Effects of Compound Biochar Substrate Coupled with Water and Nitrogen on the Growth of Cucumber Plug Seedlings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site and Materials
2.2. Experimental Design and Implementation
2.3. Sampling and Measurements
2.3.1. Measurements before Transplanting
- Plant height and total root length.
- 2.
- Total dry biomass and specific root length.
- 3.
- Water and N use efficiency.
- 4.
- Crushing resistance of the seedling pot.
2.3.2. Measurements after Transplanting
- Plant height, shoot dry biomass, total root length, and root dry biomass.
- 2.
- The leaf gas exchange parameters.
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Data Analysis of Seedlings before Transplanting
3.1.1. Analysis of Plant Height and Total Root Length
3.1.2. Analysis of Total Dry Biomass and Specific Root Length
3.1.3. Analysis of Water and N Use Efficiency
3.1.4. Analysis of Crushing Resistance of Seedling Pot
3.2. Data Analysis of Seedlings after Transplanting
3.2.1. Analysis of Plant Height, Shoot Dry Biomass, Total Root Length, and Root Dry Biomass
3.2.2. Analysis of the Leaf Gas Exchange Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- China National Bureau of Statistics. Annual Data of National Vegetable Output (10000 Tons). 2021. Available online: http://data.stats.gov.cn/easyquery.htm?cn=C01 (accessed on 9 April 2021).
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, S.; Xu, H.; Lu, D.; Xu, T.; Dai, D. Discussion on the establishment of standard system for vegetable plug seedling. In Proceedings of the 17th China Standardization Forum, Fuzhou, China, 19 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tian, J.; Duan, D.; Li, X. Design of a traction double-row fully automatic transplanter for vegetable plug seedlings. Comput. Electron. Agr. 2021, 182, 106017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Ma, G.; Han, L.; Hu, J.; Gao, F.; Liu, Y. A whole row automatic pick-up device using air force to blow out vegetable plug seedlings. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2020, 18, e0211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Han, C.; Guo, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y. Research status and development trend of key components of automatic transplanting machine. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 2019, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.; Mao, H.; Han, L.; Liu, Y.; Gao, F. Reciprocating mechanism for whole row automatic seedling picking and dropping on a transplanter. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2020, 36, 751–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ting, K.C.; Giacomelli, G.A. Factors affecting performance of sliding-needles gripper during robotic transplanting of seedlings. Trans. ASAE 1991, 7, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.M.; Lee, C.W.; Park, J.S. Influence of fertilizer concentrations on the performance of seedling grafts of cucumber grown in coir based root media. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2011, 52, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, K.; Mao, H.; Li, Q. Assessment of cucumber seedling substrate-root quality using X-ray computed tomography and scanning electron microscopy. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2016, 32, 417–427. [Google Scholar]
- Min, B.; Ha, L.; Lee, J.; Choi, S.; Lee, S. The selection proper materials to develop specialized root substrate for working with bulbonion transplanter. Prot. Hortic. Plant. Fact. 2016, 25, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, K.C.; Giacomelli, G.A.; Shen, S.J. Robot workcell for transplanting of seedlings: Part II-end-effector development. Trans. ASAE 1990, 33, 1013–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, P.; Cao, Y.; Wu, G.; Tang, W.; Xia, L. Preparation and properties of coir-based substrate bonded by modified urea formaldehyde reinsnfor seedlings. Bioresources 2018, 13, 4332–4345. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, G.; Elnaz, A.; Kazem, Z. In-situ biochar production associated with paddies: Direct involvement of farmers in greenhouse gases reduction policies besides increasing nutrients availability and rice production. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 3893–3904. [Google Scholar]
- Veysel, T.; Peter, S.; Serdar Bilen, B.; Heribert, I.; Marina, F.J. Co-inoculation effect of rhizobium and Achillea millefolium L. oil extracts on growth of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and soil microbial-chemical properties. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15178. [Google Scholar]
- Clough, T.; Condron, L.; Kammann, C.; Müller, C. A review of biochar and soil nitrogen dynamics. Agronomy 2013, 3, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaney, N.; Mamman, M.; Tahir, H.; Al-Gharib, A.; Lin, C. Effects of softwood biochar on the status of nitrogen species and elements of potential toxicity in soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 166, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; He, T.; Cao, T.; Yang, T.; Meng, J.; Chen, W. Effects of biochar application on nitrogen leaching, ammonia volatilization and nitrogen use efficiency in two distinct soils. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nut. 2017, 17, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Novak, A.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J. Role of biochar in improving sandy soil water retention and resilience to drought. Water 2021, 13, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Reddy, N.G.; Huang, X.; Chen, P.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lin, P.; Garg, A. Effects of pyrolysis temperature, feedstock type and compaction on water retention of biochar amended soil. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Mageed, T.A.; Belal, E.E.; Rady, M.O.A.; Abd El-Mageed, S.A.; Mansour, E.; Awad, M.F.; Semida, W.M. Acidified biochar as a soil amendment to drought stressed (Vicia faba L.) plants: Influences on growth and productivity, nutrient status, and water use Efficiency. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; White, P.J.; Hochholdinger, F.; Li, C. Phenotypic plasticity of the maize root system in response to heterogeneous nitrogen availability. Planta 2014, 240, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Janz, B.; Engedal, T.; de Neergaard, A. Effect of irrigation regimes and nitrogen rates on water use efficiency and nitrogen uptake in maize. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 179, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muschietti-Piana, M.P.; Cipriotti, P.A.; Urricariet, S.; Peralta, N.R.; Niborski, M. Using site-specific nitrogen management in rainfed corn to reduce the risk of nitrate leaching. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 199, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Gu, J.; Zhang, F.; Hao, L.; Cong, P.; Liu, Z. Maize yield response to water supply and fertilizer input in a semi-arid environment of Northeast China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Mao, H.; Bu, Q.; Han, L.; Gao, F. Effect of compound biochar substrate on the root growth of cucumber plug seedlings. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Mao, H.; Ma, W. Effect of different electrical conductivity on photosynthetic characteristics of cucumber leaves in greenhouse. Trans. CSAE 2011, 27, 277–281. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, X.; Mao, H.; Han, L.; Sun, H.; Yang, X. Analysis of influencing factors on force of picking plug seedlings and pressure resistance of plug seedlings. Trans. CSAM 2013, 44, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, Z. Advanced Vegetable Physiology; China Agricultural University Press: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Oikeh, S.O.; Kling, J.G.; Horst, W.J. Growth and distribution of maize roots under nitrogen fertilization in plinthite soil. Field Crops Res. 1999, 62, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Hao, X.; Du, T.; Tong, L.; Su, X.; Lu, H.; Li, X.; Huo, Z.; Li, S.; Ding, R. Improving agricultural water productivity to ensure food security in China under changing environment: From research to practice. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 179, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lv, H.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, S. Effect of biochar and nitrogen application rate on growth and water-nitrogen use efficiency of tomato. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin. 2019, 34, 198–204. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Kang, S.; Suo, L. Effects of regulated deficit irrigation on root growth in maize. Irrig. Drain. 2001, 20, 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, R.; Shafaqat, A.; Tahir, A.; Muhammad, Z.R.; Mohammad, I. Residual impact of biochar on cadmium uptake by rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown in Cd-contaminated soil. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 206, 676–683. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Shang, Z. Positive effects of apple branch biochar on wheat yield only appear at a low application rate, regardless of nitrogen and water conditions. J. Soil Sediment 2018, 18, 3235–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Ye, X.; Wang, B.; Sun, A.; Zhang, T.; Hua, X.; Wang, Z. Effects of Water-Biochar Coupling on Rice Yield and Water Use Efficiency. Water Saving Irrig. 2018, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, A.; Wang, L.; Guo, X.; Niu, Y.; Liu, S.; Mi, G.; Gao, Q. Reducing basal nitrogen rate to improve maize seedling growth, water and nitrogen use efficiencies under drought stress by optimizing root morphology and distribution. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 212, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colantoni, A.; Evic, N.; Lord, R.; Retschitzegger, S.; Proto, A.R.; Gallucci, F.; Monarca, D. Characterization of biochars produced from pyrolysis of pelletized agricultural residues. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 64, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wang, L.; Fu, X.; Le, Y. Response of straw and straw biochar returning to soil carbon budget and its mechanism. Environ. Sci. 2015, 36, 2655–2661. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Meng, J.; Huang, Y.; Liang, H.; He, T.; Lan, Y.; Chen, W. Effect of biochar on root growth, absorption of nitrogen and maize yield. J. Shenyang Agri. Univ. 2016, 47, 218–223. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, X.; Chen, F.; Wu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Wang, J.; Yuan, L.; Mi, G. Genetic improvement of root growth increases maize yield via enhanced post-silking nitrogen uptake. Eur. J. Agron. 2015, 63, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Qu, Z.; Gou, M.; Su, Y.; Huo, X. Effects of biochar amendment on soil water and nutrient utilization efficiencies and tomato growth. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2014, 33, 2187–2193. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, X.; Xue, J.; Zhao, C.; Wu, Y.; Han, F. Nutrient leaching and retention in riparian soils as influenced by rice husk biochar addition. Soil Sci. 2017, 182, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharayeie, P.; Sobhani, A.; Rahimian, M. Effect of different levels of irrigation water and potassium fertilizer on water use efficiency and quality of tomato fruit of petvarli ch. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 2006, 27, 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead, D.C.; Raistrick, N. The volatilization of ammonia from cattle urine applied to soils as influenced by soil properties. Plant. Soil 1993, 148, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omondi, M.O.; Xia, X.; Nahayo, A.; Liu, X.; Korai, P.K.; Pan, G. Quantification of biochar effects on soil hydrological properties using meta-analysis of literature data. Geoderma 2016, 274, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Y.; Han, J. Combination of biochar and nitrogen fertilizer to improve soil aggregate stability and crop yield in Lou soil. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2019, 25, 782–791. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Yan, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, F.; Huang, X. Study on gas exchange parameters and water use efficiency of spring wheat leaves under different levels of water stress. Arid. Zone Res. 2021, 38, 821–832. [Google Scholar]
- Lawson, T.; Blatt, M. Stomatal size, speed, and responsiveness impact on photosynthesis and water use efficiency. Plant Physiol. 2014, 164, 1556–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Wu, L.; Filardo, F.; Yang, X.; Zhao, X.; Fu, D. Chemical and hydraulic signals regulate stomatal behavior and photosynthetic activity in maize during progressive drought. Acta Physiol. Plant 2017, 39, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Liu, M.; Shao, H.; Li, Q.; Shi, L.; Du, F.; Zhang, Z. Investigation on the relationship between leaf water use efficiency and physio-biochemical traits of winter wheat under rained condition. Colloid Surface B 2008, 62, 280–287. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, S.; Dong, Y.; Qi, Y.; Peng, Q.; He, Y.; Liu, X. Effects of mineral fertilizer addition on leaf functional traits and photosynthetic characteristics of Leymus chinensis from a temperate grassland in Inner Mongolia in China. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2010, 30, 2535–2543. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Du, X.; Ma, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, B.; Mao, H. Classification methods for airborne disease spores from greenhouse crops based on multifeature fusion. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
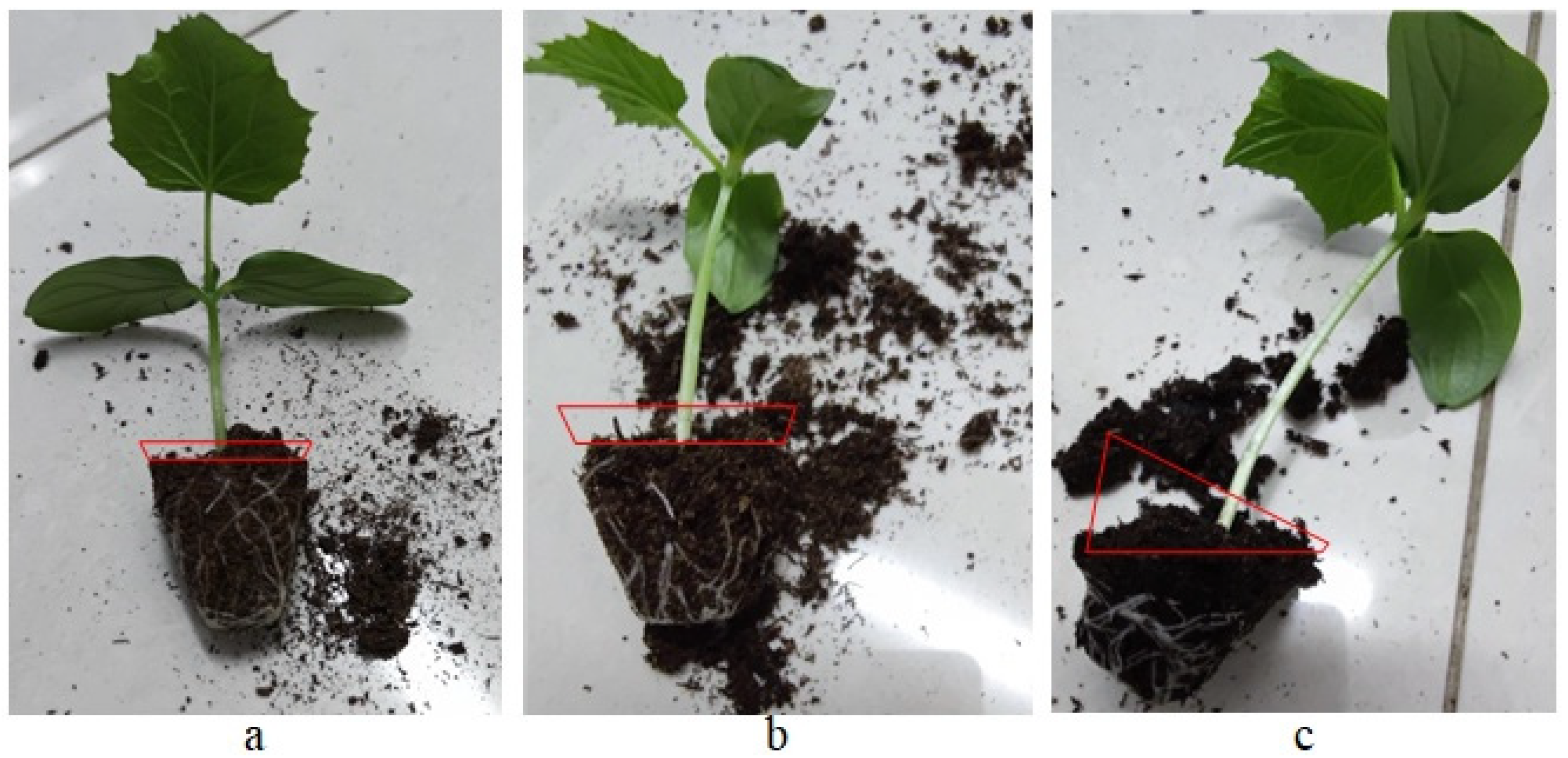
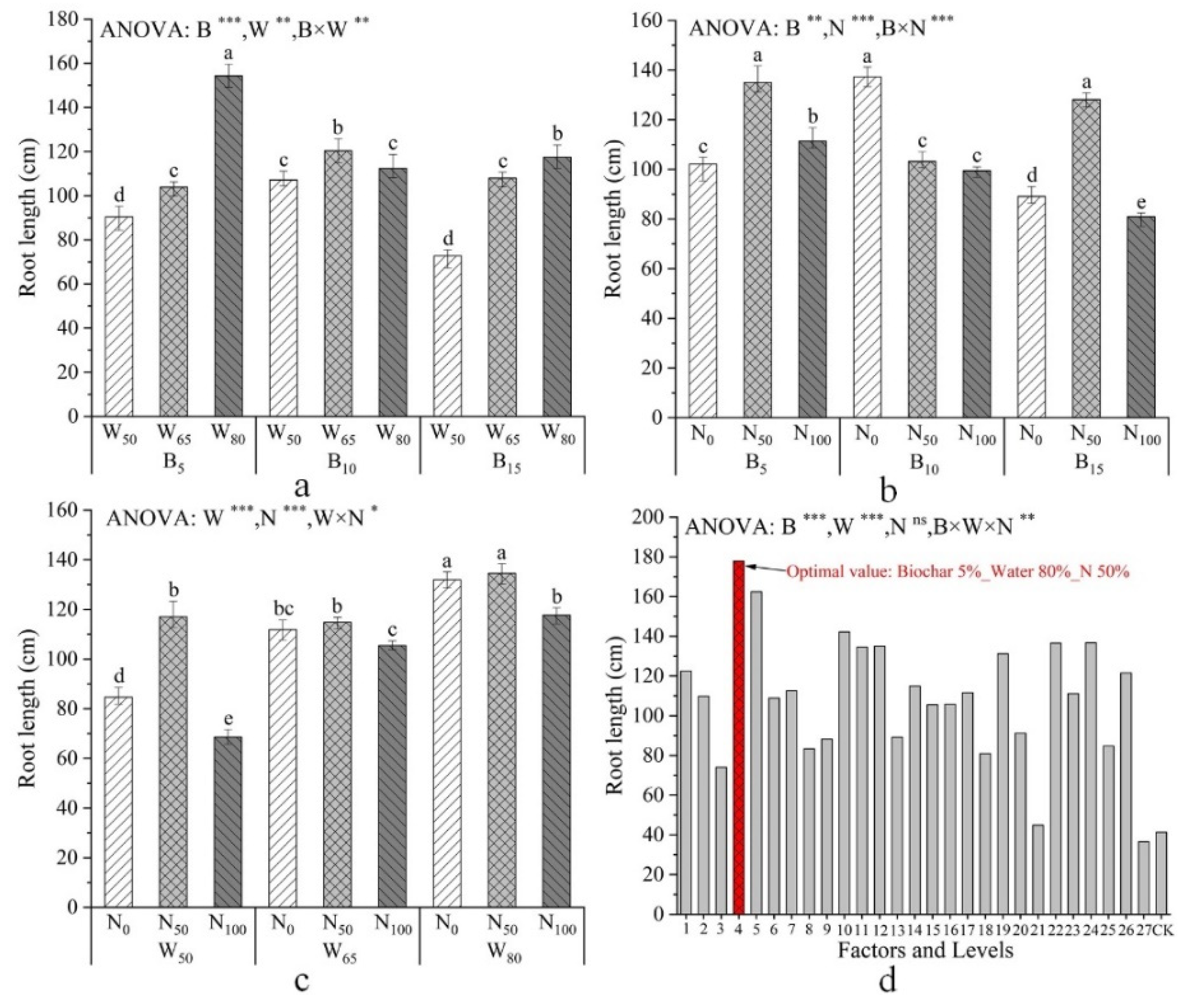

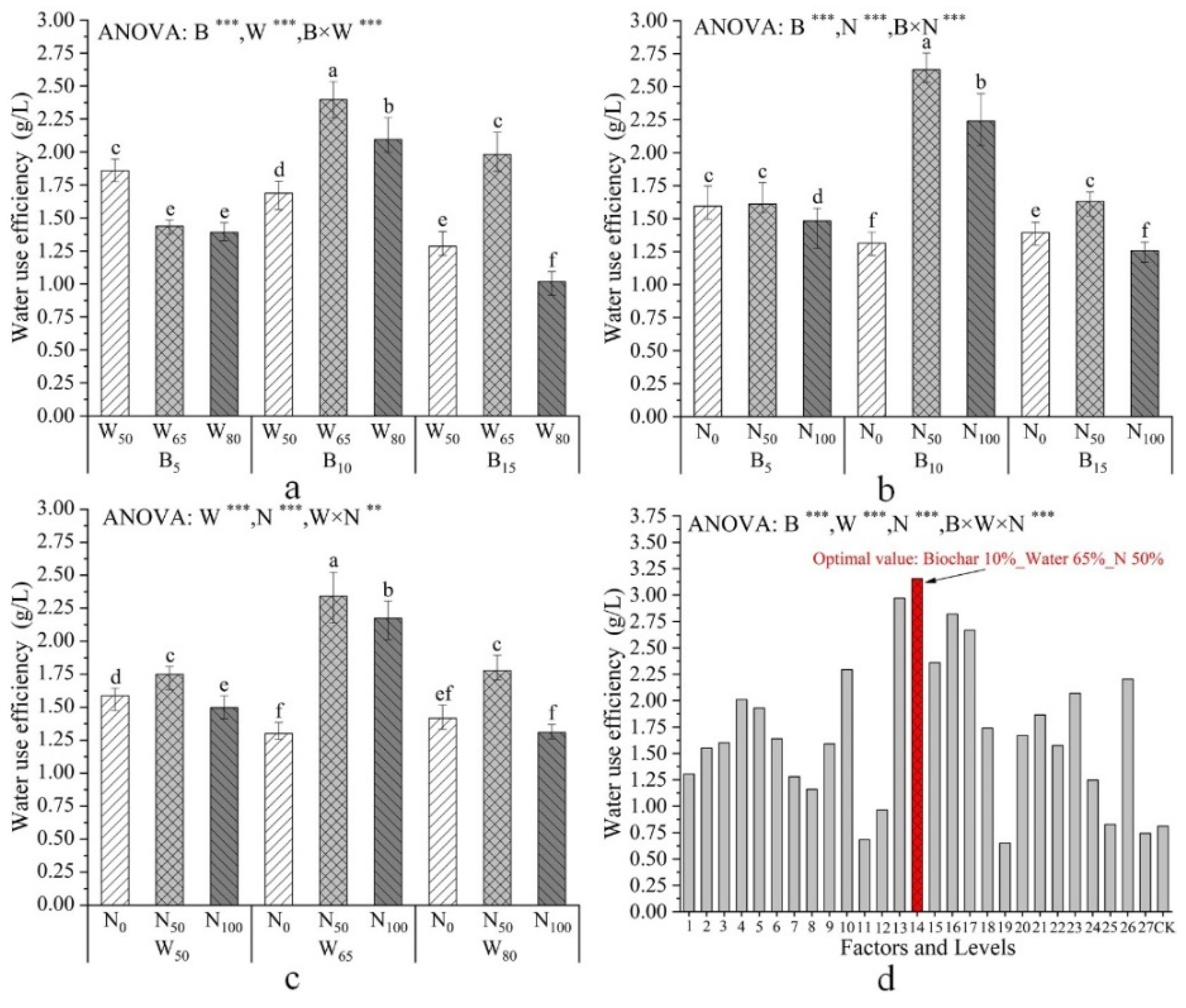
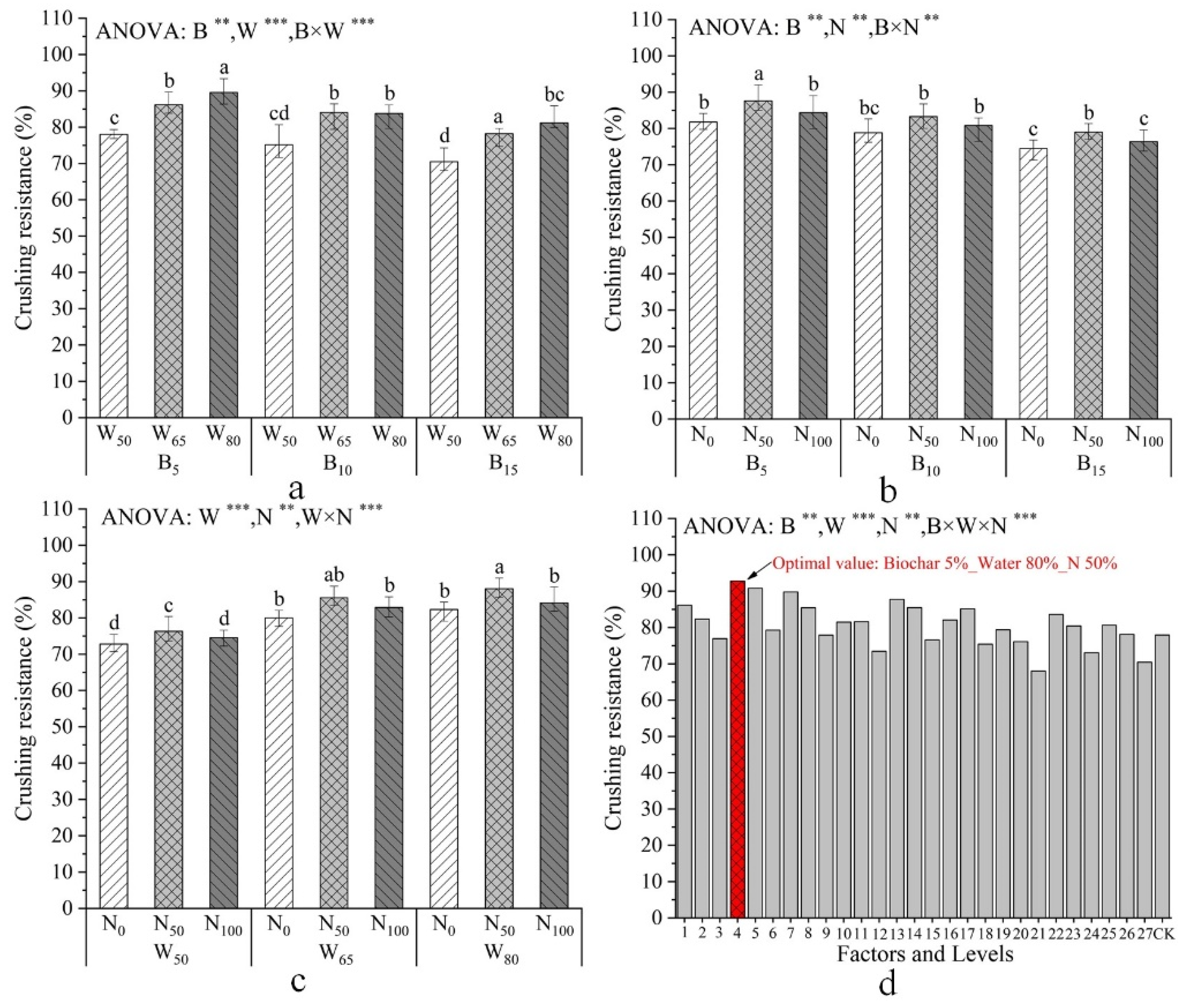

| Factors and Levels | Plant Height /mm | Total Root Length /cm | Total Dry Biomass /g | Specific Root Length /cm·mg−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biochar level (B) | ||||
| B5 | 58.4 a | 116.17 a | 0.0802 a | 23.83 a |
| B10 | 57.6 a | 113.32 a | 0.0778 b | 22.94 a |
| B15 | 52.2 b | 99.39 b | 0.0643 c | 15.27 b |
| Water level (W) | ||||
| W50 | 53.9 b | 95.10 c | 0.0674 b | 15.08 c |
| W65 | 56.4 a | 110.72 b | 0.0778 a | 21.00 b |
| W80 | 57.1 a | 125.07 a | 0.0749 a | 25.97 a |
| Nitrogen level (N) | ||||
| N0 | 55.7 b | 109.49 b | 0.0763 a | 20.54 b |
| N50 | 57.1 a | 122.13 a | 0.0737 a | 24.44 a |
| N100 | 54.4 b | 97.26 c | 0.0732 a | 17.06 c |
| Analysis of variance | ||||
| B | *** | ** | *** | *** |
| W | ** | *** | ** | *** |
| N | * | *** | ns | *** |
| B × W | * | *** | ** | * |
| B × N | *** | *** | ** | *** |
| W × N | ** | * | * | ** |
| B × W × N | *** | ** | ** | *** |
| Factors and Levels | N use Efficiency /% | Water Use Efficiency /g·L−1 | Crushing Resistance /% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biochar level (B) | |||
| B5 | 32.03 a | 1.56 b | 84.59 a |
| B10 | 30.35 a | 2.06 a | 80.99 b |
| B15 | 26.93 b | 1.43 b | 76.63 c |
| Water level (W) | |||
| W50 | 26.42 c | 1.61 b | 74.55 b |
| W65 | 29.84 b | 1.94 a | 83.81 a |
| W80 | 33.06 a | 1.50 b | 84.84 a |
| Nitrogen level (N) | |||
| N0 | --- n | 1.44 c | 78.37 c |
| N50 | 32.32 a | 1.96 a | 83.30 a |
| N100 | 27.23 b | 1.66 b | 80.54 b |
| Analysis of variance | |||
| B | ** | *** | ** |
| W | ** | *** | *** |
| N | *** | *** | ** |
| B×W | *** | *** | *** |
| B×N | *** | *** | ** |
| W×N | * | ** | *** |
| B×W×N | ns | *** | *** |
| Combination of Tests | Average Value /% | Maximum Value /% | Minimum Value /% | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B5–W80–N50 | 91.01 | 92.78 | 90.56 | 0.9582 |
| B5–W65–N50 | 89.38 | 90.41 | 88.15 | 0.9238 |
| B15–W50–N100 | 73.54 | 75.03 | 72.76 | 0.9417 |
| Factors and Levels | Plant Height /mm | Shoot DM /g | Total Root Length /cm | Root DM /g |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biochar level (B) | ||||
| B5 | 234.18 a | 2.033 a | 1150.04 a | 0.108 a |
| B10 | 218.52 b | 1.963 a | 1166.67 a | 0.104 a |
| B15 | 198.59 c | 1.937 b | 982.85 b | 0.077 b |
| Water level (W) | ||||
| W50 | 191.32 c | 1.551 b | 871.47 c | 0.074 b |
| W65 | 217.32 b | 1.837 a | 1157.97 b | 0.096 a |
| W80 | 238.64 a | 1.885 a | 1278.13 a | 0.099 a |
| Nitrogen level (N) | ||||
| N0 | 211.91 b | 1.657 b | 1103.29 b | 0.082 b |
| N50 | 228.39 a | 1.952 a | 1256.99 a | 0.104 a |
| N100 | 194.99 b | 1.625 b | 901.28 c | 0.101 a |
| B0–W100–N0 | ||||
| CK | 140.71 | 1.210 | 652.56 | 0.061 |
| Factors and Levels | Net Photosynthetic Rate /μmol(CO2)m−2s−1 | Transpiration Rate /mmol(H2O)m−2s−1 | Intercellular CO2 Concentration /μmol(CO2)mol−1 | Stomatal Conductance /mmol(H2O)m−2s−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biochar level (B) | ||||
| B5 | 14.55 a | 0.88 a | 195.05 a | 10.20 a |
| B10 | 14.44 a | 0.90 a | 195.20 a | 10.15 a |
| B15 | 14.01 b | 0.84 b | 188.03 b | 9.63 b |
| Water level (W) | ||||
| W50 | 13.51 b | 0.77 b | 192.99 b | 9.69 b |
| W65 | 14.26 a | 0.88 a | 191.37 b | 10.02 a |
| W80 | 14.53 a | 0.90 a | 197.92 a | 10.17 a |
| Nitrogen level (N) | ||||
| N0 | 14.28 a | 0.88 a | 192.70 a | 9.64 b |
| N50 | 14.41 a | 0.89 a | 193.06 a | 10.16 a |
| N100 | 13.83 b | 0.81 b | 185.51 b | 9.49 b |
| B0–W100–N0 | ||||
| CK | 13.16 | 0.75 | 176.83 | 9.13 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, G.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Hu, J.; Han, L.; Mao, H. Effects of Compound Biochar Substrate Coupled with Water and Nitrogen on the Growth of Cucumber Plug Seedlings. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2855. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112855
Ma G, Chen X, Liu Y, Hu J, Han L, Mao H. Effects of Compound Biochar Substrate Coupled with Water and Nitrogen on the Growth of Cucumber Plug Seedlings. Agronomy. 2022; 12(11):2855. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112855
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Guoxin, Xi Chen, Yang Liu, Jianping Hu, Luhua Han, and Hanping Mao. 2022. "Effects of Compound Biochar Substrate Coupled with Water and Nitrogen on the Growth of Cucumber Plug Seedlings" Agronomy 12, no. 11: 2855. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112855
APA StyleMa, G., Chen, X., Liu, Y., Hu, J., Han, L., & Mao, H. (2022). Effects of Compound Biochar Substrate Coupled with Water and Nitrogen on the Growth of Cucumber Plug Seedlings. Agronomy, 12(11), 2855. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112855









