Meta-Analysis of Factors Affecting C-N Fractions and Yield of Paddy Soils by Total Straw Return and N Fertilizer Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
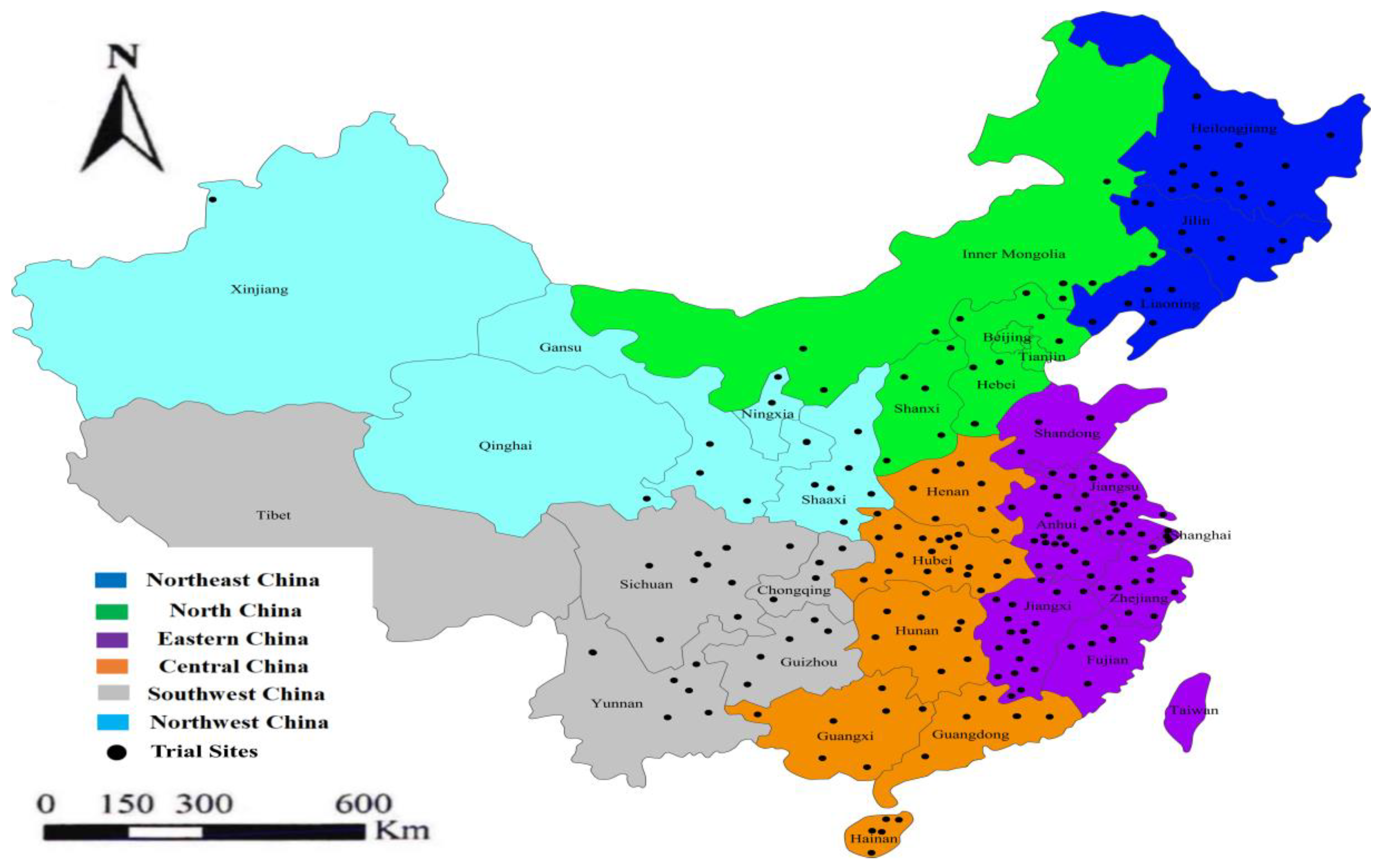
2.1. Data Acquisition
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Literature Screening and Data Extraction
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Subgroup Analysis
- (1)
- dividing the study area into six major rice-growing regions: eastern; southwestern; southern; northern; northeastern; and northwestern China;
- (2)
- classifying rice variety into three categories: early (≤125 d), medium (125–150 d), and late (≥150 d) maturity;
- (3)
- using four mean annual temperature intervals (<10 °C, 10–15 °C, 15–20 °C, and >20 °C); these were used for each test area;
- (4)
- classifying average annual precipitation in rice fields as very low (400–600 mm), low (600–800 mm), medium (800–1,500 mm), and high (>1500 mm);
- (5)
- including three types of paddy return methods: zero tillage (the straw is crushed or the whole straw is directly and evenly covered on the surface); rotary tillage (the straw is crushed and evenly scattered on the surface while the rice is harvested mechanically, then the rotary tiller is used to shallowly turn it into the plow layer); and deep tillage (the straw is crushed and evenly scattered on the surface during the mechanical harvesting of rice, then the straw is turned and buried under the soil plow layer);
- (6)
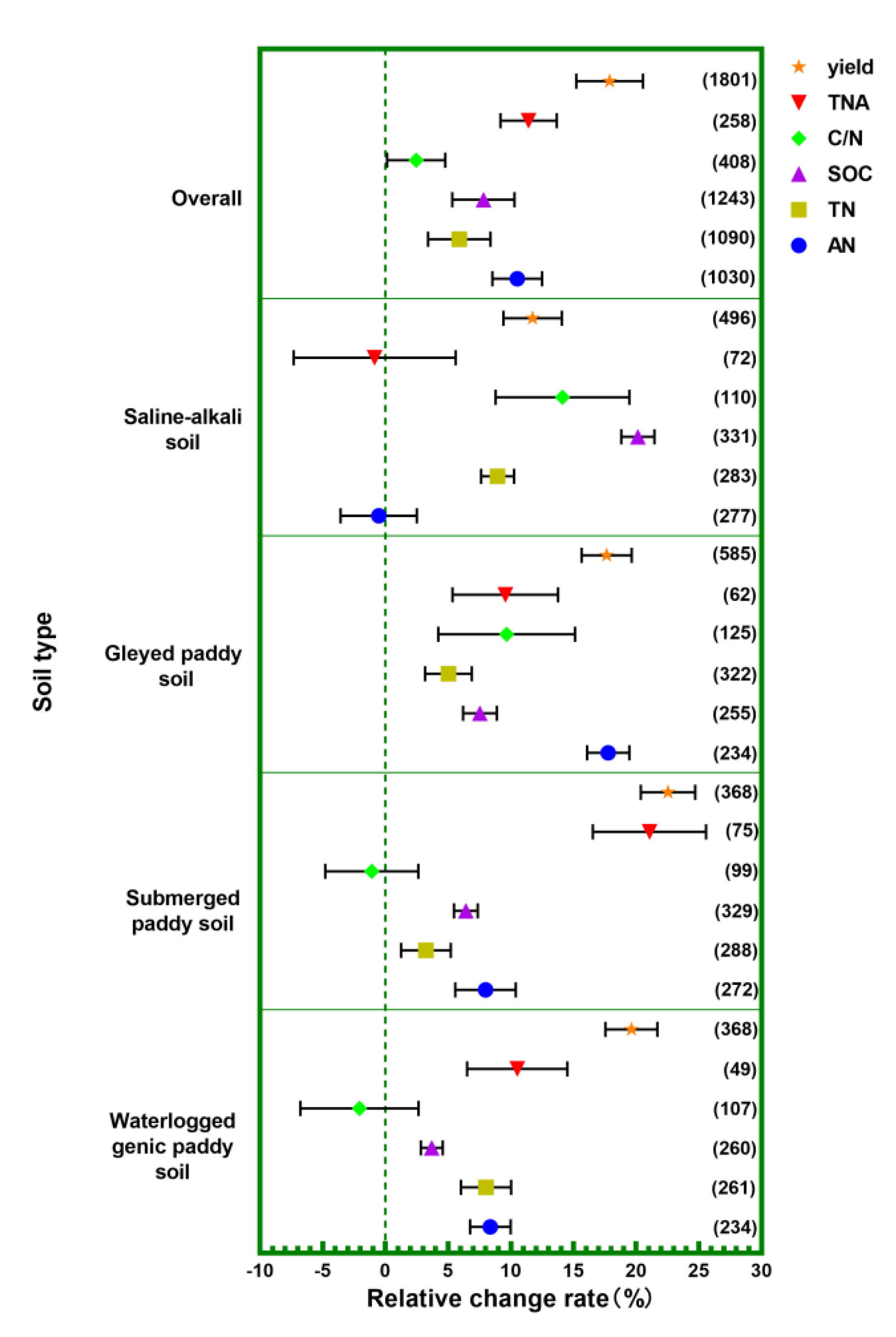
- identifying four types of paddy soils: saline-alkali soil, gleyed paddy soil, submerged paddy soil, and waterlogged genic paddy soil;
- (7)
- categorizing C-N fractions of the different soil layers into three categories: 0–5 cm, 5–10 cm, and 10–20 cm;
- (8)
- identifying N accumulation in both the plants and the seeds;
- (9)
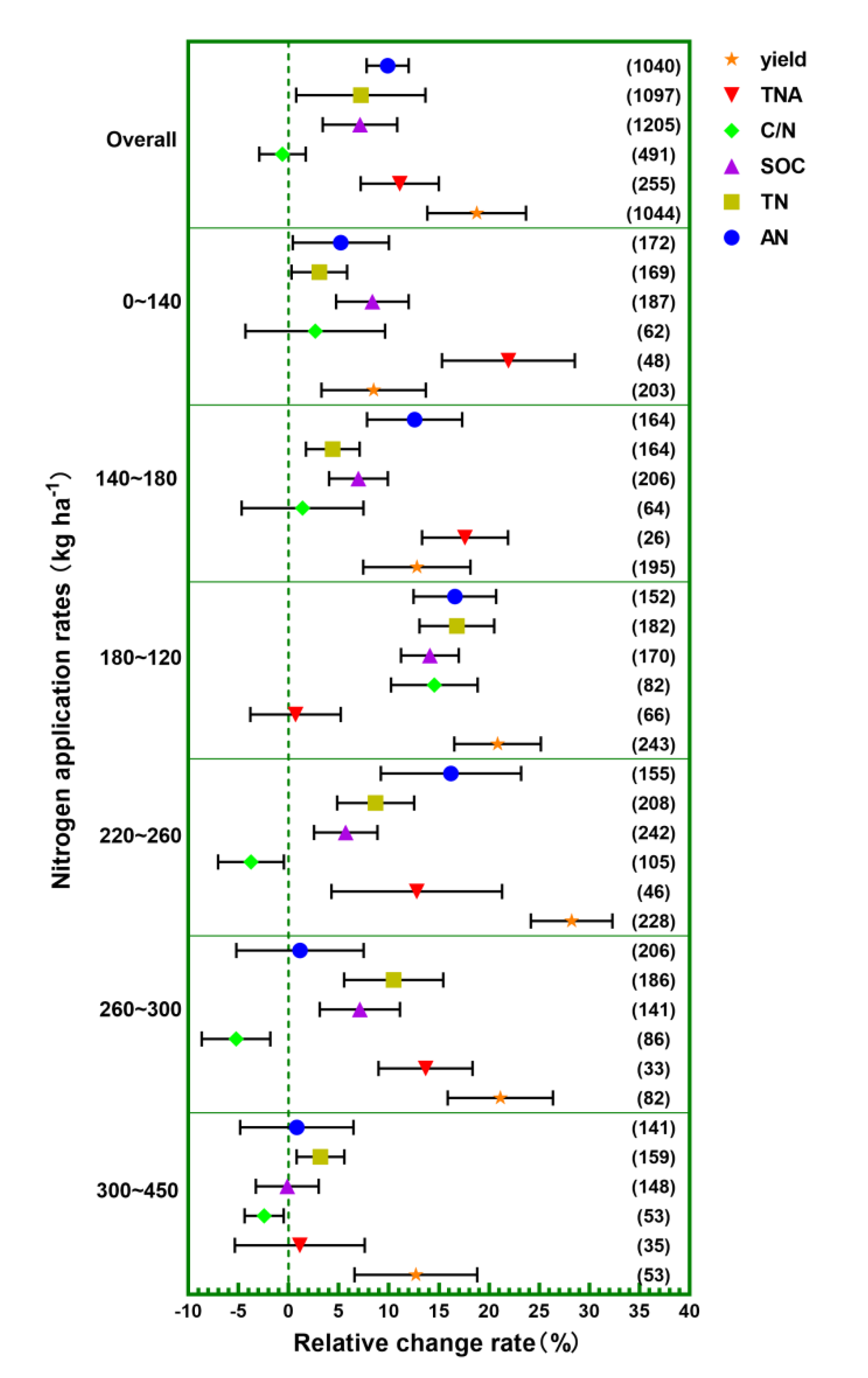
- classifying N fertilizer application rates into six categories: 0–140, 140–180, 180–220, 220–260, 260–300, and 300–450 kg ha−1. The application amount of straw-decayed bacterium (a complex flora, mostly composed of Bacillus subtilis) was divided into four categories: 0–10; 10–20; 20–30; and 30–40 kg ha−1 (straw-decayed bacterium were from: Jiangsu, Tianxiang, Beijing Century, Chengdu Hualong, Nanjing Ningliang, Shanghai Lianye, and Beijing Zhongnong).
2.6. Literature Screening
2.7. Study Indicators and Data Grouping
3. Results
3.1. Different Regions
3.2. Temperature
3.3. Precipitation
3.4. Soil Layer
3.5. Varieties
3.6. Tillage
3.7. Soil Type Conditions
3.8. N Application Rates
3.9. Decomposing Bacteria
3.10. Time
3.11. The Relative Importance of Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, W.H. Research on incineration and comprehensive utilization of crop straw. Agric. Mach. Using Maint. 2016, 4, 46–47. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.Q.; Liu, Y.S.; Hang, Y.L.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.X.; Han, Y.H. Research progress on effects of straw incorporation on soil micro-ecological environment. Microbiol. China 2022, 49, 807–816. [Google Scholar]
- Song, D.L.; Hou, S.P.; Wang, X.B.; Liang, G.Q.; Zhou, W. Nutrient resource quantity of crop straw and its potential of substituting. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2018, 24, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Suriyagoda, L.; de Costa WA, J.M.; Lambers, H. Growth and phosphorus nutrition of rice when inorganic fertiliser application is partly replaced by straw under varying moisture availability in sandy and clay soils. Plant Soil 2014, 384, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Sun, Y.; Xu, H.; Yin, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Guo, C.; Yang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Mal, J. Effects of wheat straw mulch application and nitrogen management on rice root growth, dry matter accumulation and rice quality in soils of different fertility. Paddy Water Environ. 2018, 16, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.J.; Zhao, W.Q.; Li, T. Balancing straw returning and chemical fertilizers in China: Role of straw nutrient resources. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 2695–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Lam, S.K.; Wolf, B. Trade-offs between soil carbon sequestration and reactive nitrogen losses under straw return in global agroecosystems. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 5919–5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadaf, J.; Shah, G.A.; Shahzad, K.; Ail, N.; ShahId, M.; Ail, S.; Hussain, R.A.; Ahmed, Z.I.; Traore, B.; Ismail IM, I.; et al. Improvements in wheat productivity and soil quality can accomplish by co-application of biochars and chemical fertilizers. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Cornejo, J.; Zornoza, R.; Faz, A. Carbon and nitrogen mineralization during decomposition of crop residues in a calcareous soil. Geoderma 2014, 230–231, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tveit, A.; Schwack, R.; Svenning, M.; Urich, T. Organic carbon transformations in high-Arctic peat soils: Key functions and microorganisms. ISME J. 2013, 7, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, X.L.; Zheng, B.; Lu, Y.; Duan, Z.Y.; Yin, S.U.; Lei, B.K. Effects of C/N regulated corn straw application on nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium uptake in tobacco. Acta Agric. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2012, 21, 125–129. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.G.; Lu, X.K.; Wan, L.; Chen, Z.G.; Zuo, H. Effects of wheat straw returning on rice growth and soil fertility. Crops 2003, 5, 37–38. [Google Scholar]
- Limon-Ortega, A.; Govaerts, B.; Deckers, J. Soil aggregate and microbial biomass in a permanent bed wheat-maize planting system after 12 years. Field Crops Res. 2006, 97, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwenzi, W.; Gotosa, J.; Chakanetsa, S.; Mutema, Z. Effects of tillage systems on soil organic carbon dynamics.structural stability and crop yields in irrigated wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)-cotton(Gossypium hirsutum L.)rotation in semi-arid Zimbabwe. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2009, 83, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, P.G.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhu, L.F.; Hu, Z.H.; Jin, Q.Y. Effects of straw returning coupled with N application on rice photosynthetic characteristics, nitrogen uptake and grain yield formation. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2015, 29, 282–290. [Google Scholar]
- Malhi, S.; Nyborg, M.; Goddard, T.; Puurveen, D. Long-term tillage, straw and N rate effects on quantity and quality of organic C and N in a Gray Luvisol soil. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2011, 90, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.J.; Wang, J.; Wu, P.; Huang, H.K.; Jiang, Y.X. Effect of different nitrogen application on rice yield and N uptake of white soil under wheat straw turnover. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2016, 22, 254–262. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, S.; Yuan, D.; Li, W.; He, W.; Raza, S.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Zamanian, K.; Zhao, X. Soil chemical properties depending on fertilization and management in China: A Meta-Analysis. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.J.; Cheng, W.D.; Chen, G.; Shen, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.M. Effect of straw returning and nitrogen reduction on soil nutrition, carbon pool and rice yield in rice field. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis 2019, 31, 624–630. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Jin, M.C.; Ma, C.; Chai, R.S.; Gao, S.F.; Hao, H.J. Effect of straw returning with decomposing inoculants on grain yield and potassium fertilizer utilization efficiency of rice. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China 2018, 1, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Oladele, S.O.; Adeyemo, A.J.; Awodun, M.A. Influence of rice husk biochar and inorganic fertilizer on soil nutrients availability and rain-fed rice yield in two contrasting soils. Geoderma 2019, 336, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, X. Effects of different wheat straw returning amounts on growth, yield and quality of rice. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2018, 20, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Nazia, R.; Liang, F.; Huang, S. Long-term fertilization altered labile soil organic carbon fractions in upland soil of China. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2019, 29, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, Y.L.; Xu, M.G.; Wang, W.; Sun, X.L.; Zhao, K. Return rate of straw residue affects soil organic C sequestration by chemical fertilization. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 113, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijay, S.; Shan, Y.H.; Johnson-Beebout, S.E.; Yadvinder, S. Crop residue management for lowland rice-based cropping systems in Asia. Adv. Agron. 2008, 98, 117–199. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.C.; Zhao, Y.W.; Wang, J.Z.; Zhu, P.; Cui, X.; Han, X.Z.; Xu, M.G.; Lu, C.A. The efficiency of long-term straw return to sequester organic carbon in Northeast China’s cropland. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevitch, J.; Hedges, L.V. Statistical issues in ecological Meta-analyses. Ecology 1999, 80, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philibert, A.; Loyce, C.; Makowski, D. Assessment of the quality of meta-analysis in agronomy. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 4, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, M.S.; Adams, D.C.; Gurevitch, J. Meta Win: Statistical Software for Meta-Analysis; Sinauer Associates Inc.: Sunderland, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hedges, L.V.; Gurevitch, J.; Curtis, P.S. The meta-analysis of response ratios in experimental ecology. Ecology 1999, 80, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, P.S.; Wang, X. A meta-analysis of elevated CO2 effects on woody plant mass, form, and physiology. Oecologia 1998, 113, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, P.B.; Ainsworth, E.A.; Long, S.P. How does elevated ozone impact soybean? A metaranalysis of photosynthesis, growth and yield. Plant Cell Environ. 2003, 26, 1317–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Sharma, P.K.; Singh, S.; Kumar, A. Addition of crop residues with different C:N Ratios on the release pattern of available nitrogen and sulfur in different soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2021, 52, 2912–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Yang, N.; Lu, C.; Qin, C.; Siddique, K.H.M. Soil organic carbon, total nitrogen, available nutrients, and yield under different straw returning methods. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 214, 105171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Huang, L.; Li, X.; Lu, J.; Gao, R.; Kamran, M.; Fahad, S. Effect of Clay Mineralogy and Soil Organic Carbon in Aggregates under Straw Incorporation. Agronomy 2022, 12, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wei, T.; Li, Y.L.; Wang, K.; Jia, Z.K.; Han, Q.F.; Ren, X.L. Effects of straw incorporation on the stratification of the soil organic C, total N and C:N ratio in a semiarid region of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 153, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wu, J.F.; Pan, X.H.; Tan, X.M.; Zeng, Y.J.; Shi, Q.H.; Liu, T.J.; Zeng, Y.H. Effects of long-term straw return on soil organic carbon fractions and enzyme activities in a double-cropped rice paddy in South China. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneepitak, S.; Ullah, H.; Datta, A.; Shrestha, R.P.; Shrestha, S.; Kachenchart, B. Effect of water and rice straw management practices on yield and water productivity of irrigated lowland rice in the Central Plain of Thailand. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 211, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.H.; Gao, J.P.; Liu, C.H.; Zhang, W.Z.; Lan, Y.; Li, S.H.; Meng, J.; Xu, Z.J.; Tang, L. Interactive effects of straw-derived biochar and N fertilization on soil C storage and rice productivity in rice paddies of Northeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Huang, H.; Wu, J.; Lv, G.D.; Long, B.Q.; Wu, T.; Gu, J. Effects of rice straw returning on soil nutrients rice biomass and yield. Crop Res. 2020, 34, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Tan, L.; Zhang, F. Duration of continuous cropping with straw return affects the composition and structure of sol bacterial communities in cotton feldspar. Can. J. Microbiol. 2017, 30, 1218–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.C.; Cao, C.Y.; Li, K.J.; Qiu, S.J.; Zhou, W.; He, P. Effects of long-term straw return on soil fertility, nitrogen pool fractions and crop yields on a fluvo-aquic soil in North China. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2014, 20, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, S.C.; Sarma, B.; Narzari, R.; Gogoi, L.; Kataki, R.; Garg, A.; Gogoi, N. Role of pyrolysis temperature on application dose of rice straw biochar as soil amendment. Environ. Sustain. 2022, 5, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layek, J.; Das, A.; Ghosh, P.K.; Rangappa, K.; Lal, R.; Idapuganti, R.G.; Nath, C.P.; Dey, U. Double no-till and rice straw retention in terraced sloping lands improves water content, soil health and productivity of lentil in Himalayan foothills. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 221, 105381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.X.; Su, Y.; Ning, Y.C.; Rong, G.H.; Wang, G.D.; Liu, D.; Liu, L.Y. Estimation of the effects of maize straw return on soil carbon and nutrients using response surface methodology. Pedosphere 2018, 28, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.F.; Li, G.H.; Wang, S.H.; Jin, X.; Yang, Y.M.; Chen, X.T.; Ding, C.Q.; Liu, Z.H.; Ding, Y.F. Methane emissions from rice fields under continuous straw return in the middle-lower reaches of the Yangtze River. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 1874–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.J.; Zeng, X.Z.; Chen, K.; Li, Z.; Guo, S.; Shangguan, Y.X.; Yu, H.; Tu, S.H.; Qin, Y.S. Long-term straw mulch effects on crop yields and soil organic carbon fractions at different depths under a no-ill system on the Chengdu plain, China. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 2143–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, G.; Tu, S.X.; Yang, J.C.; Zhang, J.F.; Yang, L. A field study on effects of nitrogen fertilization modes on nutrient up take, crop yield and soil biological properties in rice wheat rotation system. Agric. Sci. China 2011, 10, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroud, J.L.; Irons, D.E.; Watts, C.W.; White, R.P.; Whiemore, M.A.P. Population collapse of Lumbricus terrestris in conventional arable cultivations and response to straw applications. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 108, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.I.; Inubushi, K. Possibilities to reduce rice straw-induced global warming potential of a sandy paddy soil by combining hydrological manipulations and urea-N fertilizations. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 2675–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.G.; Li, D.C.; Li, J.M. Polyolefin-Coated urea decreases ammonia vocalization in a double rice system of southern China. Agron. J. 2013, 105, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewpradit, W.; Toomsan, B.; Vityakon, P. Regulating mineral N release and greenhouse gas emissions by mixing groundnut residues and rice straw under field conditions. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2008, 59, 640–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biljana, G.; Milka, B.J.; Marija, K.B. Phenotypic variability of bread wheat genotypes for nitrogen harvest index. Genetika 2011, 43, 419–426. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, D.J.; Yu, Y.C.; Wang, C.; Zhuang, J.G. Effects of straw incorporation plus nitrogen fertilizer on rice yield, nitrogen use efficiency and nitrogen loss. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2016, 22, 877–885. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Cheng, J.P.; Zhang, G.Z.; Xu, D.Z.; Wu, J.P.; Wu, J.H.; Yang, Z.L.; Ma, H.X. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer regimes and returning straw on N availability and forming yield of direct-sowing rice. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2011, 50, 3701–3704. [Google Scholar]
- Lampayan, R.M.; Rejesus, R.M.; Singleton, G.R.; Bouman BA, M. Adoption and economics of alternate wetting and drying water management for irigated lowland rice. Field Crops Res. 2015, 170, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouman, B.A.M.; Tuong, T.P. Field water management to save water and increase its productivity in irrigated lowland rice. Agric. Water Manag. 2001, 49, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belder, P.; Spiertz, J.H.J.; Bouman, B.A.M.; Lu, G.; Tuong, T.P. Nitrogen economy and water productivity of lowland rice under water-saving irrigation. Field Crop Res. 2005, 93, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Z.M.; Chen, X.H.; Zhao, Z.; Shi, C.; Yuan, Y.K.; Cao, L.K. Effect of fertilizer management on dry matter accumulation, yield and fertilizer use efficiency of rice cultivar ‘Huayou-14’. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2018, 26, 815–823. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.B.; Zhou, X.F.; Jiang, P.; Chen, J.N.; Zhang, R.C.; Wu, D.; Cao, F.B.; Shan, S.L.; Huang, M.; Zou, Y.B. Effect of low nitrogen rate combined with high plant density on grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency in super rice. Acta Agron. Sin. 2015, 41, 1591–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takakai, F.; Goto, M.; Watanabe, H. Effects of the autumn incorporation of rice straw and application of lime nitrogen on methane and nitrous oxide emissions and rice growth of a high-yielding paddy field in a cool-temperate region in Japan. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaihre, Y.K.; Wassmann, R.; Villegas, P.G. Impact of elevated temperatures on greenhouse gas emissions in rice systems: Interaction with straw incorporation studied in a growth chamber experiment. Plant Soil 2013, 373, 857–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Zhou, Y.N.; Lix, L.; Hou, X.P.; An, T.; Wang, Q. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer on crop residue decomposition and nutrient release under lab incubation and field conditions. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2019, 52, 1746–1760. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C.G. Effects of Rice Straw Different Incorporation Ways on Rice Yield and Nutrient Absorption Characteristics and Soil Fertility; Jiangxi Agricultural University: Nanchang, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]











| 1 N (kg ha−1) | 2 Total Cost (USD ha−1) | 3 Production Increase (%) | Net Profit (USD ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0~140 | <1574 | 8.5 | <1110 |
| 140~180 | 1574–1602 | 12.8 | 1110–1121 |
| 180~220 | 1602–1631 | 20.85 | 1121–1700 |
| 220~260 | 1631–1667 | 28.24 | 1700–2081 |
| 260~300 | 1667–1679 | 21.13 | 1700–1724 |
| 300~450 | 1679–1727 | 12.7 | 1028–1700 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Lou, Z.; Hsu, L.; Chen, D.; Piao, R.; Zhao, H.; Cui, Z. Meta-Analysis of Factors Affecting C-N Fractions and Yield of Paddy Soils by Total Straw Return and N Fertilizer Application. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3168. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123168
Zhang L, Wang Y, Lou Z, Hsu L, Chen D, Piao R, Zhao H, Cui Z. Meta-Analysis of Factors Affecting C-N Fractions and Yield of Paddy Soils by Total Straw Return and N Fertilizer Application. Agronomy. 2022; 12(12):3168. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123168
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Liqiang, Yunlong Wang, Zixi Lou, Lefei Hsu, Di Chen, Renzhe Piao, Hongyan Zhao, and Zongjun Cui. 2022. "Meta-Analysis of Factors Affecting C-N Fractions and Yield of Paddy Soils by Total Straw Return and N Fertilizer Application" Agronomy 12, no. 12: 3168. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123168
APA StyleZhang, L., Wang, Y., Lou, Z., Hsu, L., Chen, D., Piao, R., Zhao, H., & Cui, Z. (2022). Meta-Analysis of Factors Affecting C-N Fractions and Yield of Paddy Soils by Total Straw Return and N Fertilizer Application. Agronomy, 12(12), 3168. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123168






