Molecular Characterization of Diverse Wheat Genetic Resources for Resistance to Yellow Rust Pathogen (Puccinia striiformis)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Germplasm Source, Matting Design and Sowing Layout
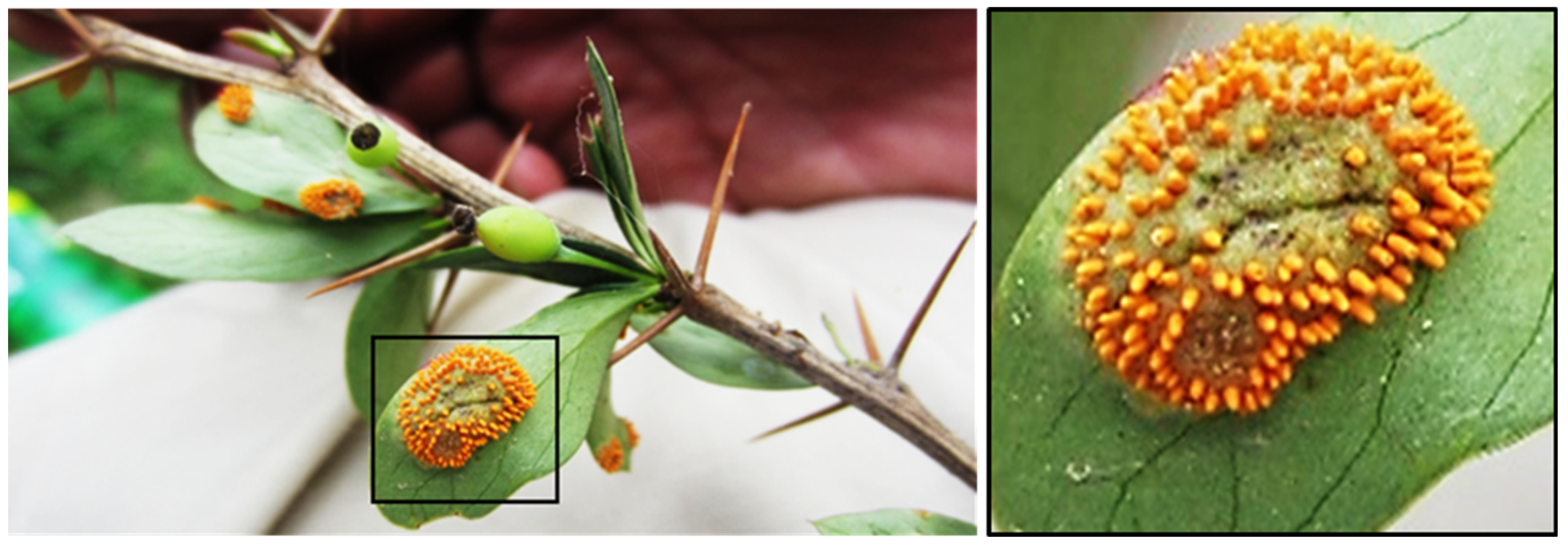
2.2. Inoculation of Breeding Germplasm
2.3. YR-Disease Severity and Host Response
2.4. Disease Assessment and Host Phenotyping
2.5. YR-Coefficient of Infection
2.6. DNA Extraction
2.7. Polymerase Chain Reaction and Genotyping
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Variable Response of Genotypes against Yellow Rust
3.2. Parental Line Response against Yellow Rust
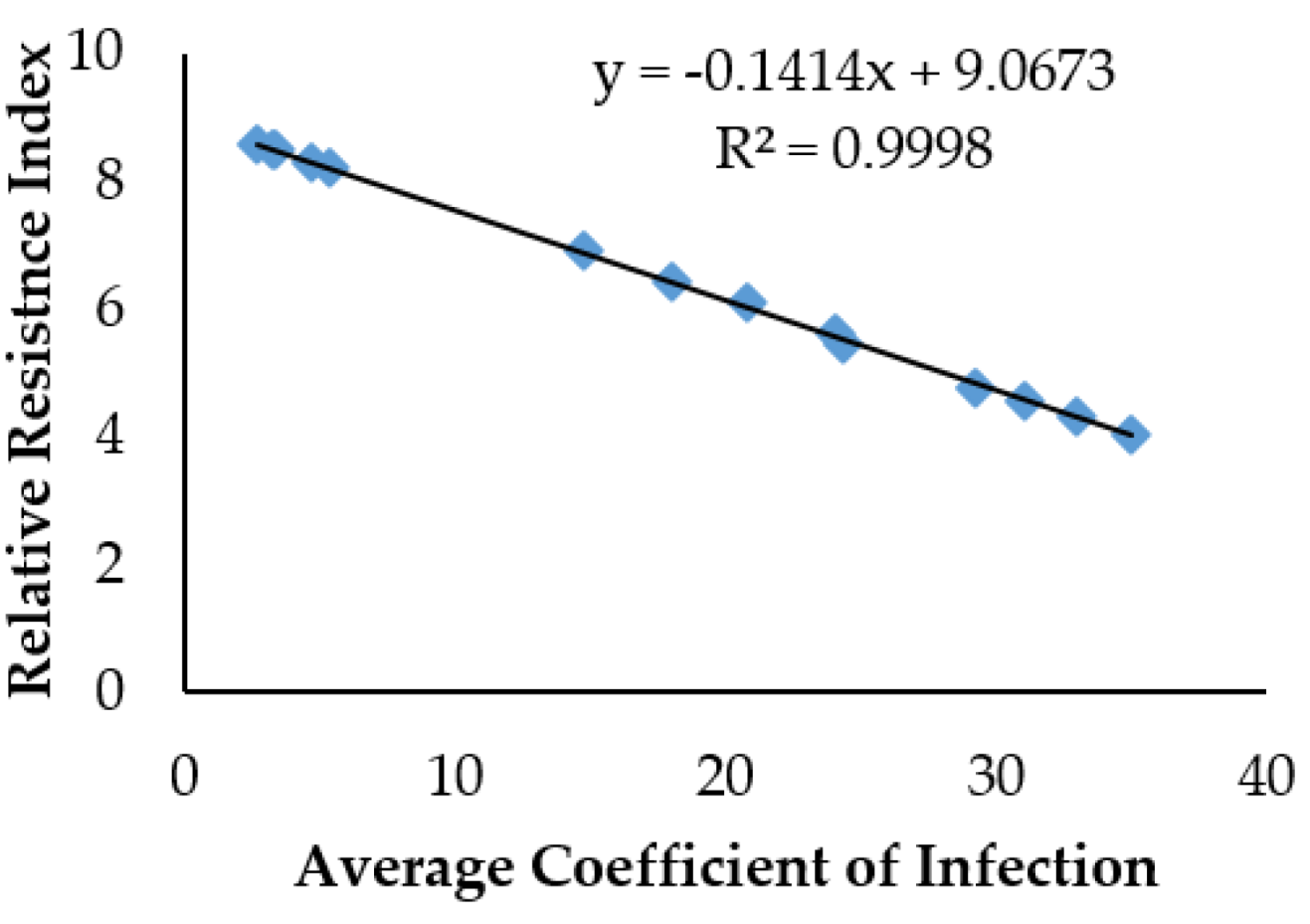
3.3. Regression between Resistance Indices
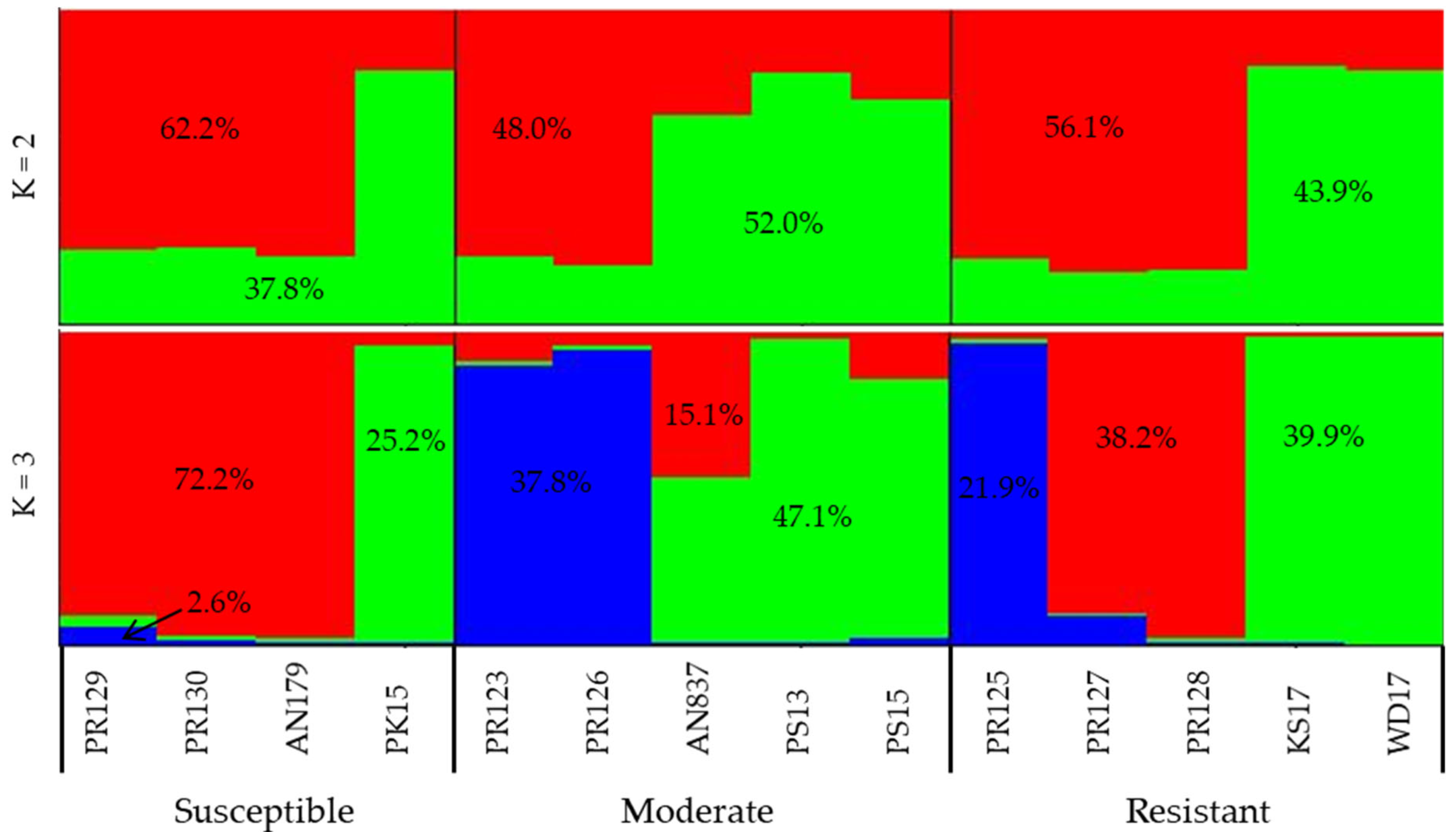
3.4. Parental Genotype Bulks Based on RRI
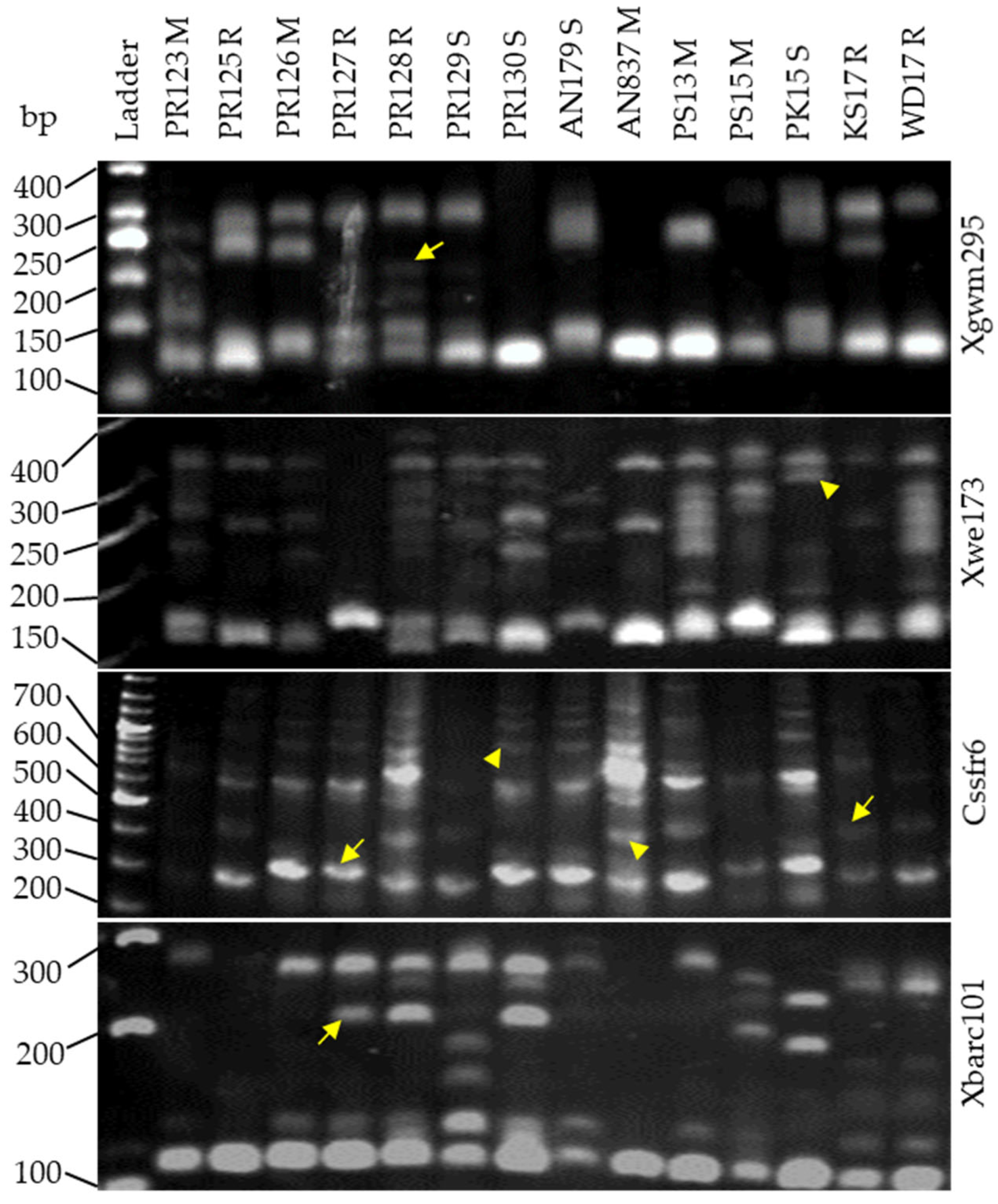
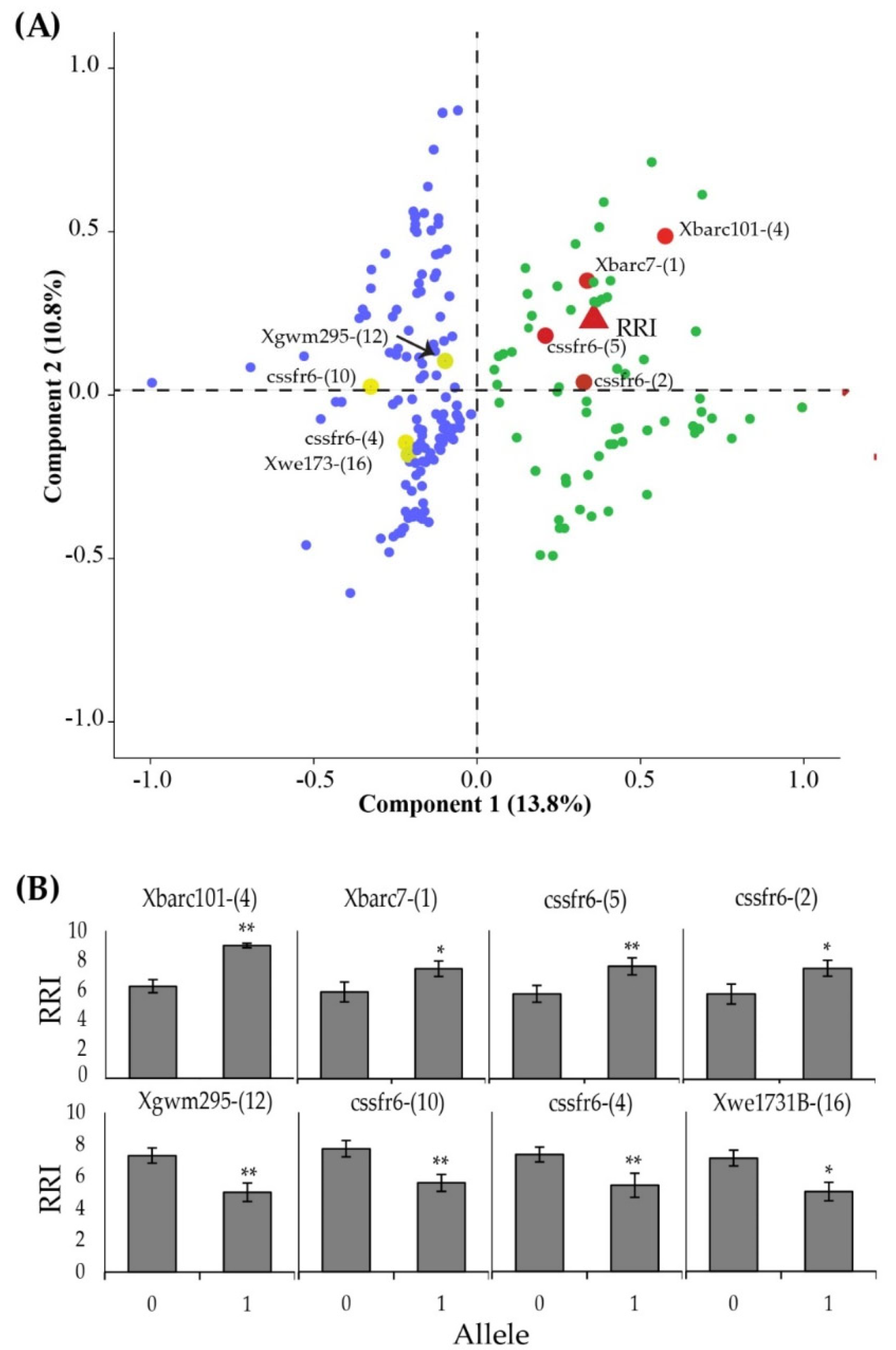
3.5. Microsatellite Polymiorphism between Resistance Bulks
3.6. Unique Allele Frequencies
3.7. Genetic Diversity Based on Microsatellite Markers
3.8. Allelic Association with RRI
3.9. Linkage of Microsatellite Markers with Yr Genes
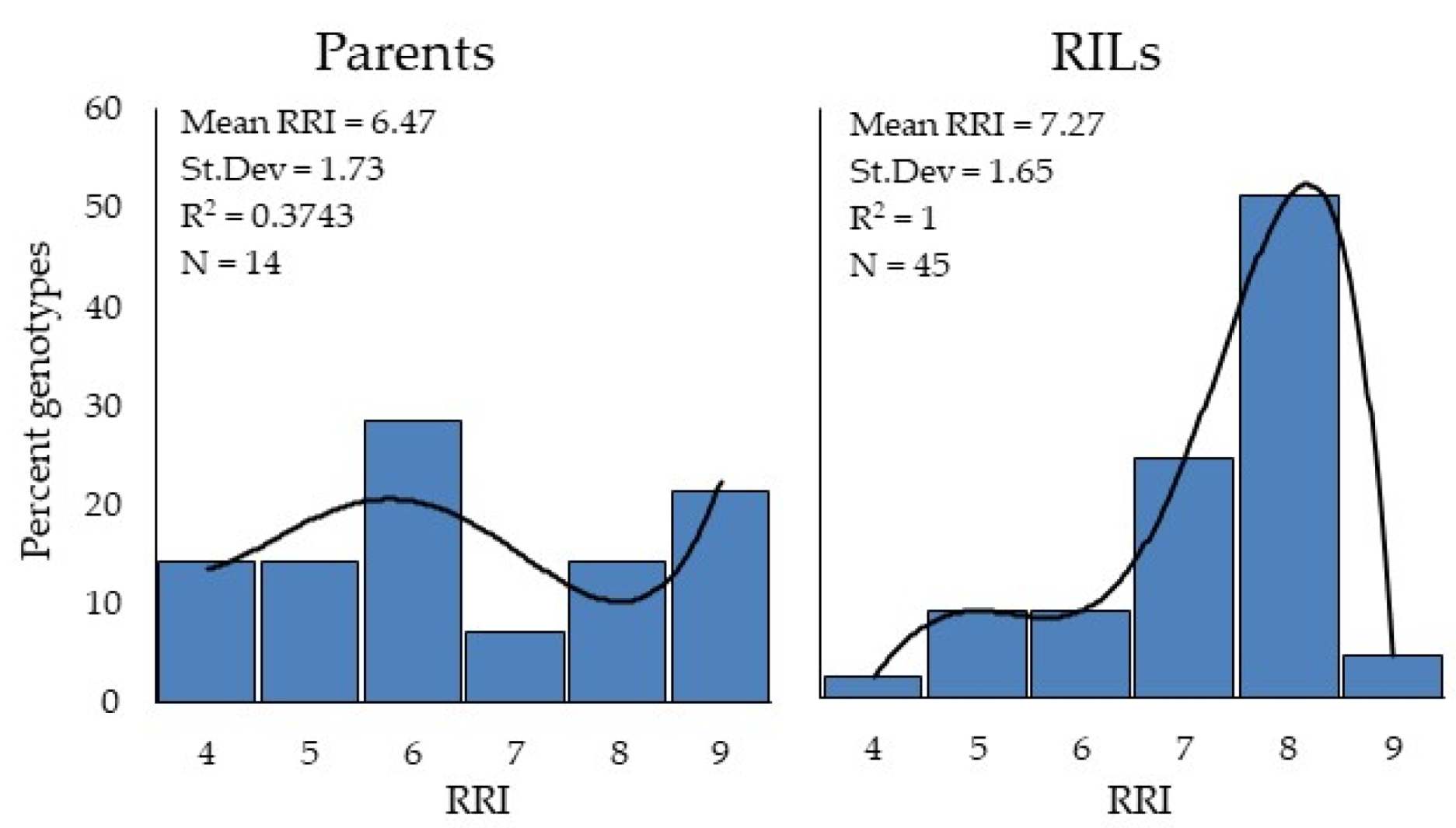
3.10. RILs Response against Yellow Rust
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shafi, U.; Mumtaz, R.; Haq, I.U.; Hafeez, M.; Iqbal, N.; Shaukat, A.; Zaidi, S.M.H.; Mahmood, Z. Wheat Yellow Rust Disease Infection Type Classification Using Texture Features. Sensors 2021, 22, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Kang, Z. Integrated control of stripe rust. In Stripe Rust; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 559–599. [Google Scholar]
- Beddow, J.M.; Pardey, P.G.; Chai, Y.; Hurley, T.M.; Kriticos, D.J.; Braun, H.J.; Park, R.F.; Cuddy, W.S.; Yonow, T. Research investment implications of shifts in the global geography of wheat stripe rust. Nat. Plants 2015, 1, 15132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Guo, Q.; Bai, B.; Shen, S.; Huang, G. Study on stripe rust (Puccinia striiformis) effect on grain filling and seed morphology building of special winter wheat germplasm Huixianhong. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, S.; Ali, S.; Kemen, E.; Nazari, K.; Bahri, B.A.; Enjalbert, J.; Hansen, J.G.; Brown, J.K.; Sicheritz-Ponten, T.; Jones, J.; et al. Molecular markers for tracking the origin and worldwide distribution of invasive strains of Puccinia striiformis. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 2790–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanfri, S.; Boulif, M.; Lahlali, R. Yellow rust (Puccinia striiformis): A serious threat to wheat production worldwide. Not. Sci. Biol. 2018, 10, 410–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. Pathogens which threaten food security: Puccinia striiformis, the wheat stripe rust pathogen. Food Secur. 2020, 12, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.; Wan, A.; Wang, M.; See, D.R.; Chen, X. Molecular characterization of wheat stripe rust pathogen (Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici) collections from nine countries. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, A.; Lewis, C.M.; Yoshida, K.; Ramirez-Gonzalez, R.H.; de Vallavieille-Pope, C.; Thomas, J.; Kamoun, S.; Bayles, R.; Uauy, C.; Saunders, D.G. Field pathogenomics reveals the emergence of a diverse wheat yellow rust population. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvet, L.; Holdgate, S.; James, L.; Thomas, J.; Mackay, I.J.; Cockram, J. The evolving battle between yellow rust and wheat: Implications for global food security. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wellings, C.; Chen, X.; Kang, Z.; Liu, T. Wheat stripe (yellow) rust caused by Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2014, 15, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Yao, J.; Zhan, G.; Chen, W.; Huang, L.; Kang, Z. Identification of eighteen Berberis species as alternate hosts of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici and virulence variation in the pathogen isolates from natural infection of barberry plants in China. Phytopathology 2013, 103, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, S.; Sajid, M.; Zhao, J.; Khan, T.; Zhan, G.; Huang, L.; Kang, Z. Identification of Berberis species collected from the Himalayan region of Pakistan susceptible to Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Gladieux, P.; Leconte, M.; Gautier, A.; Justesen, A.F.; Hovmøller, M.S.; Enjalbert, J.; de Vallavieille-Pope, C. Origin, migration routes and worldwide population genetic structure of the wheat yellow rust pathogen Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Tellier, A.; Wan, A.; Leconte, M.; de Vallavieille-Pope, C.; Enjalbert, J. Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici presents high diversity and recombination in the over-summering zone of Gansu, China. Mycologia 2010, 102, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mboup, M.; Leconte, M.; Gautier, A.; Wan, A.; Chen, W.; de Vallavieille-Pope, C.; Enjalbert, J. Evidence of genetic recombination in wheat yellow rust populations of a Chinese oversummering area. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2009, 46, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Rodriguez-Algaba, J.; Thach, T.; Sørensen, C.K.; Hansen, J.G.; Lassen, P.; Nazari, K.; Hodson, D.P.; Justesen, A.F.; Hovmøller, M.S. Yellow rust epidemics worldwide were caused by pathogen races from divergent genetic lineages. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.M.; Chng, S.; Woodman, T.L.; Warren, R.; Oliver, R.P.; Saunders, D.G. High frequency of fungicide resistance-associated mutations in the wheat yellow rust pathogen Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 3358–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. Epidemiology and control of stripe rust [Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici] on wheat. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2005, 27, 314–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. Review article: High-temperature adult-plant resistance, key for sustainable control of stripe rust. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 608–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Ullah, M.; Ahmad, W.; Shah, S.U.A. The use of modern technologies to combat stripe rust in wheat. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 25, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, S.; Shahzad, R.; Ahmad, S.; Fatima, R.; Zahid, R.; Anwar, M.; Iqbal, M.Z.; Wang, X. Role of Genetics, Genomics, and Breeding Approaches to Combat Stripe Rust of Wheat. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 580715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Q.; Wang, M.; Xia, C.; See, D.R.; Chen, X. Identification of Secreted Protein Gene-Based SNP Markers Associated with Virulence Phenotypes of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici, the Wheat Stripe Rust Pathogen. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwessinger, B.; Chen, Y.J.; Tien, R.; Vogt, J.K.; Sperschneider, J.; Nagar, R.; McMullan, M.; Sicheritz-Ponten, T.; Sorensen, C.K.; Hovmoller, M.S.; et al. Distinct Life Histories Impact Dikaryotic Genome Evolution in the Rust Fungus Puccinia striiformis Causing Stripe Rust in Wheat. Genome Biol. Evol. 2020, 12, 597–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchal, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, P.; Fenwick, P.; Steuernagel, B.; Adamski, N.M.; Boyd, L.; McIntosh, R.; Wulff, B.B.; Berry, S. BED-domain-containing immune receptors confer diverse resistance spectra to yellow rust. Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gad, M.A.; Li, H.; Alam, M.A.; Sajjad, M.; Li, M. Geographical distribution and virulence phenotypes of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici from wheat in Yunnan, China. Sci. Asia 2019, 45, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, S.; Zia, I.; Dilshad, I.; Fayyaz, M.; Noureen, N.; Farrakh, S. Identification of stripe rust resistant genes and their validation in seedling and adult plant glass house tests. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2020, 67, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta-Espino, J.; Singh, R.; Crespo-Herrera, L.A.; Villaseñor-Mir, H.E.; Rodriguez-Garcia, M.F.; Dreisigacker, S.; Barcenas-Santana, D.; Lagudah, E. Adult plant slow rusting genes confer high levels of resistance to rusts in bread wheat cultivars from Mexico. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qie, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, M.; Chen, X. Genome-Wide Mapping of Quantitative Trait Loci Conferring All-Stage and High-Temperature Adult-Plant Resistance to Stripe Rust in Spring Wheat Landrace PI 181410. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milus, E.A.; Moon, D.E.; Lee, K.D.; Mason, R.E. Race-Specific Adult-Plant Resistance in Winter Wheat to Stripe Rust and Characterization of Pathogen Virulence Patterns. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 1114–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, M.; Wan, A.; Bai, Q.; Li, M.; López, P.F.; Maccaferri, M.; Mastrangelo, A.M.; Barnes, C.W.; Cruz, D.F.C. Virulence characterization of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici collections from six countries in 2013 to 2020. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2021, 43 (Suppl. S2), S308–S322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Tao, F.; Su, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Chen, X.; Shang, H.; Hu, X. NBS-LRR Gene TaRPS2 is Positively Associated with the High-Temperature Seedling Plant Resistance of Wheat Against Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici. Phytopathology 2021, 111, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvet, L.; Percival-Alwyn, L.; Berry, S.; Fenwick, P.; Mantello, C.C.; Sharma, R.; Holdgate, S.; Mackay, I.J.; Cockram, J. Wheat genetic loci conferring resistance to stripe rust in the face of genetically diverse races of the fungus Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 301–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, M.; Ruff, T.; See, D.R.; Hu, X.; Chen, X. Characterization and Molecular Mapping of a Gene Conferring High-temperature Adult-plant Resistance to Stripe Rust Originally from Aegilops ventricosa. Plant Dis. 2022, 7692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, P.; Weldu, G.T.; Li, Z.; Liu, D. QTL mapping of adult plant resistance to stripe rust in the Fundulea 900× Thatcher RIL population. Czech J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2021, 57, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, G.E.; Mazrou, Y.S.A.; EL-Kazzaz, M.K.; Ghoniem, K.E.; Ashmawy, M.A.; Emeran, A.A.; Mabrouk, O.I.; Nehela, Y. Durability of Adult Plant Resistance Gene Yr18 in Partial Resistance Behavior of Wheat (Triticum aestivum) Genotypes with Different Degrees of Tolerance to Stripe Rust Disease, Caused by Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici: A Five-Year Study. Plants 2021, 10, 2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, M.N.; Feng, J.Y.; See, D.R.; Chao, S.M.; Chen, X.M. Combination of all-stage and high-temperature adult-plant resistance QTL confers high-level, durable resistance to stripe rust in winter wheat cultivar Madsen. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2018, 131, 1835–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, A.; Sharma, P. Development and use of molecular markers: Past and present. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2016, 36, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yao, F.; Long, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Q.; Kang, H. Genome-wide association study reveals the genetic architecture of stripe rust resistance at the adult plant stage in Chinese endemic wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Xu, Z.; Fan, X.; Zhou, Q.; Ji, G.; Wang, F.; Feng, B.; Wang, T. Genetic mapping and utilization analysis of stripe rust resistance genes in a Tibetan wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) landrace Qubaichun. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2020, 67, 1765–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Lu, J.; Zhou, M.; Zheng, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Du, M.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y. Developing stripe rust resistant wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) lines with gene pyramiding strategy and marker-assisted selection. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2020, 67, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Yao, F.; Yu, C.; Ye, X.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Q. Genome-wide association study for adult-plant resistance to stripe rust in chinese wheat landraces (Triticum aestivum L.) from the yellow and huai river valleys. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, E.; Blake, V.C.; Cooper, L.; Wight, C.P.; Michel, S.; Cagirici, H.B.; Lazo, G.R.; Birkett, C.L.; Waring, D.J.; Jannink, J.-L.; et al. GrainGenes: A data-rich repository for small grains genetics and genomics. Database 2022, 2022, baac034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, M.; Ullah, F.; Shah, L.; Ahmad, W.; Ali, M.; Munsif, F.; Zubair, A.; Ibrahim, M.; Shah, S.M.A.; Uddin, H. Identification of Three Novel QTLs Associated with Yellow Rust Resistance in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Anong-179/Khaista-17 F2 Population. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.F.; Campbell, A.; Hannah, A. A diagrammatic scale for estimating rust intensity on leaves and stems of cereals. Can. J. Res. 1948, 26, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.; Ahmad, I.; Mirza, J.; Rattu, A.; Hakro, A.; Jaffery, A. Evaluation of candidate lines against stripe and leaf rusts under national uniform wheat and barley yield trial 2000-2001. Asian J. Plant Sci. 2002, 1, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M. Uniform procedure for development and release of improved wheat varieties. Mimeogr. PARC Islamabad 1982, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Pathan, A.K.; Park, R.F. Evaluation of seedling and adult plant resistance to stem rust in European wheat cultivars. Euphytica 2007, 155, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Shou, L. Modified CTAB method for extracting genomic DNA from wheat leaf. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2013, 14, 946. [Google Scholar]
- Somers, D.J.; Isaac, P.; Edwards, K. A high-density microsatellite consensus map for bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 109, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccaferri, M.; Zhang, J.; Bulli, P.; Abate, Z.; Chao, S.; Cantu, D.; Bossolini, E.; Chen, X.; Pumphrey, M.; Dubcovsky, J. A genome-wide association study of resistance to stripe rust (Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici) in a worldwide collection of hexaploid spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2015, 5, 449–465. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Algaba, J.; Walter, S.; Sørensen, C.K.; Hovmøller, M.S.; Justesen, A.F. Sexual structures and recombination of the wheat rust fungus Puccinia striiformis on Berberis vulgaris. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2014, 70, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, N.; Yu, R.; Yu, S.; Wang, Q.; Huang, S.; Wang, H.; Singh, R.P.; Bhavani, S. Association analysis identifies new loci for resistance to Chinese Yr26-virulent races of the stripe rust pathogen in a diverse panel of wheat germplasm. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 1751–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Huerta-Espino, J.; Bhavani, S.; Herrera-Foessel, S.; Singh, D.; Singh, P.; Velu, G.; Mason, R.; Jin, Y.; Njau, P. Race non-specific resistance to rust diseases in CIMMYT spring wheats. Euphytica 2011, 179, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joukhadar, R.; Hollaway, G.; Shi, F.; Kant, S.; Forrest, K.; Wong, D.; Petkowski, J.; Pasam, R.; Tibbits, J.; Bariana, H. Genome-wide association reveals a complex architecture for rust resistance in 2300 worldwide bread wheat accessions screened under various Australian conditions. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2020, 133, 2695–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafez, Y.; Mazrou, Y.; Shahin, A.; Mehiar, F.; Eid, M.; Abdelaal, K. Yield losses in wheat genotypes caused by stripe rust (Puccinia striifarmis f. sp. tritici) in North Delta, Egypt. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2022, 50, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanzada, K.A.; Sufyan, M.; Mirza, J.I.; Saeed, M.; Fayyaz, M.; Kakar, M.Q.; Rattu, A.U.R. Yellow rust races found in 2018-19 collection from wheat growing areas of Pakistan. Pure Appl. Biol. PAB 2021, 10, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Shahin, A.; Esmaeil, R.A.; Badr, M.; Hassan, F.A.; Hafez, Y.M. Phenotypic characterization of race-specific and slow rusting resistance to stem rust disease in promising wheat genotypes. Fresenius Environ. Bull 2021, 30, 6223–6236. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, A.F.; Hassan, M.I.; Amein, K.A. Resistance potential of bread wheat genotypes against yellow rust disease under Egyptian climate. Plant Pathol. J. 2015, 31, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulbert, S.; Pumphrey, M. A time for more booms and fewer busts? Unraveling cereal–rust interactions. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2014, 27, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Klymiuk, V.; Yaniv, E.; Huang, L.; Raats, D.; Fatiukha, A.; Chen, S.; Feng, L.; Frenkel, Z.; Krugman, T.; Lidzbarsky, G. Cloning of the wheat Yr15 resistance gene sheds light on the plant tandem kinase-pseudokinase family. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrewahid, T.W.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, X.; Xia, X.; He, Z.; Liu, D.; Li, Z. QTL mapping of adult plant resistance to stripe rust and leaf rust in a Fuyu 3/Zhengzhou 5389 wheat population. Crop J. 2020, 8, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hanafi, S.; Backhaus, A.; Bendaou, N.; Sanchez-Garcia, M.; Al-Abdallat, A.; Tadesse, W. Genome-wide association study for adult plant resistance to yellow rust in spring bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Euphytica 2021, 217, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suenaga, K.; Singh, R.; Huerta-Espino, J.; William, H. Microsatellite markers for genes Lr34/Yr18 and other quantitative trait loci for leaf rust and stripe rust resistance in bread wheat. Phytopathology 2003, 93, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagudah, E.S.; Krattinger, S.G.; Herrera-Foessel, S.; Singh, R.P.; Huerta-Espino, J.; Spielmeyer, W.; Brown-Guedira, G.; Selter, L.L.; Keller, B. Gene-specific markers for the wheat gene Lr34/Yr18/Pm38 which confers resistance to multiple fungal pathogens. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 119, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsabiyera, V.; Bariana, H.S.; Qureshi, N.; Wong, D.; Hayden, M.J.; Bansal, U.K. Characterisation and mapping of adult plant stripe rust resistance in wheat accession Aus27284. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2018, 131, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen-Xiong, Y.; Fang-Ping, Y.; Dan, L.; Zhonghu, H.; Xun-Wu, S.; Xian-chun, X. Molecular characterization of slow-rusting genes Lr34/Yr18 in Chinese wheat cultivars. Agris FAO 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, D.; Qiao, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Chang, L.; Guo, H.; Zhang, S.; Chen, F.; Chang, Z. Fine mapping of a recessive leaf rust resistance locus on chromosome 2BS in wheat accession CH1539. Mol. Breed. 2022, 42, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallard, S.; Gaudet, D.; Aldeia, A.; Abelard, C.; Besnard, A.-L.; Sourdille, P.; Dedryver, F. Genetic analysis of durable resistance to yellow rust in bread wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2005, 110, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, L.R.; Santra, D.; Kidwell, K.; Yan, G.; Chen, X.; Campbell, K.G. Linkage maps of wheat stripe rust resistance genes Yr5 and Yr15 for use in marker-assisted selection. Crop Sci. 2009, 49, 1786–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Soria, M.A.; Yan, G.; Sun, J.; Dubcovsky, J. Development of Sequence Tagged Site and Cleaved Amplified Polymorphic Sequence Markers for Wheat Stripe Rust Resistance Gene Yr5. Crop Sci. 2003, 43, 2058–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, K.; Shahin, A.A.M.; Abdelkhalik, S. Efficiency of Yellow Rust Resistance Genes Yr5, Yr10, Yr15 and YrSp in Improving the Two Egyptian Bread Wheat Cultivars Sids 12 and Gemmeiza 11. Egypt. J. Agron. 2020, 42, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, A.; Riaz, A.; Ashraf, S.; Iqbal, J.; Ijaz, M.; Naz, F.; Shah, S.K. Identification of Durable Resistance against Yellow Rust. Int. J. Phytopathol. 2022, 11, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.-D.; Han, D.-J.; Wang, Q.-L.; Yuan, F.-P.; Wu, J.-H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.-J.; Huang, L.-L.; Chen, X.-M.; Kang, Z.-S. Stripe rust resistance and genes in Chinese wheat cultivars and breeding lines. Euphytica 2014, 196, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Guo, Q.; Lin, R.; Yao, Q.; Feng, J.; Wang, F.; Chen, W.; Xu, S. Postulation of stripe rust resistance genes in Chinese 40 wheat landraces and 40 commercial cultivars in the southern region of Gansu province. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2015, 48, 3834–3847. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X.; Zeng, Q.; Wu, J.; Xue, W.; Zhan, G.; Huang, L.; Kang, Z. Emerging Yr26-virulent races of Puccinia striiformis f. tritici are threatening wheat production in the Sichuan Basin, China. Plant Dis. 2015, 99, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.G.; Peng, Y.L.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Z. First detection of virulence in Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici in China to resistance genes Yr24 (=Yr26) present in wheat cultivar Chuanmai 42. Plant Dis. 2010, 94, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Singh, R.P.; Lillemo, M.; He, X.; Randhawa, M.S.; Huerta-Espino, J.; Singh, P.K.; Li, Z.; Lan, C. Two main stripe rust resistance genes identified in synthetic-derived wheat line Soru# 1. Phytopathology 2019, 109, 120–126. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, X.; See, D.; Chao, S.; Jing, J. Mapping of Yr62 and a small-effect QTL for high-temperature adult-plant resistance to stripe rust in spring wheat PI 192252. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 1449–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, A.J.; Naruoka, Y.; Chen, X.; Garland-Campbell, K.A.; Zemetra, R.S.; Carter, A.H. Mapping Stripe Rust Resistance in a BrundageXCoda Winter Wheat Recombinant Inbred Line Population. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Primer Name | Primer Sequences | Annealing Temp °C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | ||
| Xgwm11 | GGATAGTCAGACAATTCTTGTG | GTGAATTGTGTCTTGTATGCTTCC | 52 |
| Xgwm295 | GTGAAGCAGACCCACAACAC | GACGGCTGCGACGTAGAG | 54 |
| Xgwm140 | ATGGAGATATTTGGCCTACAAC | CTTGACTTCAAGGCGTGACA | 53 |
| S23M41275 | TCAACGGAACCTCCAATTTC | AGGTAGGTGTTCCAGCTTGC | 55 |
| csLV34 | GTTGGTTAAGACTGGTGATGG | TGCTTGCTATTGCTGAATAGT | 54 |
| csLVMS1 | CTCCCTCCCGTGAGTATATTC | ATCAAAATCCCATTGCCTGAC | 54 |
| Xbarc151 | TGAGGAAAATGTCTCTATAGCATCC | CGCATAAACACCTTCGCTCTTCCACTC | 53 |
| Xbarc181 | CGCTGGAGGGGGTAAGTCATCAC | CGCAAATCAAGAACACGGGAGAAAGAA | 52 |
| Xwe173 | F;GGGACAAGGGGAGTTGAAGC | GAGAGTTCCAAGCAGAACAC | 56 |
| Xwmc419 | GTTTCGGATAAAACCGGAGTGC | ACTACTTGTGGGTTATCACCAGCC | 57 |
| Xgwm191 | F;AGACTGTTGTTTGCGGGC | TAGCACGACAGTTGTATGCATG | 55 |
| Xgwm501 | GGCTATCTCTGGCGCTAAAA | TCCACAAACAAGTAGCGCC | 54 |
| Xbarc7 | CGCCATCTTACCCTATTTGATAACTA | TTGTACATTAAGTTCCCATTA | 55 |
| Xgwm429 | TTGTACATTAAGTTCCCATTA | TTTAAGGACCTACATGACAC | 57 |
| cssfr6 | CTGAGGCACTCTTTCCTGTACAAAG | GCATTCAATGAGCAATGGTTATC | 55 |
| Xbarc101 | GCTCCTCTCACGATCACGCAAAG | GCGAGTCGATCACACTATGAGCCAATG | 61 |
| SCAR1400 | CACTCTCCTCAAACCTTGCAAG | CACTCTCCTCCACTAACAGAGG | 56 |
| Xgwm 130 | AGCTCTGCTTCACGAGGAAG | CTCCTCTTTATATCGCGTCCC | 53 |
| Xgwm 251 | CAACTGGTTGCTACACAAGCA | GGGATGTCTGTTCCATCTTAG | 59 |
| SOV | DF | YR- Average Coefficient of Infection | f Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Replications | 2 | 29.9 | 1.1ns |
| Genotypes | 58 | 359.7 | 13.8 ** |
| Parents | 13 | 453.2 | 17.4 ** |
| Lines (L) | 8 | 212.8 | 8.2 * |
| Tester (T) | 4 | 1817.8 | 69.6 ** |
| L × T | 32 | 174.3 | 6.7 ns |
| RILs | 44 | 330.7 | 12.7 ** |
| Parents vs. RILs | 1 | 420.6 | 16.1 ** |
| Error | 116 | 26.1 | |
| CV(%) | -- | 14.2 |
| Parents | Disease Status | Disease Response * | ACI | CARPA | RRI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PR123 | M | 30MS | 21.3 | 33.7 | 6.0 ± 0.16 b |
| PR125 | R | 10MR | 3.7 | 5.8 | 8.3 ± 0.13 c |
| PR126 | M | 40M | 22.0 | 34.8 | 5.6 ± 0.40 ab |
| PR127 | R | 10MR | 4.7 | 7.4 | 8.2 ± 0.06 c |
| PR128 | R | 5R | 2.7 | 4.2 | 8.5 ± 0.03 c |
| PR129 | S | 30MSS | 24.1 | 38.0 | 4.8 ± 0.36 ab |
| PR130 | S | 30MSS | 28.2 | 44.5 | 4.3 ± 0.43 a |
| AN179 | S | 30S | 34.3 | 54.2 | 4.0 ± 0.70 a |
| AN837 | M | 30M | 18.3 | 29.0 | 6.4 ± 0.26 b |
| PS13 | M | 35MS | 24.3 | 38.4 | 5.5 ± 0.06 ab |
| PS15 | M | 30M | 15.3 | 24.2 | 6.9 ± 0.20 bc |
| PK15 | S | 40S | 35.2 | 55.6 | 4.5 ± 0.13 ab |
| KS17 | R | 5R | 2.3 | 3.7 | 8.7 ± 0.03 c |
| WD17 | R | 10R | 5.2 | 8.2 | 8.5 ± 0.26 c |
| Marker | Total Alleles | Shared Alleles | Unique Alleles | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | S | M | R | SM | SR | MR | SMR | S | M | R | |
| Xgwm11 | 12 | 6 | 9 | 10 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |
| Xgwm295 | 15 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Xgwm140 | 16 | 13 | 11 | 11 | 9 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| S23M4127 | 17 | 10 | 12 | 13 | 8 | 7 | 9 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| csLV34 | 19 | 10 | 11 | 15 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| csLVMS1 | 16 | 13 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Xbarc151 | 12 | 10 | 10 | 11 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 7 | |||
| Xbarc181 | 8 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 2 | ||
| Xwe173 | 18 | 10 | 14 | 15 | 7 | 7 | 13 | 6 | 2 | 1 | |
| Xwmc419 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 1 | ||
| Xgwm191 | 17 | 12 | 14 | 14 | 10 | 11 | 11 | 9 | 2 | 1 | |
| Xgwm501 | 10 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 3 | |||
| Xbarc7 | 22 | 14 | 19 | 12 | 11 | 7 | 11 | 6 | 2 | 3 | |
| Xgwm429 | 18 | 15 | 10 | 4 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 3 | |
| cssfr6 | 14 | 12 | 14 | 14 | 12 | 12 | 14 | 12 | |||
| Xbarc101 | 9 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| SCAR1400 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |||
| Xgwm130 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | |||
| Xgwm251 | 15 | 14 | 8 | 13 | 7 | 13 | 6 | 6 | 1 | ||
| Total | 256 | 185 | 190 | 190 | 136 | 137 | 146 | 111 | 22 | 20 | 17 |
| Marker | Allele# | S | M | R | Marker | Allele# | S | M | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xgwm191 | 6 | 0.106 | Xgwm251 | 10 | 0.225 | ||||
| 9 | 0.106 | Xwe173 | 1 | 0.106 | |||||
| 10 | 0.106 | 9 | 0.134 | ||||||
| Xgwm295 | 6 | 0.134 | 16 | 0.500 | |||||
| 7 | 0.106 | Xbarc101 | 4 | 0.225 | |||||
| 11 | 0.106 | 8 | 0.134 | ||||||
| 14 | 0.225 | 9 | 0.106 | ||||||
| Xgwm140 | 4 | 0.106 | Xbarc7 | 4 | 0.225 | ||||
| 5 | 0.134 | 11 | 0.106 | ||||||
| 6 | 0.134 | 13 | 0.134 | ||||||
| 10 | 0.106 | 16 | 0.225 | ||||||
| 13 | 0.134 | 21 | 0.134 | ||||||
| 14 | 0.225 | S23M4127 | 1 | 0.106 | |||||
| csLV34 | 2 | 0.225 | 3 | 0.106 | |||||
| 6 | 0.106 | 9 | 0.134 | ||||||
| 7 | 0.106 | 12 | 0.106 | ||||||
| 10 | 0.106 | 13 | 0.106 | ||||||
| 16 | 0.106 | 15 | 0.106 | ||||||
| 17 | 0.106 | csLVMS1 | 1 | 0.106 | |||||
| 18 | 0.134 | 2 | 0.134 | ||||||
| Xgwm429 | 1 | 0.106 | 11 | 0.134 | |||||
| 2 | 0.134 | 12 | 0.106 | ||||||
| 3 | 0.134 | 13 | 0.134 | ||||||
| 4 | 0.134 | 14 | 0.106 | ||||||
| 11 | 0.293 | Xbarc181 | 3 | 0.134 | |||||
| 12 | 0.106 | 5 | 0.134 | ||||||
| 14 | 0.134 | Xwmc419 | 5 | 0.106 | |||||
| 16 | 0.106 | Xgwm11 | 9 | 0.106 | |||||
| 18 | 0.134 | 11 | 0.225 | ||||||
| 12 | 0.225 |
| Crosses | Parent Disease Status | Disease Status | Disease Response | ACI | CARPA | RRI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PR123 × PS13 | M × M | M | 40MS | 30.3 | 47.9 | 5.5 ± 0.75 |
| PR123 × PS15 | M × M | R | 10MR | 6.7 | 10.6 | 8.1 ± 0.08 |
| PR123 × PK15 | M × S | S | 40MS | 32.2 | 50.9 | 4.9 ± 1.27 |
| PR123 × K17 | M × R | R | 10MR | 7.1 | 11.2 | 8.2 ± 0.14 |
| PR123 × WD17 | M × R | R | 10MR | 4.4 | 7.0 | 8.3 ± 0.14 |
| PR125 × PS13 | R × M | M | 30M | 15.2 | 24.1 | 7.2 ± 0.48 |
| PR125 × PS15 | R × M | R | 10MR | 3.9 | 6.2 | 8.3 ± 0.17 |
| PR125 × PK15 | R × S | S | 35MSS | 26.5 | 41.9 | 5.3 ± 0.39 |
| PR125 × KS17 | R × R | R | 10MR | 4.6 | 7.3 | 8.3 ± 0.17 |
| PR125 × WD17 | R × R | R | 10MR | 6.0 | 9.5 | 8.2 ± 0.40 |
| PR126 × PS13 | M × M | M | 25M | 16.5 | 26.0 | 6.5 ± 0.77 |
| PR126 × PS15 | M × M | R | 10MR | 4.2 | 6.6 | 8.4 ± 0.10 |
| PR126 × PK15 | M × S | S | 30MS | 21.8 | 34.4 | 5.8 ± 0.24 |
| PR126 × KS17 | M × R | R | 10MR | 4.6 | 7.3 | 8.4 ± 0.02 |
| PR126 × WD17 | M × R | R | 5MR | 3.5 | 5.5 | 8.5 ± 0.02 |
| PR127 × PS13 | R × M | R | 10MR | 6.6 | 10.4 | 8.0 ± 0.19 |
| PR127 × PS15 | R × M | R | 10MR | 4.0 | 6.4 | 8.4 ± 0.14 |
| PR127 × PK15 | R × S | M | 25M | 15.5 | 24.4 | 7.0 ± 0.14 |
| PR127 × KS17 | R × R | R | 10MR | 4.8 | 7.5 | 8.4 ± 0.07 |
| PR127 × WD17 | R × R | R | 10MR | 7.6 | 12.0 | 7.9 ± 0.44 |
| PR128 × PS13 | R × M | S | 20MS | 14.5 | 22.9 | 6.8 ± 0.17 |
| PR128 × PS15 | R × M | M | 5MS | 4.2 | 6.7 | 8.8 ± 0.03 |
| PR128 × PK15 | R × S | R | 10MR | 12.4 | 19.6 | 7.1 ± 0.72 |
| PR128 × KS17 | R × R | M | 20M | 10.5 | 16.6 | 7.6 ± 0.29 |
| PR128 × WD17 | R × R | R | 10RMR | 4.9 | 7.7 | 8.2 ± 0.18 |
| PR129 × PS13 | S × M | M | 30MR | 12.9 | 20.4 | 7.3 ± 0.17 |
| PR129 × PS15 | S × M | M | 30M | 15.9 | 25.2 | 6.6 ± 0.25 |
| PR129 × PK15 | S × S | S | 40MSS | 29.8 | 47.1 | 4.9 ± 0.45 |
| PR129 × KS17 | S × R | R | 10MR | 5.6 | 8.8 | 8.2 ± 0.14 |
| PR129 × WD17 | S × R | R | 10MR | 6.3 | 10.0 | 8.2 ± 0.13 |
| PR130 × PS13 | S × M | S | 30MS | 20.1 | 31.8 | 6.2 ± 0.62 |
| PR130 × PS15 | S × M | M | 25M | 12.8 | 20.2 | 7.3 ± 0.34 |
| PR130 × PK15 | S × S | S | 35MS | 25.9 | 40.9 | 5.1 ± 0.87 |
| PR130 × KS17 | S × R | M | 10M | 7.4 | 11.6 | 8.1 ± 0.17 |
| PR130 × WD17 | S × R | M | 20MR | 9.3 | 14.7 | 7.5 ± 0.20 |
| AN179 × PS13 | S × M | M | 15M | 8.8 | 13.9 | 7.8 ± 0.26 |
| AN179 × PS15 | S × M | M | 20M | 12.3 | 19.4 | 7.7 ± 0.10 |
| AN179 × PK15 | S × S | S | 60S | 56.7 | 89.5 | 0.9 ± 0.40 |
| AN179 × KS17 | S × R | R | 5R | 1.4 | 2.2 | 8.8 ± 0.04 |
| AN179 × WD17 | S × R | R | 20MR | 9.9 | 15.6 | 7.8 ± 0.26 |
| AN837 × PS13 | M × M | S | 20MS | 12.9 | 20.3 | 7.2 ± 0.16 |
| AN837 × PS15 | M × M | S | 30MS | 27.0 | 42.7 | 5.5 ± 0.28 |
| AN837 × PK15 | M × S | M | 25M | 16.7 | 26.3 | 6.7 ± 0.85 |
| AN837 × KS17 | M × R | M | 20M | 12.2 | 19.3 | 7.2 ± 0.21 |
| AN837 × WD17 | M × R | R | 10RMR | 4.7 | 7.5 | 8.3 ± 0.17 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saeed, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Ahmad, W.; Tayyab, M.; Attacha, S.; Khan, M.N.; Jadoon, S.A.; Shah, S.J.; Zeb, S.; Shah, L.; et al. Molecular Characterization of Diverse Wheat Genetic Resources for Resistance to Yellow Rust Pathogen (Puccinia striiformis). Agronomy 2022, 12, 2951. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12122951
Saeed M, Ibrahim M, Ahmad W, Tayyab M, Attacha S, Khan MN, Jadoon SA, Shah SJ, Zeb S, Shah L, et al. Molecular Characterization of Diverse Wheat Genetic Resources for Resistance to Yellow Rust Pathogen (Puccinia striiformis). Agronomy. 2022; 12(12):2951. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12122951
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaeed, Muhammad, Muhammad Ibrahim, Waqas Ahmad, Muhammad Tayyab, Safira Attacha, Mudassar Nawaz Khan, Sultan Akbar Jadoon, Syed Jehangir Shah, Shaista Zeb, Liaqat Shah, and et al. 2022. "Molecular Characterization of Diverse Wheat Genetic Resources for Resistance to Yellow Rust Pathogen (Puccinia striiformis)" Agronomy 12, no. 12: 2951. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12122951
APA StyleSaeed, M., Ibrahim, M., Ahmad, W., Tayyab, M., Attacha, S., Khan, M. N., Jadoon, S. A., Shah, S. J., Zeb, S., Shah, L., Munsif, F., Zubair, A., Lu, J., Si, H., & Ma, C. (2022). Molecular Characterization of Diverse Wheat Genetic Resources for Resistance to Yellow Rust Pathogen (Puccinia striiformis). Agronomy, 12(12), 2951. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12122951






