Product Type, Rice Variety, and Agronomic Measures Determined the Efficacy of Enhanced-Efficiency Nitrogen Fertilizer on the CH4 Emission and Rice Yields in Paddy Fields: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
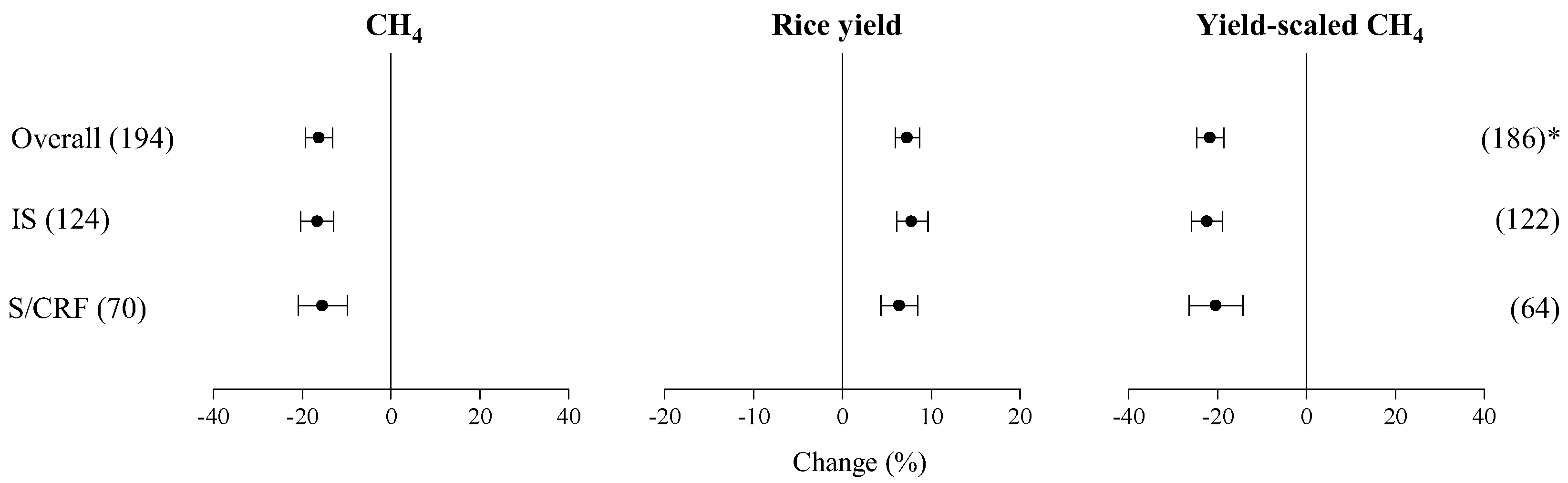
3.1. Overall Effect of EENFs
3.2. Differences among EENF Products
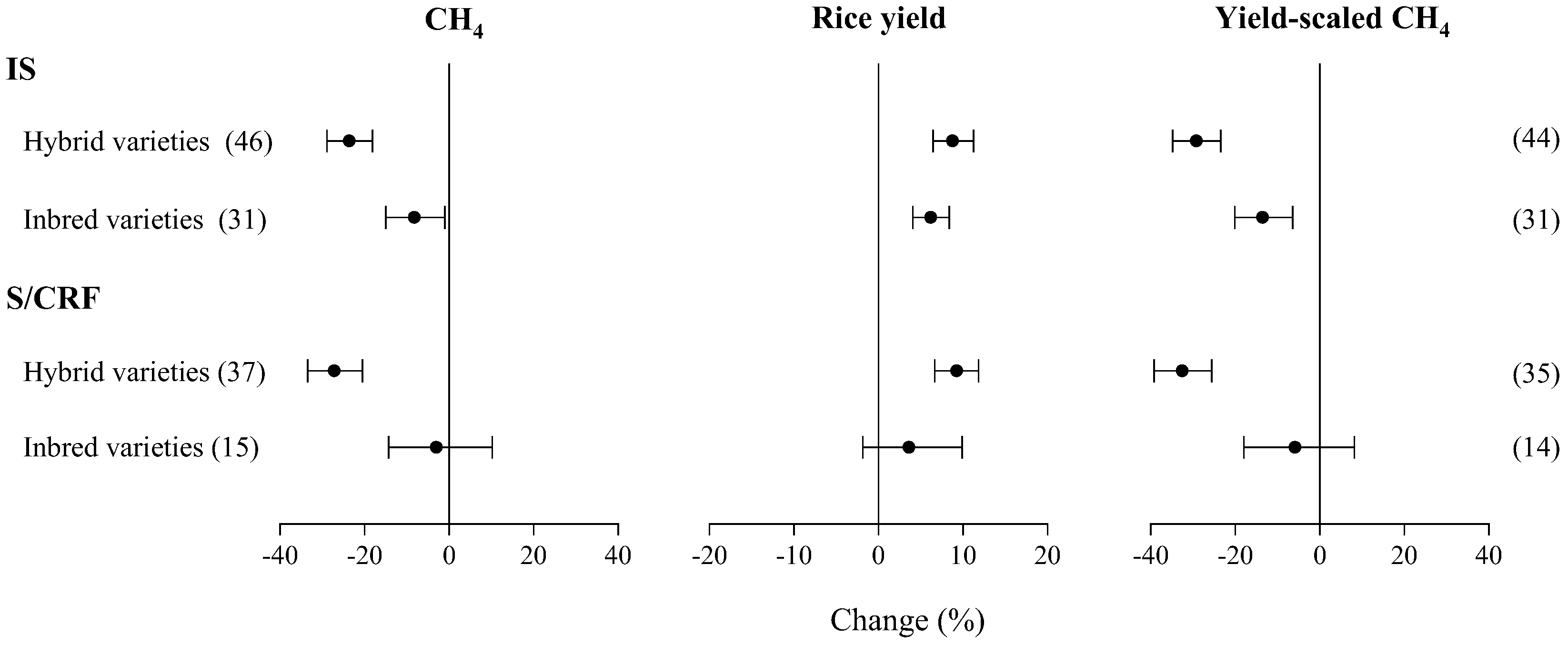
3.3. Impacts of Rice Varieties
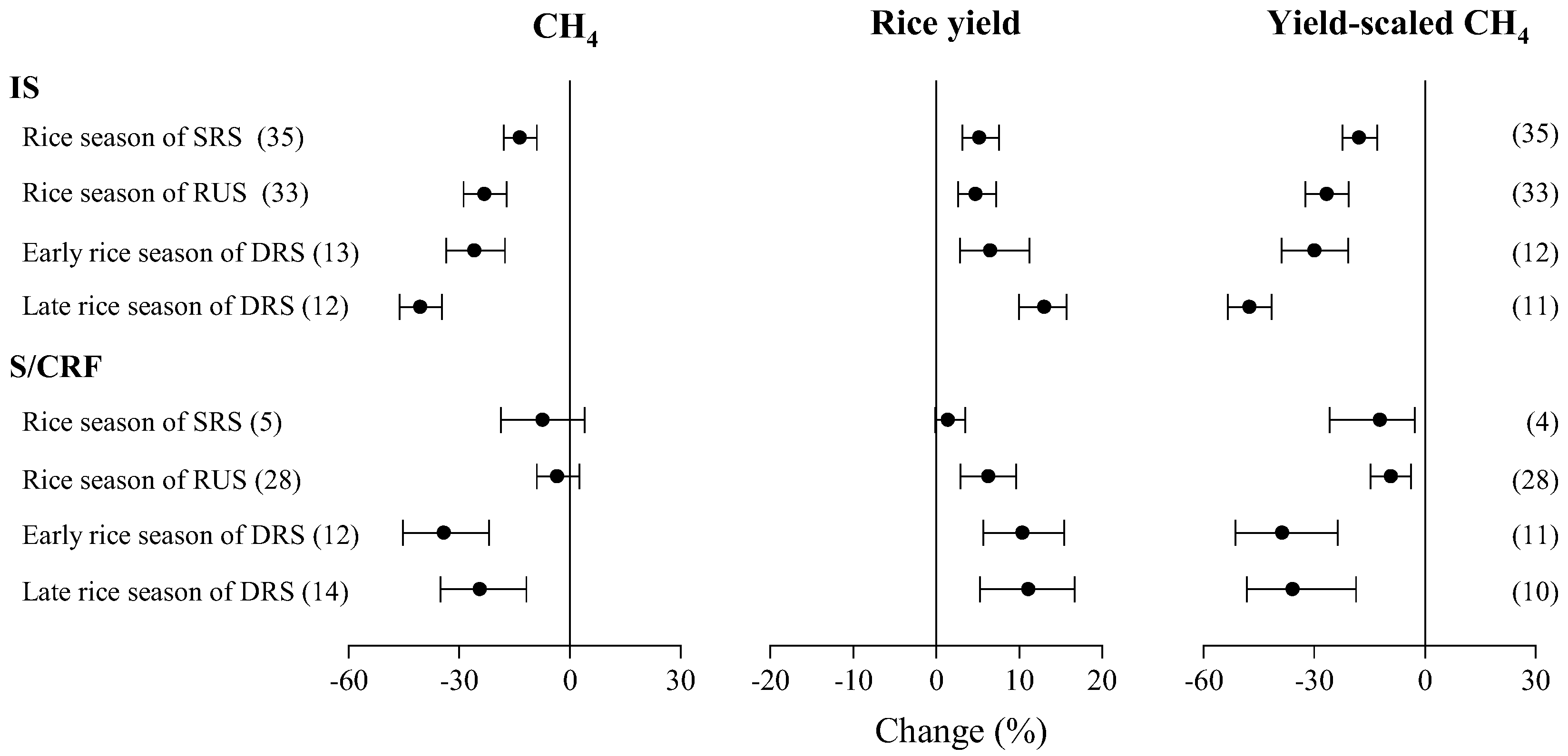
3.4. Impacts of Cropping Systems
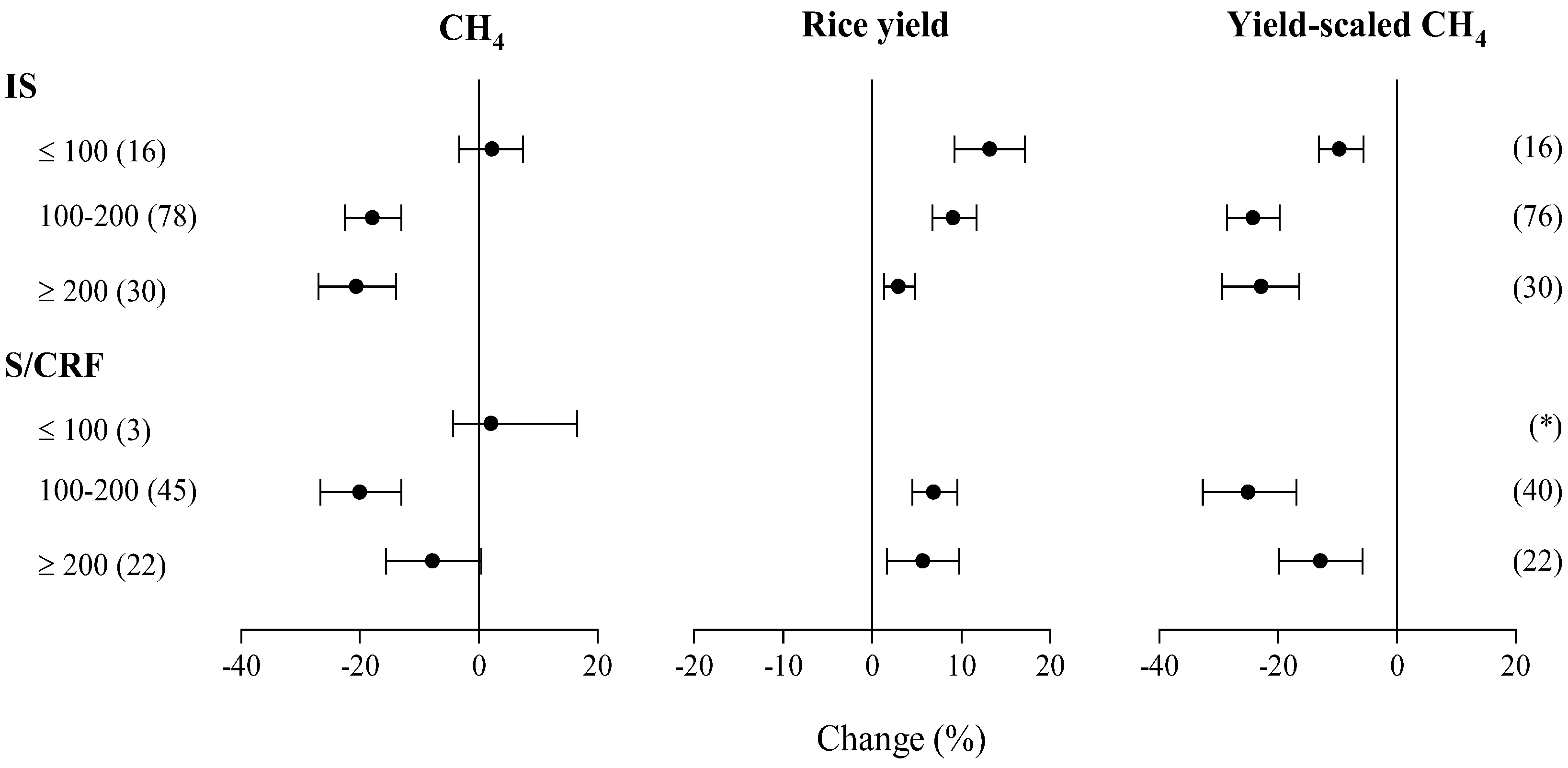
3.5. Impacts of Fertilizer N Application Rates
3.6. Impacts of Water Management Methods
4. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAOSTAT. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data (accessed on 28 October 2021).
- Alexandratos, N.; Bruinsma, J. World Agriculture towards 2030/2050: The 2012 Revision; ESA Working Paper 12-03; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Davidson, E.A.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Searchinger, T.D.; Dumas, P.; Shen, Y. Managing nitrogen for sustainable development. Nature 2015, 528, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladha, J.K.; Tirol-Padre, A.; Reddy, C.K.; Cassman, K.G.; Verma, S.; Powlson, D.S.; van Kessel, C.; de B. Richter, D.; Chakraborty, D.; Pathak, H. Global nitrogen budgets in cereals: A 50-year assessment for maize, rice and wheat production systems. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Shan, Y.; Xu, H. Effects of nitrogen fertilization on CH4 emissions from rice fields. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2007, 53, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Mer, J.; Roger, P. Production, oxidation, emission and consumption of methane by soils: A review. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2001, 37, 25–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dannenberg, S.; Conrad, R. Effect of rice plants on methane production and rhizospheric metabolism in paddy soil. Biogeochemistry 1999, 45, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodelier, P.L.E.; Roslev, P.; Henckel, T.; Frenzel, P. Stimulation by ammonium-based fertilizers of methane oxidation in soil around rice roots. Nature 2000, 403, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banger, K.; Tian, H.; Lu, C. Do nitrogen fertilizers stimulate or inhibit methane emissions from rice fields? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 3259–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halvorson, A.D.; Snyder, C.S.; Blaylock, A.D.; Del Grosso, S.J. Enhanced-Efficiency Nitrogen Fertilizers: Potential Role in Nitrous Oxide Emission Mitigation. Agron. J. 2014, 106, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell, C.J.; Han, K.; Bryant, R.B.; Schmidt, J.P. Nitrous Oxide Emissions with Enhanced Efficiency Nitrogen Fertilizers in a Rainfed System. Agron. J. 2014, 106, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimkpa, C.O.; Fugice, J.; Singh, U.; Lewis, T.D. Development of fertilizers for enhanced nitrogen use efficiency—Trends and perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, H.; Yan, X.; Yagi, K. Evaluation of effectiveness of enhanced-efficiency fertilizers as mitigation options for N2O and NO emissions from agricultural soils: Meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.; Liu, L.; Hu, S.; Compoton, J.E.; Greaver, T.L.; Li, Q. How inhibiting nitrification affects nitrogen cycle and reduces environmental impacts of anthropogenic nitrogen input. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Li, F.; Deng, A.; Feng, X.; Fang, F.; Zhang, W. Integrated assessment of the impact of enhanced-efficiency nitrogen fertilizer on N2O emission and crop yield. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 231, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalos, D.; Jeffery, S.; Sanz-Cobena, A.; Guardia, G.; Vallejo, A. Meta-analysis of the effect of urease and nitrification inhibitors on crop productivity and nitrogen use efficiency. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 189, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Wan, Y.; Qin, X.; Gao, Q.; Liu, S.; Li, J. Modifying nitrogen fertilizer practices can reduce greenhouse gas emissions from a Chinese double rice cropping system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 215, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, A.; Adhya, T. Effects of organic nitrification inhibitors on methane and nitrous oxide emission from tropical rice paddy. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C. Effects of controlled-release fertilizer on rice grain yield, nitrogen use efficiency, and greenhouse gas emissions in a paddy field with straw incorporation. Field Crops Res. 2020, 253, 107814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.K.; Zhang, L.L.; Song, Y.C.; Li, Y.H.; Gong, P.; Wu, Z.J.; Yang, L.J.; Li, D.P. Effects of stabilized N fertilizer combined with straw returning on rice yield and emission of N2O and CH4 in a paddy field. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Yu, H.; Zhang, G.; Xu, H.; Ma, J. Combination of wet irrigation and nitrification inhibitor reduced nitrous oxide and methane emissions from a rice cropping system. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 17426–17436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Wu, Y.-Z.; Tang, S.-R.; Hu, Y.-L.; Lai, Q.-Q.; Wen, D.-N.; Meng, L.; Wu, C.-D. Effects of Different Fertilization Modes on Greenhouse Gas Emission Characteristics of Paddy Fields in Hot Areas. Chin. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 2426–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wu, L.H.; Dai, F.; Dong, C.H. Effects of combined biochemical inhibitors and fertilization models on CH4 and N2O emission from yellow clayey field during rice growth season. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2018, 34, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Liu, T.; Cao, C.; Li, C. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer sources and tillage practices on greenhouse gas emissions in paddy fields of central China. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 144, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.Y.; Yang, Y.T.; Ma, J.; Xu, H.; Lv, S.H.; Yuan, J.; Dong, Y.J. Effect of nitrification inhibitor application on CH4 and N2O emissions from plastic mulching rice fields. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2017, 26, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; Swain, C.; Sethi, S.; Dalai, P.; Bhattachrayya, P.; Kumar, A.; Tripathi, R.; Shahid, M.; Panda, B.; Kumar, U.; et al. Crop establishment and nitrogen management affect greenhouse gas emission and biological activity in tropical rice production. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 104, 80–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Li, Y.E.; Zhou, S.H.; Su, R.R.; Wan, Y.F.; Wang, B.; Cai, W.W.; Guo, C.; Qin, X.B.; Gao, Q.Z.; et al. Synergistic effects of water-saving irrigation, polymer-coated nitrogen fertilizer and urease/nitrification inhibitor on mitigation of greenhouse gas emission from the double rice cropping system. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2016, 49, 3958–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Trinh, M.; Tesfai, M.; Borrell, A.; Nagothu, U.S.; Bui, T.P.L.; Quynh, V.D.; Thanh, L.Q. Effect of organic, inorganic and slow-release urea fertilisers on CH4 and N2O emissions from rice paddy fields. Paddy Water Environ. 2017, 15, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Xu, Z.W.; Wang, B.; Ren, T.; Wan, Y.F.; Zou, J.L.; Lu, J.W.; Li, X.K. Effects of slow/controlled release urea on annual CH4 and N2O emissions in paddy field. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 27, 1489–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Zhu, P.; Li, C.; Liu, C. Inhibitory Effects of 3,4-Dimethylpyrazole Phosphate on CH4 and N2O Emissions in Paddy Fields of Subtropical China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, Y.E.; Wan, Y.F.; Qin, X.B.; Gao, Q.Z. Effect and assessment of controlled release fertilizer and additive treatments on greenhouse gases emission from a double rice field. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2014, 47, 314–323. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Wan, Y.; Wang, B.; Waqas, M.A.; Cai, W.; Guo, C.; Zhou, S.; Su, R.; Qin, X.; et al. Combination of modified nitrogen fertilizers and water saving irrigation can reduce greenhouse gas emissions and increase rice yield. Geoderma 2018, 315, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Ma, Y.H.; Yang, S.Y.; Jiang, B.; Zuo, H.F.; Yan, X.Y.; Ma, J. Effects of different fertilization techniques on the emission of methane and nitrous oxide from single cropping rice. J. Agro-Envrion. Sci. 2013, 32, 2093–2098. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Ma, J.; Yang, Y.; Yu, H.; Song, K.; Dong, Y.; Lv, S.; Xu, H. Achieving low methane and nitrous oxide emissions with high economic incomes in a rice-based cropping system. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 259, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Q.; Tang, S.H.; Pang, Y.W.; Huang, X.; Huang, Q.Y.; Li, P.; Fu, H.T.; Yang, S.H. Emissions of CH4 and N2O from paddy soil in south China under different fertilization patterns. J. Agro-Envrion. Sci. 2014, 33, 2478–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Ren, T.; Li, P.; Wang, B.; Zou, J.; Hussain, S.; Cong, R.; Wu, L.; Lu, J.; Li, X. Producing more grain yield of rice with less ammonia volatilization and greenhouse gases emission using slow/controlled-release urea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 26, 2569–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.X. Effects of Fertilization on Emission of Methane and Nitrous Oxide from Rice—Wheat Rotation Field in Chao Lake Basin. Master’s thesis, Anhui Agricultural University, Hefei, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jumadi, O.; Hartono, H.; Masniawati, A.; Iriany, R.N.; Makkulawu, A.T.; Inubushi, K. Emissions of nitrous oxide and methane from rice field after granulated urea application with nitrification inhibitors and zeolite under different water managements. Paddy Water Environ. 2019, 17, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.W. Shifts in Agricultural Production Regime Effect on Greenhouse Gases (CO2, CH4 and N2O) Emission from Rice-Based Cropping Systems in Southeast China. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, R.Y. Effect of Modified Urea on Emission of Greenhouse Gases from Farmland. Master’s thesis, Southwest Agricultural University, Chongqing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, J.; Shi, Y.; Liang, W.; Wu, J.; Wang, C.; Huang, G. Methane and Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Rice Field and Related Microorganism in Black Soil, Northeastern China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2005, 73, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R. Effects of Easy and Simple Fertilization Modes on Yield Formation Greenhouse Gas Emission of Ratoon Rice LY 6326. Master’s thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Zeng, K.; Song, Y. Biological nitrification inhibitor for reducing N2O and NH3 emissions simultaneously under root zone fertilization in a Chinese rice field. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, H.F. Effects of Different Fertilization Techniques on the Emission of Methane and Nitrous Oxide from the Rice—Wheat Rotation Cropland of Chao Lake Basin. Master’s thesis, Anhui Agricultural University, Hefei, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.-L.; Tang, S.-R.; Tao, K.; He, Q.-X.; Tian, W.; Qing, X.-H.; Wu, Y.-Z.; Meng, L. Effects of Optimizing Fertilization on N2O and CH4 Emissions in a Paddy-Cowpea Rotation System in the Tropical Region of China. Chin. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 5182–5190. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Y.; Liu, G.; Ma, J.; Zhang, G.-B.; Xu, H. Effects of Urea and Controlled Release Urea Fertilizers on Methane Emission from Paddy Fields: A Multi-Year Field Study. Pedosphere 2014, 24, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Fang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, Y.; Liu, S.; Zou, J. Low greenhouse gases emissions associated with high nitrogen use efficiency under optimized fertilization regimes in double-rice cropping systems. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 160, 103846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.F. Effect of Fertilization Management on Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Soil Microbial Properties in Rice—Wheat Rotation System. Master’s thesis, China Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rath, A.K.; Swain, B.; Ramakrishnan, B.; Panda, D.; Adhya, T.; Rao, V.; Sethunathan, N. Influence of fertilizer management and water regime on methane emission from rice fields. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1999, 76, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, T.A.; Fan, X.L. Effects of controlled release fertilizer and straw mulching upland rice on CH4 and N2O emissions from late rice field. J. Northwest A&F Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2015, 43, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Yuan, J.; Luo, J.; Lindsey, S.; Xiang, J.; Lin, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, Z.; Ding, W. Combined application of biochar with urease and nitrification inhibitors have synergistic effects on mitigating CH4 emissions in rice field: A three-year study. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhya, T.; Bharati, K.; Mohanty, S.; Ramakrishnan, B.; Rao, V.; Sethunathan, N.; Wassmann, R. Methane Emission from Rice Fields at Cuttack, India. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2000, 58, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Li, M.; Han, Y.; Deng, O.; Tang, X.; Luo, L.; Zeng, J.; Chen, G.; Yuan, S.; Wang, C.; et al. How are annual CH4, N2O, and NO emissions from rice–wheat system affected by nitrogen fertilizer rate and type? Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 150, 103469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Majumdar, D.; Jain, M. Methane and nitrous oxide emissions from an irrigated rice of North India. Chemosphere 2003, 51, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Zhang, H.; Han, Y.; Deng, O.; Tang, X.; Luo, L.; Zeng, J.; Chen, G.; Wang, C.; Gao, X. Regulating CH4, N2O, and NO emissions from an alkaline paddy field under rice–wheat rotation with controlled release N fertilizer. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 18246–18259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, H.; Prasad, S.; Bhatia, A.; Singh, S.; Kumar, S.; Singh, J.; Jain, M. Methane emission from rice–wheat cropping system in the Indo-Gangetic plain in relation to irrigation, farmyard manure and dicyandiamide application. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 97, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abao, E.B.; Bronson, K.; Wassmann, R.; Singh, U. Simultaneous Records of Methane and Nitrous Oxide Emissions in Rice-Based Cropping Systems under Rainfed Conditions. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2000, 58, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malla, G.; Bhatia, A.; Pathak, H.; Prasad, S.; Jain, N.; Singh, J. Mitigating nitrous oxide and methane emissions from soil in rice–wheat system of the Indo-Gangetic plain with nitrification and urease inhibitors. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Q.; Pang, Y.W.; Yang, S.H.; Lu, Y.S.; Fu, H.T.; Li, P.; Jiang, R.P.; Tang, S.H. Methane and nitrous oxide emissions in paddy field as influenced by fertilization. Eco. Environ. Sci. 2013, 22, 1432–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, H.; Cai, Z.; Yagi, K. Methane and nitrous oxide emissions from rice paddy soil as influenced by timing of application of hydroquinone and dicyandiamide. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2009, 85, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Xie, H.K.; Ding, W.H.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.G.; Li, H. The impacts of CH4 and N2O net emission under one-off fertilization of rape- paddy replanting system. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2018, 51, 3972–3984. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, D.K.; Bhatia, A.; Kumar, A.; Das, T.; Jain, N.; Tomer, R.; Malyan, S.K.; Fagodiya, R.; Dubey, R.; Pathak, H. Mitigation of greenhouse gas emission from rice–wheat system of the Indo-Gangetic plains: Through tillage, irrigation and fertilizer management. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 230, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.V.; Gurevitch, J.; Curtis, P.S. The meta-analysis of response ratios in experimental ecology. Ecology 1999, 80, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, M.S.; Adams, D.C.; Gurevitch, J. Metawin: Statistical Software for Meta-Analysis, version 2.1; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Linquist, B.A.; Adviento-Borbe, M.A.; Pittelkow, C.M.; van Kessel, C.; van Groenigen, K.J. Fertilizer management practices and greenhouse gas emissions from rice systems: A quantitative review and analysis. Field Crop. Res. 2012, 135, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linquist, B.A.; Liu, L.; van Kessel, C.; van Groenigen, K.J. Enhanced efficiency nitrogen fertilizers for rice systems: Meta-analysis of yield and nitrogen uptake. Field Crop. Res. 2013, 154, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Lam, S.K.; Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Tang, Q.; Yan, X. Can knowledge-based N management produce more staple grain with lower greenhouse gas emission and reactive nitrogen pollution? A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsden, K.A.; Marín-Martínez, A.J.; Vallejo, A.; Hill, P.W.; Jones, D.L.; Chadwick, D.R. The mobility of nitrification inhibitors under simulated ruminant urine deposition and rainfall: A comparison between DCD and DMPP. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2016, 52, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tindaon, F.; Benckiser, G.; Ottow, J.C.G. Evaluation of ecological doses of the nitrification inhibitors 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) and 4-chloromethylpyrazole (ClMP) in comparison to dicyandiamide (DCD) in their effects on dehydrogenase and dimethyl sulfoxide reductase activity in soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2012, 48, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Wu, W.; Peng, S.; Shah, F.; Huang, J.; Cui, K.; Liu, H.; Nie, L. Improvement of early seedling growth of dry direct-seeded rice by urease inhibitors application. Aust. J. Crop. Sci. 2012, 6, 525–531. [Google Scholar]
- Aly, S.; Soliman, S.; Ismail, M.; Awad, E.; El-Sherbieny, A. The efficiency of modified urea labelled with N-15 by rice plant. Egypt. J. Soil Sci. 2001, 41, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Hang, X.; Deng, A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W. Aboveground morphological traits do not predict rice variety effects on CH4 emissions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 208, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Gon, H.A.C.D.; Kropff, M.J.; van Breemen, N.; Wassmann, R.; Lantin, R.S.; Aduna, E.; Corton, T.M.; van Laar, H.H. Optimizing grain yields reduces CH4 emissions from rice paddy fields. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12021–12024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Sun, F.; Yuan, S.; Peng, S.; Wang, F. Different mechanisms underlying the yield advantage of ordinary hybrid and super hybrid rice over inbred rice under low and moderate N input conditions. Field Crop. Res. 2018, 216, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L. Hybrid rice in China. In Hybrid Rice Technology; Ahmed, M.I., Viraktamath, B.C., Vijaya, C.H.M., Eds.; Di-rectorate of Rice Research: Hyderabad, India, 1996; pp. 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.-G.; Zhou, X.-Q.; Li, L.-J.; Liu, C.-G.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.-D. Relationship between Root Morphological Characteristics and Yield Components of Major Commercial Indica Rice in South China. Acta Agron. Sin. 2013, 39, 1899–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Qiu, Q.; Lu, Y. Microbial mechanism for rice variety control on methane emission from rice field soil. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 16, 3085–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yuan, S.; Wang, X.; Yu, X.; Peng, S. High yields of hybrid rice do not require more nitrogen fertilizer than inbred rice: A meta-analysis. Food Energy Secur. 2021, 10, e276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Lei, T.; Cao, F.; Chen, J.; Shan, S.; Zou, Y. Grain yield responses to nitrogen rate in two elite double-cropped inbred rice cultivars released 41 years apart. Field Crop. Res. 2020, 259, 107970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Huang, Y.; Jia, B.; Wang, S.; Dou, F.; Samonte, S.O.P.; Chen, K.; Wang, Y. Optimization of Nitrogen Rate and Planting Density for Improving the Grain Yield of Different Rice Genotypes in Northeast China. Agronomy 2019, 9, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Z.; Deng, A.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, W. Impacts of cropping practices on yield-scaled greenhouse gas emissions from rice fields in China: A meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 164, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Yu, H.; Huang, C.; Li, D.; Zhang, H.; Jia, Y.; Wang, G.; Xi, B. Discrepant responses of methane emissions to additions with different organic compound classes of rice straw in paddy soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Hang, X.; Lamine, S.M.; Jiang, Y.; Afreh, D.; Qian, H.; Feng, X.; Zheng, C.; Deng, A.; Song, Z.; et al. Interactive effects of straw incorporation and tillage on crop yield and greenhouse gas emissions in double rice cropping system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 250, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussoline, W.; Esposito, G.; Giordano, A.; Lens, P.N.L. The Anaerobic Digestion of Rice Straw: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 43, 895–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, B.; Opoku, A.; De Neve, S.; Boeckx, P.; Van Cleemput, O.; Hofman, G. Influence of DCD and DMPP on soil N dynamics after incorporation of vegetable crop residues. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2006, 43, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Li, J.; Guan, Y.; Liang, Y.; Hu, B.; Lv, J.; Chu, G. Effects of urease and nitrification inhibitors on the soil mineral nitrogen dynamics and nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions on calcareous soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 9155–9164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inselsbacher, E.; Umana, N.H.-N.; Stange, F.C.; Gorfer, M.; Schüller, E.; Ripka, K.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S.; Hood-Novotny, R.; Strauss, J.; Wanek, W. Short-term competition between crop plants and soil microbes for inorganic N fertilizer. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronson, E.L.; Helliker, B.R. Methane flux in non-wetland soils in response to nitrogen addition: A meta-analysis. Ecology 2010, 91, 3242–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaviv, A. Advances in controlled-release fertilizers. Adv. Agron. 2001, 71, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Song, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, W.; Li, S.; Yu, Y. The characteristics of yield-scaled methane emission from paddy field in recent 35-year in China: A meta-analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 161, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Boeckx, P.; Van Cleemput, O.; Zhou, L. Urease and nitrification inhibitors to reduce emissions of CH4 and N2O in rice production. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2002, 64, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
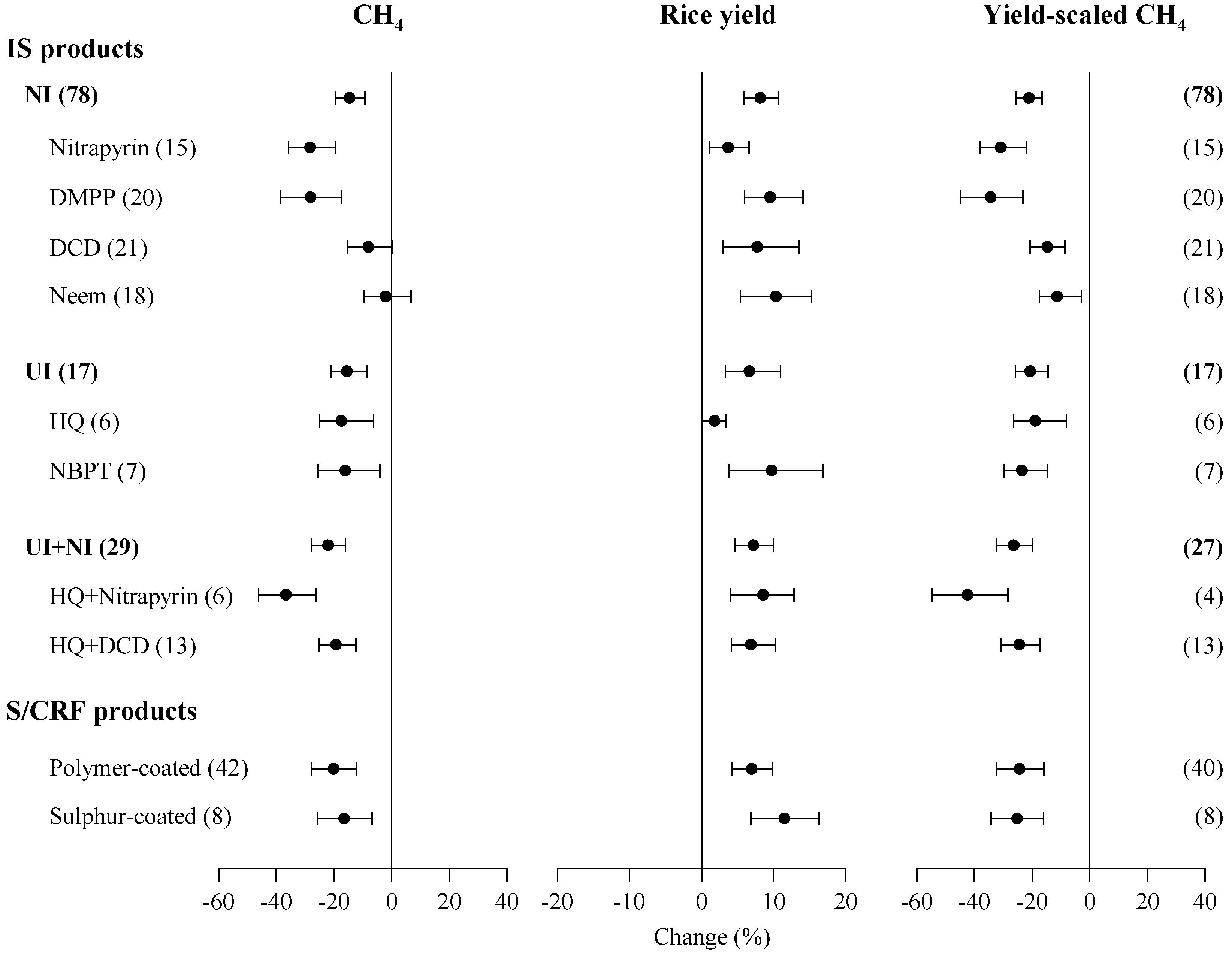

| Id | Country | Number of Comparisons | Type of EENF | Reference | Id | Country | Number of Comparisons | Type of EENF | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | China | 2 | UI + NI | [20] | 24 | China | 4 | NI | [21] |
| 2 | China | 2 | UI + NI | [22] | 25 | China | 12 | NI, S/CRF | [17] |
| 3 | China | 10 | UI, NI, UI + NI | [23] | 26 | China | 2 | S/CRF | [24] |
| 4 | China | 2 | NI | [25] | 27 | India | 8 | NI | [26] |
| 5 | China | 4 | UI + NI, S/CRF | [27] | 28 | Vietnam | 4 | UI | [28] |
| 6 | China | 2 | NI, S/CRF | [29] | 29 | China | 7 | NI | [30] |
| 7 | China | 8 | NI, UI + NI, S/CRF | [31] | 30 | China | 4 | UI + NI, S/CRF | [32] |
| 8 | China | 2 | UI, S/CRF | [33] | 31 | China | 8 | NI, UI + NI, S/CRF | [34] |
| 9 | China | 6 | UI, S/CRF | [35] | 32 | China | 12 | NI, S/CRF | [36] |
| 10 | China | 2 | UI, S/CRF | [37] | 33 | Indonesia | 6 | NI, S/CRF | [38] |
| 11 | China | 6 | UI + NI, S/CRF | [39] | 34 | China | 4 | S/CRF | [19] |
| 12 | China | 3 | NI, UI + NI, S/CRF | [40] | 35 | China | 1 | S/CRF | [41] |
| 13 | China | 14 | NI, S/CRF | [42] | 36 | China | 3 | NI, UI + NI | [43] |
| 14 | China | 2 | UI, S/CRF | [44] | 37 | China | 1 | UI + NI | [45] |
| 15 | China | 4 | S/CRF | [46] | 38 | China | 2 | S/CRF | [47] |
| 16 | China | 1 | S/CRF | [48] | 39 | India | 2 | NI, S/CRF | [49] |
| 17 | China | 1 | S/CRF | [50] | 40 | China | 9 | UI, NI, UI + NI | [51] |
| 18 | India | 2 | NI | [52] | 41 | China | 4 | S/CRF | [53] |
| 19 | India | 3 | NI | [54] | 42 | China | 4 | S/CRF | [55] |
| 20 | India | 2 | NI | [56] | 43 | Philippines | 1 | S/CRF | [57] |
| 21 | India | 4 | UI, NI | [58] | 44 | China | 2 | S/CRF | [59] |
| 22 | China | 3 | UI + NI | [60] | 45 | China | 1 | S/CRF | [61] |
| 23 | India | 6 | NI | [18] | 46 | India | 2 | NI | [62] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, T.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Xu, C.; Fang, F.; Li, F. Product Type, Rice Variety, and Agronomic Measures Determined the Efficacy of Enhanced-Efficiency Nitrogen Fertilizer on the CH4 Emission and Rice Yields in Paddy Fields: A Meta-Analysis. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2240. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102240
Yang T, Wang M, Wang X, Xu C, Fang F, Li F. Product Type, Rice Variety, and Agronomic Measures Determined the Efficacy of Enhanced-Efficiency Nitrogen Fertilizer on the CH4 Emission and Rice Yields in Paddy Fields: A Meta-Analysis. Agronomy. 2022; 12(10):2240. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102240
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Tong, Mengjie Wang, Xiaodan Wang, Chunchun Xu, Fuping Fang, and Fengbo Li. 2022. "Product Type, Rice Variety, and Agronomic Measures Determined the Efficacy of Enhanced-Efficiency Nitrogen Fertilizer on the CH4 Emission and Rice Yields in Paddy Fields: A Meta-Analysis" Agronomy 12, no. 10: 2240. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102240
APA StyleYang, T., Wang, M., Wang, X., Xu, C., Fang, F., & Li, F. (2022). Product Type, Rice Variety, and Agronomic Measures Determined the Efficacy of Enhanced-Efficiency Nitrogen Fertilizer on the CH4 Emission and Rice Yields in Paddy Fields: A Meta-Analysis. Agronomy, 12(10), 2240. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12102240





