Exogenous Melatonin Improves the Quality Performance of Rice under High Temperature during Grain Filling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Stress Treatments
2.2. Flower Tagging and Sampling
2.3. Analysis of Photosynthetic and Stress Resistance Characteristics of Leaves
2.4. Preparation of Seed Samples and Starch Isolation
2.5. Total Starch Content and Starch Fine Structure Analysis
2.6. RVA and DSC Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
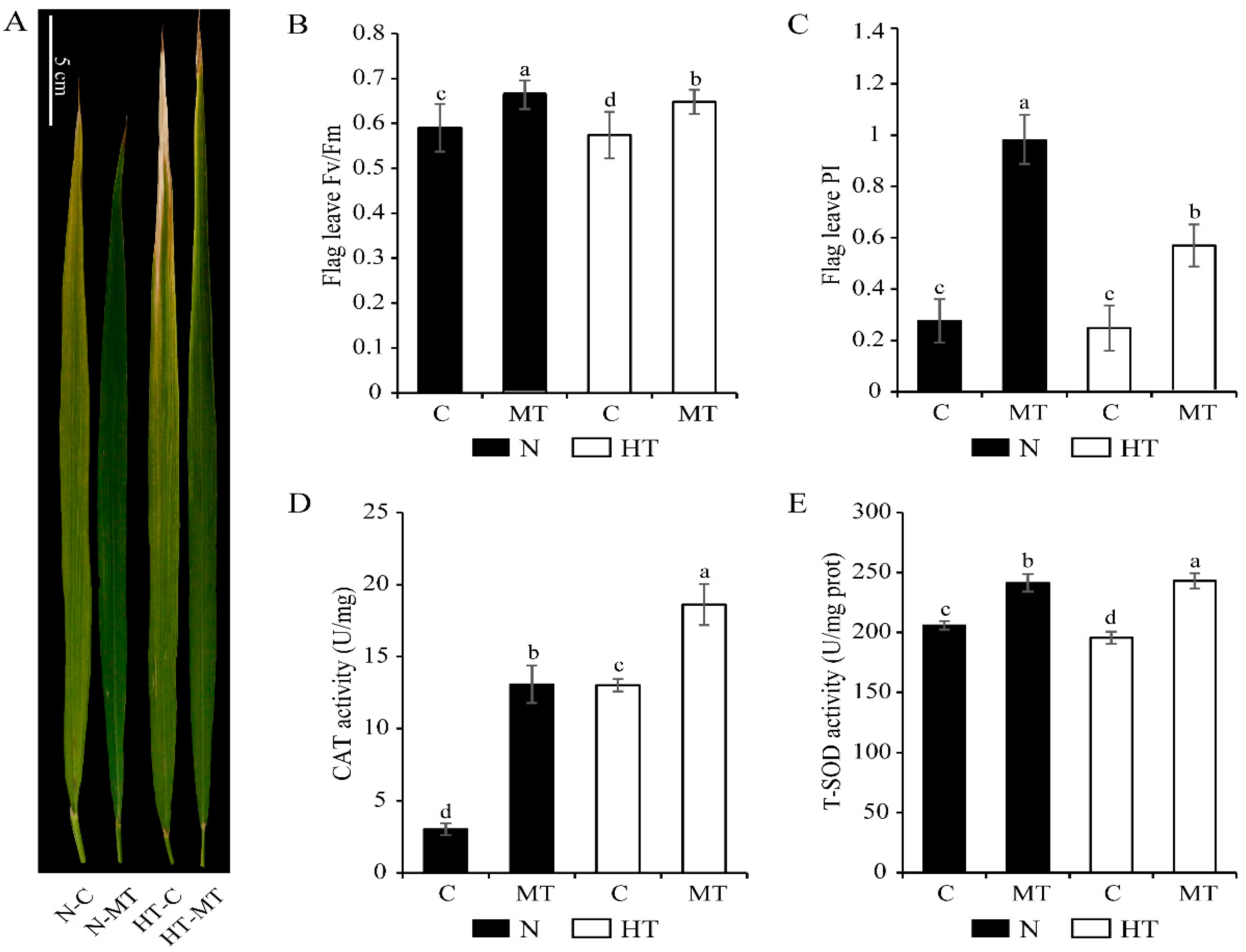
3.1. Exogenous Melatonin Enhanced the Resistance of Rice to High Temperature Stress
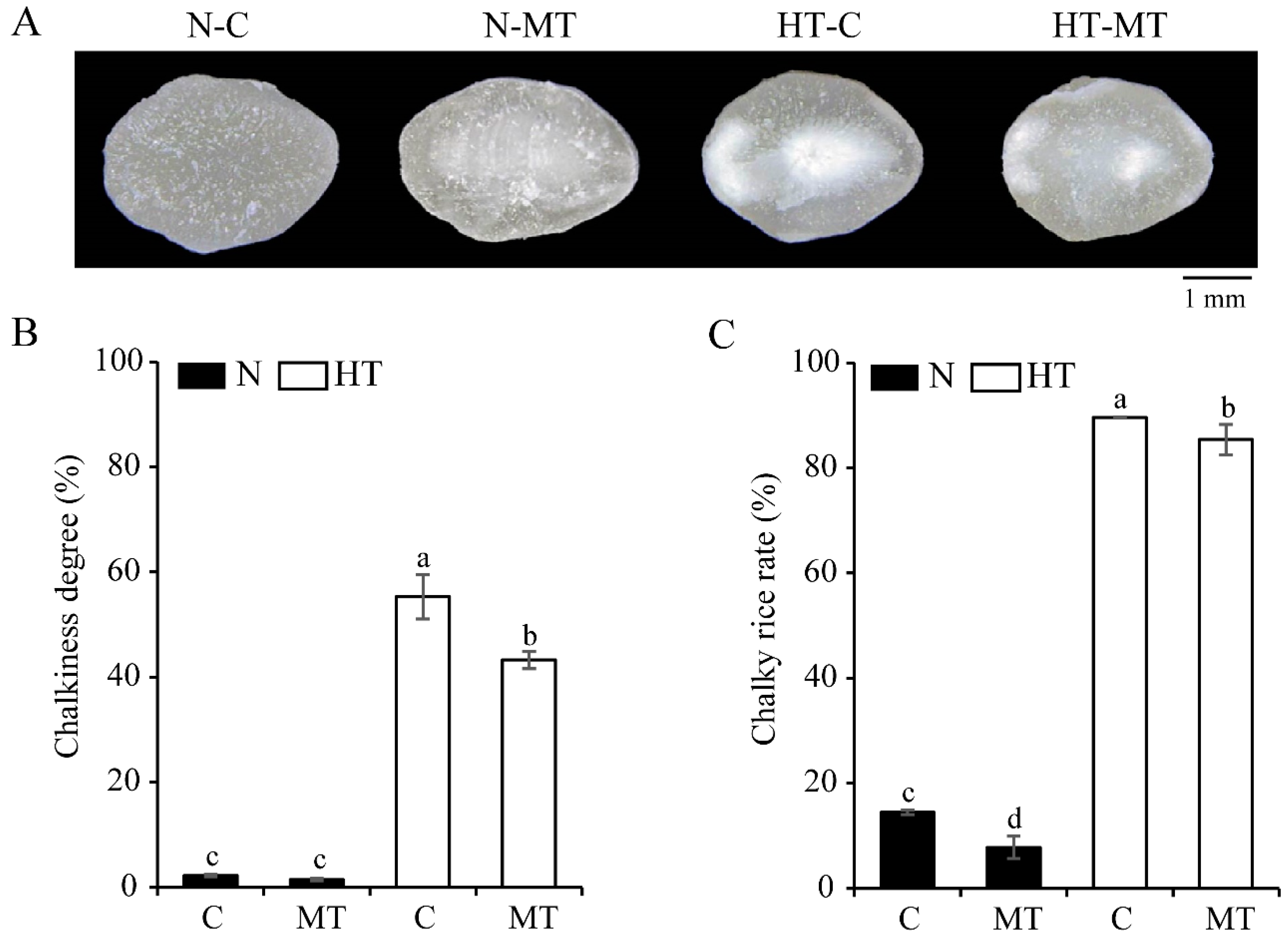
3.2. Exogenous Melatonin Improves the Grain Appearance Quality
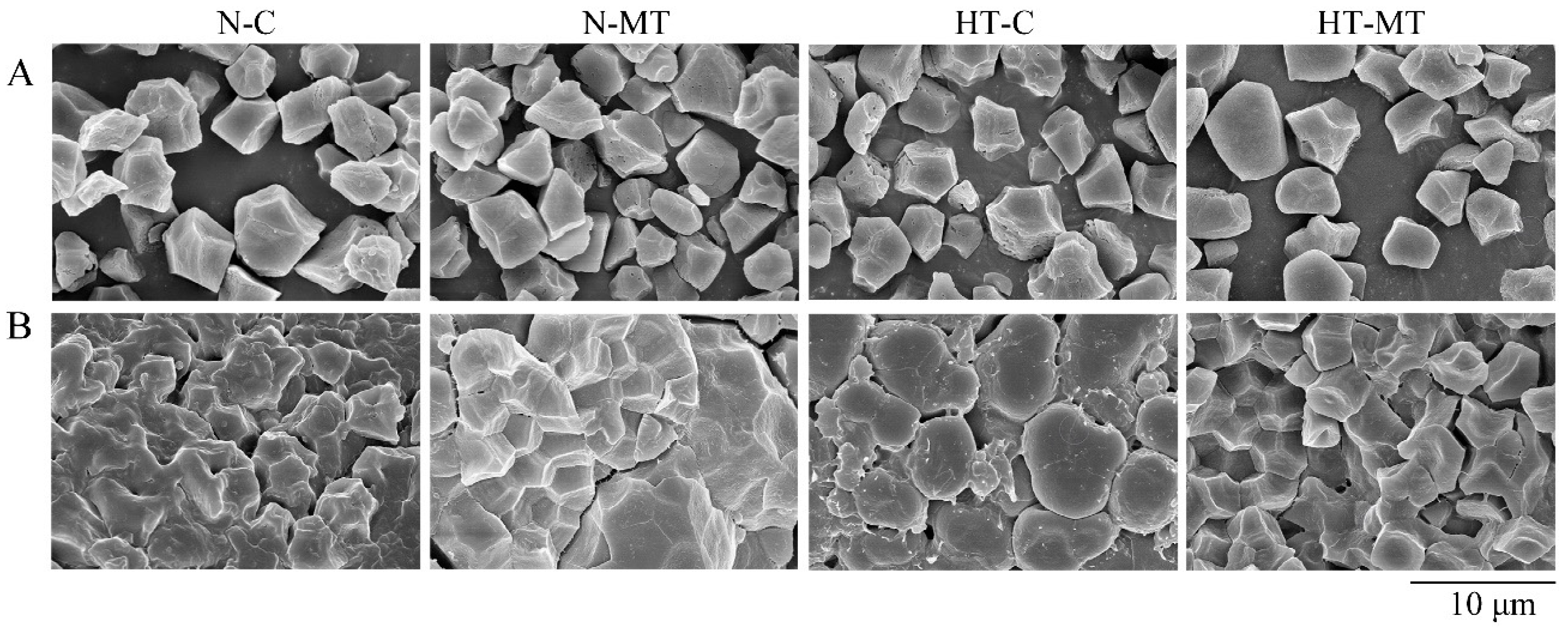
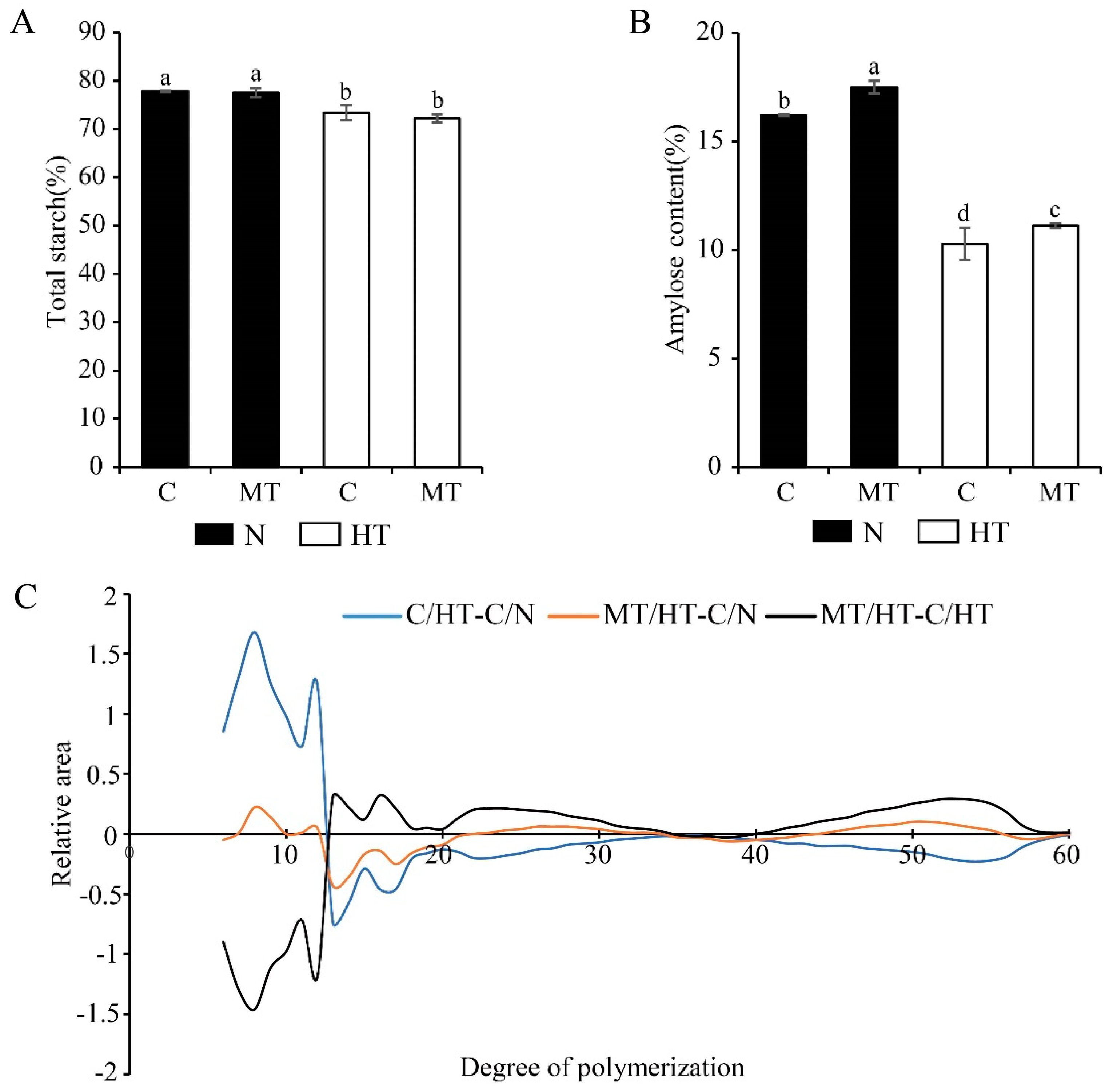
3.3. Effect of Exogenous Melatonin on Starch Synthesis in Endosperm
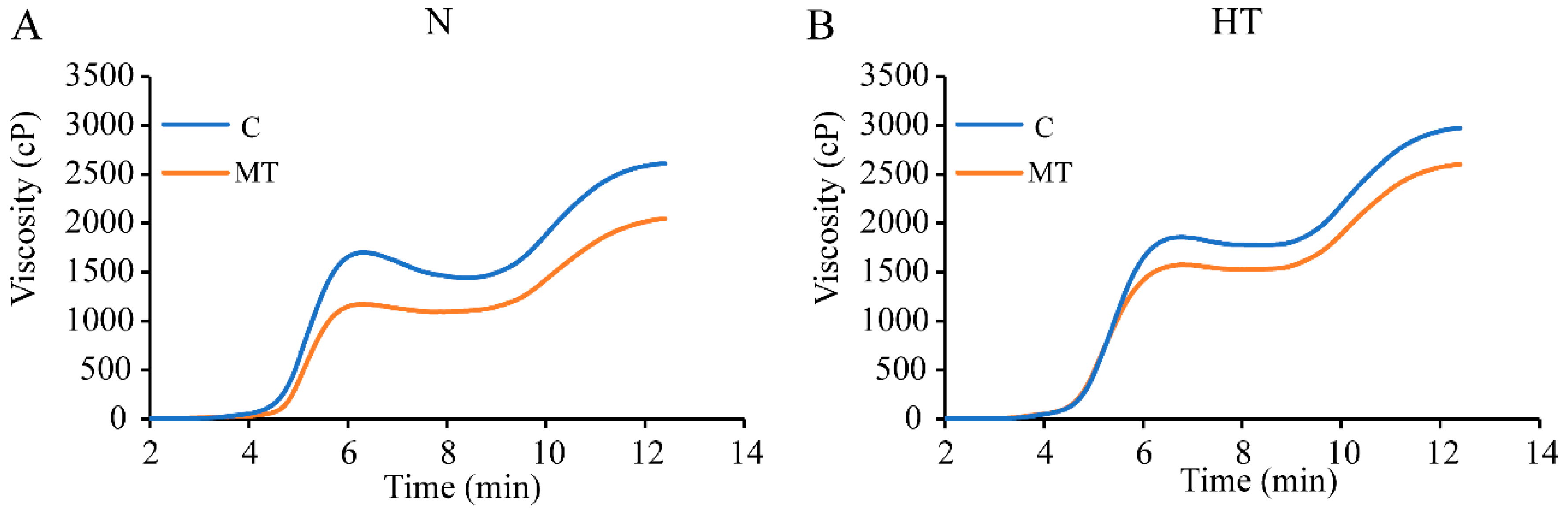
3.4. Effect of Exogenous Melatonin on Pasting Properties of Rice in Response to High Temperature
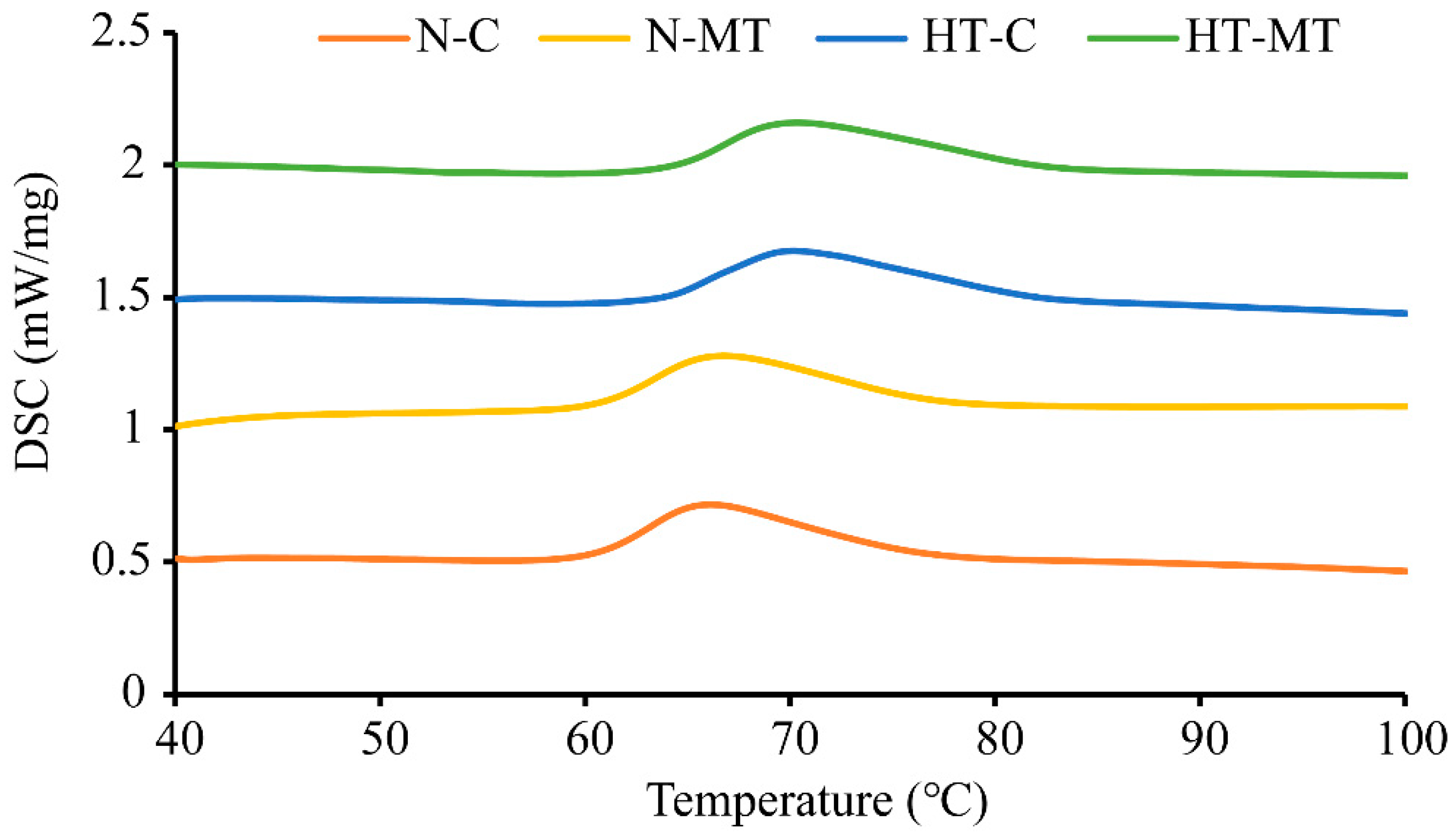
3.5. Effect of Exogenous Melatonin on Gelatinization Temperature of Rice in Response to High Temperature
4. Discussion
4.1. Melatonin Enhanced the Antioxidant Capacity of Rice Leaves under High Temperature Stress
4.2. Melatonin Stabilized the Starch Synthesis in Rice under High Temperature
4.3. The Future Application of Melatonin in Rice Cultivation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, L.; Lu, Y.; Li, Q.; Fan, X.; Tang, S.; et al. A rare Waxy allele coordinately improves rice eating and cooking quality and grain transparency. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2020, 63, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katano, K.; Honda, K.; Suzuki, N. Integration between ROS regulatory systems and other signals in the regulation of various types of heat responses in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nievola, C.C.; Carvalho, C.P.; Carvalho, V.; Rodrigues, E. Rapid responses of plants to temperature changes. Temperature 2017, 4, 371–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, E.; Chen, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, Q. Effects of high temperature on the fine structure of starch during the grain-filling stages in rice: Mathematical modeling and integrated enzymatic analysis. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 99, 2865–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Yu, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, E.; Gilbert, R.G.; Liu, Q. New insights into amylose and amylopectin biosynthesis in rice endosperm. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 230, 115656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Li, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, E.; Li, Q.; Tao, K.; Yu, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; et al. The interaction between amylose and amylopectin synthesis in rice endosperm grown at high temperature. Food Chem. 2019, 301, 125258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syahariza, Z.; Sar, S.; Hasjim, J.; Tizzotti, M.J.; Gilbert, R. The importance of amylose and amylopectin fine structures for starch digestibility in cooked rice grains. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, M.; Ouwerkerk, P.B.F. Molecular and environmental factors determining grain quality in rice. Food Energy Secur. 2012, 1, 111–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevame, A.Y.M.; Emon, R.M.; Malek, M.A.; Hasan, M.M.; Alam, A.; Muharam, F.M.; Aslani, F.; Rafii, M.Y.; Ismail, M.R. Relationship between high temperature and formation of chalkiness and their effects on quality of rice. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1653721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, S.; Matsuda, T.; Tajima, S.; Nitta, Y. Effect of high temperature at ripening stage on the reserve accumulation in seed in some rice cultivars. Plant Prod. Sci. 2002, 5, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patindol, J.A.; Siebenmorgen, T.J.; Wang, Y.-J.; Lanning, S.B.; Counce, P.A. Impact of elevated nighttime air temperatures during kernel development on starch properties of field-grown rice. Cereal Chem. 2014, 91, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lanning, S.B.; Siebenmorgen, T.J.; Ambardekar, A.A.; Counce, P.A.; Bryant, R.J. Effects of nighttime air temperature during kernel development of field-grown rice on physicochemical and functional properties. Cereal Chem. 2012, 89, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patindol, J.; Wang, Y.J. Fine structures and physicochemical properties of starches from chalky and translucent rice kernels. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 2777–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashida, K.; Iida, S.; Yasui, T. Morphological, physical, and chemical properties of grain and flour from chalky rice mutants. Cereal Chem. 2009, 86, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, A.B.; Case, J.D.; Takahashi, Y.; Lee, T.H.; Mori, W. Isolation of melatonin, the pineal gland factor that lightens melanocytes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Vico, A.; Lardone, P.J.; Álvarez-Sánchez, N.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, A.; Guerrero, J.M. Melatonin: Buffering the immune system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 8638–8683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jan, J.E.; Reiter, R.J.; Wasdell, M.B.; Bax, M. The role of the thalamus in sleep, pineal melatonin production, and circadian rhythm sleep disorders. J. Pineal Res. 2008, 46, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posmyk, M.M.; Janas, K.M. Melatonin in plants. Acta Physiol. Plant 2009, 31, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afreen, F.; Zobayed, S.; Kozai, T. Melatonin in Glycyrrhiza uralen-sis: Response of plant roots to spectral quality of light and UV-B radiation. J. Pineal Res. 2006, 41, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murch, S.J.; Campbell, S.S.B.; Saxena, P.K. The role of serotonin and melatonin in plant morphogenesis: Regulation of auxin-induced root organogenesis in in vitro-cultured explants of St. John’s Wort (Hypericum perforatum L.). In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 2001, 37, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnao, M.B.; Ruiz, J.H. Melatonin: A new plant hormone and/or a plant master regulator? Trends Plant Sci. 2019, 24, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnao, M.B.; Hernández-Ruiz, J. Protective effect of melatonin against chlorophyll degradation during the senescence of barley leaves. J. Pineal Res. 2009, 46, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Sun, K.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, X. Exogenous melatonin enhances cold, salt and drought stress tolerance by improving antioxidant defense in tea plant (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze). Molecules 2019, 24, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mandal, M.K.; Kousik, C. Differential roles of the plant secondary metabolite melatonin in plant-host resistance and pathogen suppression. Phytopathology 2018, 108, e12505. [Google Scholar]
- Pardo-Hernández, M.; López-Delacalle, M.; Rivero, R. ROS and NO regulation by melatonin under abiotic stress in plants. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Rui, C.; Zhang, H.; Xu, N.; Dai, M.; Chen, X.; Lu, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; et al. Melatonin improves cotton salt tolerance by regulating ROS scavenging system and Ca2+ signal transduction. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 693690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnao, M.B.; Ruiz, J.H. Melatonin and its relationship to plant hormones. Ann. Bot. 2018, 121, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arnao, B.M.; Hernández-Ruiz, J. Melatonin against environmental plant stressors: A review. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2021, 22, 413–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.E.; Cui, J.M.; Li, G.X.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, Z.W.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, H.Y. Effect of salicylic acid on the antioxidant system and photosystem II in wheat seedlings. Biol. Plant. 2016, 60, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Jiang, C.; Ye, T.; Tan, D.-X.; Reiter, R.J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, R.; Chan, Z. Comparative physiological, metabolomic, and transcriptomic analyses reveal mechanisms of improved abiotic stress resistance in bermudagrass [Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers.] by exogenous melatonin. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, F.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Z. Effect of UV-C treatment on modulating antioxidative system and proline metabolism of bamboo shoots subjected to chilling stress. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2015, 37, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.H.; Bo, H.; Ding, C.B.; Zhang, Z.W.; Chen, Y.E.; Chao, H. Effects of melatonin on anti-oxidative systems and photosystem Ⅱ in cold-stressed rice seedlings. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byeon, Y.; Back, K. Melatonin synthesis in rice seedlings in vivo is enhanced at high temperatures and under dark conditions due to increased serotonin N-acetyltransferase and N-acetylserotonin methyltransferase activities. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 56, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, X.; Zhao, J.; Sun, X.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, D.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Q. Exogenous Melatonin Improves the Quality Performance of Rice under High Temperature during Grain Filling. Agronomy 2022, 12, 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12040949
Fan X, Zhao J, Sun X, Zhu Y, Li Q, Zhang L, Zhao D, Huang L, Zhang C, Liu Q. Exogenous Melatonin Improves the Quality Performance of Rice under High Temperature during Grain Filling. Agronomy. 2022; 12(4):949. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12040949
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Xiaolei, Jie Zhao, Xiaosong Sun, Yun Zhu, Qianfeng Li, Lin Zhang, Dongsheng Zhao, Lichun Huang, Changquan Zhang, and Qiaoquan Liu. 2022. "Exogenous Melatonin Improves the Quality Performance of Rice under High Temperature during Grain Filling" Agronomy 12, no. 4: 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12040949
APA StyleFan, X., Zhao, J., Sun, X., Zhu, Y., Li, Q., Zhang, L., Zhao, D., Huang, L., Zhang, C., & Liu, Q. (2022). Exogenous Melatonin Improves the Quality Performance of Rice under High Temperature during Grain Filling. Agronomy, 12(4), 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12040949







