Can Split Application of Slow-Release Fertilizer Improve Wheat Yield, Nitrogen Efficiency and Their Stability in Different Ecological Regions?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
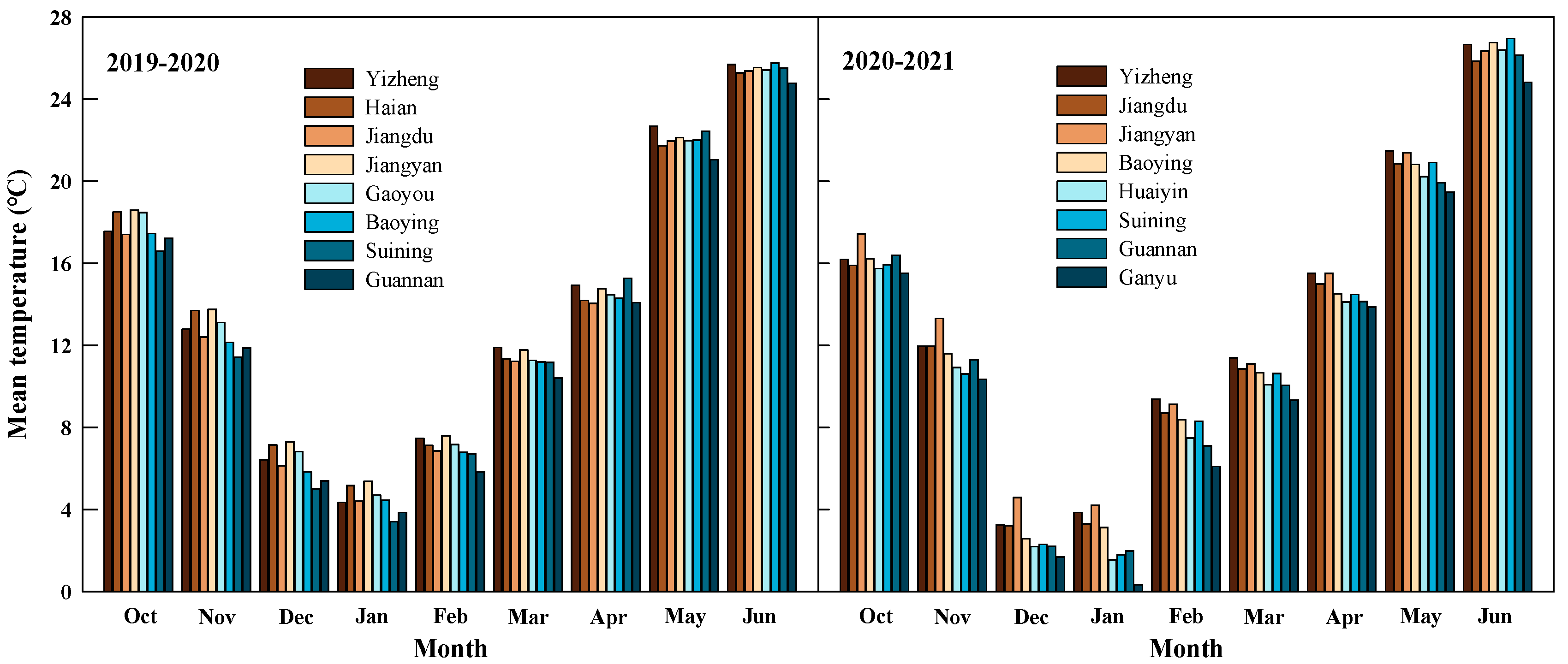
2.1. Materials and Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sampling and Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis of Data
3. Results
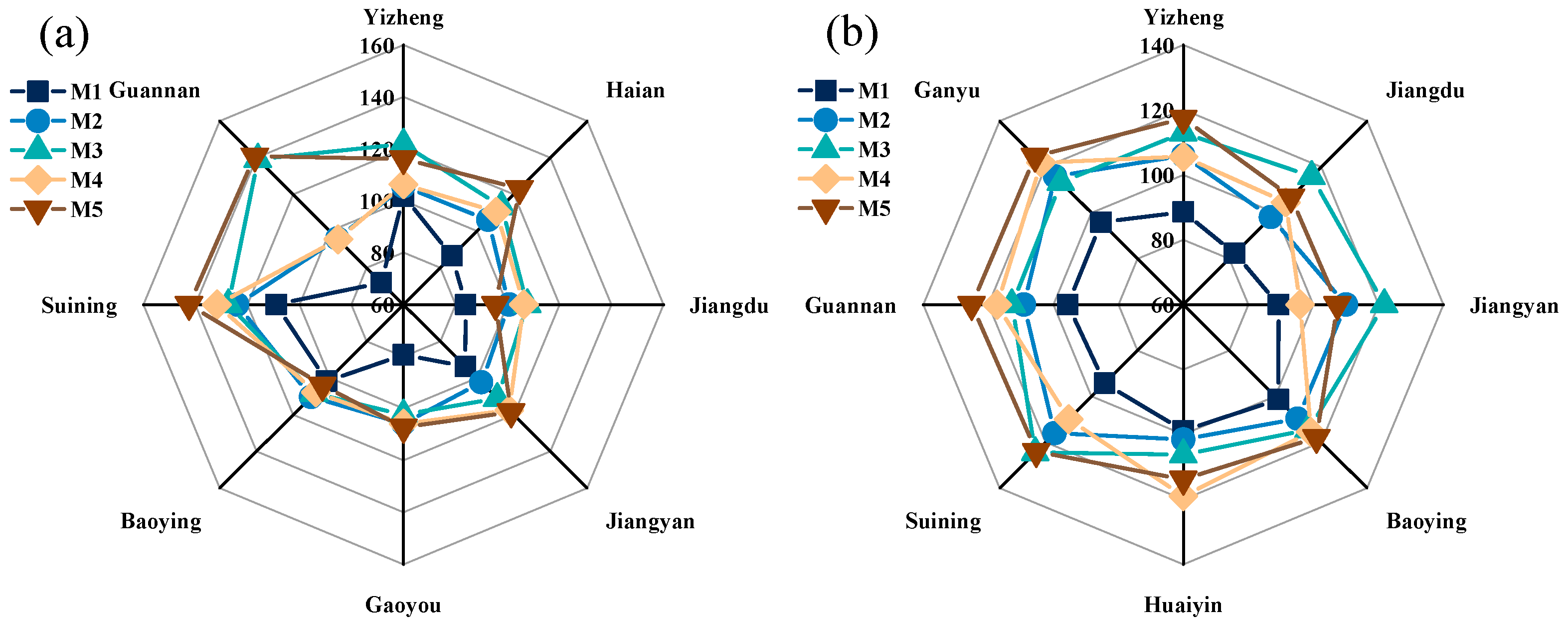
3.1. Grain Yield and Yield Components
3.1.1. Grain Yield
3.1.2. Yield Components
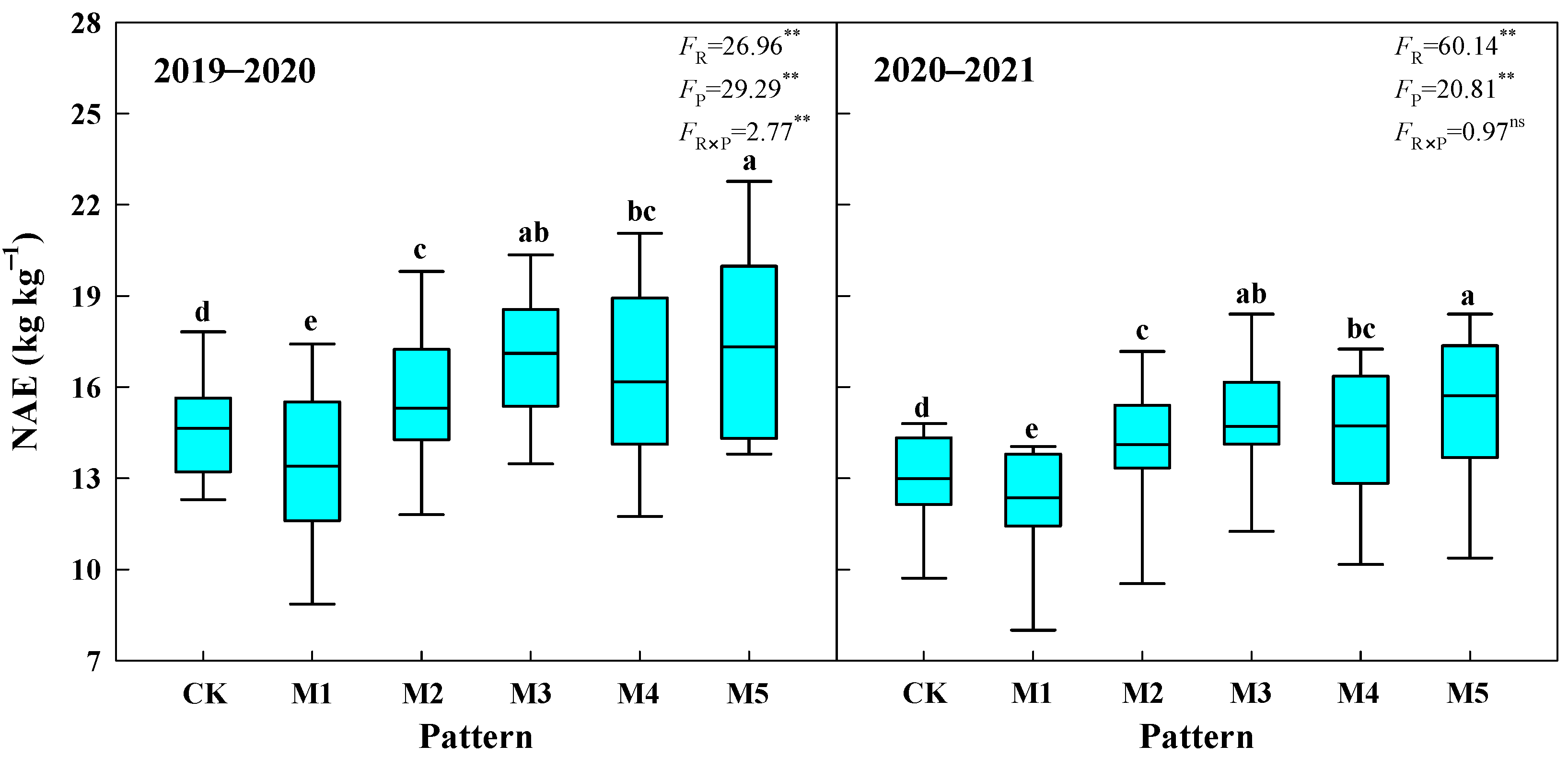
3.2. Nitrogen Agronomic Efficiency
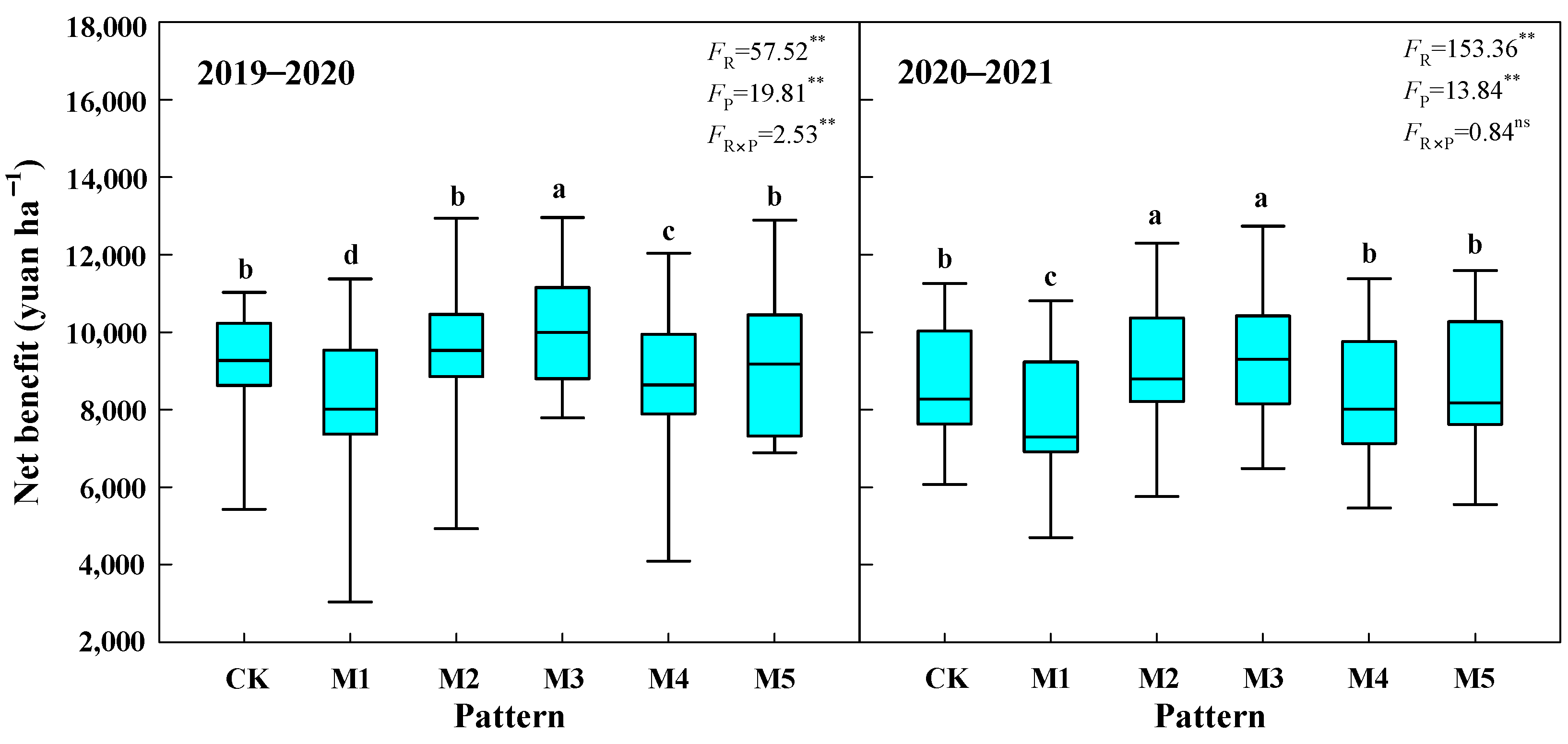
3.3. Economic Benefit
4. Discussion
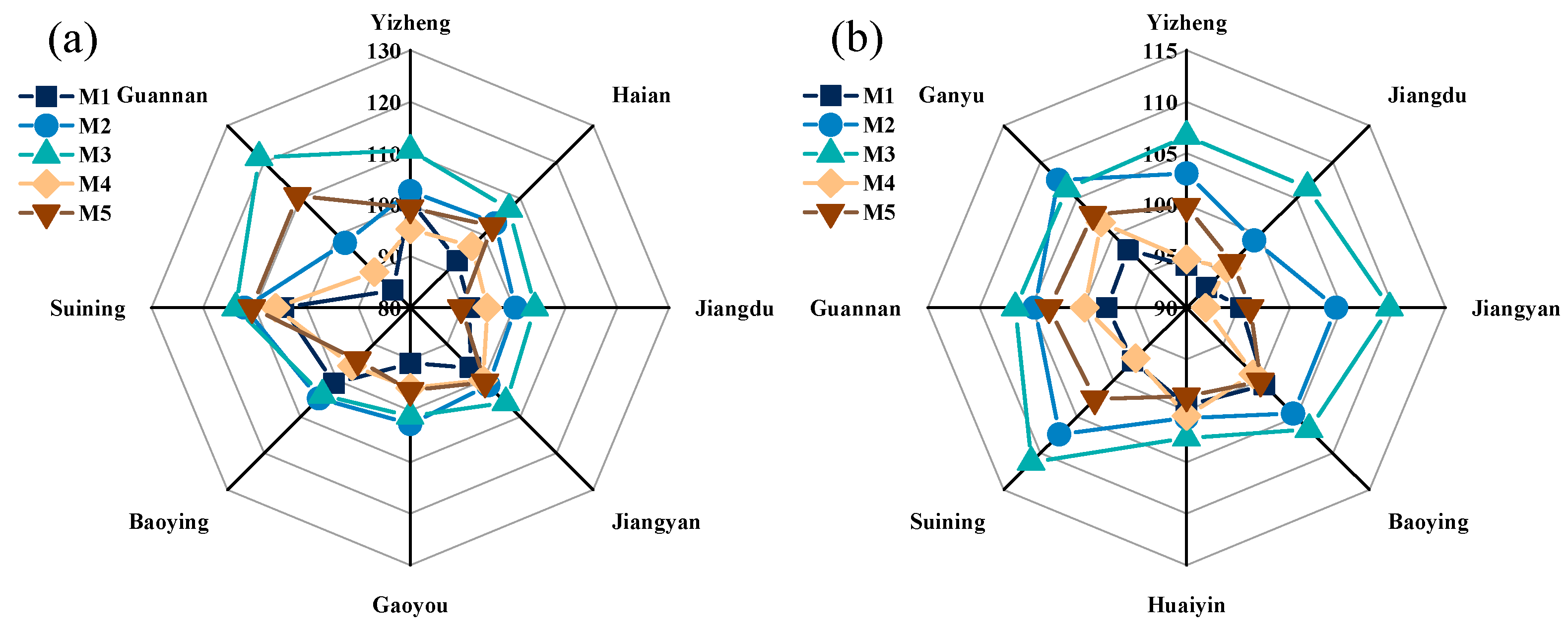
4.1. Synergies of NAE, Yield and Benefit of Wheat under Different Fertilization Patterns
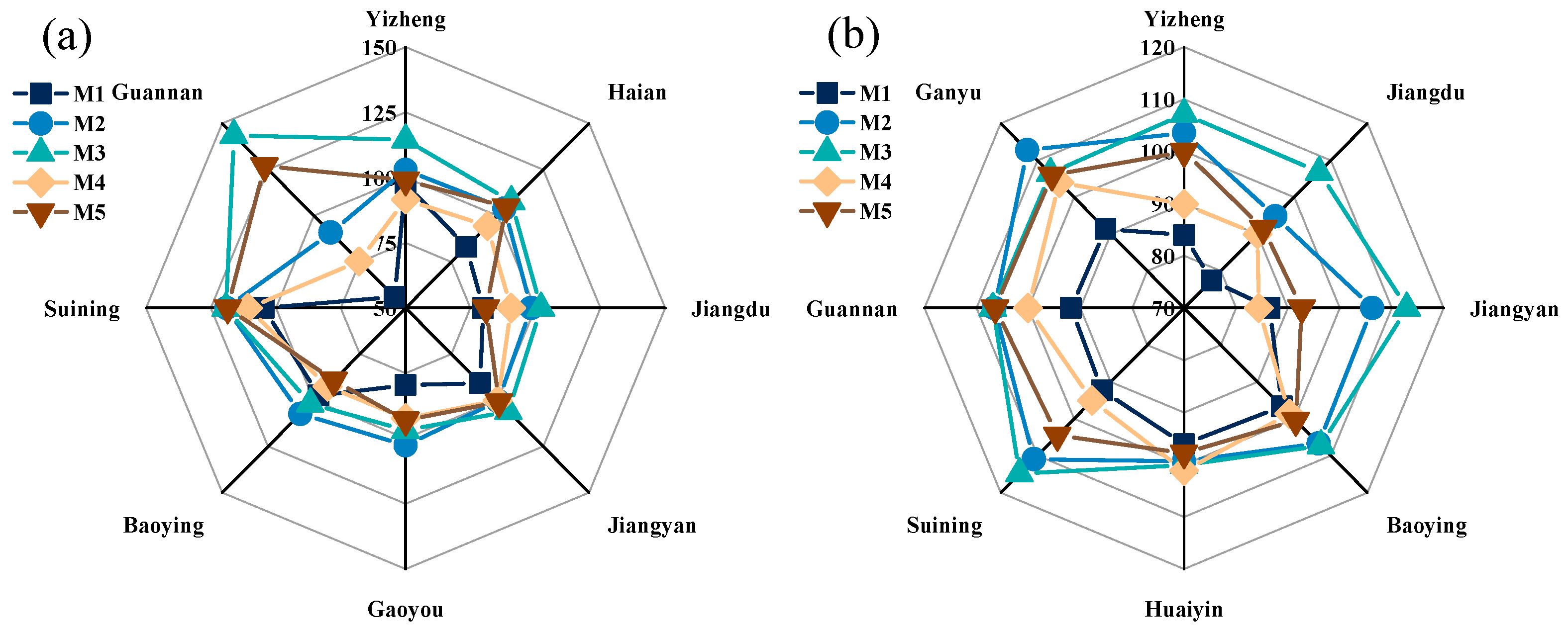
4.2. Assessment of Environmental Adaptability of Different Fertilization Patterns
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Liu, H.J.; Huang, G.; Zhang, R.; Yang, H.Y. Nitrate nitrogen accumulation and leaching pattern at a winter wheat: Summer maize cropping field in the North China Plain. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Velthof, G.; Wang, F.; Qin, W.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, J.; Lesschen, J.; Ma, W.; et al. Nitrogen and phosphorus use efficiencies and losses in the food chain in China at regional scales in 1980 and 2005. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 434, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Zhao, X.; Ye, X. Exploring a suitable nitrogen fertilizer rate to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and ensure rice yields in paddy fields. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.; Han, W.; Zhang, W.; Christie, P.; Goulding, K.; Vitousek, P.; Zhang, F. Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosas, F.; Babcock, B.A.; Hayes, D.J. Nitrous oxide emission reductions from cutting excessive nitrogen fertilizer applications. Clim. Chang. 2015, 132, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyu, T.; Shen, J.; Ma, J.; Ma, P.; Li, M. Hybrid rice yield response to potted-seedling machine transplanting and slow-release nitrogen fertilizer application combined with urea topdressing. Crop J. 2020, 9, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Lu, H.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, B. Combining controlled-release urea and normal urea to improve the nitrogen use efficiency and yield under wheat-maize double cropping system. Field Crops Res. 2016, 197, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otteson, B.N.; Mergoum, M.; Ransom, J.K. Seeding rate and nitrogen management effects on spring wheat yield and yield components. Agron. J. 2007, 99, 1615–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cui, Z.; Fan, M.; Vitousek, P.; Zhao, M.; Ma, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yan, X.; Yang, J.; et al. Producing more grain with lower environmental costs. Nature 2014, 514, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Buresh, R.; Huang, J.; Yang, J.; Zou, Y.; Zhong, X.; Wang, G.; Zhang, F. Strategies for overcoming low agronomic nitrogen use efficiency in irrigated rice systems in China. Field Crops Res. 2006, 96, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Lu, X.; Gu, S.; Guo, X. Improving nutrient and water use efficiencies using water-drip irrigation and fertilization technology in Northeast China. Agron. Water Manag. 2020, 241, 106352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wen, X.; Liao, Y.; Liu, Y. Effect of non-structural carbohydrate accumulation in the stem pre-anthesis on grain filling of wheat inferior grain. Field Crops Res. 2017, 211, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, G.; Chen, D.; Qu, H.; Ma, W. Identifying the limiting factors driving the winter wheat yield gap on smallholder farms by agronomic diagnosis in North China Plain. J. Integ. Agron. 2019, 18, 1701–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Xi, Y.; Cui, T.; Anten, N.; Weiner, J.; Li, X.; Turner, N.; Zhao, Y.; Li, F. Yield components, reproductive allometry and the tradeoff between grain yield and yield stability in dryland spring wheat. Field Crops Res. 2020, 257, 107930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhou, H.; Gao, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhang, M. Developing water and nitrogen budgets of a wheat-maize rotation system using auto-weighing lysimeters: Effects of blended application of controlled-release and un-coated urea. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoji, S.; Delgado, J.; Mosier, A.; Miura, Y. Use of controlled release fertilizers and nitrification inhibitors to increase nitrogen use efficiency and to conserve air and water quality. Commun. Soil Sci. Plan. 2001, 32, 1051–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaviv, A. Advances in controlled-release fertilizers. Adv. Agron. 2001, 71, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Tao, W.; Gao, S.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, G. Effects of different types of slow- and controlled-release fertilizers on rice yield. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 1503–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, S.L. Long-term effects of controlled release urea application on crop yields and soil fertility under rice-oilseed rape rotation system. Field Crops Res. 2015, 184, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Shen, T.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, M.; Tang, Y.; Allen, S. Controlled-release urea reduced nitrogen leaching and improved nitrogen use efficiency and yield of direct-seeded rice. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 220, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.; Wu, R.; Selles, F.; Harker, K.; Clayton, G.; Bittman, S.; Zebarth, B.; Lupwayi, N. Crop yield and nitrogen concentration with controlled release urea and split applications of nitrogen as compared to non-coated urea applied at seeding. Field Crops Res. 2012, 127, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmaha, B.S.; Sims, A.L. Yield and Protein Response of Wheat Cultivars to Polymer-Coated Urea and Urea. Agron. J. 2013, 105, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kubar, M.; Feng, M.; Sayed, S.; Shar, A.; Rind, N.; Ullah, H.; Kalhoro, S.; Xie, Y.; Yang, C.; Yang, W.; et al. Agronomical traits associated with yield and yield components of winter wheat as affected by nitrogen managements. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 4852–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fageria, N.K.; Baligar, V.C. Enhancing nitrogen use efficiency in crop plants. Adv. Agron. 2005, 88, 97–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Wang, M.; Zheng, G.; Yao, Y.; Tao, R.; Zhu, M.; Ding, J.; Li, C.; Guo, W.; Zhu, X. Twice-split application of controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer met the nitrogen demand of winter wheat. Field Crops Res. 2021, 267, 108163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, J.F.; Wiese, R.; Flowerday, D. Managing farming systems for nitrate control: A research review from Management Systems Evaluation Areas. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 1866–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Nelson, J.; Chu, C.; Shi, L.; Huang, S.; Liu, D. Chromosomal locations and genetic relationships of tiller and spike characters in wheat. Euphytica 2002, 125, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Huang, M.; Zhou, Q.; Cai, J.; Wang, X.; Cao, W.; Dai, T.; et al. Increasing plant density improves grain yield, protein quality and nitrogen agronomic efficiency of soft wheat cultivars with reduced nitrogen rate. Field Crops Res. 2021, 267, 108145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafoor, I.; Habib-ur-Rahman, M.; Ali, M.; Afzal, M.; Ahmed, W.; Gaiser, T.; Ghaffar, A. Slow-release nitrogen fertilizers enhance growth, yield, NUE in wheat crop and reduce nitrogen losses under an arid environment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 43528–43543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Barański, M.; Hasanaliyeva, G.; Korkut, R.; Kalee, H.; Leifert, A.; Winter, S.; Janovska, D.; Willson, A.; Barkla, B.; et al. Effect of irrigation, fertiliser type and variety on grain yield and nutritional quality of spelt wheat (Triticum spelta) grown under semi-arid conditions. Food Chem. 2021, 358, 129826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, J.; Feng, Y.; Shang, M.; Bo, X.; Gao, Z.; Chen, F.; Chu, Q. Optimizing tillage method and irrigation schedule for greenhouse gas mitigation, yield improvement, and water conservation in wheat–maize cropping systems. Agron. Water Manag. 2021, 248, 106762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, L.; Cheng, D.; Liu, M.; Geng, Y. Controlled release urea improved nitrogen use efficiency, yield, and quality of wheat. Agron. J. 2011, 103, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, W.; Zheng, S.; Yang, X.; Wu, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. Comparison of yield and nitrogen use efficiency of different types of nitrogen fertilizers for different rice cropping systems under subtropical monsoon climate in China. Eur. J. Agron. 2017, 90, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Fan, X.; Wan, Y.; Geng, Y.; Zhang, M. Polymer-Coated Tablet Urea Improved Rice Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 1837–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Liang, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Gu, J.; Guo, R.; Li, L. Alternate wetting and drying irrigation and controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer in late-season rice. Effects on dry matter accumulation, yield, water and nitrogen use. Field Crops Res. 2013, 144, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Sun, H.; Chen, Y.; Luo, J.; Ge, S.; Yao, Q.; Du, S.; Wang, D.; Li, W.; Wang, J. High yield and stability analysis of cotton varieties in Bazhou comparative experiment. Xinjiang Agron. Sci. Technol. 2021, 4, 4–6. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhi, S.; Grant, C.; Johnston, A.; Gill, K. Nitrogen fertilization management for no-till cereal production in the Canadian great plains: A review. Soil Tillage Res. 2001, 60, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Ning, T.; Xu, C.; Wang, P. Canopy morphological changes and water use efficiency in winter wheat under different irrigation treatments. J. Integr. Agron. 2020, 19, 1105–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Gu, R.; Xu, K.; Guo, B.; Dai, Q.; Huo, Z.; Wei, H. Split application of a mixture of controlled-release and common urea for improving quality and agronomic and economic performance in wheat production. Crop Sci. 2021, 61, 4402–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenkel, M.E. Slow- and Controlled-Release and Stabilized Fertilizers: An Option for Enhancing Nutrient Use Efficiency in Agriculture, 2nd ed.; International Fertilizer Industry Association (IFA): Paris, France, 2010; pp. 21–54. ISBN 978-2-9523139-7-1. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, D.; Gu, F. Materials for sustained and controlled release of nutrients and molecules to support plant growth. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaf, A.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, M.; Ma, Q.; Irshad, S.; Xu, D.; Aleem, M.; Zhang, X.; Gull, S.; Li, F.; et al. Effects of environmental stresses (heat, salt, waterlogging) on grain yield and associated traits of wheat under application of sulfur-coated Urea. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhao, D.; Liu, S.; Liao, Y.; Han, J. Can controlled-release urea replace the split application of normal urea in China? A meta-analysis based on crop grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency. Field Crops Res. 2022, 275, 108343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
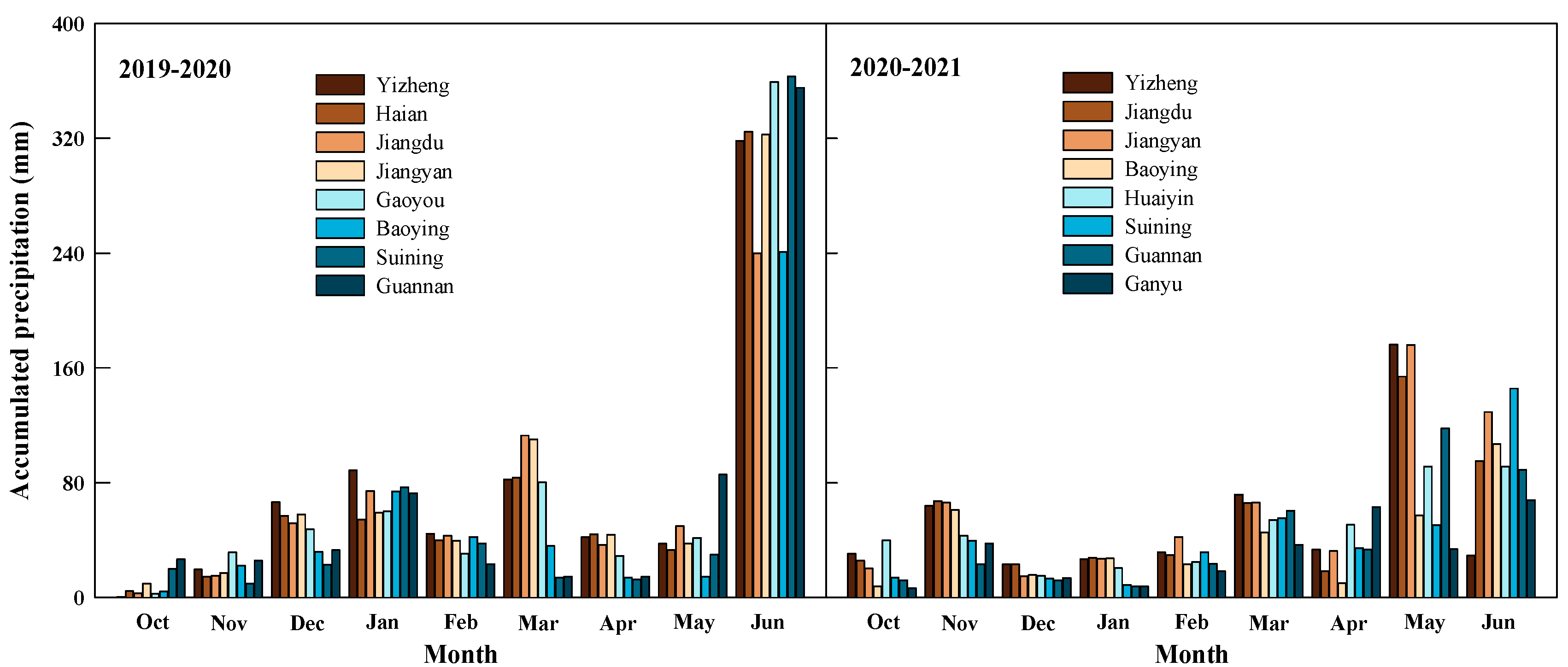
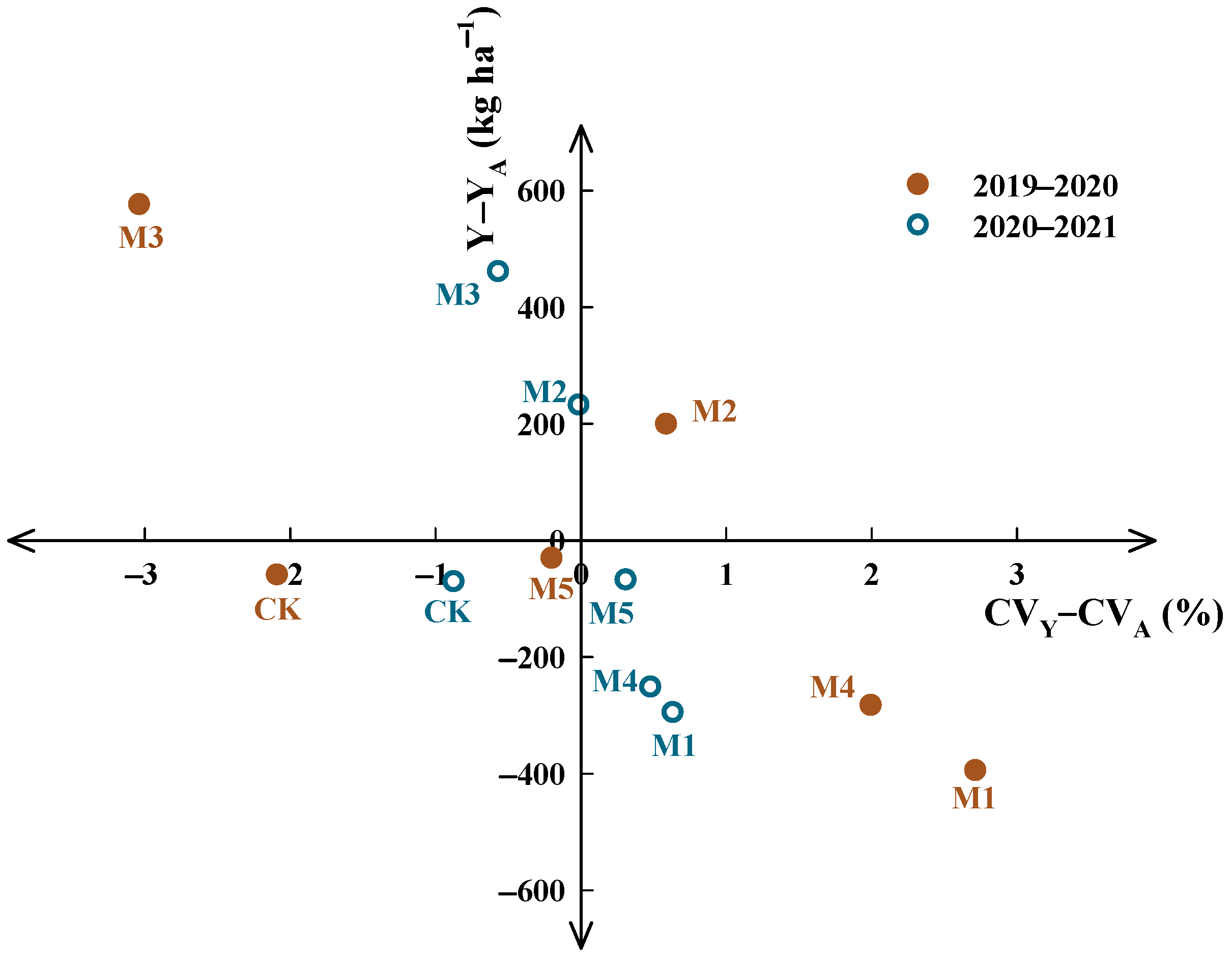
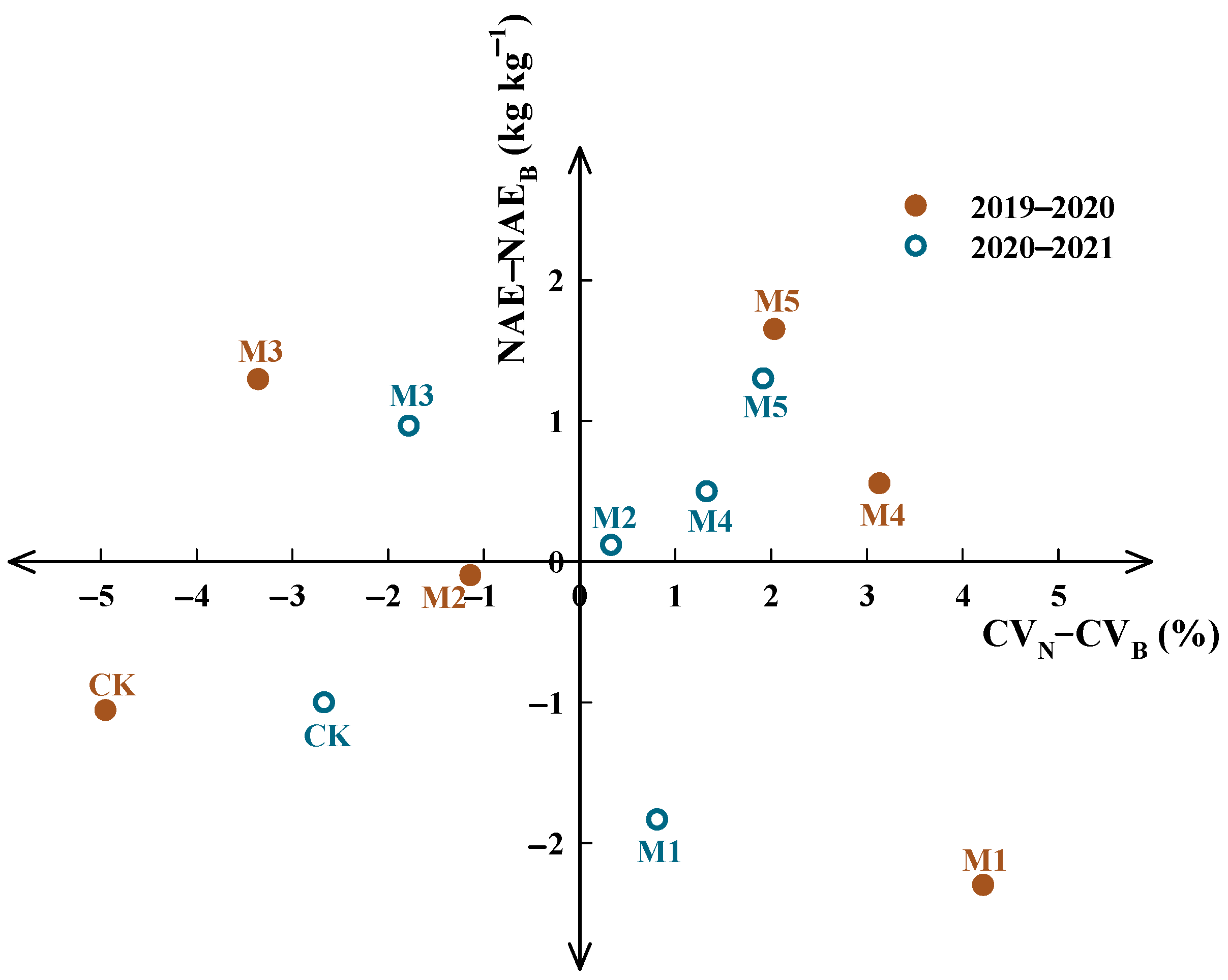
| Site | Wheat Varieties | Sowing Date (Month-Day) | Harvest Date (Month-Day) | Soil Texture | Nutritional Characteristics of the Top Soil (0–20 cm Depth) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic Matter (g kg−1) | Available N (mg kg−1) | Available P (mg kg−1) | Available K (mg kg−1) | |||||
| 2019–2020 | ||||||||
| Yizheng | Yangami 23 | 11-1 | 5-27 | Clay loam | 35.1 | 127.0 | 6.9 | 111.9 |
| Haian | Nongmai 88 | 11-3 | 5-29 | Loam | 32.3 | 116.3 | 23.6 | 133.8 |
| Jiangdu | Mingmai 133 | 11-9 | 5-29 | Medium loam | 25.5 | 87.6 | 27.4 | 57.0 |
| Jiangyan | Nongmai 88 | 11-11 | 5-31 | Clay loam | 35.1 | 98.6 | 21.1 | 149.4 |
| Gaoyou | Yangfumai 4 | 10-29 | 5-29 | Clay | 36.4 | 103.8 | 5.8 | 160.1 |
| Baoying | Ningmai 26 | 11-7 | 6-1 | Clay | 19.6 | 89.7 | 26.5 | 134.5 |
| Suining | Xumai 818 | 10-30 | 6-5 | Sandy loam | 22.6 | 96.7 | 35.0 | 143.7 |
| Guannan | Huaimai 33 | 11-6 | 6-10 | Clay | 12.8 | 58.6 | 19.6 | 102.0 |
| 2020–2021 | ||||||||
| Yizheng | Yangmai 23 | 11-3 | 6-5 | Clay loam | 36.2 | 119.9 | 8.63 | 109.2 |
| Jiangdu | Yangfumai 4 | 11-2 | 6-4 | Medium loam | 30.5 | 76.3 | 23.5 | 87.0 |
| Jiangyan | Nongmai 88 | 10-31 | 6-3 | Clay loam | 33.4 | 108.7 | 22.3 | 134.6 |
| Baoying | Zhenmai 12 | 11-6 | 6-5 | Clay | 19.4 | 82.6 | 25.6 | 122.5 |
| Huaiyin | Huaimai 52 | 10-30 | 6-10 | Clay | 22.1 | 90.3 | 46.1 | 94.2 |
| Suining | Xumai 818 | 10-23 | 6-10 | Clay loam | 25.8 | 101.3 | 28.3 | 129.6 |
| Guannan | Huaimai 33 | 10-30 | 6-12 | Clay | 13.6 | 63.4 | 18.4 | 99.7 |
| Ganyu | Huaimai 46 | 10-30 | 6-20 | Clay | 20.8 | 74.2 | 14.2 | 130.1 |
| Pattern | N Rate (kg ha−1) | N Fertilizer Types and N Management |
|---|---|---|
| CK | 270 | 100% N U, basal:tillering:jointing:booting = 50%:10%:20%:20% |
| M1 | 270 | 100% N SRF applied once before sowing |
| M2 | 270 | 60% N SRF applied before sowing; 40% N U top-dressed at jointing stage |
| M3 | 270 | 60% N SRF applied before sowing; 40% N SRF top-dressed at re-greening stage |
| M4 | 229.5 | 60% N SRF applied before sowing; 40% N U top-dressed at jointing stage |
| M5 | 229.5 | 60% N SRF applied before sowing; 40% N SRF top-dressed at re-greening stage |
| Yield Component | Correlation Coefficient with Yield | Direct Path Coefficient | Indirect Path Coefficient | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spikes | Kernels per Spike | TGW | Total | |||
| 2019–2020 | ||||||
| Spikes | 0.799 ** | 1.134 | - | −0.335 | 0.000 | −0.335 |
| Kernels per spike | −0.048 ns | 0.583 | −0.652 | - | 0.021 | −0.631 |
| TGW | 0.311 * | 0.266 | −0.001 | 0.046 | - | 0.045 |
| 2020−2021 | ||||||
| Spikes | 0.828 ** | 1.215 | - | −0.417 | 0.030 | −0.388 |
| Kernels per spike | −0.399 ** | 0.711 | −0.713 | - | −0.398 | −1.110 |
| TGW | 0.311 * | 0.676 | 0.053 | v0.419 | - | −0.365 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Q.; Tao, R.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Zhu, M.; Ding, J.; Li, C.; Guo, W.; Zhu, X.; et al. Can Split Application of Slow-Release Fertilizer Improve Wheat Yield, Nitrogen Efficiency and Their Stability in Different Ecological Regions? Agronomy 2022, 12, 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12020407
Ma Q, Tao R, Ding Y, Zhang X, Li F, Zhu M, Ding J, Li C, Guo W, Zhu X, et al. Can Split Application of Slow-Release Fertilizer Improve Wheat Yield, Nitrogen Efficiency and Their Stability in Different Ecological Regions? Agronomy. 2022; 12(2):407. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12020407
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Quan, Rongrong Tao, Yonggang Ding, Xinbo Zhang, Fujian Li, Min Zhu, Jinfeng Ding, Chunyan Li, Wenshan Guo, Xinkai Zhu, and et al. 2022. "Can Split Application of Slow-Release Fertilizer Improve Wheat Yield, Nitrogen Efficiency and Their Stability in Different Ecological Regions?" Agronomy 12, no. 2: 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12020407
APA StyleMa, Q., Tao, R., Ding, Y., Zhang, X., Li, F., Zhu, M., Ding, J., Li, C., Guo, W., Zhu, X., & Sheng, H. (2022). Can Split Application of Slow-Release Fertilizer Improve Wheat Yield, Nitrogen Efficiency and Their Stability in Different Ecological Regions? Agronomy, 12(2), 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12020407











