Influence of Different Irrigation Water Qualities and Irrigation Techniques on the Soil Attributes and Bacterial Community Structure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
- i.
- APRI with RW and SDI (RSA);
- ii.
- FI with RW and SDI (RSF);
- iii.
- APRI with RW and FUI (RFA);
- iv.
- FI with RW and FUI (RFF);
- v.
- APRI with CW and SDI (WSA);
- vi.
- FI with CW and SDI (WSF);
- vii.
- APRI with CW and FUI (WFA); and
- viii.
- FI with CW and FUI (WFF).
2.2. Water, Soil, and Plant Measurement and Analysis
2.3. The Bacterial Communities in the Soils
2.4. Data and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Attributes
3.2. Soil Heavy Metal
3.3. Composition and Diversity of Soil Bacterial Communities
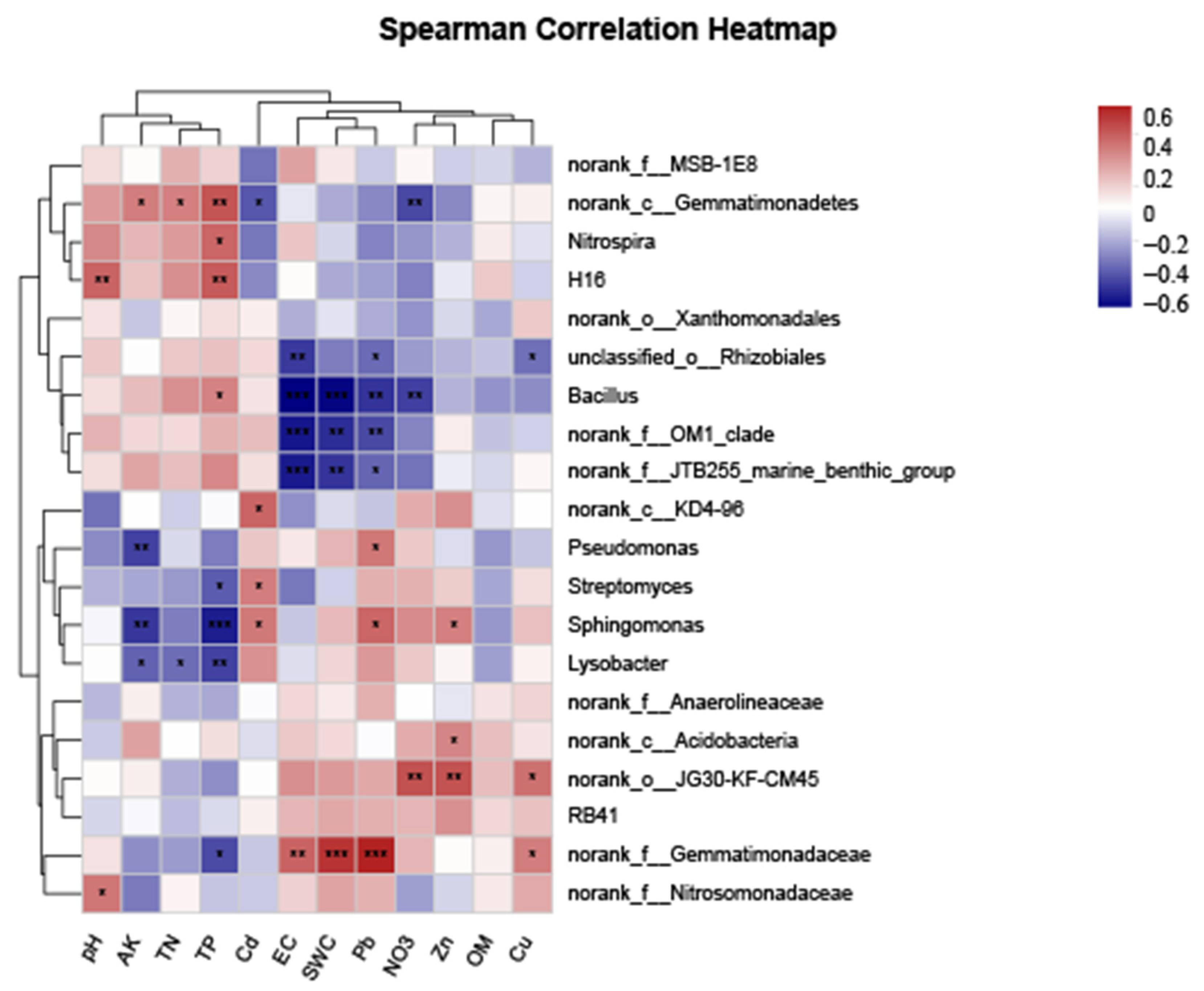
3.4. Taxonomic Composition of Soil Bacterial Communities and Correlations between the Microbial Community and Soil Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Physicochemical Properties and Heavy Metal Characteristics
4.2. Influences of Soil Environmental Parameters on Bacterial Community Structure and Composition
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiao, Y.; Shao, J.L.; Cui, Y.L.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Q.L. Groundwater circulation and hydrogeochemical evolution in Nomhon of Qaidam Basin, northwest China. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 126, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, M.S.; El-Abedin, T.Z.; Al-Ghobari, H.M. Rational water use by applying regulated deficit and partial root-zone drying irrigation techniques in tomato under arid conditions. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2019, 79, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tran, Q.K.; Schwabe, K.A.; Jassby, D. Wastewater reuse for agriculture: A development of a regional water reuse decision-support model (RWRM) for cost-effective irrigation sources. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9390–9399. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.I.; Muscolo, A.; Farooq, M.; Ahmad, W. Sustainable use and management of non-conventional water resources for rehabilitation of marginal lands in arid and semiarid environments. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 221, 462–476. [Google Scholar]
- WWAP. UNESCO World Water Assessment Programme. In The United Nations World Water Development Report 2019: Leaving No One Behind; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hashem, M.S.; Guo, W.; Qi, X.B.; Li, P. Assessing the effect of irrigation with reclaimed water using different irrigation techniques on tomatoes quality parameters. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2856. [Google Scholar]
- Maryam, B.; Büyükgüngör, H. Wastewater reclamation and reuse trends in Turkey: Opportunities and Challenges. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 30, 100501. [Google Scholar]
- Zolti, A.; Green, S.J.; Ben Mordechay, E.; Hadar, Y.; Minz, D. Root microbiome response to treated wastewater irrigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaganti, V.N.; Ganjegunte, G.; Niu, G.; Ulery, A.; Flynn, R.; Enciso, J.M.; Meki, M.N.; Kiniry, J.R. Effects of treated urban wastewater irrigation on bioenergy sorghum and soil quality. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 228, 105894. [Google Scholar]
- Zouari, M.; Bloem, E.; Souguir, D.; Schnug, E.; Hanchi, B.; Hachicha, M. Evaluation of selected plant species under drained saline and waterlogged conditions in pots when irrigated with treated wastewater. Water Environ. J. 2020, 34, 551–560. [Google Scholar]
- Pedrero, F.; Camposeo, S.; Pace, B.; Cefola, M.; Vivaldi, G.A. Use of reclaimed wastewater on fruit quality of nectarine in Southern Italy. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 203, 186–192. [Google Scholar]
- Du, S.Q.; Kang, S.Z.; Li, F.S.; Du, T.S. Water use efficiency is improved by alternate partial root-zone irrigation of apple in arid northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 179, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.B.; Li, F.S.; Kang, S.Z. Alternate partial root-zone drip irrigation improves water and nitrogen use efficiencies of sweet-waxy maize with nitrogen fertigation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, R.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Wang, X.C.; Rengel, Z.; Zhang, W.J.; Shu, L.Z. Alternate partial root-zone drip irrigation with nitrogen fertigation promoted tomato growth, water and fertilizer-nitrogen use efficiency. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 233, 106049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, P.M.; Lobos, P.; Durán, K.; Olguín, J.; Cea, D.; Schaffer, B. Partial root-zone drying irrigation, shading, or mulching effects on water savings, productivity and quality of ‘Syrah’ grapevines. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 240, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, B.; Sina, B.; Mohamad, M.; Vahid, R. Effects of partial root-zone irrigation on the water use efficiency and root water and nitrate uptake of corn. Water 2018, 10, 526. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, W.; Gu, T.; Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Lin, X.; Huang, Q.; Shen, W. The effects of mineral fertilizer and organic manure on soil microbial community and diversity. Plant Soil 2010, 326, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Niu, W.Q.; Zhang, M.Z.; Li, Y. Effect of alternate partial root-zone drip irrigation on soil bacterial communities and tomato yield. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 119, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.R.; Wang, H.G.; Jia, B.; Li, D.X.; Fang, Q.; Li, R.Q. Irrigation has a higher impact on soil bacterial abundance, diversity and composition than nitrogen fertilization. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Jeffries, T.C.; Trivedi, C.; Anderson, I.C.; Lai, K.T.; McNee, M.; Flower, K.; Singh, B.P.; Minkey, D.; et al. Soil aggregation and associated microbial communities modify the impact of agricultural management on carbon content. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 3070–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zornoza, R.; Acosta, J.A.; Bastida, F.; Domínguez, S.G.; Toledo, D.M.; Faz, A. Identification of sensitive indicators to assess the interrelationship between soil quality, management practices and human health. Soil 2015, 1, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frenk, S.; Hadar, Y.; Minz, D. Resilience of soil bacterial community to irrigation with water of different qualities under Mediterranean climate. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 559–569. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, E.P.; Fan, X.Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.; Neal, A.L.; Hu, C.; Gao, F. Variations in soil and plant-microbiome composition with different quality irrigation waters and biochar supplementation. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 142, 99–109. [Google Scholar]
- Bastida, F.; Torres, I.F.; Romero-Trigueros, C.; Baldrian, P.; Větrovsky, T.; Bayona, J.M.; Alarcón, J.J.; Hernández, T.; García, C.; Nicolás, E. Combined effects of reduced irrigation and water quality on the soil microbial community of a citrus orchard under semi-arid conditions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 104, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.R.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Bi, L.; Zhu, J.; He, J.Z. Consistent responses of soil microbial taxonomic and functional attributes to mercury pollution across China. Microbiome 2018, 6, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, S.D. Soil and Agro-Chemical Analysis Methods; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 25–38. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.Q.; Sun, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, H.; Tang, D. Effects of soil heavy metal pollution on microbial activities and community diversity in different land use types in mining areas. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 20215–20226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Hu, Y.; Guan, X.; Xu, L. Advances in research of reclaimed water irrigation in China. Irrig. Drain. 2020, 69, 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.X.; Kang, Y.H.; Wan, S.Q.; Wei, H.; Jiang, S.J.; Zhang, T.B. Soil salinity management with drip irrigation and its effects on soil hydraulic properties in north china coastal saline soils. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 115, 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Demir, A.D.; Sahin, U. Effects of different irrigation practices using treated wastewater on tomato yields, quality, water productivity, and soil and fruit mineral contents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 24856–24879. [Google Scholar]
- Minhas, P.S.; Saha, J.K.; Dotaniya, M.L.; Sarkar, A.; Saha, M. Wastewater irrigation in India: Current status, impacts and response options. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 152001. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.M.; Xiao, Y.; Yin, S.Y.; Liu, H.L.; Men, B.H.; Hao, Z.Y.; Qian, P.; Yan, H.J.; Hao, Q.C.; Niu, Y.; et al. Impact of Long-Term Reclaimed Water Irrigation on the Distribution of Potentially Toxic Elements in Soil: An In-Situ Experiment Study in the North China Plain. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 649. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Lu, S.; Peng, C.; Jiao, W.; Wang, M. Accumulation of Cd in agricultural soil under long-term reclaimed water irrigation. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.B.; Xie, F.H.; Zhang, X.L.; Pei, L.; Tang, Y. Health evaluation on migration and distribution of heavy metal Cd after reclaimed water drip irrigation. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 841–848. [Google Scholar]
- Troldborg, M.; Duckett, D.; Allan, R.; Hastings, E.; Hough, R.L. A risk-based approach for developing standards for irrigation with reclaimed water. Water Res. 2017, 126, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaskhoussy, K.; Kahlaoui, B.; Messoudi Nefzi, B.; Jozdan, O.; Dakheel, A.; Hachicha, M. Effect of treated wastewater irrigation on heavy metals distribution in a Tunisian soil. Engieering Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2015, 5, 805–810. [Google Scholar]
- Schimel, J.; Balser, T.C.; Wallenstein, M. Microbial stress-response physiology and its implications for ecosystem function. Ecology. 2007, 88, 1386–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.P.N.; Luo, Z.H.; Dong, Z.Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, B.B.; Guo, H.X.; Guo, X.N.; Li, W.J. Metagenomic analysis further extends the role of Chloroflexi in fundamental biogeochemical cycles. Environ. Res. 2022, 209, 112888. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, N.L.; Challacombe, J.F.; Janssen, P.H.; Henrissat, B.; Coutinho, P.M.; Wu, M.; Barabote, R.D. Three genomes from the phylum Acidobacteria provide insight into the lifestyles of these microorganisms in soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 2046–2056. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.H.; Gong, H.L.; Guo, X.Y. Rhizosphere bacterial community of Typha angustifolia L. and water quality in a river wetland supplied with reclaimed water. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 2883–2893. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Gómez, B.; Richter, M.; Schüler, M.; Pinhassi, J.; Acinas, S.G.; González, J.M.; Pedrós-Alió, C. Ecology of marine Bacteroidetes: A comparative genomics approach. Isme J. 2013, 7, 1026–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Maeder, P.; Fliessbach, A.; Dubois, D.; Gunst, L.; Fried, P.; Niggli, U. Soil fertility and biodiversity in organic farming. Science 2002, 296, 1694–1697. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.W.; Shen, Q.L.; Wang, L.; Qiu, G.Y.; Shi, J.C.; Xu, J.M.; Brookes, P.C.; Liu, X.M. Effects of Cd, Cu, Zn and their combined action on microbial biomass and bacterial community structure. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhalnina, K.; Dias, R.; Quadros, P.D.D.; Davis-Richardson, A.; Camargo, F.A.O.; Clark, I.M.; McGrath, S.P.; Hirsch, P.R.; Triplett, E.W. Soil pH determines microbial diversity and composition in the park grass experiment. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 69, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fierer, N.; Jackson, R.B. The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.H.; Cao, Y.T.; Guan, X.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Hao, Z.Y.; Hu, W.; Chen, L. Microbial assessments of soil with a 40-year history of reclaimed wastewater irrigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 696–705. [Google Scholar]
- Morugán-Coronado, A.; García-Orenes, F.; Mcmillan, M.; Pereg, L. The effect of moisture on soil microbial properties and nitrogen cyclers in Mediterranean sweet orange orchards under organic and inorganic fertilization. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.C.; Dong, C.X.; Wu, J.H.; Liu, X.W.; Wu, Y.X.; Chen, X.B.; Yu, S.X. Ecological effects of soil properties and metal concentrations on the composition and diversity of microbial communities associated with land use patterns in an electronic waste recycling region. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Pardo, T.; Clemente, R.; Epelde, L.; Garbisu, C.; Bernal, M.P. Evaluation of the phytostabilisation efficiency in a trace elements contaminated soil using soil health indicators. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 268, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Wu, J.; You, A.; Huang, B.; Cao, C. Effects of heavy metals on soil microbial community structure and diversity in the rice (Oryza sativa L. subsp. Japonica, Food Crops Institute of Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences) rhizosphere. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 63, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beattie, R.E.; Henke, W.; Campa, M.F.; Hazen, T.C.; McAliley, L.R.; Campbell, J.H. Variation in microbial community structure correlates with heavy-metal contamination in soils decades after mining ceased. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 126, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y.M.; Huang, H.Y.; Mou, L.C.; Ru, J.L.; Zhao, J.H.; Xiao, S. Long-term and high-concentration heavy-metal contamination strongly influences the microbiome and functional genes in Yellow River sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar]





| Index | pH | Cd /μg·L−1 | Cu /mg·L−1 | Pb /mg·L−1 | Zn /mg·L−1 | CODMn /mg·L−1 | TN /mg·L−1 | TP /mg·L−1 | EC /ds·m−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reclaimed water | 7.84 | 0.0021 | 0.035 | 0.026 | 0.772 | 17.6 | 29.57 | 1.95 | 2.06 |
| Clean water | 7.32 | 0.0004 | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.016 | 7.2 | 4.63 | 0.23 | 1.62 |
| Soil Texture | Bulk Density /g·cm−3 | OM /g·kg−1 | TP /g·kg−1 | TN /g·kg−1 | EC /μS·cm−1 | NO3−-N /mg·kg−1 | pH | Pb /mg·kg−1 | Cd /mg·kg−1 | Cu /mg·kg−1 | Zn /mg·kg−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sandy loam | 1.40 | 19.9 | 1.70 | 0.89 | 657.05 | 68.2 | 8.81 | 12.08 | 0.126 | 25.94 | 90.08 |
| Treatments (1) | TN /g·kg−1 | EC /μS·cm−1 | OM /g·kg−1 | pH | TP /g·kg−1 | NO3−-N /g·kg−1 | SWC (2) /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Significance Based on Three-Way ANOVA (F Value) | |||||||
| Water Type | 11.86 ** | 7.77 * | NS | NS | 30.15 *** | 33.82 *** | 25.61 *** |
| RW | 0.77 B | 792.8 a | 22.95 a | 8.70 a | 1.61 B | 61.1 A | 20.18 A |
| CW | 0.83 A | 751.8 b | 22.89 a | 8.74 a | 1.84 A | 33.3 B | 17.00 B |
| Irrigation Methods | NS | NS | NS | NS | NS | 7.33 * | NS |
| FI | 0.81 a | 777.8 a | 23.55 a | 8.71 a | 1.72 a | 40.71b | 18.70 a |
| APRI | 0.79 a | 766.8 a | 22.29 a | 8.73 a | 1.73 a | 53.64a | 18.49 a |
| Irrigation Techniques | 5.18 * | 42.41 *** | NS | NS | NS | NS | 5.19 * |
| FUI | 0.82 a | 829.5 A | 23.39 a | 8.74 a | 1.76 a | 48.32 a | 19.31 a |
| SDI | 0.78 b | 715.2 B | 22.45 a | 8.70 a | 1.69 a | 46.03 a | 17.88 b |
| Water Type × Irrigation Methods | 5.26 * | 0.37 | 7.62 * | 1.03 | 1.01 | 4.54 * | 0.07 |
| Water Type × Irrigation Techniques | 3.85 | 5.14 * | 3.00 | 0.14 | 7.50 * | 44.24 *** | 0.08 |
| Irrigation Methods × Irrigation Techniques | 0.18 | 5.99 * | 9.47 ** | 6.64 * | 3.89 | 47.32 *** | 1.12 |
| Water Type × Irrigation Methods × Irrigation Techniques | 5.50 * | 0.99 | 0.93 | 0.05 | 10.72** | 0.14 | 0.58 |
| Treatments | Cd /mg·kg−1 | Pb /mg·kg−1 | Zn /mg·kg−1 | Cu /mg·kg−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Significance Based on Three-Way ANOVA (F Value) | ||||
| Water Type | 41.04 *** | 42.41 *** | 4.60 * | 5.64 * |
| RW | 1.71 A | 16.88 a | 95.95 a | 26.64 a |
| CW | 1.56 B | 15.22 b | 92.97 b | 24.76 b |
| Irrigation Methods | 1.47 | 0.29 | NS | 4.37 * |
| FI | 0.162 a | 15.98 a | 95.13 a | 26.53 a |
| APRI | 0.165 a | 16.12 a | 93.79 a | 24.87 b |
| Irrigation Techniques | 102.82 *** | 5.90 * | NS | NS |
| FUI | 0.175 A | 16.36 a | 93.67 a | 25.79 a |
| SDI | 0.152 B | 15.74 b | 95.25 a | 25.61 a |
| Water Type × Irrigation Methods | 0.05 | 6.97 * | 0.86 | 1.72 |
| Water Type × Irrigation Techniques | 20.55 *** | 1.81 | 1.23 | 33.33 *** |
| Irrigation Methods × Irrigation Techniques | 15.78 ** | 19.08 *** | 1.50 | 34.13 *** |
| Water Type × Irrigation Methods × Irrigation Techniques | 0.155 | 0.90 | 0.58 | 0.63 |
| Treatments | Richness | Diversity | Ace | Good’s Coverage | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sobs | Chao1 | Shannon | PD | Simpson | |||
| RSA | 2511 ± 45 a | 3123 ± 24 ab | 6.67 ± 0.07 bc | 202.0 ± 4.8 ab | 3155 ± 32 ab | 0.9743 ± 0.0005 bc | 0.0032 ± 0.0006 ab |
| RSF | 2503 ± 14 ab | 3106 ± 14 ab | 6.74 ± 0.02 ab | 203.0 ± 1.6 ab | 3126 ± 8 abc | 0.9746 ± 0.0002 abc | 0.0025 ± 0.0002 ab |
| RFA | 2512 ± 21 a | 3089 ± 24 ab | 6.78 ± 0.03 a | 204.1 ± 2.2 a | 3198 ± 32 bcd | 0.9752 ± 0.0007 ab | 0.0023 ± 0.0001 b |
| RFF | 2477 ± 45 ab | 3017 ± 54 c | 6.68 ± 0.12 abc | 200.8 ± 3.4 ab | 3057 ± 43 d | 0.9756 ± 0.0004 a | 0.0037 ± 0.0017 ab |
| WSA | 2445 ± 32 b | 3063 ± 78 bc | 6.66 ± 0.01 bc | 197.5 ± 4.2 b | 3075 ± 64 cd | 0.9750 ± 0.001 ab | 0.0030 ± 0.0001 ab |
| WSF | 2513 ± 9 a | 3153 ± 21 a | 6.69 ± 0.02 abc | 202.1 ± 1.6 ab | 3181 ± 24 a | 0.9738 ± 0.0005 c | 0.0028 ± 0.0001 ab |
| WFA | 2520 ± 48 a | 3151 ± 16 a | 6.73 ± 0.07 ab | 203.0 ± 4.0 ab | 3150 ± 22 ab | 0.9743 ± 0.0006 bc | 0.0026 ± 0.0002 ab |
| WFF | 2465 ± 18 ab | 3061 ± 15 bc | 6.61 ± 0.04 c | 198.2 ± 3.4 ab | 3083 ± 26 cd | 0.9750 ± 0.0003 ab | 0.0039 ± 0.0012 a |
| Significance based on three-way ANOVA (F value) | |||||||
| Water Type | 0.869 | 2.306 | 3.293 | 2.780 | 0.850 | 3.743 | 0.259 |
| R | 2501 a | 3080 a | 6.72 a | 202.5 a | 3109 a | 0.9748 a | 0.0029 a |
| C | 2486 a | 3111 a | 6.67 a | 197.7 a | 3122 a | 0.9747 a | 0.0031 a |
| Irrigation Methods | 0.225 | 2.148 | 1.525 | 0.182 | 0.238 | 0.081 | 2.167 |
| FI | 2490 a | 3084 a | 6.68 a | 201.0 a | 3124 a | 0.9748 a | 0.0032 a |
| APRI | 2497 a | 3107 a | 6.71 a | 201.6 a | 3107 a | 0.9746 a | 0.0028 a |
| Irrigation Techniques | 0.005 | 4.151 | 0.208 | 0.066 | 6.692 * | 8.149 * | 0.926 |
| FUR | 2494 a | 3092 a | 6.70 a | 201.5 a | 3097 b | 0.9750 a | 0.0031 a |
| SDI | 2493 a | 3098 a | 6.69 a | 201.2 a | 3134 a | 0.9744 b | 0.0028 a |
| Water Type × Irrigation Methods | 1.112 | 2.135 | 0.312 | 0.144 | 3.743 | 2.097 | 0.042 |
| Water Type × Irrigation Techniques | 0.958 | 3.830 | 0.301 | 0.107 | 3.283 | 2.505 | 0.134 |
| Irrigation Methods × Irrigation Techniques | 8.038 * | 14.76 ** | 12.095 ** | 6.315 * | 10.515 ** | 4.627 * | 8.446 * |
| Water Type × Irrigation Methods × Irrigation Techniques | 3.284 | 4.221 | 0.095 | 0.885 | 7.838 * | 4.172 | 0.303 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, W.; Li, P.; Qi, X.; Hashem, M.S.; Xiao, Y.; She, Y. Influence of Different Irrigation Water Qualities and Irrigation Techniques on the Soil Attributes and Bacterial Community Structure. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3170. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123170
Guo W, Li P, Qi X, Hashem MS, Xiao Y, She Y. Influence of Different Irrigation Water Qualities and Irrigation Techniques on the Soil Attributes and Bacterial Community Structure. Agronomy. 2022; 12(12):3170. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123170
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Wei, Ping Li, Xuebin Qi, Mahmoud S. Hashem, Yatao Xiao, and Yingjun She. 2022. "Influence of Different Irrigation Water Qualities and Irrigation Techniques on the Soil Attributes and Bacterial Community Structure" Agronomy 12, no. 12: 3170. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123170
APA StyleGuo, W., Li, P., Qi, X., Hashem, M. S., Xiao, Y., & She, Y. (2022). Influence of Different Irrigation Water Qualities and Irrigation Techniques on the Soil Attributes and Bacterial Community Structure. Agronomy, 12(12), 3170. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123170







