in citrus orchards of Zhejiang Province. J. Zhejiang Agric. Sci. 2019, 60, 208–211. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.B.; Lin, W.J.; Li, X.J.; Li, F.; Zhuang, M.L.; Zhu, D.H.; Guo, J.X.; Chen, L.S.; Li, T. Research on soil acidification characteristics of Guanxi pomelo orchards. Non-Wood For. Res. 2020, 38, 169–176. [Google Scholar]
- Alekseeva, T.; Alekseev, A.; Xu, R.K.; Zhao, A.Z.; Kalinin, P. Effect of soil acidification induced by a tea plantation on chemical and mineralogical properties of Alfisols in eastern China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2011, 33, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.Y.; Cai, L.Y.; Qi, Y.P.; Yang, L.T.; Lai, N.W.; Chen, L.S. Increasing nutrient solution pH alleviated aluminum-induced inhibition of growth and impairment of photosynthetic electron transport chain in citrus sinensis seedlings. Biomed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 9058715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, S.A.; Ashraf, U.; Tanveer, M.; Khan, I.; Hussain, S.; Zohaib, A.; Abbas, F.; Saleem, M.F.; Wang, L.C. Drought tolerance in three maize cultivars is related to differential osmolyte accumulation, antioxidant defense system, and oxidative damage. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.W.; Chen, X.H.; Ji, Z.J.; Yan, X.J.; Kong, K.P.; Cai, Y.Y.; Zhu, Q.C.; Muneer, M.A.; Zhang, F.S.; Wu, L.Q. Reducing aluminum is the key nutrient management strategy for ameliorating soil acidification and improving root growth in an acidic citrus orchard. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazuo, S.; Akira, T. Acidity neutralization mechanism in a forested watershed in Central Japan. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1996, 88, 313–329. [Google Scholar]
- Haynes, R.J.; Naidu, R. Influence of lime, fertilizer and manure applications on soil organic matter content and soil physical conditions: A review. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 1998, 51, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarsalmi, A.; Tamminen, P.; Kukkola, M.; Levula, Y. Effects of liming on chemical properties of soil, needle nutrients and growth of Scots pine transplants. For. Ecol. Manag. 2011, 262, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, J.D. A review of research on the effect of lime on New Zealand soils and pastures. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 2020, 63, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.S.; Adriano, D.C.; Curtin, D. Soil acidification and liming interactions with nutrient and heavy metal transformation and bioavailability. Adv. Agron. Acad. Press 2003, 78, 215–272. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Xiang, Y.S.; Lu, J.W. Effect of lime dosage on pH value and available nutrient content of acid soil. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2017, 4, 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- de Souza, R.F.; Faquin, V.; Torres, P.; Baliza, D.P. Liming and organic fertilizer: Influence on phosphorus adsorption in soils. Rev. Bras. De Cienc. Do Solo 2006, 30, 975–983. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, C.; Baier, R.; Goettlein, A.; Weis, W. Changes in soil, seepage water and needle chemistry between 1984 and 2004 after liming an N-saturated Norway spruce stand at the Hoglwald, Germany. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 233, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prietzel, J.; Rehfuess, K.E.; Stetter, U.; Pretzsch, H. Changes of soil chemistry, stand nutrition, and stand growth at two Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) sites in Central Europe during 40 years after fertilization, liming, and lupine introduction. Eur. J. For. Res. 2008, 127, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston-Mafham, J.; Boddy, L.; Randerson, P.F. Analysis of microbial community functional diversity using sole-carbon-source utilisation profiles—A critique. Fems Microbiol. Ecol. 2002, 42, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Sheng, H.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, Y.Z. Remediation of Cd-contaminated acidic paddy fields with four-year consecutive liming. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 188, 109903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ji, X.; Chao, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, J.; Peng, H. Effects of increasing lime application rates on microbial diversity and community structure in paddy soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 161, 103837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenberg, M.; Stenberg, B.; Rydberg, T. Effects of reduced tillage and liming on microbial activity and soil properties in a weakly-structured soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2000, 14, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Huang, X.; Yao, H.; Huang, C. Effect of lime application on microbial community in acidic tea orchard soils in comparison with those in wasteland and forest soils. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlett, M.; Hopkins, D.W.; Moffett, B.F.; Harris, J.A. The effect of earthworms and liming on soil microbial communities. Biol. Fertil. Soils. 2009, 45, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pansu, M.; Gautheyrou, J. Handbook of Soil Analysis: Mineralogical, Organic and Inorganic Methods; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Available online: https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-540-31211-6 (accessed on 9 December 2022).
- Lu, R.K. Methods of Soil Agricultural Chemical Analysis; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, S.R. Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soils by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate; Misc. Pap.; The Institute for Agricultural Research: Zaria, Nigeria, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, X.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Luo, Y.; Yang, Q.H.; Zhang, L.L.; Yang, P.; Feng, B.L. Responses of rhizosphere soil properties, enzyme activities and microbial diversity to intercropping patterns on the Loess Plateau of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.W.; Chen, F.; Wang, F.H.; Liu, D.B.; Wan, Y.F.; Yu, C.B.; Hu, F.L.; Wang, Y.H. Study of classification of the soil nutrient status of citrus orchard in Hubei Province. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2002, 4, 390–394. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.M. Indices and Assessment of Soil Quality; SciPress: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- Vanbreemen, N.; Driscoll, C.T.; Mulder, J. Acidic deposition and internal proton sources in acidification of soils and waters. Nature 1984, 307, 599–604. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Yang, J.L.; Zhao, X.R.; Yang, S.H.; Zhang, G.L. Contribution of different proton sources to the acidification of red soil with maize cropping in subtropical China. Geoderma 2021, 392, 114995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neale, S.P.; Shah, Z.; Adams, W.A. Changes in microbial biomass and nitrogen turnover in acidic organic soils following liming. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1997, 29, 1463–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Guo, Z.H.; Peng, C.; Xiao, X.Y.; Feng, W.L.; Huang, B.; Ran, H.Z. Immobilization of cadmium and improvement of bacterial community in contaminated soil following a continuous amendment with lime mixed with fertilizers: A four-season field experiment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 171, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.F.; Fu, Q.L.; Shui, J.G.; Wu, Y.W. Effect of liming on acidity and exchangeable calcium and magensium of red soil in central Zhejiang. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 1999, 2, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, Y.; Jie, H.; Zhang, W.J.; Niu, Y.R.; Wang, D.C. Effect of biochar amendment on agricultural soil phosphorus availability: A review. J. Henan Agric. Univ. 2021, 55, 199–205, 220. [Google Scholar]
- Bolan, N.S.; Naidu, R.; Syers, J.K.; Tillman, R.W. Surface charge and solute interactions in soils. Adv. Agron. 1999, 67, 87–140. [Google Scholar]
- Soon, Y.K.; Miller, M.H. Changes in rhizosphere due to NH4+ and NO3− fertilization and phosphorus uptake by corn seedlings (ZEA MAYS-L). Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1977, 41, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.H.; Zhu, Z.X. The effect of pH on phosphate sorption in soils and its possible mechanism. Acta Pedol. Sin. 1991, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, D.; Xiao, W.F.; Li, G.H. Advance on study of liming on acid soils. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2010, 26, 206–213. [Google Scholar]
- Slangen, J.; Kerkhoff, P. Nitrification inhibitors in agriculture and horticulture—A literature-review. Fertil. Res. 1984, 5, 1–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorland, E.; van den Berg, L.; van de Berg, A.J.; Vermeer, M.L.; Roelofs, J.; Bobbink, R. The effects of sod cutting and additional liming on potential net nitrification in heathland soils. Plant Soil 2004, 265, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bending, G.D.; Turner, M.K.; Rayns, F.; Marx, M.C.; Wood, M. Microbial and biochemical soil quality indicators and their potential for differentiating areas under contrasting agricultural management regimes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 1785–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.; Ding, L.; Tang, Z.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Duan, G.L. Microbial response to CaCO3 application in an acid soil in southern China. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 79, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Z.; Sheng, H.; Yin, Z.R.; Xiao, H.C.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, P. Response of microbial community in purple mud of double-cropped rice fields to 5-year continuous application of organic amendment and liming. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 53, 482–491. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, L.; Han, X.G. Mechanisms of soil acidification reducing bacterial diversity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 81, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhalnina, K.; Dias, R.; de Quadros, P.D.; Davis, R.A.; Camargo, F.; Clark, I.M.; McGrath, S.P.; Hirsch, P.R.; Triplett, E.W. Soil pH determines microbial diversity and composition in the park grass experiment. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 69, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, P.; Nahas, E. Bacterial diversity in soil in response to different plants, phosphate fertilizers and liming. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2002, 33, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Liang, F. Diversities of Firmicutes in four hot springs in Yunnan and Tibet. Biotechnology 2015, 25, 32–82. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Fang, L.; Beiyuan, J.; Cui, Y.X.; Peng, Q.; Zhu, S.L.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X.C. Improvement of alfalfa resistance against Cd stress through rhizobia and arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi co-inoculation in Cd-contaminated soil. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 277, 116758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ren, H.Y.; Liu, J.J.; Tian, Y.; Lu, S.G. Soil acidification induced decline disease of Myrica rubra: Aluminum toxicity and bacterial community response analyses. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 45435–45448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakao, N.Y.; Yasuda, T.; Jolima, Y.; Yamanaka, S.; Hiraishi, A. Enhanced growth of acidocella facilis and related acidophilic bacteria at high concentrations of Aluminum. Microbes Environ. 2002, 17, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.W.; Ma, C.Q.; Fan, L.M.; Wang, Y.Z.; Yuan, Y.B. Soil amendment alters soil physicochemical properties and bacterial community structure of a replanted apple orchard. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 216, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Y.; Ji, J.; Hou, H. Long-term application of manures plus chemical fertilizers sustained high rice yield and improved soil chemical and bacterial properties. Eur. J. Agron. 2017, 90, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Bradford, M.A.; Jackson, R.B. Toward an ecological classification of soil bacteria. Ecology 2007, 88, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, X.; Li, Z.; Cheng, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Lei, M. Liming alters microbial community composition and its co-occurrence patterns in Cd- and Pb-contaminated agricultural soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 166, 104064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaichikova, M.V.; Berestovskaya, Y.Y.; Akimov, V.N.; Kizilova, A.K.; Vasilieva, L.V. Xanthobacter xylophilus sp nov.; a member of the xylotrophic mycobacterial community of low-mineral oligotrophic waters. Microbiology 2010, 79, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Shi, P.; Wei, G. Co-occurrence patterns of soybean rhizosphere microbiome at a continental scale. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 118, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Deng, Y.; Luo, F.; He, Z.; Tu, Q.; Zhi, X. Functional molecular ecological networks. mBio 2010, 1, e00169-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Liao, Q.; Wang, P.F.; Yuan, Q.S.; Hu, B.; Xing, X.L.; Xu, H.S. Effects of Reservoir Water Depth on Different Plankton Communities and Keystone Species of Network Interaction. Environ. Sci. 2022, 1–15, 2263–2277. [Google Scholar]
| No. | Soil Type | pH | ExA (cmol/kg) | SOM (g/kg) | TN (g/kg) | Olsen-P (mg/kg) | AK (mg/kg) | Clay Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | Anthrosol | 4.02 | 4.24 | 38.46 | 1.93 | 135.26 | 710.52 | 24.68 |
| b | Anthrosol | 4.11 | 2.35 | 27.00 | 1.86 | 609.06 | 609.06 | 23.03 |
| c | Luvisol | 3.75 | 6.35 | 43.44 | 2.19 | 110.22 | 110.22 | 22.44 |
| d | Anthrosol | 3.72 | 2.85 | 15.59 | 0.79 | 79.79 | 377.71 | 11.96 |
| Degree | Extremely Low | Low | Medium | High | Extremely High |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AK (mg/kg) | <60 | 60~100 | 100~150 | 150~200 | >200 |
| AP (mg/kg) | <10 | 10~20 | 20~40 | 40~60 | >60 |
| AN (mg/kg) | <30 | 30~90 | 90~160 | 160~280 | >280 |
| SOM (g/kg) | <15 | 15~20 | 20~30 | 30~40 | >40 |
| pH | <4.5 | 4.5~5.4 | 5.4~6.5 | 6.5~8.5 | >8.5 |
| CK | L0.6 | L1.2 | L2.4 | L4.8 | L7.2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nodes | 35 | 42 | 53 | 63 | 69 | 72 |
| Edges | 225 | 290 | 426 | 631 | 527 | 451 |
| Average degree | 12.86 | 13.81 | 16.08 | 20.03 | 15.28 | 12.36 |
| Diameter | 4 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| Density | 0.378 | 0.337 | 0.309 | 0.323 | 0.225 | 0.174 |
| Modularity | 0.298 | 0.416 | 0.339 | 0.311 | 0.393 | 0.442 |
| Average clustering coefficient | 0.657 | 0.703 | 0.633 | 0.631 | 0.566 | 0.570 |
| Average path length | 1.748 | 1.908 | 1.922 | 1.804 | 2.043 | 2.296 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, Z.; Ren, B.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, M. Chemical and Biological Response of Four Soil Types to Lime Application: An Incubation Study. Agronomy 2023, 13, 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13020504
Ding Z, Ren B, Chen Y, Yang Q, Zhang M. Chemical and Biological Response of Four Soil Types to Lime Application: An Incubation Study. Agronomy. 2023; 13(2):504. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13020504
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Zhifeng, Bailin Ren, Yuhang Chen, Qiongyao Yang, and Mingkui Zhang. 2023. "Chemical and Biological Response of Four Soil Types to Lime Application: An Incubation Study" Agronomy 13, no. 2: 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13020504
APA StyleDing, Z., Ren, B., Chen, Y., Yang, Q., & Zhang, M. (2023). Chemical and Biological Response of Four Soil Types to Lime Application: An Incubation Study. Agronomy, 13(2), 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13020504





