VNT4, a Derived Formulation of Glutacetine® Biostimulant, Improved Yield and N-Related Traits of Bread Wheat When Mixed with Urea-Ammonium-Nitrate Solution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Experiment Design under Contrasting Conditions (Experiment 1)
2.2. 15N Experiment under Field Conditions (Experiment 2, Site 4)
2.3. N and 15N Analyses
2.4. Elemental Analysis in Flag Leaves
2.5. Grain Yield Components and N Use Efficiency
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
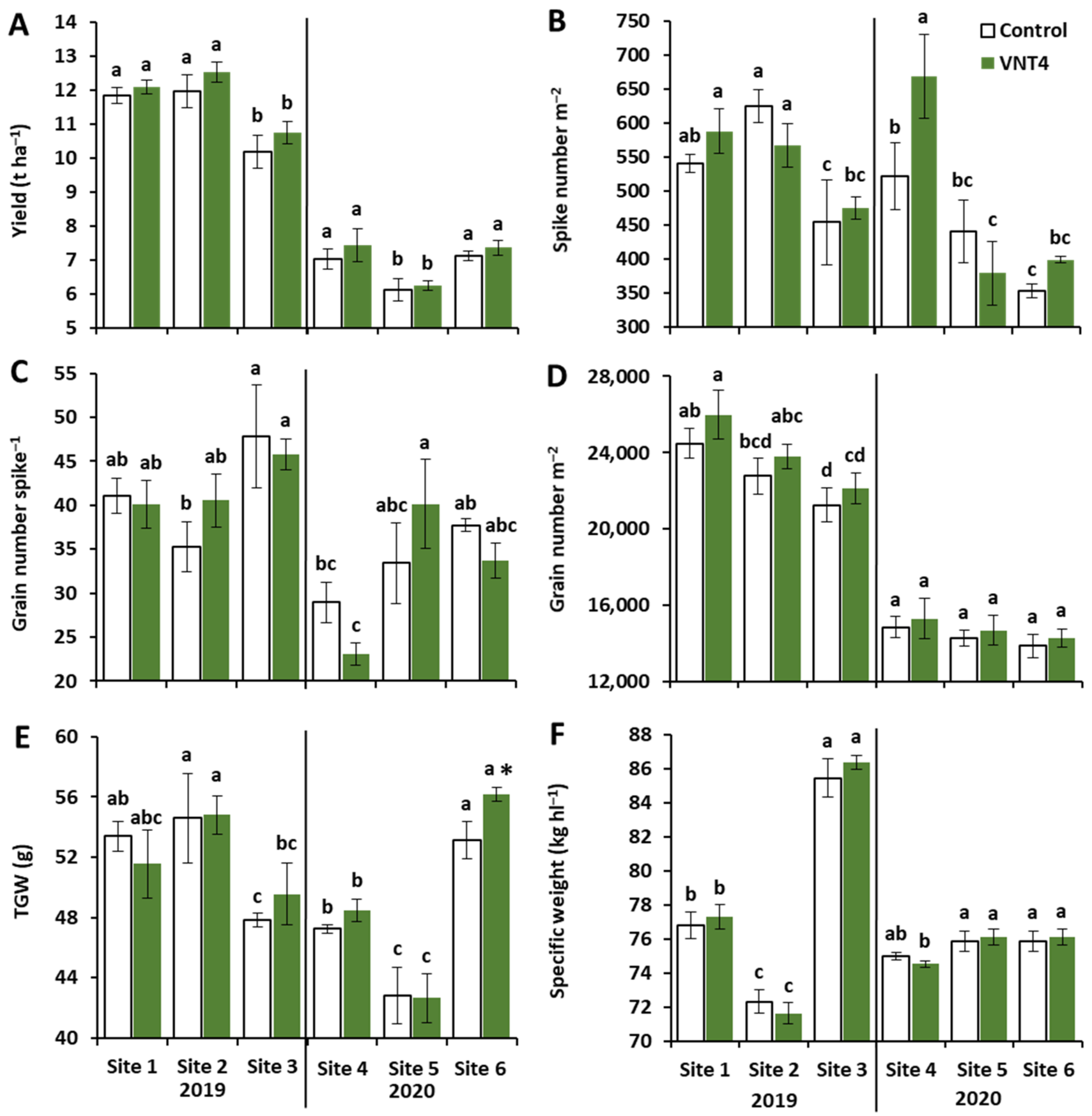
3.1. Experiment 1: Study of the Impact of VNT4 on Grain Yield, Yield Components and N-Related Traits under Six Contrasting Field Trials
3.1.1. Impacts of Year, Site and VNT4 on Grain Yield and Its Components
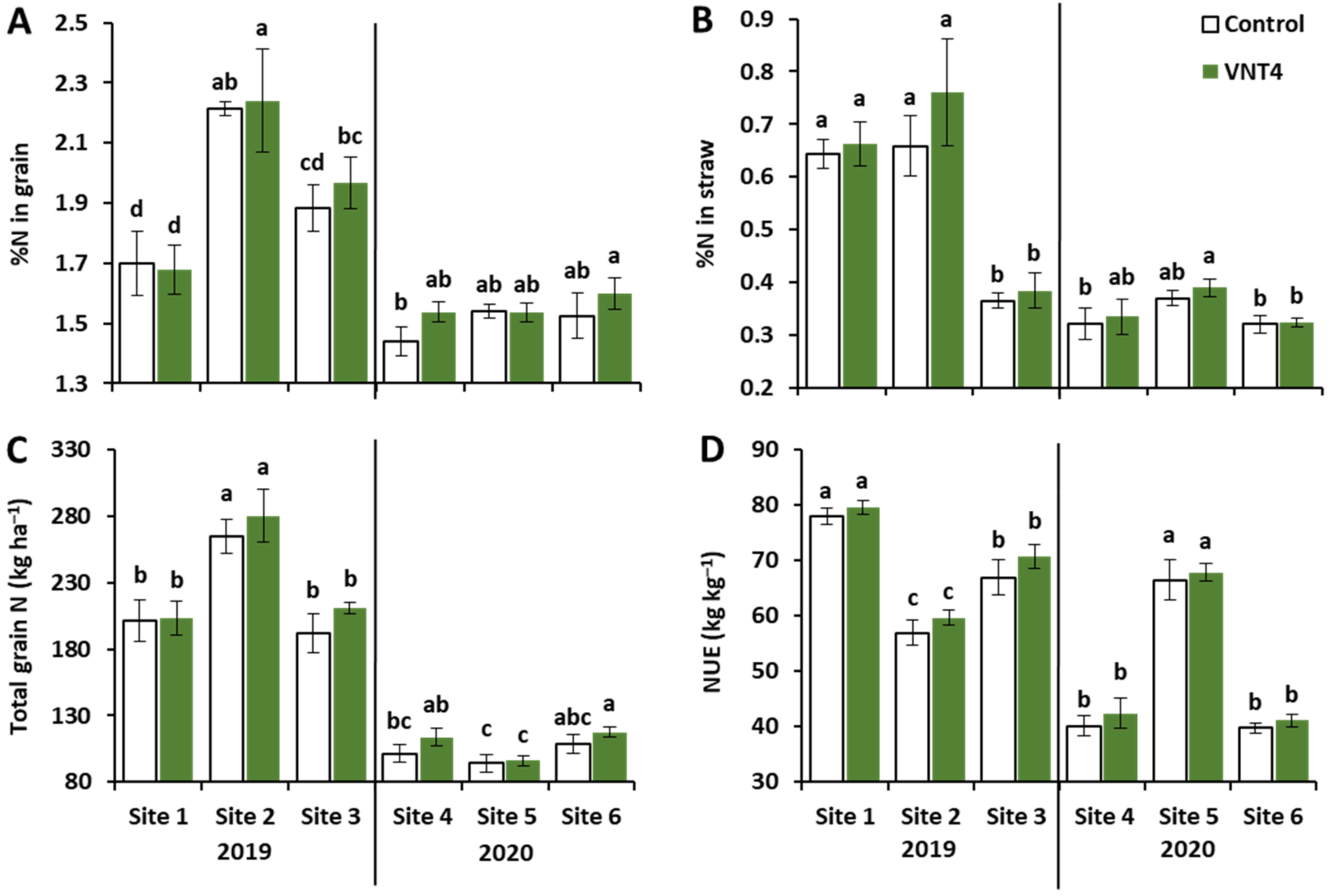
3.1.2. Effects of Year, Site and VNT4 on N-Related Traits
3.2. Experiment 2: Dynamics of Growth, Total N and N Uptake Using the 15N Labelling Method
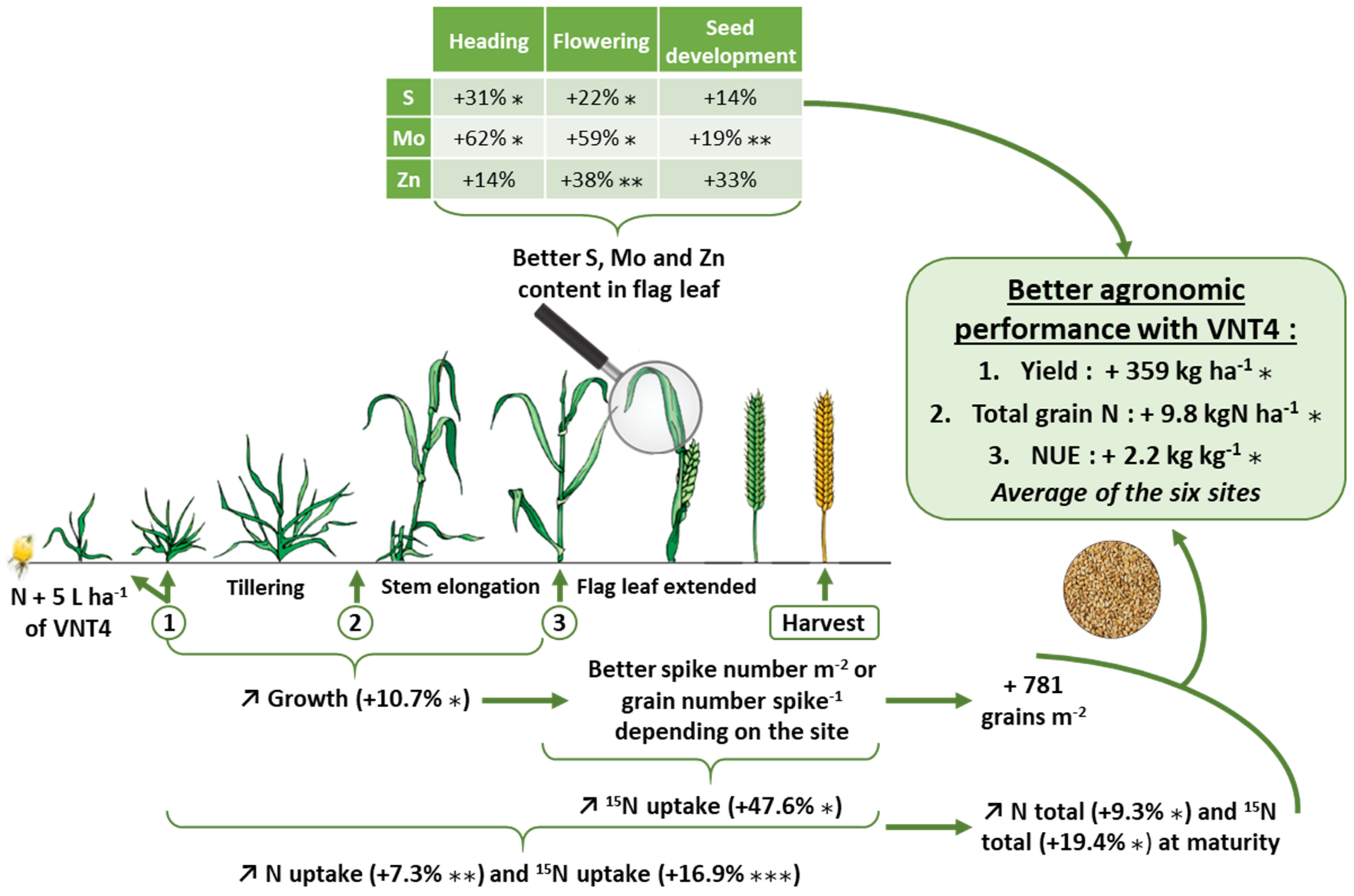
3.2.1. Impacts of VNT4 on Growth during the Crop Cycle
3.2.2. Effects of VNT4 on Total N and 15N Uptake during the Crop Cycle
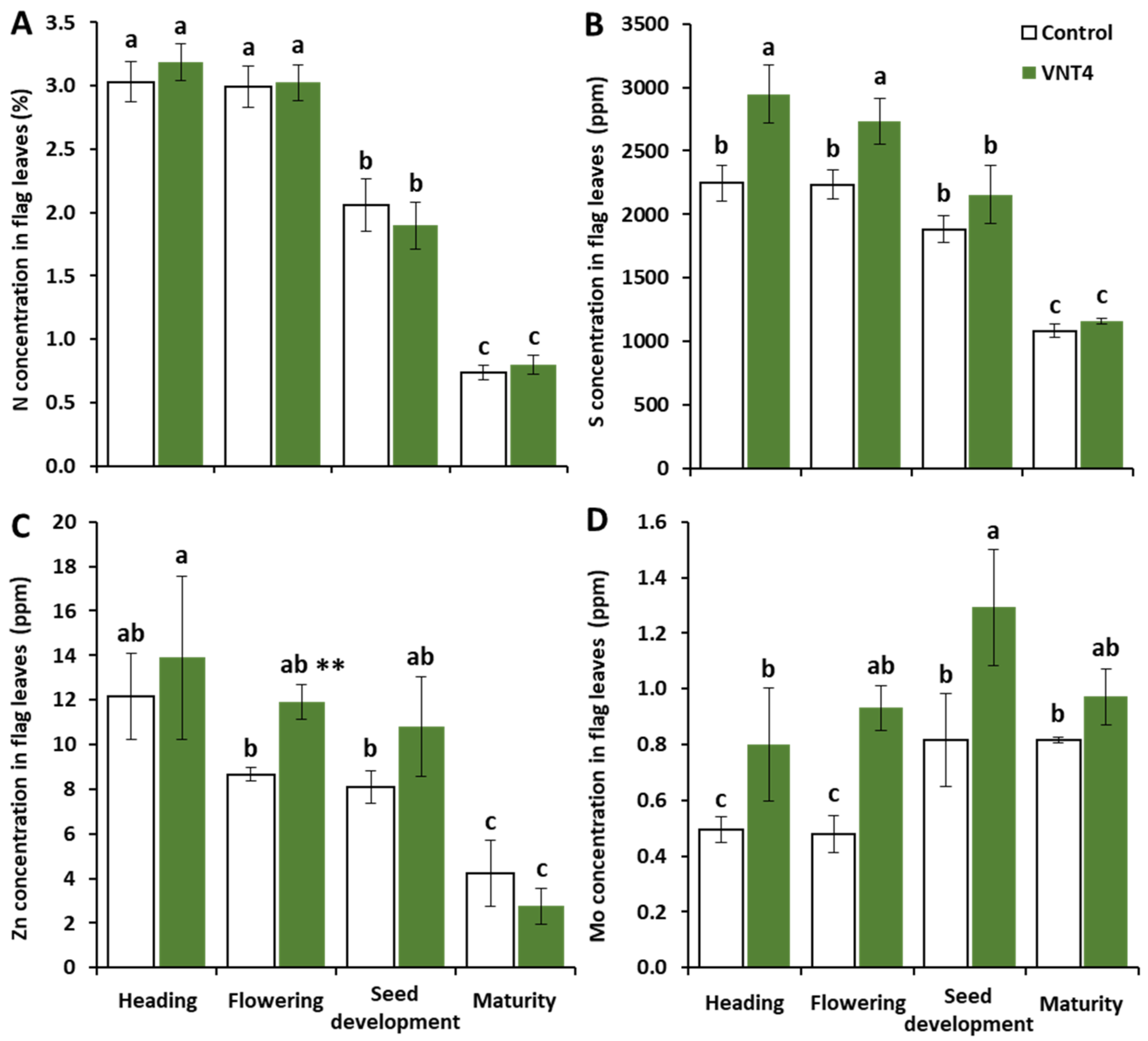
3.2.3. Impacts of VNT4 on Elemental Contents in Flag Leaves
4. Discussion
4.1. VNT4 Improved Yield by Increasing Grain Number per Square Metre and/or TGW Despite Strong Year and Site Effects
4.2. VNT4 Increased Total Grain N and NUE Irrespective of the Pedoclimatic Conditions and the N Supply
4.3. The Beneficial Impacts of VNT4 Are also Related to the Enhancement of Plant Growth and Improvements in S, Zn and Mo Contents in Flag Leaves
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Erisman, J.W.; Sutton, M.A.; Galloway, J.; Klimont, Z.; Winiwarter, W. How a Century of Ammonia Synthesis Changed the World. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 636–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Tian, H. Global Nitrogen and Phosphorus Fertilizer Use for Agriculture Production in the Past Half Century: Shifted Hot Spots and Nutrient Imbalance. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2017, 9, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Cassman, K.G.; Matson, P.A.; Naylor, R.; Polasky, S. Agricultural Sustainability and Intensive Production Practices. Nature 2002, 418, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, W.L.; Kidwell, K.K.; McCracken, V.A.; Bolton, R.P.; Allen, M. Economically Optimal Wheat Yield, Protein and Nitrogen Use Component Responses to Varying N Supply and Genotype. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Räbiger, T.; Andres, M.; Hegewald, H.; Kesenheimer, K.; Köbke, S.; Quinones, T.S.; Böttcher, U.; Kage, H. Indirect Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Oilseed Rape Cropping Systems by NH3 Volatilization and Nitrate Leaching as Affected by Nitrogen Source, N Rate and Site Conditions. Eur. J. Agron. 2020, 116, 126039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanantenasoa, M.M.J.; Génermont, S.; Gilliot, J.-M.; Bedos, C.; Makowski, D. Meta-Modeling Methods for Estimating Ammonia Volatilization from Nitrogen Fertilizer and Manure Applications. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 236, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Saxena, A. Sources and Leaching of Nitrate Contamination in Groundwater. Curr. Sci. 2020, 118, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misselbrook, T.H.; Van Der Weerden, T.J.; Pain, B.F.; Jarvis, S.C.; Chambers, B.J.; Smith, K.A.; Phillips, V.R.; Demmers, T.G.M. Ammonia Emission Factors for UK Agriculture. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Weerden, T.J.; Luo, J.; Di, H.J.; Podolyan, A.; Phillips, R.L.; Saggar, S.; de Klein, C.A.M.; Cox, N.; Ettema, P.; Rys, G. Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Urea Fertiliser and Effluent with and without Inhibitors Applied to Pasture. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 219, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormier, F.; Foulkes, J.; Hirel, B.; Gouache, D.; Moënne-Loccoz, Y.; Gouis, J.L. Breeding for Increased Nitrogen-Use Efficiency: A Review for Wheat (T. Aestivum L.). Plant Breed. 2016, 135, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkesford, M.J. Genetic Variation in Traits for Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Wheat. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 2627–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, R.; Yadav, R. Genetics Analysis of Nitrogen Use Efficiency Component Traits under Nitrogen-Limiting Environment. Cereal Res. Commun. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, R.; Mirsky, S.B.; Tully, K.L. Cover Crops Reduce Nitrate Leaching in Agroecosystems: A Global Meta-Analysis. J. Environ. Qual. 2018, 47, 1400–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Sun, X.; Hussain, S.; Ali, U.; Rana, M.S.; Rasul, F.; Saleem, M.H.; Moussa, M.G.; Bhantana, P.; Afzal, J.; et al. Molybdenum-Induced Effects on Nitrogen Metabolism Enzymes and Elemental Profile of Winter Wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.) Under Different Nitrogen Sources. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Zhao, P.; Shi, H.; Wang, Y.; Qin, S.; Liu, H. Nitrogen Supply Enhances Zinc Uptake and Root-to-Shoot Translocation via up-Regulating the Expression of TaZIP3 and TaZIP7 in Winter Wheat (Triticum Aestivum). Plant Soil 2019, 444, 501–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, F.; Provenzano, M.E.; Sestili, F.; Ruggeri, R. Synergistic Effect of Sulfur and Nitrogen in the Organic and Mineral Fertilization of Durum Wheat: Grain Yield and Quality Traits in the Mediterranean Environment. Agronomy 2018, 8, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohan, J.-P.; Le Souder, C.; Guicherd, C.; Lorgeou, J.; Du Cheyron, P.; Bonnefoy, M.; Decarrier, A.; Piraux, F.; Laurent, F. Combining Breeding Traits and Agronomic Indicators to Characterize the Impact of Cultivar on the Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Bread Wheat. Field Crop. Res. 2019, 242, 107588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maignan, V.; Bernay, B.; Géliot, P.; Avice, J.-C. Biostimulant Effects of Glutacetine® and Its Derived Formulations Mixed with N Fertilizer on Post-Heading N Uptake and Remobilization, Seed Yield and Grain Quality in Winter Wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossmann, A.; Buchner, P.; Savill, G.P.; Powers, S.J.; Hawkesford, M.J.; Mühling, K.H. Foliar N Application at Anthesis Stimulates Gene Expression of Grain Protein Fractions and Alters Protein Body Distribution in Winter Wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossmann, A.; Scherf, K.A.; Rühl, G.; Greef, J.M.; Mühling, K.H. Effects of a Late N Fertiliser Dose on Storage Protein Composition and Bread Volume of Two Wheat Varieties Differing in Quality. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 102944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moll, R.H.; Kamprath, E.J.; Jackson, W.A. Analysis and Interpretation of Factors Which Contribute to Efficiency of Nitrogen Utilization. Agron. J. 1982, 74, 562–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taulemesse, F.; Le Gouis, J.; Gouache, D.; Gibon, Y.; Allard, V. Post-Flowering Nitrate Uptake in Wheat Is Controlled by N Status at Flowering, with a Putative Major Role of Root Nitrate Transporter NRT2.1. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbottin, A.; Lecomte, C.; Bouchard, C.; Jeuffroy, M.-H. Nitrogen Remobilization during Grain Filling in Wheat. Crop Sci. 2005, 45, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörtensteiner, S.; Feller, U. Nitrogen Metabolism and Remobilization during Senescence. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalos, D.; Jeffery, S.; Sanz-Cobena, A.; Guardia, G.; Vallejo, A. Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Urease and Nitrification Inhibitors on Crop Productivity and Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 189, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, H.; Yan, X.; Yagi, K. Evaluation of Effectiveness of Enhanced-Efficiency Fertilizers as Mitigation Options for N2O and NO Emissions from Agricultural Soils: Meta-Analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krol, D.J.; Forrestal, P.J.; Wall, D.; Lanigan, G.J.; Sanz-Gomez, J.; Richards, K.G. Nitrogen Fertilisers with Urease Inhibitors Reduce Nitrous Oxide and Ammonia Losses, While Retaining Yield in Temperate Grassland. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Huf, M.; Olfs, H.-W. Effect of the Nitrification Inhibitor DMPP on Nitrous Oxide Emissions and the Stabilization of Ammonium Following the Injection of Dairy Slurry and Digestate in a Soil-Column Experiment. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolajsen, M.T.; Pacholski, A.S.; Sommer, S.G. Urea Ammonium Nitrate Solution Treated with Inhibitor Technology: Effects on Ammonia Emission Reduction, Wheat Yield, and Inorganic N in Soil. Agronomy 2020, 10, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artola, E.; Cruchaga, S.; Ariz, I.; Moran, J.F.; Garnica, M.; Houdusse, F.; Mina, J.M.G.; Irigoyen, I.; Lasa, B.; Aparicio-Tejo, P.M. Effect of N-(n-Butyl) Thiophosphoric Triamide on Urea Metabolism and the Assimilation of Ammonium by Triticum Aestivum L. Plant Growth Regul. 2011, 63, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano-Hinojosa, A.; Correa-Galeote, D.; González-López, J.; Bedmar, E.J. Effect of Nitrogen Fertilisers on Nitrous Oxide Emission, Nitrifier and Denitrifier Abundance and Bacterial Diversity in Closed Ecological Systems. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 103380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanin, L.; Venuti, S.; Tomasi, N.; Zamboni, A.; De Brito Francisco, R.M.; Varanini, Z.; Pinton, R. Short-Term Treatment with the Urease Inhibitor N-(n-Butyl) Thiophosphoric Triamide (NBPT) Alters Urea Assimilation and Modulates Transcriptional Profiles of Genes Involved in Primary and Secondary Metabolism in Maize Seedlings. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Ortiz, R.; Naranjo, M.Á.; Ruiz-Navarro, A.; Atares, S.; García, C.; Zotarelli, L.; San Bautista, A.; Vicente, O. Enhanced Agronomic Efficiency Using a New Controlled-Released, Polymeric-Coated Nitrogen Fertilizer in Rice. Plants 2020, 9, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C. Effects of Controlled-Release Fertilizer on Rice Grain Yield, Nitrogen Use Efficiency, and Greenhouse Gas Emissions in a Paddy Field with Straw Incorporation. Field Crop. Res. 2020, 253, 107814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Liu, L.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shi, R. Application of Controlled Release Urea Improved Grain Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omara, P.; Aula, L.; Oyebiyi, F.B.; Eickhoff, E.M.; Carpenter, J.; Raun, W.R. Biochar Application in Combination with Inorganic Nitrogen Improves Maize Grain Yield, Nitrogen Uptake, and Use Efficiency in Temperate Soils. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Ortiz, R.; Naranjo, M.Á.; Ruiz-Navarro, A.; Caballero-Molada, M.; Atares, S.; García, C.; Vicente, O. New Eco-Friendly Polymeric-Coated Urea Fertilizers Enhanced Crop Yield in Wheat. Agronomy 2020, 10, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lv, J.; Coulter, J.A.; Xie, J.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Tang, C.; Niu, T.; Gan, Y. Slow-Release Fertilizer Improves the Growth, Quality, and Nutrient Utilization of Wintering Chinese Chives (Allium Tuberosum Rottler Ex Spreng.). Agronomy 2020, 10, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, A.H.; Debnath, T.; Das, U.; Prity, S.A.; Haque, A.; Rahman, M.M.; Parvez, M.S. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Alleviate Fe-Deficiency Symptoms in Sunflower by Increasing Iron Uptake and Its Availability along with Antioxidant Defense. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 150, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.L.; Spaepen, S.; du Jardin, P.; Delaplace, P. Biostimulant Effects of Rhizobacteria on Wheat Growth and Nutrient Uptake Depend on Nitrogen Application and Plant Development. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2019, 65, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Jardin, P. Plant Biostimulants: Definition, Concept, Main Categories and Regulation. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhin, O.I.; Lubyanov, A.A.; Yakhin, I.A.; Brown, P.H. Biostimulants in Plant Science: A Global Perspective. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellagi, A.; Quillere, I.; Hirel, B. Beneficial Soil-Borne Bacteria and Fungi: A Promising Way to Improve Plant Nitrogen Acquisition. J. Exp. Bot. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, E.-A.; Ahmed, N.; Durieu, C.; Grieu, P.; Lamaze, T. Marine and Fungal Biostimulants Improve Grain Yield, Nitrogen Absorption and Allocation in Durum Wheat Plants. J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 158, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Lv, D.G.; Qin, S.J.; Yang, L.; Ma, H.Y.; Liu, G.C. Changes in Photosynthesis, Fluorescence, and Nitrogen Metabolism of Hawthorn (Crataegus Pinnatifida) in Response to Exogenous Glutamic Acid. Photosynthetica 2010, 48, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, C.; Arkoun, M.; Jamois, F.; Schwarzenberg, A.; Yvin, J.-C.; Etienne, P.; Laîné, P. Silicon Promotes Growth of Brassica Napus L. and Delays Leaf Senescence Induced by Nitrogen Starvation. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laîné, P.; Haddad, C.; Arkoun, M.; Yvin, J.-C.; Etienne, P. Silicon Promotes Agronomic Performance in Brassica Napus Cultivated under Field Conditions with Two Nitrogen Fertilizer Inputs. Plants 2019, 8, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.L.; Glaes, J.; Spaepen, S.; Bodson, B.; du Jardin, P.; Delaplace, P. Biostimulant Effects of Bacillus Strains on Wheat from in Vitro towards Field Conditions Are Modulated by Nitrogen Supply. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2019, 182, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouphael, Y.; Colla, G. Synergistic Biostimulatory Action: Designing the Next Generation of Plant Biostimulants for Sustainable Agriculture. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, P.; Nelson, L.; Kloepper, J.W. Agricultural Uses of Plant Biostimulants. Plant Soil 2014, 383, 3–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, M.A.; Giuliani, M.M.; Flagella, Z.; Reyneri, A.; Blandino, M. Impact of Nitrogen Fertilisation Strategies on the Protein Content, Gluten Composition and Rheological Properties of Wheat for Biscuit Production. Field Crop. Res. 2020, 107829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styczen, M.E.; Abrahamsen, P.; Hansen, S.; Knudsen, L. Analysis of the Significant Drop in Protein Content in Danish Grain Crops from 1990–2015 Based on N-Response in Fertilizer Trials. Eur. J. Agron. 2020, 115, 126013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkesford, M.J.; Buchner, P.; Riche, A.B. Nutrient Dynamics in Wheat. In Annual Plant Reviews Online; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Xie, Y.; Hu, L.; Feng, B.; Li, S. Remobilization of Vegetative Nitrogen to Developing Grain in Wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.). Field Crop. Res. 2016, 196, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, Z.; Cai, R.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Yin, Y. Physiological and Molecular Response of Wheat Roots to Nitrate Supply in Seedling Stage. Agric. Sci. China 2011, 10, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Wu, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, J.; Qiang, S.; Guo, J.; Xiang, Y.; Zou, H.; Wu, L. Dynamic Change and Accumulation of Grain Macronutrient (N, P and K) Concentrations in Winter Wheat under Different Drip Fertigation Regimes. Field Crop. Res. 2020, 250, 107767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkesford, M.J.; Riche, A.B. Impacts of G x E x M on Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Wheat and Future Prospects. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Sootahar, M.; Zeng, X.; Wang, Y.; Su, S.; Soothar, P.; Bai, L.; Kumar, M.; Zhang, Y.; Mustafa, A.; Ye, N. The Short-Term Effects of Mineral- and Plant-Derived Fulvic Acids on Some Selected Soil Properties: Improvement in the Growth, Yield, and Mineral Nutritional Status of Wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.) under Soils of Contrasting Textures. Plants 2020, 9, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maignan, V.; Géliot, P.; Avice, J.-C. Glutacetine® Biostimulant Applied on Wheat under Contrasting Field Conditions Improves Grain Number Leading to Better Yield, Upgrades N-Related Traits and Changes Grain Ionome. Plants 2021, 10, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colla, G.; Hoagland, L.; Ruzzi, M.; Cardarelli, M.; Bonini, P.; Canaguier, R.; Rouphael, Y. Biostimulant Action of Protein Hydrolysates: Unraveling Their Effects on Plant Physiology and Microbiome. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancashire, P.D.; Bleiholder, H.; Boom, T.V.D.; Langelüddeke, P.; Stauss, R.; Weber, E.; Witzenberger, A. A Uniform Decimal Code for Growth Stages of Crops and Weeds. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1991, 119, 561–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comité Français d’Etude et de Développement de la Fertilisation Raisonnée (COMIFER). Calcul De La Fertilisation Azotée; COMIFER: Paris, France, 2000; ISBN 978-2-910393-09-0. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, C.A. Use of NBPT and Ammonium Thiosulphate as Urease Inhibitors with Varying Surface Placement of Urea and Urea Ammonium Nitrate in Production of Hard Red Spring Wheat under Reduced Tillage Management. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastri, A.; Toderi, G.; Bernati, E.; Govi, G. Ammonia Volatilization and Yield Response from Urea Applied to Wheat with Urease (NBPT) and Nitrification (DCD) Inhibitors. Agrochimica 2000, 44, 231–239. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, C.M.; Engel, R.E.; Chen, C.; Wallander, R.; Jones, C.A. Late-Fall, Winter, and Spring Broadcast Applications of Urea to No-Till Winter Wheat II. Fertilizer N Recovery, Yield, and Protein as Affected by NBPT. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2017, 81, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, A.; Wang, Z.; Roelcke, M.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F.; Pasda, G.; Zerulla, W.; Wissemeier, A.H.; Liu, X. Effect of a New Urease Inhibitor on Ammonia Volatilization and Nitrogen Utilization in Wheat in North and Northwest China. Field Crop. Res. 2015, 175, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, F.S.; Filho, M.C.M.T.; Buzetti, S.; Pagliari, P.H.; Santini, J.M.K. Can NBPT Urease Inhibitor in Combination with Azospirillum Brasilense Inoculation Improve Wheat Development? Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2020, 117, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A. Additions of Ammonium Sulfate and Urease Inhibitor with Urea to Improve Spring Wheat and Sugar Beet Yield. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2018, 64, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, Y.A.; Chen, C.; Jensen, T. Urease and Nitrification Inhibitors Impact on Winter Wheat Fertilizer Timing, Yield, and Protein Content. Agron. J. 2016, 108, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Q.; Perveen, R.; El-Esawi, M.A.; Ali, S.; Hussain, S.M.; Amber, M.; Iqbal, N.; Rizwan, M.; Alyemeni, M.N.; El-Serehy, H.A.; et al. Low Doses of Cuscuta Reflexa Extract Act as Natural Biostimulants to Improve the Germination Vigor, Growth, and Grain Yield of Wheat Grown under Water Stress: Photosynthetic Pigments, Antioxidative Defense Mechanisms, and Nutrient Acquisition. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimzadeh, J.; Alikhani, H.A.; Etesami, H.; Pourbabaei, A.A. Improved Phosphorus Uptake by Wheat Plant (Triticum Aestivum L.) with Rhizosphere Fluorescent Pseudomonads Strains Under Water-Deficit Stress. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popko, M.; Michalak, I.; Wilk, R.; Gramza, M.; Chojnacka, K.; Górecki, H. Effect of the New Plant Growth Biostimulants Based on Amino Acids on Yield and Grain Quality of Winter Wheat. Molecules 2018, 23, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Shi, W.; Zhou, M.; Ma, X.; Zhang, H. Effect of Biochar on Nitrogen Use Efficiency, Grain Yield and Amino Acid Content of Wheat Cultivated on Saline Soil. Plant Soil Environ. 2019, 65, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Liu, X.; Hu, A.; Song, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z. Effects of Biochar-Based Controlled Release Nitrogen Fertilizer on Nitrogen-Use Efficiency of Oilseed Rape (Brassica Napus L.). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Wang, K.; Zheng, X. Effects of Nitrification Inhibitors (DCD and DMPP) on Nitrous Oxide Emission, Crop Yield and Nitrogen Uptake in a Wheat–Maize Cropping System. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 2427–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekowski, A.; Wimmer, M.A.; Hitzmann, B.; Hermannseder, B.; Hahn, H.; Zörb, C. Application of Urease Inhibitor Improves Protein Composition and Bread-Baking Quality of Urea Fertilized Winter Wheat. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Luo, Y.; Kong, X.; Huang, C.; Wang, Z. Interactions Between Exogenous Cytokinin and Nitrogen Application Regulate Tiller Bud Growth via Sucrose and Nitrogen Allocation in Winter Wheat. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Liu, Z.; Hao, L.; Song, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Gao, Q.; Liu, X. Effects of Enterobacter Cloacae HG-1 on the Nitrogen-Fixing Community Structure of Wheat Rhizosphere Soil and on Salt Tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, M.; Aery, N.C. Influence of Silicon on Growth, Relative Water Contents and Uptake of Silicon, Calcium and Potassium in Wheat Grown in Nutrient Solution. J. Plant Nutr. 2008, 31, 1867–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Boada, R.; Marini, C.; Llugany, M.; Valiente, M. Influence of a Plant Biostimulant on the Uptake, Distribution and Speciation of Se in Se-Enriched Wheat (Triticum Aestivum L. Cv. Pinzón). Plant Soil 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kichey, T.; Le Gouis, J.; Sangwan, B.; Hirel, B.; Dubois, F. Changes in the Cellular and Subcellular Localization of Glutamine Synthetase and Glutamate Dehydrogenase During Flag Leaf Senescence in Wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.). Plant Cell Physiol. 2005, 46, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Hu, C.; Hussain, S.; Rana, M.S.; Riaz, M.; Afzal, J.; Aziz, O.; Elyamine, A.M.; Farag Ismael, M.A.; Sun, X. Molybdenum-Induced Effects on Photosynthetic Efficacy of Winter Wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.) under Different Nitrogen Sources Are Associated with Nitrogen Assimilation. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 141, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Song, K.; Sun, L.; Qin, Q.; Jiang, T.; Jiang, Q.; Xue, Y. Morpho-Physiological and Transcriptome Analysis Provide Insights into the Effects of Zinc Application on Nitrogen Accumulation and Metabolism in Wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabak, M.; Lepiarczyk, A.; Filipek-Mazur, B.; Lisowska, A. Efficiency of Nitrogen Fertilization of Winter Wheat Depending on Sulfur Fertilization. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleto, I.; de la Peña, M.; Rodríguez-Escalante, J.; Bejarano, I.; Glauser, G.; Aparicio-Tejo, P.M.; González-Moro, M.B.; Marino, D. Leaves Play a Central Role in the Adaptation of Nitrogen and Sulfur Metabolism to Ammonium Nutrition in Oilseed Rape (Brassica Napus). BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesse, H.; Nikiforova, V.; Gakière, B.; Hoefgen, R. Molecular Analysis and Control of Cysteine Biosynthesis: Integration of Nitrogen and Sulphur Metabolism. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 1283–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforova, V.J.; Kopka, J.; Tolstikov, V.; Fiehn, O.; Hopkins, L.; Hawkesford, M.J.; Hesse, H.; Hoefgen, R. Systems Rebalancing of Metabolism in Response to Sulfur Deprivation, as Revealed by Metabolome Analysis of Arabidopsis Plants. Plant Physiol. 2005, 138, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migge, A.; Bork, C.; Hell, R.; Becker, T.W. Negative Regulation of Nitrate Reductase Gene Expression by Glutamine or Asparagine Accumulating in Leaves of Sulfur-Deprived Tobacco. Planta 2000, 211, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zörb, C.; Steinfurth, D.; Gödde, V.; Niehaus, K.; Mühling, K.H. Metabolite Profiling of Wheat Flag Leaf and Grains during Grain Filling Phase as Affected by Sulfur Fertilisation. Funct. Plant Biol. 2012, 39, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Juhasz, A.; Islam, S.; Diepeveen, D.; Zhang, J.; Wang, P.; Ma, W. Impact of Mid-Season Sulphur Deficiency on Wheat Nitrogen Metabolism and Biosynthesis of Grain Protein. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Plessis, A.; Vincent, J.; Duchateau, N.; Besson, A.; Dardevet, M.; Prodhomme, D.; Gibon, Y.; Hilbert, G.; Pailloux, M.; et al. Transcriptional and Metabolic Alternations Rebalance Wheat Grain Storage Protein Accumulation under Variable Nitrogen and Sulfur Supply. Plant J. 2015, 83, 326–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carciochi, W.D.; Divito, G.A.; Fernández, L.A.; Echeverría, H.E. Sulfur Affects Root Growth and Improves Nitrogen Recovery and Internal Efficiency in Wheat. J. Plant Nutr. 2017, 40, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poisson, E.; Trouverie, J.; Brunel-Muguet, S.; Akmouche, Y.; Pontet, C.; Pinochet, X.; Avice, J.-C. Seed Yield Components and Seed Quality of Oilseed Rape Are Impacted by Sulfur Fertilization and Its Interactions with Nitrogen Fertilization. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ertani, A.; Schiavon, M.; Trentin, A.; Malagoli, M.; Nardi, S. Effect of an Alfalfa Plant-Derived Biostimulant on Sulfur Nutrition in Tomato Plants. In Molecular Physiology and Ecophysiology of Sulfur, Proceedings of the International Plant Sulfur Workshop, Freiburg-Munzigen, Germany, 2014; De Kok, L.J., Hawkesford, M.J., Rennenberg, H., Saito, K., Schnug, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 215–220. ISBN 978-3-319-20137-5. [Google Scholar]
- Siwik-Ziomek, A.; Szczepanek, M. Soil Enzyme Activity and Sulphur Uptake by Oilseed Rape Depending on Fertilization and Biostimulant Application. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Soil Plant Sci. 2018, 68, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.-L.; Zhang, F.-M.; Sun, K.; Zhang, W.; Dai, C.-C. Fungal Endophyte Phomopsis Liquidambari Improves Iron and Molybdenum Nutrition Uptake of Peanut in Consecutive Monoculture Soil. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2019, 19, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Lu, L.; Xie, R.; Zhang, M.; Jernstedt, J.; Hou, D.; Ramsier, C.; Brown, P. Supplemental Macronutrients and Microbial Fermentation Products Improve the Uptake and Transport of Foliar Applied Zinc in Sunflower (Helianthus Annuus L.) Plants. Studies Utilizing Micro X-Ray Florescence. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 5, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Component | Concentration | |
|---|---|---|
| Glutamic acid (%) | 3.6 | |
| Organic acids (%) | 7.4 | |
| Total soluble sugars (g L−1) | 34.4 | |
| Elements (%) | Cl | 18.2 |
| Ca | 13.4 | |
| C | 11.5 | |
| N | 0.88 | |
| K | 0.29 | |
| Na | 0.18 | |
| Mo | 0.18 | |
| Elements (ppm) | S | 140 |
| B | 20 | |
| Mg | 11 | |
| Si | 11 | |
| P | 10.2 | |
| Cu | 1.1 | |
| Ni | 0.6 | |
| Co | 0.4 | |
| Zn | 3.5 | |
| Se | 0.06 | |
| Parameter | Global ANOVA | ANOVA 2019 | ANOVA 2020 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site | Treat. | S × T | Site | Treat. | S × T | Site | Treat. | S × T | |
| Yield | *** | * | 0.951 | *** | 0.073 | 0.813 | *** | 0.238 | 0.875 |
| Spike m−2 | *** | 0.289 | 0.050 | ** | 0.894 | 0.189 | *** | 0.261 | 0.074 |
| Grain spike−1 | *** | 0.952 | 0.142 | * | 0.733 | 0.370 | ** | 0.857 | 0.123 |
| Grain m−2 | *** | 0.065 | 0.994 | ** | 0.085 | 0.906 | 0.262 | 0.397 | 0.999 |
| TGW | *** | 0.267 | 0.455 | ** | 0.977 | 0.519 | *** | 0.117 | 0.318 |
| Specific weight | *** | 0.687 | 0.524 | *** | 0.636 | 0.433 | ** | 0.959 | 0.597 |
| %N in grain | *** | 0.148 | 0.672 | *** | 0.678 | 0.816 | 0.226 | 0.123 | 0.454 |
| %N in straw | *** | 0.291 | 0.995 | *** | 0.210 | 0.567 | * | 0.448 | 0.906 |
| Total grain N | *** | * | 0.835 | *** | 0.232 | 0.727 | ** | 0.089 | 0.575 |
| NUE | *** | * | 0.893 | *** | 0.075 | 0.819 | *** | 0.291 | 0.965 |
| Control | VNT4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerial biomass (gDW m−2) | Tillering | 44.4 ± 4.0 | 47.1 ± 9.7 |
| Stem elongation | 348.0 ± 64.8 | 381.7 ± 78.1 | |
| Flag leaf extended | 867.8 ± 77.0 | 958.6 ± 17.4 | |
| Maturity | 2041.9 ± 257.3 | 1965.1 ± 159.1 | |
| N total in aerial parts (gN m−2) | Tillering | 1.57 ± 0.30 | 1.96 ± 0.55 |
| Stem elongation | 8.36 ± 1.94 | 9.59 ± 1.65 | |
| Flag leaf extended | 9.25 ± 0.74 | 10.18 ± 0.91 | |
| Maturity | 14.27 ± 0.50 | 15.60 ± 0.21 * | |
| 15N total in aerial parts (mgN m−2) | Tillering | 6.84 ± 2.45 | 11.16 ± 5.06 |
| Stem elongation | 100.00 ± 22.62 | 116.86 ± 19.68 | |
| Flag leaf extended | 95.84 ± 8.11 | 105.88 ± 7.87 | |
| Maturity | 126.22 ± 6.08 | 150.74 ± 9.56 * | |
| Harvest Index | 0.36 ± 0.07 | 0.39 ± 0.05 | |
| N Harvest Index | 0.71 ± 0.04 | 0.73 ± 0.04 | |
| 15N Harvest Index | 0.76 ± 0.04 | 0.80 ± 0.06 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maignan, V.; Coquerel, R.; Géliot, P.; Avice, J.-C. VNT4, a Derived Formulation of Glutacetine® Biostimulant, Improved Yield and N-Related Traits of Bread Wheat When Mixed with Urea-Ammonium-Nitrate Solution. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11051013
Maignan V, Coquerel R, Géliot P, Avice J-C. VNT4, a Derived Formulation of Glutacetine® Biostimulant, Improved Yield and N-Related Traits of Bread Wheat When Mixed with Urea-Ammonium-Nitrate Solution. Agronomy. 2021; 11(5):1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11051013
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaignan, Victor, Raphaël Coquerel, Patrick Géliot, and Jean-Christophe Avice. 2021. "VNT4, a Derived Formulation of Glutacetine® Biostimulant, Improved Yield and N-Related Traits of Bread Wheat When Mixed with Urea-Ammonium-Nitrate Solution" Agronomy 11, no. 5: 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11051013
APA StyleMaignan, V., Coquerel, R., Géliot, P., & Avice, J.-C. (2021). VNT4, a Derived Formulation of Glutacetine® Biostimulant, Improved Yield and N-Related Traits of Bread Wheat When Mixed with Urea-Ammonium-Nitrate Solution. Agronomy, 11(5), 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11051013








