Growth Indexes and Yield Prediction of Summer Maize in China Based on Supervised Machine Learning Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
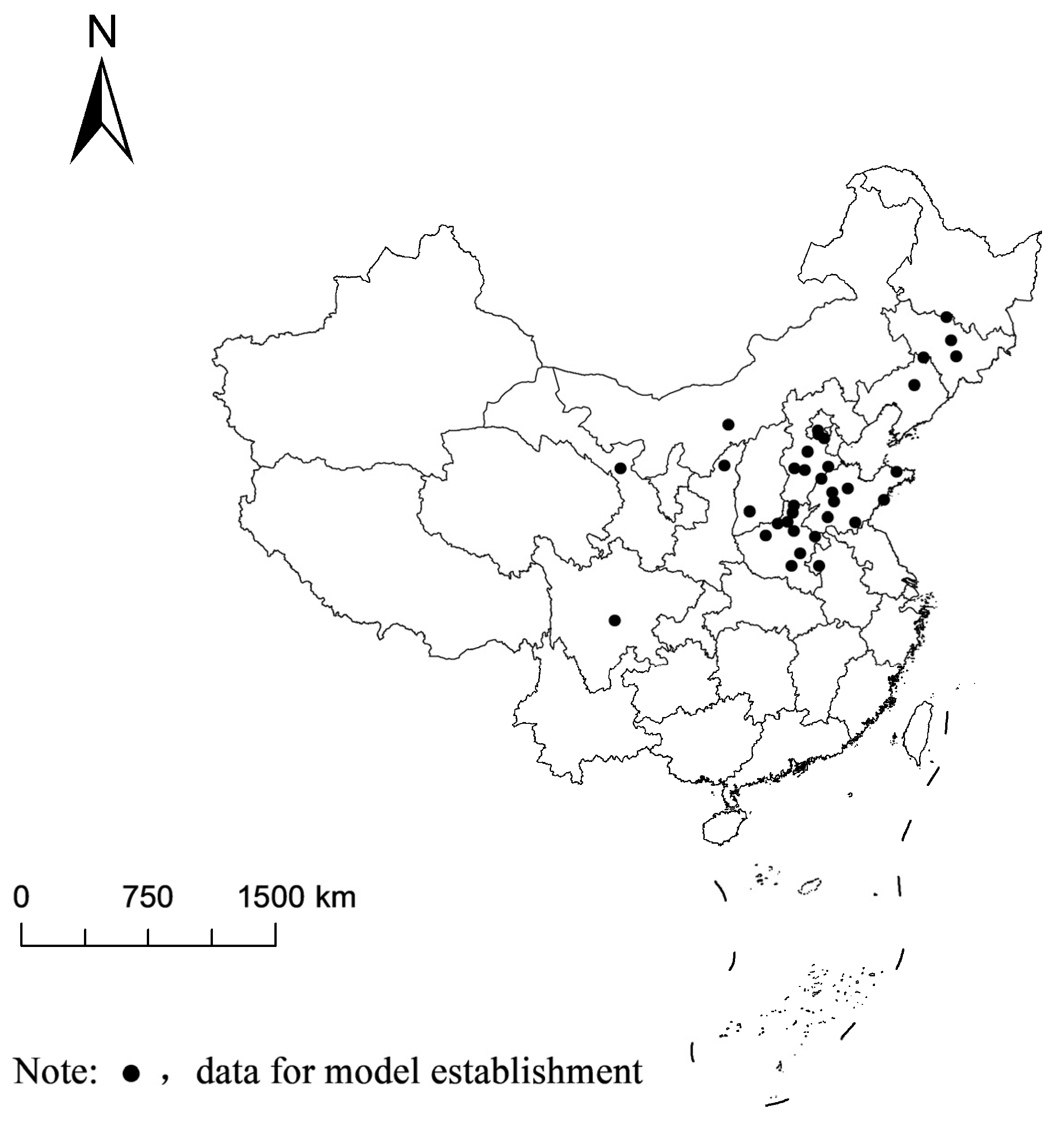
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Research Methods
2.2.1. Method Introduction
2.2.2. Gaussian Process Regression Model
2.3. Error Analysis
3. Result
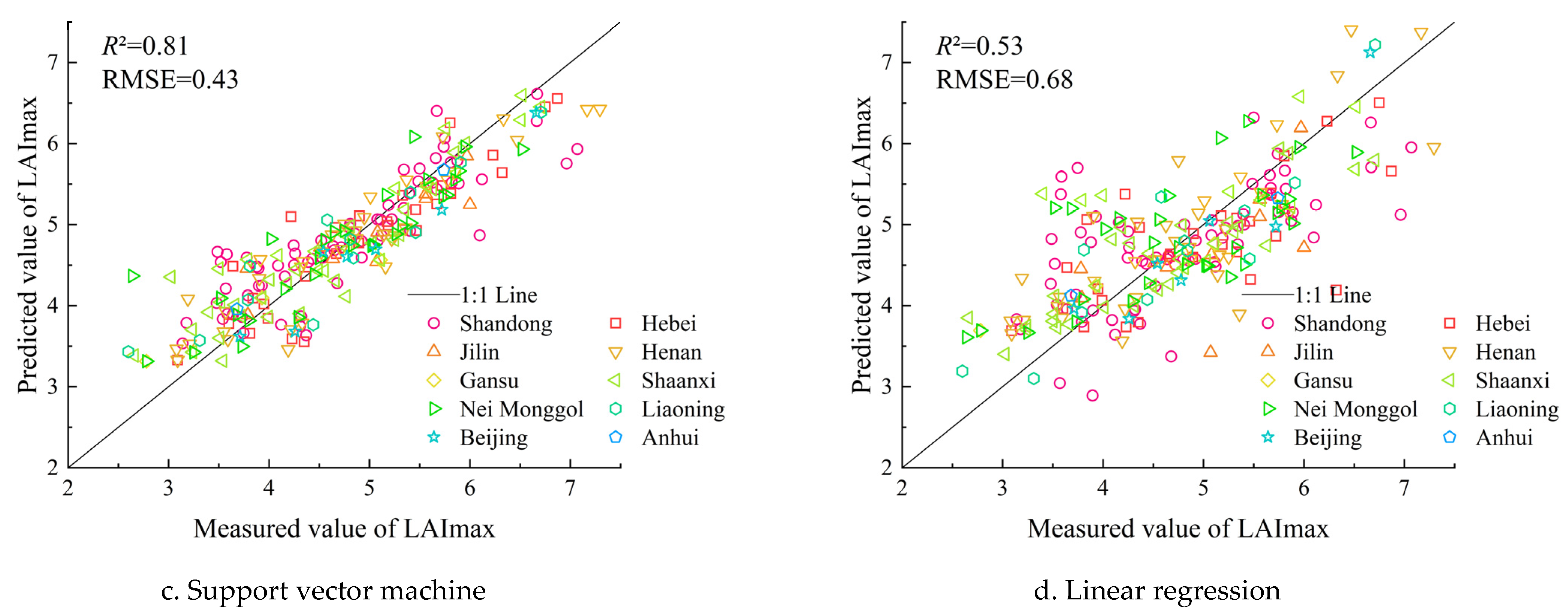
3.1. Prediction Model for Maximum Leaf Area Index
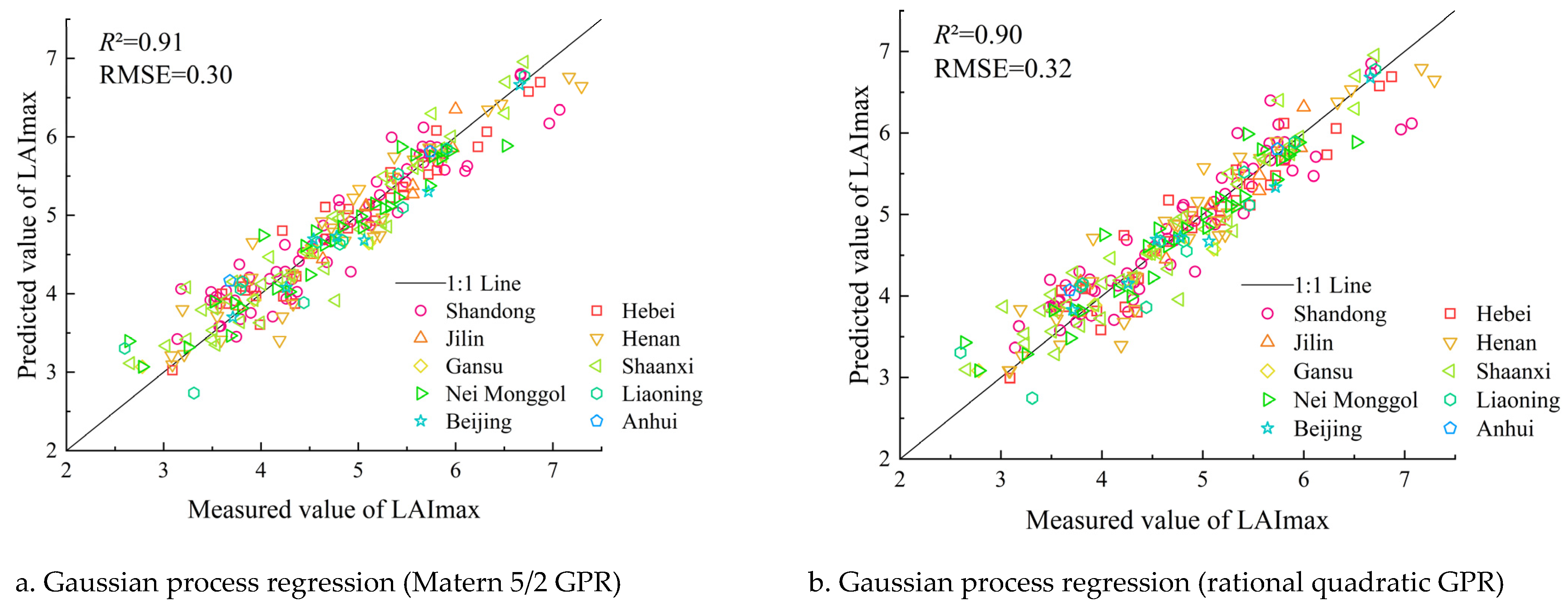
3.1.1. Model Comparison
3.1.2. Model Verification
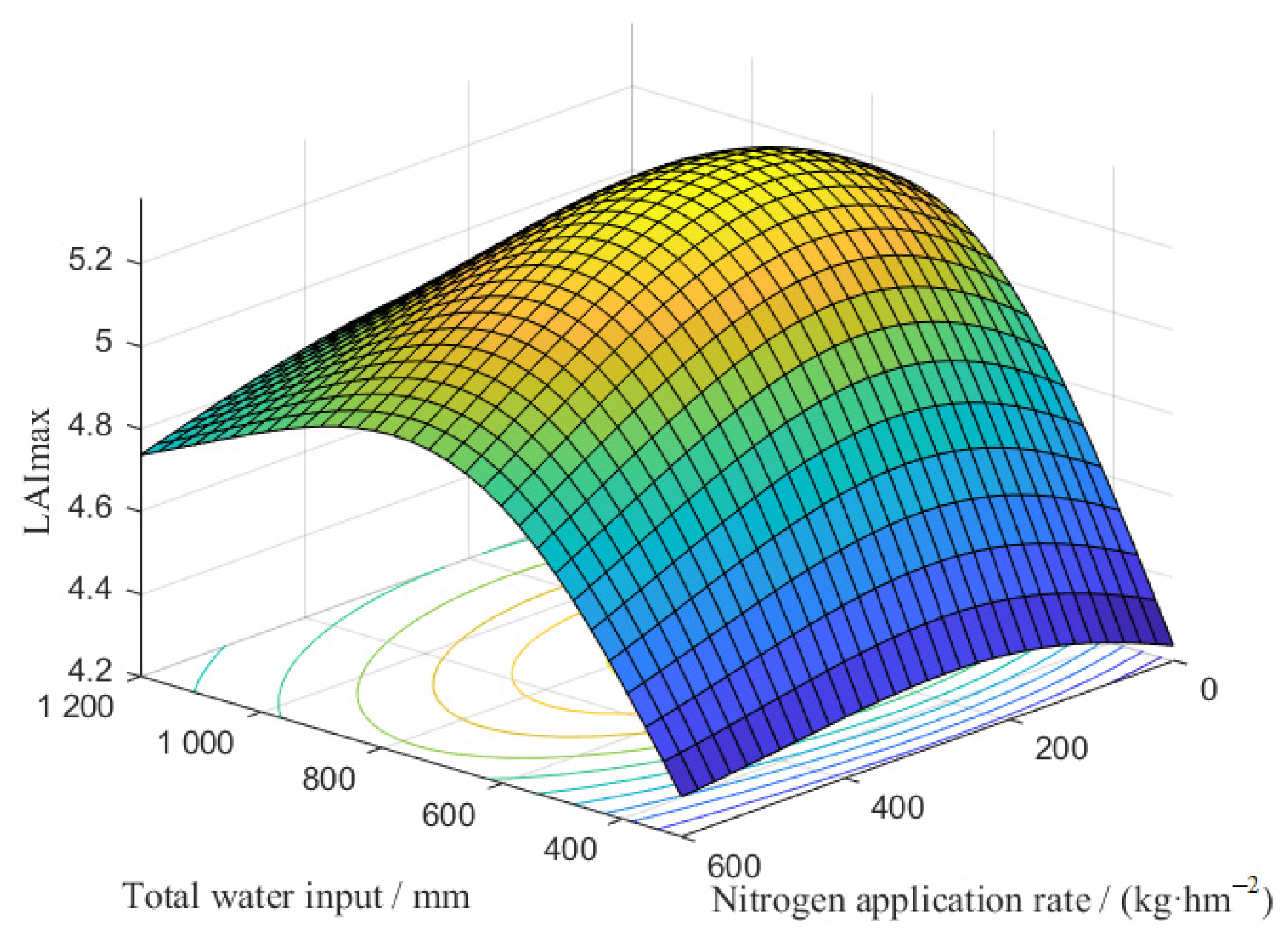
3.1.3. Water and Nitrogen Coupling Function
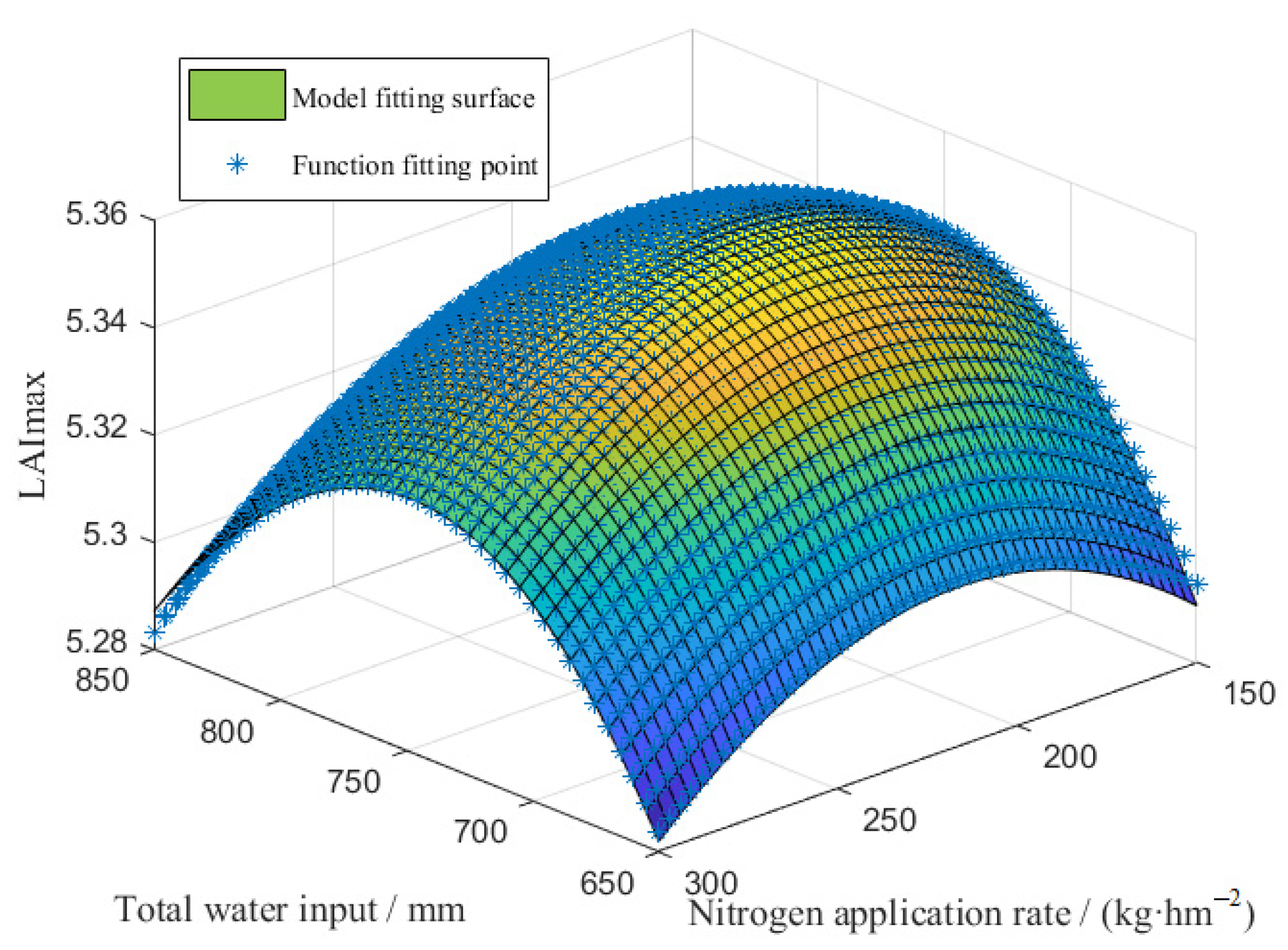
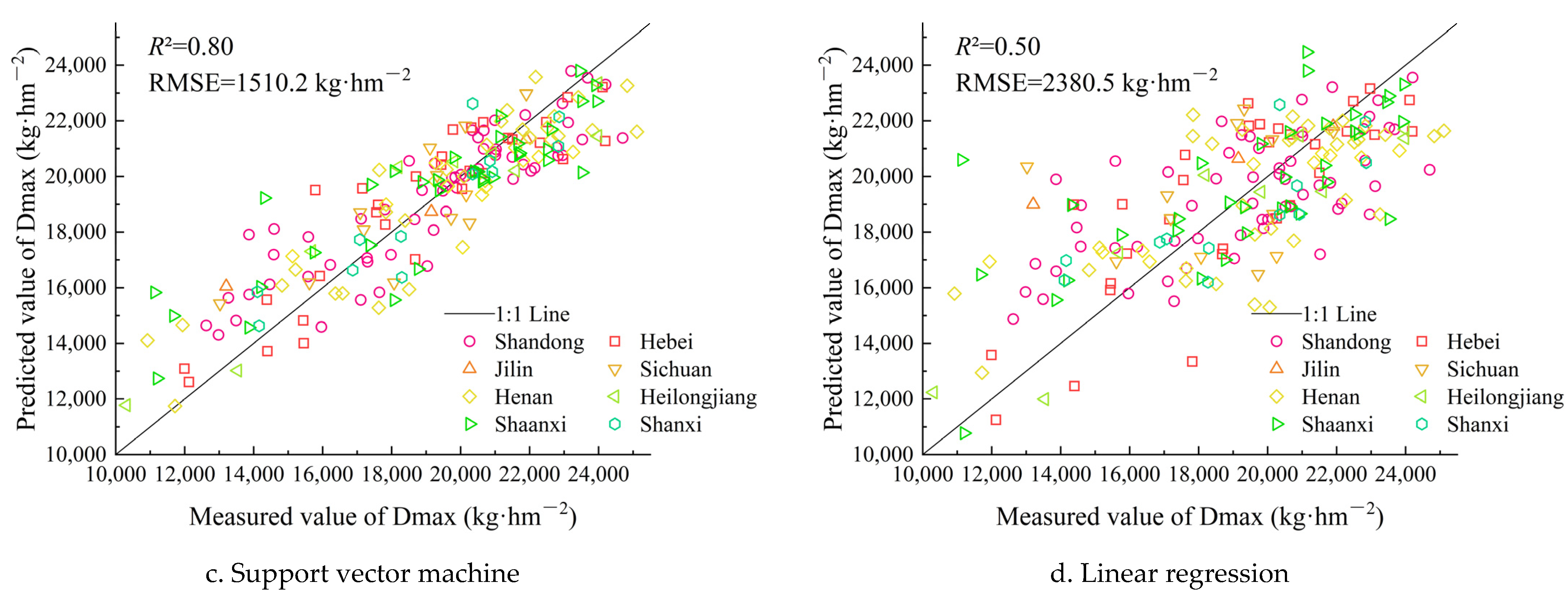
3.2. Prediction Model for Maximum Dry Matter Mass
3.2.1. Model Comparison
3.2.2. Model Verification
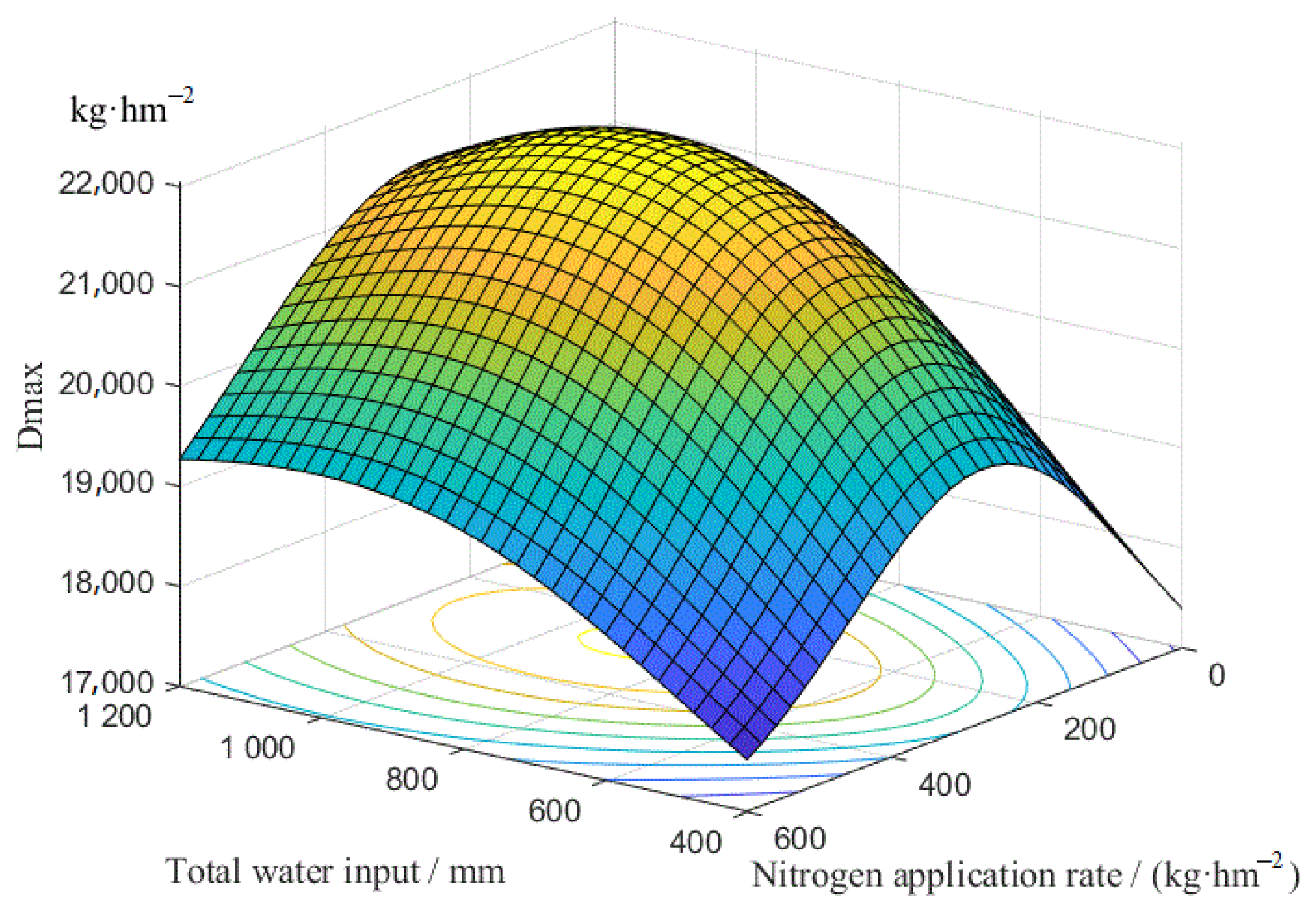
3.2.3. Water and Nitrogen Coupling Function
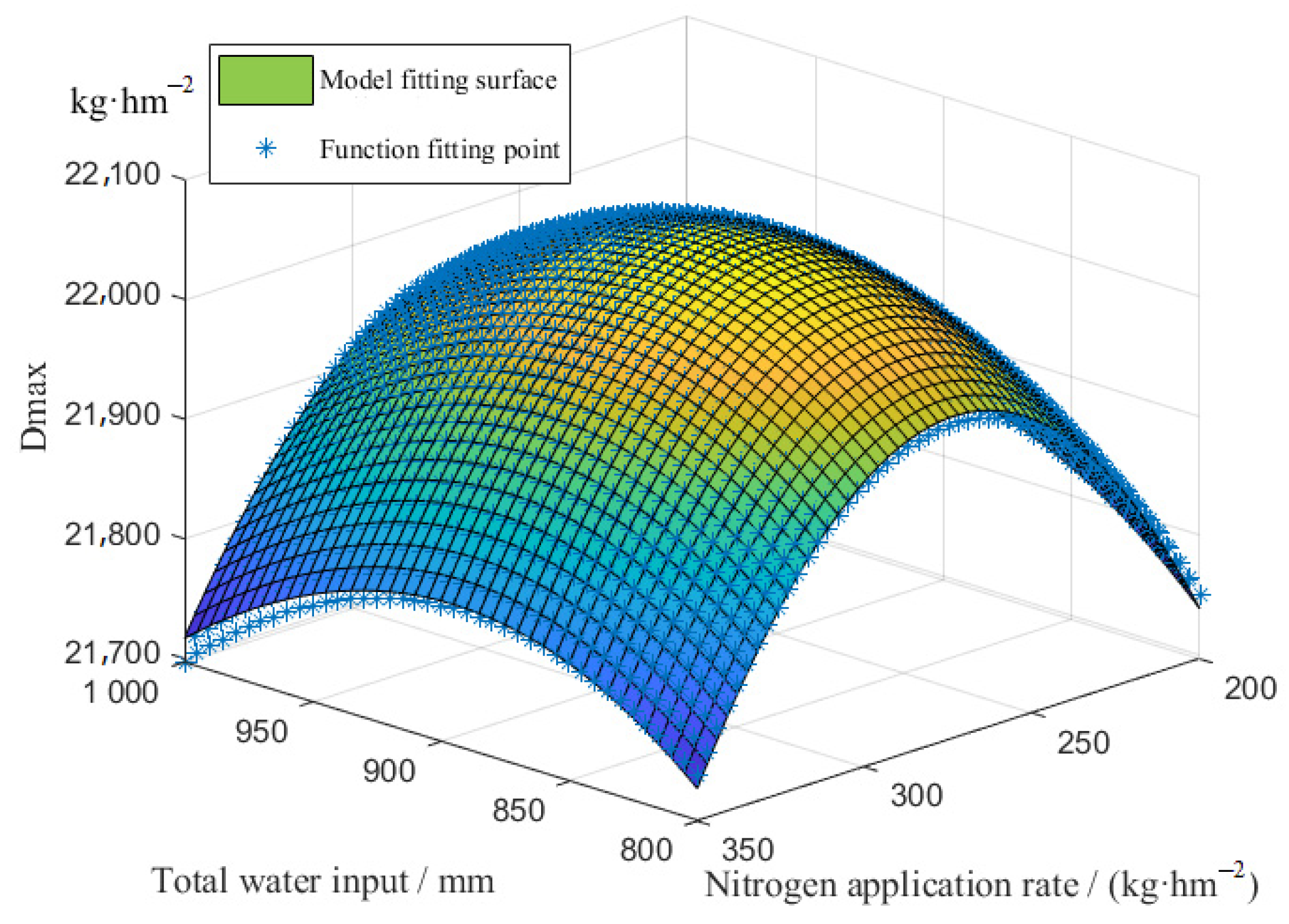
3.3. Prediction Model for Yield
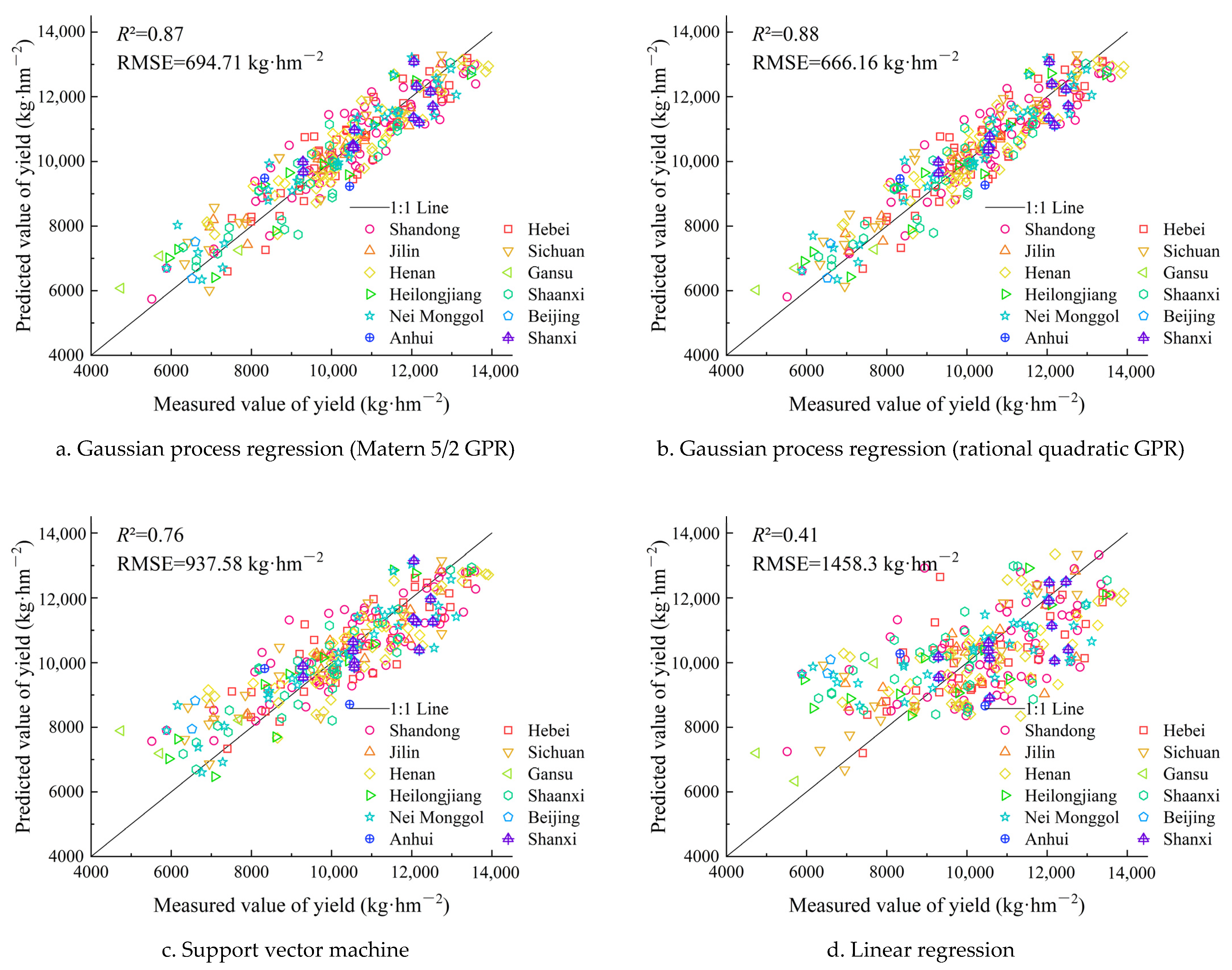
3.3.1. Model Comparison
3.3.2. Model Verification
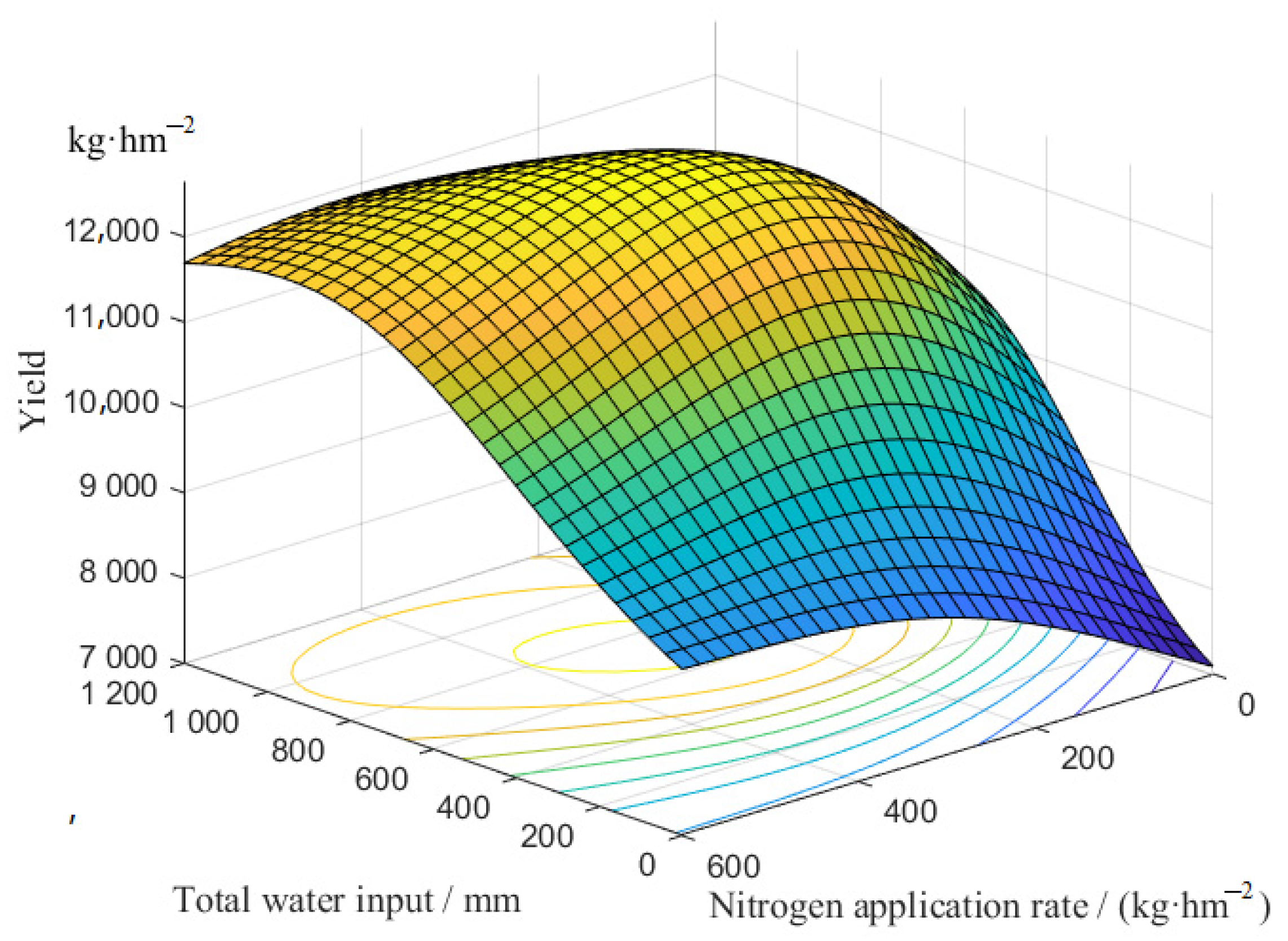
3.3.3. Water and Nitrogen Coupling Function

4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Based on the prediction model accuracy, the Gaussian process regression model was the best for the summer maize LAImax, Dmax and yield. The models with the rational quadratic kernel and Matern kernel had similar performance and good fitting effects. The R2 values of the models were larger than 0.87, and the rRMSE values were lower than 7%. The SVM model was the second best model, and the linear regression model was the worst;
- (2)
- In this study, the measured optimal values for the LAImax, Dmax and Y of summer maize used for verification were 5.21, 22088.92 kg/hm2 and 12337.5 kg/hm2, respectively. The corresponding optimal values obtained with the machine learning model were 5.36, 22054.0 kg/hm2 and 12639 kg/hm2, respectively. Moreover, the corresponding total water input and nitrogen application amount were basically consistent with the measured ranges from the field experiments;
- (3)
- Based on the prediction model, a water–fertilizer coupling scheme suitable for local conditions could be obtained from the field soil quality data and plant density in different regions. This scheme is significant for guiding summer maize production. The water-fertilizer coupling functions for the LAImax, Dmax and Y of summer maize were constructed with the validation data-set for the experimental area. The values of R2 were 0.9971, 0.9975 and 0.9957, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Agriculture Database [DB/OL]. FAOSTAT. 2018. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#home (accessed on 26 November 2022).
- Zhao, J.; Yang, X.G.; Sun, S. Constraints on maize yield and yield stability in the main cropping regions in China. Eur. J. Agron. 2018, 99, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.C.; Li, Y.X. Relationship between maize growth and development and environment. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2014, 2, 87–88. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Zhao, J.; Dong, S.; Zhao, M.; Li, C.; Cui, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Xue, J.; Wang, L.; et al. Advances and Prospects of Maize Cultivation in China. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2017, 50, 1941–1959, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.X.; Zhu, T.Y.; Liu, H. Effects of Successive Application of Biochar on Soil Improvement and Maize Yield of Black Soil Region. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2022, 53, 291–301. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.X. Mechanism of Vertical Partial Root-Zone Alternative Irrigation on Growth, Physiological and Yield of Summer Maize; Northwest A&F University: Xianyang, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Fujimori, S.; Hasegawa, T.; Krey, V.; Riahi, K.; Bertram, C.; Bodirsky, B.L.; Bosetti, V.; Callen, J.; Després, J.; Doelman, J.; et al. A multi-model assessment of food security implications of climate change mitigation. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etherm, A. Introduction to Machine Learning; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ciampitti, I.A.; Makowski, D.; Fernandez, J.; Lacasa, J.; Lemaire, G. Does water availability affect the critical N dilution curves in crops? A case study for maize, wheat, and tall fescue crops. Field Crops Res. 2021, 273, 108301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Gu, X.; Wang, E.; Chen, H.; Ge, G.; Zhang, C. Dynamic estimation of summer maize biomass based on parameter adjustment of crop growth model. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 136–142. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, X.; Lei, Q.Y.; Liu, F. Effects of drip irrigation nitrogen coupling on dry matter accumulation and yield of Summer Maize in arid areas of China. Field Crops Res. 2021, 274, 108321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momen, A.; Koocheki, A.; Mahallati, M.N. Analysis of the variations in dry matter yield and resource use efficiency of maize under different rates of nitrogen, phosphorous and water supply. J. Plant Nutr. 2020, 43, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.H.; Mo, X.G.; Xiang, Y.Q. Research Advances on Crop Growth Models. Acta Agron. Sin. 2003, 29, 750–758. [Google Scholar]
- Kipkulei, H.K.; Bellingrath-Kimura, S.D.; Lana, M.; Ghazaryan, G.; Baatz, R.; Boitt, M.; Chisanga, C.B.; Rotich, B.; Sieber, S. Assessment of Maize Yield Response to Agricultural Management Strategies Using the DSSAT–CERES-Maize Model in Trans Nzoia County in Kenya. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2022, 16, 557–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, T.D.; Foster, T.; Schultz, D.M. Assessing the value of adapting irrigation strategies within the season. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 275, 107986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, E.; Irmak, S.; Yaghouti, H. Performance of WOFOST model for simulating maize growth, leaf area index, biomass, grain yield, yield gap, and soil water under irrigation and rainfed conditions. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2022, 148, 05021005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, A.; Govind, A.; Qureshi, A.S.; Feike, T.; Rizk, M.S.; Shabana, M.M.; Kheir, A.M. Coupling process-based models and machine learning algorithms for predicting yield and evapotranspiration of maize in arid environments. Water 2022, 14, 3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maarten, R.D.; Pieter, P.P.; Ruben, V.V. Machine learning in chemical engineering: Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Engineering 2021, 7, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.T. Predicting agricultural soil carbon using machine learning. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhao, Y.X.; Zhang, G.; Gao, P.; Yang, R. Method for forecasting winter wheat first flowering stage based on machine learning algorithm. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 162–171. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Song, J.; Miu, C.C.; Tang, J. Mobile Cloud Computing Research Progress and Trends. Chin. J. Comput. 2017, 40, 273–295. [Google Scholar]
- Liakos, K.G.; Busato, P.; Moshou, D.; Pearson, S.; Bochtis, D. Machine learning in agriculture: A review. Sensors 2018, 18, 2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.C.; Yan, F.L.; Fan, X.K.; Li, G.; Liu, X.; Lu, J.S.; Wang, Y.; Ma, W.Q. Effects of irrigation and fertilization levels on grain yield and water-fertilizer use efficiency of drip-fertigation spring maize in Ningxia. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.R.; Lv, X.; Yi, X.; Ma, L.L.; Qi, Y.Q.; Hou, D.Y.; Zhang, Z. Monitoring of cotton leaf area index using machine learning. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. 2021, 37, 152–162. [Google Scholar]
- Su, L.J.; Liu, Y.H.; Wang, Q.J. Rice growth model in China based on growing degree days. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. 2020, 36, 162–174. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.R.; Liu, K.; Zhang, J.W.; Ren, B.Z. Effects of Phosphorus Levels on Growth and Yield of Summer Maize. Shandong Agric. Sci. 2018, 50, 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhong, W.W.; Wang, X.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Zhou, X.B. Effect of Cultivation Measures of Previous Winter Wheat on Following Summer Maize Photosynthesis Characteristics and Yield. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin. 2017, 32, 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.M.; Cong, X.; Mu, X.Y.; Xing, H.B.; Zhang, L.Z.; Dong, W.X.; Xu, Z.H.; Pang, G.B. Effects of water and fertilizer application on growth and yield of summer maize. Water Sav. Irrig. 2020, 8, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.; Wu, X.Y.; Wang, D.; Lin, X.; Zhang, J.P. Combined Effects of Water and Nitrogen Application on Growth and Water Use of Summer Maize under Drip Irrigation. J. Irrig. Drain. 2020, 39, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.; Wang, D.; Wu, X.Y.; Wu, Y.Q.; Lin, X.; Zhang, J.P. Effects of Nitrogen Reduction on Growth and Water-Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Summer Maize. J. Maize Sci. 2022, 30, 158–165. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Dong, J.; Cui, Y.F. Coupling Effect of Water and Fertilizer on Summer Maize. Shandong Agric. Sci. 2011, 12, 82–83. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, L.Y.; Song, X.Y.; Liu, S.T. Effect of Water and Fertilizer Coupling on Foliar Index and Biomass at Different Growth Stages of Summer Maize. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2014, 30, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.Z.; Liu, G.L.; Zhang, H.Y. The Relationship of Light and Temperature Factor and Yield Maize. Acta Agric. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2001, 10, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Tao, H.B.; Huang, S.B.; Xu, L.N.; Yang, L.H.; Qi, L.P.; Wang, P. Effects of Nitreogen Patterns on Nitrogen Use and Yield Benefit of Summer Maize. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2013, 27, 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, Z.G.; Liu, P.; Li, C.; Qi, J.Y.; Ma, S.T.; Pu, C.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.L. Effects of Biochar on Soil Water and Growth of Summer Corn in the North China Plain. J. Maize Sci. 2019, 27, 142–150. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.Y.; Zheng, C.L.; Li, J.K.; Ma, J.Y.; Cui, Y.H. Effect of long-term fertilization on photosynthetic property and yield of summer maize. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2009, 17, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Zhao, M.; Li, C.F.; Ge, J.Z.; Hou, H.P.; Li, Q.; Hou, L.B. Effect of Sowing-Date and Planting Density on Dry Matter Accumulation Dynamic and Establishment of Its Simulated Model in Maize. Acta Agron. Sin. 2010, 36, 2143–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.X.; Zhang, H.F.; Ma, W.Q.; Wei, J. Effects of Nitrogen Application Rates on Yield and Nitrogen Utilization of Summer Maize. J. Maize Sci. 2014, 22, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, L.L.; Liu, W.Z.; Li, S.W.; Wen, H.D. Effects of water and fertilizer coupling on biological characteristics and yields of summer maize. J. Agric. Univ. Hebei 2012, 35, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, L.H.; Tao, H.B.; Xia, L.K.; Zhang, Y.J.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, J.R.; Wang, P. Canopy Structure and Photosynthesis Traits of Summer Maize under Different Planting Densities. Acta Agron. Sin. 2008, 3, 447–455. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, L.P.; Liu, W.W.; Cao, G.J. Dynamic Study on the Organism Yield Accumulation of Corn in Different Yield Treatments. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2010, 38, 16793–16795. [Google Scholar]
- Du, T.H.; Fang, X.Q.; Liu, Z.Y. Effects of different planting densities on maize yield of Jidan 631. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2017, 15, 25–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, F.; Zeng, Z.H. Effect of soybean-maize rotation and fertilization on the agronomic trait and grain yield of maize. J. China Agric. Univ. 2013, 18, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.X.; Chen, X.H.; Tang, Y.Q.; Zhang, F.S.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, C.C.; Liu, J.; Xu, K.W. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer on dry matter accumulation and yield in wheat/maize/soybean intercropping systems. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2014, 23, 73–83. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.X.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, C.C.; Huang, W.; Tang, Y.Q.; Xu, K.W. Dry matter accumulation, yield and nitrogen use efficiency of crops rotation and intercropping systems in Sichuan. J. China Agric. Univ. 2013, 18, 68–79. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.Y.; Wang, X.B.; Wang, Z.M. Effect of slow-release fertilizer and tillage practice on grain yield and nitrogen efficiency of summer maize. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2016, 22, 821–829. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.S.; Huang, F.U.; Zhang, S.J.; Liu, Y.X.; Hou, L.X. Study on population physiological indices of summer maize with high yield on eastern Henan plain. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2013, 52, 4054–4057. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, F.F.; Zhang, Z.J.; Gao, Z.L.; Feng, Y.H. Experimental study on high water content of summer maize in eastern Henan. Henan Water Resour. South–North Water Divers. 2013, 16, 104–105. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Lu, D.W. Study on the absorption, accumulation and distribution of nitrogen and phosphorus in summer maize in north Henan province. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2018, 46, 52–55. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, S.G.; Li, L.; Wan, H.L.; Cai, S.L.; Wei, Y.Q.; Zhao, H.L.; Luo, Y. Study on physiological indexes of colony of new maize variety luoyu 818. Acta Agric. Jiangxi 2014, 26, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.W.; Zhao, B.X.; Wan, H.L.; Lei, X.B.; Chen, R.L.; Li, L.; Wei, Y.Q.; Zhao, H.L.; Luo, Y. Study on group dynamic indexes of ‘Luoyu 863’ of maize. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2013, 29, 96–101. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.Z.; Zhang, G.H.; Li, Y.C.; Zhu, Z.K.; Li, B.F. Effects of recommended fertilization on growth, development, yield and economic benefit of superhigh-yielding summer maize. Acta Agric. Jiangxi 2011, 23, 105–107. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.G.; Wu, H.Q.; Wang, G.Y. A study on the irrigation way of summer corn in sandy soil. J. Desert Res. 1999, 2, 74–77. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.T.; Chen, G.J. Effects of community efficiency on the photosynthetic-physiological characters and seed yield of summer maize. J. Henan Inst. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2014, 42, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.H.; Huang, H.; Liu, J.J. Effects of balanced application of NPK fertilizer on summer maize under high water and fertilizer conditions. Bull. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2011, 5, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, W.B.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zheng, E.N.; Liu, M. Nitrogen-water coupling affects nitrogen utilization and yield of film-mulched maize under drip irrigation. J. Irrig. Drain. 2019, 38, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, D.F.; Qin, A.Z.; Liu, Z.D.; Zhang, J.Y.; Liu, Z.J.; Zhao, B.; Xiao, J.F. Effects of irrigation and fertilization levels on grain yield and water and N use efficiency of drip-fertigation summer maize in the north China plain. J. Irrig. Drain. 2019, 38, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Luan, Y.; Wen, G.; Dong, P. Research on the leaf area index, dry matter accumulation with yield of seed maize under different irrigation methods. Agric. Res. Arid. Areas 2017, 35, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B.W.; Pang, Y.; Yu, Y.L.; Wang, C.H. Effect of ratios of nitrogen to potassium on dry matter accumulation, yield and quality of corn in cold area. J. Maize Sci. 2014, 22, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.S.; Xue, J.Q.; Lu, H.D. Study on physiological indexes of high yield population of new maize variety Shandan 8806. J. Maize Sci. 2005, 3, 83–85. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.M.; Luo, W.H.; Liu, P.Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, R.; Li, J. Regulation effects of water saving and nitrogen reduction on dry matter and nitrogen accumulation, transportation and yield of summer maize. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2021, 54, 3183–3197. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.D.; Xue, J.Q.; Ma, G.S. Study on different groups receive light posture and photosynthesis character of summer maize. J. Maize Sci. 2008, 16, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, P.C.; Du, Y.C.; Kong, G.D.; Yu, H.R. Plant density and nitrogen amount affecting the yield of maize (‘Yidan52’ and ‘Yidan81’). Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2018, 34, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L.J.; Cui, Z.H.; Wu, D. Planting density of different plant type summer corn canopy structure and the effect of photosynthetic potential. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2010, 3, 116–118+121. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.X.; Yu, P.; Li, M.Z.; Liao, Q.; Liu, A.J. Effects of Water and Fertilizer Coupling on plant height and yield of summer corn with drip irrigation. Shandong Chem. Ind. 2017, 46, 53–54+62. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Huang, X.F.; Gong, S.H. Effects of water deficit on soil moisture and temperature regimes in subsurface drip irrigated summer corn field. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2012, 43, 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, C.W.; Huang, Y.D.; Huang, W.J.; Wang, J.H.; Zhao, C.J.; Liu, L.Y. Study on colony leaf area index of summer maize by remote sensing vegetation indexes method. J. Anhui Agric. Univ. 2004, 31, 392–397. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.S.; Li, J.C.; Qu, J.H.; Wei, F.Z.; Liu, L.; Meng, J.J.; Li, X.Y.J. Analysis on yield characters and adaptability of new summer maize variety in Taihe county. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2009, 25, 155–157. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Li, L.; Hong, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L. Effects of nitrogen application and irrigation on grain yield, water and nitrogen utilizations of summer maize. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci. 2012, 18, 1354–1361. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Su, L.J.; Wang, Q.J. Cotton growth model under drip irrigation with film mulching: A case study of Xinjiang, China. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 2417–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.S.; Geng, C.M.; Cui, X.L.; Li, M.Y.; Hu, T.T. Determination of summer maize leaf critical nitrogen dilution curve based on leaf area index. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2021, 52, 319–326. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Sun, X.M.; Li, H.Q.; Wang, J.Z.; Zhao, H.J. Effects of water and nitrogen coupling on dry matter accumulation and nitrogen Distribution in Zhengdan 958 Maize. Henan Sci. 2014, 32, 516–523. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, C.E.; Williams, C.K.I. Gaussian Processes for Machine Learning; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, C.E.; Nickisch, H. Gaussian processes for machine learning (GPML) toolbox. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2010, 11, 3011–3015. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, J.; Jiang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Jiang, J. Evaluating the prediction performance of different kernal functions in kernel based software reliability models. Chin. J. Comput. 2013, 36, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.L.; Zhou, X.H.; Sun, J.; Yu, X.; Yuan, H.T.; Liu, J.B.; Han, Y. A survey of machine learning based database techniques. Chin. J. Comput. 2020, 43, 2019–2049. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Duan, Y.R. Retail products sales forecast based on clustering and machine learning. Comput. Syst. Appl. 2021, 30, 188–194. [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao, T.C.; Heng, L.; Steduto, P.; Rojas-Lara, B.; Raes, D.; Fereres, E. AquaCrop—The FAO crop model to simulate yield response to water: III. Parameterization and testing for maize. Agron. J. 2009, 101, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.W.; Hoogenboom, G.; Porter, C.H.; Boote, K.J.; Batchelor, W.D.; Hunt, L.A.; Wilkens, P.W.; Singh, U.; Gijsman, A.J.; Ritchie, J.T. The DSSAT cropping system model. Eur. J. Agron. 2003, 18, 235–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, K.; Wang, L.; Shi, L.; Yang, J. Coupling model of EPIC-Nitrogen2D and crop growth, soil water, nitrogen dynamics in winter wheat. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 141–151. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, A.; Minli, Y.; Elahi, E.; Yousaf, K.; Ahmad, R.; Iqbal, T. Quantification of mechanization index and its impact on crop productivity and socio-economic factors. Int. Agric. Eng. J. 2017, 26, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Kayad, A.; Sozzi, M.; Gatto, S.; Whelan, B.; Sartori, L.; Marinello, F. Ten years of corn yield dynamics at field scale under digital agriculture solutions: A case study from North Italy. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 185, 106126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G. Estimation of a mechanization index and its impact on production and economic factors—A case study in India. Biosyst. Eng. 2006, 93, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| District | Yield | Leaf Area Index | Dry Matter Accumulation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Size | Data Source | Sample Size | Data Source | Sample Size | Data Source | |
| Shandong | 78 | [26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34] | 73 | [26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33] | 60 | [26,27,28,29,30,31] |
| Hebei | 44 | [35,36,37,38,39,40,41] | 24 | [35,36,37,41] | 30 | [35,36,37,38] |
| Jilin | 13 | [42,43,44] | 10 | [43,44] | 3 | [42] |
| Sichuan | 12 | [45,46] | 12 | [45,46] | ||
| Henan | 52 | [47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57] | 36 | [47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55] | 42 | [47,49,50,51,52,53,57,58] |
| Gansu | 3 | [59] | 3 | [59] | ||
| Heilongjiang | 9 | [60] | 9 | [60] | ||
| Shaanxi | 34 | [61,62] | 39 | [61,62,63] | 34 | [61,62] |
| Nei Monggol | 30 | [64] | 30 | [64] | ||
| Liaoning | 12 | [65] | ||||
| Beijing | 14 | [66,67] | 7 | [67,68] | ||
| Anhui | 2 | [69] | 2 | [70] | ||
| Shanxi | 12 | [70] | 12 | [70] | ||
| Total | 303 | 236 | 202 | |||
| Treatment | Total Water Input (mm) | Nitrogen Application Rate (kg⋅hm−2) | Measured Value of LAImax | Predicted Value of LAImax | Relative Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 434 | 0 | 2.79 | 4.63 | 65.95 |
| 2 | 434 | 90 | 3.27 | 4.74 | 44.95 |
| 3 | 434 | 150 | 3.87 | 4.78 | 23.51 |
| 4 | 434 | 210 | 4.04 | 4.81 | 19.06 |
| 5 | 659 | 0 | 3.35 | 5.10 | 52.24 |
| 6 | 659 | 90 | 3.98 | 5.23 | 31.41 |
| 7 | 659 | 150 | 5.08 | 5.28 | 3.94 |
| 8 | 659 | 210 | 5.16 | 5.30 | 2.71 |
| 9 | 734 | 0 | 3.52 | 5.16 | 46.6 |
| 10 | 734 | 90 | 4.26 | 5.28 | 23.94 |
| 11 | 734 | 150 | 5.13 | 5.33 | 3.9 |
| 12 | 734 | 210 | 5.21 | 5.35 | 2.69 |
| Treatment | Total Water Input (mm) | Nitrogen Application Rate (kg⋅hm−2) | Measured Yield (kg⋅hm−2) | Predicted Yield (kg⋅hm−2) | Relative Error (%) | Measured Dmax (kg⋅hm−2) | Predicted Dmax (kg⋅hm−2) | Relative Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 593.5 | 0 | 10,169 | 10,518 | 3.43 | 16,830 | 18,479 | 9.8 |
| 2 | 593.5 | 180 | 11,712 | 12,199 | 4.16 | 18,592 | 20,597 | 10.79 |
| 3 | 593.5 | 240 | 11,986 | 12,351 | 3.05 | 19,859 | 20,940 | 5.44 |
| 4 | 593.5 | 300 | 10,124 | 12,321 | 21.69 | 18,567 | 20,966 | 12.92 |
| 5 | 790.2 | 0 | 9956 | 10,777 | 8.25 | 19,115 | 19,456 | 1.79 |
| 6 | 790.2 | 180 | 11,622 | 12,325 | 6.05 | 20,023 | 21,551 | 7.63 |
| 7 | 790.2 | 240 | 12,338 | 12,543 | 1.67 | 21,388 | 21,874 | 2.27 |
| 8 | 790.2 | 300 | 10,448 | 12,615 | 20.75 | 20,006 | 21,893 | 9.43 |
| 9 | 987 | 0 | 9931 | 10,610 | 6.84 | 18,896 | 19,901 | 5.32 |
| 10 | 987 | 180 | 11,265 | 11,899 | 5.63 | 18,865 | 21,707 | 15.06 |
| 11 | 987 | 240 | 11,722 | 12,142 | 3.58 | 21,437 | 21,957 | 2.42 |
| 12 | 987 | 300 | 11,679 | 12,281 | 5.16 | 22,089 | 21,948 | 0.64 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, L.; Wen, T.; Tao, W.; Deng, M.; Yuan, S.; Zeng, S.; Wang, Q. Growth Indexes and Yield Prediction of Summer Maize in China Based on Supervised Machine Learning Method. Agronomy 2023, 13, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010132
Su L, Wen T, Tao W, Deng M, Yuan S, Zeng S, Wang Q. Growth Indexes and Yield Prediction of Summer Maize in China Based on Supervised Machine Learning Method. Agronomy. 2023; 13(1):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010132
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Lijun, Tianyang Wen, Wanghai Tao, Mingjiang Deng, Shuai Yuan, Senlin Zeng, and Quanjiu Wang. 2023. "Growth Indexes and Yield Prediction of Summer Maize in China Based on Supervised Machine Learning Method" Agronomy 13, no. 1: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010132
APA StyleSu, L., Wen, T., Tao, W., Deng, M., Yuan, S., Zeng, S., & Wang, Q. (2023). Growth Indexes and Yield Prediction of Summer Maize in China Based on Supervised Machine Learning Method. Agronomy, 13(1), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010132







