Effects of Short-Term Tillage Managements on CH4 and N2O Emissions from a Double-Cropping Rice Field in Southern of China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
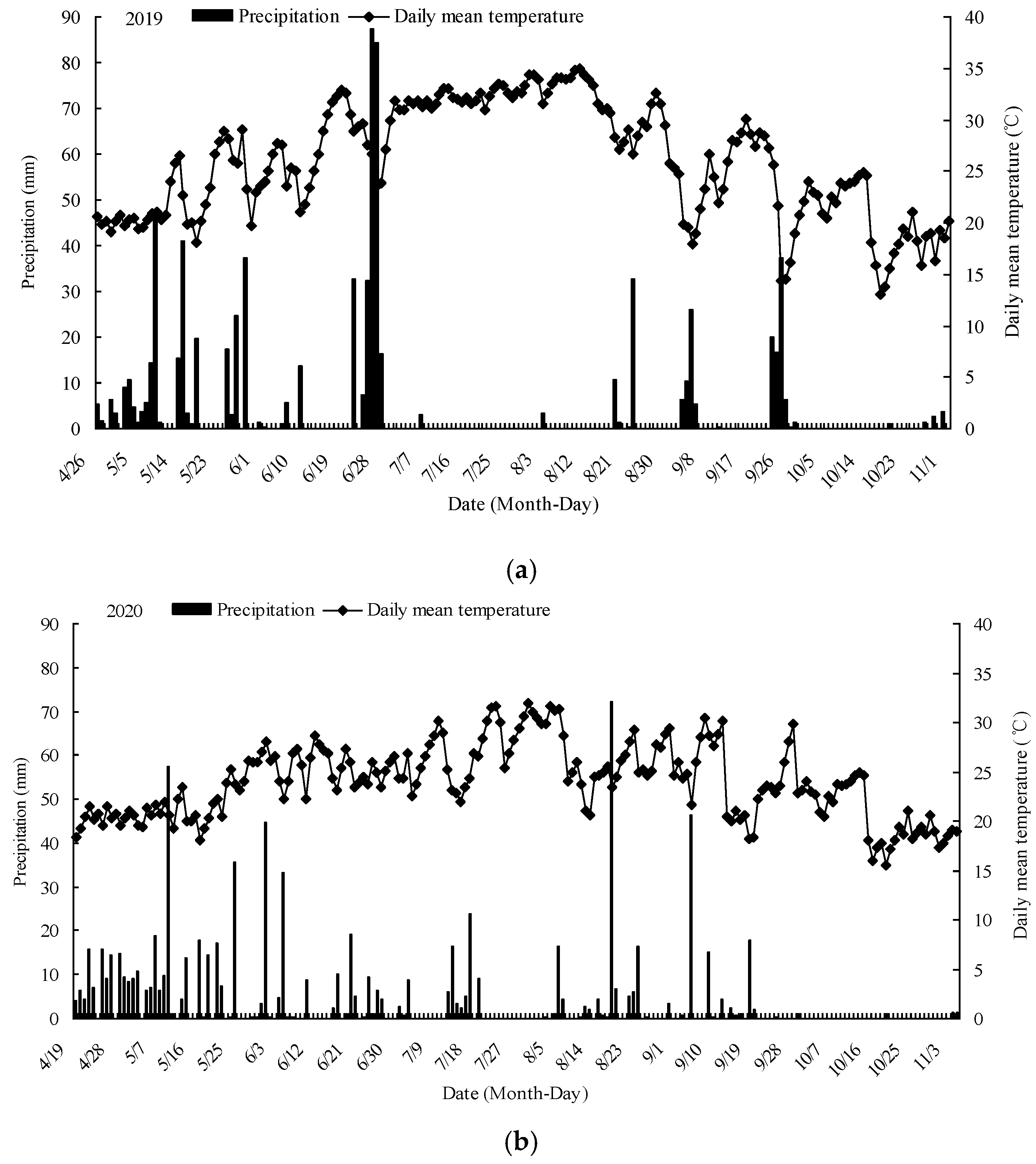
2.1. Sites and Cropping System
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Soil Sample and Greenhouse Gas Collection
2.4. Laboratory Analysis
2.4.1. Soil Bulk Density
2.4.2. SOC and SOC Stock
2.4.3. N2O and CH4 Emissions
2.5. Rice Yield
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. SOC Content and SOC Stock
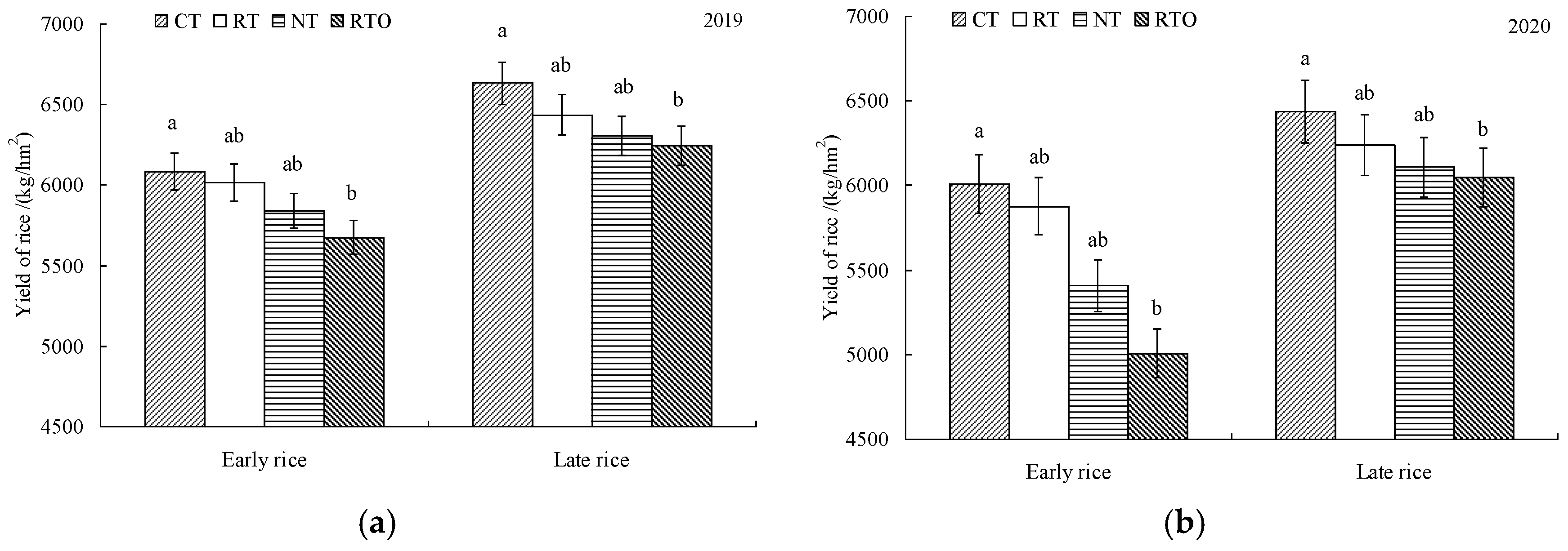
3.2. Early Rice and Late Rice Yield
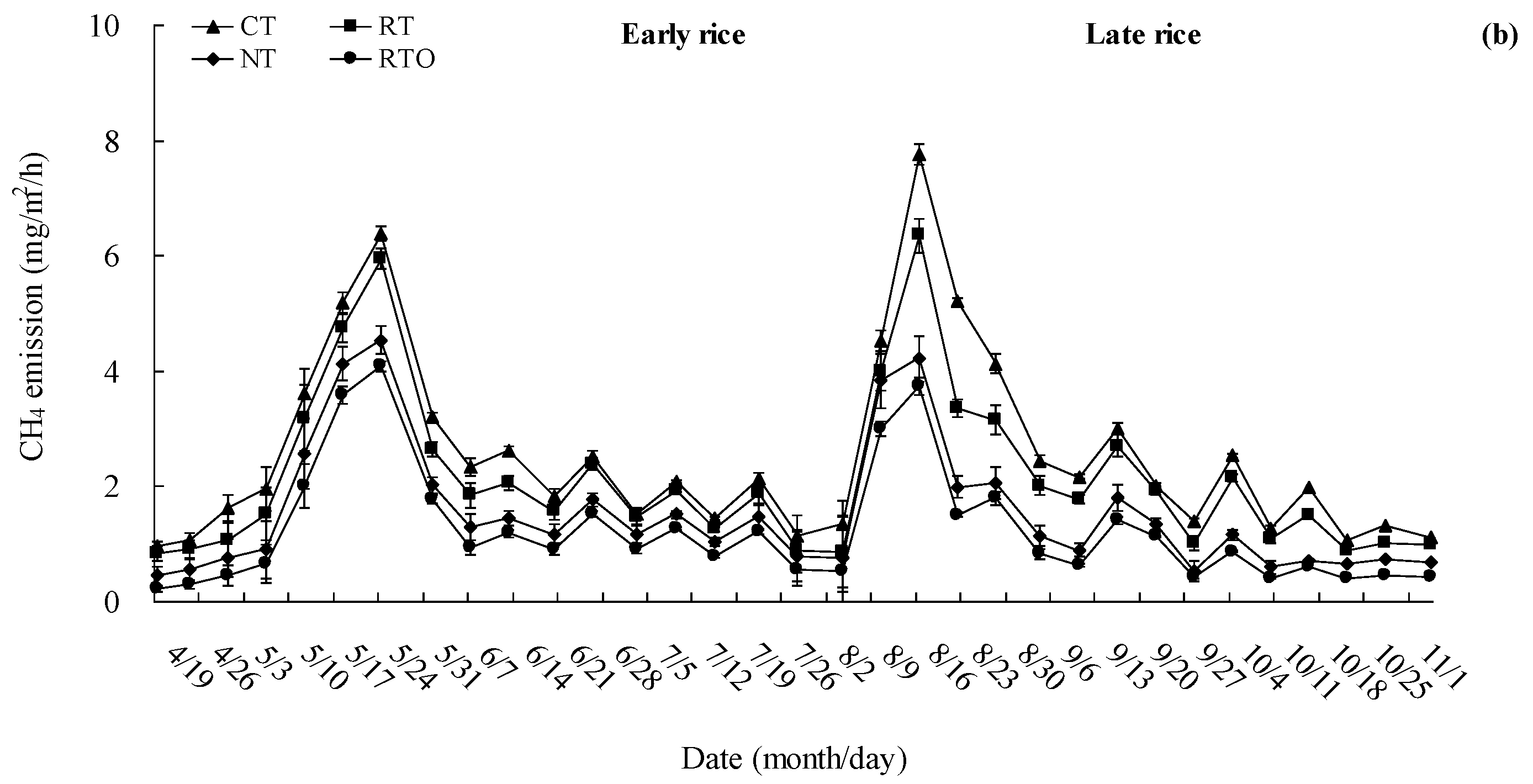
3.3. CH4 Emission Flux
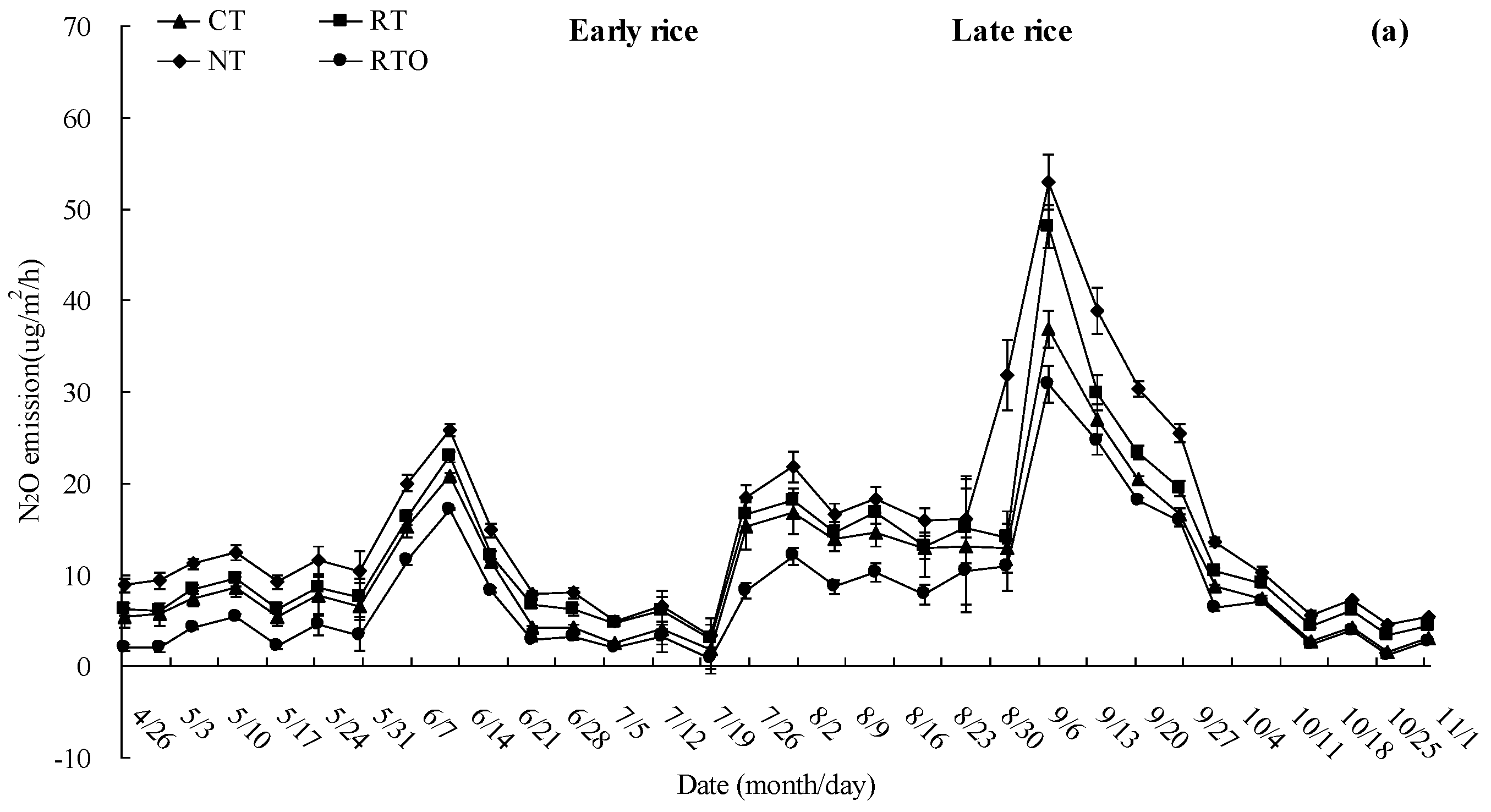
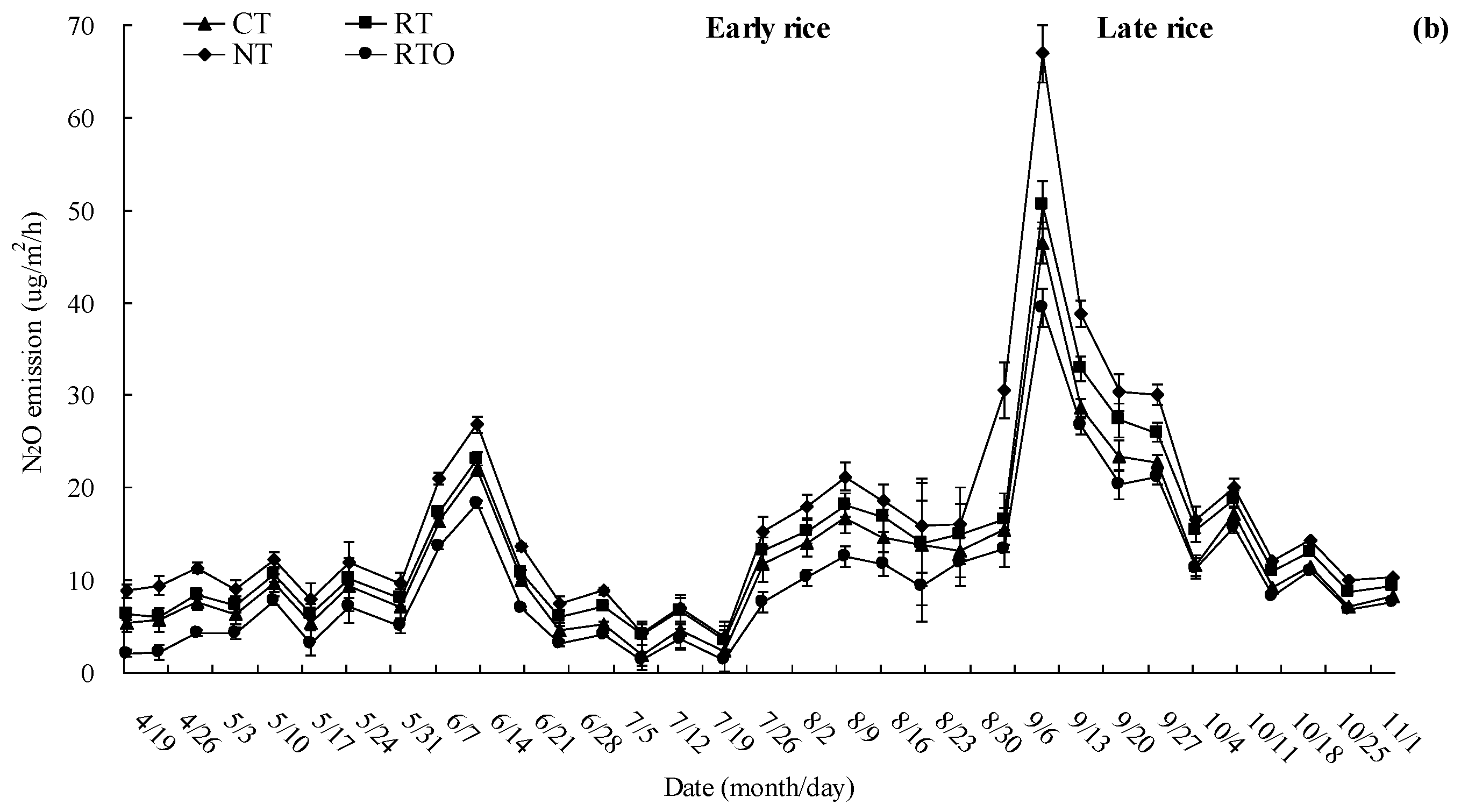
3.4. N2O Emission Flux
3.5. Cumulative Emissions of N2O and CH4 from Paddy Field
3.6. Comprehensive GWP of CH4 and N2O from Paddy Field
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Tillage Management on SOC Content and SOC Stock
4.2. Effects of Tillage Management on CH4 and N2O Emissions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balesdent, J.; Basile-Doelsch, I.; Chadoeuf, J.; Cornu, S.; Derrien, D.; Fekiacova, Z.; Hatté, C. Atmosphere–soil carbon transfer as a function of soil depth. Nature 2018, 559, 599–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza-Bonilla, D.; Álvaro-Fuentes, J.; Cantero-Martínez, C. Identifying soil organic carbon fractions sensitive to agricultural management practices. Soil Till. Res. 2014, 139, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheng, H.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Ge, T.D.; Wang, G.H. Loss of labile organic carbon from subsoil due to land-use changes in subtropical China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 88, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.Y.; Zhao, X.; He, C.; Virk, A.L.; Jing, Z.H.; Liu, Q.Y.; Wang, X.; Kan, Z.R.; Xiao, X.P.; Zhang, H.L. Effects of long-term tillage regimes on the vertical distribution of soil iron/aluminum oxides and carbon decomposition in rice paddies. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Goulding, K.; Smith, K.; Powlson, D.; Smith, J.; Falloon, P. Including trace gas fluxes in estimates of the carbon mitigation potential of UK agricultural land. Soil Use Manage. 2000, 16, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.J.; Zhang, Z.S.; Wang, D.D.; Li, C.F.; Cao, C.G. Effects of short-term conservation management practices on soil organic carbon fractions and microbial community composition under a rice-wheat rotation system. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2015, 51, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.D.; Zhang, H.L.; Dikgwatlhe, S.B.; Xue, J.F.; Qiu, K.C.; Tang, H.M.; Chen, F. Soil carbon storage and strafification under different tillage/residue-management practices in double rice cropping system. J. Integr. Agr. 2015, 14, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qi, J.Y.; Zhang, X.Z.; Li, S.S.; Virk, A.L.; Zhao, X.; Xiao, X.P.; Zhang, H.L. Effects of tillage and residue management on soil aggregates and associated carbon storage in a double paddy cropping system. Soil Till. Res. 2019, 194, 104339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.D.; Zhang, H.L.; Xue, J.F.; Liu, S.L.; Chen, F. A nine-year study on the effects of tillage on net annual global warming potential in double rice-cropping systems in Southern China. Soil Till. Res. 2021, 206, 104797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Bai, X.L.; Xue, J.F.; Chen, Z.D.; Tang, H.M.; Chen, F. Emissions of CH4 and N2O under different tillage systems from double-cropped paddy fields in southern China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.X.; Chen, Y.Q.; Sui, P.; Gao, W.S. Estimation of net greenhouse gas balance using crop- and soil-based approaches, two case studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 456–457, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dendooven, L.; Patino-Zúniga, L.; Verhulst, N.; Luna-Guido, M.; Marsch, R.; Govaerts, B. Global warming potential of agricultural systems with contrasting tillage and residue management in the central highlands of Mexico. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 152, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kessel, C.; Venterea, R.; Six, J.; Adviento-Borbe, M.A.; Linquist, B.; van Groenigen, K.J. Climate, duration, and N placement determine N2O emissions in reduced tillage systems: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.M.; Xiao, X.P.; Li, C.; Shi, L.H.; Cheng, K.K.; Li, W.Y.; Wen, L.; Xu, Y.L.; Wank, K. Microbial carbon source utilization in rice rhizosphere soil with different tillage practice in a double cropping rice field. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Pu, C.; Ma, S.T.; Liu, S.L.; Xue, J.F.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.Q.; Li, S.S.; Lal, R.; Chen, F.; et al. Management-induced greenhouse gases emission mitigation in global rice production. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 649, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.Y.; Ren, W.D.; Sun, B.H.; Zhang, S.L. Effects of contrasting soil management regimes on total and labile soil organic carbon fractions in a loess soil in China. Geoderma 2012, 177–178, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.M.; Xiao, X.P.; Li, C.; Tang, W.G.; Cheng, K.K.; Pan, X.C.; Wang, K.; Li, W.Y. Effects of different soil tillage systems on soil carbon management index under double-cropping rice field in southern China. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Q.; Yang, X.; Gao, C.; Wu, P.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Shen, Q.; Zou, J.; Guo, S. Net annual global warming potential and greenhouse gas intensity in Chinese double rice cropping systems: A 3-year field measurement in long-term fertilizer experiments. Glob. Change Biol. 2011, 17, 2196–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, G.R.; Hartge, K.H. Bulk density. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Part I: Physical and Mineralogical Methods Agronomy Monograph No. 9; Klute, A., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; pp. 363–375. [Google Scholar]
- Ellert, B.H.; Bettany, J.R. Calculation of organic matter and nutrients stored in soils under contrasting management regimes. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1995, 75, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thelen, K.; Fronning, B.; Kravchenko, A.; Min, D.; Robertson, G. Integrating livestock manure with a corn–soybean bioenergy cropping system improves short-term carbon sequestration rates and net global warming potential. Biomass Bioenerg. 2010, 34, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, S.R.; Pu, Y.L.; Li, T.; Xu, X.X.; Jia, Y.X.; Deing, O.P.; Gong, G.S. Dynamics of soil labile organic carbon fractions and C-cycle enzyme activities under straw mulch in Chengdu Plain. Soil Till. Res. 2016, 155, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, B.N.; Meena, V.S.; Alam, N.M.; Dogra, P.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Sharma, N.K.; Mishra, P.K. Impact of conservation practices on soil aggregation and the carbon management index after seven years of maize-wheat cropping system in the Indian Himalayas. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 216, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbitz, K.; Kaiser, K.; Fiedler, S.; Kölbl, A.; Amelung, W.; Bräuer, T.; Cao, Z.; Don, A.; Grootes, P.; Jahn, R.; et al. The carbon count of 2000 years of rice cultivation. Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, Y.B.; Kim, P.J. Silicate fertilization in no-tillage rice farming for mitigation of methane emission and increasing rice productivity. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 132, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ussiri, D.A.; Lal, R.; Jarecki, M.K. Nitrous oxide and methane emissions from long-term tillage under a continuous corn cropping system in Ohio. Soil Till. Res. 2009, 104, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.S.; Cao, C.G.; Guo, L.J.; Li, C.F. Emissions of CH4 and CO2 from paddy fields as affected by tillage practices and crop residues in central China. Paddy Water Environ. 2016, 14, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhu, B.; Huang, Y.; Hao, Q. Methane and nitrous oxide emissions from three paddy rice based cultivation systems in southwest China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 23, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M.; Akramkhanov, A.; Saggar, S. Nitrous oxide emissions from a New Zealand cropped soil: Tillage effects, spatial and seasonal variability. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 93, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elder, J.W.; Lal, R. Tillage effects on gaseous emissions from an intensively farmed organic soil in North Central Ohio. Soil Till. Res. 2008, 8, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Pan, G.; Smith, P.; Luo, T.; Li, L.; Zheng, J. Carbon footprint of China’s crop production—an estimation using agro-statistics data over 1993–2007. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 142, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, K.T.; Nonaka, R.; Win, A.T.; Sasada, Y.; Toyota, K.; Motobayashi, T. Effects of water saving irrigation and rice variety on greenhouse gas emissions and water use efficiency in a paddy field fertilized with anaerobically digested pig slurry. Paddy Water Environ. 2015, 13, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Frolking, S.; Xiao, X.; Moore, B.I.; Boles, S.; Qiu, J.; Huang, Y.; Salas, W.; Sass, R. Modeling impacts of farming management alternatives on CO2, CH4, and N2O emissions, a case study for water management of rice agriculture of China. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 2005, 19, GB3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, S.; Buresh, R.J.; Huang, J.; Zhong, X.; Zou, Y.; Yang, J. Improving nitrogen fertilization in rice by site-specific N management. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Years | Treatments | BD (g cm−3) | SOC (g kg−1) | SOC Stock (Mg ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | CT | 1.10 ± 0.03 b | 23.54 ± 0.68 a | 51.79 ± 1.50 a |
| RT | 1.14 ± 0.04 b | 22.26 ± 0.64 ab | 50.75 ± 1.47 ab | |
| NT | 1.21 ± 0.04 a | 20.93 ± 0.61 b | 50.65 ± 1.46 ab | |
| RTO | 1.17 ± 0.03 ab | 20.15 ± 0.58 b | 47.15 ± 1.36 b | |
| 2020 | CT | 1.10 ± 0.03 b | 23.59 ± 0.67 a | 51.90 ± 1.48 a |
| RT | 1.15 ± 0.03 b | 22.36 ± 0.63 ab | 51.43 ± 1.46 ab | |
| NT | 1.22 ± 0.04 a | 21.01 ± 0.60 b | 51.26 ± 1.45 ab | |
| RTO | 1.17 ± 0.03 ab | 20.18 ± 0.56 c | 47.22 ± 1.35 b |
| Years | Treatments | CH4 | N2O | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early Rice | Late Rice | Total | Early Rice | Late Rice | Total | ||
| 2019 | CT | 4.50 ± 0.12 a | 7.69 ± 0.22 a | 12.19 ± 0.35 a | 0.015 ± 0.001 c | 0.032 ± 0.001 c | 0.047 ± 0.002 c |
| RT | 3.81 ± 0.11 b | 5.31 ± 0.15 b | 9.12 ± 0.26 b | 0.018 ± 0.001 b | 0.037 ± 0.001 b | 0.055 ± 0.002 b | |
| NT | 2.66 ± 0.08 c | 3.28 ± 0.10 c | 5.95 ± 0.17 c | 0.022 ± 0.001 a | 0.046 ± 0.001 a | 0.068 ± 0.002 a | |
| RTO | 2.03 ± 0.06 d | 2.56 ± 0.07 d | 4.59 ± 0.13 d | 0.010 ± 0.001 d | 0.025 ± 0.001 d | 0.035 ± 0.001 d | |
| 2020 | CT | 5.35 ± 0.15 a | 6.53 ± 0.18 a | 11.87 ± 0.34 a | 0.017 ± 0.001 c | 0.040 ± 0.001 c | 0.057 ± 0.002 c |
| RT | 4.66 ± 0.11 b | 5.26 ± 0.15 b | 9.92 ± 0.28 b | 0.019 ± 0.001 b | 0.046 ± 0.001 b | 0.065 ± 0.002 b | |
| NT | 3.53 ± 0.10 c | 3.55 ± 0.10 c | 7.08 ± 0.21 c | 0.024 ± 0.001 a | 0.054 ± 0.001 a | 0.078 ± 0.002 a | |
| RTO | 2.87 ± 0.08 d | 2.81 ± 0.08 d | 5.68 ± 0.16 d | 0.012 ± 0.001 d | 0.035 ± 0.001 d | 0.047 ± 0.001 d | |
| Years | Treatments | CH4 Emission (g m−2) | N2O Emission (g m−2) | GWP of CH4 (kg CO2 ha−1) | GWP of N2O (kg CO2 ha−1) | GWP of CH4 and N2O (kg CO2 ha−1) | Early and Late Rice Grain Yield (kg ha−1) | Per yield GWP CO2 (kg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | CT | 12.19 ± 0.35 a | 0.047 ± 0.002 c | 3051.77 ± 88.10 a | 140.26 ± 5.85 c | 3192.02 ± 92.14 a | 12,718.5 ± 367.2 a | 0.25 ± 0.01 a |
| RT | 9.12 ± 0.26 b | 0.055 ± 0.002 b | 2283.19 ± 65.91 b | 164.13 ± 4.73 b | 2447.32 ± 70.64 b | 12,454.5 ± 359.5 ab | 0.20 ± 0.01 b | |
| NT | 5.95 ± 0.17 c | 0.068 ± 0.002 a | 1489.58 ± 43.01 c | 202.92 ± 4.04 a | 1692.51 ± 48.85 c | 12,150.0 ± 350.7 ab | 0.14 ± 0.01 c | |
| RTO | 4.59 ± 0.13 d | 0.035 ± 0.001 d | 1149.11 ± 33.17 d | 104.45 ± 3.01 d | 1253.55 ± 36.18 d | 11,922.0 ± 344.2 b | 0.11 ± 0.01 d | |
| 2020 | CT | 11.87 ± 0.34 a | 0.057 ± 0.002 c | 2971.65 ± 85.78 a | 170.10 ± 5.74 c | 3141.75 ± 90.01 a | 12,343.9 ± 356.3 a | 0.25 ± 0.01 a |
| RT | 9.92 ± 0.28 b | 0.065 ± 0.002 b | 2483.47 ± 71.69 b | 193.97 ± 4.93 b | 2677.44 ± 76.68 b | 12,112.6 ± 349.7 ab | 0.22 ± 0.01 b | |
| NT | 7.08 ± 0.21 c | 0.078 ± 0.002 a | 1772.48 ± 51.16 c | 232.77 ± 4.22 a | 2005.24 ± 57.36 c | 11,515.9 ± 332.4 ab | 0.17 ± 0.01 c | |
| RTO | 5.68 ± 0.16 d | 0.047 ± 0.001 d | 1421.99 ± 41.04 d | 140.26 ± 3.19 d | 1562.24 ± 44.23 d | 11,055.8 ± 319.2 b | 0.14 ± 0.01 d |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, H.; Li, C.; Shi, L.; Cheng, K.; Wen, L.; Li, W.; Xiao, X. Effects of Short-Term Tillage Managements on CH4 and N2O Emissions from a Double-Cropping Rice Field in Southern of China. Agronomy 2022, 12, 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12020517
Tang H, Li C, Shi L, Cheng K, Wen L, Li W, Xiao X. Effects of Short-Term Tillage Managements on CH4 and N2O Emissions from a Double-Cropping Rice Field in Southern of China. Agronomy. 2022; 12(2):517. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12020517
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Haiming, Chao Li, Lihong Shi, Kaikai Cheng, Li Wen, Weiyan Li, and Xiaoping Xiao. 2022. "Effects of Short-Term Tillage Managements on CH4 and N2O Emissions from a Double-Cropping Rice Field in Southern of China" Agronomy 12, no. 2: 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12020517
APA StyleTang, H., Li, C., Shi, L., Cheng, K., Wen, L., Li, W., & Xiao, X. (2022). Effects of Short-Term Tillage Managements on CH4 and N2O Emissions from a Double-Cropping Rice Field in Southern of China. Agronomy, 12(2), 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12020517






