Effect of Urease Inhibitors and Nitrification Inhibitors Combined with Seaweed Extracts on Urea Nitrogen Regulation and Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site and Soils
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Soil and Maize Sampling
2.4. Soil and Plant Analyses
2.5. Calculations and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. The Transformation of N
3.1.1. The Contents of Urea-N in Soils
3.1.2. The Contents of NH4+-N in Soils
3.1.3. The Contents of NO3−-N in Soils
3.2. Soil Nitrification Inhibition Rate of Different Treatments at the Seedling Stage
3.3. The Changes in Enzyme Activity
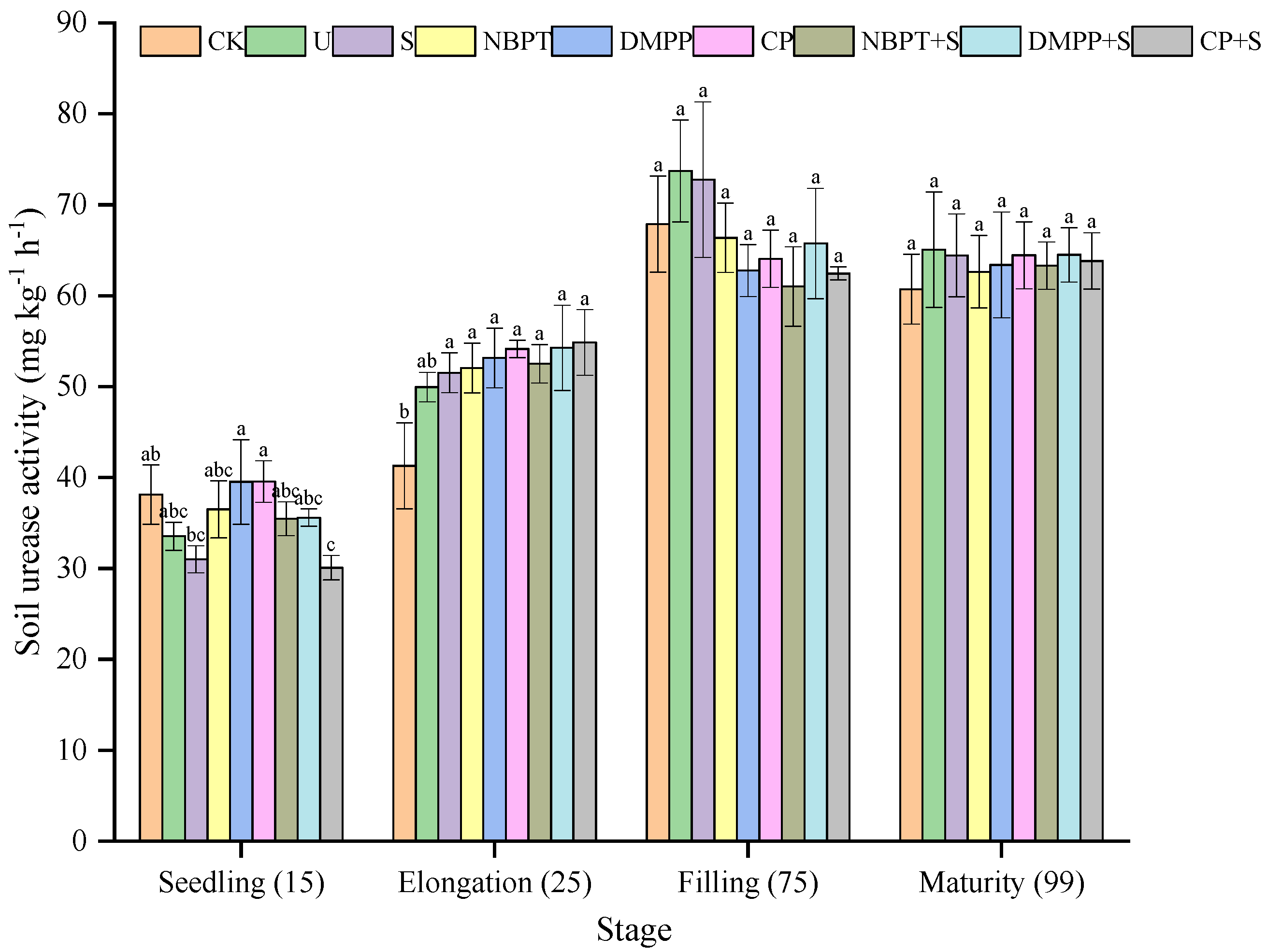
3.3.1. Soil Urease Activity of Different Treatments
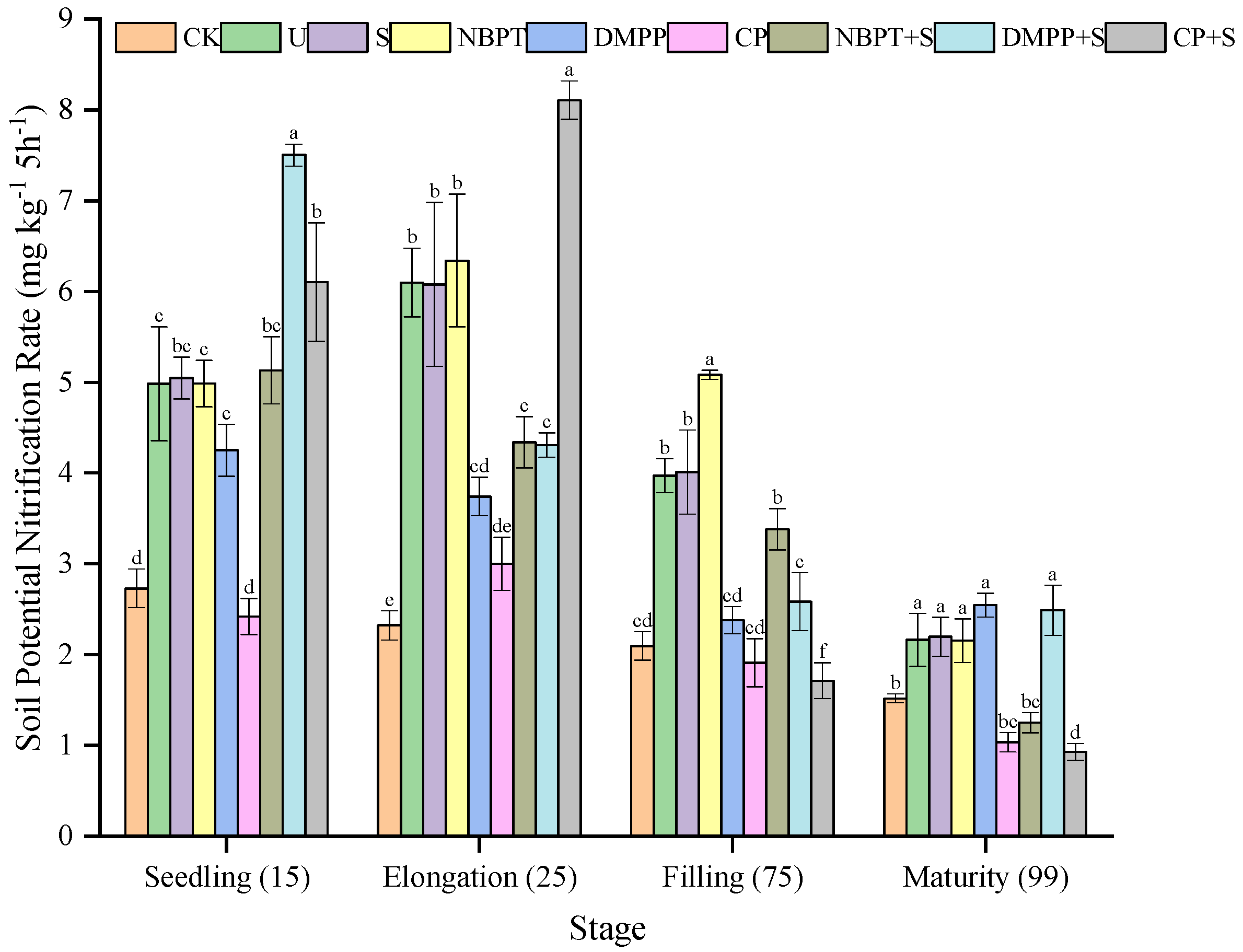
3.3.2. Soil Potential Nitrification Rate (PNR) of Different Treatments
3.3.3. Soil Nitrate Reductase (NR) Activity of Different Treatments
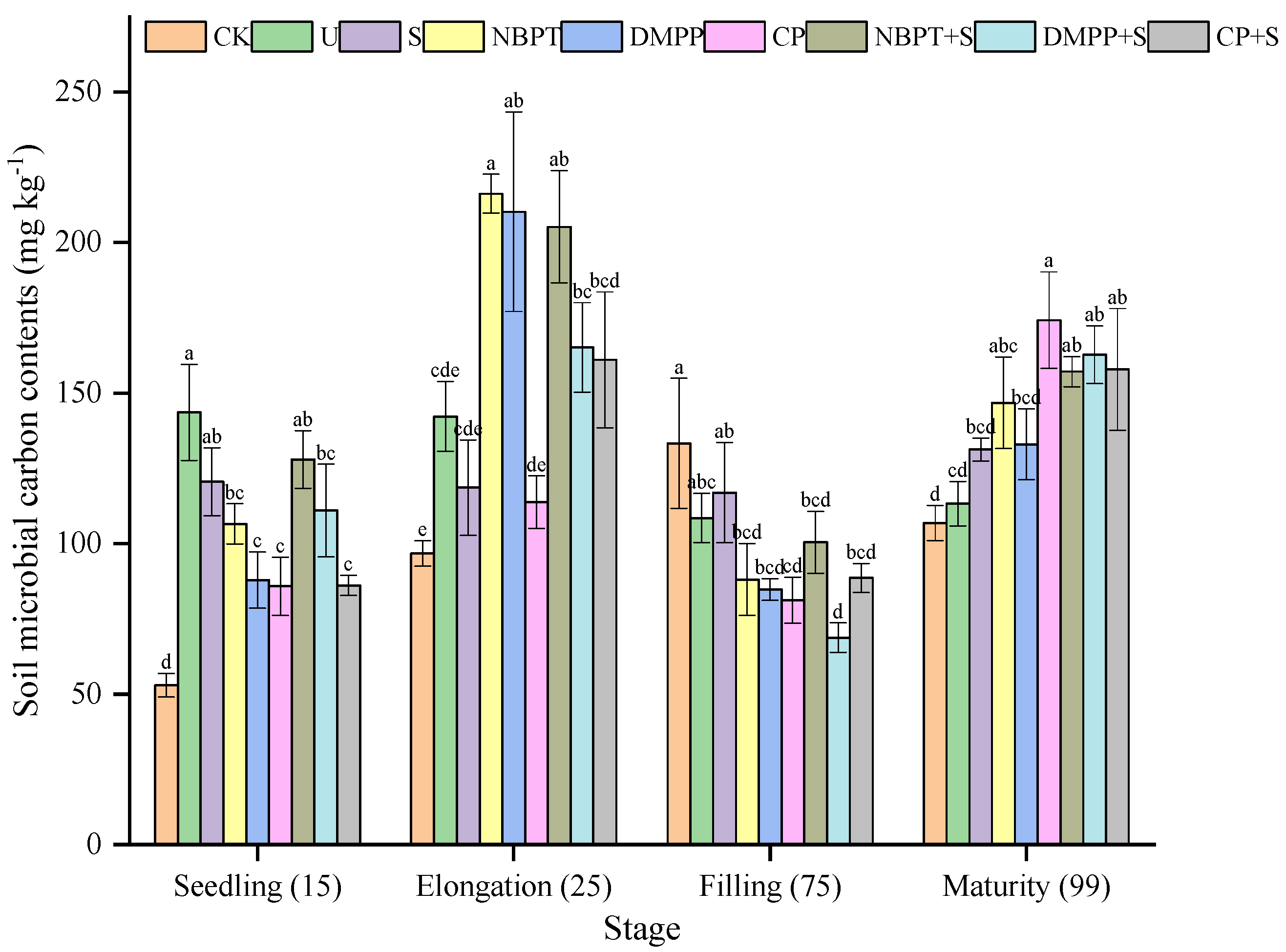
3.4. Soil Microbial Biomass Carbon (MBC) Contents of Different Treatments
3.4.1. Maize Plant Physiological and Biological Indicators of Different Treatments
3.4.2. Maize Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE) of Different Treatments
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of SE and Inhibitors on Soil Biochemical Parameters
4.2. Effects of Inhibitors and SE on Physiological and Biological Indexes of Maize Plants and NUE
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, J.S.; Hu, T.T.; Zhang, B.C.; Wang, L.; Yang, S.H.; Fan, J.L.; Yan, S.C.; Zhang, F.C. Nitrogen fertilizer management effects on soil nitrate leaching, grain yield and economic benefit of summer maize in northwest China. Agr. Water Manag. 2021, 247, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosier, A.R. Environmental challenges associated with needed increases in global nitrogen fixation. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosys. 2002, 63, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.T.; Xing, G.X.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhang, L.J.; Liu, X.J.; Cui, Z.L.; Yin, B.; Christie, P.; Zhu, Z.L.; et al. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, A.G.; Shrawat, A.K.; Muench, D.G. Can less yield more? Is reducing nutrient input into the environment compatible with maintaining crop production? Trends Plant Sci. 2004, 12, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, D.; Britto, D.T.; Shi, W.M.; Kronzucker, H.J. Nitrogen transformations in modern agriculture and the role of biological nitrification inhibition. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.L.; Chen, D.L. Nitrogen fertilizer use in China-Contributions to food production, impacts on the environment and best management strategies. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosys. 2002, 63, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.S.; Niu, S.L. A global analysis of soil acidification caused by nitrogen addition. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, C.S.; Bruulsema, T.W.; Jensen, T.L.; Fixen, P.E. Review of greenhouse gas emissions from crop production systems and fertilizer management effects. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 133, 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manunza, B.; Deiana, S.; Pintore, M.; Gessa, C. The binding mechanism of urea, hydroxamic acid and N-(N-butyl)-phosphoric triamide to the urease active site. A comparative molecular dynamics study. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1999, 31, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacherl, B.; Amberger, A. Effect of the nitrification inhibitors dicyandiamide, nitrapyrin and thiourea on Nitrosomonas-europaea. Fertil. Res. 1990, 22, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannelli, T.; Hooper, A.B. Oxidation of nitrapyrin to 6-chloropicolinic acid by the ammonia-oxidizing bacterium nitrosomo-nas-europaea. Appl. Environ. Microb. 1992, 58, 2321–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalos, D.; Jeffery, S.; Sanz-Cobena, A.; Guardia, G.; Vallejo, A. Meta-analysis of the effect of urease and nitrification inhibitors on crop productivity and nitrogen use efficiency. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 189, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarr, M.A.; Zanatta, J.A.; Dieckow, J.; Ribeiro, R.H.; Rachwal, M.F.G.; Stahl, J. Nitrous oxide and methane emissions from soil and nitrogen uptake by eucalyptus fertilized with enhanced efficiency fertilizers. Plant Soil 2021, 463, 615–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimczyk, M.; Siczek, A.; Schimmelpfennig, L. Improving the efficiency of urea-based fertilization leading to reduction in ammonia emission. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.G.; Chen, Y.X.; Ye, X.Z.; Tian, G.M.; Zhang, Z.J. Influence of the DMPP (3,4-dimethyl pyrazole phosphate) on nitrogen transformation and leaching in multi-layer soil columns. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.G.B.; Sequeira, C.H.; Sermarini, R.A.; Otto, R. Urease inhibitor NBPT on ammonia volatilization and crop productivity: A meta-analysis. Agron. J. 2017, 109, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; Bolan, N.S.; Saggar, S. Impact of urease inhibitor on ammonia and nitrous oxide emissions from temperate pasture soil cores receiving urea fertilizer and cattle urine. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 465, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Li, D.P.; Wu, Z.J.; Xue, Y.; Xiao, F.R.; Zhang, L.L.; Song, Y.C.; Li, Y.H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, J.M.; et al. Effects of nitrification inhibitors on soil nitrification and ammonia volatilization in three soils with different pH. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacinthe, P.A.; Pichtel, J.R. Interaction of nitrapyrin and dicyandiamide with soil humic compounds. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, L.; Ottaiano, L.; Polimeno, F.; Maglione, G.; Amato, U.; Arena, C.; Di Tommasi, P.; Mori, M.; Magliulo, V. Effects of 3,4-dimethylphyrazole phosphate-added nitrogen fertilizers on crop growth and N2O emissions in Southern Italy. Plant Soil Environ. 2013, 59, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, G.; Von Tucher, S.; Schmidhalter, U. Effectiveness of 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate as nitrification inhibitor in soil as influenced by inhibitor concentration, application form, and soil matric potential. Pedosphere 2008, 18, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufeld, J.D.; Knowles, R. Inhibition of nitrifiers and methanotrophs from an agricultural humisol by allylsulfide and its implications for environmental studies. Appl. Environ. Microb. 1999, 65, 2461–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- du Jardin, P. Plant biostimulants: Definition, concept, main categories and regulation. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobek, M.; Frac, M.; Cybulska, J. Plant Biostimulants: Importance of the Quality and Yield of Horticultural Crops and the Improvement of Plant Tolerance to Abiotic Stress-A Review. Agronomy 2019, 9, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.P.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.T.; Chen, L.; Liu, Z.Y.; Wang, X.J.; Yan, P.S.; Qin, S. Responses of soil microbial communities to a short-term application of seaweed fertilizer revealed by deep amplicon sequencing. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 125, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.; Rayirath, U.P.; Subramanian, S.; Jithesh, M.N.; Rayorath, P.; Hodges, D.M.; Critchley, A.T.; Craigie, J.S.; Norrie, J.; Prithiviraj, B. Seaweed Extracts as Biostimulants of Plant Growth and Development. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2009, 28, 386–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craigie, J.S. Seaweed extract stimuli in plant science and agriculture. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011, 23, 371–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasankari, S.; Venkatesalu, V.; Anantharaj, M.; Chandrasekaran, M. Effect of seaweed extracts on the growth and biochemical constituents of Vigna sinensis. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1745–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goni, O.; Quille, P.; O’Connell, S. Ascophyllum nodosum biostimulants and their role in enhancing tolerance to drought stress in tomato plants. Plant Physiol Bioch. 2018, 126, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.S.S.; Fleming, C.; Selby, C.; Rao, J.R.; Martin, T. Plant biostimulants: A review on the processing of macroalgae and use of extracts for crop management to reduce abiotic and biotic stresses. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 465–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.R.; Li, D.P.; Xue, Y.; Song, Y.C.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Y.J.; Li, Y.H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, J.M.; Cui, Y.K. Effect of stability urea combined with laminarin and biochemical inhibitor on rice in black soil and loess. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 36, 352–360. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Juliastuti, S.R.; Baeyens, J.; Creemers, C. Inhibition of nitrification by heavy metals and organic compounds: The ISO 9509 test. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2003, 20, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schollenberger, C.J. Determination of soil organic matter. Soil Sci. 1945, 59, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.J.; Zhang, L.L.; Geisseler, D.; Wu, Z.J.; Gong, P.; Xue, Y.; Yu, C.X.; Juan, Y.H.; Horwath, W.R. Available c and n affect the utilization of glycine by soil microorganisms. Geoderma 2016, 283, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommers, L.E.; Nelson, D.W. Determination of total phosphorus in soils-rapid perchloric-acid digestion procedure. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1972, 36, 902–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.Q.; Zhu, Y.G.; Li, H.Y.; Smith, S.E.; Smith, F.A. Effects of forms and rates of potassium fertilizers on cadmium uptake by two cultivars of spring wheat (triticum aestivum, l.). Environ. Int. 2004, 29, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammon, N. Determination of total potassium and sodium in sandy soils by flame photometer. Soil Sci. 1951, 71, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvaney, R.L.; Bremner, J.M. Modified diacetyl monoxime method for colorimetric determination of urea in soil extracts. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1979, 10, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracken, C.J.; Lanigan, G.J.; Richards, K.G.; Muller, C.; Tracy, S.R.; Grant, J.; Krol, D.J.; Sheridan, H.; Lynch, M.B.; Grace, C.; et al. Sward composition and soil moisture conditions affect nitrous oxide emissions and soil nitrogen dynamics following urea-nitrogen application. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, M.A. Microbiological and Biochemical Properties. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, S.C.; Stark, J.M.; Davidson, E.A.; Firestone, M.K. Nitrogen mineralization, immobilization, and nitrification. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelmagid, H.M.; Tabatabai, M.A. Nitrate reductase-activity of soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.K.; Yan, C.R.; Mei, X.R.; He, W.Q.; Bing, S.H.; Ding, L.P.; Liu, Q.; Liu, S.A.; Fan, T.L. Long-term effect of chemical fertilizer, straw, and manure on soil chemical and biological properties in northwest China. Geoderma 2010, 158, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Li, D.P.; Wu, Z.J.; Zhang, L.L.; Xue, Y.; Gong, P.; Song, Y.C.; Li, X.H.; Xiao, F.R.; Yang, L.J.; et al. Effects of combined nitrification inhibitors on nitrogen transformation, maize yield and nitrogen uptake in two different soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2022, 53, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.L.; Suter, H.C.; Islam, A.; Edis, R. Influence of nitrification inhibitors on nitrification and nitrous oxide (N2O) emission from a clay loam soil fertilized with urea. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Cobena, A.; Misselbrook, T.H.; Arce, A.; Mingot, J.I.; Diez, J.A.; Vallejo, A. An inhibitor of urease activity effectively reduces ammonia emissions from soil treated with urea under Mediterranean conditions. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2008, 126, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiglmayr, K.; Philippot, L.; Hartwig, U.A.; Kandeler, E. Structure and activity of the nitrate-reducing community in the rhizosphere of Lolium perenne and Trifolium repens under long-term elevated atmospheric pCO2. Fems. Microbiol. Ecol. 2004, 49, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiglmayr, K.; Philippot, L.; Kandeler, E. Functional stability of the nitrate-reducing community in grassland soils towards high nitrate supply. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 2980–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.V.; Recous, S.; Stockdale, E.A.; Fillery, I.R.P.; Jensen, L.S.; Hatch, D.J.; Goulding, K.W.T. Gross nitrogen fluxes in soil: Theory, measurement and application of 15N pool dilution techniques. Adv. Agron. 2003, 79, 69–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.J.; Lu, S.B.; Huo, Y.L.; Guan, Z.P.; Liu, B.A.; Wei, W. Do genetically modified plants affect adversely on soil microbial communities? Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 235, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.H.; Guo, X.Y.; Wang, J.H.; Liu, K.L.; Guo, X.D. Study on growth and development rule of different parts of maize root. J. Maize Sci. 2007, 15, 82. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Domanski, G. Carbon input by plants into the soil. Review. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2000, 163, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bais, H.P.; Weir, T.L.; Perry, L.G.; Gilroy, S.; Vivanco, J.M. The role of root exudates in rhizosphere interations with plants and other organisms. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 233–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.L.; Liu, L.L.; Hu, S.J.; Compton, J.E.; Greaver, T.L.; Li, Q.L. How inhibiting nitrification affects nitrogen cycle and reduces environmental impacts of anthropogenic nitrogen input. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, M.; Massimino, D.; Daguenet, A. Daily patterns under life-cycle of a maize crop.2. mineral-nutrition, root respiration and root excretion. Physiol. Plantarum. 1978, 44, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanstaden, J.; Upfold, S.J.; Drewes, F.E. Effect of seaweed concentrate on growth and development of the marigold Tagetes patula. J. Appl. Phycol. 1994, 6, 427–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Sahoo, D. Effect of seaweed liquid extract on growth and yield of Triticum aestivum var. Pusa Gold. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011, 23, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, M.; Bar-Tal, A.; Ofek, M.; Minz, D.; Muller, T.; Yermiyahu, U. The use of biostimulants for enhancing nutrient uptake. Adv. Agron. 2015, 130, 141–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, N.; Henke, C.; Forrestal, P.J. Efficacy of the nitrification inhibitor 3,4 dimethylpyrazol succinic acid (DMPSA) when combined with calcium ammonium nitrate and ammonium sulphate-A soil incubation experiment. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrochano-Monsalve, M.; Gonzalez-Murua, C.; Bozal-Leorri, A.; Lezama, L.; Artetxe, B. Mechanism of action of nitrification inhibitors based on dimethylpyrazole: A matter of chelation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grierson, P.F.; Adams, M.A. Plant species affect acid phosphatase, ergosterol and microbial P in a Jarrah (Eucalyptus marginata Donn ex Sm.) forest in south-western Australia. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, C.G. Seaweed extracts—Unique ocean resource. J. Chem. Educ. 1974, 51, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, E.M.; Oosterhuis, D.M.; Snider, J.L.; Mozaffari, M. Physiological and yield responses of field-grown cotton to application of urea with the urease inhibitor NBPT and the nitrification inhibitor DCD. Eur. J. Agron. 2012, 43, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, A.; Yazar, K.; Sabir, F.; Kara, Z.; Yazici, M.A.; Goksu, N. Vine growth, yield, berry quality attributes and leaf nutrient content of grapevines as influenced by seaweed extract (Ascophyllum nodosum) and nanosize fertilizer pulverizations. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 175, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, F.; Palencia, P.; Alonso, D.; Oliveira, J.A. Advances in the study of nitrification inhibitor DMPP in strawberry. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 226, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behle, R.W.; Wu, S.H.; Toews, M.D.; Duffield, K.R.; Shapiro-Ilan, D.I. Comparing production and efficacy of Cordyceps javanica with Cordyceps fumosorosea. J. Econ. Entomol. 2022, 115, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, R.E.; Towey, B.D.; Gravens, E. Degradation of the urease inhibitor NBPT as affected by soil pH. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2015, 79, 1674–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.R.; Cantarella, H.; Menegale, M.L.D. Ammonia volatilization losses from surface-applied urea with urease and nitrification inhibitors. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 52, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, P.K.; Taggert, B.I.; Chen, D.; Wille, U. Degradation of the Nitrification Inhibitor 3,4-Dimethylpyrazole Phosphate in Soils: Indication of Chemical Pathways. ACS Agric. Sci. Technol. 2021, 1, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, G.; von Tucher, S.; Schmidhalter, U. Influence of soil parameters on the effect of 3,4-dimethylpyrazole-phosphate as a nitrification inhibitor. Biol. Fert. Soils 2001, 34, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
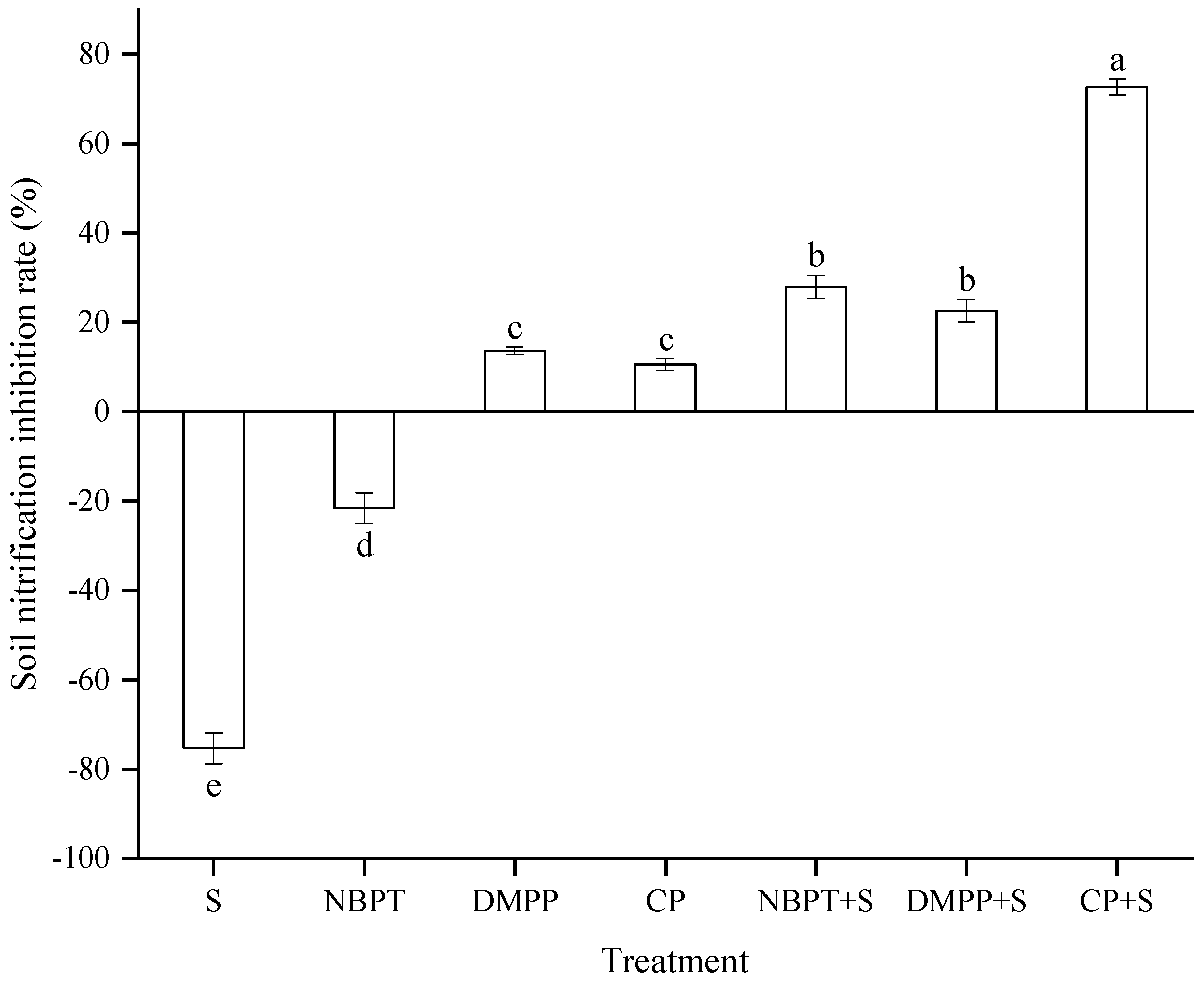

| Soil Type | Texture Class | pH | Organic Matter (g/kg) | Total N (g/kg) | NH4+-N (mg/kg) | NO3−-N (mg/kg) | Total Phosphorus (g/kg) | Available Phosphorus (mg/kg) | Total Potassium (g/kg) | Available Potassium (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| loess | loam | 8.01 | 31.26 | 1.14 | 9.17 | 10.70 | 0.67 | 11.45 | 40.45 | 257.37 |
| Treatments | Seedling (15) | Elongation (25) | Filling (75) | Maturity (99) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 18.8 ± 2.8 c | 13.7 ± 0.24 b | 16.1 ± 2.2 a | 15.9 ± 1.7 a |
| U | 15.1 ± 1.4 c | 13.8 ± 0.6 b | 10.2 ± 0.4 bc | 16.4 ± 2.3 a |
| S | 16.9 ± 2.7 c | 12.3 ± 0.7 b | 7.8 ± 0.6 c | 9.5 ± 0.8 bc |
| NBPT | 17.0 ± 1.9 c | 12.9 ± 2.3 b | 10.5 ± 1.1 bc | 8.2 ± 1.0 c |
| DMPP | 18.0 ± 1.4 c | 14.4 ± 0.4 b | 13.5 ± 2.0 ab | 11.8 ± 1.1 b |
| CP | 255.5 ± 22.7 a | 22.2 ± 2.0 a | 9.7 ± 1.8 bc | 10.8 ± 0.4 bc |
| NBPT + S | 16.8 ± 3.2 c | 14.7 ± 1.7 b | 11.1 ± 1.1 bc | 11.0 ± 0.5 bc |
| DMPP + S | 15.3 ± 1.6 c | 14.2 ± 2.9 b | 13.1 ± 0.7 ab | 17.0 ± 0.4 a |
| CP + S | 93.8 ± 12.2 b | 15.3 ± 0.4 b | 9.8 ± 0.1 bc | 10.8 ± 0.7 bc |
| Treatments | Seedling (15) | Elongation (25) | Filling (75) | Maturity (99) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 15.5 ± 0.6 g | 1.9 ± 0.1 def | 2.3 ± 0.1 d | 3.6 ± 0.2 a |
| U | 298.8 ± 28.9 c | 2.0 ± 0.0 def | 2.8 ± 0.2 d | 3.8 ± 0.2 a |
| S | 532.1 ± 22.8 a | 1.5 ± 0.4 f | 6.4 ± 0.5 b | 2.7 ± 0.1 b |
| NBPT | 363.2 ± 10.2 b | 4.5 ± 0.1 a | 6.3 ± 0.1 b | 2.6 ± 0.3 b |
| DMPP | 258.0 ± 2.6 d | 2.8 ± 0.2 bc | 6.3 ± 0.4 b | 3.7 ± 0.2 a |
| CP | 267.2 ± 3.9 cd | 2.5 ± 0.2 cd | 2.4 ± 0.1 d | 3.4 ± 0.3 a |
| NBPT + S | 215.4 ± 7.9 e | 3.2 ± 0.4 b | 8.3 ± 0.1 a | 2.6 ± 0.1 b |
| DMPP + S | 231.5 ± 7.5 de | 2.4 ± 0.2 cde | 6.2 ± 0.4 b | 3.4 ± 0.3 a |
| CP + S | 81.7 ± 5.3 f | 1.7 ± 0.1 ef | 4.4 ± 0.2 c | 2.3 ± 0.2 b |
| Treatment | Chlorophyll | Leaf Area (cm2) | Hight (cm) | Stalk Thickness (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 7.0 ± 0.3 d | 133.2 ± 2.6 d | 243.3 ± 13.5 b | 17.3 ± 1.6 b |
| U | 27.2 ± 3.7 c | 507.4 ± 24.9 c | 260.3 ± 3.8 ab | 22.0 ± 0.4 a |
| S | 44.7 ± 2.4 ab | 577.0 ± 17.5 bc | 263.3 ± 2.3 ab | 23.1 ± 1.7 a |
| NBPT | 50.6 ± 5.7 ab | 605.0 ± 30.8 ab | 259.0 ± 6.1 ab | 23.4 ± 2.0 a |
| DMPP | 40.6 ± 3.0 b | 638.8 ± 48.1 ab | 263.3 ± 8.5 ab | 23.7 ± 2.9 a |
| CP | 47.9 ± 6.2 ab | 684.6 ± 16.0 a | 270.0 ± 7.0 a | 25.4 ± 1.4 a |
| NBPT + S | 52.8 ± 2.4 a | 598.7 ± 40.6 b | 271.0 ± 3.6 a | 22.0 ± 1.3 ab |
| DMPP + S | 52.4 ± 2.5 a | 624.4 ± 19.6 ab | 275.7 ± 4.0 a | 21.4 ± 1.0 ab |
| CP + S | 53.6 ± 3.2 a | 592.8 ± 23.1 b | 257.0 ± 8.2 ab | 22.4 ± 1.3 a |
| Treatment | Total Biomass (g/Pot) | Grain Yield (g/Pot) | Root Biomass (g/Pot) | Shoot/ Root Ratio | Plant N Uptake (g/Pot) | NUE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 20.3 ± 2.6 d | 9.4 ± 1.0 c | 2.0 ± 0.3 c | 9.3 ± 2.5 d | 0.2 ± 0.0 e | - |
| U | 174.7 ± 7.8 c | 81.5 ± 3.2 b | 11.7 ± 1.4 b | 14.1 ± 2.3 cd | 2.2 ± 0.1 d | 47.0 ± 3.4 d |
| S | 365.7 ± 16.2 ab | 197.8 ± 10.6 a | 12.4 ± 2.3 b | 29.1 ± 5.7 ab | 3.5 ± 0.2 abc | 77.3 ± 4.1 abc |
| NBPT | 376.3 ± 22.9 ab | 176.7 ± 11.7 a | 17.2 ± 3.0 ab | 21.1 ± 2.3 abc | 3.8 ± 0.2 ab | 84.8 ± 4.1 ab |
| DMPP | 339.4 ± 7.8 b | 172.4 ± 9.1 a | 19.4 ± 2.7 a | 16.7 ± 2.0 cd | 3.1 ± 0.2 c | 68.2 ± 4.1 c |
| CP | 398.3 ± 22.9 ab | 200.0 ± 10.8 a | 12.4 ± 1.7 b | 31.7 ± 6.6 a | 3.6 ± 0.1 abc | 80.5 ± 1.9 abc |
| NBPT + S | 349.0 ± 21.5 ab | 172.1 ± 17.1 a | 15.2 ± 2.4 ab | 22.3 ± 3.1 abc | 3.4 ± 0.3 bc | 74.7 ± 7.0 bc |
| DMPP + S | 399.5 ± 35.7 a | 199.2 ± 23.1 a | 19.0 ± 3.0 a | 20.5 ± 4.6 bc | 4.0 ± 0.1 a | 89.1 ± 2.7 a |
| CP + S | 376.5 ± 25.5 ab | 186.8 ± 11.0 a | 16.9 ± 1.9 ab | 21.4 ± 2.0 abc | 3.6 ± 0.3 abc | 80.0 ± 7.9 abc |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, F.; Li, D.; Zhang, L.; Du, Y.; Xue, Y.; Cui, L.; Gong, P.; Song, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Effect of Urease Inhibitors and Nitrification Inhibitors Combined with Seaweed Extracts on Urea Nitrogen Regulation and Application. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2504. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102504
Xiao F, Li D, Zhang L, Du Y, Xue Y, Cui L, Gong P, Song Y, Zhang K, Zhang Y, et al. Effect of Urease Inhibitors and Nitrification Inhibitors Combined with Seaweed Extracts on Urea Nitrogen Regulation and Application. Agronomy. 2022; 12(10):2504. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102504
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Furong, Dongpo Li, Lili Zhang, Yandi Du, Yan Xue, Lei Cui, Ping Gong, Yuchao Song, Ke Zhang, Yiji Zhang, and et al. 2022. "Effect of Urease Inhibitors and Nitrification Inhibitors Combined with Seaweed Extracts on Urea Nitrogen Regulation and Application" Agronomy 12, no. 10: 2504. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102504
APA StyleXiao, F., Li, D., Zhang, L., Du, Y., Xue, Y., Cui, L., Gong, P., Song, Y., Zhang, K., Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, J., & Cui, Y. (2022). Effect of Urease Inhibitors and Nitrification Inhibitors Combined with Seaweed Extracts on Urea Nitrogen Regulation and Application. Agronomy, 12(10), 2504. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102504










