Abstract
Wheat is the third largest grown crop after maize and rice worldwide. Integrated use of chemical and biofertilizers have the potential to improve crop yield and quality due to their growth-promoting attributes. Therefore, the present study planned to evaluate the effectiveness of endophytic (Paenibacillus sp. strain (ZE11), Bacillus subtilis (ZE15) and Bacillus megaterium (ZE32)) and rhizobacterial strains (Bacillus subtilis (ZR2) Bacillus subtilis (ZR3) and Bacillus megaterium strain (ZR19)), solely and in combination, to increase the productivity of wheat and microbial activity in the rhizosphere. The maximum increase in microbial biomass carbon (44%), available phosphorous (30%), ammonium–nitrogen (24%), nitrate–nitrogen (37%), iron (10%), zinc (11%) and bacterial population (31%) was recorded by co-inoculation of ZE11 + ZR3. Subsequently, co-inoculation of ZE11+ZR3 showed a maximum increase of 31%, 29%, 30%, 27%, 33%, 30%, 25%, 9%, 15%, 9%, 18% and 26% in superoxidase dismutase (SOD), peroxidase dismutase (POD), catalase (CAT), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), polyphenol oxidase (PPO) and peroxidase (POX), grain yield, nitrogen, phosphorous, potassium, iron and zinc in grains, respectively, as compared to uninoculated control. The sole inoculation of ZR19 showed maximum harvest index (45.5%). The sole inoculation of endophytes and rhizobacteria has a significant effect on growth, physiology, and wheat crop yield. However, co-inoculation had a better effect and can be used to develop multi-strain biofertilizer to promote growth and yield of crops.
1. Introduction
Wheat as a significant grain crop has gained importance in gross domestic production (GDP) in Pakistan. Among winter crops, wheat is an important grain crop for achieving the country’s food security [1]. Being a staple food of Pakistan’s entire population, about 72% of calories and proteins are supplied through wheat in a regular diet. In Pakistan, the highest use of wheat per capita (120 kg year−1) was documented by the Pakistan Agriculture Research Council [2]. As wheat has considerable use in Pakistan, it is cultivated on a large area, which makes Pakistan among the top ten wheat-producing countries in the world [3].
It is estimated that the yield potential of wheat in Pakistan is still less than other competing countries; therefore, there is a need to address this yield gap. Hence the per hectare annual wheat yield in the country is below the required amount for population [2]. The factors that have caused a lower yield in potential are: late sowing of wheat due to delayed maturity and harvesting of cotton, rice and sugarcane; inaccessibility of quality inputs such as seed, fertilizers, weedicide and pesticide; degradation of soil, temperature variability, drought, and shortage of irrigation water; and consequently, the poor management of available resources [4]. Improper drainage of excessive water is also an essential factor in limiting wheat production [2].
To overcome these constraints, it is necessary to enhance the yield of wheat per unit area by using new varieties that have the potential to give more grain yield and/or introduce new approaches and technologies. Among the new technologies, biofertilizers have been receiving the attention of researchers during the last few decades. Biofertilizers came into view as an encouraging component of an integrated nutrient supply system in agriculture [5]. Biofertilizers can be defined as a group of living microorganisms applied in agriculture through seed inoculation and foliar and soil application [6]. These microbes make an association in the rhizosphere (rhizospheric bacteria) or interior of the plant (endophytic bacteria) and improve plant growth by competing with pathogens and facilitating the host plant in acquiring nutrients [7,8]. Biofertilizers promote plant growth by supplying nutrients through biological nitrogen fixation or by increasing the availability of insoluble nutrients in the soil and by the synthesis of growth-promoting substances [9,10]. Microorganisms such as nitrogen-fixing and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria tend to change-over atmospheric nitrogen to plant-accessible form and production of enzymes and solubilization of the insoluble phosphate from organic and inorganic phosphate sources [11].
Biofertilizers are economically attractive and ecological means of improving the quality and quantity of crops [12]. These are less expensive and improve crop growth and quality of crops by stimulating direct or indirect release of plant hormones [13]. The mechanism adopted by microbes for the promotion of plant growth also includes the production of phytohormones such as auxin, gibberellins and cytokinins [14]. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) improve root development and plant growth through solubilization of insoluble P and excretion of plant growth promoting hormones [15].
Consequently, PGPR have been used as a potential tool to produce bio-fortified food grains [16]. Rhizospheric and endophytic bacteria are free-living bacteria that are voluntarily associated with the rhizosphere and inside plant roots, directly co-relating in improving the growth and yield of plants [17,18]. In recent years, the use of beneficial microbes in cereals revealed constructive aftermath on promoting the productivity of diverse crops in variable environments under diverse environmental conditions [19,20]. For instance, phosphorous-solubilizing bacteria such as Pseudomonas and Bacillus species on the sole and a combined introduction to soil seems to be quite beneficial as they increase grain yield, tiller formation, and P content [21].
The combined application of endophytic and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria isolated from the wheat rhizosphere could be perceived to have distinct effects on plant growth [22]. The present study hypothesized that phosphate-solubilizing endophytic bacteria and rhizobacteria increase growth, yield and mineral contents in grains of wheat through solubilization and enhanced uptake of minerals. Hence, biofertilizers in agricultural production assume special significance, particularly in the present context of expensive chemical fertilizers. The research objective was to conceive the effectiveness and role of biofertilizers such as phosphate-solubilizing endophytic bacteria and rhizobacteria in improving soil health and productivity of the wheat crop. In the current study, we determined the impact of endophytic bacteria and rhizobacteria strains on soil physico-chemical and biological characteristics and their role in improving crop growth, physiology, grain yield and quality of wheat grains.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Inoculation of Wheat Seed
Wheat variety Johar-2016 was purchased from Regional Agriculture Research Institute (RARI), Bahawalpur. Our pre-isolated and identified endophytic bacteria, i.e., Paenibacillus sp. strain ZE11 (MN003399), Bacillus subtilis strain ZE15 (MN003400), Bacillus megaterium strain ZE32 (MN003401), and rhizobacteria, i.e., Bacillus subtilis strain ZR2 (MN007184), Bacillus subtilis strain ZR3 (MN007185) and Bacillus megaterium strain ZR19 (MN007186), were used alone and as co-inoculation [22]. The used strains were already characterized and reported positive for indole-3 acetic acid (IAA) production, exopolysaccharide (EPS) production, siderophores production, urease activity, hydrogen cyanide (HCN) production, catalase activity and oxidase activity. In our previous study, the root colonization of these strains was well reported in the growth room trial [22]. The strains were inoculated in Luria Bertani (LB) liquid culture [23] and incubated at 30 ± 1 °C in the rotary shaker (Shell lab, S19R-2, Sheldon manufacturing, Cornelius, OR 97113, USA) at 100 rpm. The overnight broth culture with a bacterial population of 107 colony forming units (CFU) mL−1 with an observed optical density of 0.45 at 540 nm was used for seed inoculation. For this purpose, the slurry was prepared by mixing sterilized peat, broth culture (respective bacterial strain) and 20% sugar solution (sterilized) in ratio 5:4:1. In the case of co-inoculation, an equal amount (1:1) of broth cultures of endophytic bacteria and rhizobacteria were used to prepare the slurry. For uninoculated control, sterilized peat with sterilized broth (autoclaved) were coated on seeds.
2.2. Pot Trial
A pot trial was conducted under natural conditions in wirehouse to evaluate the potential of endophytic bacteria and phosphate-solubilizing rhizobacteria for improving the rhizospheric properties of soil and wheat productivity under natural conditions. The soil was collected from the research area, thoroughly mixed, ground and sieved with two mesh size sieves for pot trial. Each pot is filled with 12 kg of soil. Before pot filling, soil samples were collected and analyzed for physico-chemical characteristics (Supplementary Table S1). The experiment was laid out in a completely randomized design (CRD) with three replications. Ten (10) treatments comprising sole and co-inoculation of selected compatible isolates [22] from endophytic bacteria and phosphate-solubilizing rhizobacteria were as T1: Control, T2: ZE11, T3: ZE15, T4: ZE32, T5: ZR2, T6: ZR3, T7: ZR19, T8: ZE11+ZR3, T9: ZE15+ZR2 and T10: ZE32+ZR19. Ten (10) inoculated seeds were sown in pots, and after, germination population was maintained as three plants pot−1. The recommended doses of phosphorous (P) and potassium (K) (90 and 60 kg ha−1) were applied at the time of sowing in the form of diammonium phosphate and sulfate of potash, respectively, while recommended dose of nitrogen (N) (120 kg ha−1) was applied in three splits after germination at 30-day intervals. Good quality tap water that meets the fitness criteria for irrigation water was used to irrigate the pots. All agronomic practices were carried out according to need.
2.3. Soil Analyses
2.3.1. Determination of Microbial Population
For the determination of the bacterial population, rhizospheric soil samples were collected at the time of harvesting. A standard serial dilution and pour plate technique was used to measure bacterial population in terms of colony-forming units (CFU) [24].
2.3.2. Determination of Microbial Biomass Carbon
Microbial biomass carbon was estimated by the chloroform fumigation and extraction method [25,26]. For this purpose, 30 g fresh soil was fumigated with alcohol-free chloroform in a desiccator at 25 °C for 72 h. Extraction was performed in 100 mL of 0.5 M K2SO4 by 1 h shaking on a reciprocating mechanical shaker. At the same time, 30 g unfumigated soil was also prepared.
For microbial biomass carbon, 8 mL of filtrate was taken in a digestion tube followed by 0.2 mL of K2Cr2O7, 0.07 g of HgO and 15 mL of 2:1 mixture of H2SO4 and HPO3. The tube was placed on a digester block to digest material at 250 °C for 2 h. After cooling, the mixture was diluted with 25 mL distilled water and titrated against 0.2 N Fe(NH2)2(SO4)2·6H2O using phenanthroline indicator until color changed from bluish-green to reddish-brown. For final calculations of microbial biomass carbon, the biomass carbon in unfumigated soil was subtracted from the biomass carbon in fumigated soil.
2.3.3. Determination of Nitrate and Ammonium Nitrogen
The 10 g air-dried soil sample and 50 mL of 2 M KCl extraction solution were mixed in a conical flask (250 mL) thoroughly for 30 min on a reciprocating mechanical shaker. The color infiltrate was developed with NED-sulfanilamide solution and measured at absorbance 520 nm. The concentration of nitrate–nitrogen was calculated using a calibration curve developed with 0, 5, 10, 15 and 20 ppm standards. A method blank was also prepared and subtracted from sample readings to measure nitrate–nitrogen concentration [27,28]. A similar filtrate (2 M KCl) was used to measure ammonium–nitrogen by distillation and titration against 0.01 N H2SO4 [29].
2.4. Plant Analyses
At physiological maturity, plants were analyzed for physiological attribute (SPAD chlorophyll value and relative water content) and antioxidant enzyme activities. After maturity, growth parameters were measured and yield data were calculated. For mineral analyses, 0.2 g homogeneous dry plant sample was mixed in 6 mL concentrated H2SO4 in a 100 mL conical flask and placed overnight at standard room temperature. With 1 mL H2O2 in an overnight flask, it was heated through the hot plate at 300 °C for 1 h. The last step was performed until the appearance of transparent or milkfish white color. The sample was diluted up to the mark and preserved for further analyses. The macronutrient (N, P and K) and micronutrient (Fe and Zn) were measured using the standard protocol [30].
Determination of Antioxidant Enzymes
One-half gram (0.5 g) of fresh leaf sample was taken in pre-cooled mortar placed on ice. It was ground in 4 mL of pre-cooled phosphate buffer solution (Na2HPO·12H2O (16.385 g) + NaH2PO4·2H2O (0.663 g) dissolved in distilled water and made into final volume of 1000 mL) with pH 7.8. After homogenization of the sample on ice, 4 mL phosphate buffer solution was added and mixed thoroughly. The mixture was centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 20 min at 4 °C. The supernatant was collected in Eppendorf tubes and immediately analyzed for antioxidant enzyme activities. If storage was required, then it was preserved at −20 °C.
For various antioxidant enzyme activities such as ascorbate peroxidase (APX), catalase (CAT), peroxidase (POD), superoxide dismutase (SOD), polyphenol oxidase (PPO) and peroxidase (POX), a reaction mixture was prepared to develop color, and absorbance was recorded on a spectrophotometer (Model Carry 60, UV-Vis, Agilent Tech., Santa Clara, CA, USA). A blank was also run throughout the procedure without enzyme extract, and enzyme activities were measured using equations described by [31].
2.5. Statistical Analyses
Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA using statistical software statistix 8.1, and means were compared with LSD at p ≤ 0.05 [32].
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacillus and Paenibacilus Strains on Soil Biological Properties
The impact of sole and combined application of endophytic bacteria and rhizobacteria on soil biological properties of rhizospheric soil is described in (Figure 1). All treatments significantly improved soil biochemical properties. However, co-inoculation showed more promising results as compared to sole inoculation. Among sole inoculation, the strain Bacillus megaterium ZR19 showed a 22% increase in available phosphorous. However, the co-inoculation of Paenibacillus sp. ZE11 + Bacillus subtilis ZR3 showed the highest available phosphorous, which was 30% more than control. Among co-inoculation, ZE32+ZR19 revealed distinct development in soil physicochemical characteristics. Both strains were identified as Bacillus megaterium.
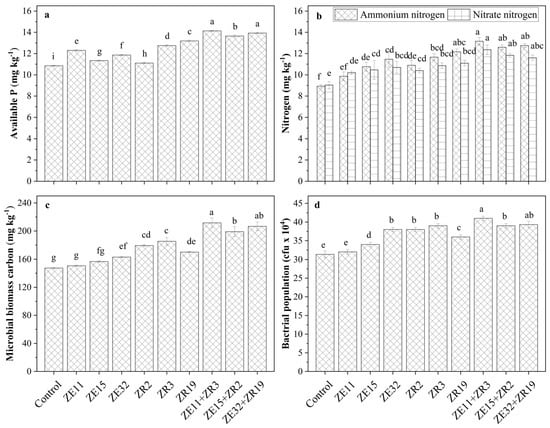
Figure 1.
Effect of Bacillus and Paenibacillus species on soil biological properties. Bars followed by the same letter(s) are not significantly different according to the least significance difference (LSD) test at p ≤ 0.05. (a) Available phosphorous content in the soil, (b) ammonium and nitrate nitrogen in soil, (c) microbial biomass carbon, and (d) bacterial population per gram of soil.
Furthermore, the sole inoculation of Paenibacillus sp. ZE11 had a nonsignificant impact on the bacterial population over the uninoculated control. The sole inoculation of Bacillus subtilis ZR3 gained 24% in the bacterial population, which is identical to the co-inoculation of Bacillus subtilis ZE15 + Bacillus subtilis ZR2. Co-inoculation of Paenibacillus sp. ZE11 + Bacillus subtilis ZR3 was observed with the highest increase in the bacterial population at 31%. The results revealed that the change in soil biochemical attributes such as microbial biomass carbon, ammonium and nitrate nitrogen was nonsignificant by inoculation of strains Paenibacillus sp. ZE11 and Bacillus subtilis ZE15. However, these traits were recorded at their highest due to co-inoculation of Paenibacillus sp. ZE11 + Bacillus subtilis ZR3 with recorded increases of 9%, 31%, 19% and 15%, respectively.
3.2. Plant Antioxidative Status Affected by Inoculation of Phosphate-Solubilizing Endophytic and Rhizobacteria
The antioxidative status of wheat crop was significantly influenced due to sole as well as co-inoculation of endophytic bacteria and rhizobacteria strains in pot trial (Figure 2). The antioxidants PPO, POD, SOD, CAT, APX and POX significantly increased by sole as well as co-inoculation of endophytic bacteria and rhizobacteria strains. The activity of POD, at 24% more than control, was characterized by sole inoculation of Bacillus megaterium ZE32 and co-inoculation of Bacillus subtilis ZE15 + Bacillus subtilis ZR2. For antioxidant enzymes activities, Bacillus megaterium ZR19 showed more promising results among all sole-inoculated treatments, with an increase of 23% and 18% in PPO and APX, respectively, along with an increase of 21% in SOD, POX and CAT. Co-inoculation of endophytic bacteria and rhizobacteria strains provided notable outcomes compared with sole inoculation. Co-inoculation of Paenibacillus sp. ZE11 + Bacillus subtilis ZR3 showed a maximum increase of 33%, 29%, 31%, 30%, 27% and 30% in PPO, POD, SOD, CAT, APX and POX, respectively.
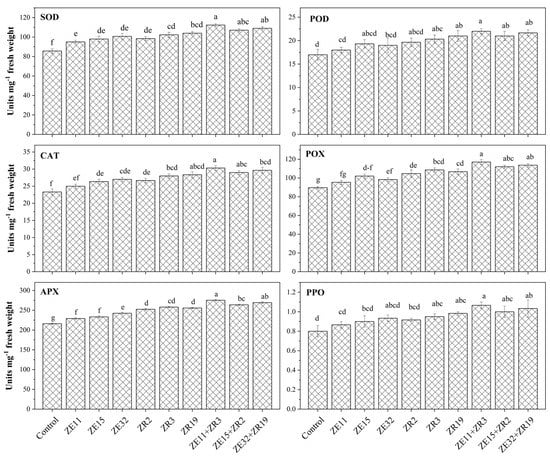
Figure 2.
Influence of Bacillus and Paenibacillus species on antioxidative status of wheat. Data are presented as mean of three replicates. Bars followed by same letter(s) are not significantly different according to least significance difference (LSD) test at p ≤ 0.05. PPO, polyphenol peroxidase activity; POD, peroxidase dismutase activity; SOD, superoxide dismutase activity; CAT, catalase activity; APX, ascorbate peroxidase activity; POX, peroxidase activity.
3.3. Effect of Endophytic Bacteria and Rhizobacteria Strains on Growth, Physiology and Yield of Wheat
Effect of phosphate-solubilizing endophytic bacteria and rhizobacteria strains on growth, physiology and yield are presented in Table 1. All sole-inoculated treatments showed similar results for relative water content that were slightly higher than control but were non-significant. However, co-inoculation showed a significant increase in relative water content. Subsequently, SPAD value was significantly improved by sole as well as co-inoculation. The maximum increase of 7% and 16% in relative water contents and SPAD value, relatively, was observed by co-inoculation of Paenibacillus sp. ZE11 + Bacillus subtilis ZR3. The sole inoculation of Bacillus subtilis ZR3 showed maximum increase in wheat growth followed by Bacillus megaterium ZE32. Sole inoculation of Paenibacillus sp. ZE11 showed non-significant increase in dry shoot biomass, dry root biomass and straw yield. However, grain yield was significantly improved by all applied treatments. Among sole inoculation, Bacillus subtilis ZR3 showed a maximum increase of 19% and 11% in dry shoot and root biomass, respectively. Furthermore, a maximum increase in grain yield (24%) and straw yield (16%) was recorded by Bacillus megaterium ZR19. However, co-inoculation of Paenibacillus sp. ZE11 + Bacillus subtilis ZR3 increased for all of the treatments regarding dry shoot biomass, dry root biomass, grain yield and straw yield at 24%, 17%, 15% and 25%, respectively, whereas the increase in harvest index as compared to control was non-significant by all applied treatments. The maximum harvest index (45.6%) was observed by sole inoculation of Bacillus megaterium ZR19 followed by 45.9% recorded by co-inoculation of Bacillus subtilis ZE15 + Bacillus subtilis ZR2, whereas the minimum harvest index (43.4%) was calculated in uninoculated control.

Table 1.
Influence of Bacillus and Paenibacillus species on growth, physiology and yield of wheat in a pot trial.
3.4. Effect of Endophytic Bacteria and Rhizobacteria Strains on Mineral Concentration in Wheat Grain
The data presented in Figure 3, describe the effectiveness of sole and co-inoculation of endophytic bacteria and rhizobacteria strains to improve macro- and micronutrient content in wheat grain. All applied treatments provided significant results for N, P, and K content in grain. Nitrogen content was maximized at 3.1% in grain through co-inoculation of Paenibacillus sp. ZE11 + Bacillus subtilis ZR3. Sole inoculation of Bacillus megaterium ZE32 and Bacillus subtilis ZR3 exhibited a similar effect on N content in grain, whereas, up to a 6% increase in N, P and K were recorded in root, shoot and grain, respectively, provided by sole inoculation of Bacillus megaterium ZR19. Elevation in the results of all co-inoculated treatments was discrete in contrast with sole-inoculated treatments. Among co-inoculated treatments, Paenibacillus sp. ZE11 + Bacillus subtilis ZR3 had more promising results regarding N, P and K content, providing a gain of 9%, 11% and 12%, respectively.
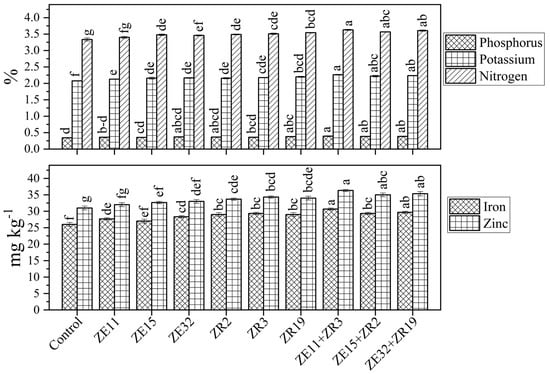
Figure 3.
Influence of Bacillus and Paenibacillus species on mineral concentration in grain of wheat. Data are presented as mean of three replicates. Bars followed by same letter(s) are not significantly different according to least significant difference (LSD) test at p ≤ 0.05.
Furthermore, all sole-inoculated treatments were identified with similar effects on Fe content in grain. Statistically similar results for the concentration of Zn in roots were characterized by all of the co-inoculated treatments. However, Paenibacillus sp. ZE11 + Bacillus subtilis ZR3 expressed a 10% and 11% rise in Fe and Zn in grain, respectively. Among sole inoculation, Bacillus megaterium ZR19 was marked with better effects in the case of Fe and Zn content in wheat.
4. Discussion
The results of the present study revealed that the application of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and endophytic bacteria improved soil biological and chemical properties such as microbial population in the rhizosphere, microbial biomass carbon, available P, nitrate nitrogen and ammonium nitrogen. The bacterial population increased by the inoculation of endophytic bacteria and rhizobacteria. An increase in bacterial population through seed inoculation has already been reported [33]. The enhanced bacterial population is directly related to improved microbial biomass carbon, and available phosphorous, nitrate–nitrogen and ammonium–nitrogen [34]. Furthermore, seed inoculation of biofertilizers enhances microbial activity through multiplication, plays a role in nutrient cycling, and promotes plant growth for sustainable agriculture [35]. The improvement in the nutrient status of soil (available phosphorous, nitrate–nitrogen and ammonium–nitrogen) was due to the biological nitrogen fixation, nutrient solubilization and mineralization and production of bacterial metabolites that enhanced plant growth [36]. The improvement in microbial biomass carbon (MBC) in applied treatments determined the soil health, as it acts as a substrate for nutrient regulation in soil [37]. This might be directly related to high soil organic matter and improved soil biochemical properties [38].
Endophytic bacteria and rhizobacteria can improve the nutritional status of soil that leads to improved uptake of nutrients, ultimately resulting in increased growth and yield of wheat. The bacterial isolates were found to improve soil biochemical properties beneficial for wheat growth. The PGPR is environmentally friendly, has no toxic effects, decreases dependence on chemical fertilizers, and plays an essential role in soil replenishing [39]. PGPR overcomes the harmful effect caused by salinity and makes more nutrients available to plants [40,41]. The sole and combined use of phosphate-solubilizing endophytic bacteria and rhizobacteria strains optimized the growth of wheat, resulting in an increase in yield supported by the conducted research. The recorded outcomes were similar to previous research [41,42]. Enhancement in growth seems to develop a thick root structure accompanied by a large take-up of nutrients, and improvements in soil chemical features, fertility status and bacterial activity in root surroundings [43].
Similarly, biofertilizers increase crop growth and yield under nonstressed conditions [44]. Previously, the promotion of growth and yield of the crop through enhanced accessibility of nutrients and improvement in soil health was well documented through applying biofertilizers [45]. The PGPR directly affects the development of roots, causing an increase in surface area and change of nutrient uptake through solubilization of insoluble nutrients such as converting insoluble phosphorus into an absorbable form [42,46]. The outcomes of combined use of PGPR and Rhizobium, including improvement in microbial activity and nutritional status of soil, were reported [47].
The conducted research reveals a remarkable gain in antioxidant enzyme activities such as SOD, POD, APX, CAT, POX, APX and PPO in contrast with control by inoculation/co-inoculation of endophytic bacteria and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria. Maintaining nutrient equilibrium in the rhizosphere might be recognized to raise these biological activities. Williamsons et al. [48] observed these increments due to GR gene expression, which correlates with the introduction of bacteria to soil. In the case of antioxidative reactions and processes of metabolism in plants, similar results were observed [49]. The introduction of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria raised the antioxidant enzyme activities. Paenibacillus sp. and Bacillus subtilis were observed to cause a development in antioxidant enzyme activities of maize [50]. The inoculation of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) improved the antioxidant enzyme system that reduced the harmfulness of reactive oxygen species (ROS) through reduced production of H2O2 that may shield membrane lipids from deterioration [51].
Bacterial isolates have a variable effect of improving wheat growth. In the present study, improvement in the growth and yield of wheat was recorded by inoculation and co-inoculation of endophytic bacteria and rhizobacteria strains to solubilize phosphorous. However, the effect was more intense in co-inoculation of Paenibacillus sp. ZE11 + Bacillus subtilis ZR3. This promotes growth, and the yield may be endorsed by various factors such as increased enzymatic activities, release of growth-promoting hormones, and enhanced availability of nutrients by endophytic and P Solubilizing bacteria [52]. Increased yield could be considered due to P-solubilizing bacteria making phosphorous available to plants in an abundant form that causes more uptake and more assimilation by the plant in development [20,53], suggesting an increase in the growth of plants upon the introduction of PGPR.
The grains of wheat were analyzed for mineral content, and the results revealed that the co-inoculation of phosphate-solubilizing endophytic bacteria and rhizospheric bacteria expressively improved nutrient uptake, leading to the deposition of some essential nutrients such as N, P, K, Fe and Zn in concentrations higher than control. As these constituents are also acquired by the native microbes and their application, the microbial population results in heterogeneity. These colonies make essential nutrients available by solubilization and mineralization, causing a higher concentration of these elements in plants [54]. The inoculation of Rhizobium and rhizospheric bacteria separately raised nitrogen supply to plants due to gain in nodule formation, and they supported the activity in the rhizosphere [13,42]. These results are well matched with the findings of [11,55], who observed a rise in nutrient contents in the root, shoot and grain of different crops upon inoculation of PGPR. A consistent approach to improve nutrient availability is to admit the benefits of PGPR and their nutrient-solubilizing ability. In the current study, pre-identified endophytic bacterial strains Paenibacillus sp. ZE11, Bacillus subtilis ZE15 and Bacillus megaterium ZE32 and rhizobacterial strains Bacillus subtilis ZR2, Bacillus subtilis ZR3 and Bacillus megaterium ZR19 were tested under pot condition to evaluate their potential for improvement in the productivity of wheat. Sole inoculation of these strains significantly improves soil fertility status and productivity of wheat. However, co-inoculation of Paenibacillus sp.ZE11 + Bacillus subtilis ZR3 showed better results than all applied treatments. Thus, both Paenibacillus sp. ZE11 and Bacillus subtilis ZR3 strains can be used to develop a potential biofertilizer to promote productivity on a sustainable basis.
5. Conclusions
The phosphate-solubilizing endophytic and rhizobacterial sole and co-inoculated strains enhanced microbial activities in rhizospheric soil and were responsible for adequate mineralization, solubilization and uptake of nutrients. Co-inoculation of endophytic bacterial strain Paenibacillus sp. ZE11 and rhizobacterial strain Bacillus subtilis ZR3 gave more promising results as compared to sole inoculation. Plant growth, yield, antioxidative activities and mineral content in grain were significantly improved by co-inoculation. Thus, it can be concluded that these strains performed multifarious functions in the rhizosphere and improved the crop productivity and quality of grains on a sustainable basis. Hence, this consortium can be further explored in the farmer’s field and used to develop a novel biofertilizer for wheat.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy12030551/s1, Table S1: Physico-chemical characteristics of soil prior to sowing.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A. and A.M.; methodology, Z.I. and B.; software, A.H.; formal analysis, M.B.; investigation, M.B. and A.M.; resources, A.D., B. and M.A.; data curation, Z.I.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.I.; writing—review and editing, A.M., A.H. and M.B.; visualization, A.D. and B.; supervision, M.A. and A.H.; project administration, M.A., X.W. and A.M.; funding acquisition, X.W. and A.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was supported by the project of Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic, grant number FCH-S-21-7398.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Soil Microbiology and Biotechnology Laboratory, Department of Soil Science, Faculty of Agriculture and Environment, The Islamia University of Bahawalpur for the facilitation of research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Raza, A.; Williams, D. Grain and Feed Update-Pakistan; Gain Report Number, PK1704; Global Agricultural information Network, USDA Foreign Agriculture Service, USDA Staff: Washington, DC, USA, 2017.
- PARC-Pakistan Agriculture Research Council. Wheat in Pakistan: A status paper. In National Coordinator Wheat, Plant Sciences Division; Pakistan Agriculture Research Council: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, A.; Naveed, M.; Abbas, T.; Saeed, Q.; Hussain, A.; Ashraf, M.N.; Minggang, X. Growth response of wheat and associated weeds to plant antagonistic rhizobacteria and fungi. Ital. J. Agron. 2019, 14, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Latief, E.A. Use of Azospirillum and Azobacter bacteria as biofertilizers in cereal crops: A review. Int. J. Res. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- Rasche, F.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Emmerling, C.; Belz, R.; Musyoki, M.K.; Zimmermann, J.; Martin, K. A preview of perennial grain agriculture: Knowledge gain from biotic interactions in natural and agricultural ecosystems. Ecosphere 2017, 8, e02048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Umar, W.; Ayub, M.A.; Ur Rehman, M.Z.; Ahmad, H.R.; Farooqi, Z.U.R.; Shahzad, A.; Rehman, U.; Mustafa, A.; Nadeem, M. Nitrogen and phosphorus use efficiency in agroecosystems. In Resources Use Efficiency in Agriculture; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 213–257. [Google Scholar]
- Hardoim, P.; Overbeek, L.S.; Berg, G.; Pirttilea, A.M.; Compant, S.; Campisano, A.; Doring, M.; Sessitsch, A. The hidden world within plants: Ecological and evolutionary considerations for defining functioning of microbial endophytes. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2015, 79, 293–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saeed, Q.; Xiukang, W.; Haider, F.U.; Kučerik, J.; Mumtaz, M.Z.; Holatko, J.; Naseem, M.; Kintl, A.; Ejaz, M.; Naveed, M.; et al. Rhizosphere Bacteria in Plant Growth Promotion, Biocontrol, and Bioremediation of Contaminated Sites: A Comprehensive Review of Effects and Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Ahmad, I.; Hilger, T.H.; Nadeem, S.M.; Akhtar, M.F.Z.; Jamil, M.; Hussain, A.; Zahir, Z.A. Preliminary study on phosphate solubilizing Bacillus subtilis strain Q3 and Paenibacillus sp. strain Q6 for improving cotton growth under alkaline conditions. Peer J. 2018, 6, e5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, M.A.; Naveed, M.; Mustafa, A.; Abbas, A. The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly of Rhizosphere Microbiome: Probiotics and Plant Health; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 253–290. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, M.; Zahir, Z.A.; Jamil, M.; Nazli, F.; Iqbal, Z. Field application of ACC-deaminase biotechnology for improving chickpea productivity in Bahawalpur. Soil Environ. 2017, 36, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Chittora, D.; Meena, M.; Barupal, T.; Swapnil, P.; Sharma, K. Cyanobacteria as a source of biofertilizers for sustainable agriculture. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 22, 100737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, M.Z.; Ahmad, M.; Jamil, M.; Asad, S.A.; Hafeez, F. Bacillus strains as potential alternate for zinc biofortification of maize grains. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2018, 20, 1779–1786. [Google Scholar]
- Dalve, P.D.; Mane, S.V.; Nimbalkar, R.R. Effect of biofertilizers on growth, flowering and yield of gladiolus. Asian J. Hortic. 2009, 4, 227–229. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, M.; Hussain, A.; Akhtar, M.F.Z.; Hye, M.Z.; Iqbal, Z.; Naz, T.; Iqbal, M.M. Effectiveness of multi-strain biofertilizer in combination with organic sources for improving the productivity of chickpea in drought ecology. Asian J. Agric. Biol. 2017, 5, 228–237. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, D.; Prasanna, R. Potential of microbes in the biofortification of Zn and Fe in dietary food grains. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 40, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Dasgupta, C.N.; Das, C. Cell growth kinetics of chlorella sorokiniana and nutritional values of its biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 167, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Ali, S.; Shahid, M.A.; Mustafa, A.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Curá, J.A. Insights into the Interactions among Roots, Rhizosphere, and Rhizobacteria for Improving Plant Growth and Tolerance to Abiotic Stresses: A Review. Cells 2021, 10, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, M.Z.; Barry, K.M.; Baker, A.L.; Nichols, D.S.; Ahmad, M.; Zahir, Z.A.; Britz, M.L. Production of lactic and acetic acids by Bacillus sp. ZM20 and Bacillus cereus following exposure to zinc oxide: A possible mechanism for Zn solubilization. Rhizosphere 2019, 12, 100170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Ahmad, M.; Mumtaz, M.Z.; Ali, S.; Sarfraz, R.; Naveed, M.; Jamil, M.; Damalas, C.A. Integrated application of organic amendments with alcaligenes sp. AZ9 improves nutrient uptake and yield of maize (Zea mays). J. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 29, 1277–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Naseer, I.; Hussain, A.; Mumtaz, M.Z.; Mustafa, A.; Hilger, T.H.; Zahir, Z.A.; Xu, M. Appraising endophyte–plant symbiosis for improved growth, nodulation, nitrogen fixation and abiotic stress tolerance: An experimental investigation with chickpea. (Cicer arietinum L.). Agronomy 2019, 9, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iqbal, Z.; Ahmad, M.; Jamil, M.; Akhtar, M.F.Z. Appraising the potential of integrated use of bacillus strains for improving wheat growth. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2020, 24, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Bertani, G. Studies on lysogenesis I: The mode of phage liberation by lysogenic Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1951, 62, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexander, J.; Parsons, B.V. Functional Family Therapy; Brooks/Cole Publishing Company: Three Lakes, WI, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.M.; Ingram, J.S.I. Tropical Soil Biology and Fertility: A Handbook of Methods; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 1993; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Okalebo, J.R.; Gathua, K.W.; Woomer, P.L. Laboratory Methods of Soil and Plant Analysis: A Working Manual; Tropical Soil Biology and Fertility Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Brewer, P.G.; Riley, J.P. The automatic determination of nitrate in sea water. Deep. Sea Res. Oceanogr. Abstr. 1965, 12, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.R.; Condron, L.M.; Clough, T.J.; Fiers, M.; Stewart, A.; Hill, R.A.; Sherlock, R.R. Biochar induced soil microbial community change: Implications for biogeochemical cycling of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus. Pedobiologia 2011, 54, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahrawat, K.L.; Ponnamperuma, F.N. Measurement of exchangeable NH+4 in tropical rice soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1978, 42, 282–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryan, J.; Estefan, G.; Rashid, A. Soil and Plant Analysis Laboratory Manual, 2nd Ed; International Center for Agriculture in Dry Areas (ICARDA): Aleppo, Syria, 2001; 172p. [Google Scholar]
- Bach, D.R.; Friston, K.J.; Dolan, R.J. An improved algorithm for model-based analysis of evoked skin conductance responses. Biol. Psychol. 2013, 94, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steel, R.G.D.; Torrie, J.H.; Dicky, D.A. Principles and Procedures of Statistics: A Biometrical Approach, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill Book International Co.: Singapore, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, A.; Zahir, Z.A.; Ditta, A.; Tahir, M.U.; Ahmad, M.; Mumtaz, M.Z.; Hayat, K.; Hussain, S. Production and implication of bio-activated organic fertilizer enriched with zinc-solubilizing bacteria to boost up maize (Zea mays L.) production and biofortification under two cropping seasons. Agronomy 2020, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anli, M.; Baslam, M.; Tahiri, A.; Raklami, A.; Symanczik, S.; Boutasknit, A.; Ait-El-Mokhtar, M.; Ben-Laouane, R.; Toubali, S.; Ait Rahou, Y. Biofertilizers as strategies to improve photosynthetic apparatus, growth, and drought stress tolerance in the date palm. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 516818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Bai, Z.; Bao, L.; Xue, L.; Zhang, S.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhuang, G.; Zhuang, X. Bacillus subtilis biofertilizer mitigating agricultural ammonia emission and shifting soil nitrogen cycling microbiomes. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 105989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.M.; Reddy, C.G.; Phogat, M.; Korav, S. Role of bio-fertilizers towards sustainable agricultural development: A review. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2018, 7, 1915–1921. [Google Scholar]
- Usmani, Z.; Kumar, V.; Rani, R.; Gupta, P.; Chandra, A. Changes in physico-chemical, microbiological and biochemical parameters during composting and vermicomposting of coal fy ash: A comparative study. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 16, 4647–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukashe, N.S.; Mupambwa, H.A.; Green, E.; Mnkeni, P.N.S. Inoculation of fy ash amended vermicompost with phosphate solubilizing bacteria (Pseudomonas fuorescens) and its infuence on vermi-degradation, nutrient release and biological activity. Waste Manag. 2019, 84, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.; Naveed, M.; Saeed, Q.; Ashrah, M.N.; Hussain, A.; Abbas, T.; Kamran, M.; Minggang, X. Application potentials of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and fungi as an alternative to conventional weed control methods. Sustain. Crop Prod. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaharoona, B.; Arshad, M.; Zahir, Z.A. Effect of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria containing ACC-deaminase on maize (Zea mays L.) growth under axenic conditions and on nodulation in mung bean (Vigna radiata L.). Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 42, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadeem, S.M.; Hamed, M.; Asghar, M.J.; Abbas, G.; Saeed, N.A. Screening of mungbean (Vigna radiate L. Wilczek) genotypes against sucking insect pests under natural field conditions. Pak. J. Zool. 2014, 46, 863–866. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, M.; Zahir, Z.A.; Nadeem, S.M.; Nazli, F.; Jamil, M.; Jamshaid, M.U. Physiological response of mung bean to Rhizobium and Pseudomonas based biofertilizers under salinity stress. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 51, 555–562. [Google Scholar]
- El-Husseini, M.M.; Helmut, B.; Helmut, J. The biofertilising effect of seed dressing with PGPR Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB 42 combined with two levels of mineral fertilizing in African cotton production. Arch. Phytopathol. 2012, 45, 2261–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Zahir, Z.A.; Asghar, H.N.; Asghar, M. The combined application of rhizobial strains and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria improves growth and productivity of mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) under salt-stressed conditions. Ann. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 1321–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.A.; Khalid, M.; Shahzad, S.M.; Ahmad, M.; Soleman, N.; Akhtar, N. Integrated use of Rhizobium leguminosarum, plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and enriched compost for improving growth, nodulation and yield of lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.). Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2013, 72, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aziz, M.Z.; Yaseen, M.; Naveed, M.; Wang, X.; Fatima, K.; Saeed, Q.; Mustafa, A. Polymer-Paraburkholderia phytofirmans PsJN coated diammonium phosphate enhanced microbial survival, phosphorous use efficiency, and production of wheat. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Zahir, Z.A.; Asghar, H.N.; Asghar, M. Inducing salt tolerance in mung bean through co-inoculation with rhizobia and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) containing 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase. Can. J. Microbiol. 2011, 57, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, J.D.; Hirsch-Wyncott, M.E.; Larkins, B.A.; Gelvin, S. Differential accumulation of a transcript driven by the CaMV 35S promoter in transgenic tobacco. Plant Physiol. 1989, 90, 1570–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foyer, C.; Lelandais, M.; Galap, C.; Kunert, K.J. Effects of elevated cytosolic glutathione reductase activity on the cellular glutathione pool and photosynthesis in leaves under normal and stress conditions. Plant Physiol. 1991, 97, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mumtaz, M.; Ahmad, M.; Jamil, M.; Hussain, T. Zinc solubilizing Bacillus spp. potential candidates for biofortification in maize. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 202, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabiei, Z.; Hosseini, S.J.; Pirdashti, H.; Hazrati, S. Physiological and biochemical traits in coriander affected by plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria under salt stress. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.; Akhtar, M.F.U.Z.; Jamil, M.; Latif, M.; Ahmad, I. Pesticide tolerant plant growth promoting rhizobacteria isolated from rhizosphere of okra. Soil Environ. 2015, 34, 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, M.; Pataczek, L.; Hilger, T.H.; Zahir, Z.A.; Hussain, A.; Rasche, F.; Schafleitner, R.; Solberg, S.O. Perspectives of Microbial Inoculation for Sustainable Development and Environmental Management. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ijaz, A.; Mumtaz, M.Z.; Wang, X.; Ahmad, M.; Saqib, M.; Maqbool, H.; Zaheer, A.; Wang, W.; Mustafa, A. Insights Into Manganese Solubilizing Bacillus spp. for Improving Plant Growth and Manganese Uptake in Maize. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 719504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, A.; Arshad, M.; Zahir, Z.A.; Asghar, M. Prospects of zinc solubilizing bacteria for enhancing growth of maize. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 52, 915–992. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).