Kompetitive Allele Specific PCR (KASP) Markers for Potato: An Effective Tool for Increased Genetic Gains
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
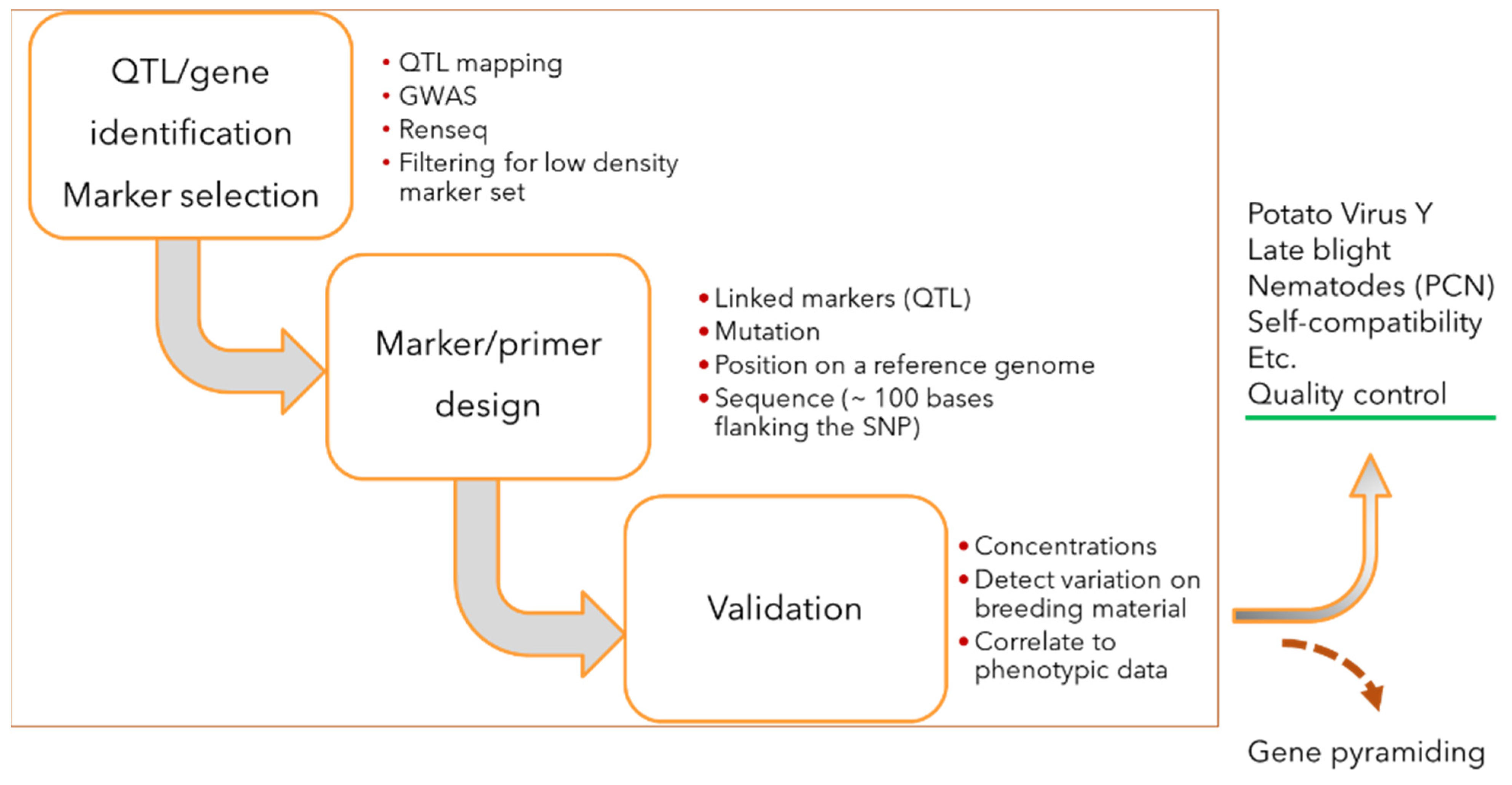
2.1. Trait KASP Marker Development
2.2. Assay Verification and Routine Analysis
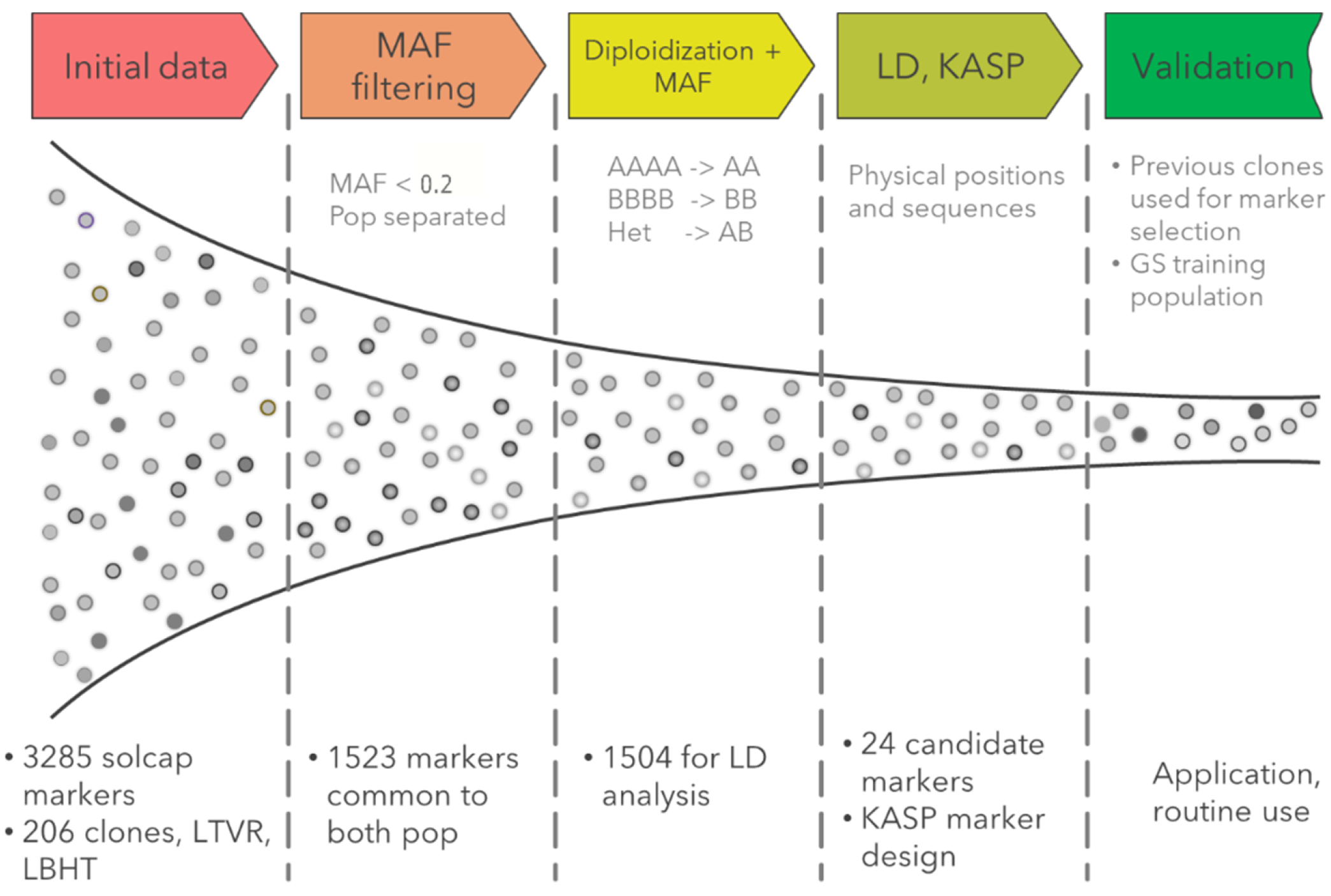
2.3. QC Marker Selection Pipeline
2.4. Routine Analysis with QC KASP Markers
2.4.1. Study Design
2.4.2. QC Data Analysis
3. Results
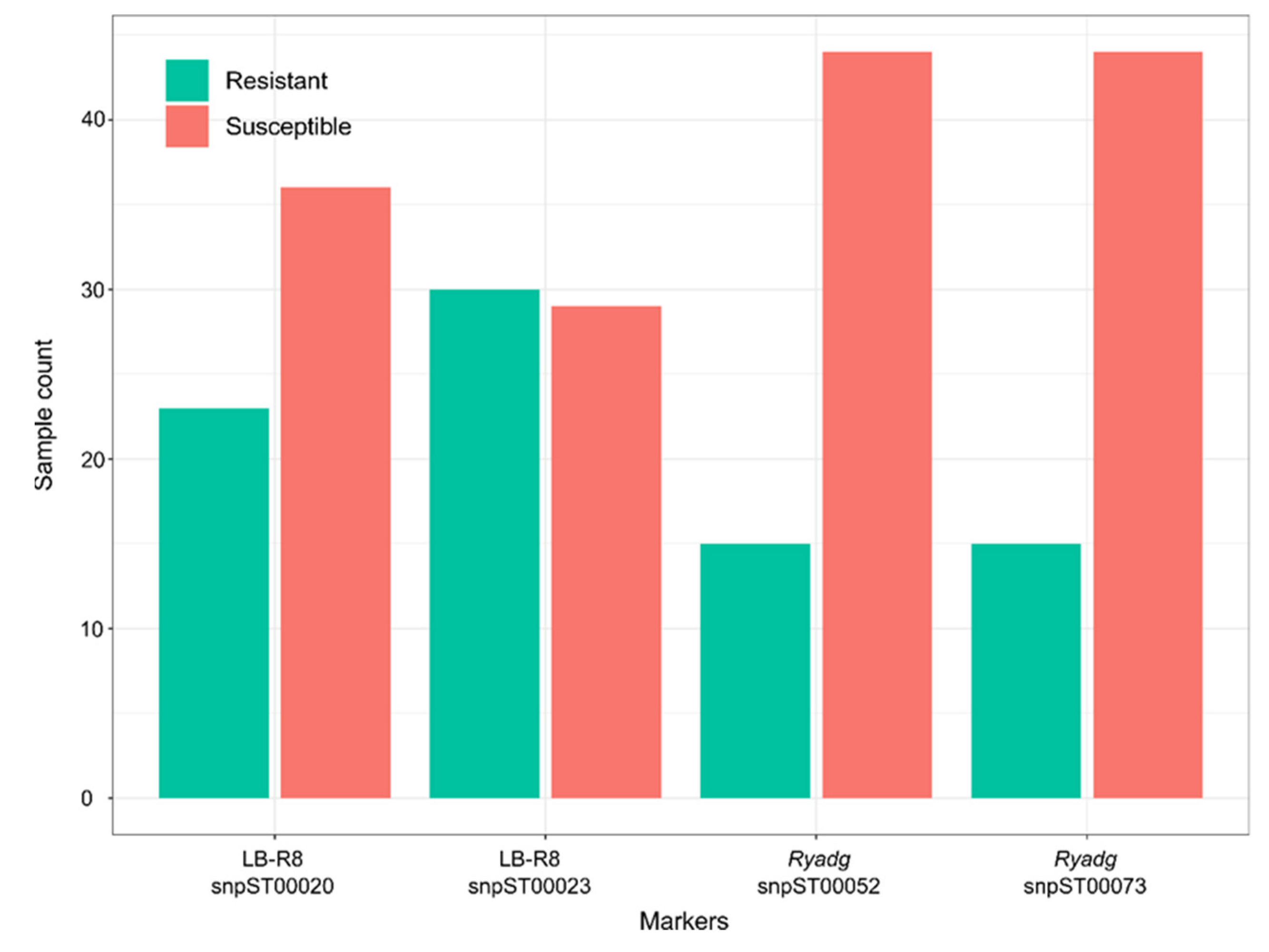
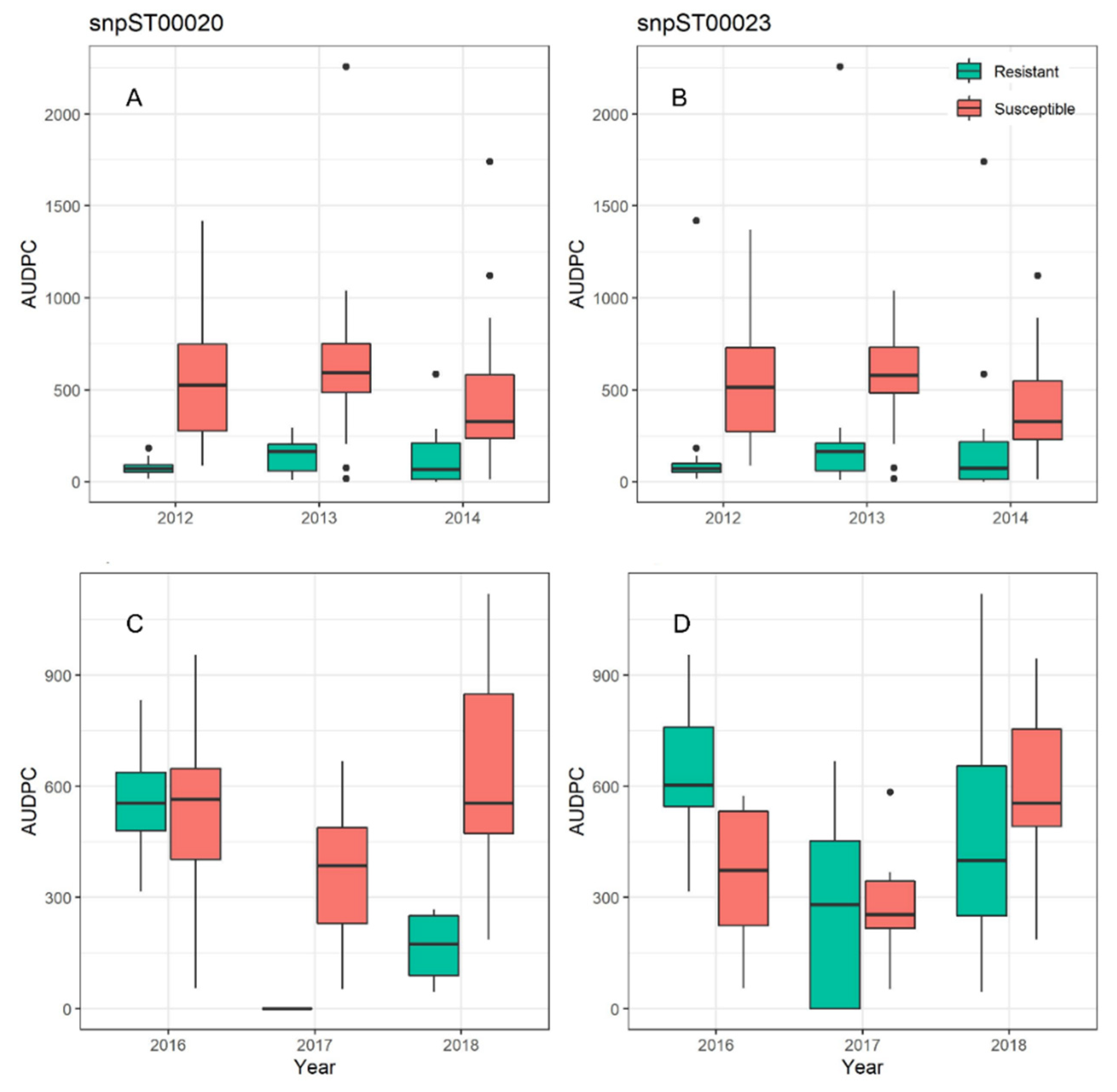
3.1. Trait Markers for Late Blight and PVY Resistance
3.2. Markers Tested on Two Different Breeding Populations
3.3. Tetraploid Calls Enhance QC Marker Efficiency
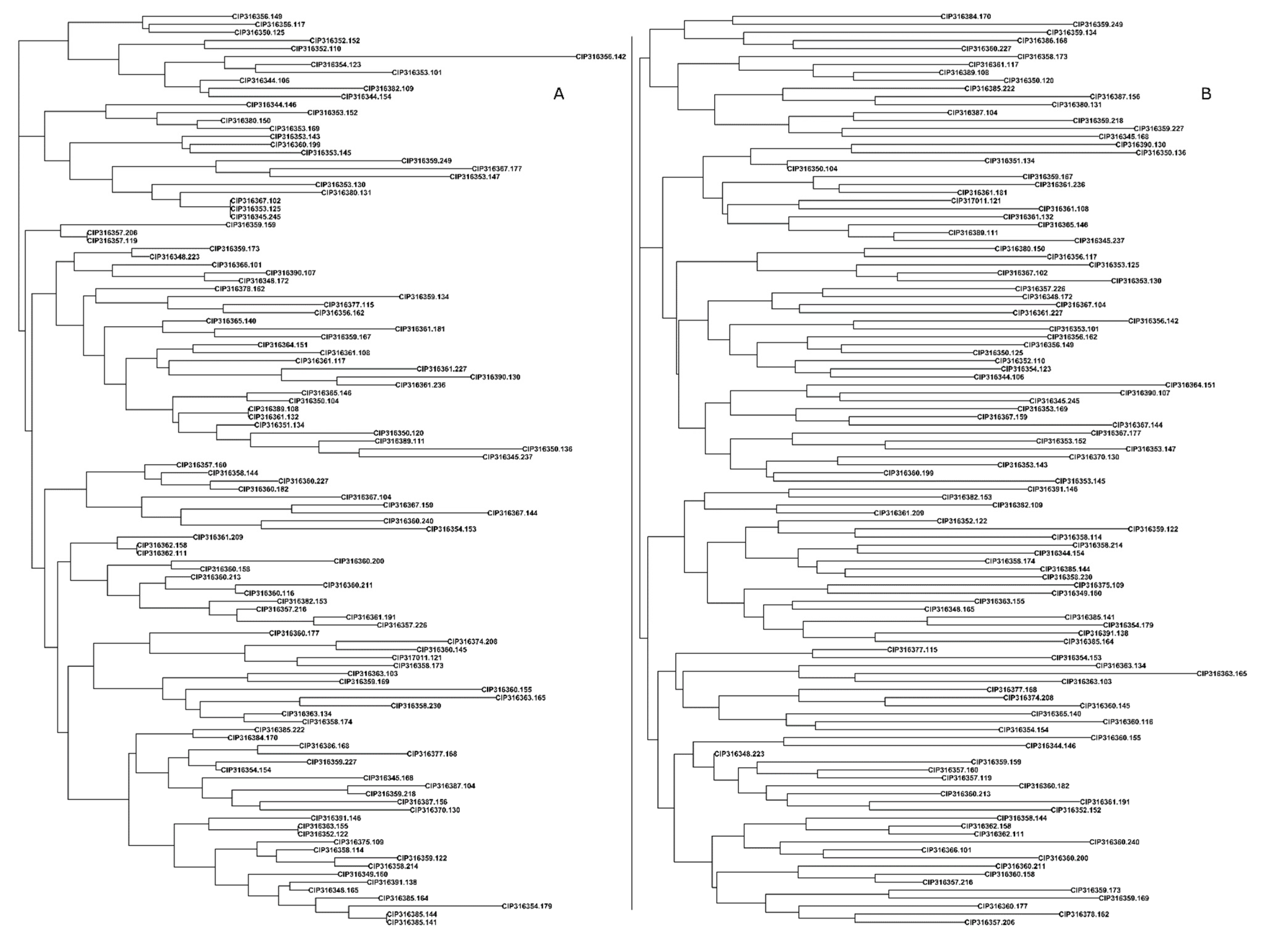
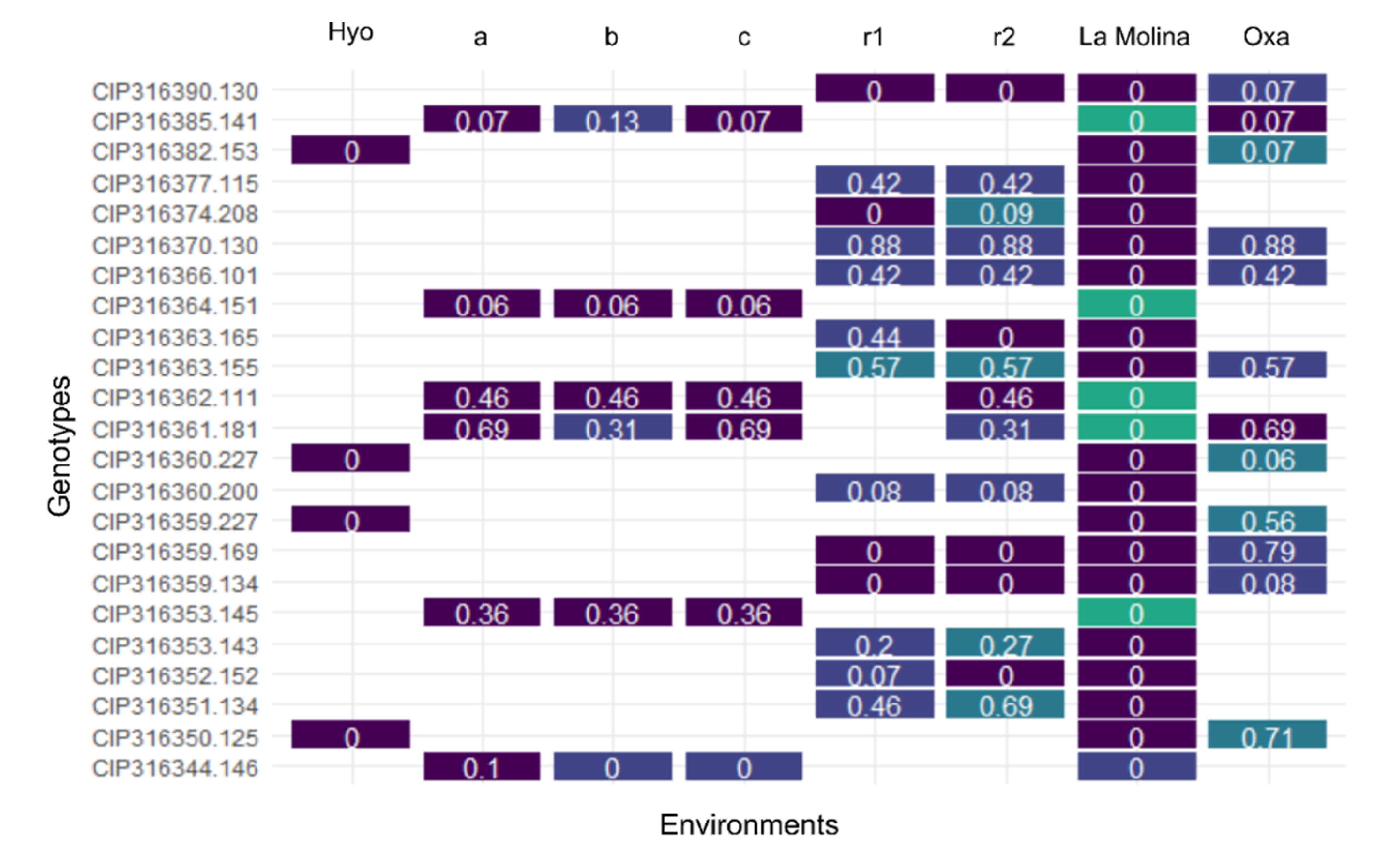
3.4. Discrepancy in Breeding Material Genetic Identity Revealed by QC Markers
3.5. Routine Use of KASP Markers
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jansky, S.H.; Spooner, D.M. The Evolution of Potato Breeding. In Plant Breeding Reviews; Goldman, I., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; Volume 41, pp. 169–214. [Google Scholar]
- Bonierbale, M.W.; Amoros, W.R.; Salas, E.; de Jong, W. Potato Breeding. In The Potato Crop; Hugo, C., Ortiz, O., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 163–217. [Google Scholar]
- Gemenet, D.C.; Kitavi, M.; David, M.; Ndege, D.; Ssali, R.T.; Swanckaert, J.; Makunde, G.; Yencho, G.C.; Gruneberg, W.; Carey, E.; et al. Development of diagnostic SNP markers for quality assurance and control in sweetpotato [Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.] breeding programs. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lacomme, C.; Jacquot, E. General characteristics of Potato virus Y (PVY) and its impact on potato production: An overview. In Potato Virus Y: Biodiversity, Pathogenicity, Epidemiology and Management; Lacomme, C., Glais, L., Bellstedt, D., Dupuis, B., Karasev, A., Jacquot, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-3-319-58858-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hooker, W. Compendium of Potato Diseases; Hooker, W., Ed.; American Phytopathological Society: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Haverkort, A.J.; Struik, P.C.; Visser, R.G.F.; Jacobsen, E. Applied Biotechnology to Combat Late Blight in Potato Caused by Phytophthora Infestans. Potato Res. 2009, 52, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.K.; Cunningham, A.A.; Patel, N.G.; Morales, F.J.; Epstein, P.R.; Daszak, P. Emerging infectious diseases of plants: Pathogen pollution, climate change and agrotechnology drivers. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2004, 19, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastry, K.S.; Zitter, T.A. Ecology and Epidemiology of Virus and Viroid Diseases of Tropical Crops. In Plant Virus and Viroid Diseases in the Tropics; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fry, W.E.; Birch, P.; Judelson, H.S.; Grünwald, N.; Danies, G.; Everts, K.; Gevens, A.J.; Gugino, B.K.; Johnson, D.A.; Johnson, S.B.; et al. Five Reasons to Consider Phytophthora infestans a Reemerging Pathogen. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 966–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Slater, A.T.; Cogan, N.O.I.; Hayes, B.; Schultz, L.; Dale, M.F.B.; Bryan, G.; Forster, J.W. Improving breeding efficiency in potato using molecular and quantitative genetics. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 2279–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishnan, A.P.; Ritland, C.E.; Sevillano, R.H.B.; Riseman, A. Review of Potato Molecular Markers to Enhance Trait Selection. Am. J. Potato Res. 2015, 92, 455–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, M.; Sharma, S.; Yadav, S.; Kumar, S. Management of Late Blight of Potato. In Potato-From Incas to All Over the World; Yildiz, M., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 83–106. ISBN 978-1-78923-255-4. [Google Scholar]
- Hannukkala, A.O.; Kaukoranta, T.; Lehtinen, A.; Rahkonen, A. Late-blight epidemics on potato in Finland, 1933?2002; increased and earlier occurrence of epidemics associated with climate change and lack of rotation. Plant Pathol. 2007, 56, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, O.; Winters, P.; Fano, H. La Percepción de los Agricultores sobre el Problema del Tizón Tardío o Rancha (Phytophthora infestans) su Manejo: Estudio de Casos en Cajamarca, Perú. Rev. Latinoam. Papa 2016, 11, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, K.; Morikawa, Y.; A Sorri, V.; Valkonen, J.; Gebhardt, C.; Watanabe, K.N. Development of SCAR markers to the PVY resistance gene Ryadg based on a common feature of plant disease resistance genes. Genome 2000, 43, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigneti, G.; Garcia-Mas, J.; Baulcombe, D.C. Molecular mapping of the potato virus Y resistance gene Rysto in potato. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1997, 94, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, M.D.R.; Vidalon, L.J.; Montenegro, J.D.; Riccio, C.; Guzmán, F.; Bartolini, I.; Ghislain, M. Molecular and genetic characterization of the Ryadg locus on chromosome XI from Andigena potatoes conferring extreme resistance to potato virus Y. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2018, 131, 1925–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.-S.; Schwarzfischer, A. Development of STS Markers for Selection of Extreme Resistance (Ry sto ) to PVY and Maternal Pedigree Analysis of Extremely Resistant Cultivars. Am. J. Potato Res. 2008, 85, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Sutherland, D.; Dickison, V.; Singh, M.; Murphy, A.M.; De Koeyer, D. Development and Validation of High-Resolution Melting Markers Derived from Rysto STS Markers for High-Throughput Marker-Assisted Selection of Potato Carrying Rysto. Phytopathology 2016, 106, 1366–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fulladolsa, A.C.; Navarro, F.M.; Kota, R.; Severson, K.; Palta, J.P.; Charkowski, A.O. Application of Marker Assisted Selection for Potato Virus Y Resistance in the University of Wisconsin Potato Breeding Program. Am. J. Potato Res. 2015, 92, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottoman, R.J.; Hane, D.C.; Brown, C.R.; Yilma, S.; James, S.R.; Mosley, A.R.; Crosslin, J.M.; Vales, M.I. Validation and Implementation of Marker-Assisted Selection (MAS) for PVY Resistance (Ry adg gene) in a Tetraploid Potato Breeding Program. Am. J. Potato Res. 2009, 86, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitworth, J.L.; Novy, R.G.; Hall, D.G.; Crosslin, J.M.; Brown, C.R. Characterization of Broad Spectrum Potato Virus Y Resistance in a Solanum tuberosum ssp. andigena-Derived Population and Select Breeding Clones Using Molecular Markers, Grafting, and Field Inoculations. Am. J. Potato Res. 2009, 86, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, J.E.; Bryan, G.J.; Ramsay, G. Genetic Resources (Including Wild and Cultivated Solanum Species) and Progress in their Utilisation in Potato Breeding. Potato Res. 2006, 49, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodewald, J.; Trognitz, B. Solanumresistance genes againstPhytophthora infestansand their corresponding avirulence genes. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 14, 740–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karki, H.S.; Jansky, S.H.; Halterman, D.A. Screening of Wild Potatoes Identifies New Sources of Late Blight Resistance. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, J.K.; Siddappa, S.; Singh, B.P.; Kaushik, S.K.; Chakrabarti, S.K.; Bhardwaj, V.; Chandel, P. Molecular markers for late blight resistance breeding of potato: An update. Plant Breed. 2013, 132, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Vossen, E.; Sikkema, A.; Hekkert, B.T.L.; Gros, J.; Stevens, P.; Muskens, M.; Wouters, D.; Pereira, A.; Stiekema, W.; Allefs, S. An ancientRgene from the wild potato speciesSolanum bulbocastanumconfers broad-spectrum resistance toPhytophthora infestansin cultivated potato and tomato. Plant J. 2003, 36, 867–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefańczyk, E.; Plich, J.; Janiszewska, M.; Smyda-Dajmund, P.; Sobkowiak, S.; Śliwka, J. Marker-assisted pyramiding of potato late blight resistance genes Rpi-rzc1 and Rpi-phu1 on di- and tetraploid levels. Mol. Breed. 2020, 40, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakosy-Tican, E.; Thieme, R.; König, J.; Nachtigall, M.; Hammann, T.; Denes, T.-E.; Kruppa, K.; Molnár-Láng, M. Introgression of Two Broad-Spectrum Late Blight Resistance Genes, Rpi-Blb1 and Rpi-Blb3, From Solanum bulbocastanum Dun Plus Race-Specific R Genes Into Potato Pre-breeding Lines. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, R. Genomic-Led Potato Breeding for Increasing Genetic Gains: Achievements and Outlook. Crop Breed. Genet. Genom. 2020, 2, e200010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junfeng The Potato Genome Sequencing Consortium Genome sequence and analysis of the tuber crop potato. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 475, 189–195. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S.K.; Bolser, D.; De Boer, J.; Sonderkaer, M.; Amoros, W.; Carboni, M.F.; D’Ambrosio, J.M.; De La Cruz, G.; Di Genova, A.; Douches, D.S.; et al. Construction of Reference Chromosome-Scale Pseudomolecules for Potato: Integrating the Potato Genome with Genetic and Physical Maps. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2013, 3, 2031–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hardigan, M.A.; Crisovan, E.; Hamilton, J.; Kim, J.; Laimbeer, P.; Leisner, C.P.; Manrique-Carpintero, N.C.; Newton, L.; Pham, G.M.; Vaillancourt, B.; et al. Genome Reduction Uncovers a Large Dispensable Genome and Adaptive Role for Copy Number Variation in Asexually Propagated Solanum tuberosum. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 388–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pham, G.M.; Hamilton, J.P.; Wood, J.C.; Burke, J.T.; Zhao, H.; Vaillancourt, B.; Ou, S.; Jiang, J.; Buell, C.R. Construction of a chromosome-scale long-read reference genome assembly for potato. GigaScience 2020, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasheed, A.; Hao, Y.; Xia, X.; Khan, A.; Xu, Y.; Varshney, R.; He, Z. Crop Breeding Chips and Genotyping Platforms: Progress, Challenges, and Perspectives. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 1047–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, C.; Holme, J.; Anthony, J. SNP Genotyping: The KASP Assay. In Crop Breeding: Methods and Protocols, Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 1145, pp. 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Semagn, K.; Babu, R.; Hearne, S.; Olsen, M. Single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping using Kompetitive Allele Specific PCR (KASP): Overview of the technology and its application in crop improvement. Mol. Breed. 2014, 33, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist-Kreuze, H.; De Boeck, B.; Unger, P.; Gemenet, D.; Li, X.; Pan, Z.; Sui, Q.; Qin, J.; Woldegjorgis, G.; Negash, K.; et al. Global multi-environment resistance QTL for foliar late blight resistance in tetraploid potato with tropical adaptation. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2021, 11, jkab251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist-Kreuze, H.; Gastelo, M.; Perez, W.; Forbes, G.A.; De Koeyer, D.; Bonierbale, M. Phenotypic Stability and Genome-Wide Association Study of Late Blight Resistance in Potato Genotypes Adapted to the Tropical Highlands. Phytopathology 2014, 104, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihovilovich, E.; Aponte, M.; Bonierbale, M. Dataset for: Standard Evaluation Trial for Potato Virus Y 2018. Available online: https://doi.org/10.21223/P3/I0IRHA (accessed on 15 November 2018). [CrossRef]
- Mihovilovich, E.; Aponte, M.; Bonierbale, M.; Espinoza, J. Dataset for: Standard Evaluation Trial for Late Blight Resistance Documentation of CIP advanced Breeding Clones 2017. Available online: https://doi.org/10.21223/P3/ZYYGPX (accessed on 15 November 2018). [CrossRef]
- Gastelo, M.; Diaz, L.; Landeo, J.A.; Bonierbale, M. New elite potato clones with heat tolerance, late blight and virus resistance to address climate change. In Potato and Sweetpotato in Africa: Transforming the Value Chains for Food and Nutrition Security; Low, J., Nyongesa, M., Quinn, S., Parker, M., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2015; pp. 133–154. ISBN 9781780644202. [Google Scholar]
- Felcher, K.J.; Coombs, J.J.; Massa, A.N.; Hansey, C.N.; Hamilton, J.; Veilleux, R.E.; Buell, C.R.; Douches, D.S. Integration of Two Diploid Potato Linkage Maps with the Potato Genome Sequence. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landeo, J. Breeding for horizontal resistance to late blight in potato free of R genes. In Control Integrado de las Principales Enfermedades Fungosas de la Papa; Seminario taller: Bellavista, Colombia, 1993; pp. 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Fumagalli, M. Assessing the Effect of Sequencing Depth and Sample Size in Population Genetics Inferences. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crawford, J.E.; Lazzaro, B.P. Assessing the Accuracy and Power of Population Genetic Inference from Low-Pass Next-Generation Sequencing Data. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maruki, T.; Lynch, M. Genotype Calling from Population-Genomic Sequencing Data. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2017, 7, 1393–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warnes, G.; Gorjanc, G.; Leisch, F.; Man, M. Package Genetics-Population Genetics 2012. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/genetics/index.html (accessed on 15 December 2019).
- Team, R.C. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing 2021. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 5 June 2021).
- Voorrips, R.; Gort, G. fitTetra: FitTetra is an R Package for Assigning Tetraploid Genotype Scores 2013. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=fitTetra (accessed on 21 January 2021).
- Paradis, E.; Schliep, K. ape 5.0: An environment for modern phylogenetics and evolutionary analyses in R. Bioinformatics 2018, 35, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruana, B.; Rodoni, B.; Constable, F.; Slater, A.; Cogan, N. Genome Enhanced Marker Improvement for Potato Virus Y Disease Resistance in Potato. Agronomy 2021, 11, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, G.; Perez, W.; Andrade-Piedra, J. Field Assessment of Resistance in Potato to Phytophthora infestans: International Cooperators Guide; International Potato Center: Lima, Peru, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gopal, J.; Singh, B.P. Screening potatoes for resistance to late blight (Phytophthora infestans) under field conditions. Potato Res. 2003, 46, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douches, D.S.; Maas, D.; Jastrzebski, K.; Chase, R.W. Assessment of Potato Breeding Progress in the USA over the Last Century. Crop. Sci. 1996, 36, 1544–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wricke, G.; Weber, E. Quantitative Genetics and Selection in Plant Breeding; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 1986; ISBN 978-3-11-007561-8. [Google Scholar]
- Semagn, K.; Beyene, Y.; Makumbi, D.; Mugo, S.; Prasanna, B.M.; Magorokosho, C.; Atlin, G. Quality control genotyping for assessment of genetic identity and purity in diverse tropical maize inbred lines. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2012, 125, 1487–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertiro, B.T.; Ogugo, V.; Worku, M.; Das, B.; Olsen, M.; Labuschagne, M.; Semagn, K. Comparison of Kompetitive Allele Specific PCR (KASP) and genotyping by sequencing (GBS) for quality control analysis in maize. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Zavala, C.; Ortega, N.; Petroli, C.; Franco, J.; Burgueño, J.; Costich, D.E.; Hearne, S.J. The Development of Quality Control Genotyping Approaches: A Case Study Using Elite Maize Lines. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndjiondjop, M.N.; Semagn, K.; Zhang, J.; Gouda, A.C.; Kpeki, S.B.; Goungoulou, A.; Wambugu, P.; Drame, K.N.; Bimpong, I.K.; Zhao, D. Development of species diagnostic SNP markers for quality control genotyping in four rice (Oryza L.) species. Mol. Breed. 2018, 38, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| SNP ID | Intertek Id | Gene/QTL | Reference Sequence | Chromosome | Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S9_61261167 | snpST00020 | R8-QTL | tgaaggtattcatttttctgatgaaatgcattcctggacttttcttcatc[a/c]tgtttgggcgctctttgtacaggacatgcattgctgttttctccccccca | 9 | 67380076 |
| solcap_snp_c2_56418 | snpST00023 | R8-QTL | ggatactgtcgcaatggttgttgcaacggcaataactatgagtgctatag[t/g]tgctgttaattatggggagcaataaatatttgtaatggcaaagatgtaat | 9 | 66379267 |
| M6F1R4_711 | snpST00052 | Ryadg | aaacatgagctactcggggtcaccacttaacaaagattttagttagataa[g/a]gacagaatacaaaatccactaactatcacatttatcacggatgggttcca | 11 | 2499608 |
| M6F1R4_817 | snpST00073 | Ryadg | acgtgctaactagttagggattcaaattcaagattgtattaaacccggat[a/g]tacatatacagggaagctttaaccacacatgcaaggttcagatatcca | 11 | 2499502 |
| La Molina | Huancayo | Oxapampa | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total samples (number of clones) | 114 (114) | 224 (114) | 38 (38) | 376 (114) |
| r1 samples | 96 | |||
| r2 samples | 77 | |||
| r1 within plot samples | 17 |
| SNP ID | Marker Name | Location † | Concordance ‡ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Late blight resistance | |||
| snpST0010 | GBS_S9_58779951 | Chr9: 58779951 | 93% |
| snpST0012 | GBS_S9_59226671 | Chr9: 59226671 | 0% |
| snpST0013 | GBS_S9_59301204 | Chr9: 59301204 | 92% |
| snpST0014 | GBS_S9_59997331 | Chr9: 59997331 | 95% |
| snpST0015 | GBS_S9_60067335 | Chr9: 60067335 | 95% |
| snpST0016 | GBS_S9_60225630 | Chr9: 60225630 | 71% |
| snpST0017 | GBS_S9_60510506 | Chr9: 60510506 | 90% |
| snpST0018 | GBS_S9_61095507 | Chr9: 61095507 | 93% |
| snpST0019 | GBS_S9_61205320 | Chr9: 61205320 | 0% |
| snpST0020* | GBS_S9_61261167 | Chr9: 61261167 | 99% |
| snpST0023* | solcap_snp_c2_56418 | Chr9: 60182930 | 97% |
| PVY resistance | |||
| snpST0049 | M6F1R4_672 | Chr:11: 1708290 | 0% |
| snpST0050 | M6F1R4_679 | Chr:11: 1708297 | 50% |
| snpST0051 | M6F1R4_691 | Chr:11: 1708309 | 45% |
| snpST0052* | M6F1R4_711 | Chr11: 1708329 | 100% |
| snpST0053 | M6F1R4_732 | Chr11: 1708350 | 74% |
| snpST0054 | M6F1R4_739 | Chr11: 1708357 | 55% |
| snpST0071 | M6F1R4_797 | Chr11: 1708415 | 99% |
| snpST0072 | M6F1R4_798 | Chr11: 1708416 | 0% |
| snpST0073* | M6F1R4_817 | Chr11: 1708435 | 100% |
| Marker ID | Trait | Number of Clones | α | β | s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| snpST00052 | PVY | 78 | 0.0 | 0.16 | 0.83 |
| snpST00073 | PVY | 78 | 0.0 | 0.16 | 0.83 |
| snpST00020 | Late blight | 73 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.88 |
| snpST00023 | Late blight | 77 | 0.22 | 0.35 | 0.65 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kante, M.; Lindqvist-Kreuze, H.; Portal, L.; David, M.; Gastelo, M. Kompetitive Allele Specific PCR (KASP) Markers for Potato: An Effective Tool for Increased Genetic Gains. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2315. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112315
Kante M, Lindqvist-Kreuze H, Portal L, David M, Gastelo M. Kompetitive Allele Specific PCR (KASP) Markers for Potato: An Effective Tool for Increased Genetic Gains. Agronomy. 2021; 11(11):2315. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112315
Chicago/Turabian StyleKante, Moctar, Hannele Lindqvist-Kreuze, Leticia Portal, Maria David, and Manuel Gastelo. 2021. "Kompetitive Allele Specific PCR (KASP) Markers for Potato: An Effective Tool for Increased Genetic Gains" Agronomy 11, no. 11: 2315. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112315
APA StyleKante, M., Lindqvist-Kreuze, H., Portal, L., David, M., & Gastelo, M. (2021). Kompetitive Allele Specific PCR (KASP) Markers for Potato: An Effective Tool for Increased Genetic Gains. Agronomy, 11(11), 2315. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112315






