Abstract
Nitrogen is one of the essential nutrients for rape growth and development, of which the demand is large. In order to reveal the response of rhizosphere microbial diversity on oilseed rape to the nitrogen fertilizer, four nitrogen application rates of N (170 kgN/hm2), N50% (85 kgN/hm2), N70% (119 kgN/hm2) and N150% (255 kgN/hm2) were set. The diversity and community structure of soil bacteria and fungi in seedling, flowering and mature stages of oilseed rape were analyzed based on the high-throughput sequencing technology. The results of rhizosphere soil microbial analysis showed that the dominant bacteria phyla were Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, Acidobacteria, Bacteroidetes and Cyanobacteria. The dominant fungi phyla were Ascomycota, Olpidiomycota and Basidiomycota. NMDS analysis showed that the community structure of soil bacteria and fungi changed significantly under nitrogen treatment. Cluster analysis showed that the bacteria at seedling and flowering stage had little effect under the condition of less nitrogen application, while the fungi had little effect on the rhizosphere soil microbial flora at flowering stage. At seedling stage, the diversity and richness of bacterial community in the rhizosphere of oilseed rape were lower under low nitrogen application (85 kgN/hm2). Bacteria and fungi in the rhizosphere soil of flowering oilseed rape maintained a higher community diversity under the condition of high nitrogen (255 kgN/hm2). The diversity of rhizosphere bacterial community was higher under conventional N application than under other N application.
1. Introduction
As an important oil crop, oilseed rape is widely planted in the world. It is not only an important source of edible oil, but also an important raw material of biomass energy. It was found that incorporating oilseed rape into the rotation system could significantly increase the yield of subsequent crops [1,2]. Oilseed rape planting is highly dependent on fertilizer, and proper application of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizer can significantly improve the yield components of winter oilseed rape to achieve yield increase, among which nitrogen has the most comprehensive and significant effect [3,4]. In the case of oilseed rape planting without nitrogen fertilizer, the yield of direct seeding winter oilseed rape decreased by 78.7% and that of transplanting winter oilseed rape decreased by 66.7%, and direct seeding winter oilseed rape was more sensitive to nitrogen deficiency [3]. Compared with normal fertilization, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium deficiency in direct seeding of winter oilseed rape decreased seed yield by 61%, 38.3% and 14.4%, respectively [4]. Among the N, P, and K nutrients, the absolute yield reduction of winter oilseed rape caused by N deficiency was the highest. Nitrogen is mainly absorbed by inorganic salt ions and a small amount of amino acids, polypeptides, or proteins from the soil solution by the root hairs in the mature area of root tips [5,6] and transported to the aboveground. Adequate nitrogen nutrition is very important to maintain plant photosynthesis and growth. Nitrogen is one of the essential nutrients for the growth and development of oilseed rape with a large demand [7], and winter oilseed rape has a high demand for nitrogen [8,9].
Oilseed rape is a crop with large nitrogen demand, and sufficient nitrogen supply can effectively promote photosynthesis of oilseed rape, increase dry matter accumulation and nitrogen absorption of plant, and increase the number of branches and pod so as to improve grain yield, which is an important guarantee for high and stable yield of oilseed rape [8,10,11]. Nitrogen uptake in oilseed rape is mainly at the pre-anthesis and flowering stage, and the amount of nitrogen uptake after anthesis is significantly reduced. During pod development, 73% of nitrogen comes from the transfer of leaf, stem and root system [12]. Studies have shown that the yield of oilseed rape is closely related to the rate of material accumulation from seedling stage to pre-flowering stage [13,14]. In the latter stage of oilseed rape, the leaf is deleafed, and the yield and harvest index of two oilseed rape varieties with different nitrogen efficiency types are significantly reduced [15]. It is concluded that nitrogen accumulation before anthesis and nitrogen transfer after anthesis are of great significance to the formation of oilseed rape yield. Li et al. [16] applied nitrogen fertilizer in different growth stages of oilseed rape, and found that the application of nitrogen fertilizer before sowing had the most obvious effect on oilseed rape yield increase. Fatty acid composition of oilseed rape is mainly determined by the characteristics of varieties, but also affected by nitrogen application to a certain extent [17,18].
Soil microorganisms are an important factor affecting soil ecological processes, closely related to soil nutrient cycling, decomposition of organic matter, and transformation of carbon, nitrogen and other elements [19,20,21], and play an important role in maintaining soil quality and ecosystem stability. Soil nitrogen mineralization is affected by soil temperature, moisture, soil properties (microorganisms, soil pH, aeration, etc.) [22,23,24]. Microorganisms as the most active components of soil ecosystem, play an important role in plant growth and development and community succession. Studies have shown that soil microorganisms can interact with the roots of crops, and changes in their quantity and species directly affect plant growth and soil quality, while plant species and planting methods also have a stable impact on the structure and function of soil microbial community [25,26,27]. At the same time, soil microbial community structure is an important indicator reflecting soil fertility and health status [28,29,30]. Therefore, soil microbial community determines and promotes the material circulation and energy flow of farmland soil ecosystem. The functional diversity of soil microorganisms, the range of functions that soil microbial communities can perform and the implementation process of these functions are closely related to soil functions, and are of great significance to soil ecological functions and natural element circulation.
Rhizosphere is the closest surface between plant and soil, and it is also the place where plant roots, soil, microorganisms and environment interact. The change of rhizosphere microbial community structure and functional diversity resulted in the decrease of beneficial microorganisms and the increase of fungal diseases, leading to crop yield reduction [31]. Crop growth period is also one of the factors affecting the abundance of key microbial functional genes in soil [32,33]. Nutrient requirements and different types of root exudates at different growth stages are the important reasons for the difference in microbial abundance. Because different crops release different types and quantities of secretions from their roots during the growth process, crop growth will have specific effects on soil microorganisms [34]. Studies have shown that the inoculation of S.rhizophila, R.sphaeroides, and B.amyloliquefaciens in oilseedrape rhizosphere soil can promote ammoniation, promote the conversion of organic nitrogen to inorganic nitrogen, and significantly increase the total nitrogen content of the plant [35]. The addition of rhizosphere growth-promoting bacteria can enhance the ability of plants to obtain nutrients by stimulating root growth, dissolving soil insoluble phosphorus and fixing nitrogen [36,37].
In recent years, studies on functional diversity of microbial communities in oilseed rape rhizosphere soil have found that oilseed rape rhizosphere bacteria can improve the ability of oilseed rape rhizosphere remediation, promote the degradation of the pollutant phenol, and improve the remediation efficiency of Cd, Pb and Zn contaminated soil [38,39,40,41]. However, there are a few studies on functional diversity of microbial communities in the rhizosphere soil of oilseed rape under nitrogen application during cultivation. The study on the diversity of rhizosphere soil microflora of oilseed rape will provide great importance for rational application of nitrogen fertilizer, improvement of rhizosphere microflora composition and promotion of growth and development of oilseed rape.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The tested oilseed rape was winter oilseed rape XY15(Brassica napus L.), which was provided by Hunan Branch of National Oilseed Crops Improvement Center. The experiment was carried out in Yunyuan Teaching and Experimental Base of Hunan Agricultural University (26°10′ N, 119°23′ E) from October 2019 to June 2020. The experimental soil was field soil. In the experimental field, rice and oilseed rape were rotated in irrigated and upland fields all the year round. The soil pH was 5.65, total nitrogen 1.98 g/kg, alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen 127.90 mg/kg, available phosphorus 43.10 mg/kg, available potassium 137.51 mg/kg and organic matter 23.83 g/kg. The fertilizers used in the study are carbamide (N 46%), superphosphate (P2O5 12%), and muriate (K2O 60%).
2.2. Test Design
Using potted planting, four treatments were set up, i.e., conventional nitrogen application (170 kgN/hm2; N), 50% routine nitrogen application (85 kgN/hm2; N50%), 70% conventional nitrogen application (119 kgN/hm2; N70%), and high nitrogen fertilization (255 kgN/hm2; N150%), 1.96 g, 0.98 g, 1.372 g, and 2.94 g carbamide were applied to each basin. One plant of oilseed rape was planted in each pot, and nine pots were planted in each treatment, a total of 36pots.Except for the differences in the dosage of nitrogen fertilizer, the use amount of phosphate fertilizer and potassium fertilizer are constant—90 kg P2O5/hm2 of phosphate and 120kg K2O /hm2 of potassium that are evenly applied into the pot as the form of base manure.
The top diameter of the pot is 28 cm, the bottom diameter is 20 cm, and the height is 18 cm. The pot is filled with 6 kg of screened air-dried soil. The bottom of the basin is sealed to prevent water and nutrients from leaching away. The oilseeds were sowed on 11 October, and one robust seedling was transplanted in each pot on 8 November.During oilseed rape growth, transparent baffle was used to block rain, according to the soil moisture, ensuring appropriate watering.
2.3. Sampling
The rhizosphere soil was sampled at the seedling stage (90 days after sowing), flowering stage (161 days after sowing) and pod maturity stage (202 days after sowing). Three pots of rhizosphere soil were collected for each stage and each treatment. Only rhizosphere soil was collected. When oilseed rape was pulled out, the soil close to the root surface was gently peeled off with aseptic scissors. The rhizosphere soil was immediately taken back to the laboratory and stored in a refrigerator at 4 °C for the determination of rhizosphere soil microorganisms.
2.4. DNA Extraction
Soil DNA was extracted using PowerSoil DNA Isolation Kit (MoBio Laboratories, Carlsbad, CA, USA) following the manual. Purity and quality of the genomic DNA were checked on 1% agarose gels and a NanoDrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific: Beijing, China).
2.5. PCR Amplification
The V3-4 hypervariable region of bacterial 16S rRNA gene were amplified with the primers 338F(5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3′) and 806R (5′-GGACTACNNGGGTATCTAAT-3′) [42]. Fungal ITS region was amplified on Eppendorf Mastercycler Gradient Thermocycler, with the primers ITS1F (5-CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA-3) and ITS2 (5-TGCGTTCTTCATCGATGC-3) [42]. For each soil sample, 8-digit barcode sequence was added to the 5′ end of the forward and reverse primers (provided by Allwegene Company, Beijing, China). The PCR was carried out on a Mastercycler Gradient using 25 μL reaction volumes, containing 12.5 μL 2×Taq PCR Master Mix, 3 μL BSA (2ng/μL), 1 μL forward primer (5 μM), 1 μL reverse primer (5 μM), 2 μL template DNA, and 5.5 μL ddH2O. Cycling parameters were 95 °C for 5 min, followed by 28 cycles of 95 °C for 45 s, 55 °C for 50 s, and 72 °C for 45 s with a final extension at 72 °C for 10 min. The PCR products were purified using a Agencourt AMPure XP Kit.
2.6. High Throughput Sequencing
Deep sequencing was performed on Miseq platform at Allwegene Company (Beijing, China). After the run, image analysis, base calling and error estimation were performed using Illumina Analysis Pipeline Version 2.6.
2.7. Microbial Community Analysis
The raw data were first screened and sequences were removed from consideration if they were shorter than 230 bp, had a low quality score (≤20), contained ambiguous bases or did not exactly match to primer sequences and barcode tags, and separated using the sample-specific barcode sequences. Qualified reads were clustered into operational taxonomic units (OTUs) at a similarity level of 97% [43] use Uparse algorithm of Vsearch (v2.7.1) software. For bacteria, the Ribosomal Database Project (RDP) Classifier tool was used to classify all sequences into different taxonomic groups against SILVA128 database [44]. For fungi, the BLAST tool was used to classify all sequences into different taxonomic groups against Unite database.
2.8. Statistical Analyses
QIIME (v1.8.0) was used to generate rarefaction curves and to calculate the richness and diversity indices based on the OTU information. To compare the membership and structure of communities in different samples, heatmaps were generated with the top 20 OTUs using Mothur [45]. Based on the results of taxonomic annotation and relative abundance, R (v3.6.0) software was used for bar-plot diagram analysis. To examine the similarity between different samples, clustering analyses and PCA were analyzed by R (v3.6.0) based on the OTU information from each sample [46]. The evolution distances between microbial communities from each sample were calculated using Bray Curtis algorithms and represented as an Unweighted Pair Group Method with Arithmetic Mean (UPGMA) clustering tree describing the dissimilarity (1-similarity) between multiple samples [47]. A Newick-formatted tree file was generated through this analysis.
3. Results
3.1. OTUs Number Analysis of Bacteria and Fungi
It can be seen from Figure 1 that the total number of bacterial OTUs treated with conventional nitrogen (N), 50% conventional nitrogen (N50%), 70% conventional nitrogen (N70%) and high nitrogen fertilizer (N150%) in oilseed rape seedling stage were 4545, 3676, 4384 and 4541, respectively. The total number of fungal OTUs was 957, 1117, 1049 and 1025, respectively. The total number of bacterial OTUs in the four treatments at flowering stage was 4155, 4542, 4005, 4683, and the total number of fungus OTUs was 615, 759, 816, 817, respectively. The total number of bacterial OTUs in the four treatments at maturity stage were 6425, 5872, 5484, 5514, and the total number of fungal OTUs were 1294, 1411, 1416, 1272, respectively. The number of unique bacterial OTUs in the four treatments at seedling stage accounted for 17.54%, 14.53%, 18.41%, and 20.59% of the total number of each treatment, and the number of fungus OTUs accounted for 21.32%, 26.32%, 25.17% and 26.54% of the total number of each treatment. The number of unique bacterial OTUs in the four treatments at flowering stage accounted for 15.07%, 15.85%, 13.53% and 17.55% of the total number of each treatment, and the number of fungus OTUs accounted for 19.02%, 25.43%, 29.90% and 27.05% of the total number of each treatment. The number of unique bacterial OTUs in the four treatments at maturity stage accounted for 15.78%, 12.86%, 12.24% and 12.97% of the total number of each treatment, and the number of fungus OTUs accounted for 10.51%, 16.16%, 16.45%, and 14.7% of the total number of each treatment. It can be seen that at the seedling stage, the number of bacterial OTUs treated by N50% is the least, while that of fungi is just the opposite. The number of OTUs of bacteria and fungi was the highest under N150% treatment at flowering stage. The number of OTUs of bacteria and fungi with conventional nitrogen application was the highest at the stage of silique maturity.
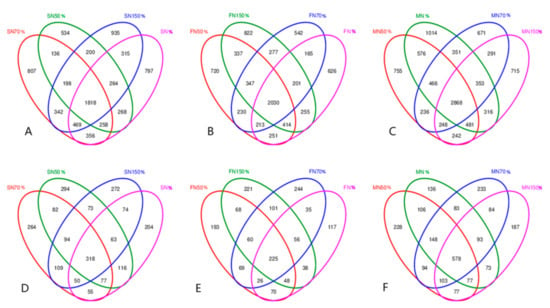
Figure 1.
Venn diagram based on OTUs of bacteria and fungi in oilseed rape rhizosphere soil. (A): OTUs number of bacteria in Seedling Stage; (B): OTUs number of bacteria in flowering stage; (C): OTUs number of bacteria in maturity stage; (D): OTUs number of fungi in Seedling Stage; (E): OTUs number of fungi in flowering stage; (F): OTUs number of fungi in maturity stage.
3.2. Alpha Diversity Index Analysis
The Chao1 index measures the species richness, that is, how many species are there, and the Shannon index is the species diversity. Alpha diversity index of bacteria and fungi in oilseed rape rhizosphere soil is shown in Figure 2. Shannon index and Chao1 index under N50% treatment at seedling stage were significantly lower than those under other treatments, and the diversity and richness of bacteria were the lowest. Fungi Shannon index and Chao1 index under N50% treatment were higher than those under the other three treatments, but the differences were not significant. Nitrogen application at seedling stage had little effect on the diversity of the soil fungal community. At flowering stage, the Shannon index of bacteria under N150% treatment was the highest, while that under N treatment was the lowest, with no significant difference among all treatments. The Shannon index of fungal N70% treatment was the highest, significantly higher than that of the other three treatments. The Chao1 index of bacteria under N150% treatment was significantly higher than that under N and N70% treatment, and the Chao1 index of bacteria under N50% treatment was also significantly higher than that under N70% treatment. The Chao1 index of fungi under N150% treatment was the largest, while that under N treatment was the smallest, and the difference was significant. At maturity stage, the Shannon index and Chao1 index of bacteria under N treatment were the highest, and the Chao1 index under N treatment was significantly higher than that under the other three treatments. There was no significant difference in Shannon index and Chao1 index among fungal treatments. It can be seen that different nitrogen application levels at seedling stage had little effect on the diversity of soil fungal community, and the diversity and richness of bacterial community in the rhizosphere of oilseed rape were lower under low nitrogen application conditions. Bacteria and fungi in the rhizosphere soil of flowering oilseed rape maintained a higher community diversity under the condition of high nitrogen. The rhizosphere bacterial community diversity under conventional N application was higher than that under other N application, but there was no significant difference in fungal community diversity among different treatments.
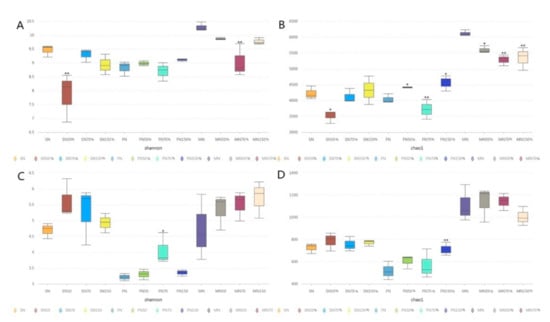
Figure 2.
Alpha diversity index analysis of rhizosphere soil bacteria and fungi. (A,B) represent Scheme 1 index of bacteria; (C,D) represent Shannon index and Chao1 index; * and ** indicate significant differences at the 0.05 and 0.01 levels, respectively.
3.3. Analysis of Microbial Community Structure
3.3.1. Isolation and Analysis of the Total Samples by the Colonization Structure of the Hydrophylum
Classified groups with 1% relative abundance of bacteria and fungi were selected at the phylum level, and the other species were merged into others as shown in Figure 3. Unclassified represents species that have not received taxonomic notes. Relative abundance of bacteria 1% Proteobacteria, Chloroflexi, Acidobacteria, Actinobacteria, Gemmatimonadetes, Bacteroidetes, Saccharibacteria, Nitrospirae, Firmicutes, Verrucomicrobia, Planctomycetes, Latescibacteria, and Cyanobacteria accounted for 13 species, accounting for 97.68% of the bacterial community. The dominant phyla were Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, Acidobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Cyanobacteria, etc., and their relative abundance was all above 5%. Proteobacteria had the highest average relative abundance (39.60%), followed by Actinobacteria (13.56%), Acidobacteria (11.07%), and Bacteroidetes (8.89%), respectively. Proteobacteria was insensitive under different nitrogen application levels, and the relative abundance of Proteobacteria was not significantly different at seedling and mature stages, but decreased only under low nitrogen application at flowering stage. The relative abundance of Actinobacteria and Acidobacteria was significantly affected by the nitrogen concentration at the seedling stage. The relative abundance of Actinobacteria and Acidobacteria was also lower with the lower nitrogen application rate. Compared with the normal nitrogen application rate, the relative abundance of Actinobacteria and Acidobacteria decreased by 5.06% and 9.18%, respectively. The relative abundance of Actinobacteria at flowering stage was significantly higher than that at seedling and mature stage, and the relative abundance of N150% was lower than that at N condition, 6.33%, and 11.81%, respectively, than that at N50%. The relative abundance of Acidobacteria was significantly affected by the amount of nitrogen application at the flowering stage, and the relative abundance of N70% increased by 8.71% and 6.85%, respectively, compared with the amount of nitrogen application. The relative abundance of Bacteroidetes in seedling stage was higher than that in flowering and mature stage, and there were differences between different nitrogen application levels in seedling stage and flowering stage. The relative abundance of Cyanobacteria under the treatment of 50% at seedling stage was significantly higher than that of other nitrogen application levels, the highest at the treatment of N at flowering stage and the highest at the maturity stage.
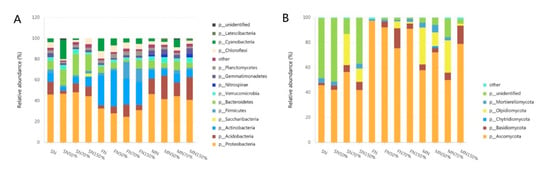
Figure 3.
Analysis of difference in colony structure of each sample at phylum level. (A): Bacteria; (B): Fungi.
The species in the fungal community were Ascomycota, Basidiomycota, Mortierellomycota, Chytridiomycota, Olpidiomycota, the dominant phyla with relative abundance greater than 5% were Ascomycota, Olpidiomycota and Basidiomycota. There was no significant difference in the relative abundance of Ascomycota at the seedling stage, but the N treatment had the highest relative abundance at the flowering stage, reaching 97.42%. The relative abundance of Ascomycota at maturity stage was the lowest under N70% treatment, which was significantly different from other N treatments. The relative abundance of Olpidiomycota under N and N50% treatments was less than 1% at seedling and flowering stage, and only the relative abundance of Olpidiomycota under N70% and N150% treatments was detected, and the relative abundance of Olpidiomycota under N70% treatment was significantly higher than that under N150%. At maturity stage, the relative abundance of N treatment was the highest (29.49%), followed by N70% (25.88%), N150% (1.63%) and N50% treatment (11%). The relative abundance of Basidiomycota at seedling stage was the lowest (1.82%) under N treatment, and the highest (6.53%) under N150% treatment. Basidiomycota at flowering stage was the highest (15.98%) under N70% treatment, which was significantly higher than the other three treatments. Basidiomycota had the highest relative abundance (14.55%) at maturity stage under high nitrogen treatment, which was significantly higher than the other three treatments.
Under different nitrogen application backgrounds, the significance test and analysis of the differences between dominant phylum treatments in the rhizosphere samples of oilseed rape at seedling, flowering, and mature stages showed (Table 1) that the structure of soil microbial community in the rhizosphere of oilseed rape significantly changed, and there were differences in bacteria and fungi, as well as some differences in the changes under different nitrogen application levels.

Table 1.
Analysis of the significance of differences between dominant phyla treatments in the rhizosphere samples of oilseed rape at seedling, flowering and mature stages.
3.3.2. The Whole Sample Belongs to the Breakdown Structure Analysis of Hydrophylla
Classifications with 1% relative abundance of bacteria and fungi were selected at the genus level, and other species were merged into others as shown in Figure 4. Unclassified represents species that have not received taxonomic notes. There were 45 bacterial genera and 34 fungal genera in species with 1% relative abundance of bacteria. The bacteria are Pedobacter, Sphingomonas, Pseudomonas, Flavobacterium, Oryzihumus, Dyella, Bryum_argenteum_var._argenteum, Massilia, Pseudarthrobacter, and Bacillus ten species, were dominant strains, and showed different dominant genera in different periods. At seedling stage, the dominant strains of Sphingomonas and Pseudomonas maintained a high abundance under N and N150%, and the relative abundance of Flavobacterium was the highest under low N treatment. Pseudarthrobacter abundance at flowering stage was the highest under N50% treatment and decreased with the increase of N application rate, which was 1.22 and 2.98 times that of N and N150% treatment, respectively. The relative abundance of Bacillus was the highest under N70% treatment, which was 1.34 times of that under N150% treatment. Under the condition of N70% at mature stage, the number of dominant bacteria genera was abundant, including 4 species, including Dyella, Massilia, Sphingomonas, and Pseudarthrobacter. The dominant fungi in different treatment stages were Cladosporium, Alternaria, Emericellopsis, Olpidium, and Fusarium. Alternaria and Cladosporium were the dominant genera at flowering stage. The relative abundance of Alternaria increased significantly with the increase of nitrogen application rate, and increased by 29.94%, 27.79% and 31.35%, respectively, compared with that of N50%, N and N70%, while that of Cladosporium was the opposite. It was 22.07%, 8.16 and 3.78% lower than that under N50%, N and N70% treatment, respectively. Olpidium under N70% treatment maintained a higher relative abundance than other treatments at each stage, Fusarium only had a higher relative abundance under N treatment at seedling stage, and Emericellopsis had a higher relative abundance under N treatment at both flowering and maturity stage. Different nitrogen application levels significantly affected the rhizosphere soil bacterial and fungal community composition at different growth stages, especially the dominant bacterial genera were significantly different under low nitrogen and high nitrogen conditions, and the difference of fungi was mainly reflected in the flowering stage.
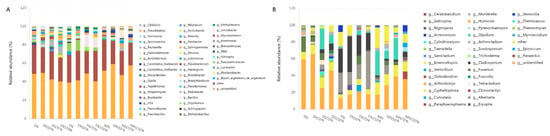
Figure 4.
Microflora structure fromall samples at the genus level. (A) Bacteria; (B) Fungi.
The results of heatmap and cluster tree analysis (Top20) showed that the dominant bacteria genera of the samples treated with higher nitrogen application rate were grouped into a similar group, and the dominant bacteria genera of the samples treated with higher abundance at seedling and flowering stage were grouped into a group. The dominant bacteria genera of the rhizosphere soil at seedling and flowering stage were more abundant under N150% treatment (Figure 5A). The results of heatmap and cluster tree analysis (Top20) showed that the fungal communities of all samples were basically the same and similar according to the growth period, and they clustered into a group. The dominant bacteria were mainly concentrated at the flowering stage, while the non-dominant bacteria were more abundant in the samples treated with higher nitrogen fertilizer at the mature stage (Figure 5B).
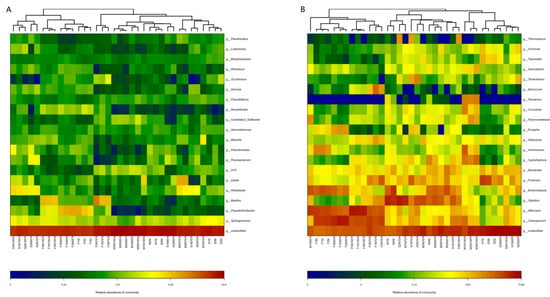
Figure 5.
Histogram and heatmap from twenty samples at the level of genus. (A) Bacteria; (B) Fungi.
3.4. Beta Diversity Analysis between Samples
When the stress of non-metric multidimensional calibration method (NMDS) is less than 0.2, it indicates that the analysis has a certain reliability. The closer the sample is in the coordinate graph, the higher the similarity is. NMDS analysis of bacteria and fungi was obtained based on the Bray-Curtis distance algorithm, and the stress values of the analysis results were all less than 0.2, indicating that the NMDS analysis results were reasonable (Figure 6). PCA analysis showed that the bacterial and fungal community composition of the treated samples were significantly different in different quadrants (Figure 7). Bacterial PC1 and PC2 accounted for 23.99% and 14.49% of the results, and fungal PC1 and PC2 accounted for 25.64% and 15.06% of the results, respectively, which were contributed by growth period factor and nitrogen application rate factor, respectively. There was a positive correlation between N, N50%, N70%, N150% and the first and second principal components of bacteria and fungi at the maturity stage. There was a negative correlation between the four treatments and the first principal component and a positive correlation between the four treatments and the second principal component at the flowering stage. At the seedling stage, N, N50% and N70% of bacteria were positively correlated with the first principal component and negatively correlated with the second principal component, while N150% was negatively correlated with the first and second principal components. At the seedling stage, N, N50% and N150% were positively correlated with the first principal component and negatively correlated with the second principal component, while N70% was positively correlated with the first and second principal components. At flowering stage, N50% and N were negatively correlated with the first and second principal components, while N70% and N150% were negatively correlated with the first principal component and positively correlated with the second principal component. The results indicated that the amount of nitrogen fertilizer had a great influence on the rhizosphere soil microflora types in different growth stages of oilseedrape. Hierarchical cluster analysis of bacteria and fungi showed that bacteria and fungi clustered into two groups according to the growth stage, and each group clustered under different nitrogen application rates (Figure S1). Bacteria at seedling stage and flowering stage had less influence under less nitrogen application, while fungi showed less influence on rhizosphere soil microbial community types at flowering stage.
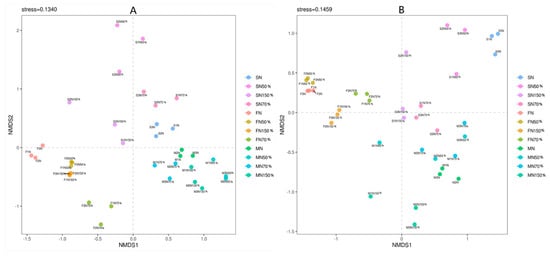
Figure 6.
NMDS analysis of all samples. (A) Bacteria; (B) Fungi.
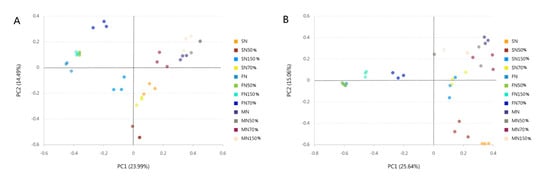
Figure 7.
Principal component analysis (PCA) of all samples. (A): Principal component analysis of bacterial; (B): principal component analysis of bacterial fungi.
4. Discussion
4.1. The Growth and Development Stages of Oilseedrape Determine the Composition of Rhizosphere Microbial Community
Plants can control their rhizosphere microbial composition [48], select specific microbial functions according to growth and development needs [49], and support, restrict, or terminate microbial growth and activities [50]. Such interaction exists in both directions, and microorganisms can also adapt to the rhizosphere environment through locomotion, chemotaxis, quorum sensing and remodeling of bacterial community [50]. Rhizosphere microbial communities influence plant nutrition and health [51,52], and that, on the contrary, these communities may be influenced by plant growth stages [53]. For example, Proteobacteria had a high relative abundance at different nitrogen application levels at both seedling and maturity stages. However, at flowering stage, the abundance of Proteobacteria was significantly lower than that at seedling and maturity stages regardless of high nitrogen application or low nitrogen application. Actinobacteria showed the opposite trend. The relative abundance of Actinobacteria at flowering stage was significantly higher than that at seedling and maturity stage. The relative abundance of Ascomycota was 97.42% at the flowering stage. Based on the analysis of oilseed rape rhizosphere community under different nitrogen application in three stages, our results were consistent with previous studies, in which oilseed rape growth stage was determined to be an important determinant of rhizosphere microbial composition [53,54].
4.2. The Rhizosphere Microbiome Was Selectively Enriched by Different Nitrogen Application Rates
Rhizosphere microorganisms are the regulators of nutrient transformation and transport between soil and root system. The diversity of soil microbial community reflects the overall dynamic change of the community. Studies have shown that the dominant phyla of soil bacteria include Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, Chloroflexi, Acidobacteria, Firmicutes, Verrucomicrobia, and Gemmatimonadetes. The dominant phyla of fungi include Ascomycota, Basidiomycota, Basidiomycota, and Chytridiomycota [55]. This study found that Proteobacteria, Chloroflexi, Acidobacteria, Actinobacteria, Gemmatimonadetes, Firmicutes, Verrucomicrobia, Ascomycota, Basidiomycota, Mortierellomycota, and Chytridiomycota were basically consistent with the above studies. However, the rhizosphere of oilseedrape also showed some unique dominant phyla, examples include Bacteroidetes, Saccharibacteria, Nitrospirae, Planctomycetes, Latescibacteria, Cyanobacteria, and Olpidiomycota. Bacteroidetes and Planctomycetes have been reported as the dominant phyla of oilseed rape rhizosphere [56].
Nitrogen application changed the relative abundance of each microbial community. For example, the relative abundance of Actinobacteria and Acidobacteria at seedling stage under N50% treatment decreased by 5.06% and 9.18% compared with that under N treatment, respectively. The relative abundance of Acidobacteria was also significantly affected by the amount of nitrogen application at the flowering stage. Studies have shown that Acidobacteria is positively correlated with soil nitrogen content [57], and nitrogen application increases soil nitrogen content, thus increasing the relative abundance of Acidobacteria. Fierer et al. [58] believed that when nitrogen in the soil increased, the abundance of some eutrophic bacteria, such as Proteobacteria, would increase. In this study, the relative abundance of Proteobacteria was lower at seedling and mature stages than that of low nitrogen fertilization, which may be related to the vulnerability and sensitivity of the farmland soil ecosystem, but the specific mechanism needs to be further studied. The relative abundance of Ascomycota ranged from 41.95% to 97.42%, and Ascomycota occupied the dominant position of soil flora, which was most obvious at flowering stage. This may be related to its strong environmental adaptability. Cyanobacteria is a detected dominant phylum of oilseed rape rhizosphere soil microorganisms. Cyanobacteria can fix nitrogen [59], increase the availability of phosphorus and release auxin that promotes plant growth [60]. The relative abundance of Cyanobacteria in oilseed rape mature stage was the highest under N70% treatment, followed by N treatment. Cyanobacteria may be involved in promoting nitrogen supply in fertilizer and nitrogen accumulation in later growth stage of oilseed rape. Furthermore, Cyanobacteria can produce H2 as a by-product of nitrogen fixation [61]. Cyanobacteria participates in the metabolism of Chloroflexi through a symbiotic way [35]. Therefore, Chloroflexi may be related to the nutrient supply capacity of soil and the promotion of plant growth, which is worthy of further study.
4.3. Correlation between Nitrogen Uptake and Utilization Characteristics and Microbial Community in Growth Stage of Oilseed Rape
As an active element, nitrogen in plants is in a dynamic process of constant absorption, assimilation, transport, and distribution during the growth and development stage of crops [62]. Our previous studies found that with the increase of fertilizer application rate, oilseed rape root system preferred to take up nitrogen from fertilizer and could obtain higher nitrogen accumulation. This may be due to the adaptation of roots to the rhizosphere environment after application of nitrogen fertilizer. Host-microbiome interactions had been verified to prove that plant’s stage of growth affects the formation of rhizosphere microbials [51,53]. For example, at the seedling stage, the number of bacterial OTUs was the lowest, while the number of fungus OTUs was the highest in N50% treatment. The number of OTUs of bacteria and fungi was the highest under N150% treatment at flowering stage. The number of OTUs of bacteria and fungi treated by N was the highest at the stage of pod maturity. The results indicated that the increase of nitrogen application rate could maintain the number of microbial community in the later growth stage of oilseed rape. The UPGMA cluster tree also showed that the community composition of soil bacteria and fungi changed significantly with different nitrogen application levels. The results of Shannon index and Chao1 index showed that the bacterial diversity and abundance in N treatment at maturity stage were high, and there was no significant difference in fungal richness at maturity stage, but the abundance in N150% treatment was high.
5. Conclusions
The composition of dominant microflora in the rhizosphere of oilseed rape was not affected by the amount of nitrogen application and growth stage, but its relative abundance was related to the amount of nitrogen application, which was different in different growth stages. The bacterial community was more active than the fungal community at the late growth stage, and the community diversity was higher under the condition of high nitrogen fertilization. In the process of oilseed rape cultivation, the application of basal fertilizer should be considered to increase the application rate of nitrogen fertilizer, so as to meet the demand of nitrogen in the later growth period of oilseed rape and maintain a rich rhizosphere microbial community. In addition, we also found Bacteroidetes, Saccharibacteria, Nitrospirae, Planctomycetes, Latescibacteria, Cyanobacteria, and Olpidiomycota, and other endemic dominant bacteria phyla of oilseed rape rhizosphere. Whether these dominant fungi affect the nutrient uptake and utilization of oilseed rape roots remains to be further studied. In this study, the distribution difference of microbial community in the rhizosphere soil of oilseed rape was discussed under the background of different nitrogen application rates. The study on the diversity of microbial community in the rhizosphere soil of oilseed rape will provide important guiding significance for rational application of nitrogen fertilizer, improvement of microbial community composition in the rhizosphere of oilseed rape and promotion of growth and development of oilseed rape.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy11081539/s1, Figure S1: Hcluster of all samples. (A): Hierarchical cluatering of bacterial; (B): Hierarchical cluatering of fungi.
Author Contributions
Y.Z., C.G. and M.G. designed the experiment. M.X. and Y.Z. conducted the experiment. C.G. and M.G. helped and provided useful suggestions during the experiment. M.X. and Y.Z. processed and analyzed data and wrote the first draft. C.G. and M.G. revised and edited the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. 31130040) and the High-Tech Research and Development Program 863 (grant No. 2011AA10A104).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ren, T.; Li, H.; Lu, J.; Bu, R.; Li, X.; Cong, R.; Lu, M. Crop rotation-dependent yield responses to fertilization in winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Crop J. 2015, 3, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Weiser, C.; Fuß, R.; Kage, H.; Flessa, H. Do farmers in Germany exploit the potential yield and nitrogen benefits from preceding oilseed rape in winter wheat cultivation? Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2018, 64, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; Ren, T.; Li, X.; Cong, R.; Zhang, M.; Yousaf, M.; Lu, J. Establishment Method Affects Oilseed Rape Yield and the Response to Nitrogen Fertilizer. Agron. J. 2014, 106, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Li, X.-K.; Ren, T.; Cong, R.-H.; Lu, J.-W. Nutrient deficiency limits population development, yield formation, and nutrient uptake of direct sown winter oilseed rape. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.J.; Fan, X.; Shen, Q.; Smith, S.J. Amino acids and nitrate as signals for the regulation of nitrogen acquisition. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 59, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Näsholm, T.; Kielland, K.; Ganeteg, U. Uptake of organic nitrogen by plants. New Phytol. 2009, 182, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, R.F.; Bolland, M.D.A. Comparing the Nitrogen and Potassium Requirements of Canola and Wheat for Yield and Grain Quality. J. Plant Nutr. 2009, 32, 2008–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathke, G.-W.; Behrens, T.; Diepenbrock, W. Integrated nitrogen management strategies to improve seed yield, oil content and nitrogen efficiency of winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.): A review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 117, 80–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.-B.; Li, Y.-N.; Du, Y.-D. Effects of ridge-furrow film mulching and nitrogen fertilization on growth, seed yield and water productivity of winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) in Northwestern China. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 200, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, H. Sowing date and nitrogen rate effects on growth, yield and yield components of two summer rapeseed cultivars. Eur. J. Agron. 2003, 19, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, P.; Spink, J.; Foulkes, J.; White, P. The physiological basis of genotypic differences in nitrogen use efficiency in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Field Crops Res. 2010, 119, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagoli, P.; Laine, P.; Rossato, L.; Ourry, A. Dynamics of Nitrogen Uptake and Mobilization in Field-grown Winter Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus) From Stem Extension to Harvest. II. An 15N-labelling-based Simulation Model of N Partitioning between Vegetative and Reproductive Tissues. Ann. Bot. 2005, 95, 1187–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diepenbrock, W. Yield analysis of winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.): A review. Field Crops Res. 2000, 67, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labra, M.H.; Struik, P.C.; Evers, J.B.; Calderini, D.F. Plasticity of seed weight compensates reductions in seed number of oilseed rape in response to shading at flowering. Eur. J. Agron. 2017, 84, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulas, A.; Behrens, T.; Wiesler, F.; Horst, W.J.; Erley, G.S.A. Defoliation affects seed yield but not N uptake and growth rate in two oilseed rape cultivars differing in post-flowering N uptake. Field Crops Res. 2015, 179, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Q.; Yang, T.; Nie, Z.; Chen, G.; Hu, L. Responses of plant development, biomass and seed production of direct sown oilseed rape (Brassica napus) to nitrogen application at different stages in Yangtze River Basin. Field Crops Res. 2016, 194, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Abdin, M.Z. Interactive Effect of Sulphur and Nitrogen on the Oil and Protein Contents and on the Fatty Acid Profiles of Oil in the Seeds of Rapeseed (Brassica campestris L.) and Mustard (Brassica juncea L. Czern. and Coss.). J. Agron. Crop. Sci. 2000, 185, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, L.; Qiu, G.; Wang, T.; Liu, C.; Yang, Y.; Feng, B.; Chen, C.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Z. Effects of Sowing Season on Agronomic Traits and Fatty Acid Metabolic Profiling in Three Brassica napus L. Cultivars. Metabolites 2019, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardgett, R.D.; van der Putten, W. Belowground biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 515, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, U.N.; Wall, D.H.; Six, J. Soil Biodiversity and the Environment. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2015, 40, 63–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobard, M.; Pessiot, J.; Nouaille, R.; Sime-Ngando, T. Microbial diversity supporting dark fermentation of waste. Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 549–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, I.; Delfosse, O.; Mary, B. Carbon and nitrogen mineralization in acidic, limed and calcareous agricultural soils: Apparent and actual effects. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros, G.H. Predicting soil N mineralization using organic matter fractions and soil properties: A re-analysis of literature data. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 45, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, R.; Lu, J.; Ren, T.; Liu, B.; Li, X.; Cong, R. Particulate Organic Matter Affects Soil Nitrogen Mineralization under Two Crop Rotation Systems. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, E.; Gebbing, T.; Abel, C.; Sim, A.; Telfer, G. Rhizodeposition shapes rhizosphere microbial community structure in organic soil. New Phytol. 2007, 173, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhauer, N.; Scheu, S.; Jousset, A. Bacterial Diversity Stabilizes Community Productivity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishaq, S.L. Plant-microbial interactions in agriculture and the use of farming systems to improve diversity and productivity. AIMS Microbiol. 2017, 3, 335–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, T.; Chen, X.; Yuan, H.; Li, B.; Zhu, H.; Peng, P.; Li, K.; Jones, D.L.; Wu, J. Microbial biomass, activity, and community structure in horticultural soils under conventional and organic management strategies. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2013, 58, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Orenes, F.; Morugán-Coronado, A.; Zornoza, R.; Scow, K. Changes in Soil Microbial Community Structure Influenced by Agricultural Management Practices in a Mediterranean Agro-Ecosystem. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossio, D.; Girvan, M.S.; Verchot, L.; Bullimore, J.; Borelli, T.; Albrecht, A.; Scow, K.; Ball, A.; Pretty, J.; Osborn, A.M. Soil Microbial Community Response to Land Use Change in an Agricultural Landscape of Western Kenya. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 49, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Chen, H.; Yang, Y.H.; Chen, T.; Lin, R.Y.; Chen, X.J.; Lin, W.X. Effects of contiInuous cropping on bacterial community diversity in rhizosphere soil of Rehmanniaglutinosa. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2010, 21, 2843–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mougel, C.; Offre, P.; Ranjard, L.; Corberand, T.; Gamalero, E.; Robin, C.; Lemanceau, P. Dynamic of the genetic structure of bacterial and fungal communities at different developmental stages of Medicago truncatulaGaertn. cv. Jemalong line J5. New Phytol. 2006, 170, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houlden, A.; Timms-Wilson, T.M.; Day, M.J.; Bailey, M.J. Influence of plant developmental stage on microbial community structure and activity in the rhizosphere of three field crops. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 65, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhalnina, K.; Louie, K.B.; Hao, Z.; Mansoori, N.; da Rocha, U.N.; Shi, S.; Cho, H.; Karaoz, U.; Loqué, D.; Bowen, B.P.; et al. Dynamic root exudate chemistry and microbial substrate preferences drive patterns in rhizosphere microbial community assembly. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Bai, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, X.; Wang, N.; Du, X.; Fan, H.; Zhuang, G.; Bohu, T.; et al. Unraveling Mechanisms and Impact of Microbial Recruitment on Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus L.) and the Rhizosphere Mediated by Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, E.; Smith, D. Intracellular and extracellular PGPR: Commonalities and distinctions in the plant–bacterium signaling processes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Kamala-Kannan, S.; Sub, H.S.; Seong, C.K.; Lee, G.W. Biological control of Phytophthora blight in red pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) using Bacillus subtilis. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yan, Z.; Gu, D.; Li, D.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Su, L.; Ao, Y. Characterization of cadmium-resistant rhizobacteria and their promotion effects on Brassica napus growth and cadmium uptake. J. Basic Microbiol. 2019, 59, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, P.S.; Ontañon, O.M.; Armendariz, A.L.; Talano, M.A.; Paisio, C.E.; Agostini, E. Brassica napus hairy roots and rhizobacteria for phenolic compounds removal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 20, 1310–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pareniuk, O.; Shavanova, K.; Laceby, J.P.; Illienko, V.; Tytova, L.; Levchuk, S.; Gudkov, I.; Nanba, K. Modification of 137Cs transfer to rape (Brassica napus L.) phytomass under the influence of soil microorganisms. J. Environ. Radioact. 2015, 149, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.X.; Yan, J.L.; He, H.D.; Yang, D.J.; Xiao, L.; Zhong, T.; Yuan, M.; De Cai, X.; Bin Li, S. Characterization of Bacteria in the Rhizosphere Soils of Polygonum Pubescens and Their Potential in Promoting Growth and Cd, Pb, Zn Uptake by Brassica napus. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2013, 16, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munyaka, P.M.; Eissa, N.; Bernstein, C.N.; Khafipour, E.; Ghia, J.-E. Antepartum Antibiotic Treatment Increases Offspring Susceptibility to Experimental Colitis: A Role of the Gut Microbiota. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.R.; Wang, Q.; Cardenas, E.; Fish, J.; Chai, B.; Farris, R.J.; Kulam-Syed-Mohideen, A.S.; McGarrell, D.M.; Marsh, T.; Garrity, G.; et al. The Ribosomal Database Project: Improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 37, D141–D145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jami, E.; Israel, A.; Kotser, A.; Mizrahi, I. Exploring the bovine rumen bacterial community from birth to adulthood. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sheng, H.-F.; He, Y.; Wu, J.-Y.; Jiang, Y.-X.; Tam, N.F.-Y.; Zhou, H.-W. Comparison of the Levels of Bacterial Diversity in Freshwater, Intertidal Wetland, and Marine Sediments by Using Millions of Illumina Tags. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 8264–8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.-T.; Peng, X.; Deng, G.-H.; Sheng, H.-F.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.-W.; Tam, N.F.-Y. Illumina Sequencing of 16S rRNA Tag Revealed Spatial Variations of Bacterial Communities in a Mangrove Wetland. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 66, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgarelli, D.; Schlaeppi, K.; Spaepen, S.; Van Themaat, E.V.L.; Schulze-Lefert, P. Structure and Functions of the Bacterial Microbiota of Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2013, 64, 807–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgarelli, D.; Garrido-Oter, R.; Münch, P.C.; Weiman, A.; Dröge, J.; Pan, Y.; McHardy, A.C.; Schulze-Lefert, P. Structure and Function of the Bacterial Root Microbiota in Wild and Domesticated Barley. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venturi, V.; Keel, C. Signaling in the Rhizosphere. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, C.R.; Copeland, J.; Wang, P.W.; Guttman, D.S.; Kotanen, P.M.; Johnson, M.T.J. Assembly and ecological function of the root microbiome across angiosperm plant species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1157–E1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A.; Rothballer, M.; Schmid, M. Lorenz Hiltner, a pioneer in rhizosphere microbial ecology and soil bacteriology research. Plant Soil 2007, 312, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarnalakshmi, K.; Yadav, V.; Tyagi, D.; Dhar, D.W.; Kannepalli, A.; Kumar, S. Significance of Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria in Grain Legumes: Growth Promotion and Crop Production. Plants 2020, 9, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, J.A.; Santos-Medellin, C.M.; Liechty, Z.S.; Nguyen, B.; Lurie, E.; Eason, S.; Phillips, G.; Sundaresan, V. Compositional shifts in root-associated bacterial and archaeal microbiota track the plant life cycle in field-grown rice. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2003862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-C.; Han, Z.-Z.; Ruan, X.-Y.; Chai, J.; Jiang, S.-W.; Zheng, R. Composting swine carcasses with nitrogen transformation microbial strains: Succession of microbial community and nitrogen functional genes. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 688, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkarmiri, K.; Mahmood, S.; Ekblad, A.; Alström, S.; Högberg, N.; Finlay, R. Identifying the Active Microbiome Associated with Roots and Rhizosphere Soil of Oilseed Rape. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e01938-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Dong, Y.; Hou, L.; Deng, N.; Jiao, R. Acidobacteria Community Responses to Nitrogen Dose and Form in Chinese Fir Plantations in Southern China. Curr. Microbiol. 2017, 74, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fierer, N.; Bradford, M.; Jackson, R.B. Toward an ecological classification of soil bacteria. Ecology 2007, 88, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.S.; Kumar, A.; Rai, A.N.; Singh, D.P. Cyanobacteria: A Precious Bio-resource in Agriculture, Ecosystem, and Environmental Sustainability. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Sharma, N.K.; Prasad, S.B.; Yadav, S.S.; Narayan, G.; Rai, A. The freshwater cyanobacterium Anabaena doliolum transformed with ApGSMT-DMT exhibited enhanced salt tolerance and protection to nitrogenase activity, but became halophilic. Microbiology 2013, 159, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatt, C.G.; Liu, Z.; Ludwig, M.; Kühl, M.; Jensen, S.I.; A Bryant, D.; Ward, D.M. Temporal metatranscriptomic patterning in phototrophic Chloroflexi inhabiting a microbial mat in a geothermal spring. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiltz, S.; Munier-Jolain, N.; Jeudy, C.; Burstin, J.; Salon, C. Dynamics of Exogenous Nitrogen Partitioning and Nitrogen Remobilization from Vegetative Organs in Pea Revealed by 15N in Vivo Labeling throughout Seed Filling. Plant Physiol. 2005, 137, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).