NMR Fingerprint Comparison of Cultivated Sideritis spp. from Cyprus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Infusions and NMR Spectroscopic Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs over the Nearly Four Decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubert, J.; Nuzillard, J.-M.; Renault, J.-H. Dereplication strategies in natural product research: How many tools and methodologies behind the same concept? Phytochem. Rev. 2017, 16, 55–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karousou, R.; Deirmentzoglou, S. The herbal market of Cyprus: Traditional links and cultural exchanges. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 133, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charami, M.-T.; Lazari, D.; Karioti, A.; Skaltsa, H.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D.; Souleles, C. Antioxidant and antiinflammatory activities of Sideritis perfoliata subsp. perfoliata (Lamiaceae). Phytother. Res. 2008, 22, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrysargyris, A.; Kloukina, C.; Vassiliou, R.; Tomou, E.-M.; Skaltsa, H.; Tzortzakis, N. Cultivation strategy to improve chemical profile and anti-oxidant activity of Sideritis perfoliata L. subsp. perfoliata. Ind. Crop Prod. 2019, 140, 111694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lall, N.; Chrysargyris, A.; Lambrechts, I.; Fibrich, B.; van Staden, A.B.; Twilley, D.; De Canha, M.N.; Oosthuizen, C.B.; Bodiba, D.; Tzortzakis, N. Sideritis perfoliata (subsp. perfoliata) nutritive value and its potential medicinal properties. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanoğlu, D.Y.; Hanoğlu, A.; Yusufoğlu, H.; Demirci, B.; Başer, K.H.C.; Çalış, İ.; Yavuz, D.Ö. Phytochemical Investigation of Endemic Sideritis cypria Post. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2020, 14, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytra, K.; Tomou, E.-M.; Chrysargyris, A.; Drouza, C.; Skaltsa, H.; Tzortzakis, N. Traditionally Used Sideritis cypria Post: Phytochemistry, Nutritional Content, Bioactive Compounds of Cultivated Populations. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lytra, K.; Tomou, E.-M.; Chrysargyris, A.; Christofi, M.-D.; Miltiadous, P.; Tzortzakis, N.; Skaltsa, H. Bio-guided investigation of Sideritis cypria Post. methanol extract driven by in vitro antioxidant and cytotoxic assays. Chem. Biodivers. 2021, 18, e2000966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hand, R.; Hadjikyriakou, G.N.; Christodoulou, C.S. Flora of Cyprus—A Dynamic Checklist (Continuously Updated). 2011. Available online: http://www.flora-of-cyprus.eu (accessed on 27 April 2021).
- European Medicines Agency (EMA); Committee on Herbal Medicinal Products (HMPC). Assessment Report on Sideritis scardica Griseb.; Sideritis clandestina (Bory & Chaub.) Hayek; Sideritis raeseri Boiss. & Heldr.; Sideritis syriaca L., Herba; EMA/HMPC/39455/2015; European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tomou, E.; Chatzopoulou, P.; Skaltsa, H. NMR analysis of cultivated Sideritis euboea Heldr. Phytochem. Anal. 2019, 31, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomou, E.-M.; Papaemmanouil, C.D.; Diamantis, D.A.; Kostagianni, A.D.; Chatzopoulou, P.; Mavromoustakos, T.; Tzakos, A.G.; Skaltsa, H. Anti-Ageing Potential of S. euboea Heldr. Phenolics. Molecules 2021, 26, 3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, H.; Sasaki, H.; Morota, T.; Chen, M.; Mitsuhashi, H. Six iridoids glycosides from Rehmannia glutinosa. Phytochemistry 1989, 25, 2705–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śawia̧tek, L.; Lehmann, D.; Chaudhuri, R.K.; Sticher, O. Occurrence of melittoside in the seeds of Plantago media. Phytochemistry 1981, 20, 2023–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, O.; Peña, R.C.; Montenegro, G. Iridoids from Stachys grandidentata (Labiatae). Z. Naturforsch. C J. Biosci. 2001, 56, 902–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- González-Burgos, E.; Carretero, M.E.; Gómez-Serranillos, M.P. Sideritis spp.: Uses, chemical composition and pharmacological activities—A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 135, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żyżelewicz, D.; Kulbat-Warycha, K.; Oracz, J.; Żyżelewicz, K. Polyphenols and Other Bioactive Compounds of Sideritis Plants and Their Potential Biological Activity. Molecules 2020, 25, 3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venditti, A.; Bianco, A.; Nicoletti, M.; Quassinti, L.; Bramucci, M.; Lupidi, G.; Vitali, L.A.; Papa, F.; Vittori, S.; Petrelli, D.; et al. Characterization of secondary metabolites, biological activity and glandular trichomes of Stachys tymphaea Hausskn. from the Monti Sibillini National Park (Central Apennines, Italy). Chem. Biodiver. 2014, 11, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aneva, I.; Zhelev, P.; Kozuharova, E.; Danova, K.; Nabavi, S.F.; Behzad, S. Genus Sideritis, section Empedoclia in southeastern Europe and Turkey–Studies in ethnopharmacology and recent progress of biological activities. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 27, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
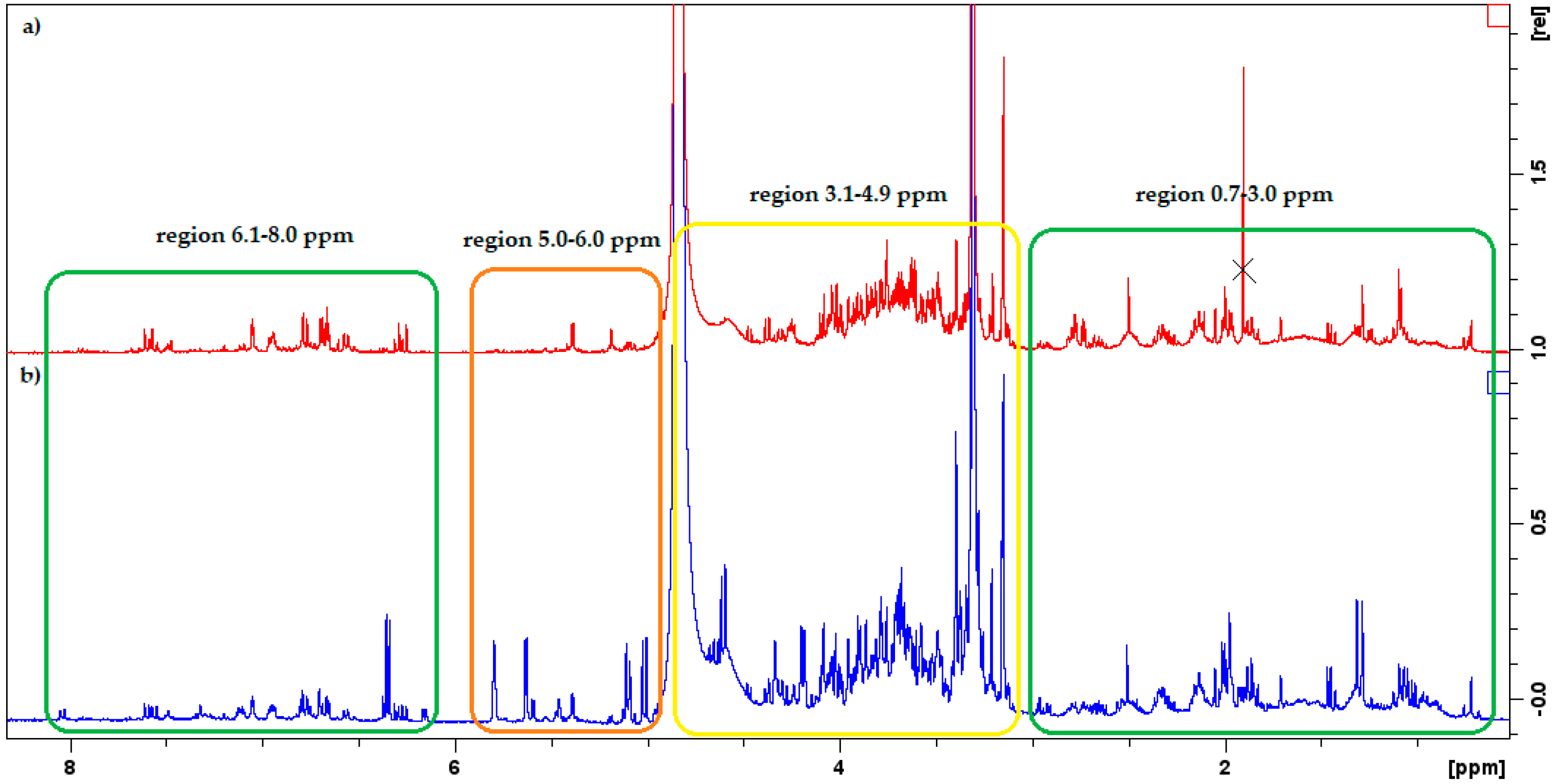
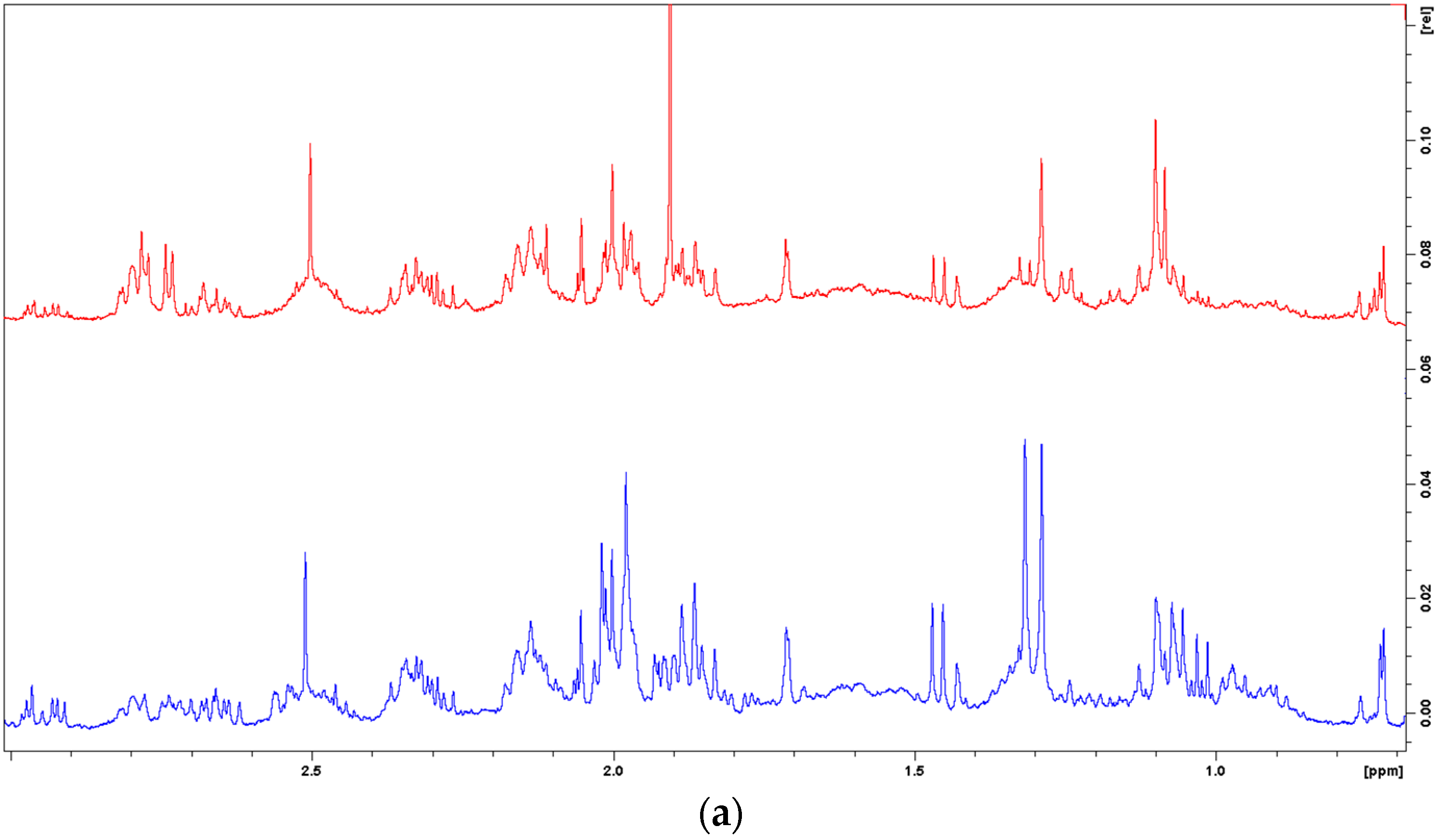
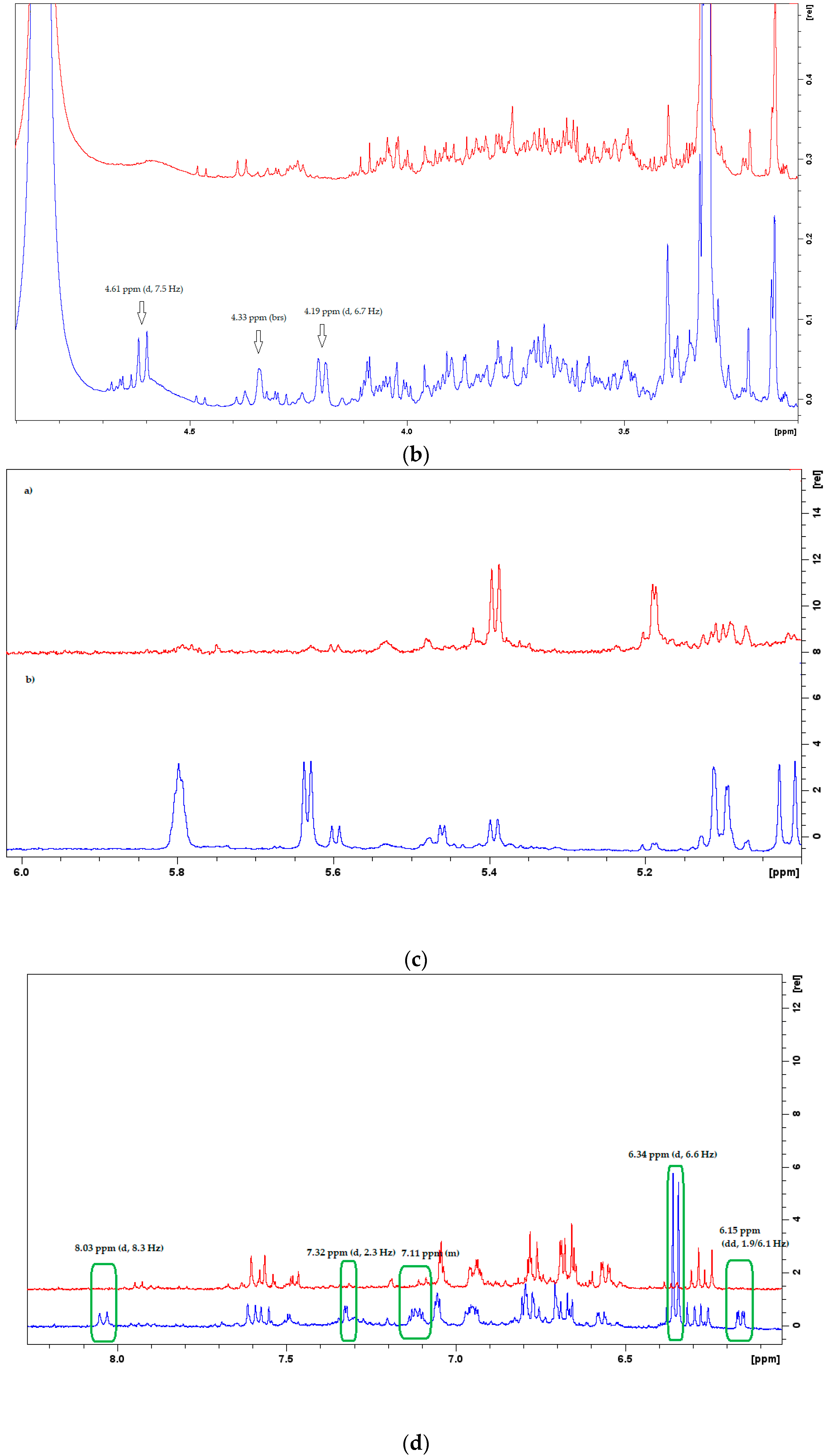
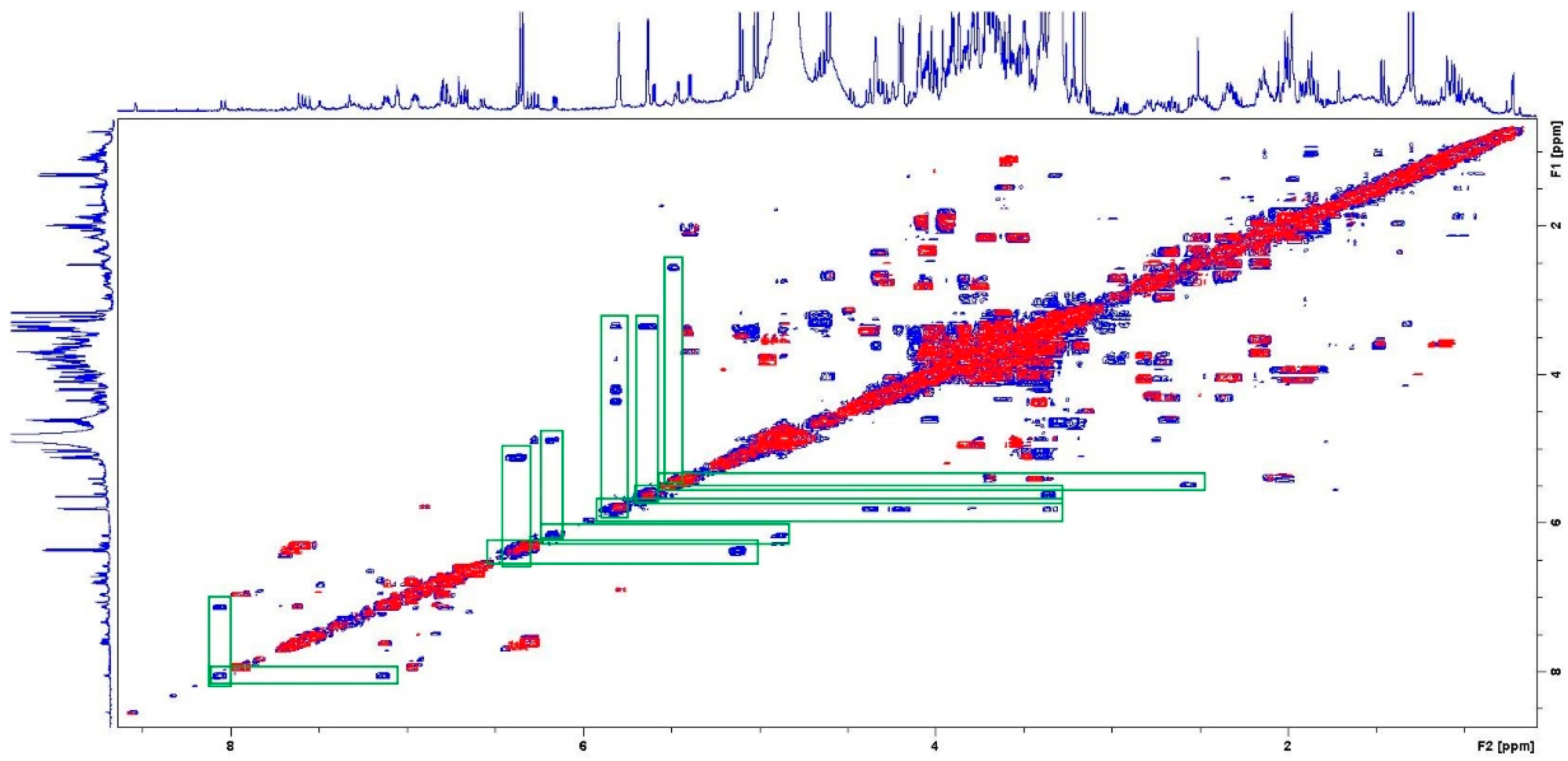
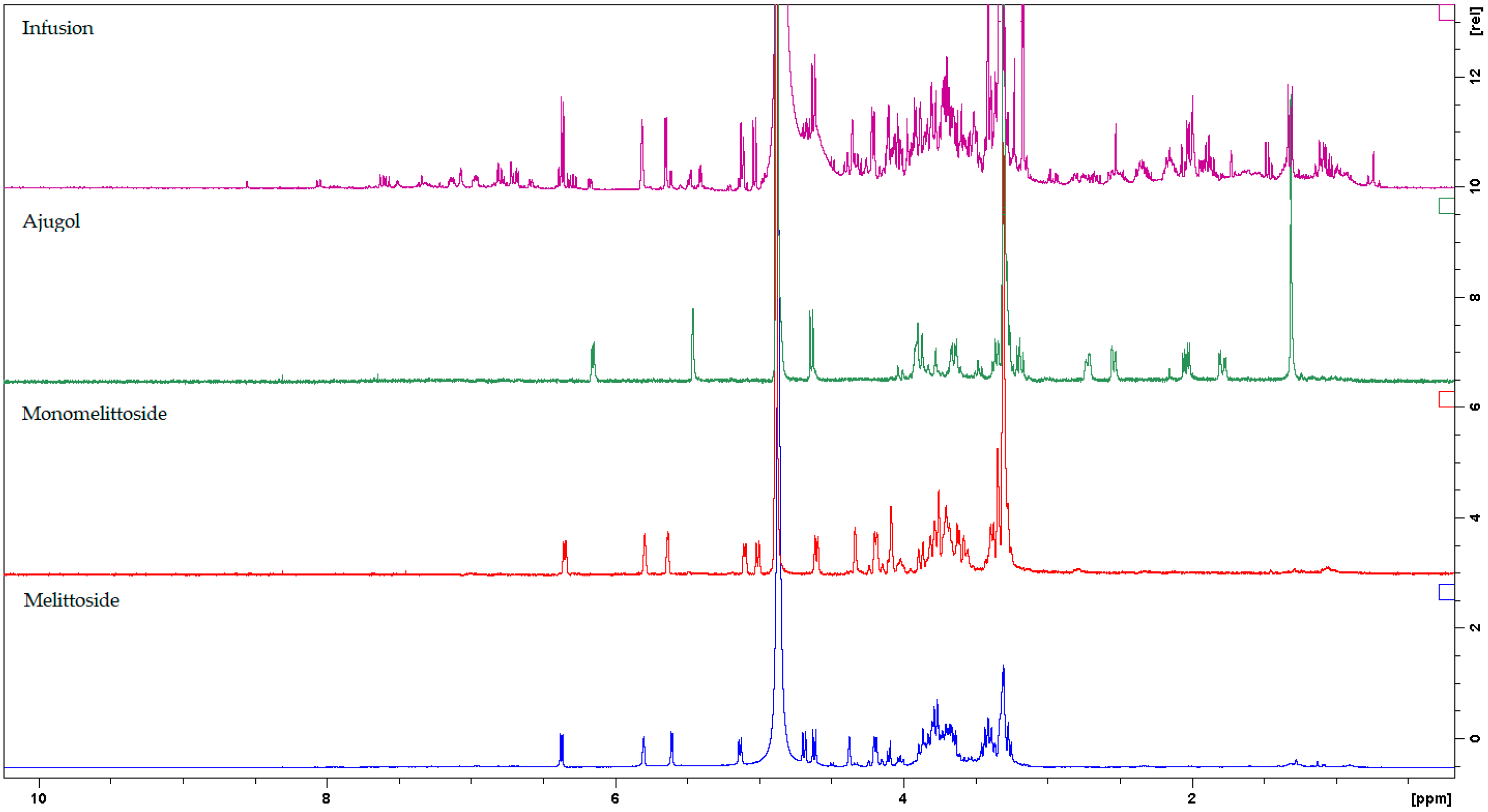
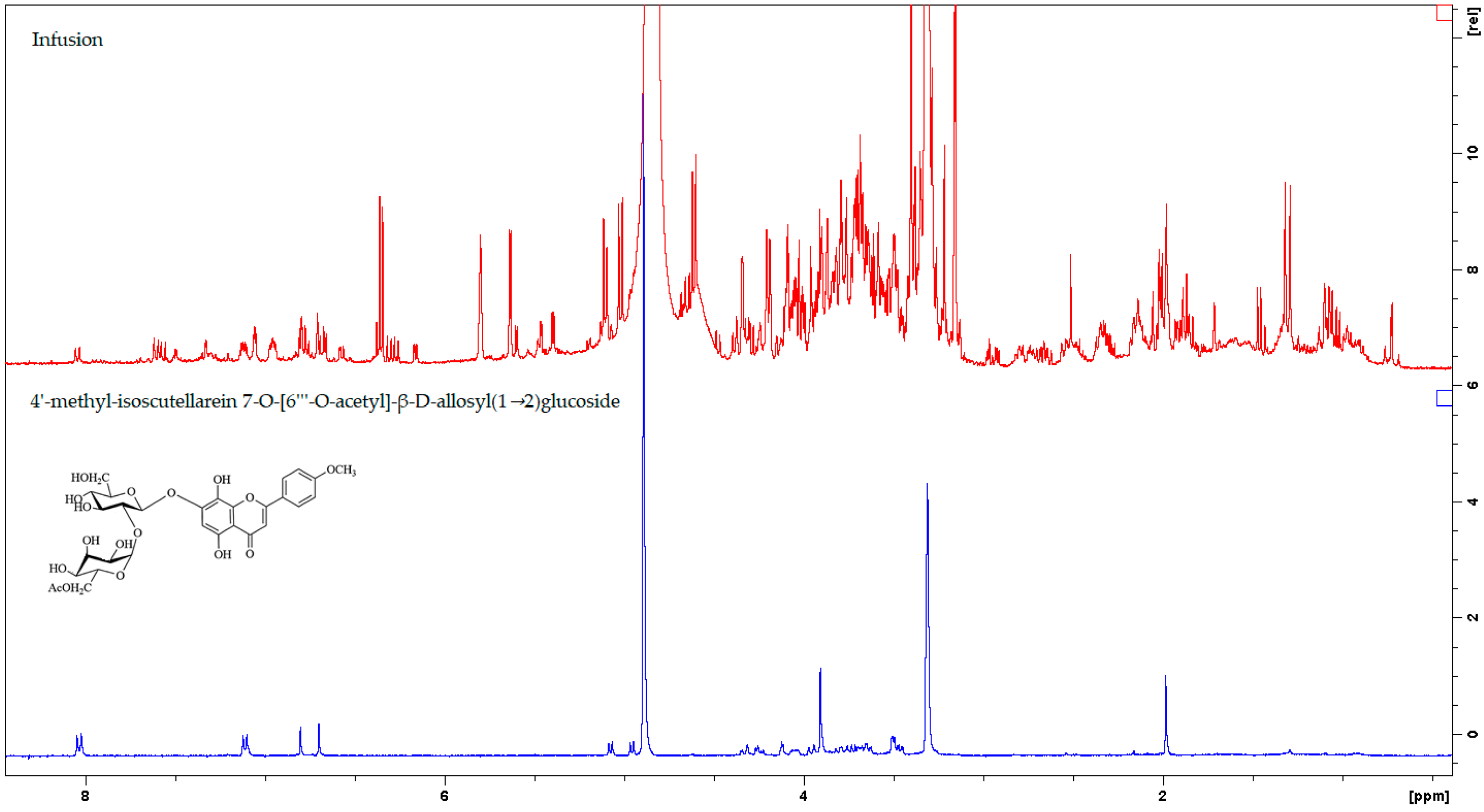
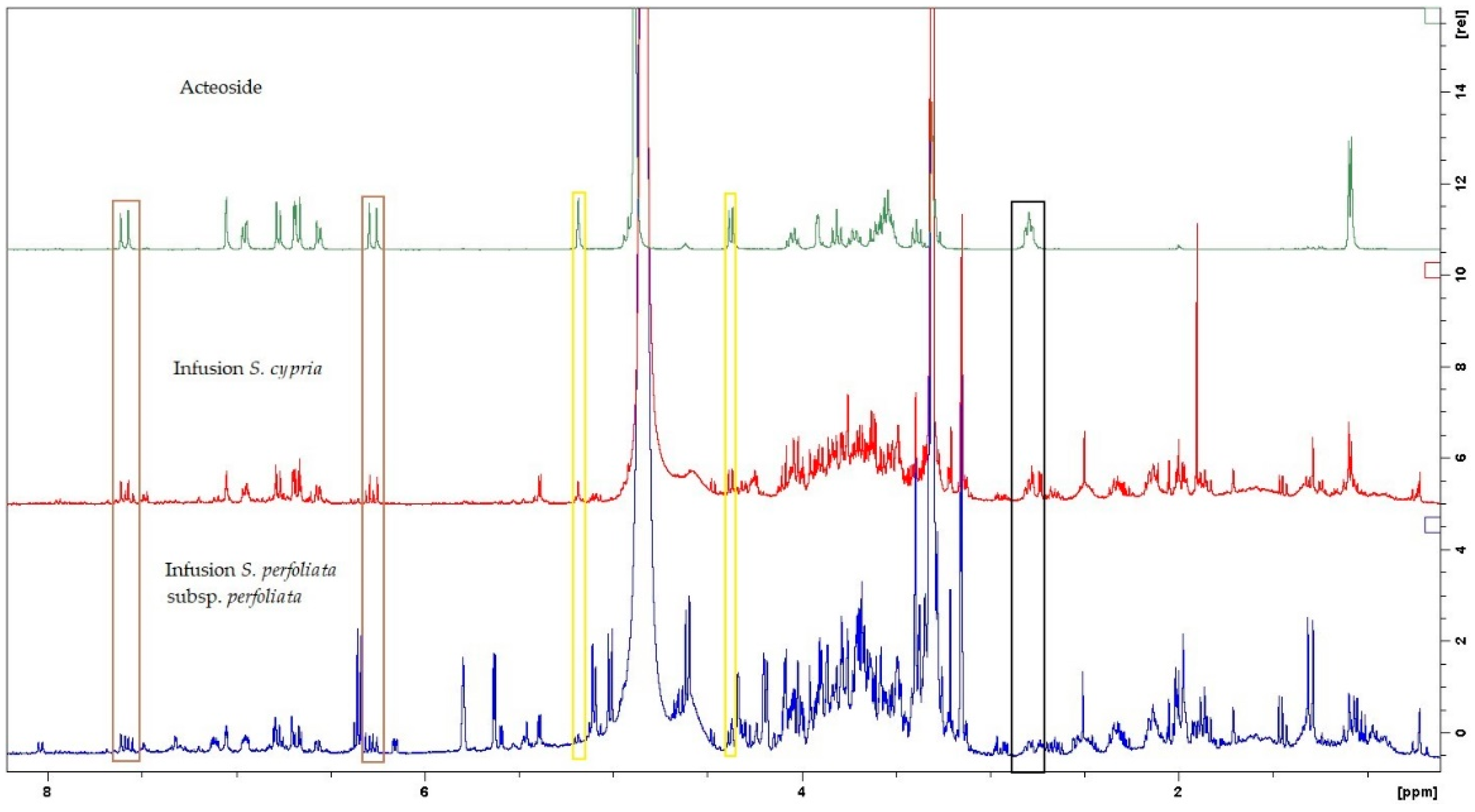
| Chemical Compound | δH1 (ppm) | δH2 (ppm) |
|---|---|---|
Ajugol | Aglycon: 6.16 (dd, H-3), 5.46 (d, H-1), 4.87 (*, H-4), 3.93 (m, H-6), 2.73 (dd, H-5), 2.54 (dd, H-9), 2.04 (dd, H-7a), 1.79 (dd, H-7b), 1.31 (s, CH3-10) Glucose: 4.64 (d, H-1′), 3.20–3.90 (H-2′ to H-6′) | Aglycon: 6.16 (dd, H-3), 5.46 (d, H-1), *(H-4), *(H-6), 2.73 (*, H-5), 2.55 (dd, H-9), 2.05 (dd, H-7a), 1.79 (dd, H-7b), 1.32 (s, CH3-10) Glucose: 4.64 (d, H-1′), *(H-2′ to H-6′) |
| Melittoside derivatives 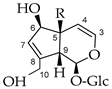 Monomelittoside R=OH Melittoside R=O-Glc | Monomelittoside Aglycon: 6.35 (dd, H-3), 5.79 (s, H-7), 5.64 (d, H-1), 5.10 (d, H-4), 4.34 (brs, H-6), 4.22 (d, H2-10), 3.35 (*, H-9) Glucose: 4.60 (d, H-1′), 3.28–3.88 (H-2′ to H-6′) Melittoside Aglycon: 6.37 (dd, H-3), 5.80 (s, H-7), 5.60 (d, H-1), 5.12 (d, H-4), 4.38 (brs, H-6), 4.20 (d, H2-10), 3.31 (*, H-9) Glucose: 4.61 (d, H-1′), 3.26–3.90 (H-2′ to H-6′) Glucose: 4.67 (d, H-1″), 3.25–3.90 (H-2″ to H-6″) | Monomelittoside Aglycon: 6.35 (dd, H-3), 5.80 (s, H-7), 5.63 (d, H-1), 5.10 (d, H-4), 4.33 (brs, H-6), 4.19 (d, H2-10), * (H-9) Glucose: 4.61 (d, H-1′), * (H-2′ to H-6′) Melittoside Aglycon: 6.35 (dd, H-3), 5.80 (s, H-7), 5.63 (d, H-1), 5.10 (d, H-4), 4.37 (brs, H-6), 4.19 (d, H2-10), *(H-9) Glucose: 4.61 (d, H-1′), * (H-2′ to H-6′) Glucose: 4.67 (d, H-1″), * (H-2″ to H-6″) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomou, E.-M.; Lytra, K.; Chrysargyris, A.; Tzortzakis, N.; Skaltsa, H. NMR Fingerprint Comparison of Cultivated Sideritis spp. from Cyprus. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1503. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11081503
Tomou E-M, Lytra K, Chrysargyris A, Tzortzakis N, Skaltsa H. NMR Fingerprint Comparison of Cultivated Sideritis spp. from Cyprus. Agronomy. 2021; 11(8):1503. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11081503
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomou, Ekaterina-Michaela, Krystalia Lytra, Antonios Chrysargyris, Nikolaos Tzortzakis, and Helen Skaltsa. 2021. "NMR Fingerprint Comparison of Cultivated Sideritis spp. from Cyprus" Agronomy 11, no. 8: 1503. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11081503
APA StyleTomou, E.-M., Lytra, K., Chrysargyris, A., Tzortzakis, N., & Skaltsa, H. (2021). NMR Fingerprint Comparison of Cultivated Sideritis spp. from Cyprus. Agronomy, 11(8), 1503. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11081503









