Abstract
Understanding phosphorus (P) dynamics in tropical sandy soil treated with organic residues of contrasting quality is crucial for P management using organic amendments. This research determined P fractions in a tropical sandy soil under the application of organic residues of different quality, including groundnut stover (GN), tamarind leaf litter (TM), dipterocarp leaf litter (DP), and rice straw (RS). The organic residues were applied at the rate of 10 t DM ha−1 year−1. The P fractions were examined by a sequential extraction procedure. Organic residue application, regardless of residue quality, resulted in P accumulation in soils. For unamended soil, 55% of total P was mainly associated with Al (hydr)oxides. Organic residue application, regardless of residue quality, diminished the NH4F-extractable P (Al-P) fraction, but it had a nonsignificant effect on NaOH-extractable P (Fe-P). The majority of Al-P and Fe-P fractions were associated with crystalline Al and Fe (hydr)oxides. NH4Cl-extractable P (labile P), NaHCO3-extractable P (exchangeable P and mineralizable organic P), HCl-extractable P (Ca-P), and residual P fractions in soil were significantly increased as a result of the incorporation of organic residues. The application of organic residues, particularly those high in ash alkalinity, increase soil pH, labile P, and Ca-P fractions. In contrast, applications of residues high in lignin and polyphenols increase residual P fraction, which is associated with organo-mineral complexes and clay mineral kaolinite.
1. Introduction
Sandy soils in the tropics are recognized to be infertile because of their high sand content (>85%), low soil pH, usually ranging from 4.0 to 5.5, low cation exchange capacity, low water-holding capacity, low soil organic matter, and low plant nutrient contents, particularly phosphorus (P) [1,2]. Phosphorus is an essential element for plant growth. Soils in many regions are low in available P because P is adsorbed by soil minerals (e.g., kaolinite (Al2Si2O5(OH)4), goethite (α-FeOOH), hematite (Fe2O3), and gibbsite (Al(OH)3)) and lost by leaching and runoff [3,4,5,6]. Consequently, the addition of P fertilizers plays a vital role in ensuring the sustainability of food production systems.
The P dynamics in soils are mainly associated with P adsorbed on soil constituents, such as clay minerals, aluminum (Al) and iron (Fe) (hydr)oxides, and soil organic matter [7,8,9,10]. Frossard et al. [11] reported that the total P contents in topsoil (0–15 cm) range from 50 to 3000 mg kg−1, depending on the parent materials, soil types, and soil management practices (e.g., fertilization, manuring, and cropping systems). Generally, most P (50–75%) in mineral soils is mainly associated with Al and Fe (hydr)oxides in acidic soils and with calcium (Ca) in calcareous soils [12,13].
It has been known that the application of organic materials (e.g., manure, composts, organic residues) can be used as alternative sources for plant nutrients [14,15,16] and can solve many problems pertaining to the physicochemical properties of sandy soils in tropical regions [1,16,17,18,19]. Noack et al. [20] considered organic residues as a source of P that contributes to various pools of soil P. The P concentrations in organic residues are dependent on the types and parts of plants [16,18,19]. Similar to nitrogen (N), organic P undergoes mineralization before it is available to plants in inorganic forms. It is well-established that mineralization occurring in applied organic materials is dependent on the biochemical quality of the organic materials, including contents of N, lignin, and polyphenols [21]. The application of organic materials (e.g., animal manure) increased P in topsoil in the form of P adsorbed onto Al and Fe (hydr)oxides, poorly crystalline calcium phosphate, and mineralizable organic P [22].
Previous studies have shown that the long-term application of organic residues of different biochemical quality to tropical sandy soils positively affects soil organic carbon accumulation, N transformation, soil aggregate formation, and plant nutrient availability [1,16,23,24,25]. With particular attention to P, the application of organic residues positively improves soil P availability due to increasing the phosphatase enzyme activities [26]. The recent study by Sukitprapanon et al. [16] reported that the long-term application of organic residues of different biochemical qualities, particularly those with elevated amounts of ash alkalinity, increases available P in a tropical sandy soil. In addition, the application of organic residues has environmental benefits such as the mitigation of greenhouse gas, retention of heavy metals and rare earth elements, and adsorption of pesticides in soils [27,28,29,30]. Although these aforementioned works have shed light on the effects of organic material application on soil quality and environment, there is limited knowledge on the dynamics of P in soils undergoing the incorporation of organic residues of contrasting quality. Understanding P fractions affected by organic amendment/fertilizer is crucial for effective P management of agricultural soils.
Therefore, this research hypothesized that the application of organic residues with different biochemical quality affects P fractions in tropical sandy soils. The addition of organic residues will enhance labile P, exchangeable P, and mineralizable organic P, and Ca-bound P fractions, but it will decrease P fractions, which are associated with Al and Fe oxide minerals as reported by previous studies [5]. Since organic residues have various chemical compositions [1,16,22], the application of organic residues with high N, low lignin, and low polyphenols, which are easily mineralized, will increase the labile P fraction, while the addition of residues with low N, high lignin, and high polyphenols, which are resistant to mineralization, leads to an increase of exchangeable P and mineralizable organic P fraction. The objectives of this research were (1) to determine P forms using a sequential extraction procedure and (2) to study the relationship between P fractions and soil properties in a tropical sandy soil that has experienced organic residues of different biochemical quality. This study will help better understand the effects of diverse organic residues on soil P dynamics in a sandy soil in a tropical region.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site Characteristics
The study site was a long-term field experiment that had been carried out over 22 years since 1995 at a research station of the Field Crops Research Center, Ministry of Agriculture and Co-Operatives, in Khon Kaen province, Northeast Thailand (UTM coordinate: 48Q 267648E, 1808314N). The land use of the experiment had been converted from deciduous forests 50 years ago and planted with field crops (e.g., casava and sugarcane) prior to the establishment of the present field experiment in 1995. The present experiment has been annually incorporated by organic residues of different quality to study their long-term effects on soil quality. The climate in this study area is a tropical savanna with an average temperature of 24 °C in winter and 29 °C in summer and an average rainfall of 224 mm in summer and 1104 mm in the rainy season [31]. The soil was classified as Typic Kandiustult, according to Key to Soil Taxonomy 2014 [32]. The initial physicochemical characteristics of the sandy soils used in this study were reported by Vityakon et al. [1]. Soil texture of the topsoil (0–15 cm) was sandy containing 93% sand, 5% silt, and 2% clay. Furthermore, the topsoil is strongly acid (pH H2O = 5.5) and has a low soil organic carbon content (0.21%) [1].
2.2. Experimental Design and Soil Sampling
The field experiment had five treatments arranged in a randomized complete block design with three replications. The five treatments included (1) without organic residues (control) (CT), (2) groundnut (Arachis hypogaea) stover (GN), (3) tamarind (Tamarindus indica) leaf litter (TM), (4) rice (Oryza sativa) straw (RS), and (5) dipterocarp (Dipterocarpus tuberculatus) leaf litter (DP). The chemical properties of these organic residues are shown in Table 1. The GN is considered a high-quality organic residue because it contains a high content of nitrogen (N) (1.7%) but low content of recalcitrant substances such as lignin (L) (9.9%) and polyphenols (Pp) (1.6%), while TM is considered a medium-quality residue because it contains high contents of N (1.7%) and also high lignin (17%) and polyphenol (4.6%). The RS and DP are classified as low-quality organic residues based on their low contents of N (1.0% and 0.40%, respectively); however, DP contains higher amounts of lignin (25%) and polyphenol (5.0%) than RS (3.6 and 1.5% for lignin and polyphenol, respectively) [1]. The C/N ratios of GN, TM, DP, and RS are 22, 23, 40, and 86 (Table 1). Based on the critical C/N ratio of 24, GN and TM are easily mineralized by microorganisms, whereas DP and RS are slow to be mineralized [16]. Although TM has a similar C/N ratio to GN, the turnover rate of TM was slower than that of GN because TM contains higher amounts of lignin and polyphenols than GN. The RS is more rapidly decomposed than DP, because the former contains lower amounts of lignin and polyphenols (Table 1).

Table 1.
Chemical properties of organic residues used in this study.
The organic residues used in this research were applied at the rate of 10 t DM ha−1 year−1 to bare soil plots 4 m × 4 m in size. The application rate at 10 t DM ha−1 year−1 used in this research was based on the amounts of residues (e.g., RS, GN) that are left in the field after harvesting the crops. Sukitprapanon et al. [16] reported that P concentrations in GN, TM, DP, and RS used for year 22 of the experiment were 2169, 763, 480, and 655 mg kg−1 (Table 1), which accounted for inputs of 22, 7.6, 4.8, and 6.6 kg P ha−1 year−1, respectively.
The organic residues were incorporated into a soil depth of 0–15 cm, which is the common plow layer of agricultural soils in Thailand. The residue application was annual in early May before the start of the rainy season. The plots were kept weed free by monthly to bimonthly manual removal using hand hoes.
Five soil samples were randomly collected from the 2 m × 2 m area at the center of each plot from 0 to 15 cm of the soil surface after 1 year of the organic residues incorporation (May 2017) (year 22 of the experiment). The five soil samples in each plot were homogeneously mixed to form a single composite sample. Composite samples were air-dried and sieved at 2 mm for analysis of physicochemical properties.
2.3. Chemical Analysis
Soil pH (H2O) was measured in water using a ratio of 1:1 soil to water [33]. Total organic carbon (TOC) was determined by the wet combustion method [34]. Cation exchange capacity (CEC) was determined by the 1 M ammonium acetate (NH4OAc), pH 7 method [33]. Concentrations of aluminum (Al), iron (Fe), and phosphorus (P) in poorly crystalline oxides were determined using ammonium oxalate extraction, and those in well crystalline oxides were determined using dithionite citrate bicarbonate extraction [33]. The total P concentration in bulk soil samples was measured on aqua regia digest (3:1 HCl:HNO3 at 130 °C for 1 h in a digestion block [35]. The concentrations of Al, Fe, and P in extracts were measured by inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES, Analytik Jena, PQ 9000). The degree of P saturation (DPS) was reported as the molar ratio between P and the major sorbent matrix constituents of acidic soil, namely Fe + Al contents, extracted by ammonium oxalate extraction. The DPS was calculated by the following equation [5].
where P-ox, Al-ox, and Fe-ox are the concentrations of oxalate extractable P, Al, and Fe, respectively.
DPS (%) = P-ox/(Al-ox + Fe-ox)
Most soil constituents, including organic matter, clay minerals, Al and Fe (hydr)oxides, and some trioctahedral micas (mostly biotite), were completely dissolved by aqua regia, while quartz, feldspars, dioctahedral micas (mostly muscovite), and amphiboles were dissolved to a limited extent [36]. Hereafter, the result of P, measured by aqua regia digest, will be referred to as total P concentration.
The clay fraction (<0.002 mm) of bulk soil samples of each plots was separated by the sedimentation method [37]. The mineralogical compositions of bulk soil and clay samples were analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) using an XPert3 powder diffractometer with a Pixel detector (CuKα radiation 45 kV, 40 mA).
2.4. Sequential Extraction Procedure
The sequential extraction procedure (SEP) used to determine forms of P in bulk soil samples in this study was first described by Abdala et al. [5], and it was developed from the SEP according to Zhang and Kovar [38]. This information provides a full assessment of the geochemical behaviors of P in a tropical sandy soil after the incorporation of organic residues of contrasting quality [5,7,39]. This procedure determined (1) the labile fraction (water soluble and easily desorbable forms) (1 M NH4Cl, 1:40 soil:solution, 1 h extraction), (2) Al-bound P fraction (0.5 M NH4F at pH 8.2, 1:40 soil:solution, 1 h extraction), (3) exchangeable P and mineralizable organic P fraction (0.5 M NaHCO3 at pH 8.5, 1:40 soil:solution, 18 h extraction), (4) Fe-bound P fraction (0.1 M NaOH + 1 M NaCl, 1:40 soil:solution, 18 h extraction), (5) Ca-bound P fraction (1 M HCl, 1:40 soil:solution, 18 h extraction), and (6) residual P fraction (the difference between total concentrations and the sum of the first 5 steps). The extractants were shaken in an end-over-end shaker at 15 rpm for the specified times and then centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 15 min. The supernatants were filtered through a 0.25 µm nylon membrane filter. The concentrations of P in various extracts were measured by ICP-OES.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
An analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by mean comparisons using the least significant difference (LSD) test was used to determine the effects of residue treatment and their interactions on chemical properties. Principal component analysis (PCA) was used to determine the similar geochemical behavior of P fractions and soil properties and to group soil samples based on their chemical properties. The analyses of ANOVA, regression, and PCA were carried out using Statistica software version 8.0 for Windows. The statistical significance level was p < 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Application Effects of Organic Residues of Different Quality on Soil Chemical and Mineralogical Properties
Selected soil chemical properties of the tropical sandy soils influenced by the addition of organic residues of differing quality are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Mean values for the selected chemical properties of sandy soils, which had been incorporated by organic residues of different biochemical quality 1.
The pH (H2O) of the soils ranged between 4.5 and 6.9. The pH (H2O) values of the residue-treated sandy soils were significantly higher than that of the control. The TM-treated soil had the highest pH value (6.9), which was an increase of 2.4 pH units over the control. The pH value of the high-quality residue GN-treated soil was lower than those of the low-quality residue-treated counterparts, which is due to the production of H+ during the mineralization of organic N [40]. A bivariate relationship showed that TOC had a positive relationship with pH (H2O) (R2 = 0.50) (P < 0.05) (Figure 1a), indicating that the addition of organic residue can neutralize the protons (H+) in soil solution. Sukitprapanon et al. [16] reported that TM contains higher concentration of ash alkalinity than GN, DP, and RS. Consequently, TM-treated soil has a higher soil pH value than the other soils.
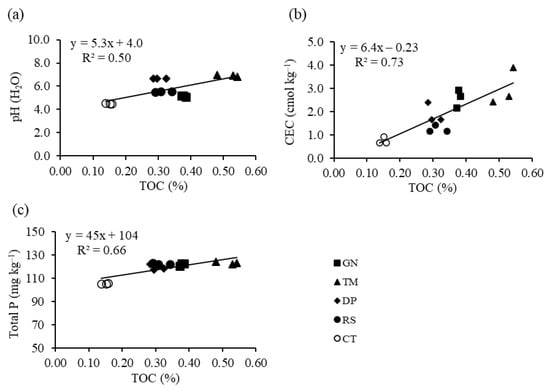
Figure 1.
Bivariate relationships between total organic carbon (TOC) and pH (H2O) (a), TOC and cation exchange capacity (CEC) (b), and TOC and total P (c) for the tropical sandy soil under the incorporation of organic residues of differing biochemical quality.
The organic residue incorporation resulted in significantly increased TOC in all residue treatments compared to the control. The highest increase in TOC was for TM-treated soils (0.52%) (Table 2), which is because the TOC in TM-treated soil is stabilized and stored mainly in soil microaggregates (0.053–0.25 mm-sized) [25]. Carbon compounds, including labile and recalcitrant compounds, in organic residues interact with N in promoting stabilization in microaggregates [25]. Furthermore, the TM contains elevated amounts of allelopathic compounds, particularly tannin, which have an adverse effect on bacterial and fungal activities in soils [41]. The residue-treated soils had CEC values approximately 1.6–4.0 times higher than control soil (0.75 cmol kg−1) (Table 2). The bivariate relationship revealed that CEC had a positive relationship with TOC (R2 = 0.73) (p < 0.05) (Figure 1b), indicating that the addition of organic materials can enhance the negatively charged sites in tropical sandy soils [42].
Total P concentrations in soils ranged between 106 and 123 mg kg−1 (Table 2). The residue-treated soils contained significantly higher total P concentrations than the control soil (Table 2). There is a positive relationship between TOC and total P with R2 = 0.66 (p < 0.05) (Figure 1c), indicating that organic residue incorporation plays an important role in P accumulation. Although organic residues had various amounts of total P (Table 1), the total P concentrations in residue-treated soils were not significantly different from each other (Table 2), indicating that the different amounts of P inputs did not significantly affect the total P concentrations in the sandy soil. Based on the similar soil total P concentrations among the residue-treated soils, it was likely that various amounts of P inputs, derived from organic residues, did not significantly affect the P fractions, either. The DPS values of the tropical sandy soils ranged between 9.1 and 14% (Table 2), which is below the critical level of 25% saturation, indicating that P adsorption onto surfaces of Al and Fe (hydr)oxides was not completely saturated [5]. Values lower than the critical level of DPS indicate that the risk of P loss in tropical sandy soils via leaching is limited, although the soils contain low amounts of clay particles. The P losses are partly due to frequent weed removal from the experimental plots. Although other plausible factors for P losses including runoff and leaching may exist, they were not determined in this study.
The amounts of dithionite-extractable Fe (Fe-d) were 2.9- to 4.9-fold higher than oxalate-extractable Fe (Fe-ox), whereas the amounts of dithionite-extractable Al (Al-d) were 6.4–42% lower than oxalate-extractable Al (Al-ox) (Table 2). These results indicate that most Fe occurs in well crystalline (hydr)oxides, while Al occurs in poorly crystalline (hydr)oxides that form in the soil. Apart from high-quality residue GN incorporation, oxalate-extractable P (P-ox) concentrations in soils with low N residue incorporation, particularly DP and RS, significantly decreased compared to those in the control soil (Table 2). However, there was no significant different between GN (78 mg kg−1) and control (84 mg kg−1) soils (Table 2). It has been reported that organic components (e.g., lignin and cellulose) released from added organic residues can inhibit P sorption onto the surface of Fe/Al (hydr)oxide minerals [42,43,44,45]. The addition of the N-rich residue GN did not significantly lower the amounts of P-ox in soils compared to control, because control and GN-treated soils were under strongly acidic conditions (soil pH < 5.5), which is suitable for the adsorption of P on Fe/Al (hydr)oxides [41].
Our results showed that the incorporation of organic amendments had no effects on soil mineral composition. Quartz (SiO2) was the dominant mineral in both the bulk samples and clay fractions in all treatments. In addition, kaolinite (Al2Si2O5(OH)4) was the dominant clay mineral (Table 3). As these soil samples contained small amounts of clay fraction (approximately 2%) consisting of kaolinite and inert minerals, quartz, and anatase (TiO2), the application of organic materials to these soils is essential to improve their fertility and productivity.

Table 3.
Mineralogical compositions in bulk soil samples and clay fractions of topsoil (0–15 cm) of sandy soils in year 22 of the incorporation of organic residues of different biochemical quality 1.
3.2. Phosphorus Fractions
Phosphorus fractions in the tropical sandy soil amended with organic residues of differing quality are shown in Figure 2. Clearly, the P fractions in the unamended tropical sandy soil were mostly associated with the NH4F-extractable P (Al-P) fraction (55% of total P), followed in decreasing order of relative contents by NaOH-extractable P (Fe-P) (15%), NaHCO3-extractable P (exchangeable P and mineralizable organic P) (11%), residual P (9.4%), NH4Cl-extractable P (labile P) (9.0%), and HCl-extractable P (Ca-P) (0.32%) fractions (Figure 2).
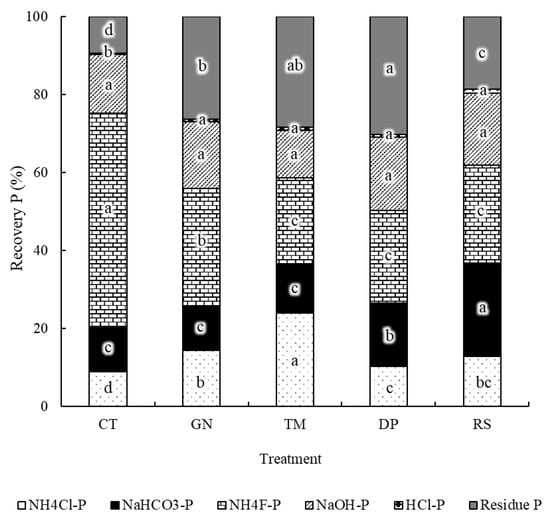
Figure 2.
The proportions of phosphorus (%) in a tropical sandy soil as influenced by the incorporation of organic residues of contrasting quality including control soil (CT), groundnut stover-treated soil (GN), tamarind leaf litter-treated soil (TM), dipterocarp leaf litter-treated soil (DP), and rice straw-treated soil (RS). Significant differences within a P fraction among treatments are indicated by different letters (a, b, c, d) at p < 0.05.
With the incorporation of organic residues, the proportion of NH4F-extractable P significantly decreased to the range between 22 and 30% of total P (Figure 2). The lowest proportion of Al-P was found in the soils treated with TM (22% of total P), DP (24% of total P), and RS (25% of total P). In contrast, the NaOH-extractable P in organic residue-treated soils was a similar proportion to that in control soil, which indicated that the incorporation of organic residues of differing quality had little effect on the transformation of P-sorbing Fe (hydr)oxides in the soil. This study highlights that P was mostly adsorbed onto Al-OH sites on Al-bearing minerals, such as gibbsite (Al(OH)3), boehmite (AlOOH), Al-substituted goethite, and Al-substituted hematite ((AlFe)2O3) [23,46].
The incorporation of organic residues significantly increased concentrations of HCl-extractable P, NH4Cl-extractable P, NaHCO3-extractable P, and residual P fractions in soils (Figure 2). The P proportion extracted by HCl was very small, ranging from 0.32 to 1.1% of total P. The HCl-extractable P in organic residue-treated soils (0.61–1.1% of total P) increased 2- to 3-fold over those in the control soil (0.32% of total P). Calcium in organic residues is released into the soil during organic residue mineralization [16], and it can precipitate phosphate [47].
The highest proportion of P extracted by NH4Cl was in TM-treated soils (24% of total P), followed by GN (14%), RS (13%), DP (10%), and CT (9.0%) (Figure 2). The proportions of NaHCO3-extractable P in RS-, DP-, TM-, and GN-treated soils were 24%, 16%, 13%, and 12% of total P, respectively. The values for the residue-treated soils were higher than for the control (11% of total P) (Figure 2). Several studies have reported that the addition of organic materials increases NaHCO3-extractable P fractions (e.g., [48]). This study indicates that the incorporation of organic residues, particularly low-quality ones (i.e., RS and DP), significantly increased the proportion of NaHCO3-extractable P, which is mostly associated with exchangeable P and mineralizable organic P.
The proportion of residual P in soils ranged between 9.4% and 30% of total P (Figure 2). The residual P fractions in organic residue-treated soils (19–30% of total P) were significantly higher than those in the control (9.4% of total P) (Figure 2). The residual P fraction is not dissolved by the previous sequential extractions, because this P fraction is strongly bound to Al-OH sites on clay minerals and/or to the organic part of soil colloids in the form of organo-mineral complexes [7].
3.3. Relationships between Phosphorus Fractions and Soil Properties
It has been shown that in highly weathered soils, important soil properties controlling P fractions include soil pH, TOC, and Al and Fe (hydr)oxide minerals [49]. Based on previous findings, this study investigated the relationship between P fractions and soil properties including soil pH, TOC, total P, dithionite-extractable Fe (Fe-d), dithionite-extractable Al (Al-d), oxalate-extractable Fe (Fe-ox), and oxalate-extractable Al (Al-ox).
Principal component analysis (PCA) based on standardized data of P fractions, pH (H2O), TOC, total P, Al-d, Al-ox, Fe-d, and Fe-ox showed that the first two components explained 70% of the variation (Figure 3). Attributes could be arranged into two major groups. The first group consisted of Al-d, Al-ox, Fe-d, Fe-ox, NH4F-extractable P, and NaOH-extractable P, which had associations with untreated (control) soils (Figure 3a,b). The NH4F-extractable P was positively associated with Al-d (R2 = 0.68) (p < 0.05) (Figure 4a) and to a lesser extent with oxalate-extractable Al (R2 = 0.45) (p < 0.05) (Figure 4b). These results indicate that NH4F-extractable P occurred more in the forms of crystalline Al (hydr)oxides in the soil without the addition of organic residues. In addition, NH4F-extractable P is located in the opposite quadrant to the soil pH (H2O) (Figure 3a). Bivariate relationship revealed that NH4F-extractable P was negatively associated with pH (H2O) (R2 = 0.63) (p < 0.05) (Figure 4c), reflecting the precipitation reaction between P and Al in soil solution, which yields P-bearing Al (hydr)oxide minerals under low soil pH conditions [50].
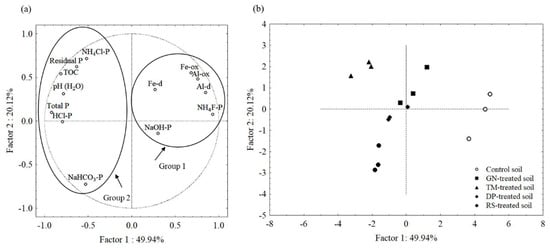
Figure 3.
Principle component analysis based on phosphorus fractionation and soil properties of tropical sandy soils, (a) distribution of properties (variables) and (b) distribution of cases. NH4Cl-P = NH4Cl-extractable P; NH4F-P = NH4F-extractable P; NaHCO3-P = NaHCO3-extractable P; HCl-P = HCl-extractable P.
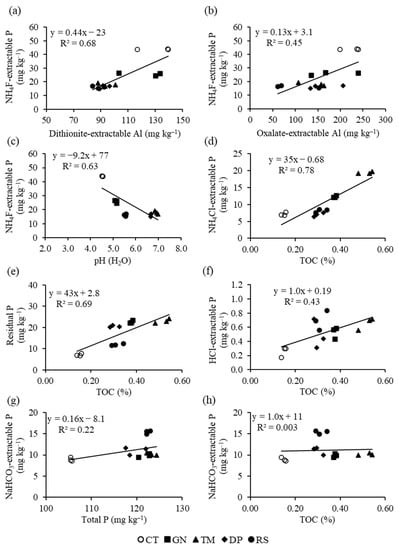
Figure 4.
Bivariate relationships between dithionite-extractable Al and NH4F-extractable P (a), oxalate-extractable Al and NH4F-extractable P (b), pH (H2O) and NH4F-extractable P (c), TOC and NH4Cl-extractable P (d), TOC and residual P (e), TOC and HCl-extractable P (f), total P and NaHCO3-extractable P (g), and TOC and NaHCO3-extractable P (h) for tropical sandy soil under the incorporation of organic residues.
Several studies have reported that P in tropical soils is mainly associated with Fe and Al (hydr)oxides (e.g., [5,22,49]). This study also indicates that much P in control soil was more closely associated with Al (hydr)oxide minerals than in other soils, because these minerals have lower solubility in the acid conditions of the untreated soils and have higher potential for anion (e.g., PO42−) adsorption than the residue-treated soils [51]. In addition, Samadi and Gilkes [52] reported that Al (hydr)oxides contain higher surface reactivity for P adsorption than do Fe (hydr)oxides. The PCA showed that the untreated soils were separated from the organic residue-treated soils because the incorporation of organic residue increases soil pH, which probably transforms crystalline Al and Fe (hydr)oxides into poorly crystalline forms [5]. Lindsay [53] stated that the decomposition of organic matter releases electrons and reducing agents, such as citrate, oxalate, and malate, into soil solution, which increases the solubilization of Al and Fe (hydr)oxides.
The second group in the PCA consisted of TOC, pH (H2O), total P, NH4Cl-extractable P, HCl-extractable P, residual P, and NaHCO3-extractable P, which were associated with organic residue-treated soils (Figure 3a,b). The PCA showed that soil pH, TOC, total P, NH4Cl-extractable P, HCl-extractable P, and residual P were closely associated with TM-treated soil, whereas NaHCO3-extractable P was associated with low-quality RS and DP-treated soils (Figure 3a,b). A bivariate relationship showed that TOC was positively related to NH4Cl-extractable P, residual P, and HCl-extractable P (R2 = 0.78, 0.69, and 0.43, respectively) (p < 0.05) (Figure 4d–f). Organic residue-treated soils, particularly TM, were enriched in these fractions, because organic residues contain high ash alkalinity, leading to an increase in soil pH [16,54]. Under alkaline conditions, HCl-extractable P accumulates in soil in the form of calcium phosphate minerals (e.g., [12,23,49,55]). Eduah et al. [56] and Sukitprapanon et al. [16] suggested that additions of lime and ash alkalinity-rich organic materials increases the concentrations of available P in acidic soils. Additionally, the residual P fraction in organic residue-treated soils, particularly TM and DP (Figure 2 and Figure 3), likely contained P retained by kaolinite and the organo-mineral complexes. According to the XRD results of this study, kaolinite was the dominant clay mineral, indicating that kaolinite is the major mineral controlling P retention and the formation of organo-mineral complexes in these soils. Gilkes and Prakongkep [57] reported that the P retention capacity of kaolinite in tropical soils was elevated, because kaolinite had a small crystal size. In addition, organic residues with high contents of lignin and polyphenol play a crucial role in soil organic carbon accumulation via humification [25]. Li and Johnson [58] reported that when the soil pH increased as a result of the addition of organic materials, Al-OH sites on kaolinite reacted with humic substances to form Al–organic complexes.
The PCA also showed that the NaHCO3-extractable P fraction (exchangeable P and mineralizable organic P) was associated with soils treated with low-quality organic residues RS and DP (Figure 3). A bivariate relationship revealed that the NaHCO3-extractable P fraction was significantly associated with total P (R2 = 0.22) (p < 0.05) (Figure 4g), but it was not significantly associated with TOC (R2 = 0.003) (p < 0.05) (Figure 4h). The low association of exchangeable P and mineralizable organic P (NaHCO3-extractable P) with TOC was in contrast with the results of Maranguit et al. [59] and Recena et al. [60], who reported that the TOC contents in soils are significantly related to organic P. Although our results showed that the NaHCO3-extractable P fractions in soils were elevated when organic incorporation was applied (Figure 2), the nonsignificant association of TOC with NaHCO3-extractable P was likely due to the diverse quality of residues used in this research. As mentioned in Section 3.1, applications of organic residues of contrasting quality generally enhanced the concentrations of TOC and total P in soils (Table 2) (Figure 1c). However, the application of low-quality organic residues RS and DP increased the proportion of NaHCO3-extractable P in soils, whereas the high- and medium-quality organic residues GN and TM had little effect (Figure 3a,b). High-quality organic residues (e.g., GN) contain high N and low lignin and polyphenol concentrations, resulting in their rapid decomposition by microorganisms [21]. Consequently, the exchangeable P and mineralizable organic P fraction (NaHCO3-extractable P) in high-quality organic residue-treated soils (e.g., GN) can easily release P into soil solution to become available for plant uptake. In contrast, low-quality organic residues containing low N, high lignin, and high polyphenol concentrations have slower rates of mineralization than their higher quality counterparts [21]. Therefore, this study indicates that the addition of organic residue and organic residue quality are important factors controlling the P forms in tropical sandy soils.
For agricultural and environmental applications, the addition of high-quality organic residues containing elevated contents of nitrogen and low contents of lignin and polyphenols into sandy soils or poorly fertile soils can help increase the available/labile forms of plant nutrients (e.g., P), because the nutrients in residues are more easily released during mineralization [16,21,61]. However, application of this type of residue into soils, which have already had high amounts of nutrients, can cause adverse effects on the environment such as eutrophicaton and leaching of P to groundwater [62]. In this case, the combination of different types of residues should be considered to synchronize the nutrient requirement of corp needs and to reduce the adverse effects on the environment [63].
4. Conclusions
This study determined the dynamics of P forms under the application of different quality organic residues. The incorporation of organic residues, regardless of their quality, led to P accumulation, as indicated by the increased total P in the sandy soil. In addition, the different amounts of P inputs did not significantly affect the total P concentrations and also did not significantly affect the P fractions in the sandy soil. The P fractions were altered under residue application relative to unamended soil such that Al-P fractions that dominated in the unamended soil were decreased, while Fe-P fractions were not affected. In addition, organic residue application led to increases in labile P, Ca-P, exchangeable P and mineralizable organic P, and residual P fractions. The application of organic residues increased soil pH. Released Ca from organic residues is likely to react with phosphate to form insoluble calcium phosphate minerals. Regarding low-quality organic residues such as DP and RS, their application resulted in elevated contents of the exchangeable P and mineralizable organic P fraction relative to their high-quality counterparts, i.e., GN. The elevated proportions of exchangeable P and mineralizable organic P fraction and residual P fraction in soil with the incorporation of TM, DP, and RS were due to the fact that the residues, containing low N, high lignin, and high polyphenols, had slower rates of decomposition and mineralization than their high-quality counterparts with high N, low lignin, and low polyphenols. The organic residues high in lignin and polyphenols contributed to the increase of residual P, which was associated with organo-mineral complexes and clay mineral kaolinite. Additionally, it was found that P loss via leaching was limited in the tropical sandy soil, as indicated by the low degree of P saturation. Further studies are required to determine the behavior of organic P forms under the application of organic residues of different quality, because organic P forms are essential sources of available P for plants. In addition, the application of organic materials into soils has several advantages to the environment relative to chemical fertilizers such as reducing eutrophication and increasing nutrient availability. Further studies on the application effects of organic residues of different quality on behaviors of P and other elements leading to their losses from tropical sandy soils are also required.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.-S.S., R.J.G., and P.V.; methodology, T.-S.S., M.J., D.T., N.P., R.J.G., and P.V.; software, T.-S.S. and N.P.; validation, T.-S.S., M.J., D.T., N.P., R.J.G., and P.V.; formal analysis, T.-S.S. and M.J.; investigation, T.-S.S., N.P. and M.J.; resources, T.-S.S.; data curation, T.-S.S., M.J., N.P., and D.T.; writing—original draft preparation, T.-S.S.; writing—review and editing, D.T., N.P., R.J.G., and P.V.; visualization, T.-S.S.; supervision, R.J.G., D.T., and P.V.; project administration, T.-S.S.; funding acquisition, T.-S.S. and P.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Thailand Research Fund (grant number MRG6180149) and Khon Kaen University.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank to staffs from Faculty of Agriculture, Khon Kaen University for advices on the chemical analyses.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Vityakon, P.; Meepech, S.; Cadisch, G.; Toomsan, B. Soil organic matter and nitrogen transformation mediated by plant residues of different qualities in sandy acid upland and paddy soils. Neth. J. Agric. Sci. 2000, 48, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, K.; Hayakawa, C.; Panitkasate, T.; Maskhao, I.; Funakawa, S.; Kosaki, T.; Nawata, E. Acidification and buffering mechanisms of tropical sandy soil in northeast Thailand. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 165, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Gilkes, R.J. Properties and distribution of iron oxides and their association with minor elements in the soils of south-western Australia. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1992, 43, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holford, I.C.R. Soil phosphorus: Its measurement, and its uptake by plants. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1997, 35, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdala, D.B.; da Silva, I.R.; Verguts, L.; Sparks, D.L. Long-term manure application effects on phosphorus speciation, kinetics and distribution in highly weathered agricultural soils. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, X. Effect of organic matter on phosphorus adsorption and desorption in a black soil from Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 187, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedley, M.J.; Stewart, J.W.B.; Chauhan, B.S. Changes in inorganic and organic soil-phosphorus fractions induced by cultivation practices and by laboratory incubation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1982, 46, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesterberg, D.; Zhou, W.Q.; Hitchison, K.J.; Beauchemin, S.; Sayers, D.E. XAFS study of adsorbed and mineral forms of phosphate. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 1999, 6, 636–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesterberg, D. Macroscale chemical properties and X-ray absorption spectroscopy of soil phosphorus. In Synchrotron-Based Techniques in Soils and Sediments; Singh, B., Grafe, M., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 313–356. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson, A.K.; Gustadsson, J.P.; Hesterberg, D. Phosphorus speciation of clay fractions from long-term fertility experiments in Sweden. Geoderma 2015, 241, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frossard, E.; Brossard, M.; Hedley, M.J.; Metherell, A. Reactions controlling the cycling of P in soils. In Phosphorus in the Global Environment; Tiessen, H., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 107–137. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson, A.K.; Hesterberg, D.; Klysubun, W.; Gustafsson, J.P. Phosphorus dynamics in Swedish agricultural soils as influenced by fertilization and mineralogical properties: Insights gained from batch experiments and XANES spectroscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566, 1410–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laakso, J.; Uusitalo, R.; Yli-Halla, M. Phosphorus speciation in agricultural catchment soils and in fresh and dried sediments of five constructed wetlands. Geoderma 2016, 271, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusiharni, E.; Gilkes, R. Minerals in the ash of Australian native plants. Geoderma 2012, 189, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakongkep, N.; Gilkes, R.J.; Wiriyakitnateekui, W. Forms and solubility of plant nutrient elements in tropical plant waste biochars. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2015, 178, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukitprapanon, T.; Jantamenchai, M.; Tulaphitak, D.; Vityakon, P. Nutrient composition of diverse organic residues and their long-term effects on available nutrients in a tropical sandy soil. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quilty, J.R.; Cattle, S.R. Use and understanding of organic amendments in Australian agriculture: A review. Soil Res. 2011, 49, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noack, S.R.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Smernik, R.J.; McBeath, T.M.; Armstrong, R.D. Crop residue phosphorus: Speciation and potential bio-availability. Plant Soil. 2012, 359, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, J.E.; Macdonald, L.M.; Smernik, R.J.; Cavagnaro, T.R. Organic amendments as phosphorus fertilizers: Chemical analysis, biological processes and plant P uptake. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 107, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noack, S.R.; McBeath, T.M.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Smernik, R.J.; Armstrong, R.D. Management of crop residues affects the transfer of phosphorus to plant and soil roots: Results from a dual-labelling experiment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 71, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, C.A.; Gachengo, C.N.; Delve, R.J.; Cadisch, G.; Giller, K.E. Organic inputs for soil fertility management in tropical agroecosystems: Application of an organic resource database. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2001, 83, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmieder, F.; Bergström, L.; Riddle, M.; Gustaffson, J.; Klysubun, W.; Zehetner, F.; Condron, L.; Kirchmann, H. Phosphorus speciation in a long-term manure-amended soil profile-Evidence from wet chemical extraction, 31P-NMR and P K-edge XANES spectroscopy. Geoderma 2018, 322, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samahadthai, P.; Vitkakon, P.; Saenjan, P. Effects of different quality plant residues on soil carbon accumulation and aggregate formation in a tropical sandy soils in Northeast Thailand as revealed by a 10-year field experiment. Land Degrad. Dev. 2010, 21, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivenge, P.; Vanlauwe, B.; Gentile, R.; Six, J. Organic resource quality influences short-term aggregate dynamics and soil organic carbon and nitrogen accumulation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puttaso, A.; Vityakon, P.; Rasche, F.; Saenjan, P.; Treloges, V.; Cadisch, G. Does organic residues quality influence carbon retention in a tropical sandy soils? Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Goh, K.M. Crop residues and management practices: Effect on soil quality, soil nitrogen dynamics, crop yield, and nitrogen recovery. Adv. Agron. 1999, 68, 197–319. [Google Scholar]
- Sukitprapanon, T.; Suddhiprakarn, A.; Kheoruenromne, I.; Gilkes, R.J. Rare earth elements in acid sulfate soils under long-term paddy rice cultivation in Thailand. Geoderma Reg. 2019, 17, e00216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Chen, S. The relationship between adsorption of heavy metal and organic matter in river sediments. Environ. Int. 1998, 24, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vischetti, C.; Manaci, E.; Casucci, C.; Bernardi, A.D.; Carninali, A. Adsorption and degradation of tree pesticides in vineyard sol and in an organic biomix. Environment 2020, 7, 113. [Google Scholar]
- Lal, R. Soil carbon sequestration to mitigate climate change. Geoderma 2004, 123, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meteorological Department. Climate of Thailand; Meteorological Department, Ministry of Information and Communication Technology: Bangkok, Thailand, 2015.
- Soil Survey Staff. Keys to Soil Taxonomy, 12th ed.; United State Department of Agriculture, Natural Resource Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- Rayment, G.E.; Lyons, D.J. Soil Chemical Methods-Australasia; CSIRO Publishing: Melbourne, Australia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 3. Chemical Method; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; SSSA Book Series; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 961–1010. [Google Scholar]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association-American Water Works Association: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, T.T. Use of partial dissolution techniques in geochemical exploration. J. Geochem. Explor. 1984, 20, 101–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindley, G.W.; Brown, G. Crystal Structures of Clay Minerals and Their X-ray Identification; Mineralogical Society Monograph No. 5; Mineralogical Society: London, UK, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Kovar, J.L. Phosphorus fractionation. In Methods for Phosphorus Analysis for Soils, Sediments, Residuals, and Waters; Pierzysnki, G.M., Ed.; North Carolina State University Press: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2000; pp. 50–59. [Google Scholar]
- Kovar, J.L.; Pierzynski, G.M. Methods of Phosphorus Analysis for Soils, Sediments, Residuals, and Waters, 2nd ed.; Southern Cooperative Series Bulletin No. 408; Virginia Tech University: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cleemput, O.V.; Boeckx, P. Nitrogen and its transformation. In Encyclopedia of Soil Science, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lawongsa, P.; Rungthong, R.; Kamolmanit, B.; Saenjan, P.; Vityakon, P. Responses of soil bacterial population to the appearance of allelopathic substances. Khon Kaen Agr. J. 2016, 44 (Suppl. 1), 983–990. [Google Scholar]
- Ellerbrock, R.H.; Gerke, H.H. Characterization of organic matter composition of soil and flow path surfaces based on physiochemical principles—A review. In Advances in Agronomy; Spark, D.L., Ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 117–177. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, L.; Riemsdijk, W.H.V.; Hiemstra, T. Factors controlling phosphate interaction with iron oxides. J. Environ. Qua. 2012, 41, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdala, D.B.; Ghosh, A.K.; Silva, I.R.; Novais, R.F.; Venegas, V.H.A. Phosphorus saturation of a tropical soil and related P leaching caused by poultry litter addition. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 16, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Qiu, H.; Hu, Y.; Wei, X.; Chen, X.; Ge, T.; Wu, J.; Su, Y. Cellulose and lignin regulate partitioning of soil phosphorus fractions and alkaline phosphomonoesterase encoding bacterial community in phosphorus-deficient soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2018, 55, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukitprapanon, T.; Suddhiprakarn, A.; Kheoruenromne, I.; Anusontpornperm, S.; Gilkes, R.J. A comparison of potential, active and post-active acid sulfate soils in Thailand. Geoderma Reg. 2016, 7, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, S.T. Interaction between plant nutrients: IV. Interaction between calcium and phosphate. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B 1993, 43, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motavalli, P.P.; Miles, R.J. Soil phosphorus fractions after 111 years of animal manure and fertilizer applications. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2002, 36, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Ma, Y.; Sanders, R.L.; Xu, C.; Li, J.; Myneni, S.C. Phosphorus speciation and transformation in long-term fertilized soil: Evidence from chemical fractionation and P K-edge XANES spectroscopy. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2017, 107, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bache, B.W.; Crooke, W.M. Interactions between aluminum, phosphorus, and pH in the response of barley to soil acidity. Plant Soil 1981, 61, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 4th ed.; CRC Press, Taylor and Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Samadi, A.; Gilkes, R.J. Forms of phosphorus in virgin and fertilized calcareous soils of Western Australia. Soil Res. 1998, 36, 585–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, W.L. Iron oxide solubilization by organic matter and its effect on iron availability. Plant Soil 1991, 130, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, A.D.; Zenneck, I.; Randall, P.J. Lead litter ash alkalinity and neutralization of soil acidity. Plant Soil. 1996, 179, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyers, E.; Strawn, D.G.; Peak, D.; Moore, A.D.; Baker, L.L.; Cade-Menun, B. Phosphorus speciation in calcareous soils following annual dairy manure amendments. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2016, 80, 1531–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eduah, J.O.; Nartey, E.K.; Abekoe, M.K.; Breuning-Madsen, H.; Andersen, M.N. Phosphorus retention and availability in three contrasting soil amended with rice husk and corn cob biochar at varying pyrolysis temperature. Geoderma 2019, 341, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilkes, R.J.; Prakongkep, N. How the unique properties of soil kaolin affect the fertility of tropical soils. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 131, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Johnson, C.E. Relationships among pH, aluminum solubility and aluminum complexation with organic matter in acid forest soils of the Northeastern United States. Geoderma 2016, 271, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranguit, D.; Guillaume, T.; Kuzyakov, Y. Land-use change affects phosphorus fractions in highly weathered tropical soils. Catena 2017, 149, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recena, R.; Cade-Menun, B.J.; Delgado, A. Organic phosphorus form in agricultural soils under Mediterranean climate. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2018, 82, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butnan, S.; Vityakon, P. The interactive effects of soil disturbance and residue quality on soil nitrogen mineralization in a tropical sandy soil. Soil Res. 2020, 58, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesch, D.; Hecky, R.; O’Melia, C.; Schindler, D.; Seitzinger, S. Eutropication of Swedish Seas, Report 5509; Swedish Environmental Protection Agency: Stockholm, Sweden, 2006.
- Myers, R.J.K.; van Noordwijk, M.; Vityakon, P. Synchrony of nutrient release and plant demand: Plant litter quality, soil environment and farmer management options. In Driven by Nature: Plant Litter Quality and Decomposition; Cadisch, G., Giller, K.E., Eds.; CAB International: Cambridge, UK, 1997; pp. 215–229. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).