Influence of Sowing Date of Winter Cereals on the Efficacy of Cinmethylin on Alopecurus myosuroides (Huds.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. Assessment of Herbicide Efficacy and A. myosuroides Density
2.2.2. Determination of Yield
2.3. Statitical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Herbicide Efficacy and A. myosuroides Density
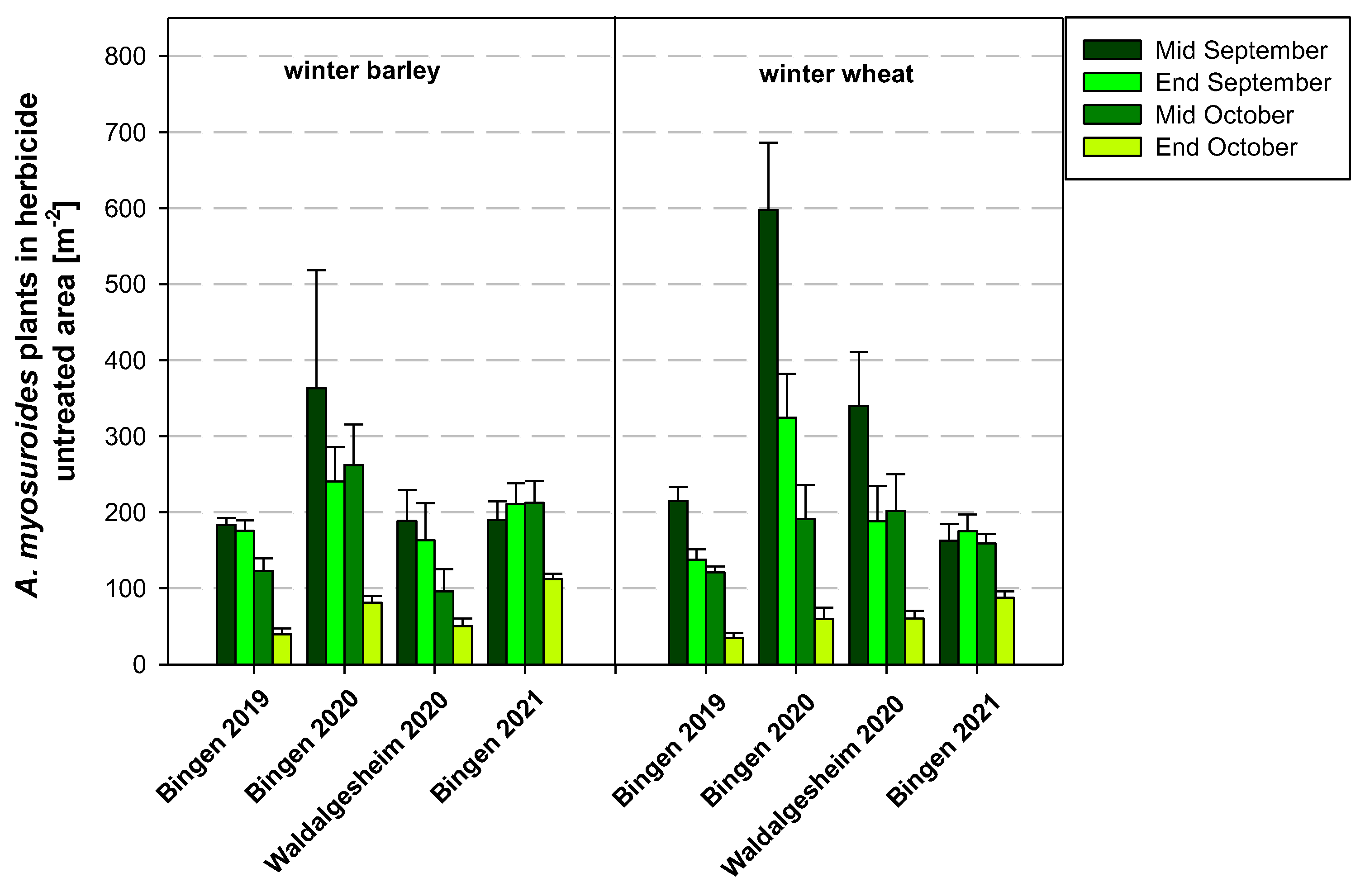
3.1.1. Occurrence of A. myosuroides in Field Trials
3.1.2. Herbicide Efficacy
3.1.3. A. myosuroides Plants and Heads in Herbicide-Treated Areas
3.2. Assessment of Density and Yield of Winter Barley and Winter Wheat
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oerke, E.-C. Crop losses to pests. J. Agric. Sci. 2006, 144, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troyer, J.R. In the beginning: The multiple discovery of the first hormone herbicides. Weed Sci. 2001, 49, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, H.W. Herbicide tolerant strains of weeds. In Hawaiian Sugar Planters Association Annual Report; Hawaiian Sugar Planters Association: Honolulu, HI, USA, 1957; pp. 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Délye, C.; Jasieniuk, M.; Le Corre, V. Deciphering the evolution of herbicide resistance in weeds. Trends Genet. 2014, 29, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heap, I. The International Herbicide-Resistant Weed Database. Available online: www.weedscience.org (accessed on 7 August 2022).
- Lutman, P.Y.W.; Moss, S.R.; Welham, S.J. A review of the effects of crop agronomy on the management of Alopecurus myosuroides. Weed Res. 2013, 53, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizantinopoulos, S.; Katranis, N. Management of Blackgrass (Alopecurus myosuroides) in Winter Wheat in Greece. Weed Technol. 1998, 12, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, A.M.; Cussans, J.W.; Lutman, P.J. A biological framework for developing a weed management support system for weed control in winter wheat: Weed competition and time of weed control. In Proceedings of the 1999 Brighton Conference Weeds, Brighton, UK, 15–18 November 1999; pp. 753–760. [Google Scholar]
- Barralis, G.; Chadoeuf, R.; Longchamp, J.P. Longevité des semences de mauvaises herbes annuelles dans un sol cultivé. Weed Res. 1988, 28, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marèchel, P.Y.; Henriet, F.; Vancutsem, F.; Bodson, B. Ecological review of black-grass (Alopecurus myosuroides Huds.) propagation abilities in relationship with herbicide resistance. Biotechnol. Agron. Soc. Environ. 2012, 16, 103–113. [Google Scholar]
- Moss, S.R.; Cussans, G.W. Variability in the susceptibility of Alopecurus myosuroides (black-grass) to chlortoluron and isoproturon. In Proceedings of the Association of Applied Biologists Aspects of Applied Biology: Conference on the Biology and Control of Weeds in Cereals, Churchill Collage, Cambridge, UK, 25–26 March 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Délye, C. Weed resistance to acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase inhibitors: An update. Weed Sci. 2005, 53, 728–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshtkar, E.; Mathiassen, S.K.; Moss, S.R.; Kudsk, P. Resistance profile of herbicide-resistant Alopecurus myosuroides (black-grass) populations in Denmark. Crop Prot. 2015, 69, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczewski, K.; Kierzek, R.; Matysiak, K. Multiple resistance to acetolactate synthase (ALS)- and acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase (ACCase)-inhibiting herbicides in black-grass (Alopecurus myosuroides Huds.) populations from Poland. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2016, 54, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, J.; Raffel, H. Evolution of Herbicide Resistance in Alopecurus myosuroides and Apera spica-venti in German Cereal Production during the last 15 years. In Proceedings of the 29th German Conference on Weed Biology and Weed Control, Braunschweig, Germany, 3–5 March 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistische Erhebung zur Anwendung von Pflanzenschutzmittel in der Praxis. Available online: https://papa.julius-kuehn.de/index.php?menuid=33 (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Dücker, R.; Parcharidou, E.; Beffa, R. Flufenacet activity is affected by GST inhibitors in blackgrass (Alopecurus myosuroides) populations with reduced flufenacet sensitivity and higher expression levels of GSTs. Weed Sci. 2020, 68, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.G. Cinmethylin, a New Herbicide Developed for use in Rice. In Pest Management in Rice; Grayson, B.T., Green, M.B., Copping, L.G., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campe, R.; Hollenbach, E.; Kämmerer, L.; Hendriks, J.; Höffken, H.W.; Kraus, H.; Lerchl, J.; Mietzner, T.; Tresch, S.; Witschel, M.; et al. A new herbicidal site of action: Cinmethylin binds to acyl-ACP thioesterase and inhibits plant fatty acid biosynthesis. Pestic Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 148, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busi, R.; Dayan, F.E.; Francis, I.; Goggin, D.; Lerchl, J.; Porri, A.; Powles, S.B.; Sun, C.; Beckie, H.J. Cinmethylin controls multiple herbicide-resistant Lolium rigidum and its wheat selectivity is P450-based. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 2601–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messelhäuser, M.H.; Saile, M.; Sievernich, B.; Gerhards, R. Effect of cinmethylin against Alopecurus myosuroides Huds. in winter cereals. Plant Soil Environ. 2021, 67, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BASF’s Luximo® Herbicide Active Substance Approved in Great Britain. Available online: https://www.agricentre.basf.co.uk/en/News-Events/BASF-Ag-Solutions-News/Luximo-is-approved-69696.html (accessed on 13 August 2022).
- University of Hertfordshire Pesticide Properties Database. Available online: http://sitem.herts.ac.uk/aeru/ppdb/en/Reports/331.htm (accessed on 5 December 2022).
- Clark, J.H.; Blair, A.M.; Moss, S.R. The testing and classification of herbicide resistant Alopecurus myosuroides (black grass). Asp. Appl. Biol. 1994, 37, 181–188. [Google Scholar]
- Mühleisen, J.; Piepho, H.P.; Maurer, H.P.; Longin, C.F.H.; Reif, J.C. Yield stability of hybrids versus lines in wheat, barley and triticale. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: http://www.r-project.org (accessed on 14 September 2022).
- Nakagawa, S.; Schielzeth, H. A general and simple method for obtaining R² from generalized linear mixed-effects models. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2013, 4, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colbach, N.; Chauvel, B.; Dürr, C.; Richard, G. Effect of environmental conditions on Alopecurus myosuroides germination. I. Effect of temperature and light. Weed Res. 2002, 42, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menegat, A.; Nilsson, A.T.S. Interaction of preventive, cultural, and direct methods for integrated weed management in winter wheat. Agronomy 2019, 9, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jursík, M.; Soukup, J.; Holec, J.; Andr, J.; Hamouzová, K. Efficacy and selectivity of pre-emergent sunflower herbicides under different soil moisture conditions. Plant Prot. Sci. 2015, 51, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russel, S.G.; Monaco, T.J.; Weber, J.B. Influence of simulated rainfall and soil moisture on herbicidal activity of cinmethylin. Weed Sci. 1990, 38, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landschreiber, M. Field Studies on the Germination Behaviour of Black-Grass (Alopecurus myosuroides Huds.) Depending on Sowing Date and Winter Wheat Variety in Northern Germany. In Proceedings of the 26th German Conference on WEED Biology and Weed Control, Braunschweig, Germany, 11–13 March 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailly, G.C.; Dale, R.P.; Archer, S.A.; Wright, D.J.; Kaundun, S.S. Role of residual herbicide for the management of multiple herbicide resistance to ACCase and ALS inhibitors in a black-grass population. Crop Prot. 2012, 34, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, C.A.; Hager, A.G.; Tranel, P.J.; Davis, A.S.; Martin, N.F.; Williams II, M.M. Future efficacy of pre-emergence herbicides in corn (Zea mays) is threatened by more variable weather. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 2683–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comont, D.; Lowe, C.; Hull, R.; Crook, L.; Hicks, H.L.; Onkokesung, N.; Beffa, R.; Childs, D.Z.; Edwards, R.; Freckleton, R.P.; et al. Evolution of generalist resistance to herbicide mixtures reveals a trade-off in resistance management. Nat. Comun. 2020, 11, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donovan, J.T.; Harker, K.N.; Clayton, G.W.; Hall, L.M. Wild oat (Avena fatua) interference in barley (Hordeum vulgare) is influenced by barley variety and seeding rate. Weed Technol. 2000, 14, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvel, B.; Guillemin, J.P.; Colbach, N. Evolution of a herbicide-resistant population of Alopecurus myosuroides Huds. in a long-term cropping system experiment. Crop Prot. 2009, 28, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Property | Unit | Cinmethylin |
|---|---|---|
| Solubility in water (20 °C) | mg L−1 | 58.0 |
| Dissociation constant (25 °C) | Not available | |
| Vapor pressure | mPa | 8.1 |
| Dissipation time 50 (field) | d | 22.4 |
| Dissipation time 90 (field) | d | 111.5 |
| Koc (soil adsorbtion) | 6850 |
| Field Trial | Site | Vegetation Season | Previous Crop | Soil Type | OM (LOI %) | pH-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bingen | 2019/20 | Lupine | Sandy loam | 2.1 | 6.9 |
| 2 | Bingen | 2020/21 | Wheat | Loam | 2.0 | 6.6 |
| 3 | Waldalgesheim | 2020/21 | Wheat | Loam | 2.2 | 7.6 |
| 4 | Bingen | 2021/22 | Maize | Loam | 2.3 | 7.5 |
| Field Trial | Alopecurus myosuroides Population | Resistance Factor | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.2 L ha−1 Axial® 50 (2) | 2.5 L ha−1 Focus® Ultra (3) | 240 g ha−1 Broadway® (4) | 330 g ha −1 Atlantis® flex (5) | ||
| 1 | Occurred | - | - | - | - |
| Sown | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 2 | Occurred (1) | 4 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| Sown | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 3 | Occurred | 4 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| Sown | - | - | - | - | |
| 4 | Occurred (1) | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Sown | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Crop | Treatment | Herbicide (Supplier (1)) | Formulation (2) | Active Ingredient | HRAC (3) Code | Concentration (g L−1 or kg−1) | Applied (g a.i. ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Winter wheat | 1 | Luxinum® (BASF SE) | EC | cinmethylin | 30 | 750 | 500 |
| Pico® 750 (BASF SE) | WDG | picolinafen | 12 | 750 | 50.25 | ||
| 2 | Herold® SC (ADAMA) | SC | flufenacet | 15 | 400 | 240 | |
| diflufenican | 12 | 200 | 120 | ||||
| Winter barley | 1 | Luxinum® (BASF SE) | EC | cinmethylin | 30 | 750 | 250 |
| Pontos® (BASF SE) | SC | flufenacet | 15 | 400 | 144 | ||
| picolinafen | 12 | 100 | 60 | ||||
| 2 | Herold® SC (ADAMA) | SC | flufenacet | 15 | 400 | 240 | |
| diflufenican | 12 | 200 | 120 |
| Field Trial | Site | Vegetation Season | Sowing Date | Precipitation (L m−2) | Average Temperature (°C) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 Days before Sowing (Sum) | 7 Days after Sowing (Sum) | 7 Days before Sowing | 7 Days after Sowing | ||||
| 1 | Bingen | 2019/20 | 16th September | 0.0 | 20.0 (1) | 17.0 | 14.0 |
| 30th September | 12.5 | 17.7 | 15.3 | 11.9 | |||
| 15th October | 7.0 | 19.4 | 13.5 | 13.5 | |||
| 30th October | 2.6 | 20.0 | 8.7 | 8.4 | |||
| 2 | Bingen | 2020/21 | 23rd September | 0.0 | 15.2 | 17.4 | 13.5 |
| 5th October | 10.1 | 9.5 | 12.7 | 12.0 | |||
| 19th October | 2.0 | 6.9 | 8.5 | 11.7 | |||
| 2nd November | 13.4 | 0.2 | 13.2 | 7.6 | |||
| 3 | Waldalgesheim | 2020/21 | 23rd September | 14.0 | 5.5 | 14.3 | 14.7 |
| 5th October | 5.0 | 4.5 | 13.4 | 10.4 | |||
| 19th October | 4.5 | 12.0 | 8.3 | 8.2 | |||
| 2nd November | 0.0 | 22.0 | 8.3 | 6.7 | |||
| 4 | Bingen | 2021/22 | 21st September | 7.7 | 4.0 | 15.8 | 15.2 |
| 5th October | 6.2 | 4.9 | 13.6 | 10.4 | |||
| 18th October | 3.0 | 10.7 | 8.8 | 8.7 | |||
| 2nd November | 10.9 | 14.8 | 8.3 | 7.0 | |||
| Responsible Variable | Crop | Random Effect | Variance | Standard Deviation | Marginal R2 | Conditional R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Herbicide efficacy [%] (1) | barley | Split plot | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.131 | 0.614 |
| Environment | 0.02 | 0.16 | ||||
| Residual | 0.03 | 0.18 | ||||
| wheat | Split plot | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.224 | 0.603 | |
| Environment | 0.03 | 0.16 | ||||
| Residual | 0.04 | 0.19 | ||||
| A. myosuroides plants m−2 herbicide-treated (2) | barley | Split plot | 0.37 | 0.61 | 0.255 | 0.763 |
| Environment | 0.94 | 0.97 | ||||
| Residual | 0.61 | 0.78 | ||||
| wheat | Split plot | 0.43 | 0.66 | 0.275 | 0.698 | |
| Environment | 0.79 | 0.89 | ||||
| Residual | 0.87 | 0.93 | ||||
| A. myosuroides heads m−2 herbicide-treated (2) | barley | Split plot | 0.53 | 0.73 | 0.303 | 0.692 |
| Environment | 0.44 | 0.66 | ||||
| Residual | 0.77 | 0.88 | ||||
| wheat | Split plot | 0.32 | 0.57 | 0.200 | 0.784 | |
| Environment | 2.36 | 1.54 | ||||
| Residual | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| Responsible Variable | Crop | Random Effect | Variance | Standard Deviation | Marginal R2 | Conditional R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cereal heads m−2 herbicide-untreated | barley | Split plot | 898.6 | 29.98 | 0.222 | 0.676 |
| Environment | 5224.6 | 72.28 | ||||
| Residual | 4370.5 | 66.11 | ||||
| wheat | Split plot | 628.0 | 25.06 | 0.561 | 0.645 | |
| Environment | 190.5 | 13.80 | ||||
| Residual | 3463.0 | 58.85 | ||||
| Cereal heads m−2 herbicide-treated | barley | Split plot | 1462.0 | 38.24 | 0.220 | 0.787 |
| Environment | 4729.0 | 68.77 | ||||
| Residual | 2328.0 | 48.25 | ||||
| wheat | Split plot | 1001.0 | 31.64 | 0.439 | 0.755 | |
| Environment | 2145.0 | 46.31 | ||||
| Residual | 2430.0 | 49.30 | ||||
| Grain yield dt/ha (86% dry matter) | barley | Split plot | 153.2 | 12.38 | 0.368 | 0.926 |
| Environment | 219.2 | 14.81 | ||||
| Residual | 49.5 | 7.04 | ||||
| wheat | Split plot | 30.0 | 5.48 | 0.410 | 0.844 | |
| Environment | 168.7 | 12.99 | ||||
| Residual | 71.2 | 8.44 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klauk, B.; Petersen, J. Influence of Sowing Date of Winter Cereals on the Efficacy of Cinmethylin on Alopecurus myosuroides (Huds.). Agronomy 2023, 13, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010037
Klauk B, Petersen J. Influence of Sowing Date of Winter Cereals on the Efficacy of Cinmethylin on Alopecurus myosuroides (Huds.). Agronomy. 2023; 13(1):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010037
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlauk, Benjamin, and Jan Petersen. 2023. "Influence of Sowing Date of Winter Cereals on the Efficacy of Cinmethylin on Alopecurus myosuroides (Huds.)" Agronomy 13, no. 1: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010037
APA StyleKlauk, B., & Petersen, J. (2023). Influence of Sowing Date of Winter Cereals on the Efficacy of Cinmethylin on Alopecurus myosuroides (Huds.). Agronomy, 13(1), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010037






