A Scientometric Analysis of Research Trends and Knowledge Structure on the Climate Effects of Irrigation between 1993 and 2022
Abstract
:1. Introduction
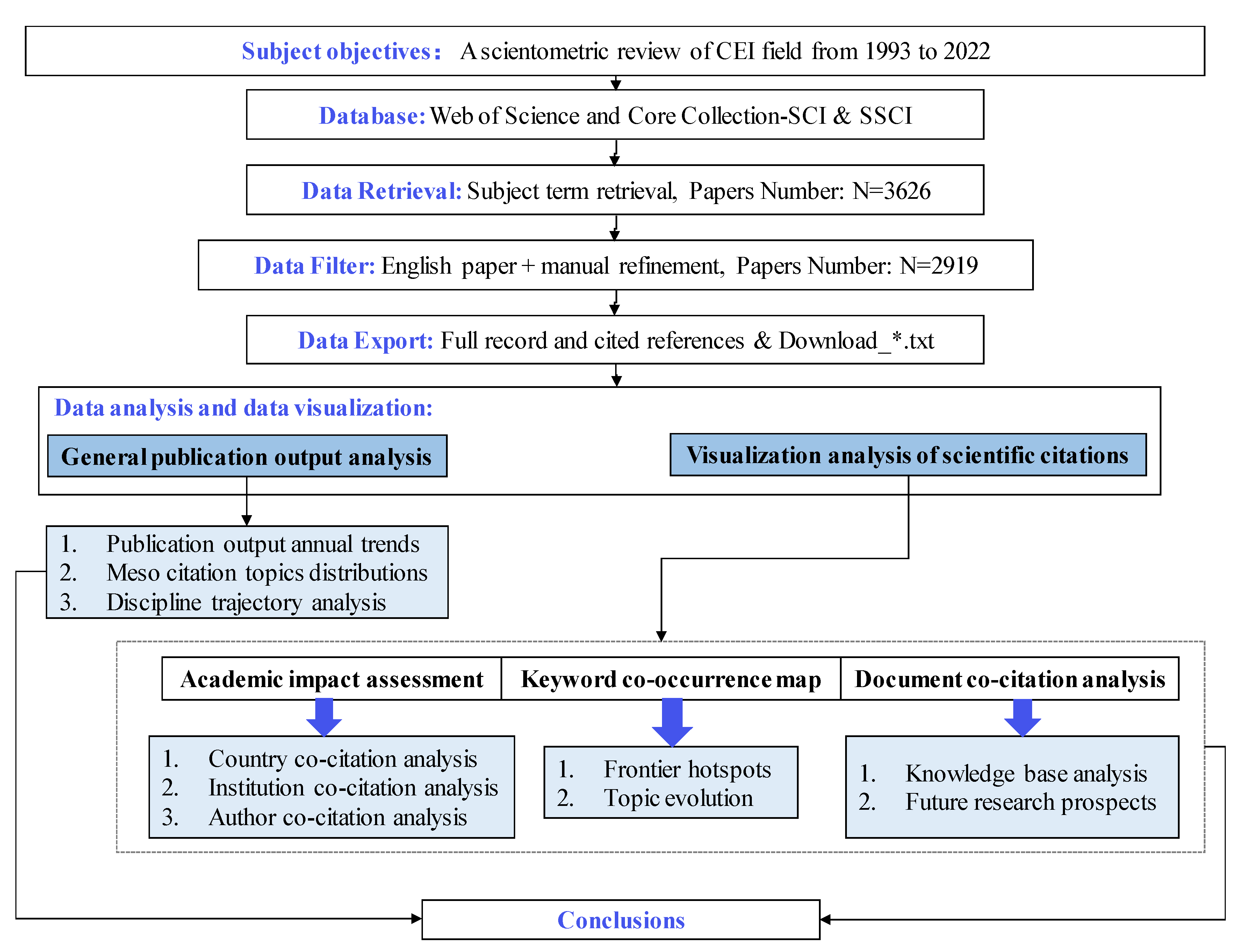
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Scientometric Analytical Research Design
2.2. Analysis Data Collection and Processing
2.3. Data Analysis Methods and Tools
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. General Analysis
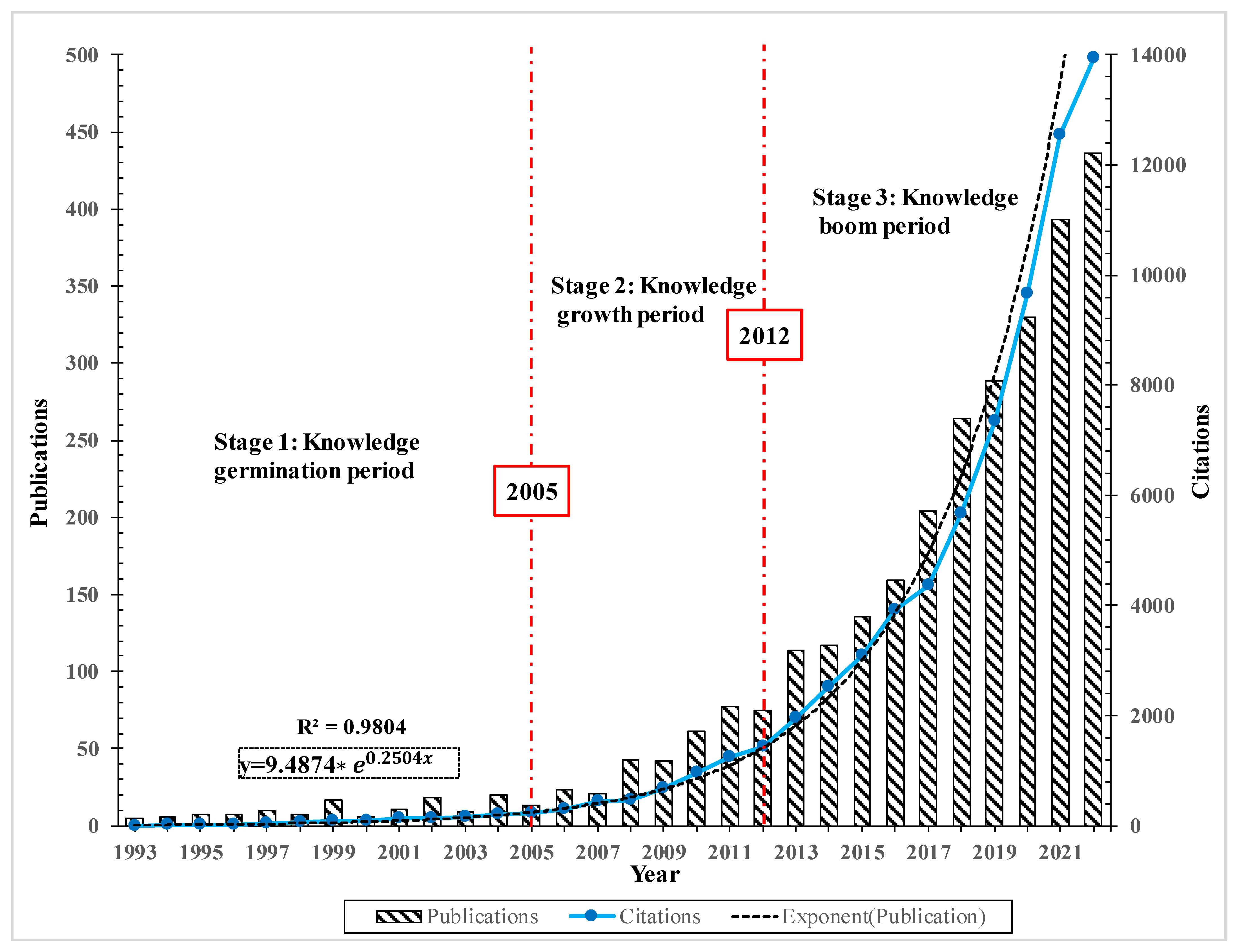
3.1.1. The Annual Trends of Publication Outputs
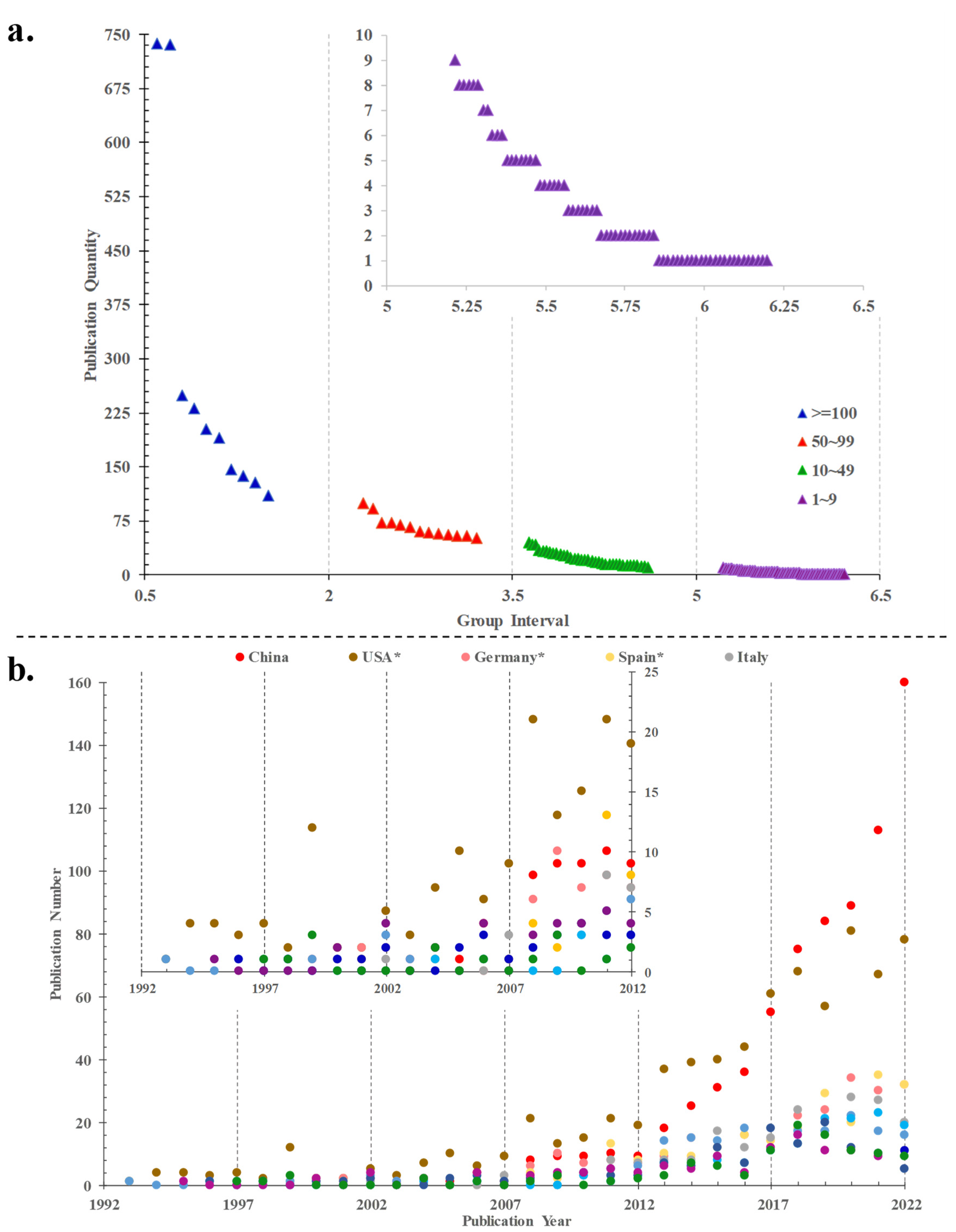
3.1.2. The Distribution Trends of Publication Outputs
3.2. Academic Impacts and Cooperation Analysis
3.2.1. Co-Country Analyses
3.2.2. Co-Institutes Analyses
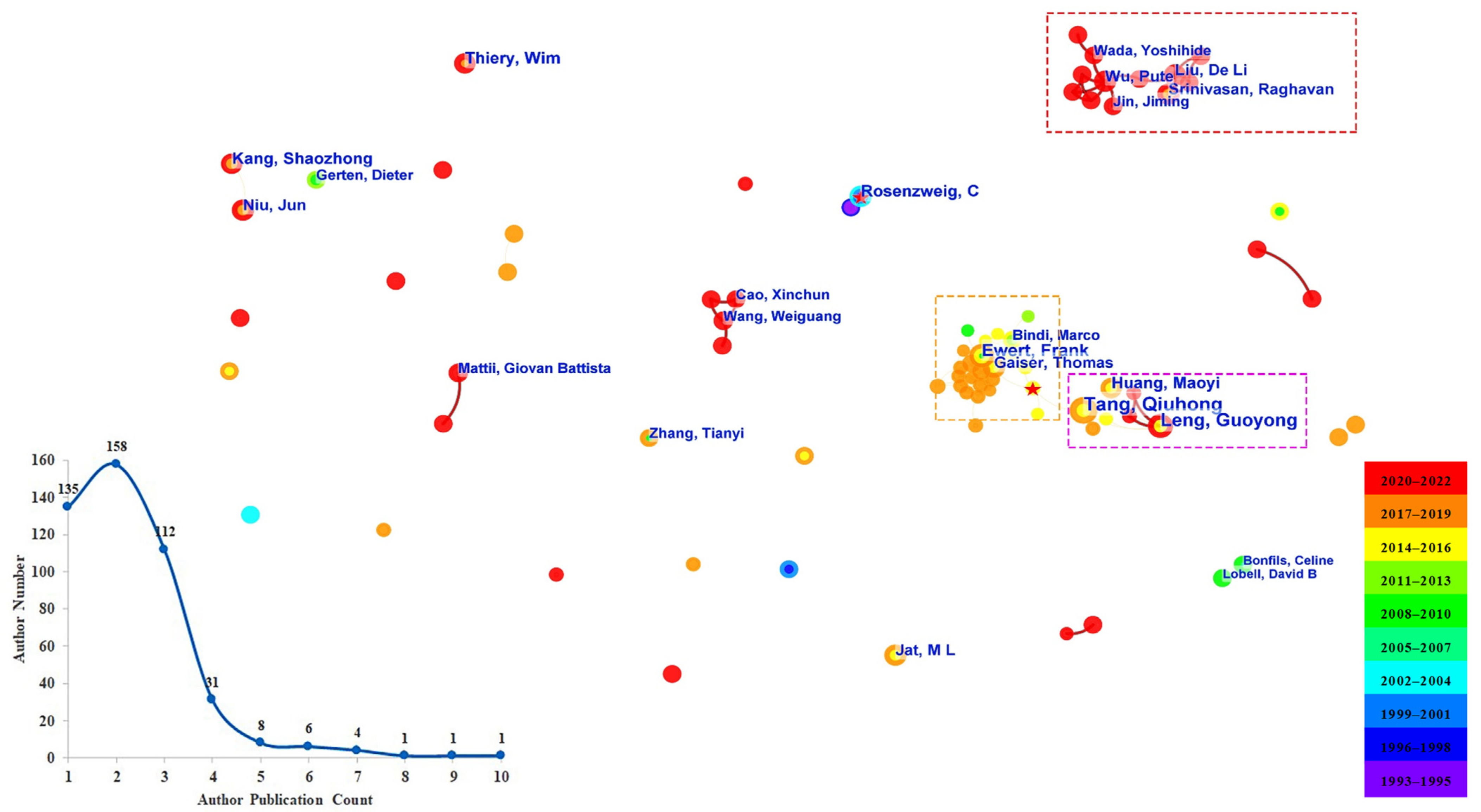
3.2.3. Co-Author Analyses
3.3. Keyword Co-Occurrence Analyses
3.3.1. Thematic Trends Analyses
3.3.2. Research Hotspots Analyses
3.4. The Knowledge Base and Intellectual Structure Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NCEP. The United Nations World Water Development Report 2021: Valuing Water; NCEP: College Park, MD, USA, 2021.
- Kundzewicz, Z.W. Climate change impacts on the hydrological cycle. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2008, 8, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Xia, J.; She, D. Analysis of Impacts of Climate Change and Human Activities on Hydrological Drought: A Case Study in the Wei River Basin, China. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 1421–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassardo, C.; Park, S.K.; Galli, M.; Sungmin, O. Climate change over the high-mountain versus plain areas: Effects on the land surface hydrologic budget in the Alpine area and northern Italy. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 3331–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liuzzo, L.; Noto, L.V.; Arnone, E.; Caracciolo, D.; La Loggia, G. Modifications in Water Resources Availability Under Climate Changes: A Case Study in a Sicilian Basin. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 1117–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Horino, H.; Kawashima, S. Numerical assessments of the impacts of climate change on regional groundwater systems in a paddy-dominated alluvial fan. Paddy Water Environ. 2016, 14, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.J.; Miller, K.A.; Hamlet, A.F.; Avis, W. Climate Change and Resource Management in the Columbia River Basin. Water Int. 2000, 25, 253–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN-Water Policy Brief on Climate Change and Water. 2019. Available online: https://www.unwater.org/water-facts/water-and-climate-change (accessed on 8 March 2023).
- United Nations Environment Programme. Climate Change, Water Scarcity and Security. 2021. Available online: https://www.unep.org/news-and-stories/speech/climate-change-water-scarcity-and-security (accessed on 8 March 2023).
- Doell, P.; Siebert, S. Global modeling of irrigation water requirements. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hof, A.; Wolf, N. Estimating potential outdoor water consumption in private urban landscapes by coupling high-resolution image analysis, irrigation water needs and evaporation estimation in Spain. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 123, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, O.; Myhre, G.; Myhre, A. Direct human influence of irrigation on atmospheric water vapour and climate. Clim. Dyn. 2004, 22, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, B.I.; Shukla, S.P.; Puma, M.J.; Nazarenko, L.S. Irrigation as an historical climate forcing. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 44, 1715–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puma, M.J.; Cook, B.I. Effects of irrigation on global climate during the 20th century. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, S.; Burke, J.; Faures, J.M.; Frenken, K.; Hoogeveen, J.; Döll, P.; Portmann, F.T. Groundwater use for irrigation—A global inventory. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 1863–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, E.M.; Niyogi, D.; Frolking, S.; Yeluripati, J.B.; Pielke, R.A., Sr.; Niyogi, N.; Vörösmarty, C.J.; Mohanty, U.C. Changes in moisture and energy fluxes due to agricultural land use and irrigation in the Indian Monsoon Belt. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L14403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kueppers, L.M.; Snyder, M.A.; Sloan, L.C. Irrigation cooling effect: Regional climate forcing by land-use change. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L03703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, W.J.; Cook, B.I.; Buenning, N.; Levis, S.; Helkowski, J.H. Effects of global irrigation on the near-surface climate. Clim. Dyn. 2009, 33, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trost, B.; Prochnow, A.; Drastig, K.; Meyer-Aurich, A.; Ellmer, F.; Baumecker, M. Irrigation, soil organic carbon and N2O emissions. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 33, 733–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Feng, J.; Miao, W. Simulating the Impacts of Irrigation and Dynamic Vegetation Over the North China Plain on Regional Climate. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 8017–8034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Tang, J.; Liu, D. Climatic effects of irrigation over the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain in China simulated by the weather research and forecasting model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 2246–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhang, W. Effect of irrigation on the soil respiration of constructed grasslands in Inner Mongolia, China. Plant Soil 2015, 395, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norero, A.L.; Ashcroft, G.L.; Keller, J. Effect of irrigation frequency on the average evapotranspiration of various crop-climate-soil systems. Trans. ASAE 1972, 15, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiery, W.; Davin, E.L.; Lawrence, D.M.; Hirsch, A.L.; Hauser, M.; Seneviratne, S.I. Present-day irrigation mitigates heat extremes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 1403–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alter, R.E.; Im, E.-S.; Eltahir, E.A.B. Rainfall consistently enhanced around the Gezira Scheme in East Africa due to irrigation. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Shi, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chu, X.; Yu, P.; Xiong, W.; Zuo, H.; Zhang, S. Agricultural irrigation-induced climatic effects: A case study in the middle and southern Loess Plateau area, China. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 2620–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J. Urban water capacity: Irrigation for heat mitigation. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2019, 78, 101397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadbent, A.M.; Coutts, A.M.; Tapper, N.J.; Demuzere, M. The cooling effect of irrigation on urban microclimate during heatwave conditions. Urban Clim. 2018, 23, 309–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimberteau, M.; Laval, K.; Perrier, A.; Polcher, J. Global effect of irrigation and its impact on the onset of the Indian summer monsoon. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 39, 1329–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Li, S.; Kang, S.; Du, T.; Guo, P.; Mao, X.; Tong, L.; Hao, X.; Ding, R.; Niu, J. Effect of drip irrigation on wheat evapotranspiration, soil evaporation and transpiration in Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 232, 106001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Eltahir, E.A.B. North China Plain threatened by deadly heatwaves due to climate change and irrigation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalimov, V.V.; Mul’chenko, Z.M. Measurement of Science: Study of the Development of Science as an Information Process; Hill, R.D., Ed.; Drexel University Library, Foreign Technology Division: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Y. Visualization analysis of high-speed railway research based on CiteSpace. Transp. Policy 2020, 85, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ibekwe-SanJuan, F.; Hou, J. The structure and dynamics of cocitation clusters: A multiple-perspective cocitation analysis. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 1386–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. Searching for intellectual turning points: Progressive knowledge domain visualization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101 (Suppl. S1), 5303–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. Science Mapping: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J. Data Inf. Sci. 2017, 2, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, Y.; Horowitz, M.; Hou, H.; Liu, Z.; Pellegrino, D. Towards an explanatory and computational theory of scientific discovery. J. Informetr. 2009, 3, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Leydesdorff, L. Patterns of connections and movements in dual-map overlays: A new method of publication portfolio analysis. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2014, 65, 334–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondel, V.D.; Guillaume, J.-L.; Lambiotte, R.; Lefebvre, E. Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2008, 2008, P10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Park, T.; Wang, X.; Piao, S.; Xu, B.; Chaturvedi, R.K.; Fuchs, R.; Brovkin, V.; Ciais, P.; Fensholt, R.; et al. China and India lead in greening of the world through land-use management. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Bollen, J.; Nelson, M.L.; Van de Sompel, H. Co-authorship networks in the digital library research community. Inf. Process. Manag. 2005, 41, 1462–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, G.; Tang, Q.; Huang, M.; Leung, L.-y.R. A comparative analysis of the impacts of climate change and irrigation on land surface and subsurface hydrology in the North China Plain. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2015, 15, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobell, D.B.; Bonfils, C. The Effect of Irrigation on Regional Temperatures: A Spatial and Temporal Analysis of Trends in California, 1934–2002. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 2063–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Hu, Z. A bibliometric analysis of linguistic research on COVID-19. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 1005487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; Wang, Y.; Lin, C.; He, M.; Hao, F.; Liu, H.; Zhu, W. Heavy metal loss from agricultural watershed to aquatic system: A scientometrics review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637–638, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spronken-Smith, R.A.; Oke, T.R. The thermal regime of urban parks in two cities with different summer climates. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 2085–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, P.K.; Mall, R.K. Climate Change and Rice Yields in Diverse Agro-Environments of India. II. Effect of Uncertainties in Scenarios and Crop Models on Impact Assessment. Clim. Chang. 2002, 52, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimball, B.A.; Mauney, J.R. Response of Cotton to Varying COz, Irrigation, and Nitrogen: Yield and Growth. Agron. J. 1993, 85, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R.; Prashant, R.D.; Linda, O.M.; Mariquita, Y.L.B.; Harry, F.H.; Alec, G.R.; Vijaya Gopal, K. Simulating the impacts of climate change on cotton production in the Mississippi Delta. Clim. Res. 2002, 22, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pl, F.; Alexander, L.; Della-Marta, P.; Gleason, B.; Haylock, M.; Klein, T.; Tc, P. Observed coherent changes in climatic extremes during 2nd half of the 20th century. Clim. Res. 2002, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Huang, X.; Chen, H.; Huang, G.; Ni, S.; Wright, J.S.; Hall, J.; Ciais, P.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Assessing the Impacts of Extreme Agricultural Droughts in China Under Climate and Socioeconomic Changes. Earth’s Future 2018, 6, 689–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large Area Hydrologic Modeling And Assessment Part I: Model Development. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eheart, J.W.; Wildermuth, A.J.; Herricks, E.E. The Effects of Climate Change and Irrigation on Criterion Low Streamflows Used for Determining Total Maximum Daily Loads. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1999, 35, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, G.; Ge, Y.; Li, H.; Han, F.; Hu, X.; Tian, W.; Tian, Y.; Pan, X.; Nian, Y.; et al. Hydrological Cycle in the Heihe River Basin and Its Implication for Water Resource Management in Endorheic Basins. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 890–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, C.C.; Wieder, W.R.; Reed, S.C.; Townsend, A.R. Experimental drought in a tropical rain forest increases soil carbon dioxide losses to the atmosphere. Ecology 2010, 91, 2313–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, S.S.; Zarin, D.J.; Capanu, M.; Littell, R.; Davidson, E.A.; Ishida, F.Y.; Santos, E.B.; Araújo, M.M.; Aragão, D.V.; Rangel-Vasconcelos, L.G.T.; et al. Moisture and substrate availability constrain soil trace gas fluxes in an eastern Amazonian regrowth forest. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2004, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Janssens, I.A.; Liu, P.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, O.J. Irrigation and enhanced soil carbon input effects on below-ground carbon cycling in semiarid temperate grasslands. New Phytol. 2007, 174, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruehr, N.K.; Martin, J.G.; Law, B.E. Effects of water availability on carbon and water exchange in a young ponderosa pine forest: Above- and belowground responses. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 164, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, X.; Shao, J.; Nie, Y.; He, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wu, Z.; Hosseini Bai, S. Interactive effects of global change factors on soil respiration and its components: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 3157–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jeong, S.-J. Irrigation enhances local warming with greater nocturnal warming effects than daytime cooling effects. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 024005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Pu, C.; Zhao, X.; Xue, J.; Zhang, R.; Nie, Z.; Chen, F.; Lal, R.; Zhang, H. Tillage effects on carbon footprint and ecosystem services of climate regulation in a winter wheat–summer maize cropping system of the North China Plain. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafee, N.; Katsaliaki, K.; Fishwick, P. Exploring the modelling and simulation knowledge base through journal co-citation analysis. Scientometrics 2014, 98, 2145–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.M.; Rosenzweig, C.; Peart, R.M.; Ritchie, J.T.; McCarl, B.A.; Glyer, J.D.; Curry, R.B.; Jones, J.W.; Boote, K.J.; Allen, L.H. Global climate change and US agriculture. Nature 1990, 345, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, J.B. Growth and water use of faba beans (Vicia faba) in a subhumid climate II. Simulation analysis of crop responses to drought. Field Crops Res. 1990, 23, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, T.D.; Jones, P.D. An improved method of constructing a database of monthly climate observations and associated high-resolution grids. Int. J. Climatol. 2005, 25, 693–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feddema, J.; Oleson, K.; Bonan, G.; Mearns, L.; Buja, L.; Meehl, G.; Washington, W. The Importance of Land-Cover Change in Simulating Future Climates. Science 2006, 310, 1674–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birthal, P.S.; Hazrana, J.; Negi, D.S.; Pandey, G. Benefits of irrigation against heat stress in agriculture: Evidence from wheat crop in India. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 255, 106950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jägermeyr, J.; Pastor, A.; Biemans, H.; Gerten, D. Reconciling irrigated food production with environmental flows for Sustainable Development Goals implementation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, B.; Piao, S.; Wang, X.; Lobell, D.B.; Huang, Y.; Huang, M.; Yao, Y.; Bassu, S.; Ciais, P.; et al. Temperature increase reduces global yields of major crops in four independent estimates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 9326–9331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegoke, J.O.; Pielke, R.A.; Eastman, J.; Mahmood, R.; Hubbard, K.G. Impact of Irrigation on Midsummer Surface Fluxes and Temperature under Dry Synoptic Conditions: A Regional Atmospheric Model Study of the U.S. High Plains. Mon. Weather Rev. 2003, 131, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddeland, I.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Skaugen, T. Effects of irrigation on the water and energy balances of the Colorado and Mekong river basins. J. Hydrol. 2006, 324, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, S.; Döll, P.; Hoogeveen, J.; Faures, J.M.; Frenken, K.; Feick, S. Development and validation of the global map of irrigation areas. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 9, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leff, B.; Ramankutty, N.; Foley, J.A. Geographic distribution of major crops across the world. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2004, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdogan, M.; Rodell, M.; Beaudoing, H.K.; Toll, D.L. Simulating the Effects of Irrigation over the United States in a Land Surface Model Based on Satellite-Derived Agricultural Data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, M.E.; Gleick, P.H. Climate change and California drought in the 21st century. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3858–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, A.L.; Wilhelm, M.; Davin, E.L.; Thiery, W.; Seneviratne, S.I. Can climate-effective land management reduce regional warming? J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 2269–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Ambika, A.K.; Asoka, A.; Aadhar, S.; Buzan, J.; Kumar, R.; Huber, M. Moist heat stress extremes in India enhanced by irrigation. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakauer, N.Y.; Cook, B.I.; Puma, M.J. Effect of irrigation on humid heat extremes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 094010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Smith, J.; Yang, L.; Baeck, M.L.; Ni, G. Regional Impacts of Urban Irrigation on Surface Heat Fluxes and Rainfall in Central Arizona. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 6393–6410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Santamouris, M.; Feng, J. On the cooling potential of irrigation to mitigate urban heat island. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 139754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karstens, K.; Bodirsky, B.L.; Dietrich, J.P.; Dondini, M.; Heinke, J.; Kuhnert, M.; Müller, C.; Rolinski, S.; Smith, P.; Weindl, I.; et al. Management-induced changes in soil organic carbon on global croplands. Biogeosciences 2022, 19, 5125–5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkwasa, A.; Chawanda, C.J.; Jägermeyr, J.; van Griensven, A. Improved representation of agricultural land use and crop management for large-scale hydrological impact simulation in Africa using SWAT+. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grogan, D.S.; Zuidema, S.; Prusevich, A.; Wollheim, W.M.; Glidden, S.; Lammers, R.B. Water balance model (WBM) v.1.0.0: A scalable gridded global hydrologic model with water-tracking functionality. Geosci. Model Dev. 2022, 15, 7287–7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Chen, S.; Qin, P.; Jia, B.; Xie, J. Research on Climate Feedback of Human Water Use and Its Impact on Terrestrial Water Cycles—Advances and Challenges. Adv. Earth Sci. 2019, 34, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Citation Topics Meso | Record | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 1 | Stage 2 | Stage 3 | 2018–2022 | 1993–2022 | |
| Oceanography, Meteorology and Atmospheric Sciences | 57 | 158 | 795 | 469 | 1010 |
| Soil Science | 23 | 53 | 255 | 173 | 331 |
| Forestry | 21 | 29 | 164 | 83 | 214 |
| Crop Science | 12 | 19 | 164 | 176 | 263 |
| Climate Change | 10 | 21 | 184 | 129 | 215 |
| Title | Year | Citations |
|---|---|---|
| China and India lead in greening of the world through land-use management | 2019 | 1084 |
| Impacts of soil and water pollution on food safety and health risks in China | 2015 | 630 |
| Constraints and potentials of future irrigation water availability on agricultural production under climate change | 2014 | 615 |
| Agricultural green and blue water consumption and its influence on the global water system | 2008 | 535 |
| Effective sea-level rise and deltas: Causes of change and human dimension implications | 2006 | 518 |
| Development and testing of the WaterGAP 2 global model of water use and availability | 2003 | 511 |
| Climate change, wine, and conservation | 2013 | 441 |
| A global perspective on wetland salinization: ecological consequences of a growing threat to freshwater wetlands | 2015 | 436 |
| Climate Change Effects on Runoff, Catchment Phosphorus Loading and Lake Ecological State, and Potential Adaptations | 2009 | 426 |
| Water conservation in irrigation can increase water use | 2008 | 414 |
| Impact of land use and land cover change on groundwater recharge and quality in the southwestern US | 2005 | 401 |
| Potential uses and limitations of crop models | 1996 | 380 |
| Effects of climate change on hydrology and water resources in the Columbia River basin | 1999 | 350 |
| Influences of natural and anthropogenic factors on surface and groundwater quality in rural and urban areas | 2015 | 345 |
| Climate change impacts on groundwater and dependent ecosystems | 2014 | 325 |
| Ecological impacts of global warming and water abstraction on lakes and reservoirs due to changes in water level and related changes in salinity | 2015 | 304 |
| Climate change and drought: a risk assessment of crop-yield impacts | 2009 | 279 |
| Impact of reservoirs on river discharge and irrigation water supply during the 20th century | 2011 | 277 |
| Irrigation cooling effect: Regional climate forcing by land-use change | 2007 | 275 |
| From leaf to whole-plant water use efficiency (WUE) in complex canopies: Limitations of leaf WUE as a selection target | 2015 | 267 |
| A reservoir operation scheme for global river routing models | 2006 | 265 |
| Effects of global irrigation on the near-surface climate | 2009 | 260 |
| ICBM: The introductory carbon balance model for exploration of soil carbon balances | 1997 | 253 |
| Global long-term observations of coastal erosion and accretion | 2018 | 244 |
| An investigation of enhanced recessions in Poyang Lake: Comparison of Yangtze River and local catchment impacts | 2014 | 241 |
| US agriculture and climate change: New results | 2003 | 240 |
| The Land Use Model Intercomparison Project (LUMIP) contribution to CMIP6: rationale and experimental design | 2016 | 238 |
| Climate change sensitivity assessment of a highly agricultural watershed using SWAT | 2009 | 238 |
| Simulating the effects of climate and agricultural management practices on global crop yield | 2011 | 220 |
| Drought predisposes pinon-juniper woodlands to insect attacks and mortality | 2013 | 219 |
| Countries | Year | Strength | Begin | End |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA | 1993 | 30.23 | 1993 | 2008 |
| Sweden | 1995 | 3.91 | 1995 | 2010 |
| The Netherlands | 1995 | 6.69 | 2000 | 2011 |
| Germany | 1999 | 4.68 | 2008 | 2009 |
| Spain | 2001 | 4.54 | 2011 | 2012 |
| Australia | 1993 | 7.75 | 2013 | 2016 |
| Finland | 2010 | 4.47 | 2015 | 2018 |
| Iran | 2001 | 4.88 | 2020 | 2022 |
| Institutions | Year | Strength | Span | Country | Freq |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wageningen University & Research | 2000 | 6.96 | 13 | The Netherlands | 63 |
| University of Nebraska Lincoln | 2005 | 3.45 | 3 | USA | 20 |
| University of Florida | 1994 | 4.04 | 11 | USA | 29 |
| University of Florence | 2011 | 3.88 | 2 | USA | 15 |
| University of Copenhagen | 2009 | 4.03 | 6 | Denmark | 14 |
| University of Colorado System | 1999 | 3.64 | 7 | USA | 9 |
| University of Colorado Boulder | 1999 | 3.64 | 7 | USA | 9 |
| University of California System | 2007 | 3.63 | 8 | USA | 82 |
| University of Arizona | 2005 | 3.78 | 9 | USA | 7 |
| University of Agriculture Faisalabad | 2018 | 4.33 | 3 | Pakistan | 23 |
| United States Department of Energy (DOE) | 1994 | 3.99 | 5 | USA | 54 |
| UDICE-French Research Universities | 2016 | 7.09 | 4 | France | 27 |
| Texas A&M University System | 1995 | 4.75 | 5 | USA | 29 |
| Texas A&M University College Station | 1995 | 3.51 | 5 | USA | 25 |
| Sun Yat-Sen University | 2020 | 3.81 | 3 | China | 8 |
| State University System of Florida | 1994 | 4.32 | 15 | USA | 42 |
| Seoul National University (SNU) | 2005 | 3.63 | 3 | Republic of Korea | 8 |
| Potsdam Institut fur Klimafolgenforschung | 1999 | 4.19 | 15 | Germany | 25 |
| National Center Atmospheric Research (NCAR)—USA | 1998 | 3.56 | 7 | USA | 14 |
| National Aeronautics & Space Administration (NASA) | 1995 | 4.26 | 16 | USA | 26 |
| NASA Goddard Space Flight Center | 1995 | 4.28 | 20 | USA | 16 |
| Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory | 2006 | 4.61 | 3 | USA | 7 |
| Institute of Geographic Sciences & Natural Resources Research | 2006 | 3.66 | 2 | China | 74 |
| Indian Institute of Technology System (IIT System) | 1998 | 5.4 | 5 | India | 27 |
| Hohai University | 2014 | 5.58 | 3 | China | 41 |
| CSIC—Estacion Experimental de Aula Dei (EEAD) | 2006 | 3.96 | 4 | Spain | 13 |
| Commonwealth Scientific & Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) | 1993 | 6.47 | 2016 | Australia | 63 |
| Columbia University | 1995 | 3.77 | 2014 | USA | 29 |
| China Institute of Water Resources & Hydropower Research | 2009 | 3.6 | 2020 | China | 27 |
| CGIAR | 1998 | 6.16 | 2017 | France | 70 |
| Cluster ID | Size | Mean Year | Label | Cluster Members (Occurrence Frequency) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 89 | 2015 | water scarcity | resources (110), evapotranspiration (98), river basin (96) |
| 1 | 76 | 2011 | photosynthesis | growth (327), photosynthesis (109), use efficiency (143) |
| 2 | 68 | 2005 | climate change | climate change (1381), model (326), irrigation (447) |
| 3 | 56 | 2010 | greenhouse gas emissions | dynamics (104), carbon dioxide (80), soil (136) |
| 4 | 46 | 2011 | food security | productivity (163), winter wheat (122), food security (106) |
| 5 | 45 | 2004 | soil temperature | soil moisture (103), nitrogen (127), carbon (78) |
| 6 | 35 | 2016 | remote sensing | scale (26), ecosystem services (33), index (30) |
| 7 | 20 | 2002 | risk assessment | yield (306), co2(43), model comparison (4) |
| 8 | 14 | 2015 | irrigation management | change impacts (99), quality (132), crop production (40) |
| Keywords | Year | Strength | 1993–2022 |
|---|---|---|---|
| carbon dioxide | 1994 | 11.01 |  |
| trends | 2007 | 10 |  |
| United States | 2005 | 9.91 |  |
| vegetation | 2007 | 9.2 |  |
| climate | 1995 | 8.88 |  |
| scenarios | 2009 | 7.88 |  |
| model | 1995 | 7.53 |  |
| growth | 1993 | 7.51 |  |
| temperature | 1998 | 7.42 |  |
| water resources | 2005 | 7.37 |  |
| elevated CO2 | 2001 | 6.71 |  |
| biomass | 1999 | 5.92 |  |
| global warming | 2002 | 5.6 |  |
| stomatal conductance | 2009 | 5.37 |  |
| land use | 2008 | 5.25 |  |
| precipitation | 1997 | 5.22 |  |
| CO2 | 1994 | 5.13 |  |
| soil moisture | 2002 | 5.06 |  |
| hydrology | 2013 | 4.82 |  |
| sensitivity | 1997 | 4.71 |  |
| dynamics | 1999 | 4.65 |  |
| global change | 1999 | 4.53 |  |
| gas exchange | 2009 | 4.36 |  |
| spring wheat | 2011 | 4.08 |  |
| organic matter | 2007 | 4.03 |  |
| adjustments | 1995 | 3.97 |  |
| California | 2009 | 3.84 |  |
| respiration | 2011 | 3.78 |  |
| swat model | 2015 | 3.71 |  |
| simulations | 2009 | 3.63 |  |
| tallgrass prairie | 1999 | 3.51 |  |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, S.; Li, S.; Wu, M.; Wang, C.; Yang, D. A Scientometric Analysis of Research Trends and Knowledge Structure on the Climate Effects of Irrigation between 1993 and 2022. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13102482
Huang S, Li S, Wu M, Wang C, Yang D. A Scientometric Analysis of Research Trends and Knowledge Structure on the Climate Effects of Irrigation between 1993 and 2022. Agronomy. 2023; 13(10):2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13102482
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Siyu, Sien Li, Mousong Wu, Chunyu Wang, and Danni Yang. 2023. "A Scientometric Analysis of Research Trends and Knowledge Structure on the Climate Effects of Irrigation between 1993 and 2022" Agronomy 13, no. 10: 2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13102482
APA StyleHuang, S., Li, S., Wu, M., Wang, C., & Yang, D. (2023). A Scientometric Analysis of Research Trends and Knowledge Structure on the Climate Effects of Irrigation between 1993 and 2022. Agronomy, 13(10), 2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13102482






