Effect of Different Nitrogen Supply on Maize Emergence Dynamics, Evaluation of Yield Parameters of Different Hybrids in Long-Term Field Experiments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
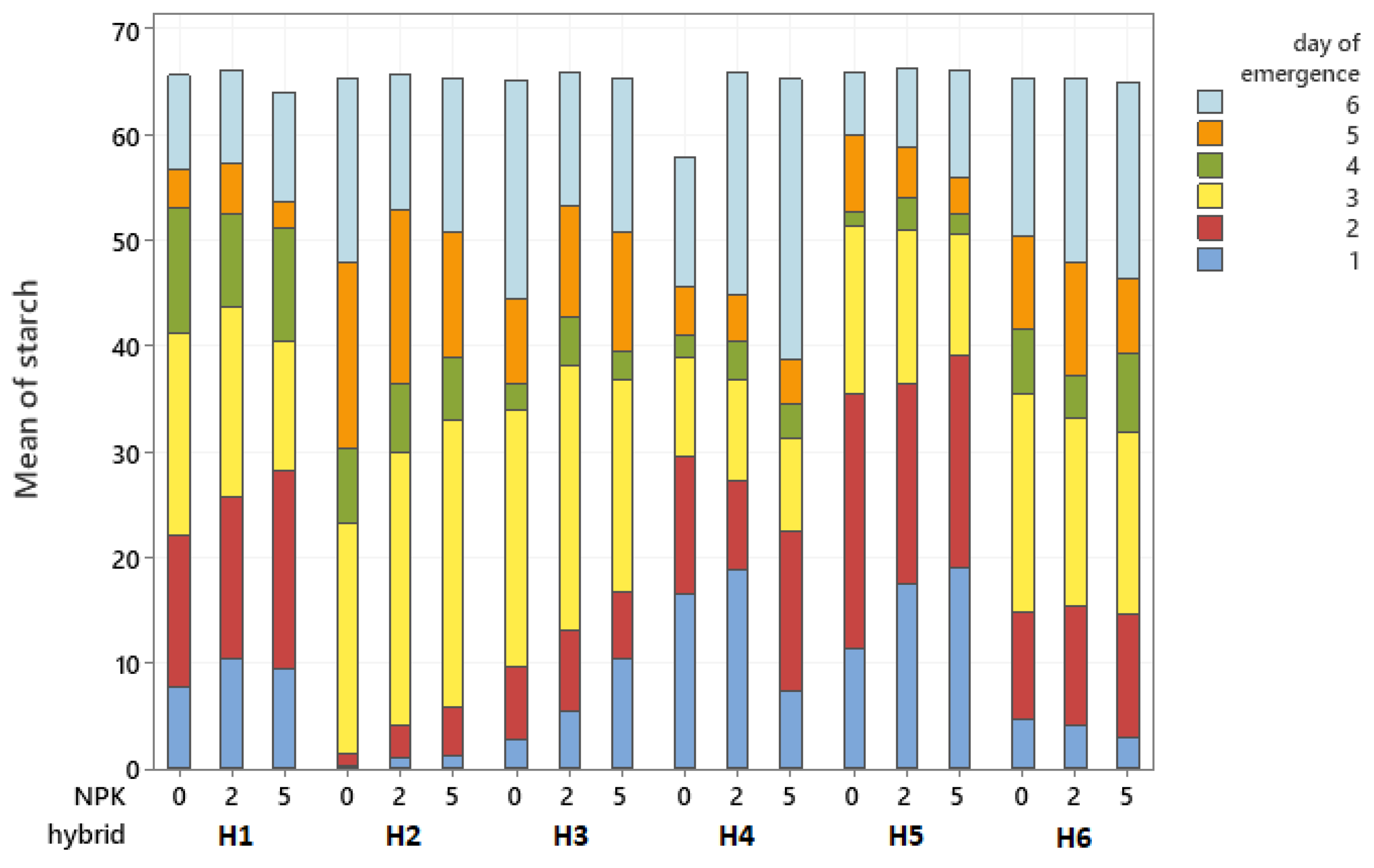
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Popp, J.; Potori, N. Az élelmezés-, energia-és környezetbiztonság összefüggései. Gazdálkodás Sci. J. Agric. Econ. 2008, 52, 528–544. [Google Scholar]
- Dowswell, C. Maize in the Third World; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kayad, A.; Sozzi, M.; Gatto, S.; Whelan, B.; Sartori, L.; Marinello, F. Ten years of corn yield dynamics at field scale under digital agriculture solutions: A case study from North Italy. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 185, 106126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, J.G.; Boelt, B.; Roltston, M.P.; Chastain, T.G. Effects of elevated CO2 and temperature on seed quality. J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 151, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Powell, A.A.; Matthews, S.; Oliveira, M.A. Seed Quality in Grain Legumes; National Agricultural Library: Beltsville, Maryland, 1984; pp. 217–285. [Google Scholar]
- Bojtor, C.; Illés, Á.; Mousavi, S.M.N.; Széles, A.; Tóth, B.; Nagy, J.; Marton, L.C. Evaluation of the Nutrient Composition of Maize in Different NPK Fertilizer Levels Based on Multivariate Method Analysis. Int. J. Agron. 2021, 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macaloney, G.; Draper, I.; Preston, J.; Anderson, K.B.; Rollins, M.J.; Thompson, B.G.; Hall, J.W.; Mcneil, B. At-line control and fault analysis in an industrial high cell density Escherichia coli fermentation, using NIR spectroscopy. Food Bioprod. Processing 1996, 74, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murungu, F.S.; Nyamugafata, P.; Chiduza, C.; Clark, L.J.; Whalley, W.R. Effects of seed priming, aggregate size and soil matric potential on emergence of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) and maize (Zea mays L.). Soil Tillage Res. 2003, 74, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biró, B.; Bidló, A.; Farsang, A.; Horváth, E.K.; Micheli, E.; Pápay, L.T. Talajvédelem, talajtan. Környezetmérnöki Tudástár 2011, 3, 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Horváth, M.; Molnár, L.; Szentirmainé, B.M. Természettudomány 5; Oktatási Hivatal: Budapest, Hungary, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, S. Controlled Deterioration: A New Vigour Test for Crop Seeds; Seed Production: London, UK, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Neal, N.P. Breeding corn for tolerance to cold. In Proceedings of the 4th Annuals Corn and Sorghum Research Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 11–13 December 1949; Volume 4, pp. 68–80. [Google Scholar]
- Pinnell, E.L. Genetic and environmental factors affecting corn seed germination at low temperatures. Agron. J. 1949, 41, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubbels, G.H. Growth of corn seedlings under low temperatures as affected by genotype, seed size, total oil, and fatty acid content of the seed. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1974, 54, 425–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, K.D.; Ma, B.L. Seed priming does not improve corn yield in a humid temperate environment. Agron. J. 2005, 97, 211–218. [Google Scholar]
- Farahani, H.A.; Moaveni, P.; Maroufi, K. Effect of hydropriming on germination percentage in sunflower (Helianthus annus L.) cultivars. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2011, 5, 2253–2258. [Google Scholar]
- Nagy, J.; Széles, A.; Horváth, É. The impact of climate change and sowing time on the yield and quality of maize (Zea mays L.). In Proceedings of the 18th Alps-Adria Scientific Workshop: Alimentation and Agri-Environment: Abstract Book, Cattolica, Italy, 1–4 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.P.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Wu, X.; He, C.; Li, Z. A quantitative trait locus for the number of days from sowing to seedling emergence in maize. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 5091–5095. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, J.P. Steep, cheap and deep: An ideotype to optimize water and N acquisition by maize root systems. Ann. Bot. 2013, 112, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, E.C.; Gupta, S.C. Corn emergence as influenced by soil temperature, matric potential, and aggregate size distribution. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1985, 49, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, M.C.D.; Carvalho, N.M. Effect of the type of environmental stress on the emergence of sunflower (Helianthus annus L.), soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merril) and maize (Zea mays L.) seeds with different levels of vigor. Seed Sci. Technol. 2003, 31, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, N.; Dwivedi, U.N. Genotypic difference in salinity tolerance of green gram cultivars. Plant Sci. 2004, 166, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wei, R.; Peng, W.; Chen, F.; Yuan, L.; Pan, Q.; Mi, G. Evaluation of maize root growth and genome-wide association studies of root traits in response to low nitrogen supply at seedling emergence. Crop J. 2020, 9, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Sehrish, K.; Shah, F.; Shah, F.; Saddam, H.; Saqib, A.; Ashfaq, A. Effect of different levels of nitrogen and phosphorus on the phenology and yield of maize varieties. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 2582–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berzsenyi, Z.; Dang, Q. Effect of sowing date and N fertilisation on the yield and yield stability of maize (Zea mays L.) hybrids in a long-term experiment. Acta Agron. Hung. 2008, 56, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddiqui, M.H.; Oad, F.C.; Jamro, G.H. Emergence and nitrogen use efficiency of maize under different tillage operations and fertility levels. Asian J. Plant Sci. 2006, 5, 508–510. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, A. Effect of Time and Rate of Nitrogen Application on Maize. Master’s Thesis, NWFP Agriculture University, Peshwar, Pakistan, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Siddique, M.; Bajwa, M.S.; Makhdum, M.I. Yield and quality of maize fodder as influenced by different stages of harvesting and nitrogen rates. Pak. J. Sci. Ind. Res. (Pak.) 1989, 32, 766–767. [Google Scholar]
- Krámer, M.; Latkoivcs, G. Az őszi búza és a kukorica műtrágyázás hatásának vizsgálata tartamkísérletben (1960-67). Agrokémia És Talajt. 1971, 20, 300–321. [Google Scholar]
- Illes, A.; Bojtor, C.; Szeles, A.; Mousavi, S.M.N.; Toth, B.; Nagy, J. Analyzing the effect of intensive and low-input agrotechnical support for the physiological, phenometric, and yield parameters of different maize hybrids using multivariate statistical methods. Int. J. Agron. 2021, 2021, 6682573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.M.N.; Árpád, I.; Csaba, B.; Janos, N. The impact of different nutritional treatments on maize hybrids morphological traits based on stability statistical methods. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2020, 32, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, O.; Keshavarz-Afshar, R.; Jahanzad, E.; Battaglia, M.L.; Luo, Y.; Sadeghpour, A. Effect of Wheat Cover Crop and Split Nitrogen Application on Corn Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, J. Komplex talajhasználati, víz-és tápanyaggazdálkodási tartamkísérletek 1983-tól a Debreceni Egyetemen. Növénytermelés 2019, 68, 5–28. [Google Scholar]
- Gombos, B.; Nagy, J. Az időjárás értékelése kukorica (Zea mays L.) tartamkísérletek eredményei alapján. Növénytermelés 2019, 68, 5–23. [Google Scholar]
- Nagy, J. Maize Production; Akadémiai Kiadó: Budapest, Hungary, 2006; p. 392. [Google Scholar]
- I1. Available online: https://www.corteva.hu/termekek-es-megoldasok/vetomagok/pioneer--hibrid-kukoricak---cortevaagriscience-hu.html (accessed on 13 January 2022).
- I2. Available online: https://www.syngenta.hu/kukorica-sy-minerva-fao-420-440 (accessed on 13 January 2022).
- I3. Available online: https://www.kite.hu/vetomag-palanta-oltvany/kukorica/fornad-hibrid-kukorica/23/116 (accessed on 13 January 2022).
- I4. Available online: https://www.kite.hu/vetomag-palanta-oltvany/kukorica/armagnac-hibrid-kukorica/23/123 (accessed on 13 January 2022).
- I5. Available online: https://www.dekalb.hu/documents/131312/1174182/Dekalb_Corn+Catalogue_2021_2022_compressed.pdf/cf8e0d21-1267-442e-9a1b-6560499428be (accessed on 13 January 2022).
- Alava, J.M.; Millar, S.J.; Salmon, S.E. The determination of wheat breadmaking performance and bread dough mixing time by NIR spectroscopy for high speed mixers. J. Cereal Sci. 2001, 33, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Villiers, A.J.; van Rooyen, M.W.; Theron, G.K.; Van De Venter, H.A. Germination of three Namaqualand pioneer species, as influenced by salinity, temperature and light. Seed Sci. Technol. 1994, 22, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- Vashisth, A.; Shantha, N. Effect on germination and early growth characteristics in sunflower (Helianthus annuus) seeds exposed to static magnetic field. J. Plant Physiol. 2010, 167, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzal, I.; Shahzad, M.A.B.; Ahmad, N.; Farooq, M. Optimization of Hormonal Priming Techniques for Alleviation of Salinity Stress in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.); Universidade de Santa Cruz do Sul: Santa Cruz do Sul, Brazil, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, M.; Majid, R.F. Pre-sowing seed treatment—A shotgun approach to improve germination, plant growth, and crop yield under saline and non-saline conditions. Adv. Agron. 2005, 88, 223–271. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasian, A.; Moemeni, J.; Rahmani, M.; Oskoii, B.; Hamidi, A.; Sedghi, M. Comparison of different hybrid maize seed size with smaller under sieve size in standard germination, cold, accelerated ageing and electrical conductivity tests. Tech. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2013, 3, 385–393. [Google Scholar]
- Hampton, J.G.; Dennis, M.T. (Eds.) . Handbook of Vigour Test Methods; International Seed Testing Association: Zurich, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Heidari, H.; Aram, F.; Mohsen, S.; Mahmood, K. Study of defoliation intensity and nitrogen rate effects on yield, yield components and germination traits of produced seed in wheat (Triticum aestivum). Agric. -Rev. De Știință Și Pract. Agric. 2013, 1/2, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Nasir, M.; Seyed, K.B.; János, N. Evaluation of Decreasing Moisture Content of Different Maize Genotypes. Acta Agrar. Debr. 2018, 74, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nafziger, E.D.; Paul, R.C.; Edwin, E.G. Response of corn to uneven emergence. Crop Sci. 1991, 31, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oskouie, B. Effect of mother plant nitrogen application on seed establishment of rapeseed. Int. J. Agrisci. 2012, 2, 444–450. [Google Scholar]
- Paterson, E.; Allan, S. Effect of nitrogen supply and defoliation on loss of organic compounds from roots of Festuca rubra. J. Exp. Bot. 2000, 51, 1449–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijanzadeh, E.; Emam, Y. Effect of defoliation and drought stress on yield components and chlorophyll content of wheat. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2010, 13, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghassemi-Golezani, K.; Bahareh, D. Effects of seed vigor on growth and grain yield of maize. Plant Breed. Seed Sci. 2014, 70, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
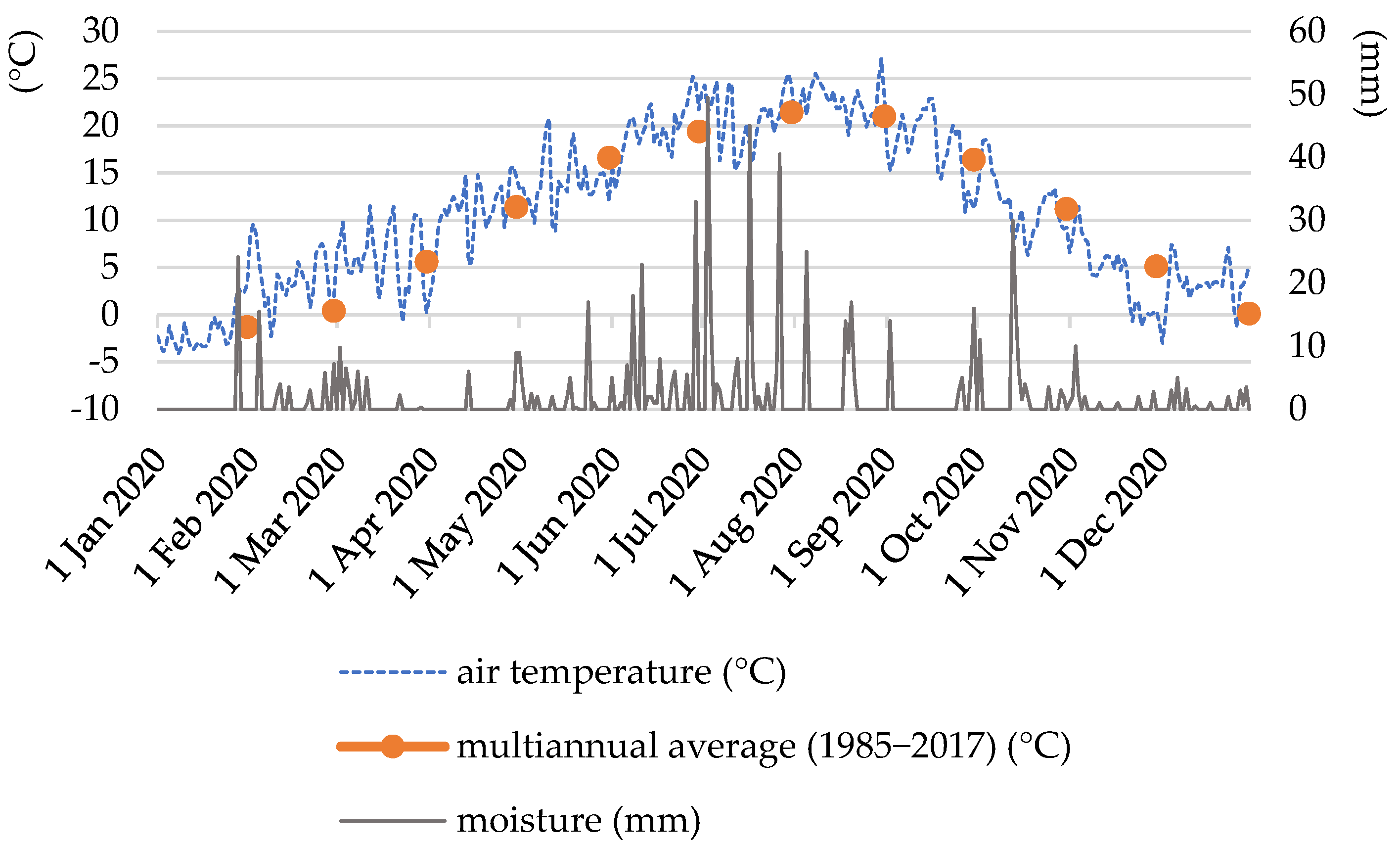
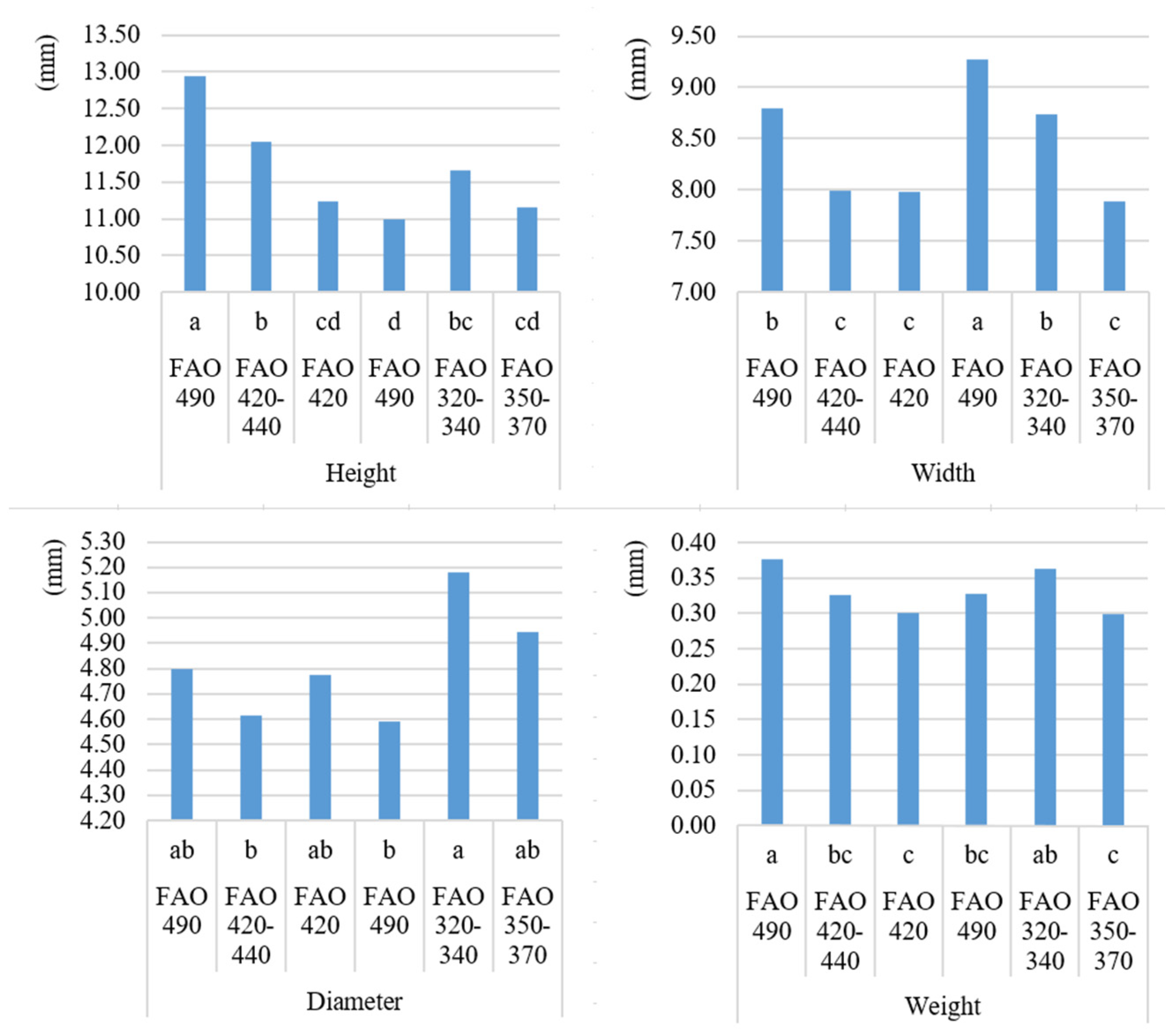
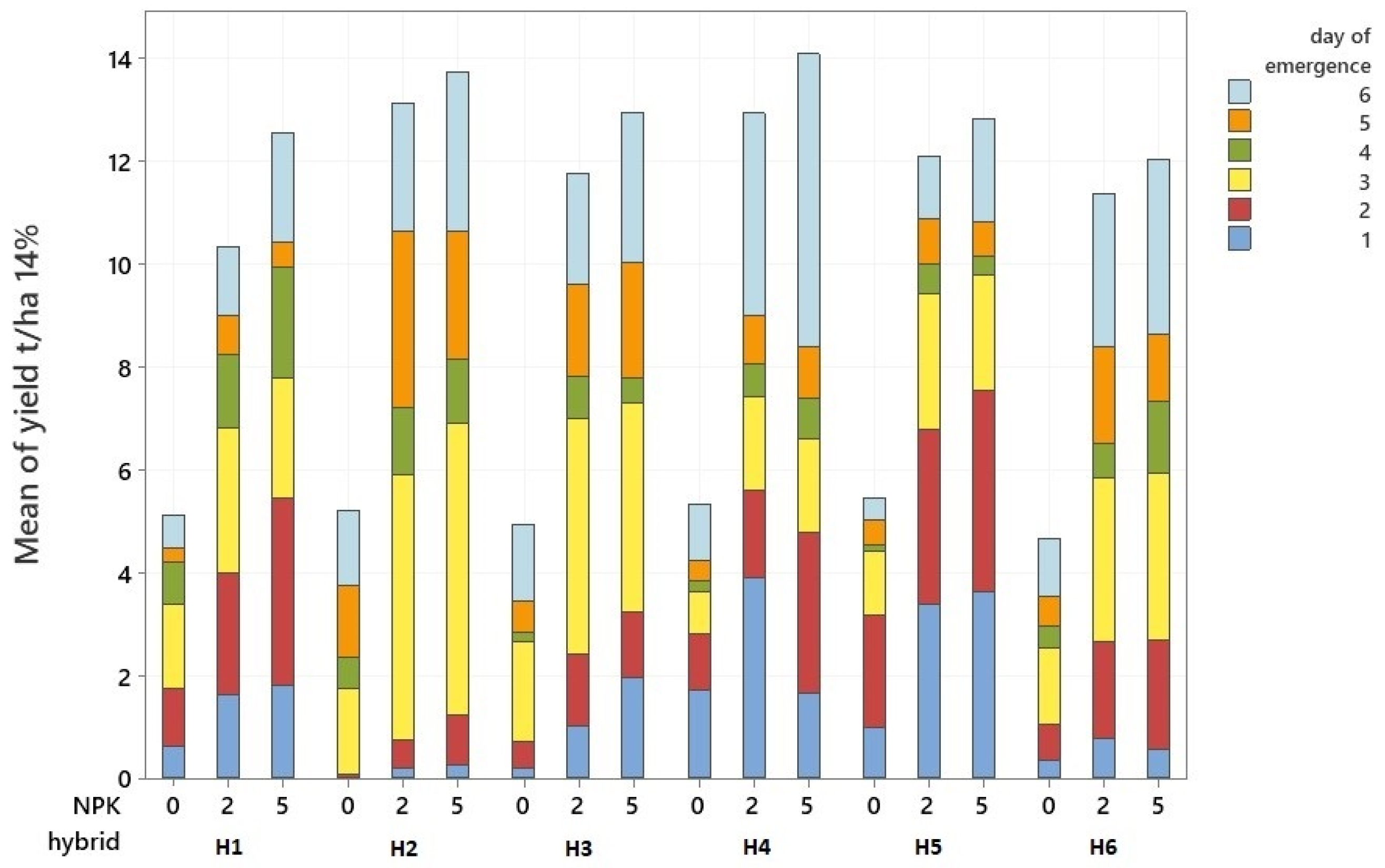
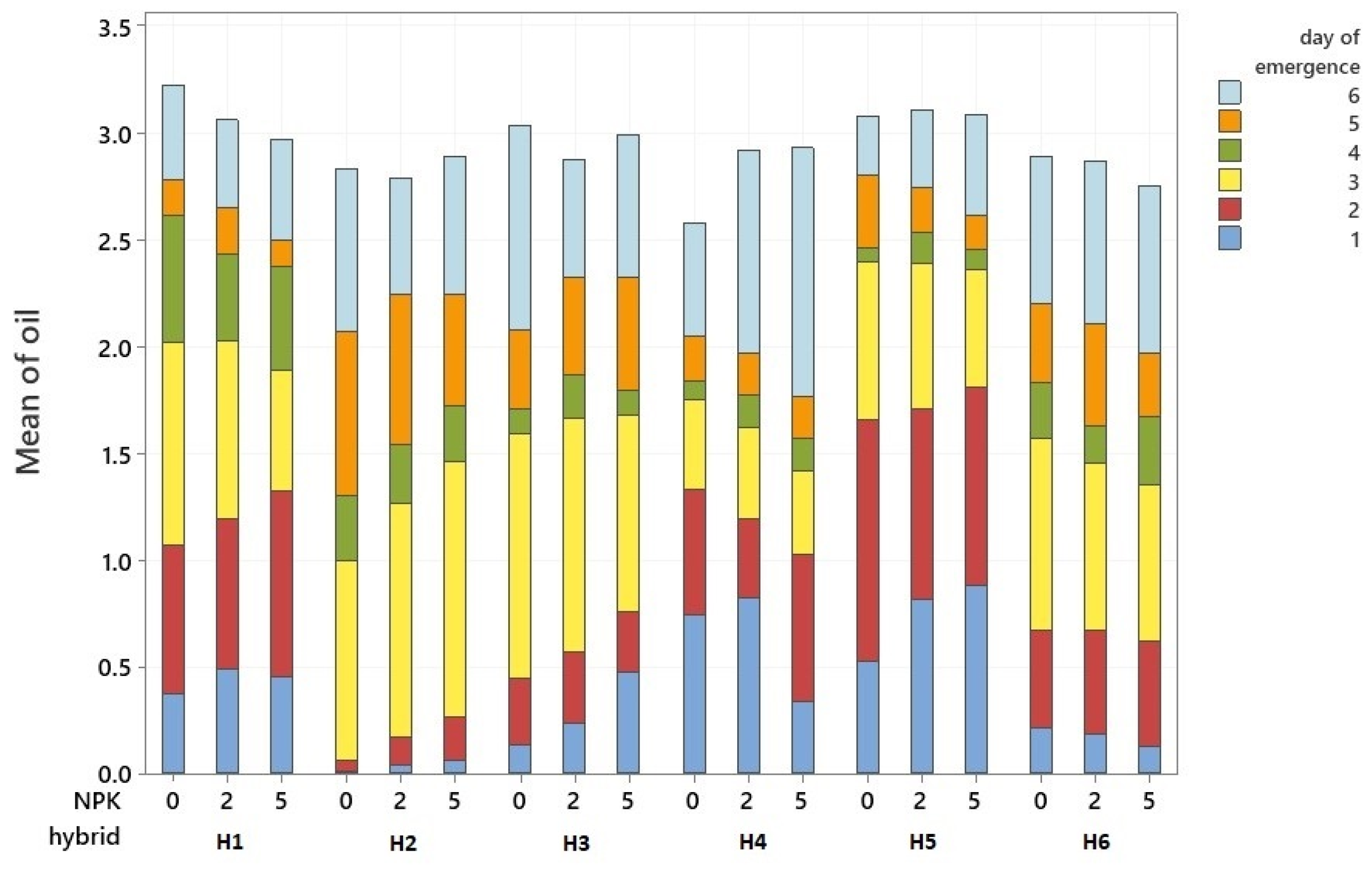


| N- Stages | pH (KCl 1:2, 5) | KA | Salt Content (m/m%) | CaCO3 (m/m%) | Organic Matter (m/m%) | Nitrogen (mg/kg) | Sulfur (mg/kg) | Potassium Oxide (mg/kg) | Sodium (mg/kg) | Phosphorus Pentoxide (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 6.15 | 38.56 | <0.02 | <0.1 | 2.16 | 1.17 | 0.78 | 185.28 | 13.59 | 52.90 |
| 2 | 5.70 | 40.28 | <0.02 | <0.1 | 2.23 | 2.30 | 6.88 | 277.44 | 9.55 | 146.65 |
| 5 | 5.57 | 36.81 | <0.02 | <0.1 | 2.02 | 2.11 | 2.81 | 277.02 | 9.22 | 129.12 |
| Source | df | Moisture | Oil | Protein | Starch | Grain Yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hybrid | 5 | 0.09 | 0.52 | 0.47 | 0.08 | 0.88 |
| N | 2 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 6.36 ** | 0.10 | 82.17 ** |
| Day of emergence | 5 | 49.68 ** | 49.06 ** | 50.01 ** | 51.05 ** | 38.74 ** |
| Hybrid * | 10 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.08 | 0.20 |
| Hybrid *day of emergence | 25 | 12.69 ** | 12.26 ** | 12.74 ** | 12.95 ** | 11.32 ** |
| N*day of emergence | 10 | 1.20 | 1.03 | 1.33 | 1.13 | 3.54 ** |
| Hybrid *N *day of emergence | 50 | 1.09 | 1.06 | 1.16 | 1.08 | 1.50 * |
| Parameters | Day of Emergence | N | Mean | Grouping | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | 3 | 72 | 4.59 | A | ||||
| 6 | 72 | 3.71 | B | |||||
| 2 | 72 | 3.07 | B | |||||
| 1 | 72 | 2.21 | C | |||||
| 5 | 72 | 2.05 | C | |||||
| 4 | 72 | 1.36 | D | |||||
| Oil | 3 | 72 | 0.79 | A | ||||
| 6 | 72 | 0.63 | B | |||||
| 2 | 72 | 0.53 | B | |||||
| 1 | 72 | 0.38 | C | |||||
| 5 | 72 | 0.35 | C | D | ||||
| 4 | 72 | 0.23 | D | |||||
| Protein | 3 | 72 | 1.52 | A | ||||
| 6 | 72 | 1.25 | B | |||||
| 2 | 72 | 1.01 | C | |||||
| 1 | 72 | 0.73 | D | |||||
| 5 | 72 | 0.68 | D | |||||
| 4 | 72 | 0.44 | E | |||||
| Grain yield | 3 | 72 | 2.68 | A | ||||
| 6 | 72 | 2.19 | B | |||||
| 2 | 72 | 1.77 | B | C | ||||
| 1 | 72 | 1.36 | C | D | ||||
| 5 | 72 | 1.20 | D | E | ||||
| 4 | 72 | 0.79 | E | |||||
| Starch | 3 | 72 | 17.68 | A | ||||
| 6 | 70 | 14.16 | B | |||||
| 2 | 72 | 11.69 | B | |||||
| 1 | 72 | 8.41 | C | |||||
| 5 | 72 | 7.89 | C | |||||
| 4 | 72 | 5.20 | D | |||||
| Parameters | Source | Df | F | Equation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grain yield | Regression | 7 | 8.21 ** | 1.040 + 0.2478 N + 0.0151 day of emergence |
| N | 1 | 55.22 ** | ||
| Day of emergence | 1 | 0.14 | ||
| Hybrid | 5 | 0.39 | ||
| Oil | Regression | 7 | 0.19 | 0.4751 + 0.00002 N + 0.0040 day of emergence |
| N | 1 | 0.00 | ||
| Day of emergence | 1 | 0.14 | ||
| Hybrid | 5 | 0.24 | ||
| Protein | Regression | 7 | 1.01 | 0.7950 + 0.0398 N+ 0.0160 day of emergence |
| N | 1 | 5.44 ** | ||
| Day of emergence | 1 | 0.61 | ||
| Hybrid | 5 | 0.20 | ||
| Moisture | Regression | 7 | 0.09 | 2.676 + 0.0155 N+ 0.0355 day of emergence |
| N | 1 | 0.10 | ||
| Day of emergence | 1 | 0.34 | ||
| Hybrid | 5 | 0.04 | ||
| Starch | Regression | 7 | 0.08 | 10.29 + 0.028 N + 0.139 day of emergence |
| N | 1 | 0.02 | ||
| Day of emergence | 1 | 0.35 | ||
| Hybrid | 5 | 0.04 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szabó, A.; Széles, A.; Illés, Á.; Bojtor, C.; Mousavi, S.M.N.; Radócz, L.; Nagy, J. Effect of Different Nitrogen Supply on Maize Emergence Dynamics, Evaluation of Yield Parameters of Different Hybrids in Long-Term Field Experiments. Agronomy 2022, 12, 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12020284
Szabó A, Széles A, Illés Á, Bojtor C, Mousavi SMN, Radócz L, Nagy J. Effect of Different Nitrogen Supply on Maize Emergence Dynamics, Evaluation of Yield Parameters of Different Hybrids in Long-Term Field Experiments. Agronomy. 2022; 12(2):284. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12020284
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzabó, Atala, Adrienn Széles, Árpád Illés, Csaba Bojtor, Seyed Mohammad Nasir Mousavi, László Radócz, and János Nagy. 2022. "Effect of Different Nitrogen Supply on Maize Emergence Dynamics, Evaluation of Yield Parameters of Different Hybrids in Long-Term Field Experiments" Agronomy 12, no. 2: 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12020284
APA StyleSzabó, A., Széles, A., Illés, Á., Bojtor, C., Mousavi, S. M. N., Radócz, L., & Nagy, J. (2022). Effect of Different Nitrogen Supply on Maize Emergence Dynamics, Evaluation of Yield Parameters of Different Hybrids in Long-Term Field Experiments. Agronomy, 12(2), 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12020284












