Isolation and Identification of Antibacterial and Antifungal Compounds from Praxelis clematidea R. M. King & H. Robinson as an Effective Potential Treatment against Rice Pathogens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Extraction and Solvent Partition of P. clematidea
2.2.2. Silica Gel Column Chromatography
2.2.3. Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC)
2.2.4. Reversed-Phase HPLC
2.2.5. Identification of the Antimicrobial Compounds
2.2.6. Antibacterial Assay against Xoo
2.2.7. Assay for Inhibitory Activity against the Mycelial Growth of P. oryzae
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
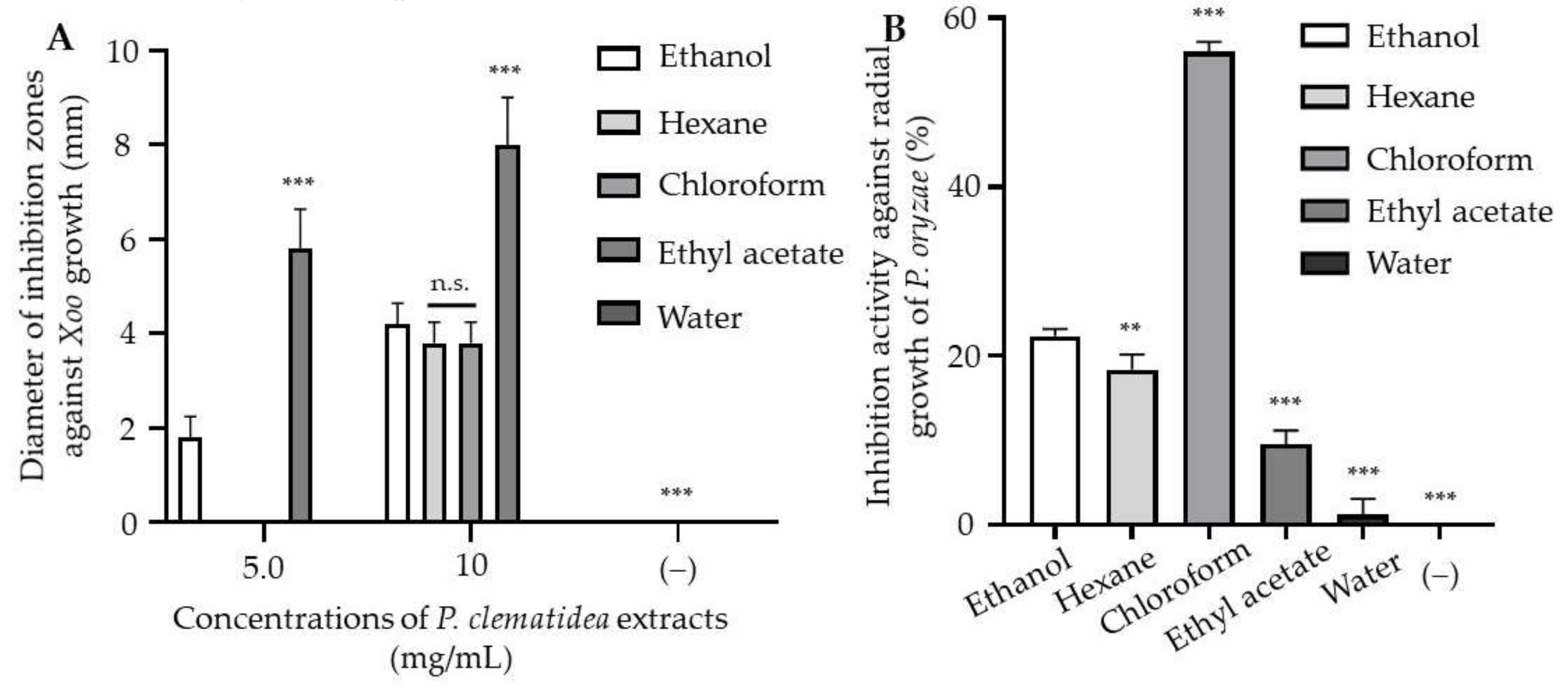
3.1. Effects of P. clematidea Extract on the Growth of Xoo and P. oryzae
3.2. Isolation of Anti-Xoo Compounds from the Ethyl Acetate Fraction
3.3. Isolation of the Antifungal Compounds from the Chloroform Fraction
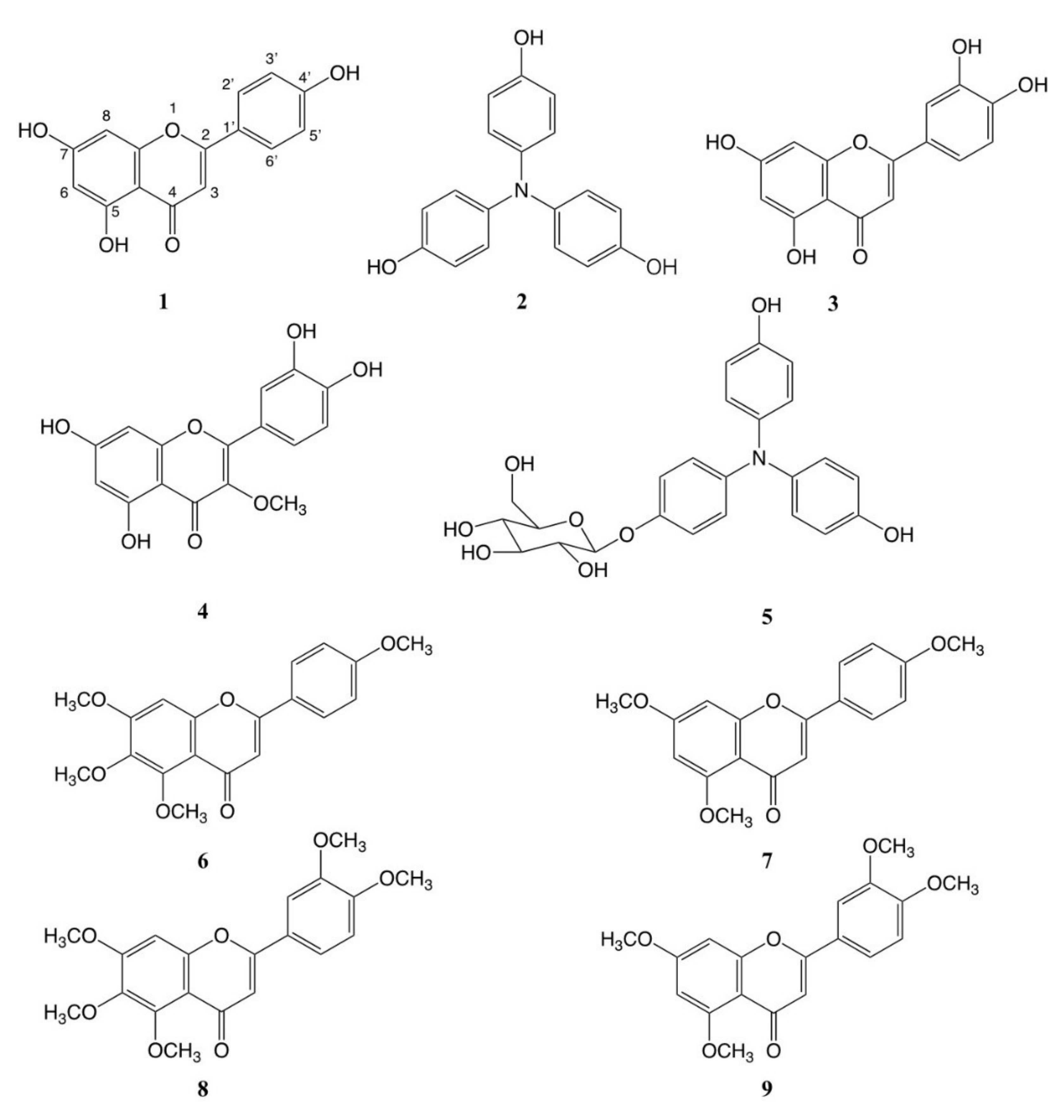
3.4. Identification of Isolated Anti-Xoo and Anti-P. oryzae Compounds except for Compound 5
3.5. Determination of The Chemical Structure of Compound 5
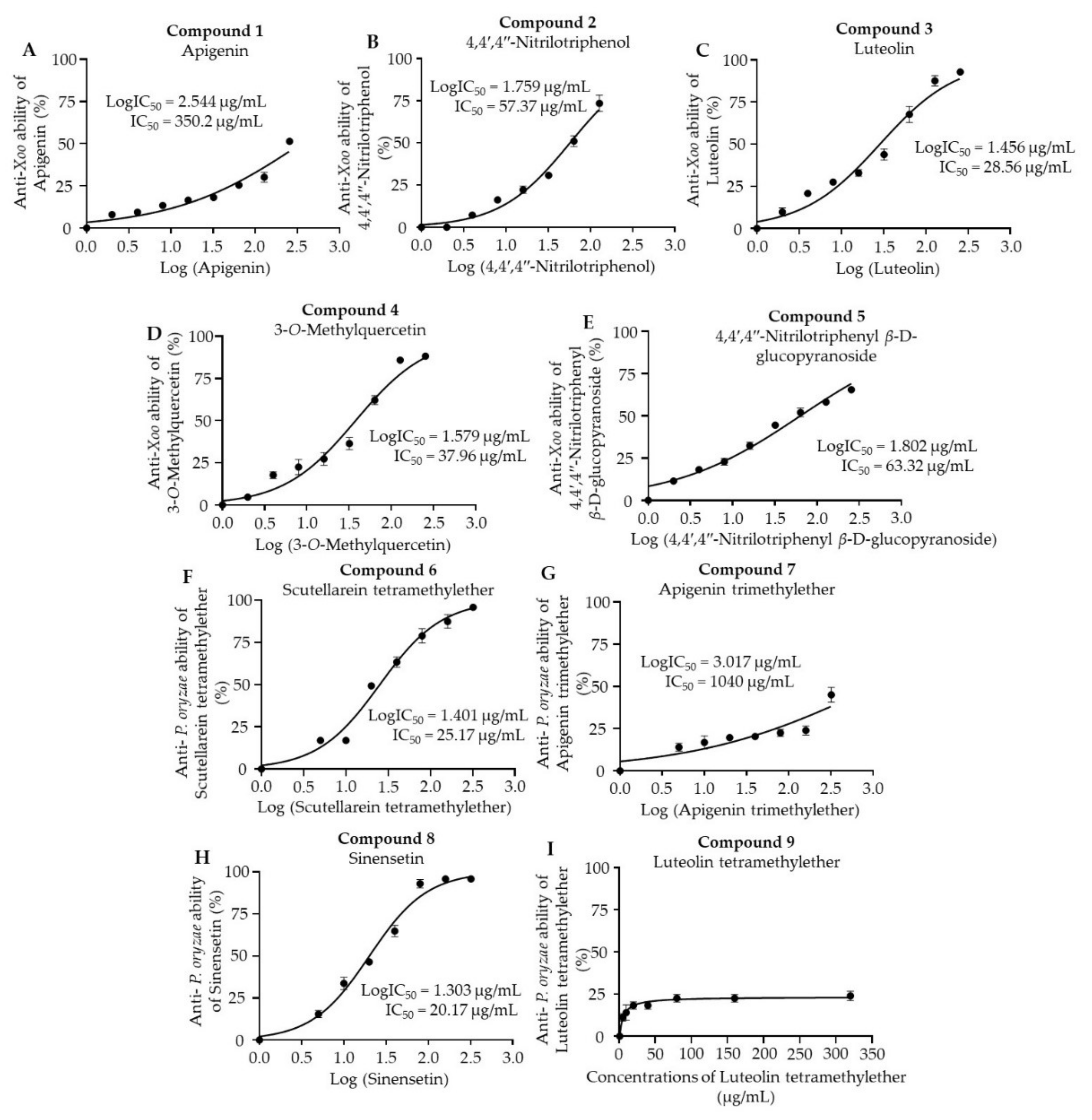
3.6. Antibacterial and Antifungal Activities of the Isolated Compounds
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, P.; Shou, H.; Xu, G.; Lian, X. Improvement of phosphorus efficiency in rice on the basis of understanding phosphate signaling and homeostasis. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2013, 16, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, Y. Molecular dynamics simulation and bioinformatics study on chloroplast stromal ridge complex from rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Bioinformatics 2016, 17, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Groth, D.E. Rice diseases and disorders in Louisiana. LSU Agric. Exp. Stn Rep. 1991, 668. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, N.; Yan, J.; Liang, Y.; Shi, Y.; He, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, X.; Peng, J. Resistance Genes and their Interactions with Bacterial Blight/Leaf Streak Pathogens (Xanthomonas oryzae) in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)—an Updated Review. Rice 2020, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ou, S.H. Rice Diseases; International Rice Research Institute (IRRI): Los Baños, Philippines, 1985; ISBN 0-85198-545-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahriar, S.A.; Imtiaz, A.A.; Hossain, M.B.; Husna, A.; Eaty, M.N.K. Review: Rice blast disease. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2020, 35, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shafiei, S.N.S.; Ahmad, K.; Ikhsan, N.; Ismail, S.I.; Sijam, K. Antibacterial activity of Acacia spp. leaves extracts against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae and screening for active phytochemical contents. IOSR J. Agric. Vet. Sci. 2017, 10, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mew, T.W. Focus on bacterial blight of rice. Plant Dis. 1993, 77, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wonni, I.; Ouedraogo, S.L.; Ouedraogo, I.; Sanogo, L. Antibacterial activity of extracts of three aromatic plants from Burkina Faso against rice pathogen, Xanthomanas oryzae. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 10, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asibi, A.E.; Chai, Q.; Coulter, J.A. Rice Blast: A Disease with Implications for Global Food Security. Agronomy 2019, 9, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.A.; Bhuiyan, M.R.; Hossain, M.S.; Sen, P.P.; Ara, A.; Siddique, M.A.; Ali, M.A. Neck blast disease influences grain yield and quality traits of aromatic rice. C. R. Biol. 2014, 337, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.W.-F.; Ser, H.L.; Khan, T.M.; Chuah, L.H.; Pusparajah, P.; Chan, K.G.; Goh, B.H.; Lee, L.H. The potential of Streptomyces as biocontrol agents against the rice blast fungus, Magnaporthe oryzae (Pyricularia oryzae). Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hubert, J.; Mabagala, R.B.; Mamiro, D.P. Efficacy of selected plant extracts against Pyricularia grisea, causal agent of rice blast disease. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Shen, Z.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Q.; He, Y. Development and evaluation of improved lines with broad-spectrum resistance to rice blast using nine resistance genes. Rice 2019, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khoa, N.Đ.; Thuy, P.T.H.; Thuy, T.T.T.; Collinge, D.B.; Jørgensen, H.J.L. Disease-reducing effect of Chromolaena odorata extract on sheath blight and other rice diseases. Phytopathology 2011, 101, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, A.Y.; Liu, C.L.; Li, M.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.N.; Li, Z.M. Design, synthesis and structure-activity relationship of novel coumarin derivatives. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enyiukwu, D.N.; Awurum, A.N.; Nwaneri, J.A. Efficacy of plant-derived pesticides in the control of myco-induced postharvest rots of tubers and agricultural products: A review. Net J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 2, 30–46. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, P.; Dubey, N.K. Exploitation of natural products as an alternative strategy to control postharvest fungal rotting of fruit and vegetables. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2004, 32, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwinn, K.D. Bioactive natural products in plant disease control. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 56, pp. 229–246. ISBN 9780444640581. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zheng, X.; Chen, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y. Exploring the potential of natural products from mangrove rhizosphere bacteria as biopesticides against plant diseases. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 2925–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naqvi, S.A.H.; Umar, U.; Hasnain, A.; Rehman, A.; Perveen, R. Effect of botanical extracts: A potential biocontrol agent for Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, causing bacterial leaf blight disease of rice. Pak. J. Agric. Res. 2018, 32, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindappa, M.; Umesha, S.; Lokesh, S. Adhatoda vasica leaf extract induces resistance in rice against bacterial leaf blight disease (Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae). Int. J. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 3, 6–14. [Google Scholar]
- Amadioha, A.C. Controlling rice blast in vitro and in vivo with extracts of Azadirachta indica. Crop Prot. 2000, 19, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Filho, A.A.; Fernandes, H.M.B.; Sousa, J.P.; Meireles, D.R.P.; Maia, G.L.A.; Barbosa Filho, J.M.; Pêssoa, H.L.F.; Lima, E.O. Antimicrobial effect of the chloroform phase of Praxelis clematidea R.M. King & Robinson. Int. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. Res. 2015, 7, 420–423. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; He, X. Anti-neuroinflammatory benzofurans and lignans from Praxelis clematidea. Fitoterapia 2020, 140, 104440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.-N.; Zhou, X.-Q.; Nong, X.-H.; Cao, J.; Hui, Y.; Wen, M.; Chen, W.-H. Phytochemical investigation of the flowers of Praxelis clematidea (Griseb.) R.M. King & H. Rob. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 35, 3504–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadwa, T.E.; Awouafack, M.D.; Sonopo, M.S.; Eloff, J.N. Antibacterial and antimycobacterial activity of crude extracts, fractions, and isolated compounds from leaves of sneezewood, Ptaeroxylon obliquum (Rutaceae). Nat. Prod. Commun. 2019, 14, 1934578X19872927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, S. Antifungal activity of different extracts of Ageratum conyzoides for the management of Fusarium solani. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 11022–11029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas-Morales, C.; Rivas-Galindo, V.M.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez, J.; Galindo-Rodriguez, S.A.; Leos-Rivas, C.; Garcia-Hernandez, D.G. Bactericidal activity, isolation and identification of most active compound from 20 plants used in traditional Mexican medicine against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Int. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 14, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, Y.H.; Te Yeh, Y.T.; Pan, S.Y.; Hsieh, S.C. Identification and structural elucidation of anti-inflammatory compounds from Chinese olive (Canarium album L.) fruit extracts. Foods 2019, 8, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mawire, P.; Mozirandi, W.; Heydenreich, M.; Chi, G.F.; Mukanganyama, S. Isolation and antimicrobial activities of phytochemicals from Parinari curatellifolia (Chrysobalanaceae). Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 2021, 8842629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, T.N.; Xuan, T.D.; Tran, H.D.; Van, T.M.; Andriana, Y.; Khanh, T.D.; Van Quan, N.V.; Ahmad, A. Isolation and purification of bioactive compounds from the stem bark of Jatropha podagrica. Molecules 2019, 24, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fossen, T.; Andersen, Ø. Spectroscopic techniques applied to flavonoids. In Flavonoids: Chemistry, Biochemistry and Applications; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2006; Volume 1, pp. 68–90. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, N.; Mahmood, R.; Rahman, H.; Haris, M. Spectrophotometric screening of potent bactericidal property of Thevetia peruviana Schum. leaf and fruit rind extracts on clinical and plant pathogens. Int. J. Appl. Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 2, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chanprapai, P.; Chavasiri, W. Antimicrobial activity from Piper sarmentosum Roxb. against rice pathogenic bacteria and fungi. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 2513–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Astiti, N.P.A.; Suprapta, D.N. Antifungal activity of teak (Tectona grandis L. F.) leaf extract against Arthrinium phaeosperum (Corda) M.B. Ellis, the cause of wood decay on Albizia falcataria (L.) Fosberg. J. Int. Soc. Southeast Asian Agric. Sci. 2012, 18, 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Suriani, N.L.; Suprapta, D.N.; Sudana, I.M.; Temaja, I.G.R.M. Antifungal activity of Piper caninum against Pyricularia oryzae Cav., the cause of rice blast disease on rice. J. Biol. Agric. Healthc. 2015, 5, 72–79. [Google Scholar]
- Van Loo, P.; De Bruyn, A.; Buděšínský, M. Reinvestigation of the structural assignment of signals in the 1H and13C NMR spectra of the flavone apigenin. Magn. Reson. Chem. 1986, 24, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, H.; Chari, V.M.; Sonnenbichler, J. 13C-NMR-spektren natürlich vorkommender flavonoide. Tetrahedron Lett. 1976, 17, 1799–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, H.; Yonekuta, Y.; Nishide, H. Dendron-combined poly(4-diphenyl- aminium-1,2-phenylenevinylene): An Isolated Multiplet Molecule. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 4889–4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozgen, U.; Sevindik, H.; Kazaz, C.; Yigit, D.; Kandemir, A.; Secen, H.; Calis, I. A new sulfated α-ionone glycoside from Sonchus erzincanicus Matthews. Molecules 2010, 15, 2593–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Montanari, A.M.; Widmer, W.W. Two new polymethoxylated flavones, a class of compounds with potential anticancer activity, isolated from cold pressed dancy tangerine peel oil solids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, V.M.; Ilyas, M.; Wagner, H.; Neszmélyi, A.; Fa-Ching, C.; Li-Kuang, C.; Yu-Chin, L.; Yu-Meei, L. 13C-NMR spectroscopy of biflavanoids. Phytochemistry 1977, 16, 1273–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahond, A.; Guilhem, J.; Hamon, J.; Hurtado, J.; Poupat, C.; Pusset, J.; Pusset, M.; Sévenet, T.; Potier, P. Bubbialine et bubbialidine, alcaloides nouveaux extraits de Zygogynum pauciflorum. J. Nat. Prod. 1990, 53, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cias, P.; Slugovc, C.; Gescheidt, G. Hole transport in triphenylamine based OLED devices: From theoretical modeling to properties prediction. J. Phys. Chem. A 2011, 115, 14519–14525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Yang, W.; Karlsson, M.; Cong, J.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Xu, B.; Hua, J.; Kloo, L.; Boschloo, G. Efficient dye-sensitized solar cells with voltages exceeding 1 v through exploring tris(4-alkoxyphenyl)amine mediators in combination with the tris(bipyridine) cobalt redox system. ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 1929–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tang, W.; Loh, K.P. Para-substituted triphenylamine as a catholyte for zinc–organic aqueous redox flow batteries. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2021, 4, 3612–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akroum, S.; Bendjeddou, D.; Satta, D.; Lalaoui, K. Antibacterial activity and acute toxicity effect of flavonoids extracted from Mentha longifolia. Am. J. Sustain. Agric. 2009, 4, 93–96. [Google Scholar]
- Manríquez-Torres, J.J.; Zúñiga-Estrada, A.; González-Ledesma, M.; Torres-Valencia, J.M. The antibacterial metabolites and proacacipetalin from Acacia cochliacantha. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2007, 51, 228–231. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Woo, E.R.; Lee, D.G. Apigenin promotes antibacterial activity via regulation of nitric oxide and superoxide anion production. J. Basic Microbiol. 2020, 60, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, W.; Liu, M.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, T. Antimicrobial mechanism of luteolin against Staphylococcus aureus and Listeria monocytogenes and its antibiofilm properties. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 142, 104056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talib, W.H.; Zarga, M.H.A.; Mahasneh, A.M. Antiproliferative, antimicrobial and apoptosis inducing effects of compounds isolated from Inula viscosa. Molecules 2012, 17, 3291–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lou, J.; Luo, C.; Zhou, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, L. Phenolic compounds from Halimodendron halodendron (Pall.) voss and their antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 11349–11364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yenjai, C.; Prasanphen, K.; Daodee, S.; Wongpanich, V.; Kittakoop, P. Bioactive flavonoids from Kaempferia parviflora. Fitoterapia 2004, 75, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han Jie, L.; Jantan, I.; Yusoff, S.D.; Jalil, J.; Husain, K. Sinensetin: An insight on its pharmacological activities, mechanisms of action and toxicity. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 553404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Cheng, D.; He, M.; Pan, S.; Yao, X.; Xu, X. Antifungal action and inhibitory mechanism of polymethoxylated flavones from Citrus reticulata Blanco peel against Aspergillus niger. Food Control. 2014, 35, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compounds | IC50 (µg/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-Xoo | Anti-P. oryzae | ||
| Ethyl acetate fraction | 1. apigenin | 350.20 ± 11.43 | N.D. |
| 2. 4,4′,4″-nitrilotriphenol | 57.37 ± 1.15 | N.D. | |
| 3. luteolin | 28.56 ± 2.73 | N.D. | |
| 4. 3-O-methylquercetin | 37.96 ± 1.27 | N.D. | |
| 5. 4,4′,4″-nitrilotriphenyl β-D-glucopyranoside | 63.32 ± 2.13 | N.D. | |
| Chloroform fraction | 6. scutellarein tetramethylether | N.D. | 25.17 ± 3.09 |
| 7. apigenin trimethylether | N.D. | 1040 ± 114.30 | |
| 8. sinensetin | N.D. | 20.17 ± 2.47 | |
| 9. luteolin tetramethylether | N.D. | ∞ | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, C.C.; Nguyen, T.Q.C.; Kanaori, K.; Binh, T.D.; Vang, L.V.; Kamei, K. Isolation and Identification of Antibacterial and Antifungal Compounds from Praxelis clematidea R. M. King & H. Robinson as an Effective Potential Treatment against Rice Pathogens. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2366. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112366
Nguyen CC, Nguyen TQC, Kanaori K, Binh TD, Vang LV, Kamei K. Isolation and Identification of Antibacterial and Antifungal Compounds from Praxelis clematidea R. M. King & H. Robinson as an Effective Potential Treatment against Rice Pathogens. Agronomy. 2021; 11(11):2366. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112366
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Cuong C., Thanh Q. C. Nguyen, Kenji Kanaori, Tran Duy Binh, Le Van Vang, and Kaeko Kamei. 2021. "Isolation and Identification of Antibacterial and Antifungal Compounds from Praxelis clematidea R. M. King & H. Robinson as an Effective Potential Treatment against Rice Pathogens" Agronomy 11, no. 11: 2366. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112366
APA StyleNguyen, C. C., Nguyen, T. Q. C., Kanaori, K., Binh, T. D., Vang, L. V., & Kamei, K. (2021). Isolation and Identification of Antibacterial and Antifungal Compounds from Praxelis clematidea R. M. King & H. Robinson as an Effective Potential Treatment against Rice Pathogens. Agronomy, 11(11), 2366. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112366








