Phosphorus Sorption following the Application of Charcoal and Sago (Metroxylon sagu) Bark Ash to Acid Soils
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Sampling and Preparation
2.2. Soil, Charcoal, and Sago Bark Ash Characterization
2.3. Phosphorus Adsorption and Desorption Determination
- S: Soil only;
- C: Charcoal only;
- A: Sago bark ash only;
- SC: 300 g soil + 15.42 g charcoal;
- SA: 300 g soil + 7.71 g sago bark ash;
- SCA: 300 g soil + 15.42 g charcoal + 7.71 g sago bark ash.
- qe = P adsorption at equilibrium (mg g−1);
- Co = Initial concentration of P (mg L−1);
- Ce = P concentration at adsorption equilibrium (mg L−1);
- V = Volume of P solution used (L);
- m = Mass of sample (g).
- qe = P adsorption at equilibrium (mg g−1);
- qmax = Maximum adsorption capacity (mg g−1);
- KL = Langmuir constant related to the binding energy (L mg−1);
- Ce = P concentration at adsorption equilibrium (mg L−1).
- qde = P desorption at equilibrium (mg g−1);
- Cdo = P concentration on sample (mg L−1); Cdo = Co − Ce;
- Cde = P concentration at desorption equilibrium (mg L−1);
- V = Volume of 0.01 M CaCl2 solution used (L);
- m = Vass of sample (g).
2.4. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phosphorus Concentration at Adsorption Equilibrium
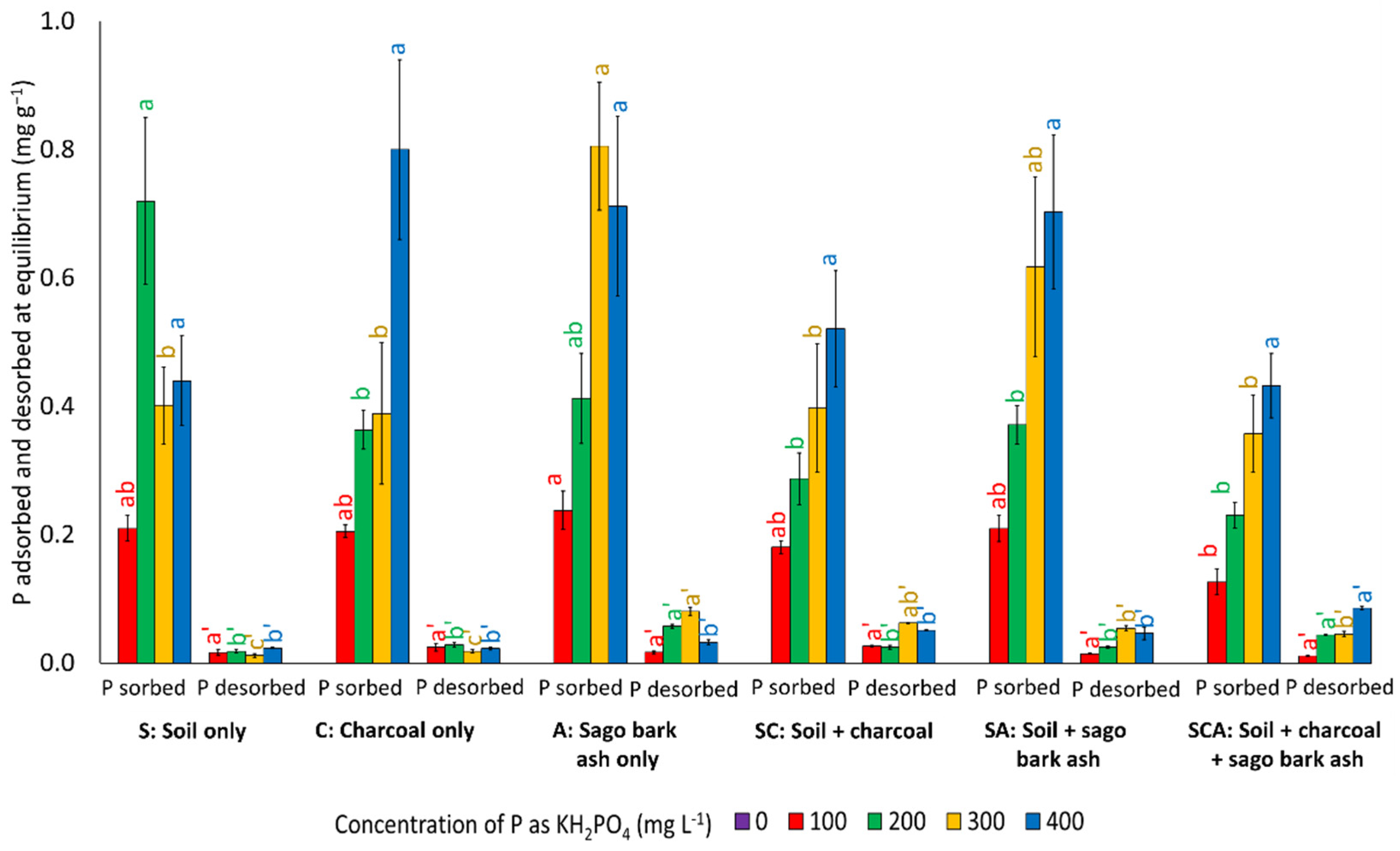
3.2. Phosphorus Adsorption
3.3. Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm
3.4. Phosphorus Concentration at Desorption Equilibrium
3.5. Phosphorus Desorption
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sims, J.T.; Pierzynski, G.M. Chemistry of phosphorus in soils. Chem. Process. Soils 2005, 8, 151–192. [Google Scholar]
- Barrow, N.J. Soil phosphate chemistry and the P-sparing effect of previous phosphate applications. Plant Soil 2015, 397, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantino, L.V.; Quirino, J.N.; Monteiro, A.M.; Abrão, T.; Parreira, P.S.; Urbano, A.; Santos, M.J. Sorption-desorption of selenite and selenate on Mg-Al layered double hydroxide in competition with nitrate, sulfate and phosphate. Chemosphere 2017, 181, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumina, L.; Kenney, J.P.; Loring, J.S.; Persson, P. Desorption mechanisms of phosphate from ferrihydrite and goethite surfaces. Chem. Geol. 2016, 427, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, R.S.; Melo, L.C.A.; Vergütz, L.; Rodríguez-Vila, A.; Covelo, E.F.; Fernandes, A.R. Adsorption and desorption kinetics and phosphorus hysteresis in highly weathered soil by stirred flow chamber experiments. Soil Till. Res. 2016, 162, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanyabui, E.; Apori, S.O.; Frimpong, K.A.; Atiah, K.; Abindaw, T.; Ali, M.; Asiamah, J.Y.; Byalebeka, J. Phosphorus sorption in tropical soils. AIMS Agric. Food 2020, 5, 599–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, O.A.; Ahmed, H.S. Phosphorus sorption capacity as a guide for phosphorus availability of selected Sudanese soil series. Afr. Crop Sci. J. 2012, 20, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Tsado, P.A.; Osunde, O.A.; Igwe, C.A.; Adeboye, M.K.A.; Lawal, B.A. Phosphorus sorption characteristics of some selected soil of the Nigerian Guinea Savanna. Int. J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 2, 613–618. [Google Scholar]
- Tening, A.S.; Foba-Tendo, J.N.; Yakum-Ntaw, S.Y.; Tchuenteu, F. Phosphorus fixing capacity of a volcanic soil on the slope of mount Cameroon. Agric. Biol. J. N. Am. 2013, 4, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maluf, H.J.G.M.; Silva, C.A.; Curi, N.; Norton, L.D.; Rosa, S.D. Adsorption and availability of phosphorus in response to humic acid rates in soils limed with CaCO3 or MgCO3. Ciência E Agrotecnologia 2018, 42, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limousin, G.; Gaudet, J.P.; Charlet, L.; Szenknect, S.; Barthes, V.; Krimissa, M. Sorption isotherms: A review on physical bases, modeling and measurement. Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 249–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamungang, N.E.B.; Mvondo-Zé, A.D.; Ghogomu, J.N.; Mofor, N.A. Evaluation of phosphorus sorption characteristics of soils from the Bambouto sequence (West Cameroon). Int. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 10, 860–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, A.; Muhammad, D.; Jamal, H. Application of adsorption isotherms in evaluating the influence of humic acid and farmyard manure on phosphorous adsorption and desorption capacity of calcareous soil. World Sci. News 2018, 107, 136–149. [Google Scholar]
- Palanivell, P.; Ahmed, O.H.; Omar, L.; Abdul Majid, N.M. Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium Adsorption and Desorption Improvement and Soil Buffering Capacity Using Clinoptilolite Zeolite. Agronomy 2021, 11, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ch’ng, H.Y. Phosphorus Management for Tropical Acid Soils Using Amendments from Agro-Industrial Wastes. Doctoral Thesis, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hasbullah, N.A. Use of Clinoptilolite Zeolite to Improve Efficiency of Phosphorus Use in Acid Soils. Doctoral Thesis, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gichangi, E.M. Effects of organic amendments on the transformations and bioavailability of phosphorus in soils: A review. Discov. Agric. 2019, 5, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Maru, A.; Haruna, A.O.; Asap, A.; Majid, N.M.A.; Maikol, N.; Jeffary, A.V. Reducing Acidity of Tropical Acid Soil to Improve Phosphorus Availability and Zea mays L. Productivity through Efficient Use of Chicken Litter Biochar and Triple Superphosphate. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ch’ng, H.Y.; Haruna, A.O.; Majid, N.M.N.A.; Jalloh, M.B. Improving soil phosphorus availability and yield of Zea mays L. using biochar and compost derived from agro-industrial wastes. Ital. J. Agron. 2019, 14, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palanivell, P.; Ahmed, O.H.; Latifah, O.; Abdul Majid, N.M. Adsorption and desorption of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and soil buffering capacity following application of chicken litter biochar to an acid soil. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dixon, R.K.; Wisniewski, J. Global Forest systems: An uncertain response to atmospheric pollutants and global climate change. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1995, 85, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyoucos, G.J. Hydrometer method improved for making particle size analysis of soils. Agron. J. 1962, 54, 464–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peech, H.M. Hydrogen-ion Activity. In Methods of Soil Analysis Chemical and Microbiological Properties; Black, C.A., Evans, D.D., White, J.L., Ensminger, L.E., Clark, F.E., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1965; pp. 914–926. [Google Scholar]
- Chefetz, B.; Hatcher, P.H.; Hadar, Y.; Chen, Y. Chemical and biological characterization of organic matter during composting of municipal solid waste. J. Environ. Qual. 1996, 25, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.M. Total Nitrogen. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2; Black, C.A., Evans, D.D., Ensminger, L.E., White, J.L., Clark, F.F., Dinauer, R.C., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1965; pp. 1149–1178. [Google Scholar]
- Cottenie, A. Soil testing and plant testing as a basis of fertilizer recommendation. FAO Soils Bull. 1980, 38, 70–73. [Google Scholar]
- Rowell, D.L. Soil Science: Methods and Application; Longman Publishers Ltd.: London, UK, 1994; p. 169. [Google Scholar]
- Bernas, B. New method for decomposition and comprehensive analysis of silicates by atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 1968, 40, 1682–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehlich, A. Determination of P, Ca, Mg, K, Na and NH4. Short Test Methods Used in Soil Testing Division; Department of Agriculture: Raleigh, NC, USA, 1953.
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramananthan, S. Soil of Malaysia: Their Characteristics and Identification; Academy of Sciences Malaysia: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2000; Volume 1, pp. 11–125.
- Free, H.F.; McGill, C.R.; Rowarth, J.S.; Hedley, M.J. The effect of biochars on maize (Zea mays) germination. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 2010, 53, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndor, E.; Dauda, S.N.; Azagaku, E.D. Response of maize varieties (Zea mays) to biochar amended soil in Lafia, Nigeria. J. Exp. Agric. Int. 2015, 5, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandre, M.; Parn, H.; Ots, K. Short-term effects of wood ash on the soil and the lignin concentration and growth of Pinus sylvestris L. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 223, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozolincius, R.; Buozyte, R.; Varnagiryte, K.I. Wood ash and nitrogen influence on ground vegetation cover and chemical composition. Biomass Bioenergy 2007, 31, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perucci, P.; Monaci, E.; Onofri, A.; Vischetti, C.; Casucci, C. Changes in physico-chemical and biochemical parameters of soil following addition of wood ash: A field experiment. Eur. J. Agron. 2008, 28, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graetz, D.A.; Nair, V.D. Phosphorus sorption isotherm determination. In Methods of Phosphorus Analysis for Soils, Sediments, Residuals, and Waters; Southern Cooperative Series Bulletin 408; Kovar, J.L., Pierzynski, G.M., Eds.; Virginia Tech University: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2009; pp. 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Mozaffari, M.; Sims, J.T. Phosphorus availability and sorption in Atlantic Coastal Plain watershed dominated by animal-based agriculture. Soil Sci. 1994, 157, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallade, Y.E.; Sims, J.T. Phosphorus transformations in the sediments of Delaware’s agricultural drainageways: I. Phosphorus forms and sorption. J. Environ. Qual. 1997, 26, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.D.; Graetz, D.A.; Reddy, K.R. Dairy manure influences on phosphorus retention capacity of Spodosols. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R.; O’Connor, G.A.; Gale, P.M. Phosphorus sorption capacities of wetland soils and stream sediments impacted by dairy effluent. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, E.H.; Ketterings, Q.M.; Kleinman, P.J. Measuring and predicting the phosphorus sorption capacity of manure-amended soils. Soil Sci. 2007, 172, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kithome, M.; Paul, J.W.; Lavkulich, L.M.; Bomke, A.A. Kinetics of ammonium adsorption and desorption by the natural zeolite clinoptilolite. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1998, 62, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Jiang, A.; Wang, H. Adsorption and Desorption Characteristics of Phosphorus on Sediments in Panzhihua Section of Jinsha River, China. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; p. 042059. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, T.; Karns, C.L.; Shimizu, K.D. A critical examination of the use of the Freundlich isotherm in characterizing molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPS). Anal. Chim. Acta. 2005, 528, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Okeola, F.O.; Odebunmi, E.O. Comparison of Freundlich and Langmuir isotherms for adsorption of methylene blue by agrowaste derived activated carbon. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2010, 4, 329–336. [Google Scholar]
- Dada, A.O.; Ojediran, J.O.; Olalekan, A.P. Sorption of Pb2+ from aqueous solution unto modified rice husk: Isotherms studies. Adv. Phys. Chem. 2013, 2013, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liang, T. Effects of exogenous rare earth elements on phosphorus adsorption and desorption in different types of soils. Chemosphere 2014, 103, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.S.; Richards, B.K.; Medrano, P.A.; DeGroot, M.; Steenhuis, T.S. Dissolved phosphorus from undisturbed soil cores: Related to adsorption strength, flow rate, or soil structure? Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.F.; Kennedy, I.R.; Choudhury, A.T.M.A.; Kecskés, M.L.; Deaker, R. Phosphorus adsorption in some Australian soils and influence of bacteria on the desorption of phosphorus. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2008, 39, 1269–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, R.; Syers, J.K.; Tillman, R.W.; Kirkman, J.H. Effect of liming and added phosphate on charge characteristics of acid soils. J. Soil Sci. 1990, 41, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyango, M.S.; Masukume, M.; Ochieng, A.; Otieno, F. Functionalized natural zeolite and its potential for treating drinking water containing excess amount of nitrate. Water SA 2010, 36, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shariatmadari, H.; Shirvani, M.; Jafari, A. Phosphorus release kinetics and availability in calcareous soils of selected arid and semiarid toposequence. Geoderma 2006, 132, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, J.F.; Ohno, T.; He, Z.; Honeycutt, C.W.; Dail, D.B. Inhibition of phosphorus sorption to goethite, gibbsite, and kaolin by fresh and decomposed organic matter. Biol. Fert. Soil 2007, 44, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Xu, R. Effects of regulation of pH and application of organic material adsorption and desorption of phosphorus in three types of acid soils. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2010, 26, 596–599. [Google Scholar]
- Haynes, R.J. Lime and phosphate in the soil-plant system. Adv. Agron. 1984, 37, 249–315. [Google Scholar]
- Sanyal, S.K.; De Datta, S.K. Chemistry of phosphorus transformations in soil. In Advances in Soil Science; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 1–120. [Google Scholar]
- Haynes, R.J.; Swift, R.S. Effects of air-drying on the adsorption and desorption of phosphate and levels of extractable phosphate in a group of acid soils, New Zealand. Geoderma 1985, 35, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, R.J.; Naidu, R. Effects of lime additions on the availability of phosphorus and sulphur in some temperate and tropical acid soils. In Plant-Soil Interactions at Low pH; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 267–274. [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar, B.; Kumar, K.; Venkatesh, M.S. Effect of liming on phosphorus adsorption and desorption behaviour of acidic Alfisols and Entisol of Meghalaya. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci. 2005, 53, 188–193. [Google Scholar]
- Paliyal, S.S.; Verma, T.S. Adsorption of added phosphorus as influenced by the application of lime and gypsum in an acid Alfisol of Himalayan region. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci. 2002, 50, 163–167. [Google Scholar]
- Hiradate, S.; Uchida, N. Effects of soil organic matter on pH-dependent phosphate sorption by soils. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2004, 50, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.; Wei, Z. Organic amendments affect phosphorus sorption characteristics in a paddy soil. Agric. Ecosyst. and Environ. 2013, 175, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, X. Effect of organic matter on phosphorus adsorption and desorption in a black soil from Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 187, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanivell, P. Organic and Mineral Amendments on Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Yield and Nutrients Recovery Efficiency. Doctoral Thesis, Universiti Putra Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur, Selangor, Malaysia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Amarh, F. Phosphorus Adsorption Isotherms of Some Selected Soils from the Eastern Region of Ghana. Doctoral Thesis, Kwame Nkrumah University, Kabwe, Zambia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Azeez, J.O.; Averbeke, W.V. Effect of manure types and period of incubation on phosphorus-sorption indices of a weathered tropical soil. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2011, 42, 2200–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Comerford, N.B. Influence of soil pH on inorganic phosphorus sorption and desorption in a humid Brazilian Ultisol. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2005, 29, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartono, A.; Funakawa, S.; Kosaki, T. Phosphorus Sorption-Desorption Characteristics of Selected Acid Upland Soils in Indonesia. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2005, 51, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johan, P.D.; Ahmed, O.H.; Omar, L.; Hasbullah, N.A. Charcoal and Sago Bark Ash on pH Buffering Capacity and Phosphorus Leaching. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.; Lotse, E.G. Kinetics of phosphate adsorption and desorption by hematite and gibbsite. Soil Sci. 1973, 116, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, N.J. On the reversibility of phosphate sorption by soils. J. Soil Sci. 1983, 34, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
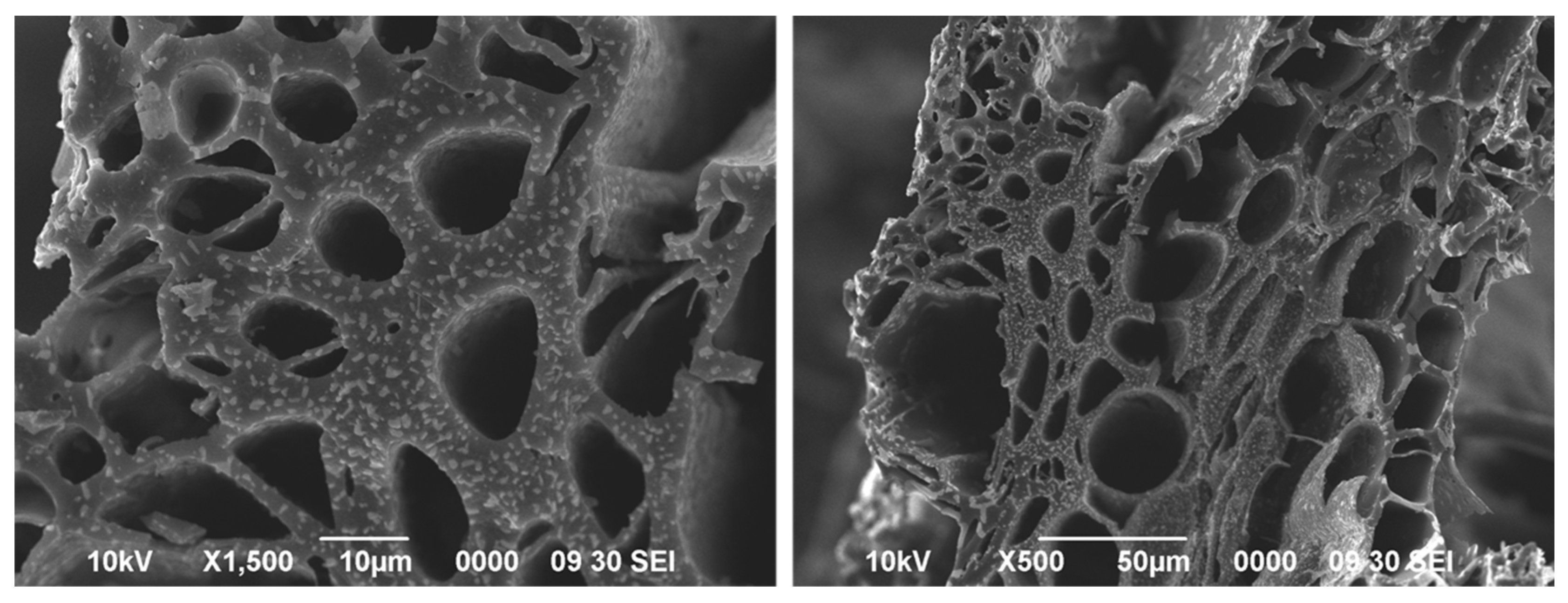

| Property | Value Obtained | Paramananthan [31] | Charcoal | Sago Bark Ash | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH (H2O) | 4.61 ± 0.05 | 4.6–4.9 | 7.74 ± 0.02 | 9.99 ± 0.03 | |
| pH (KCl) | 3.95 ± 0.01 | 3.8–4.0 | 7.31 ± 0.05 | 9.66 ± 0.02 | |
| EC (dS m−1) | 0.04 ± 0.00 | NA | 0.270 ± 0.006 | 5.75 ± 0.02 | |
| Bulk density (g cm−1) | 1.25 ± 0.04 | NA | NA | NA | |
| Total carbon (%) | 2.16 ± 0.05 | 0.57–2.51 | NA | NA | |
| Total N (%) | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.04–0.17 | NA | NA | |
| Total P (mg kg−1) | 23.65 ± 1.09 | NA | NA | NA | |
| Available P (mg kg−1) | 1.13 ± 0.02 | NA | 31.25 ± 1.15 | 55.83 ± 1.32 | |
| CEC | cmol kg−1 | 4.67 ± 0.29 | 3.86–8.46 | NA | NA |
| Exchangeable acidity | 1.15 ± 0.03 | NA | NA | NA | |
| Exchangeable Al3+ | 1.02 ± 0.03 | NA | NA | NA | |
| Exchangeable H+ | 0.13 ± 0.02 | NA | NA | NA | |
| Exchangeable K+ | 0.060 ± 0.002 | 0.05–0.19 | 3.67 ± 0.06 | 23.33 ± 0.25 | |
| Exchangeable Ca2+ | 0.020 ± 0.001 | 0.01 | 11.71 ± 0.32 | 16.77 ± 0.48 | |
| Exchangeable Mg2+ | 0.220 ± 0.003 | 0.07–0.21 | 3.37 ± 0.03 | 3.57 ± 0.03 | |
| Exchangeable Na+ | 0.030 ± 0.001 | 0.01 | 0.43 ± 0.01 | 1.51 ± 0.03 | |
| Exchangeable Mn2+ | 0.010 ± 0.001 | NA | NA | NA | |
| Exchangeable Fe2+ | 1.09 ± 0.02 | NA | 0.150 ± 0.003 | 0.030 ± 0.001 | |
| Soil texture | Sand (%): 71.9 | Sand (%): 72–76 | NA | NA | |
| Silt (%): 13.5 | Silt (%): 8–9 | ||||
| Clay (%): 14.6 | Clay (%): 16–19 | ||||
| Sandy loam | Sandy clay loam |
| Treatment | Phosphorus Concentration at Adsorption Equilibrium, Ce (mg L−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | |
| Added P (mg P L−1) | |||||
| S | nd | 83.48 ab ± 1.41 | 143.45 b ± 10.06 | 267.88 a ± 5.00 | 365.21 a ± 5.77 |
| C | nd | 83.56 ab ± 1.01 | 170.92 a ± 2.12 | 268.88 a ± 8.62 | 335.96 a ± 10.96 |
| A | nd | 80.96 b ± 2.03 | 166.98 ab ± 5.50 | 235.55 b ± 7.91 | 343.02 a ± 11.60 |
| SC | nd | 85.51 ab ± 0.56 | 177.00 a ± 3.36 | 268.21 a ± 6.95 | 358.29 a ± 7.44 |
| SA | nd | 83.21 ab ± 1.96 | 170.29 a ± 2.38 | 250.58 ab ± 11.26 | 343.75 a ± 9.63 |
| SCA | nd | 89.88 a ± 1.77 | 181.58 a ± 1.46 | 271.42 a ± 4.50 | 365.42 a ± 4.08 |
| Treatment | Phosphorus Adsorption at Equilibrium, qe (mg g−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | |
| Added P (mg P L−1) | ||||
| S | 0.21 ab ± 0.02 | 0.72 a ± 0.13 | 0.40 b ± 0.06 | 0.44 a ± 0.07 |
| C | 0.21 ab ± 0.01 | 0.36 b ± 0.03 | 0.39 b ± 0.11 | 0.80 a ± 0.14 |
| A | 0.24 a ± 0.03 | 0.41 ab ± 0.07 | 0.81 a ± 0.10 | 0.71 a ± 0.14 |
| SC | 0.18 ab ± 0.01 | 0.29 b ± 0.04 | 0.40 b ± 0.10 | 0.52 a ± 0.09 |
| SA | 0.21 ab ± 0.02 | 0.37 b ± 0.03 | 0.62 ab ± 0.14 | 0.70 a ± 0.12 |
| SCA | 0.13 b ± 0.02 | 0.23 b ± 0.02 | 0.36 b ± 0.06 | 0.43 a ± 0.05 |
| Treatment | Estimated by Langmuir Equation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regression Equation | R2 | qmax (mg g−1) | KL (L mg−1) | MBC (L mg−1) | |
| S | y = 2.28x + 93.26 | 0.72 | 0.44 | 0.02 | 8.80 × 10−3 |
| C | y = 0.39x + 414.06 | 0.10 | 2.56 | 9.42 × 10−4 | 2.41 × 10−3 |
| A | y = 0.42x + 293.49 | 0.32 | 2.38 | 1.43 × 10−3 | 3.40 × 10−3 |
| SC | y = 0.78x + 440.17 | 0.85 | 1.28 | 1.77 × 10−3 | 2.27 × 10−3 |
| SA | y = 0.27x + 380.68 | 0.46 | 3.70 | 7.09 × 10−4 | 2.62 × 10−3 |
| SCA | y = 0.41x + 682.31 | 0.75 | 2.44 | 6.01 × 10−4 | 1.47 × 10−3 |
| Treatment | Phosphorus Concentration at Desorption Equilibrium, Cde (mg L−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | |
| Added P (mg P L−1) | |||||
| S | nd | 15.22 ab ± 1.04 | 55.08 a ± 9.91 | 31.16 a ± 4.80 | 32.91 a ± 5.73 |
| C | nd | 14.43 ab ± 1.13 | 26.80 b ± 2.19 | 29.64 a ± 8.68 | 62.23 a ± 11.06 |
| A | nd | 17.68 a ± 1.91 | 28.39 b ± 5.26 | 57.99 a ± 8.32 | 54.37 a ± 11.89 |
| SC | nd | 12.34 ab ± 0.50 | 21.03 b ± 3.23 | 26.75 a ± 6.95 | 37.63 a ± 7.38 |
| SA | nd | 15.63 ab ± 1.96 | 27.69 b ± 2.37 | 45.05 a ± 10.96 | 52.52 a ± 8.81 |
| SCA | nd | 9.20 b ± 1.71 | 14.87 b ± 1.20 | 24.95 a ± 4.18 | 27.71 a ± 4.06 |
| Treatment | Phosphorus Desorption at Equilibrium, qde (mg g−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | |
| Added P (mg P L−1) | ||||
| S | 0.016 a ± 0.005 | 0.018 b ± 0.003 | 0.012 c ± 0.003 | 0.024 b ± 0.001 |
| C | 0.025 a ± 0.006 | 0.029 b ± 0.004 | 0.019 c ± 0.003 | 0.023 b ± 0.002 |
| A | 0.017 a ± 0.002 | 0.058 a ± 0.003 | 0.081 a ± 0.007 | 0.033 b ± 0.004 |
| SC | 0.027 a ± 0.001 | 0.025 b ± 0.003 | 0.063 ab ± 0.001 | 0.051 b ± 0.001 |
| SA | 0.015 a ± 0.001 | 0.025 b ± 0.001 | 0.055 b ± 0.004 | 0.047 b ± 0.010 |
| SCA | 0.012 a ± 0.001 | 0.044 a ± 0.001 | 0.045 b ± 0.004 | 0.086 a ± 0.002 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Johan, P.D.; Ahmed, O.H.; Hasbullah, N.A.; Omar, L.; Paramisparam, P.; Hamidi, N.H.; Jalloh, M.B.; Musah, A.A. Phosphorus Sorption following the Application of Charcoal and Sago (Metroxylon sagu) Bark Ash to Acid Soils. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3020. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123020
Johan PD, Ahmed OH, Hasbullah NA, Omar L, Paramisparam P, Hamidi NH, Jalloh MB, Musah AA. Phosphorus Sorption following the Application of Charcoal and Sago (Metroxylon sagu) Bark Ash to Acid Soils. Agronomy. 2022; 12(12):3020. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123020
Chicago/Turabian StyleJohan, Prisca Divra, Osumanu Haruna Ahmed, Nur Aainaa Hasbullah, Latifah Omar, Puvan Paramisparam, Nur Hidayah Hamidi, Mohamadu Boyie Jalloh, and Adiza Alhassan Musah. 2022. "Phosphorus Sorption following the Application of Charcoal and Sago (Metroxylon sagu) Bark Ash to Acid Soils" Agronomy 12, no. 12: 3020. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123020
APA StyleJohan, P. D., Ahmed, O. H., Hasbullah, N. A., Omar, L., Paramisparam, P., Hamidi, N. H., Jalloh, M. B., & Musah, A. A. (2022). Phosphorus Sorption following the Application of Charcoal and Sago (Metroxylon sagu) Bark Ash to Acid Soils. Agronomy, 12(12), 3020. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123020








