Abstract
Since the year 2012, nationwide monitoring of erosion on agricultural land has been carried out in the Czech Republic with more than 2,300 cases of erosion events recorded so far. The evaluation of the relationships between the actual manifestation of erosion and the characteristics of the 5600 erosion enclosed areas (EEAs), on which surface runoff develops after erosion-forming rainfall, are presented in this contribution. Most frequently grown crops during an erosion event include maize (49.8% of cases), rapeseed (13.7%), potatoes (8.1%) and sugar beets (2.1%). The distributions of affected erosion enclosed areas (EEAs) in terms of shares of soils with low susceptibility and medium susceptibility to compaction, drainage systems and contributing areas of critical points are bimodal; the low percentage (<10%) being more prominent than the high one (>90%). The percentage of hydrologic soil group B in EEA has the high share dominant over the low one. Unsurprisingly, erosion events have been recorded predominantly in EEAs with low forest cover and on arable land (share >90%). The distribution of EEAs across altitudes corresponds with the relief of the country. Obtained results will be used to validate the implementation of erosion-monitoring systems and for the adaptation of soil erosion prevention and mitigation measures in the sustainable land use policy.
1. Introduction
The Czech Republic (CZ) has the highest average land block size (Land Parcel Identification System, LPIS, productive blocks) for arable land in the EU [1]. According to the LPIS, the average land block size is 6.5 ha and 10.7 ha in the case of arable land. However, it is not uncommon for land blocks to be in excess of 100 ha, which can lead to intensive water erosion. More than ~60% of arable land in CZ is threatened by water erosion particularly due to large scale farming of monoculture crops prone to erosion without any erosion control measures.
This is largely a result of 1950s collectivisation of land and subsequent changes in farming practices, a reduction in the percentage of grassland in production areas, and an increase in the average field size [2]. Despite systems of complex anti-erosion measures available to farmers which could provide effective protection for soil on farm land, the majority of arable land in CZ suffers from heavy water erosion, both on slopes and in channels of concentrated runoff.
Blocks of arable land on which erosion occurs are generally large in area, with a significant gradient, and located on lengthy slopes. Due to morphological segmentation, channels of concentrated runoff often develop in these areas.
According to the World Meteorological Organization [3], among the most dangerous causes of worldwide natural disasters is intensive storm rainfall and the rapid formation of concentrated surface runoff and creating so-called flash floods which are connected with the transport of sediment and landslides. Changes in the natural climatic and hydrological cycles cause ever-increasing fluctuation in extreme events such as periods of drought or events of intense rainfall creating surface runoff with a negative impact on land and built-up land [4,5]. One of the global problems associated with surface runoff is the increasing level of urbanisation. It is estimated that, by the year 2050, urban areas will cover almost 64% of land in developing countries and 86% in developed countries [6,7]. Thus, there is an increasing risk of the product of erosion events (sediment) reaching built-up areas as a result of intensive rainfall. This can be seen in densely populated central Europe, where flooding occurs frequently, with sediment transported into built-up areas or water source areas causing extensive damage [8]. The causes and effects of soil erosion have been described by various authors from many viewpoints as geographical, geomorphological, pedological, agronomic etc. [9,10,11,12]. In order to determine the characteristics of sub-basins or contributary areas, many authors recommend geomorphometric analysis of the land which provides physical-geographical information on the catchment basin such as slope gradient, configuration and shape of relief, length of slopes, river network, etc. [13,14,15,16].
Development of the methods and geographical information systems enables the generation of basic data for multicriterial judgement and the use of various models for calculating soil loss, sediment transport, hydrological simulation etc., for the implementation of systems of complex measures to protect soil and water at the level of whole catchment basins [17,18,19].
Surface runoff, in relation to the given characteristics of a catchment basin, is one of the main elements, not only generally in the hydrological cycle that influences the amount of water delivered into the river systems [20], but is also the cause of fluvial erosion processes due to its negative effect. One of the significant factors influencing surface runoff is the low retention capability of soil and landscape due to the intensive agricultural use of the landscape [21,22] in particular. This is evident in the current state of erosion threat to arable land in various countries [23,24,25]. Other factors influencing surface runoff having a negative effect on farm land and threatening built-up areas include topographic, morphological, hydrogeological, and pedological relationships, along with the presence of vegetation cover on the land [12,17]. The retention capability of the soil and landscape and their ability to hold rainfall in the catchment basin depends on the factor of vegetation cover and the characteristics of the hydric regime of agricultural and forest soils [26]. Yin et al. [27] describe the importance and function of landscape cover in the case of the negative influence of deforestation. Manifestations include a change in surface roughness, poorer soil infiltration, and, eventually, a rapid increase in the intensity of concentrated surface runoff with distinct signs of water erosion and possible landslides. Another risk is posed by inappropriate intensive use of agricultural land where soil compaction reduces the soil’s capability to take in water, thus increasing the danger of flash flooding and the risk of the transport of erosion products—sediment—to water courses, reservoirs, and built-up areas [28,29].
Various studies [30,31,32] describe direct runoff as the amount of rainwater that drains off the soil surface after causal rainfall or snowmelt. Several authors [33,34,35] state that a crucial influence on the formation of surface runoff is played by the intensity of rainfall, the topography of terrain (gradient, length, and shape of slope), soil characteristics (texture, content of organic matter, compaction, soil erodibility), and land use.
Of equal importance are aspects of the timing of erosion-forming rainfall, in terms of the state of plant development, especially in the period between preparing the land for sowing and the crop forming an interlinked cover with an anti-erosion effect in synergy with the gradual consolidation of the soil, and an increasing level of shear stress. The shear stress level depends on the characteristics of a given soil (texture, clay, water, and humus content) [32]. It has been found that land worked under no-till methods could have up to twice the shear stress level of land worked under conventional tillage. A further significant factor is the type of vegetation cover and the level to which the soil is stabilised by plant roots [36].
Since 2012, events of erosion have been systematically recorded which provides feedback for the Ministry of Agriculture and the Ministry of the Environment on the nationwide problem of erosion and the effectiveness of implemented anti-erosion measures. The Czech Republic is the only country carrying out such systematic monitoring and evaluation of erosion events. The purpose of the Monitoring of the Erosion (MoE) is gathering, recording, and evaluating information on erosion events on agricultural land in order to create a spatial database of erosion events which provides a source for developing preventive and mitigation measures for effective erosion control including new policies [37]. Since 2017, if an evaluated erosion event meets selected criteria, the Ministry of Agriculture tightens the rules for farming on concerned land (~5500 ha so far) with respect to the subsidies. From 2021, MoE has become a part of national legislation on the protection of agricultural land against soil erosion (Decree No. 240/2021 Coll.) The actual process of monitoring erosion on agricultural land is conducted on the basis of the Ministry of Agriculture Regulation No. 15/2012 and approved procedures, which set out the obligations and the level of involvement of individual organisations. The records of erosion events (Figure 1) are compiled by trained and authorised staff of land registry offices (around 140 staff). After an erosion event report, an on-site field survey takes place with photo-documentation and information gathering on the circumstances. Eventually missing data are subsequently added. The inspection and editing of records is performed in order to maintain consistency and accuracy of the database and is carried out in the Research Institute for Soil and Water Conservation (RISWC), while supplementing the data with further analysis, e.g., from digital elevation models. Erosion events have been regularly recorded since 2012. Earlier events have also been added provided all relevant information was available; there have been 2395 entries so far, of which 319 are repeated events. This project is funded by the State Land Office (SLO).
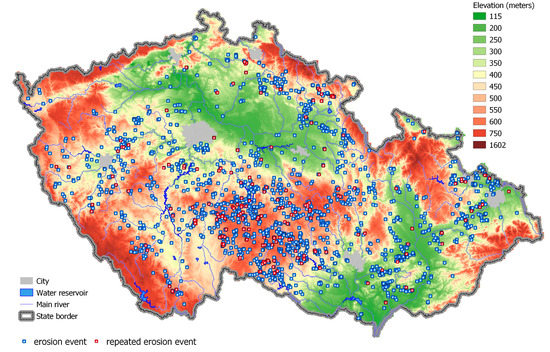
Figure 1.
Recorded erosion events in the Czech Republic up to 10 August 2022. Altitudes are given by the system Balt after normalizing.
This contribution uses data and accompanying information from MoE to investigate and evaluate individual erosion events and the characteristics of the land that (do or might) play an important role in terms of the vulnerability of the soil to water erosion, and the negative impact both on the area itself (on-site), and beyond (off-site, as transport of sediment into water courses, reservoirs, and built-up areas). Land cover (crops), the amount of arable land, and forest stands are considered as well as other parameters of locations affected by erosion events including the presence of contributing areas of critical points that may endanger municipalities below, the availability of drainage systems, the hydrological soil group percentages, the share of soil susceptible to compaction and altitude distribution of sites. Obtained results are and will be used to validate the implementation of erosion-monitoring systems and the proposal of erosion control measures for sustainable land management policy.
Given that the MoE is a unique nationwide system, the authors aim to present the availability of (verified, meaningful) data to all stakeholders including the scientific community in a compact and clean way in terms of data and visuals. This will be achieved by highlighting the features in terms of the areas affected by erosion events, thus allowing readers to draw their own conclusions. Further research beyond the scope of this contribution is expected to follow, hopefully with more participation from international experts.
2. Materials and Methods
The basic observed land unit is an enclosed erosion area (EEA, Figure 2) that is defined as a connected area of land with locally enclosed erosion processes i.e., denudation, transport, and deposition of soil [32]. It is an area of agricultural land bounded by watersheds, on which surface runoff develops, and barriers where surface runoff is interrupted. There can be several such areas within a block of land, or one EEA may cover several parts of a land block. This contribution is based on analysing a large file of 5600 EEAs affected by water erosion recorded in the years 2012–2021.
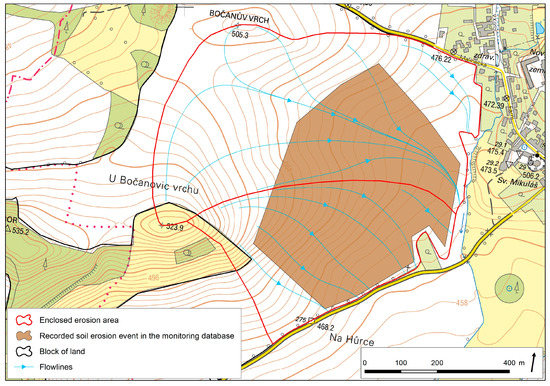
Figure 2.
An example of the relation of EEA and a reported and recorded erosion event.
An erosion event is a time limited occurrence where, due to a rainfall, soil particles are disturbed and transported from agricultural land, and this transported material is deposited as sediment. The negative effects of erosion events are the reduced depth of the soil profile on eroded areas, covering of the soil profile in sedimentation areas, creation of an erosion profile which complicates farming of the land, or the silting of roads or other non-agricultural areas, water courses, and reservoirs with soil particles. (Figure 3). For the purposes of erosion monitoring, the events are divided into the following types: sheet, rill, gully, and channel erosion. Their occurrence is as follows: channel 2.09%, gully 46.43%, rill 25.31%, sheet 26.17%.
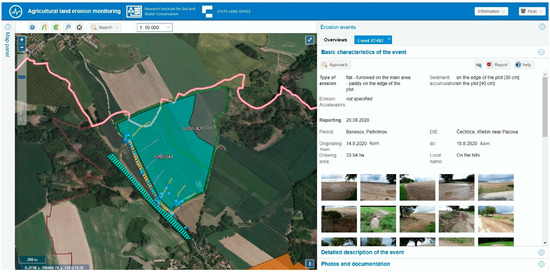
Figure 3.
An example of a recorded soil erosion event in the monitoring database (MoE).
For each erosion event, the following information is recorded and analyzed: the date and time of the occurrence, the type of erosion event (form of erosion), a description of the erosion circumstances, the character, intensity, and amount of rainfall, the area affected by erosion, the form and extent of soil degradation, the location of the event, the crops grown, the character of the vegetation cover on the land, the forms of tillage used, damage to the land and other property, photo-documentation, and a position marked on a map. All information is processed in GIS and made available to authorised users on the erosion monitoring (MoE) website https://me.vumop.cz/app/ (accessed on 15 November 2022).
To identify areas for evaluation of erosion processes, EEAs were generated for all Czech agricultural land resources (ALR) by the means of advanced GRASS GIS algorithms. The basis for analysis was the DMT 4G model (Digital Terrain Model of the Czech Republic of the 4th generation, https://geoportal.cuzk.cz, accessed on 11 November 2021) with a pixel definition of 5 × 5 m, which has a mean deviation of 1 m in broken terrain, and 0.3 m in open terrain. It was specially adapted for the purpose of hydrological analysis, so that runoff from local depressions and otherwise runoff-free areas were identified. Specifically, for generating EEAs, the model was further refined with focal analysis using a circular filter with a diameter of 9 pixels.
For roads and railways, 10 m height was added in order to ensure interruption of the runoff. The effect of hydrotechnical elements, such as culverts along roads, have not been considered due to the scope of mapping of erosion events for the entire territory of the Czech Republic. This simulated interruption can be expected at drainage embankments or landscape cuttings. On the other hand, for open water courses, their elevation was reduced by 10 m due to the same reason of interrupting surface runoff. After EEAs generation, it was necessary to minimize their number and complexity. In the first rough model, there were more than 3 million EEAs. For application purposes, they were limited in size to the boundaries of current land blocks. The total number of EEAs thus generated was 1,812,897 with an average area of 2 hectares and an average LSI index of 1.5. Within such EEA, it is now possible to assess the state of runoff and erosion processes.
All erosion events in the time period from 2012 to 2021 in 5,869 affected EEAs have been analysed in terms of:
- Distribution of EEAs according to the share of contributing areas of critical points (CPs) being the places where generated paths of concentrated surface run-off enter urbanised spaces [38]. Flooding risk arises from the threat to built-up areas lying below a given critical point. Municipal areas include whole urban zones (residential buildings in particular).
- Share of drainage systems (DS) in an EEA.
- Percentage of land types in an EEA according to the registry of the Land Parcel Identification System (LPIS), https://eagri.cz/public/app/lpisext/lpis/verejny2/plpis/ (accessed on 11 November 2021).
- Hydrologic Soil Group (HSG) share in an EEA by the category, A—soils with a high infiltration rate, B—soils with an average infiltration rate, C—soils with a low infiltration rate, D—soils with a very low infiltration rate.
- Proportion of soil compaction susceptibility categories in an EEA (SC1 slightly, SC2 moderately, SC3 heavily).
- Distribution of EEAs by altitude. 67% of the Czech Republic territory lies below 500 m above the sea level, 32% in the range 500–1000 m, and ~ 1% above 1000 m.
Data on erosion events are located using geographic coordinates (GPS) and stored in a spatial database (POSTGRESQL/POSTGIS).
For the needs of complementary analyses, a combination of data sources from the LPIS and Fundamental Base of Geographic Data of the Czech Republic (ZABAGED) have been used. ZABAGED is a digital geographic model of the territory of the Czech Republic that consists of 134 feature types such as settlements, communications, utility networks and pipelines, hydrography, administrative units and protected areas, vegetation and land cover, terrain relief, and selected data about survey control points (https://geoportal.cuzk.cz, accessed on 20 November 2022).
The database of certified/validated soil ecological units (BPEJ) has been used for soil information. BPEJ is used to evaluate the absolute and relative production capacity of agricultural land and the conditions for efficient use (https://bpej.vumop.cz/, accessed on 20 November 2022).
A preliminary overview of the data clearly indicates complex (not normal) distributions; therefore, the methods of exploratory (scatterplot, determining of basic parameters) data analysis (EDA) accompanied with nonparametric correlations (Kendall’s tau), statistical tests (Kolmogorov-Smirnov), and visualisation by histograms have been chosen for producing compact and clean visualising (the complexity of data processing lying hidden in the countrywide determination of EEAs, their characteristics, and derivation of their distribution from the monitoring of erosion events).
Final validating analyses and presentation of data have been mostly done in the R, free software environment for statistical computing and graphics (https://www.r-project.org/, accessed on 20 November 2022).
3. Results and Discussion
The recorded erosion events took place virtually in all regions of the Czech Republic with different natural conditions; 2395 in total, Figure 4.
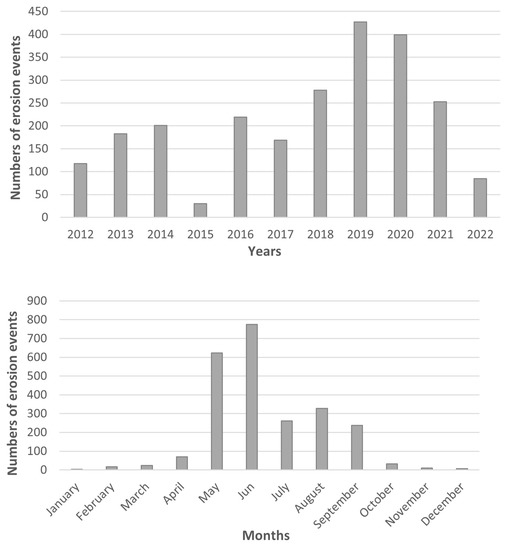
Figure 4.
Cumulative numbers of erosion events by the years and months.
Enclosed erosion areas (EEAs) affected by an erosion event had the range of the soil erodibility factor (K), given as a weighted average for every concerned plot, 0.15–0.6 with a 0.34 median. The erosive efficiency factor of rainfall (R), expressed as a local R factor value from the USLE ranges from 36.6 to 73.9 with a 53.4 median. The slope of the affected plots was calculated as a weighted average for each plot and its values range from 0.2° to 14.6° with a 3.6° median. The plot sizes in the erosion areas are distributed as follows: 24.9% between 0.4 and 5 ha, 59% between 5 and 50 ha and 16.1% of 50 ha and more. At the time of the erosion event, the following crops were most often grown on the land: maize (49.8% of cases), rapeseed (13.7%), potatoes (8.1%), sugar beets (2.1%), cereals (13.5%), and other crops (12.8%). Vegetation cover by erosion-prone crops had a negative effect, whereas maize and winter rapeseed were most frequent at the time of an erosion event in approximately 74% of the total cases. Maize was particularly problematic, as having higher participation in erosion events (49.8% of all cases) than the countrywide share of this crop (12.6% of arable land in the Czech Republic, CSO, 2021). The erosion events for winter rapeseed are at 13.7%, which is similar to its percentage in the crop structure (14.8% of arable land).
Other broad-row crops can also be problematic. Potatoes are currently grown on only about 1% of arable land, but erosion events account for 8.6% of all recorded cases. The percentage of areas with cultivated sugar beets is 2.4% in crop structure, and 2.1% in reported erosion events. The difference between the recorded cases of the erosion events for potatoes and sugar beets is due to the fact that the more erosion problematic potatoes are grown at higher altitudes and on sloped land. Cereals grown on 50.6% of arable land have a lesser occurrence of erosion events at 13.5% of the total. The composition of crops in the Czech Republic is significantly influenced by the current crop market and the economic interests of farmers. In this context, the results of our study are consistent with those obtained by other authors [39,40].
A total of 80,103 ha of agricultural land was affected by recorded erosion events in the Czech Republic within the 9-year monitored period. In terms of the frequency of the events, 81.1% of the areas were affected by 1 erosion event, 14.8% by 2, 2.7% by 3, 1% by 4, 0.3% by 5 and 0.2% by more than 5 events in the period of 2012–2021. Monitored erosion events seem to be related [12,31,32] to characteristics of the source areas.
In terms of the characteristics of affected EEAs, there is a single, stronger correlation (Figure 5, tau = −0.875), but a number of significant weaker correlations which illustrate the complex distributions as depicted by histograms below. None of the distribution seems to meet normality criteria (also verified by the one sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov, KS, tests in each case) and none but one KS two-sample test has shown any evidence for real similarity in statistical dispersion of the data (the single exception being the HSG.D and SC3, heavily). The authors mean that histograms represent the situation in a compact and clean way by allowing readers to directly see the variability highlighting the features for orientation thereby allowing readers to draw their own conclusions
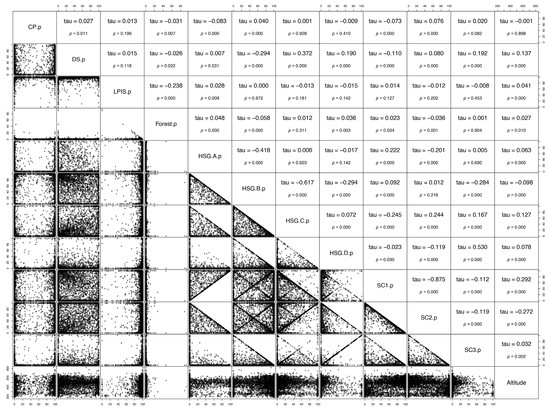
Figure 5.
Scatterplot matrix of the full dataset representing the characteristics of EEAs by parameters with Kendall’s tau correlations above the diagonal.
The number of EEAs with erosion events was 3600 in the category of < 10% coverage by contributing areas of critical points (CP) endangering municipalities (Figure 6). The second maximum (1750) was in the category of >90%, when concentrated surface runoff entered the built-up area of a municipality, which indicates the need to respond by setting stricter erosion protection rules for land located in the contributing area of the critical points.
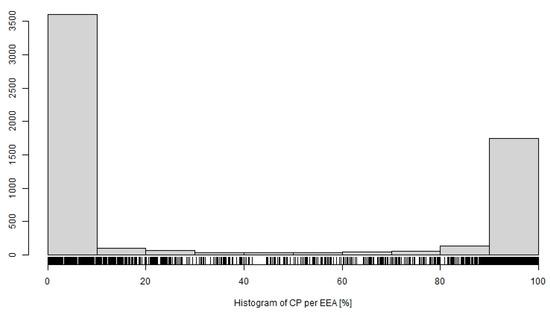
Figure 6.
Distribution of EEAs by percentage of contributing areas of critical points (CP) endangering municipalities. Characteristics of horizontal axis are as follows: Min.: 0.00%; Q1: 0.00%; Median: 0.00%; Mean: 34.44%; Q3: 98.10%; Max.: 100.00%; SD: 45.38%.
Blann et al. [41] state that the drainage of agricultural land affects the hydrology of the area (Figure 7), soil erosion, transport of nutrients and pesticides, greenhouse gas emissions and biological diversity. On drained land, there may be less surface runoff and soil erosion [42,43]. Also, Skagges et al. [44] state that erosion on the soils studied could be visibly reduced by subsurface drainage. This is confirmed by the results of two experiments in the Oregon region [45]. Research by Oygarden et al. [46] show that soil particles can be eroded from the topsoil and transported both laterally and vertically through macro-pores and cracks towards the drainage system. The importance of these cracks for the movement of water and soil particles into drainage systems has also been described in studies within basin [47,48]. However, our analysis of erosion events did not indicate a major influence of horizontal drainage on the occurrence of erosion events. The largest share of erosion events (3503) was unsurprisingly in the EEAs with <10% of drainage systems (DS), but the second maximum in the category of >90%.
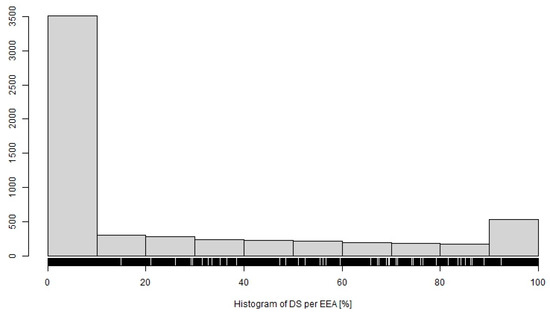
Figure 7.
Distribution of EEAs by percentage of drainage systems (DS). Characteristics of horizontal axis are as follows: Min.: 0.00%; Q1: 0.00%; Median: 0.00%; Mean: 23.45%; Q3: 43.00%; Max.:100.00%; SD: 33.62%.
In terms of the representation of land types (Figure 8) within the EEAs, arable land was most prone to erosion (5514 events in the range of >90% coverage). As expected EEAs with minimal forest stands (<10%) have been most hit, but there were (rare) recorded events also in forested areas.
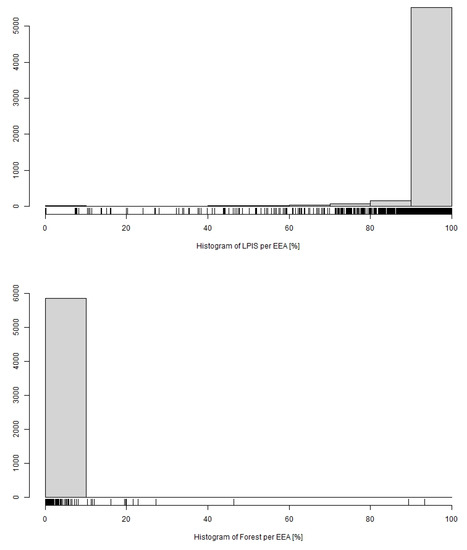
Figure 8.
Distribution of EEAs by percentage of arable (LPIS) and forested land (Forest). Characteristics of horizontal axis (LPIS) are as follows: Min.: 0.00%; Q1: 98.30%; Median: 99.60%; Mean:97.00%; Q3: 99.90%; Max.:100.00%; SD: 9.99%. Characteristics of horizontal axis (Forest) are as follows: Min.:0.00%; Q1:0.00%; Median:0.00%; Mean: 0.15%; Q3: 0.00%; Max.: 93.30%; SD: 2.00%.
The Share of Hydrologic Soil Group (HSG, Figure 9) is related to the direct outflow on an EEA. The highest occurrence was recorded on HSG B (3067 events for EEAs with >90% share), which is related to the highest areal extent of this category soils in the Czech Republic. A high percentage of other HSG in an EEA was not a major factor for erosion events, which is also in accordance with the representation of HSG on agricultural land in the Czech Republic: HSG A 8.9%, HSG B 60.3%, HSG C 19.8% and HSG D 11.1%.
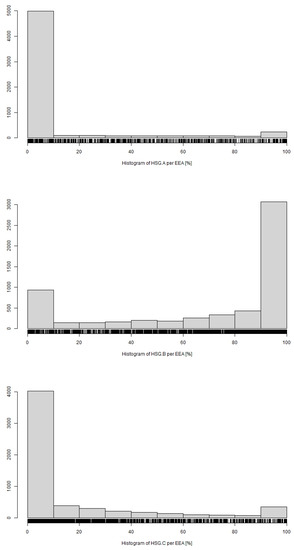

Figure 9.
Distribution of EEAs by percentage of HSG (HSG.A, B, C, D). Characteristics of horizontal axis (HSG.A) are as follows: Min.: 0.00%; Q1: 0.00%; Median: 0.00%; Mean: 9.27%; Q3: 0.00%; Max.: 100.00%; SD: 24.64%. Characteristics of horizontal axis (HSG.B) are as follows: Min.: 0.00%; Q1: 44.10%; Median: 92.50%; Mean: 70.56%; Q3: 100.00%; Max.: 100.00%; SD: 37.54%. Characteristics of horizontal axis (HSG.C) are as follows: Min.: 0.00%; Q1: 0.00%; Median: 0.00%; Mean: 15.95%; Q3: 19.70%; Max.: 100.00%; SD: 28.42%. Characteristics of horizontal axis (HSG.D) are as follows: Min.: 0.00%; Q1: 0.00%; Median: 0.00%; Mean: 4.05%; Q3: 0.00%; Max.: 100.00%; SD: 15.16%.
Compaction is considered one of the main causes of soil degradation and has a negative impact on its physical, chemical, and biological properties that can subsequently lead to increased risk of erosion, water, and nutrients runoff into waterways and increased risk of flooding [49,50,51,52]. Surface runoff and erosion increases with increasing bulk density and reduced infiltration [53]. Another risk is improper intensive use of agricultural land causing soil compaction (46% of EAAs were prone to compaction) reducing the infiltration capacity of the soil which increases the risk of erosion, surface runoff, and sediment transport into waterways, reservoirs, and built-up areas [28,29].
The highest abundance of EEAs is in the low (<10%) segment of all soil compaction (SC) susceptibility (Figure 10) categories (slightly, moderately, heavily). In the case of the slightly and moderately susceptibility to compaction soils, there are prominent second maxima in the highest share segment (>90%). The heavily susceptible have an observable rise there.
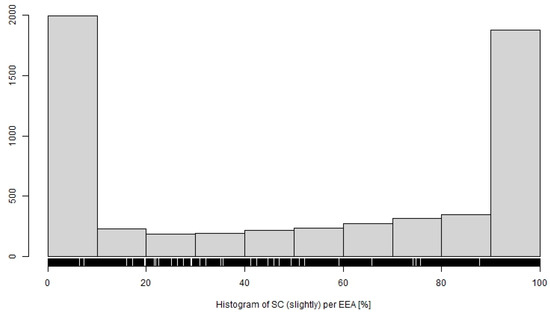

Figure 10.
Distribution of EEAs by percentage of SC (slightly, moderately, heavily). Characteristics of horizontal axis SC (slightly) are as follows: Min.: 0.00%; Q1: 0.00%; Median: 55.30%; Mean:50.42%; Q3: 98.50%, Max.: 100.00%; SD: 42.24%. Characteristics of horizontal axis SC (moderately) are as follows: Min.: 0.00%; Q1: 0.00%; Median: 36.30%; Mean: 45.46%; Q3: 98.00%; Max.: 100.00%; SD: 42.04%. Characteristics of horizontal axis SC (heavily) are as follows: Min.: 0.00%; Q1: 0.00%; Median: 0.00%; Mean: 3.95%; Q3: 0.00%; Max.: 100.00%; SD: 15.10%.
The total representation of soils in the Czech Republic with low susceptibility to compaction is 21.5%, with medium susceptibility at 16.9% and with high susceptibility at 16.2%.
Most erosion events occurred in EEAs with altitudes of 400–600 m above the sea level (3182). The second highest frequency was recorded at 200–400 m altitudes (2214). Bednář and Šarapatka [54] described the greater risk of erosion at higher altitudes for the conditions of the Czech Republic in a study on physical–geographical factors and soil degradation. There was a smaller number of erosion events above 600 m, with higher percentage/predominance of grassland, where erosion events were hardly recorded by the monitoring process (Figure 11).
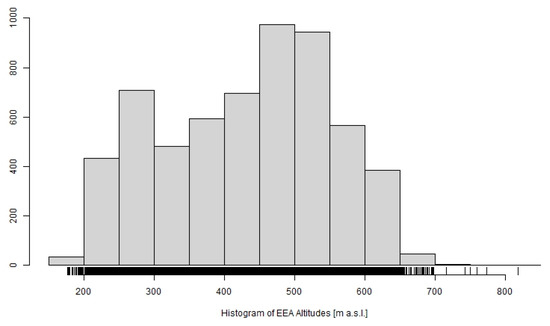
Figure 11.
Distribution of EEAs by altitudes. Characteristics of horizontal axis are as follows: Min.: 177.0 m; Q1: 333.0 m; Median: 450.0 m; Mean: 432.9 m; Q3: 523.0 m; Max.: 818.0 m; SD: 119.8 m.
4. Conclusions
Since 2012, numerous (2362) erosion events occurred in virtually all regions of the Czech Republic. The nationwide erosion monitoring records are mirrored by the distribution of affected erosion enclosed areas (EEAs) across altitudes that correspond to the relief of the country. The crops frequently grown during an erosion event include maize (49.8% of cases), rapeseed (13.7%), potatoes (8.1%), and sugar beets (2.1%). The distributions of percentages in EEA for contribution areas of critical points (CPs) include drainage systems (DS), soils with low susceptibility to compaction (SC slightly) and medium susceptibility (SC moderately) have peaks on both ends, and the low percentage (<10%) being more prominent than the high percentage end (>90%). The proportion of hydrologic soil group (HSG) B has the high percentage (>90%) that is dominant over the low one (<10%). Erosion events have been recorded predominately on arable land (LPIS, share >90%) and in EEAs with low forest cover (Forest, <10%), as expected. Low percentages (<10%) on EEAs are the most frequent for HSG A, HSG C, HSG D, and SC (heavily). The presented results indicate the need of adjusting/tightening erosion protection regulations to prevent or mitigate erosion events including floods that endanger municipalities. An adequate size of plots on soil endangered by erosion should be one of the decisive requirements for the provision of agricultural subsidies in the future. The results obtained from erosion monitoring are a good basis for updating the policy of sustainable land use, particularly when planning soil protection technologies, rules for growing erosion-prone crops, and for implementing management systems that limit erosion and increase water retention in the landscape (e.g., strip crop rotation). Further research is needed to fully utilize the unique data being collected, and comparisons with similar (but maybe on a different scale) systems are expected.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.G., M.D and B.Š.; Methodology, M.G.; Validation, M.B., J.K., B.K. and V.Z.; Formal Analysis, F.P.; Investigation, J.K.; Data Curation, M.D. and K.D.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, M.D and B.Š.; Writing—Review & Editing, B.Š. and Z.M.; Project Administration, Z.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This paper is financed and supported by Norway through the Norway Grants (Project No. 3204200006) and financed from the state budget by the Technology agency of the Czech Republic and the Ministry of the Environment of the Czech Republic under the Environment for life 2 and 5 Progamme (Project No. SS05010161, and SS02030018).
Data Availability Statement
All data generated during this study are included in this published article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Eurostat. Agriculture, Forestry and Fishery Statistics 2020 Edition; Cook, E., Ed.; Eurostat: Luxembourg, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Šarapatka, B.; Šterba, O. Optimization of Agriculture in Relation to the Multifunctional Role of the Landscape. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1998, 41, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Meteorological Organization. Natural hazards and disaster risk reduction. Available online: https://public.wmo.int/en/our-mandate/focus-areas/natural-hazards-and-disaster-risk-reduction (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Markonis, Y.; Rakovec, O.; Svoboda, M.; Trnka, M.; Kumar, R.; Hanel, M. Europe under Multi-Year Droughts: How Severe Was the 2014–2018 Drought Period? Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 034062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagl, J.; Hattermann, F.F.; Koch, H. Modelling of Climate Change Impacts on River Flow Regime and Discharge of the Danube River Considering Water Management Effects. Geophys. Res. Abstr. 2013, 15, 4677. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Floods and Climate Change: Sustainable Development and Other Imaginations. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/chronicle/article/floods-and-climate-change-sustainable-development-and-other-imaginations (accessed on 6 March 2022).
- Mei, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Yang, Z.; Ding, X.; Shao, W. Science of the Total Environment Integrated Assessments of Green Infrastructure for Flood Mitigation to Support Robust Decision-Making for Sponge City Construction in an Urbanized Watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 1394–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, M.; Kavka, P.; Krasa, J. Experimental Research of Soil Erosion Processes in the Czech Republic. In Proceedings of the SGEM 2014 International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConferences (SGEM), Albena, Bulgaria, 17–26 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Poesen, J. Challenges in Gully Erosion Research. Landf. Anal. 2011, 17, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Dotterweich, M. Geomorphology the History of Human-Induced Soil Erosion: Geomorphic Legacies, Early Descriptions and Research, and the Development of Soil Conservation—A Global Synopsis. Geomorphology 2013, 201, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.P.C. Soil Erosion and Conservation; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Toy, T.J.; Foster, G.R.; Renard, K.G. Soil Erosion: Processes, Prediction, Measurement, and Control; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, A.; Khanday, M.Y.; Rais, S. Watershed Prioritization Using Morphometric and Land Use/Land Cover Parameters: A Remote Sensing and GIS Based Approach. J. Geol. Soc. 2011, 78, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rains, S.A.; Coe, K.; Harwood, J. Incivility and Political Identity on the Internet: Intergroup Factors as Predictors of Incivility in Discussions of News Online. J. Comput. Commun. 2017, 22, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Joseph, S.; Thrivikramji, K.P. Assessment of Soil Erosion in a Monsoon-Dominated Mountain River Basin in India Using RUSLE-SDR and AHP India Using RUSLE-SDR and AHP. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2018, 63, 542–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Senciales, J.M.; Sillero-Medina, J.A.; Gyasi-Agyei, Y.; Ruiz-Sinoga, J.D.; Ries, J.B. Analysis of Weather-Type-Induced Soil Erosion in Cultivated and Poorly Managed Abandoned Sloping Vineyards in the Axarquía Region (Málaga, Spain). Air Soil Water Res. 2019, 12, 1178622119839403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, M.R.; Zahabiyoun, B.; Saghafian, B. Assessment of Climate Change Impact on Floods Using Weathergenerator and Continuous Rainfall-Runoff Model. Int. J. Clim. 2011, 32, 1997–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, J.S. Monitoring Land Use/Cover Change Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques: A Case Study of Hawalbagh Block, District Almora, Uttarakhand, India. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2015, 18, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, R.; Shi, Z.H.; Chongfa, C.; Dun, Z. Principal Component Analysis (SPCA) Assessing Soil Erosion Hazard—A Raster Based GIS Approach with Spatial Principal Component Analysis (SPCA). Earth Sci. Inform. 2015, 8, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, F.I.; Bhuiyan, N.T.; Alvee, F.M.; Rahman, A.; Maliha, M. Estimation of Erosion–Accretion Using Remote Sensing Approach: A Case Analysis on Teknaf Coastline. In Advances in Civil Engineering; Scott, A., Saitoh, M., Pal, S.K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 419–430. [Google Scholar]
- Koutsovili, E.I.; Tzoraki, O.; Theodossiou, N.; Gaganis, P. Numerical Assessment of Climate Change Impact on the Hydrological Regime of a Small Mediterranean River, Lesvos Island, Greece. Acta Hort. Reg. 2021, 24, 28–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, J.; Hartmann, T. Land for Flood Risk Management—Instruments and Strategies of Land Management for Polders and Dike Relocations in Germany. Environ. Sci. Policy 2021, 118, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, T. Novel Designs for the Reliability and Safety of Supercritical Water Oxidation Process for Sludge Treatment. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 149, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Panagos, P.; Lugato, E.; Yang, J.E.; Alewell, C.; Wuepper, D.; Montanarella, L.; Ballabio, C. Land Use and Climate Change Impacts on Global Soil Erosion by Water (2015–2070). PNAS 2020, 117, 21994–22001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Poesen, J.; Ballabio, C.; Lugato, E.; Meusburger, K.; Montanarella, L.; Alewell, C. Environmental Science & Policy the New Assessment of Soil Loss by Water Erosion in Europe. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronstert, A.; Agarwal, A.; Boessenkool, B.; Crisologo, I.; Fischer, M.; Heistermann, M.; Köhn-reich, L.; López-tarazón, J.A.; Moran, T.; Ozturk, U.; et al. Science of the Total Environment Forensic Hydro-Meteorological Analysis of an Extreme Flash Flood: The 2016-05-29 Event in Braunsbach, SW Germany. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 977–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, Y. Regional Soil Erosion Assessment Based on a Sample Survey and Geostatistics. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 1695–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosdocimi, M.; Jordán, A.; Tarolli, P.; Keesstra, S.; Novara, A.; Cerdà, A. Science of the Total Environment the Immediate Effectiveness of Barley Straw Mulch in Reducing Soil Erodibility and Surface Runoff Generation in Mediterranean Vineyards. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 547, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanckriet, S.; Asfaha, T.; Frankl, A.; Zenebe, A.; Nyssen, J. Sediment in Alluvial and Lacustrine Debris Fans as an Indicator for Land Degradation around Lake Ashenge (Ethiopia). L. Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igaz, D.; Šinka, K.; Varga, P.; Aydin, E. The Evaluation of the Accuracy of Interpolation Methods in Crafting Maps of Physical and Hydro-Physical Soil Properties. Water 2021, 13, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeček, M.; Dostál, T.; Kozlovsky-Dufková, J.; Dumbrovský, M.; Hůla, J.; Kadlec, V.; Konečná, J.; Kovář, P.; Krása, J.; Kubátová, E.; et al. Methodical Handbook—Protection of Agricultural Soils from the Soil Erosion; Publishing House of the Czech Technical University: Prague, Czech Republic, 2012. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- Holý, J. Erosion and the Environment; Publishing House of the Czech Technical University: Prague, Czech Republic, 1994. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- Antal, J.; Maderková, L.; Čimo, J.; Drgoňová, K. Analyses of Calculation Methods for Determination of Rain Erosivity for Slovak Republic. Acta Sci. Pol. Form. Circumiectus 2015, 14, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsalu, T.; Mengaw, A. GIS Based Soil Loss Estimation Using RUSLE Model: The Case of Jabi Tehinan Woreda. Nat. Resour. 2014, 5, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appels, W.M.; Bogaart, P.W.; van der Zee, S.E. Surface Runoff in Flat Terrain: How Field Topography and Runoff Generating Processes Control Hydrological Connectivity. J. Hydrol. 2016, 534, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanmaercke, M.; Panagos, P.; Vanwalleghem, T.; Hayas, A.; Foerster, S.; Borrelli, P.; Rossi, M.; Torri, D.; Casali, J.; Borselli, L.; et al. Earth-Science Reviews Measuring, Modelling and Managing Gully Erosion at Large Scales: A State of the Art. Earth-Science Rev. 2021, 218, 103637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žížala, D.; Juřicová, A.; Kapička, J.; Novotný, I. The Potential Risk of Combined Effects of Water and Tillage Erosion on the Agricultural Landscape in Czechia. J. Maps 2021, 17, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drbal, K.; Dumbrovský, M.; Muchová, Z.; Sobotková, V.; Štěpánková, P.; Šarapatka, B. Mitigation of Flood Risks with the Aid of the Critical Points Method. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Bruins, R.J.F.; Heberling, M.T. Factors Influencing Farmers’ Adoption of Best Management Practices: A Review and Synthesis. Sustainability 2018, 10, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spânu, I.-A.; Ozunu, A.; Petrescu, D.C.; Petrescu-Mag, R.M. A Comparative View of Agri-Environmental Indicators and Stakeholders’ Assessment of Their Quality. Agriculture 2022, 12, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blann, K.L.; Anderson, J.L.; Sand, G.S.; Vondracek, B. Effects of Agricultural Drainage on Aquatic Ecosystems: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 39, 909–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtson, R.; Carter, C.E.; Fouss, J.L.; Southwick, L.M. Agricultural Drainage and Water Quality in Mississippi Delta. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1995, 121, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häggblom, O.; Salo, H.; Turunen, M.; Nurminen, J.; Alakukku, L.; Myllys, M.; Koivusalo, H. Impacts of Supplementary DrainAge on the Water Balance of a Poorly Drained Agricultural Field. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 223, 105568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skagges, R.W. Field Evaluation of a Water Management Simulation Model. Trans. ASAE 1982, 25, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istok, J.D.; Kling, G.F. Effect of Subsurface Drainage on Runoff and Sediment Yield from an Agricultural Watershed in Western Oregon, U.S.A. J. Hydrol. 1983, 65, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øygarden, L.; Kværner, J.; Jenssen, P.D. Soil Erosion via Preferential Flow to Drainage Systems in Clay Soils. Geoderma 1997, 76, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, M.; Williams, J.; Monteith, J. The Water Balance of an Agricultural Catchment in the Water Balance. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1980, 31, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, I.; Parkinson, R.J. The Nature of the Tile-Drain Outflow Hydrograph in Heavy Clay Soils. J. Hydrol. 1984, 72, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheijen, F.G.A.; Jones, R.J.A.; Rickson, R.J.; Smith, C.J.; Bastos, A.C.; Keizer, J.J. Concise Overview of European Soil Erosion Research and Evaluation. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Soil Plant Sci. 2012, 62 (Suppl. 2), 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, A.R.; Morris, J.; Deeks, L.K.; Rickson, R.J.; Kibblewhite, M.G.; Harris, J.A.; Farewell, T.S.; Truckle, I. The Total Costs of Soil Degradation in England and Wales. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 119, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaoui, A.; Rogger, M.; Peth, S.; Blöschl, G. Does Soil Compaction Increase Floods? A Review. J. Hydrol. 2018, 557, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalham, M.A.; Allen, E.J.; Herry, F.X. Effects of Soil Compaction on Potato Growth and Its Removal by Cultivation. Res. Rev. 2015, 261, 1–60. [Google Scholar]
- Schack-Kirchner, H.; Fenner, P.T.; Hildebrand, E.E. Different Responses in Bulk Density and Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity to Soil Deformation by Logging Machinery on a Ferralsol under Native Forest. Soil Use Manag. 2007, 23, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednář, M.; Šarapatka, B. Relationships between Physical—Geographical Factors and Soil Degradation on Agricultural Land. Environ. Res. 2018, 164, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).