Identification of QTLs Conferring Rice Leaf Inclination Angle and Analysis of Candidate Genes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
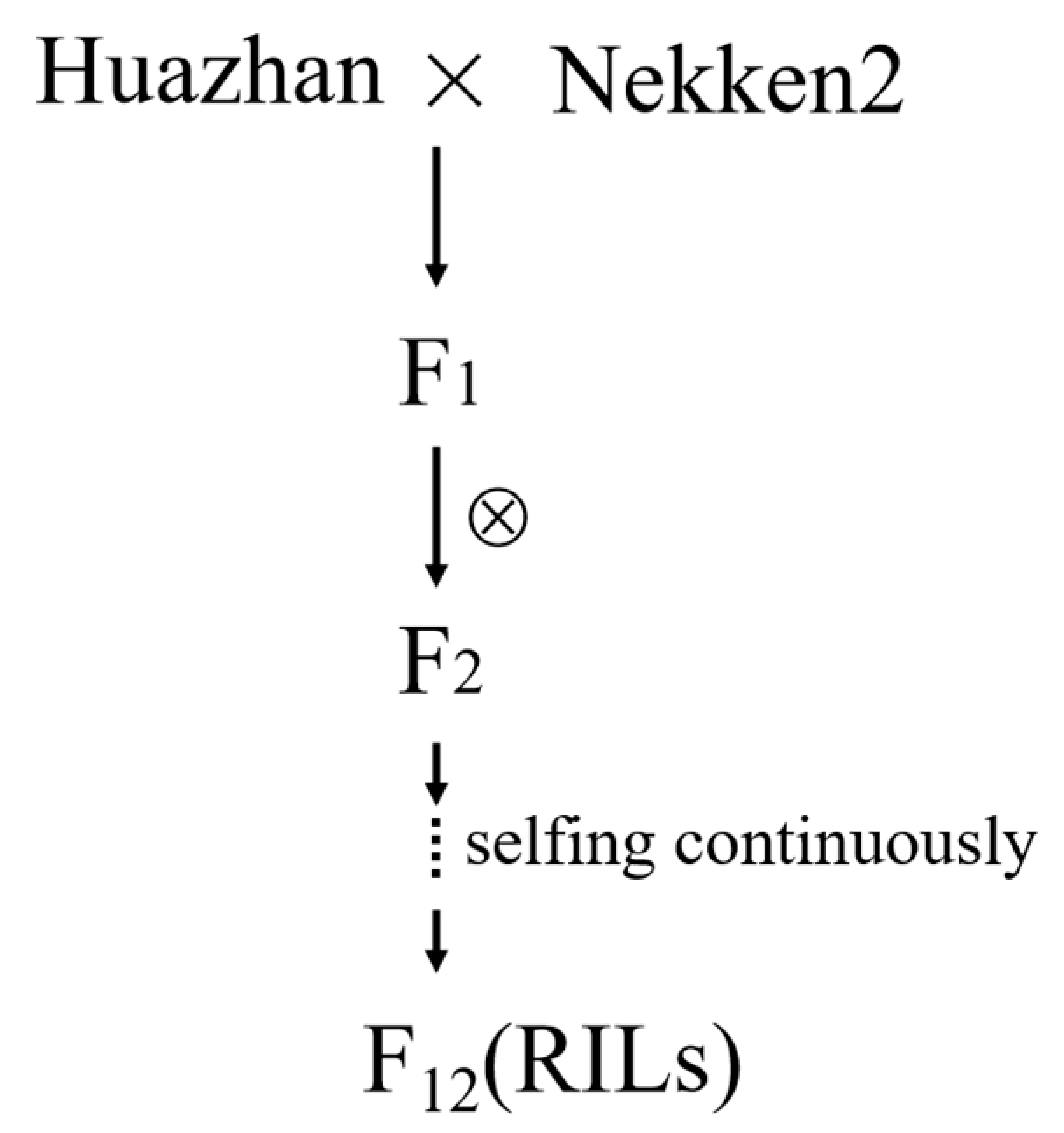
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Rice Planting and Management
2.3. Determination of the Leaf Inclination Angle
2.4. Construction of Genetic Maps
2.5. QTL Localization and Analysis
2.6. Quantitative Analysis of Gene Expression
3. Results
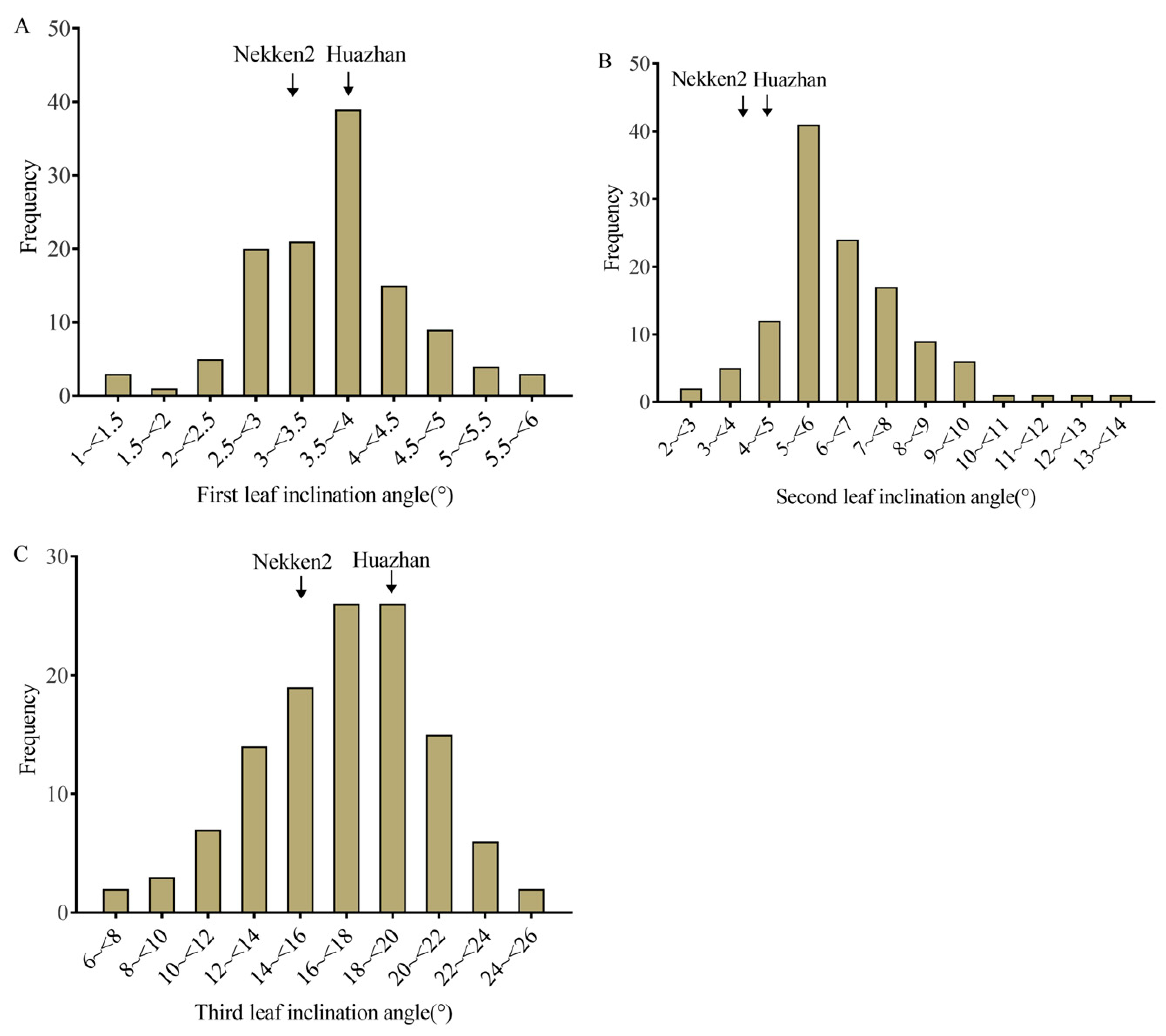
3.1. Performance of the Leaf Inclination Angle in Parent and RILs
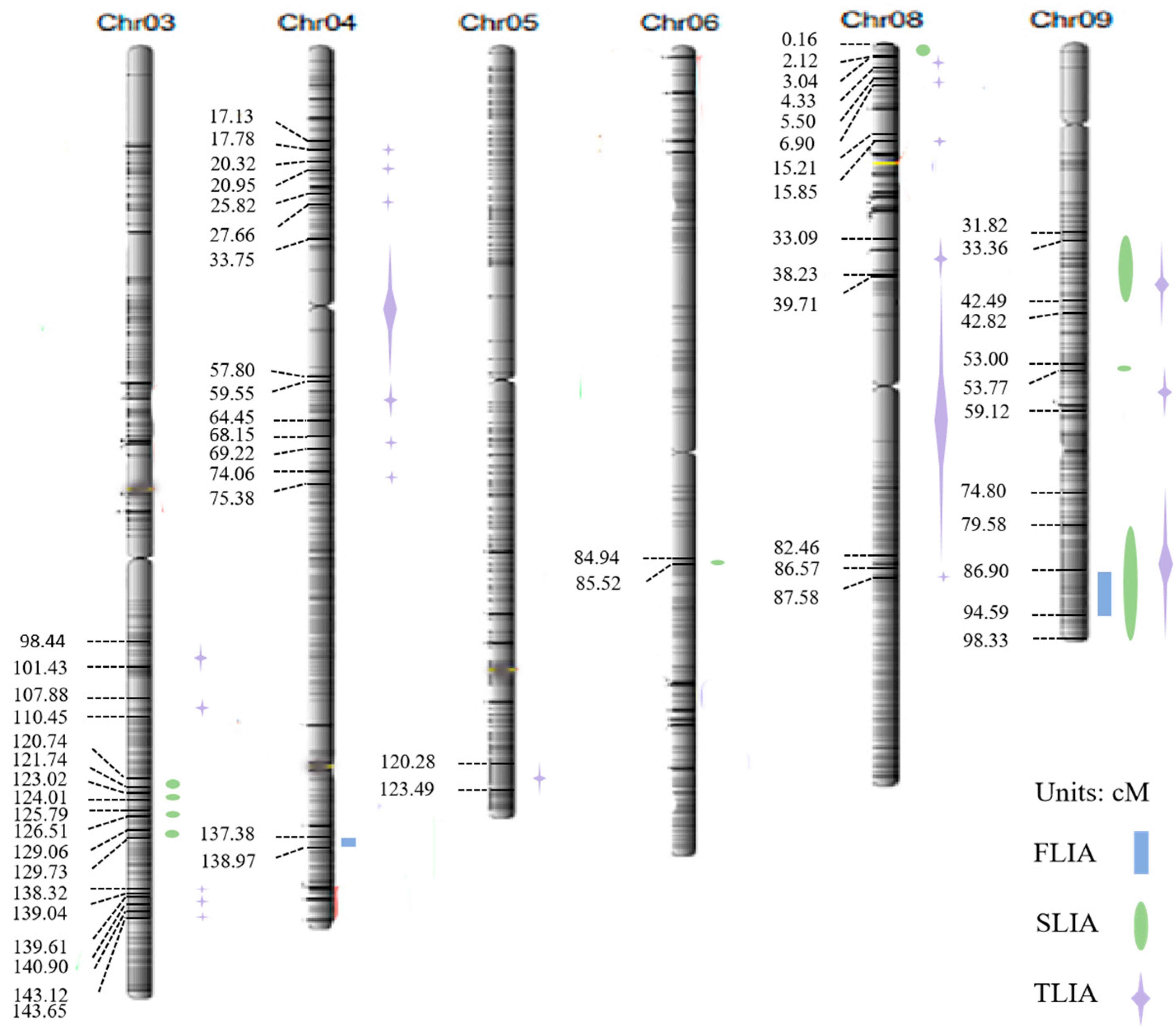
3.2. QTL Localization and Analysis
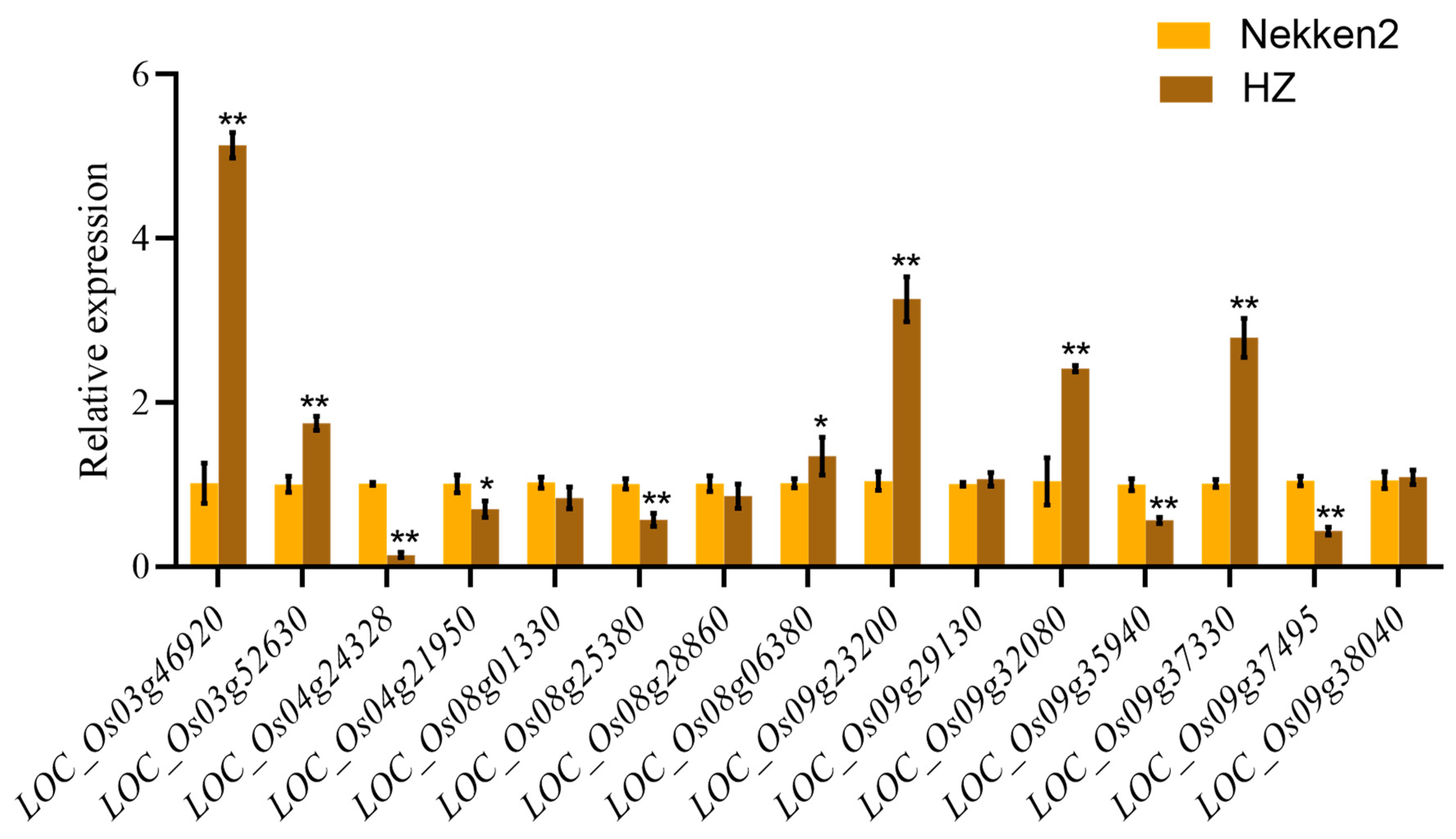
3.3. Expression Analysis of Rice Leaf Inclination-Related Genes
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leng, Y.J.; Qian, Q.; Zeng, D.L. Progress on genetic basis of rice ideal plant type. China Rice 2014, 20, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima, T.; Yang, C.H. Summary of ideal rice cultivation techniques. North. Rice 1978, 43–47. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=ohXIcpZjJKxyxfgjEiRBRAbpEzd-NPJ0sXcp0bNKsH2lBHFVPisvZFOAaonfKW6tPzjXAo_FDK_Pv2uQ4tsxmv4b8FjnroVb4oR1SI2-lxOYH7sivdg2iqzzQPz5f8Rb4-b7ay6Z3ds=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 15 July 2023).
- Yang, S.R.; Chen, W.F.; Zhang, L.B. Trends in breeding rice for ideotype. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 1988, 2, 129–135. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L.P. Super high yield breeding of hybrid rice. Hybrid. Rice 2000, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, L.; Qian, Q.; Zhang, G.H. Research advance in molecule regulation mechanism of leaf morphogenesis in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Acta Agron. Sin. 2013, 39, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.C. Studies on classification of leaf types of rice and its relation with photosynthesis. Sci. Agric. Sin. 1985, 18, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.B.; Cheng, S.H.; Cao, L.Y. Research progress on narrow leaf traits in rice. China Rice 2010, 16, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Mantilla-Perez, M.B.; Salas Fernandez, M.G. Differential manipulation of leaf angle throughout the canopy: Current status and prospects. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 5699–5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.H.; Li, H.Y. Oryza sativa BRASSINOSTEROID UPREGULATED1 LIKE1 induces the expression of a gene encoding a small leucine-rich-repeat protein to positively regulate lamina inclination and grain size in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, X.Y.; Tao, Y.F.; Jordan, D.; Borrell, A.; Hunt, C.; Cruickshank, A.; Potgieter, A.; Wu, A.; Hammer, G.; George-Jaeggli, B.; et al. Genetic control of leaf angle in sorghum and its effect on light interception. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 801–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, W.Y.; Guo, M.N.; Xu, L.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhao, H.Y.; Wang, J.M.; Yi, K.K. An SPX-RLI1 module regulates leaf inclination in response to phosphate availability in rice. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 853–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.P.; Zhou, J.; Chen, X.B. Research progress in molecular regulation mechanism of leaf inclination anglein rice (Oryza sativa L.). Chem. Life 2015, 35, 589–595. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.F.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, F.; Tong, H.N.; Wang, J.D.; Yu, J.W.; Zhang, C.Q.; Fan, X.L.; Liu, Q.Q. Abscisic acid represses rice lamina joint inclination by antagonizing brassinosteroid biosynthesis and signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, A.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Sakamoto, T.; Fujioka, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; Sazuka, T.; Ashikari, M.; Matsuoka, M. The rice SPINDLY gene functions as a negative regulator of gibberellin signaling by controlling the suppressive func- tion of the DELLA protein, SLR1, and modulating brassinosteroid synthesis. Plant J. 2006, 48, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, M.Y.; Zhang, L.Y.; Gampala, S.S.; Zhu, S.W.; Song, W.Y.; Chong, K.; Wang, Z.Y. Functions of OsBZR1 and 14-3-3 proteins in brassinosteroid signaling in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13839–13844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.L.; You, J.; Xiong, L.Z. Characterization of OsIAA1 gene, a member of rice Aux/IAA family involved in auxin and brassinosteroid hormone responses and plant morphogenesis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009, 7, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.Q.; Hu, J.; Guo, L.B.; Qian, Q.; Xue, H.W. Rice leaf inclination2, a VIN3-like protein, regulates leaf angle through modulating cell division of the collar. Cell Res. 2010, 20, 935–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.N.; Wang, S.K.; Xu, Y.X.; Yu, C.L.; Shen, C.J.; Qian, Q.; Geisler, M.; Jiang, D.A.; Qi, Y.H. The auxin response factor, OsARF19, controls rice leaf angles through positively regulating OsGH3-5 and OsBRI1. Plant Cell Environ. 2015, 38, 638–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Zhao, J.Z.; Hong, J.L.; Zhu, B.; Xia, S.; Zhu, E.G.; Han, P.F.; Zhang, K.W. Cytokinins regulate rice lamina joint development and leaf angle. Plant Physiol. 2023, 191, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.K.; Paterson, A.H.; Pinson, S.R.M.; Stansel, J.W. RFLP facilitated analysis of tiller and leaf angles in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 1999, 109, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.J.; Hiroshi, F.; Teng, S.; Hu, X.M.; Zeng, D.L.; Guo, L.B.; Qian, Q. QTL analysis of flag leaf angle in rice. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2003, 17, 219–222. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, S.; Fukuta, Y.; Morita, S.; Sato, T.; Osaki, M.; Khush, G.S. Quantitative trait loci affecting flag leaf development in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Breed. Sci. 2003, 53, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.Q.; Dai, W.M.; Fan, Y.Y.; Shen, B.; Zheng, K.L. Genetic dissection of flag leave angle and main panicle yield traits in rice. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2008, 24, 186–192. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, W.; Hu, J.; Sun, C.; Chen, G.; Jiang, H.; Zeng, D.L.; Gao, Z.Y.; Zhang, G.H.; Guo, L.B.; Li, S.G.; et al. Genetic analysis of related phenotypes of functional leaf in rice heading stage. Mol. Plant Breed. 2008, 6, 853–860. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.D.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, J.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Sun, D.Y.; Wang, X.S.; Liang, K.; Hong, D.L. Genetic analysis and QTL mapping of large flag leaf angle trait in Japonica rice. Rice Sci. 2012, 19, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Zhang, M.; Guo, L.B.; Li, X.M.; Bao, J.S.; Ma, L.Y. QTLs for rice flag leaf traits in doubled haploid populations in different environments. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 6786–6795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.H.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Li, Y.L.; Hu, C.M.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.Z.; Hong, D.L.; Dang, X.J. An analysis of natural variation reveals that OsFLA2 controls flag leaf angle in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 906912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, J.X.; Xu, L.J.; Liu, T.; Yan, Y.T.; Zhu, X.Y.; Shi, J.B.; Zhang, H.Q.; He, J.W. QTL mapping for flag leaf angle in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by genome-wide association analysis. Mol. Plant Breed. 2023. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Mazumder, S.R.; Hoque, H.; Sinha, B.; Chowdhury, W.R.; Hasan, M.N.; Prodhan, S.H. Genetic variability analysis of partially salt tolerant local and inbred rice (Oryza sativa L.) through molecular markers. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.B.; Feng, Q.; Yu, H.H.; Huang, X.H.; Zhao, Q.; Xing, Y.Z.; Yu, S.B.; Han, B.; Zhang, Q.F. Parent-independent genotyping for constructing an ultrahigh-density linkage map based on population sequencing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 10578–10583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.X.; Shang, L.G.; Yu, H.; Zeng, L.J.; Hu, J.; Ni, S.; Rao, Y.C.; Li, S.F.; Chu, J.F.; Meng, X.B.; et al. A strigolactone biosynthesis gene contributed to the rreen revolution in rice. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCouch, S.R.; Cho, Y.G.; Yano, M.; Paul, E.; Blinstrub, M.; Morishima, H.; Kinoshita, T. Report on QTL nomenclature. Rice Genet. Newsl. 1997, 14, 12–13. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.S.; Yang, B.; Xu, Z.D.; Li, F.C.; Guo, K.; Zhang, M.L.; Wang, L.Q.; Zou, W.H.; Wang, Y.T.; Peng, L.C. Global identification of multiple OsGH9 family members and their involvement in cellulose crystallinity modification in rice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e50171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.L.; Xie, Z.; Zou, X.L.; Casaretto, J.; Ho, T.H.D.; Shen, Q.J. A rice WRKY gene encodes a transcriptional repressor of the gibberellin signaling pathway in aleurone cells. Plant Physiol. 2004, 134, 1500–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.B.; Wang, S.G.; Zhang, B.C.; Shang-Guan, K.K.; Shi, Y.Y.; Zhang, D.M.; Liu, X.L.; Wu, K.; Xu, Z.P.; Fu, X.D.; et al. A Gibberellin-Mediated DELLA-NAC signaling cascade regulates cellulose synthesis in rice. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 1681–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.; Fujioka, S.; Sunohara, H.; Kamiya, N.; Hong, Z.; Inukai, Y.; Miura, K.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; et al. The role of OsBRI1 and its homologous genes, OsBRL1 and OsBRL3, in rice. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Sánchez, M.E.; Verhertbruggen, Y.; Christensen, U.; Chen, X.W.; Sharma, V.; Varanasi, P.; Jobling, S.A.; Talbot, M.; White, R.G.; Joo, M.; et al. Loss of cellulose synthase-like F6 function affects mixed-linkage glucan deposition, cell wall mechanical properties, and defense responses in vegetative tissues of rice. Plant Physiol. 2012, 159, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.H.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, X.D.; Qian, Q.; Xue, H.W. SHALLOT-LIKE1 is a KANADI transcription factor that modulates rice leaf rolling by regulating leaf abaxial cell development. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 719–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Long, Q.Z.; Huang, J.X.; Wang, Y.L.; Zhou, K.N.; Zheng, M.; Sun, J.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.H.; et al. Overexpression of OsZHD1, a zinc finger homeodomain class homeobox transcription factor, induces abaxially curled and drooping leaf in rice. Planta 2014, 239, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Zhang, B.C.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, L.; Shang-Guan, K.K.; Peng, Y.G.; Zhou, Y.H.; Zhu, Z. Brittle culm15 encodes a membrane-associated chitinase-like protein required for cellulose biosynthesis in rice. Plant Physiol. 2012, 159, 1440–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kant, S.; Bi, Y.M.; Zhu, T.; Rothstein, S.J. SAUR39, a small auxin-up RNA gene, acts as a negative regulator of auxin synthesis and transport in rice. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.J.; Zhao, H.; Li, S.L.; Han, Z.M.; Hu, G.; Liu, C.; Yang, G.Y.; Wang, G.W.; Xie, W.B.; Xing, Y.Z. Genome-wide association studies reveal that members of bHLH subfamily 16 share a conserved function in regulating flag leaf angle in rice (Oryza sativa). PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.Y.; Li, D.L.; Hu, X.X.; Liang, L.J.; Wu, G.C.; Zeng, S.Y.; Liu, E.B.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Bhanbhro, L.B.; et al. Mining of favorable marker alleles for flag leaf inclination in some rice (Oryza sativa L.) accessions by association mapping. Euphytica 2018, 214, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.Y.; Zheng, J.S.; Huang, R.Y.; Huang, Y.M.; Wang, H.C.; Jiang, L.R.; Fang, X.J. Phytohormones signaling and crosstalk regulating leaf angle in rice. Plant Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 2423–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamuro, C.; Ihara, Y.; Wu, X.; Noguchi, T.; Fujioka, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Ashikari, M.; Kitano, H.; Matsuoka, M. Loss of function of a rice brassinosteroid insensitive1 homolog prevents internode elongation and bending of the lamina joint. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 1591–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.J.; Wu, H.; Wu, D.P.; Zhang, Z.F.; Guo, Z.F.; Yang, N.; Xia, K.; Zhou, X.; Oh, K.; Matsuoka, M.; et al. Methyl jasmonate inhibits lamina joint inclination by repressing brassinosteroid biosynthesis and signaling in rice. Plant Sci. 2015, 241, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Z.; Fu, Y.C.; Zhao, S.S.; Gu, P.; Zhu, Z.F.; Sun, C.Q.; Tan, L.B. CLUSTERED PRIMARY BRANCH 1, a new allele of DWARF11, controls panicle architecture and seed size in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.D.; Lu, M.M.; Luo, Q.; Tan, F.; Zhao, Z.W.; Liu, M.Q.; He, Y.B. OsCPD1 and OsCPD2 are functional brassinosteroid biosynthesis genes in rice. Plant Sci. 2022, 325, 111482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, S.; Ashikari, M.; Fujioka, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; Yano, M.; Yoshimura, A.; Kitano, H.; Matsuoka, M.; Fujisawa, Y.; et al. A novel cytochrome P450 is implicated in brassinosteroid biosynthesis via the characterization of a rice dwarf mutant, dwarf11, with reduced seed length. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 776–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.C.; Kang, D.M.; Chen, Z.L.; Qu, L.J. Hormonal regulation of leaf morphogenesis in Arabidopsis. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2007, 49, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.Q.; Lee, C.H.; McCarthy, R.L.; Reeves, C.K.; Jones, E.G.; Ye, Z.H. Transcriptional activation of secondary wall biosynthesis by rice and maize NAC and MYB transcription factors. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011, 52, 1856–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.R.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.H.; Xie, L.L.; Zhang, Q.X.; Zhang, J.J.; Li, W.Y.; Wu, M.F.; Cui, J.S.; Wang, W.Y.; et al. Nudix hydrolase 14 influences plant development and grain chalkiness in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1054917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.H.; Yie, S.W.; Hwang, D.J. Heterologous expression of OsWRKY6 gene in Arabidopsis activates the expression of defense related genes and enhances resistance to pathogens. Plant Sci. 2011, 181, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Zhang, Z.L.; Zou, X.L.; Huang, J.; Ruas, P.; Thompson, D.; Shen, Q.J. Annotations and functional analyses of the rice WRKY gene superfamily reveal positive and negative regulators of abscisic acid signaling in aleurone cells. Plant Physiol. 2005, 137, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primer Name | Sequence (5′–3′) | Tm (°C) | Length (bp) | Amplicon Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os03g49620-F-qrt | GCAAGGAAACGTGTGGCAAT | 60.00 | 20 | 153 |
| LOC_Os03g49620-R-qrt | CTTTGCCAGGCCAAAGTCAC | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os03g52630-F-qrt | CATGCTCAGCTGGAGTGTGA | 60.00 | 20 | 166 |
| LOC_Os03g52630-R-qrt | GTCACCTACACCCACCTGTG | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os04g24328-F-qrt | TCAAGGACTGGTACGGCAAC | 60.00 | 20 | 172 |
| LOC_Os04g24328-R-qrt | GACTTGTGGACGTGGTGGAA | 60.20 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os04g21950-F-qrt | CCATGGATCTGATGGGTGGG | 59.90 | 20 | 181 |
| LOC_Os04g21950-R-qrt | GTGATCTCCCTGCAGTCCAC | 60.10 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os08g01330-F-qrt | TCAGCTACAAGGACCGCAAG | 60.00 | 20 | 158 |
| LOC_Os08g01330-R-qrt | GCGACCCTTGTAGAACACCA | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os08g25380-F-qrt | TGGGGACTTCGTCGAAACTG | 60.00 | 20 | 191 |
| LOC_Os08g25380-R-qrt | ACGGCAATGATGAGCACAGA | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os08g28860-F-qrt | ACATCTGAGGAGCGCGAAAA | 60.00 | 20 | 162 |
| LOC_Os08g28860-R-qrt | TCTTCGCTCGGGAAAGTCTG | 59.80 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os08g06380-F-qrt | CCGTCTTCCGTACCGAGAAG | 59.90 | 20 | 178 |
| LOC_Os08g06380-R-qrt | CACGAGAACCCGAACCAGAA | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os09g23200-F-qrt | GAGCAACTCCTCAAGGGACC | 60.00 | 20 | 179 |
| LOC_Os09g23200-R-qrt | AGTCAGGCCTCCCTAGAGTG | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os09g29130-F-qrt | CCCAGGAGCAGAAGGACAAG | 60.00 | 20 | 156 |
| LOC_Os09g29130-R-qrt | CCAGGGTGTGCTTGTTGTTG | 59.90 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os09g32080-F-qrt | CCATCCCCGTCTTCTGGAAC | 60.10 | 20 | 151 |
| LOC_Os09g32080-R-qrt | TGCTTCTTCTTCATCGGCGT | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os09g35940-F-qrt | AATGGGTTCGGATCTCAGGC | 59.80 | 20 | 186 |
| LOC_Os09g35940-R-qrt | ATCTCGCACGACAGCCTTAG | 59.90 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os09g37330-F-qrt | GAGAGCGATTTGGGGTTCCA | 60.00 | 20 | 200 |
| LOC_Os09g37330-R-qrt | GACAGAGCTCACAACAGCCT | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os09g37495-F-qrt | GTCTTCGGCGAGCTTCTGAT | 60.20 | 20 | 167 |
| LOC_Os09g37495-R-qrt | CTCGCCATGGAGCTCAAGAA | 60.10 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os09g38040-F-qrt | GCCTTTGGACTCTTCCTGCT | 60.00 | 20 | 192 |
| LOC_Os09g38040-R-qrt | CAGGTGAGAAGTTGGGGGTC | 60.00 | 20 |
| Trait | QTL | Chromosome | Physical Gap (bp) | Position of Support (cM) | LOD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First leaf inclination angle | qFLIA4-1 | 04 | 32047360–32418113 | 137.38–138.97 | 2.10 |
| qFLIA9-1 | 09 | 20272099–22066122 | 86.90–94.59 | 3.20 | |
| Second leaf inclination angle | qSLIA3-1 | 03 | 28166873–28398636 | 120.74–121.74 | 2.02 |
| qSLIA3-2 | 03 | 28698205–28928756 | 123.02–124.01 | 2.47 | |
| qSLIA3-3 | 03 | 29344947–29512289 | 125.79–126.51 | 2.11 | |
| qSLIA3-4 | 03 | 30106459–30262983 | 129.06–129.73 | 2.43 | |
| qSLIA6-1 | 06 | 19814308–19950243 | 84.94–85.52 | 2.72 | |
| qSLIA8-1 | 08 | 37535–484785 | 0.16–2.12 | 2.65 | |
| qSLIA9-1 | 09 | 7423269–9911482 | 31.82–42.49 | 5.94 | |
| qSLIA9-2 | 09 | 12363787–12542579 | 53.00–53.77 | 2.02 | |
| qSLIA9-3 | 09 | 18564963–22938953 | 79.58–98.33 | 5.80 | |
| Third leaf inclination angle | qTLIA3-1 | 03 | 22963993–23661505 | 98.44–101.43 | 2.33 |
| qTLIA3-2 | 03 | 25165251–25766328 | 107.88–110.45 | 2.38 | |
| qTLIA3-3 | 03 | 32267773–32435017 | 138.32–139.04 | 2.71 | |
| qTLIA3-4 | 03 | 32567335–32870078 | 139.61–140.90 | 2.02 | |
| qTLIA3-5 | 03 | 33386000–33510684 | 143.12–143.65 | 2.57 | |
| qTLIA4-1 | 04 | 3995063–4147493 | 17.13–17.78 | 2.18 | |
| qTLIA4-2 | 04 | 4739169–4886181 | 20.32–20.95 | 2.20 | |
| qTLIA4-3 | 04 | 6022948–6451666 | 25.82–27.66 | 2.15 | |
| qTLIA4-4 | 04 | 7872497–13483092 | 33.75–57.80 | 2.43 | |
| qTLIA4-5 | 04 | 13890841–15035660 | 59.55–64.45 | 2.33 | |
| qTLIA4-6 | 04 | 15898826–16146829 | 68.15–69.22 | 2.21 | |
| qTLIA4-7 | 04 | 17276270–17584975 | 74.06–75.38 | 2.38 | |
| qTLIA5-1 | 05 | 28058252–28807595 | 120.28–123.49 | 2.81 | |
| qTLIA8-1 | 08 | 712661–1010353 | 3.05–4.33 | 2.37 | |
| qTLIA8-2 | 08 | 1306603–1610665 | 5.60–6.90 | 2.50 | |
| qTLIA8-3 | 08 | 3547205–3697431 | 15.21–15.85 | 2.33 | |
| qTLIA8-4 | 08 | 7718778–8917564 | 33.09–38.23 | 2.35 | |
| qTLIA8-5 | 08 | 9263931–19235634 | 39.71–82.46 | 2.64 | |
| qTLIA8-6 | 08 | 20195421–20430444 | 86.57–87.58 | 2.32 | |
| qTLIA9-1 | 09 | 7782000–9989226 | 33.36–42.82 | 3.21 | |
| qTLIA9-2 | 09 | 12363787–13791179 | 53.00–59.12 | 2.41 | |
| qTLIA9-3 | 09 | 17448080–22938953 | 74.80–98.33 | 8.53 |
| Gene Number | Chromosome | QTL | Functions | Cloned or Not |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os03g49620 | 3 | qSLIA3-1 | BR INSENSITIVE 1-associated receptor kinase 1 precursor | Not cloned |
| LOC_Os03g52630 | 3 | qSLIA3-4 | glycoside hydrolase | Have been cloned [37] |
| LOC_Os04g24328 | 4 | qTLIA4-5 | JA-induced protein | Not cloned |
| LOC_Os04g21950 | 4 | qTLIA4-4 | WRKY transcription factor | Have been cloned [38] |
| LOC_Os08g01330 | 8 | qSLIA8-1 | NAC Transcription Factor | Have been cloned [39] |
| LOC_Os08g25380 | 8 | qTLIA8-5 | BR receptor kinase | Have been cloned [40] |
| LOC_Os08g28860 | 8 | qTLIA8-5 | NUDIX hydrolase | Not cloned |
| LOC_Os08g06380 | 8 | qTLIA8-3 | cellulose synthase-like F | Have been cloned [41] |
| LOC_Os09g23200 | 9 | qTLIA9-2 | SHAQKYF class MYB family transcription factor | Have been cloned [42] |
| LOC_Os09g29130 | 9 | qTLIA9-3 | Zn-finger transcription factor | Have been cloned [43] |
| LOC_Os09g32080 | 9 | qSLIA9-3qTLIA9-3 | membrane-associated chitinase-like protein | Have been cloned [44] |
| LOC_Os09g35940 | 9 | qFLIA9-1qSLIA9-3qTLIA9-3 | cytochrome P450 | Not cloned |
| LOC_Os09g37330 | 9 | qFLIA9-1qSLIA9-3qTLIA9-3 | small auxin-up RNA gene | Have been cloned [45] |
| LOC_Os09g37495 | 9 | qFLIA9-1qSLIA9-3qTLIA9-3 | auxin responsive protein | Not cloned |
| LOC_Os09g38040 | 9 | qFLIA9-1qSLIA9-3qTLIA9-3 | NUDIX hydrolase | Not cloned |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Yu, D.; Li, X.; Yin, W.; Lian, J.; Yang, H.; Lu, M.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; et al. Identification of QTLs Conferring Rice Leaf Inclination Angle and Analysis of Candidate Genes. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13122891
Luo Y, Zhong Q, Yu D, Li X, Yin W, Lian J, Yang H, Lu M, Li S, Zhang W, et al. Identification of QTLs Conferring Rice Leaf Inclination Angle and Analysis of Candidate Genes. Agronomy. 2023; 13(12):2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13122891
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Yiting, Qianqian Zhong, Dian Yu, Xuan Li, Wenjing Yin, Jinjin Lian, Huimin Yang, Mei Lu, Sanfeng Li, Weilin Zhang, and et al. 2023. "Identification of QTLs Conferring Rice Leaf Inclination Angle and Analysis of Candidate Genes" Agronomy 13, no. 12: 2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13122891
APA StyleLuo, Y., Zhong, Q., Yu, D., Li, X., Yin, W., Lian, J., Yang, H., Lu, M., Li, S., Zhang, W., Wang, Y., & Rao, Y. (2023). Identification of QTLs Conferring Rice Leaf Inclination Angle and Analysis of Candidate Genes. Agronomy, 13(12), 2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13122891





