Community Composition Specificities of Cyanobacteria in Paddy Soil under Different Ecological Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Soil Collection
2.2. Analyses of Soil Variables
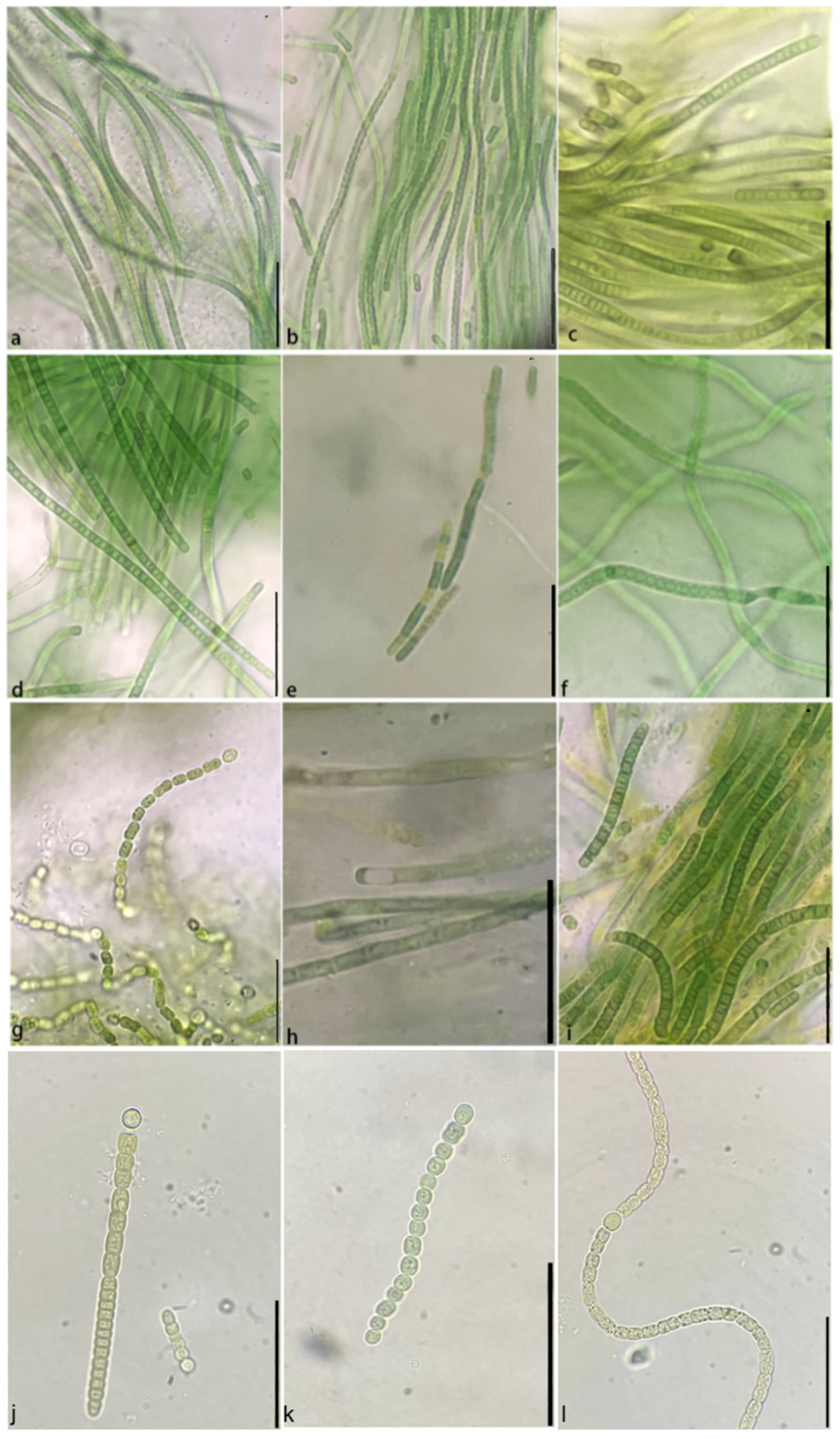
2.3. Morphological Evaluation of Cyanobacteria
2.4. DNA Extraction and Illumina MiSeq Sequencing
2.5. Data Analysis Pipeline and Operational Taxonomic Unit Taxonomic Assignment
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Climatic Conditions and Physicochemical Properties of Soil Sample Sampling Sites
3.2. Morphological Observation of Soil Cyanobacteria
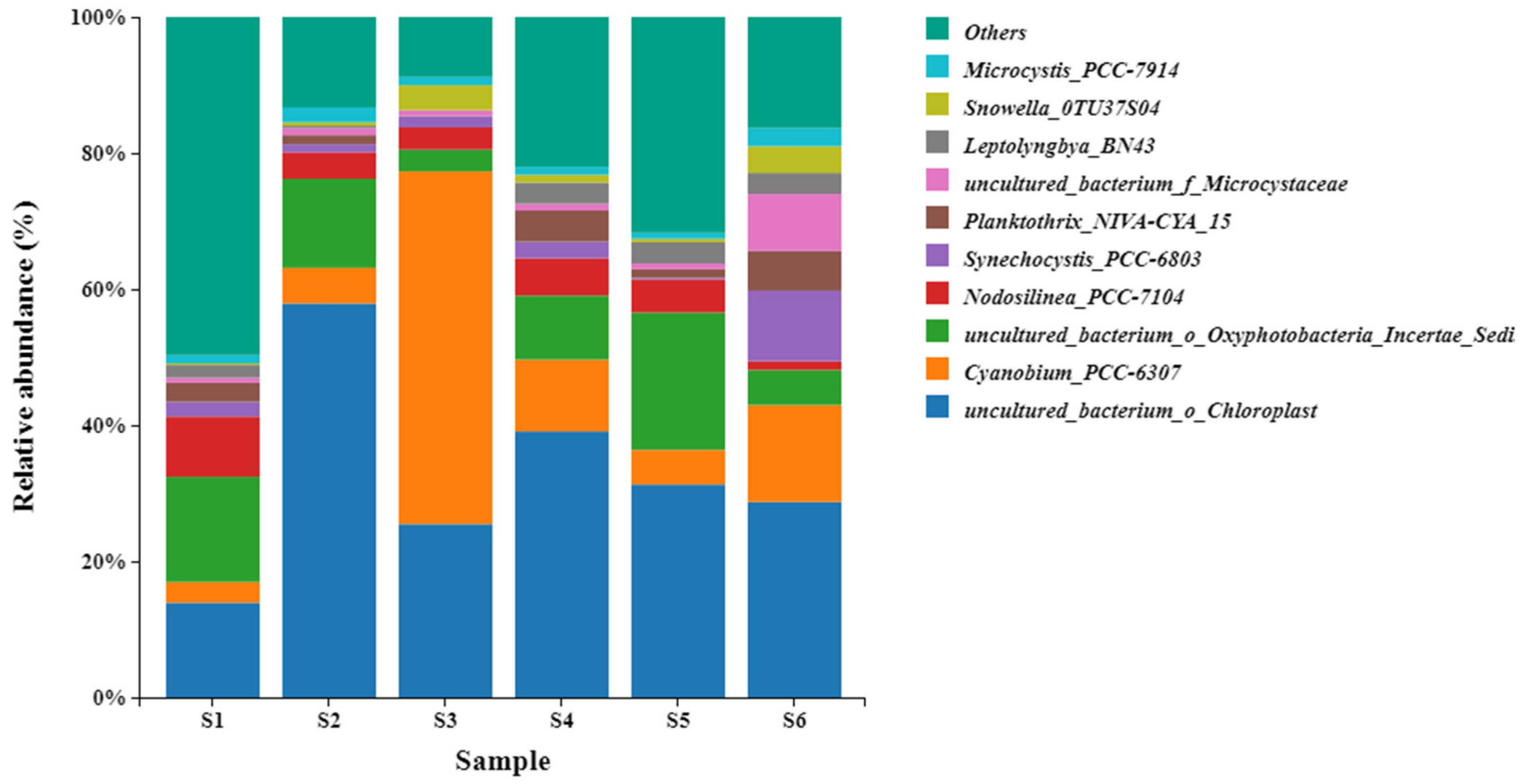
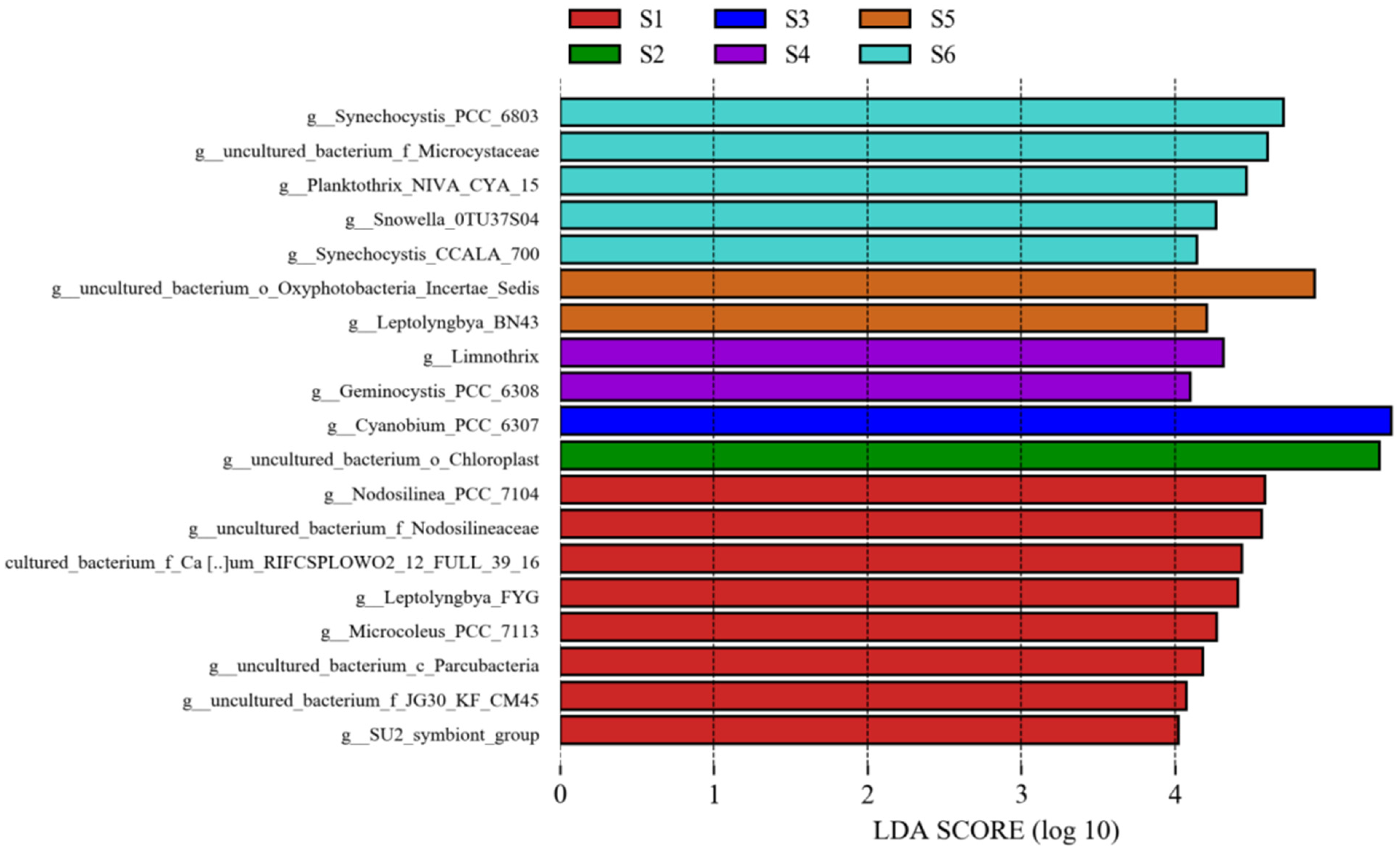
3.3. Cyanobacteria Communities Composition and Structure
3.4. Diversity Analysis of Soil Cyanobacteria Community
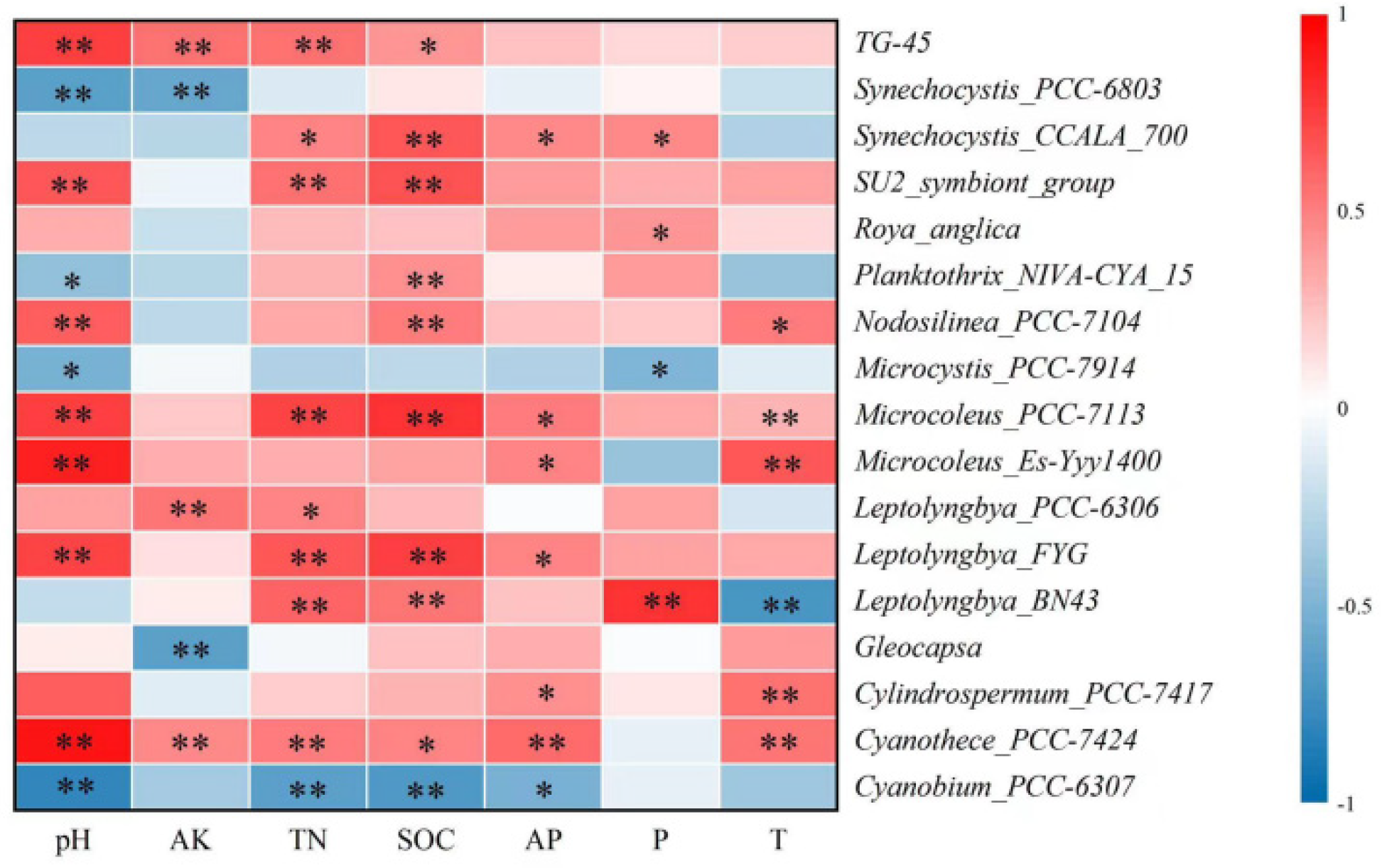
3.5. Correlation between Operational Taxonomic Units and Environmental Variables
4. Discussion
4.1. Composition of Cyanobacterial Communities in the Inter-Rhizosphere Soil of Rice
4.2. Influence of Climate on Cyanobacteria Community
4.3. Effects of Soil Properties on Cyanobacteria Community
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, B.; Li, J.L. Changes in the abundance and structure of bacterial communities in the greenhouse tomato cultivation system under long-term fertilization treatments. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 121, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaka, A.; Plak, A.; Zagórski, P.; Ozimek, E.; Rysiak, A.; Majewska, M.; Jaroszuk-Ściseł, J. Relationships between the properties of Spitsbergen soil, number and biodiversity of rhizospHere microorganisms, and heavy metal concentration in selected plant species. Plant Soil 2019, 436, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, T.; Falkowski, P.G. Genome evolution in cyanobacteria: The stable core and the variable shell. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2510–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Afkairin, A.; Ippolito, J.A.; Stromberger, M.; Davis, J.G. Solubilization of organic phosphorus sources by cyanobacteria and a commercially available bacterial consortium. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 162, 103900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, G.; Deepak-Kumar, M.J. The Nitrogen Fixation Capability of Cyanobacteria-A Natural Source as A Bio-Fertilizer For Arachis Hypogaea. Indian J. Appl. Res. 2014, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steunou, A.S.; Bhaya, D.; Bateson, M.M.; Melendrez, M.C.; Ward, D.M.; Brecht, E.; Peters, J.W.; Kühl, M.; Grossman, A.R. In situ analysis of nitrogen fixation and metabolic switching in unicellular thermophilic cyanobacteria inhabiting hot spring microbial mats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2398–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.C.; Li, J.Y.; Liu, J.L.; Yuan, C.X.; Li, Y.N.; Liu, B.R.; Yan, X.F. Temporal shifts in cyanobacterial diversity and their relationships to different types of biological soil crust in the southeastern Tengger Desert. Rhizosphere 2021, 17, 100322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchhardt, N.; Schiefelbein, U.; Abarca, N.; Boy, J.; Mikhailyuk, T.; Sipman, H.J.; Karsten, U. Diversity of algae and lichens in biological soil crusts of Ardley and King George islands, Antarctica. Antarct. Sci. 2017, 29, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Lima, N.M.M.; Muñoz-Rojas, M.; Vázquez-Campos, X.; Branco, L.H.Z. Biocrust cyanobacterial composition, diversity, and environmental drivers in two contrasting climatic regions in Brazil. Geoderma 2021, 386, 114914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Y.; Li, Q.H.; Chen, Q.; He, Y.; Yuan, Z.H.; Li, H.M.; Zhang, H.J. Variation characteristics and influencing factors of the structure of a phytoplankton community after an ecological regulation in Huaxi reservoir, Guizhou province. Res. Environ. Sci. 2020, 33, 589–598. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Li, K.; Chen, L.J.; Shen, X.Q.; Shi, W.; Guan, W.B. Phytoplankton community structure of rice-crab culture of integrated system in Ningxia. J. Shanghai Ocean Univ. 2022, 31, 411–420. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.S.; Kumar, A.; Rai, A.N.; Singh, D.P. Cyanobacteria: A precious bio-resource in agriculture, ecosystem, and environmental sustainability. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Pei, G.; Song, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, W. Discovery and application of stress-responsive sRNAs in cyanobacteria. In Synthetic Biology of Cyanobacteria; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 55–74. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.Y.; Teng, W.K.; Zhao, L.; Han, B.P.; Song, L.R.; Shu, W.S. Phylogenomics uncovers evolutionary trajectory of nitrogen fixation in Cyanobacteria. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2022, 39, msac171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbert, W.; Weber, B.; Burrows, S.; Steinkamp, J.; Büdel, B.; Andreae, M.O.; Pöschl, U. Contribution of cryptogamic covers to the global cycles of carbon and nitrogen. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yandigeri, M.S.; Yadav, A.K.; Srinivasan, R.; Kashyap, S.; Pabbi, S. Studies on mineral phosphate solubilization by cyanobacteria Westiellopsis and Anabaena. Microbiology 2011, 80, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijffels, R.H.; Kruse, O.; Hellingwerf, K.J. Potential of industrial biotechnology with cyanobacteria and eukaryotic microalgae. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayan, D.; Ray, J.G. Ecology and diversity of diatoms in Kuttanadu paddy fields in relation to soil regions, seasons and paddy-growth-stages. J. Plant Stud. 2016, 5, 2924–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurung, S.; Prasad, B. Azolla and Cyanobacteria (BGA): Potensial biofertilizer for rice. Sci. World 2005, 3, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhury, A.; Kennedy, I.R. Prospects and potentials for systems of biological nitrogen fixation in sustainable rice production. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2004, 39, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.S. Current Developments in Biological Nitrogen Fixation; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Li, H.; Xiao, J.; Sun, J.; Liu, R.; Zhang, A. Soil multifunctionality of paddy field is explained by soil pH rather than microbial diversity after 8-years of repeated applications of biochar and nitrogen fertilizer. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 853, 158620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Li, L.; Chen, S.; Shi, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhang, Q. Ecosystems; Environment, Straw returning on sloping farmland reduces the soil and water loss via surface flow but increases the nitrogen loss via interflow. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 339, 108154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Ma, K.; Wang, X.L.; Qi, L.; Liu, Y.H.; Song, P.; Liu, W.; Zhang, M.M.; Zhao, W.; Song, C.W. Increasing Italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum Lam.) regrowth via inoculation with an ammonia-oxidizing bacterial strain. Grassl. Sci. 2022, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Xue, Y.; Yu, X.; Li, C.; Hou, Y.; Zhu, H.; Jiang, L.; Zheng, W.; Feng, Z.; Li, Y. The Structure and Function of Microbial Community in RhizospHeric Soil of American Ginseng (Panax quinquefolius L.) Changed with Planting Years. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemonnier, H.; Courties, C.; Mugnier, C.; Torréton, J.-P.; Herbland, A. Nutrient and microbial dynamics in eutrophying shrimp ponds affected or unaffected by vibriosis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Zhuang, J.; Wang, J.; Fan, G.; Feng, M.; Zhang, S. Soil bacterial communities of three types of plants from ecological restoration areas and plant-growth promotional benefits of Microbacterium invictum (strain X-18). Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 926037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, H.; Madushan, N.; Rathnayake, W.; Sirisena, D.; Wijesooriya, B.; Ariyaratne, M.; Gamage, G.; Chandrajith, R.; Suriyagoda, L.; Samarasinghe, D. Comparison of extraction and detection methods of exchangeable Potassium in paddy soils in Sri Lanka. Int. Symp. Agric. Environ. 2021, 116, 92. [Google Scholar]
- Whitton, B. Cyanoprokaryota 1. Teil Chroococcales; Taylor & Francis: Milton Park, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J. Cyanoprokaryota 2. Teil/2nd Part: Oscillatoriales; Susswasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Elsevier GmbH: München, Germany, 2005; Volume 19, pp. 1–759. [Google Scholar]
- Nübel, U.; Garcia-Pichel, F.; Muyzer, G. PCR primers to amplify 16S rRNA genes from cyanobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 3327–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, K.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, W.; Liu, W.; Xu, M.; Yin, H.; Wang, A.; He, Z.; Deng, Y. Biodiversity and species competition regulate the resilience of microbial biofilm community. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 6170–6182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Keitel, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wangeci, A.N.; Dijkstra, F.A. Ecosystems; Environment, Global meta-analysis of nitrogen fertilizer use efficiency in rice, wheat and maize. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 338, 108089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jutono, D.K.K. Blue green algae in rice soils of Jogiakarta, Central Java. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1973, 5, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.S.; Chou, T.L.; Wu, J.T. Biodiversity of soil algae in the farmlands of mid-Taiwan. Bot. Stud. 2013, 54, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roger, P.A.; Kulasooriya, S. Blue-Green Algae and Rice; International Rice Research Institute: Los Baños, Philippines, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Tirol, A.C.; Roger, P.A.; Watanabe, I.; Nutrition, P. Fate of nitrogen from a blue-green alga in a flooded rice soil. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1982, 28, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.S.; Wu, J.T. Environmental factors affecting the diversity and abundance of soil photomicrobes in arid lands of subtropical Taiwan. Geomicrobiol. J. 2014, 31, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, S.N.R. Soil pH and its role in cyanobacterial abundance and diversity in rice field soils. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2007, 5, 103–113. [Google Scholar]
- Pietrasiak, N.; Regus, J.U.; Johansen, J.R.; Lam, D.; Sachs, J.L.; Santiago, L.S. Biochemistry, Biological soil crust community types differ in key ecological functions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 65, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandes, V.M.C.; Machado, D.L.N.M.; Roush, D.; Rudgers, J.; Collins, S.J.; Garcia-Pichel, F. Exposure to predicted precipitation patterns decreases population size and alters community structure of cyanobacteria in biological soil crusts from the Chihuahuan Desert. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saw, J.H.; Schatz, M.; Brown, M.V.; Kunkel, D.D.; Foster, J.S.; Shick, H.; Christensen, S.; Hou, S.; Wan, X.; Donachie, S.P. Cultivation and complete genome sequencing of Gloeobacter kilaueensis sp. nov., from a lava cave in Kīlauea Caldera, Hawai’i. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecht, J.S.; Zia, A.; Clemins, P.J.; Schroth, A.W.; Winter, J.M.; Oikonomou, P.D.; Rizzo, D.M. Modeling the sensitivity of cyanobacteria blooms to plausible changes in precipitation and air temperature variability. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 151586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megharaj, M.; Kookana, K.; Singleton, S. Activities of fenamiphos on native algal population and some enzyme activities in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1999, 39, 1549–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, R.; Jaiswal, P.; Nayak, S.; Sood, A.; Kaushik, B.D. Cyanobacterial diversity in the rhizosphere of rice and its ecological significance. Indian J. Microbiol. 2009, 49, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, X.; Guan, D.; Wei, D.; Zhao, B.; Ma, M.; Chen, S.; Li, L.; Cao, F.; Li, J. Long-term fertilization changes bacterial diversity and bacterial communities in the maize rhizosphere of Chinese Mollisols. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 125, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Sun, X.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, J.; Pan, G.J.E. Change in active microbial community structure, abundance and carbon cycling in an acid rice paddy soil with the addition of biochar. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2016, 67, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
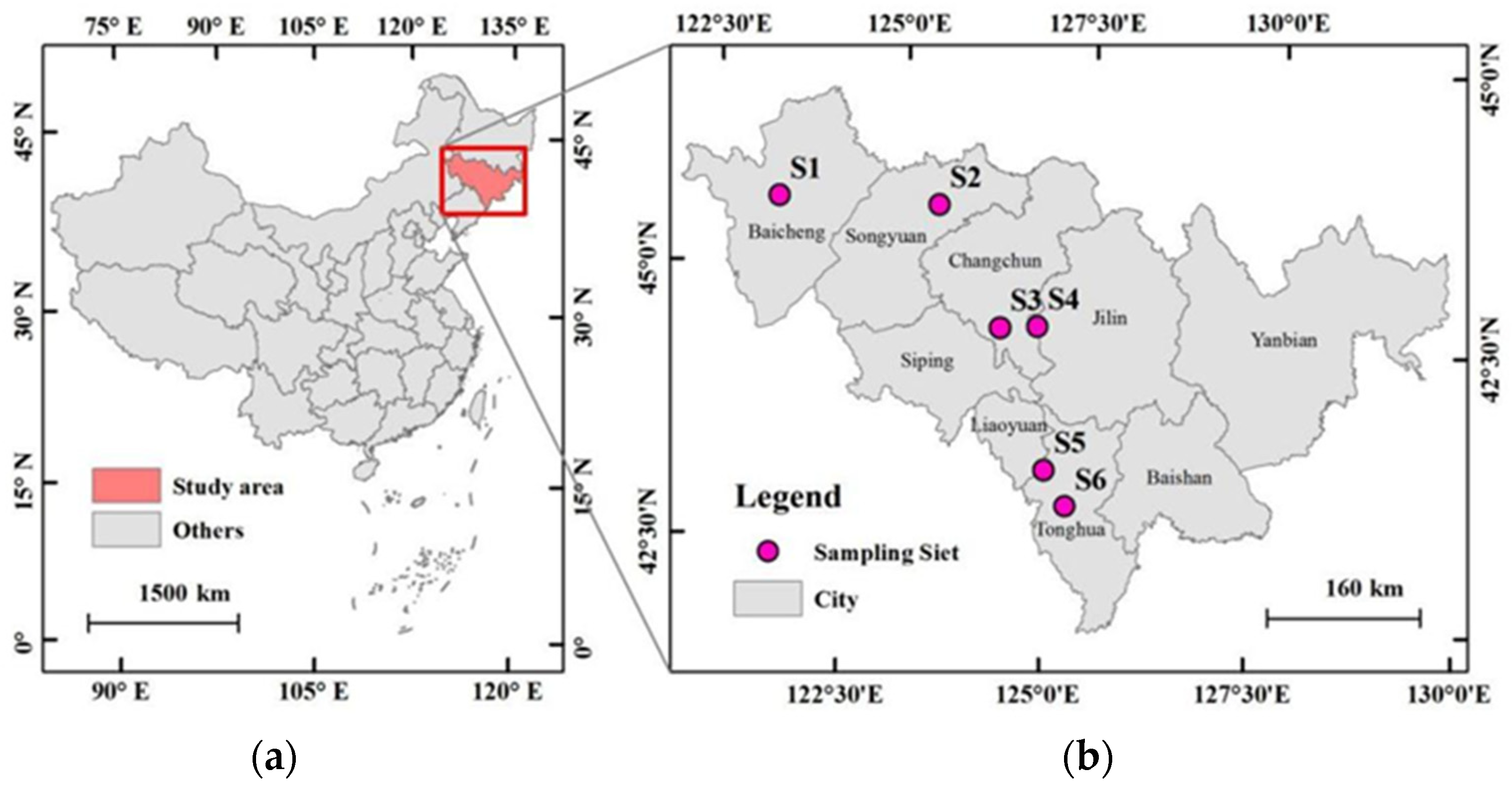



| Sample Sites | GPS Coordinates | Ecoregion | Average Precipitation (mm) | Average Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 45°40′ N, 122°88′ E | Arid plains | 200.7 d | 12.5 a |
| S2 | 45°03′ N, 124°96′ E | Arid plains | 106.1 f | 12.2 b |
| S3 | 43°80′ N, 125°41′ E | Humid plains | 199.5 e | 12.1 b |
| S4 | 43°74′ N, 125°89′ E | Hilly and semi-mountainous | 287.5 b | 11.6 c |
| S5 | 42°42′ N, 125°59′ E | Hilly and semi-mountainous | 301.6 a | 11.3 d |
| S6 | 42°05′ N, 125°75′ E | Hilly and semi-mountainous | 236.4 c | 11.1 e |
| Sample Sites | SOC (g·kg−1) | TN (g·kg−1) | AN (mg·kg−1) | AP (mg·kg−1) | AK (mg·kg−1) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 15.19 ± 0.06 a | 2.16 ± 0.03 d | 17.89 ± 0.00 e | 25.01 ± 1.03 a | 202.50 ± 1.70 c | 8.01 ± 0.04 a |
| S2 | 10.80 ± 0.56 d | 2.63 ± 0.04 c | 22.68 ± 0.32 d | 13.88 ± 0.25 c | 233.20 ± 1.10 b | 7.35 ± 0.01 c |
| S3 | 5.31 ± 1.04 e | 1.96 ± 0.01 e | 44.01 ± 0.04 b | 14.43 ± 0.13 c | 201.10 ± 1.10 c | 6.65 ± 0.03 d |
| S4 | 12.02 ± 0.12 c | 2.63 ± 0.06 c | 24.78 ± 1.35 d | 13.74 ± 0.00 c | 183.80 ± 3.40 d | 6.49 ± 0.03 e |
| S5 | 15.07 ± 0.23 a | 3.32 ± 0.06 a | 139.65 ± 1.71 a | 22.84 ± 0.27 a | 306.50 ± 1.70 a | 7.41+0.01 b |
| S6 | 13.60 ± 0.42 b | 2.81 ± 0.03 b | 34.52 ± 2.96 c | 17.83+2.29 b | 206.50 ± 1.70 c | 6.05 ± 0.03 f |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, J.; He, X.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Wu, L.; Li, S.; Wang, D.; Yang, M.; Wu, Z. Community Composition Specificities of Cyanobacteria in Paddy Soil under Different Ecological Conditions. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3090. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123090
Song J, He X, Wang S, Yang X, Wu L, Li S, Wang D, Yang M, Wu Z. Community Composition Specificities of Cyanobacteria in Paddy Soil under Different Ecological Conditions. Agronomy. 2022; 12(12):3090. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123090
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Jian, Xu He, Shuwen Wang, Xue Yang, Lei Wu, Siyuan Li, Dongchao Wang, Meiying Yang, and Zhihai Wu. 2022. "Community Composition Specificities of Cyanobacteria in Paddy Soil under Different Ecological Conditions" Agronomy 12, no. 12: 3090. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123090
APA StyleSong, J., He, X., Wang, S., Yang, X., Wu, L., Li, S., Wang, D., Yang, M., & Wu, Z. (2022). Community Composition Specificities of Cyanobacteria in Paddy Soil under Different Ecological Conditions. Agronomy, 12(12), 3090. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123090









