Alleviating Soil Acidification and Increasing the Organic Carbon Pool by Long-Term Organic Fertilizer on Tobacco Planting Soil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sampling and Measurement
2.4. Calculations and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
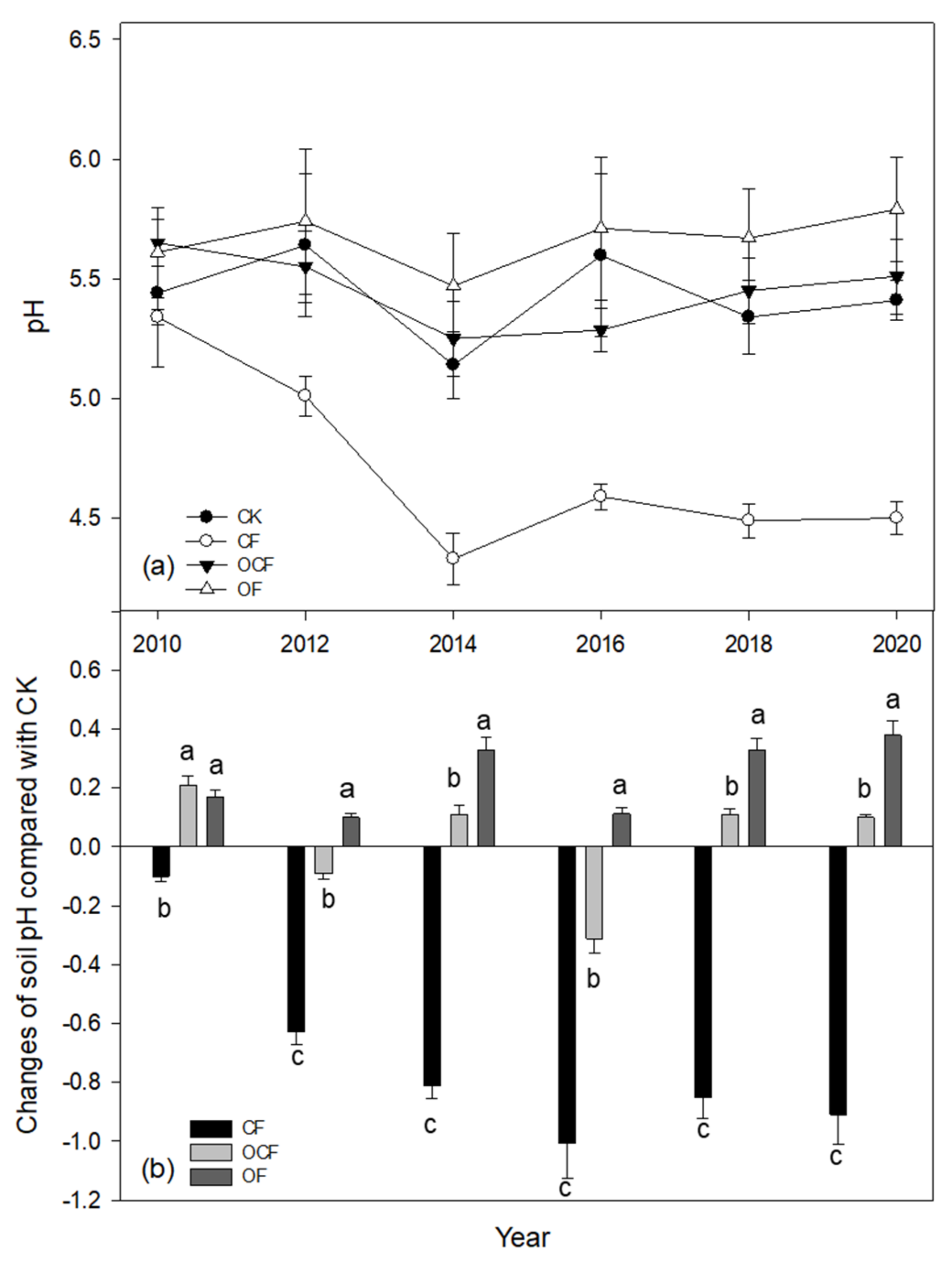
3.1. Changes of Soil PH over Ten Years
3.2. Soil PH, Ec and Soil Exchangeable Acid
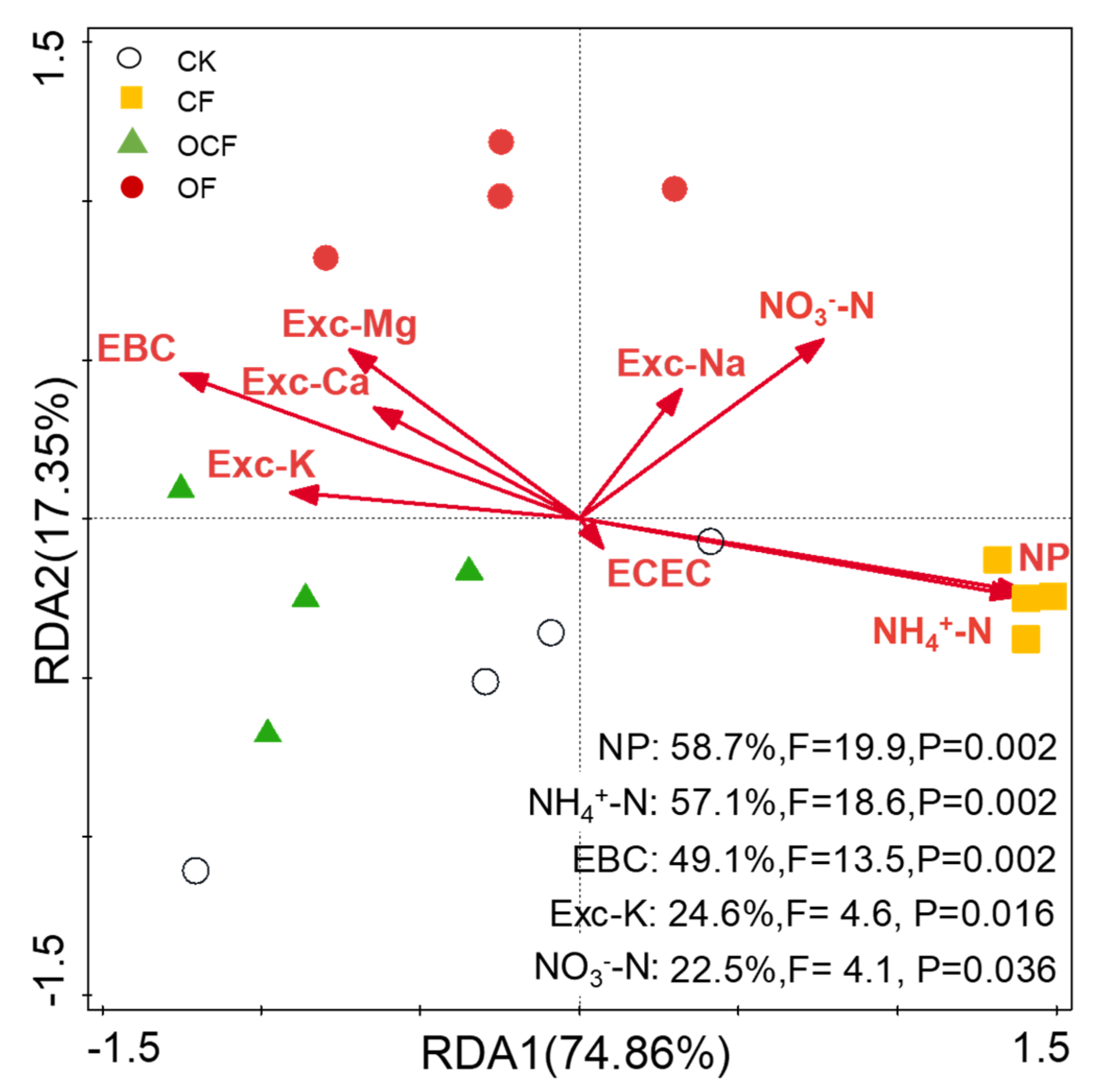
3.3. Soil Cation Exchange Capacity
3.4. Soil NO3−-N, NH4+-N and NP
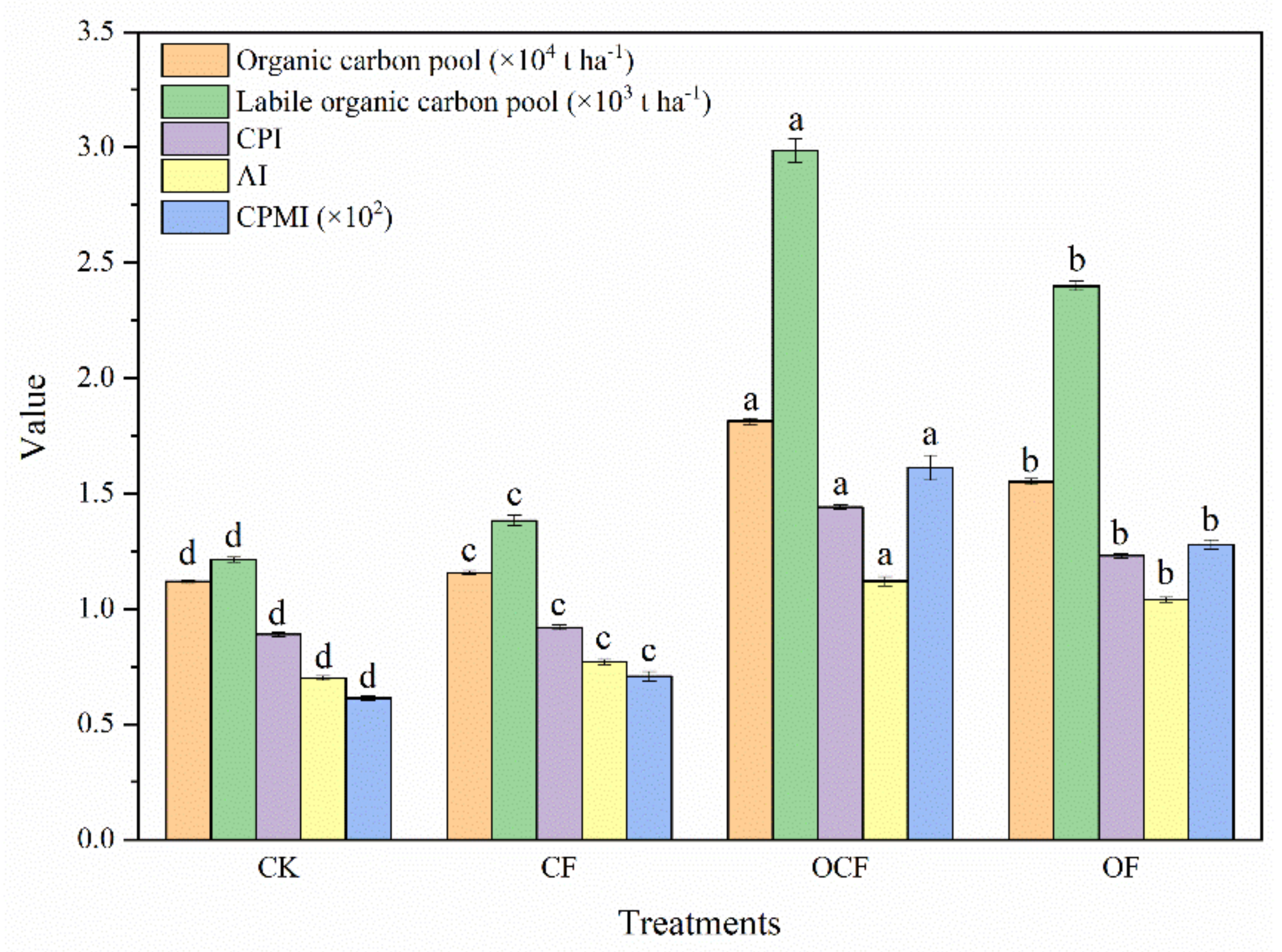
3.5. Soil Organic Carbon Pool
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects on Soil Acidification
4.2. Effects on Soil Cation Exchange Capacity and Nitrification, and Their Relationships with Soil Acidification
4.3. Response and Causes of Organic Carbon Pool in the Process of Fertilization Regulating Soil Acidification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, G.H.; Zhang, S.T.; Liu, X.J.; Jiang, Q.P.; Ding, W. Soil acidification amendments change the rhizosphere bacterial community of tobacco in a bacterial wilt affected field. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 9781–9791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.T.; He, X.H.; Liang, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Xu, C.; Shi, X.J. Long-term tobacco plantation induces soil acidification and soil base cation loss. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 5442–5450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.P.; Costa, S.E.V.G.A.; Anghinoni, I.; Kunrath, T.R.; Balerini, F.; Cecagno, D.; Carvalho, P.C.F. Soil acidification and basic cation use efficiency in an integrated no-till crop-livestock system under different grazing intensities. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 195, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.Q.; He, M.X.; Deng, M.J. Effects of soil acidification on soil nutrients and quality of flue-cured tobacco and its countermeasures. Chin. Tob. Sci. 2009, 29, 51–54. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Schroder, J.L.; Zhang, H.; Girma, K.; Raun, W.R.; Penn, C.J.; Payton, M.E. Soil acidification from long-term use of nitrogen fertilizers on winter wheat. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, P.J.; Kochenderfer, J.N.; Coble, D.W.; Adams, M.B. Soil leachate responses during 10 years of induced whole-watershed acidification. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2002, 140, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barak, P.; Jobe, B.O.; Krueger, A.R.; Peterson, L.A.; Laird, D.A. Effects of long-term soil acidification due to nitrogen fertilizer inputs in Wisconsin. Plant Soil 1997, 197, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xia, F.; Liu, X.M.; He, Y.; Xu, J.M.; Brookes, P.C. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer on the acidification of two typical acid soils in South China. J. Soil. Sediments 2014, 14, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, W.D.; Cleveland, C.C.; Halada, L.; Hresko, J.; Baron, J.S. Negative impact of nitrogen deposition on soil buffering capacity. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 767–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.T.; He, X.H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Shi, X.J. Soil acidification under long-term tobacco plantation results in alterations of mineralogical properties in an Alisol. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2016, 62, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, D.W. The role of soil organic matter in maintaining soil quality in continuous cropping systems. Soil Till. Res. 1997, 43, 131–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.R.; Li, Z.P.; Che, Y.P.; Han, F.X.; Liu, M. Soil organic C, nutrients, microbial biomass, and grain yield of rice (Oryza sativa L.) after 18 years of fertilizer application to an infertile paddy soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2011, 47, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, C.; Liang, G.Q.; Sun, J.W.; He, P.; Tang, S.H.; Yang, S.H.; Zhou, W.; Wang, X.B. The alleviation of acid soil stress in rice by inorganic or organic ameliorants is associated with changes in soil enzyme activity and microbial community composition. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2015, 51, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.; Xu, H.; Muhammad, M.A.; Syed, A.A.S.; Sun, N.; Qudsia, S.; Muhammad, K.; Muhammad, N.; Manuel, C.; Gao, H.J.; et al. Long-term fertilization enhanced carbon mineralization and maize biomass through physical protection of organic carbon in fractions under continuous maize cropping. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 165, 103971. [Google Scholar]
- Abrar, M.M.; Xu, M.G.; Shah, S.A.A.; Aslam, M.W.; Aziz, T.; Mustafa, A.; Ashraf, M.N.; Zhou, B.K.; Ma, X.Z. Variations in the profile distribution and protection mechanisms of organic carbon under long-term fertilization in a Chinese Mollisol. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 138181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adnan, M.; Xu, M.G.; Syed, A.A.S.; Muhammad, M.A.; Sun, N.; Wang, B.; Cai, Z.J.; Qudsia, S.; Muhammad, N.; Khalid, M.; et al. Soil aggregation and soil aggregate stability regulate organic carbon and nitrogen storage in a red soil of southern China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110894. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, M.N.; Jusheng, G.; Lei, W.; Mustafa, A.; Waqas, A.; Aziz, T.; Khan, W.U.D.; Hussain, B.; Farooq, M.; Wenju, Z.; et al. Soil microbial biomass and extracellular enzyme–mediated mineralization potentials of carbon and nitrogen under long-term fertilization (>30 years) in a rice–rice cropping system. J. Soils Sediments 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.H.; Merbold, L.; Leitner, S.; Pelster, D.E.; Okoma, S.A.; Ngetich, F.; Onyango, A.A.; Pellikka, P.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. The effects of climate on decomposition of cattle, sheep and goat manure in Kenyan tropical pastures. Plant Soil 2020, 451, 325–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaoude, L.A.; Castaldi, P.; Nassif, N.; Pinna, M.V.; Garau, G. Biochar and compost as gentle remediation options for the recovery of trace elements-contaminated soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.X.; Xu, J.L.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, D.; Li, L.W.; Li, W.; Sheng, L.X. Effects of long-term application of organic fertilizer on improving organic matter content and retarding acidity in red soil from China. Soil Till. Res. 2019, 195, 104382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.P.; Liu, Z.H.; Li, Y.; Zhong, Z.W.; Sun, M.; Jing, Y.P. Effects of long-term located fertilization on wheat yield and soil nutrients of three types of soils in shandong province. Agric. Sci. Tech. 2014, 15, 400–406. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ren, C.J.; Zhao, F.Z.; Kang, D.; Yang, G.H.; Han, X.H.; Tong, X.G.; Feng, Y.Z.; Ren, G.X. Linkages of C:N:P stoichiometry and bacterial community in soil following afforestation of former farmland. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 376, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Irmak, S.; Padhi, J. Effects of cover crops on soil quality: Part II. Soil exchangeable bases (potassium, magnesium, sodium, and calcium), cation exchange capacity, and soil micronutrients (zinc, manganese, iron, copper, and boron). J. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 73, 652–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.E.; Zeglin, L.H.; Wanzek, T.A.; Myrold, D.D.; Bottomley, P.J. Dynamics of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria populations and contributions to soil nitrification potentials. ISME J. 2012, 6, 2024–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandeler, E. Potential nitrification test. In Methods in Soil Biology; Schinner, F.O., Öhlinger, R., Kandeler, E., Margesin, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 146–148. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, F.C.B.; Bayer, C.; Zanatta, J.A.; Dieckow, J.; Mielniczuk, J.; He, Z.L. Carbon management index based on physical fractionation of soil organic matter in an Acrisol under long-term no-till cropping systems. Soil Till. Res. 2007, 96, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, G.J.; Lefroy, R.D.; Lisle, L. Soil carbon fractions based on their degree of oxidation, and the development of a carbon management index for agricultural systems. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1995, 46, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Yang, H.S.; Liu, J.; Wu, J.S.; Chen, W.P.; Wu, J.; Zhu, L.Q.; Bian, X.M. Effects of ditch-buried straw return on soil organic carbon and rice yields in a rice—Wheat rotation system. Catena 2015, 127, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukshana, F.; Butterly, C.R.; Baldock, J.A.; Tang, C.X. Model organic compounds differ in their effects on pH changes of two soils differing in initial pH. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2011, 47, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-del Amo, E.; Baneras, L. Effects of high nitrate input in the denitrification-DNRA activities in the sediment of a constructed wetland under varying C/N ratios. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 159, 106098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, M.Y.; Hui, R.; Sui, T.Y.; Yang, L.; Du, W.B.; Dong, Z.R. A 4-year field measurement of N2O emissions from a maize-wheat rotation system as influenced by partial organic substitution for synthetic fertilizer. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 263, 110384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, R.K.; Power, J.F. Use of crop residue and manure to conserve water and enhance nutrient availability and pearl millet yields in an arid tropical region. Soil Till. Res. 1997, 41, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Riaz, M.; Zhang, M.Y.; Liu, B.; El-Desouki, Z.; Jiang, C.C. Biochar increases nitrogen use efficiency of maize by relieving aluminum toxicity and improving soil quality in acidic soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 196, 110531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aini, I.N.; Ezrin, M.H.; Aimrun, W. Relationship between Soil Apparent Electrical Conductivity and pH Value of Jawa Series in Oil Palm Plantation. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2014, 2, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.F.; Cai, A.D.; Liu, K.L.; Huang, J.; Wang, B.R.; Li, D.C.; Qaswar, M.; Feng, G.; Zhang, H.M. The links between potassium availability and soil exchangeable calcium, magnesium, and aluminum are mediated by lime in acidic soil. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 19, 1382–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.R. Aluminum ions. In Chemistry of Variable Charge Soils; Yu, T.R., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 369–385. [Google Scholar]
- Mehmood, K.; Li, J.Y.; Jiang, J.; Shi, R.Y.; Liu, Z.D.; Xu, R.K. Amelioration of an acidic ultisol by straw-derived biochars combined with dicyandiamide under application of urea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nottidge, D.O.; Nottidge, C.C. Effect of different rates of wood ash on exchangeable aluminum, growth, nodulation, nitrogen accumulation and grain yield of soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill) in an acid ultisol. Glob. J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 11, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, B.B.; Wang, X.M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, K.; Xie, P.; Ji, H.B. The optimum pH and Eh for simultaneously minimizing bioavailable cadmium and arsenic contents in soils under the organic fertilizer application. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 135299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, M.C.; Habermann, G.; do Amaral, C.L.; Rosa, A.L.; Pinheiro, M.H.O.; Da Costa, F.B. Vochysia tucanorum Mart.: An aluminum-accumulating species evidencing calcifuge behavior. Plant Soil 2017, 419, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramos, F.T.; Dores, E.F.D.C.; Weber, O.L.D.S.; Beber, D.C.; José, H.C.; Maia, J.C.D.S. Soil organic matter doubles the cation exchange capacity of tropical soil under no-till farming in Brazil. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 3595–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.Q.; Fang, K.; Wang, G.Q.; Peng, Y.F.; Zhang, D.Y.; Li, F.; Zhou, G.Y.; Yang, Y.H. Responses of exchangeable base cations to continuously increasing nitrogen addition in alpine steppe: A case study of Stipa purpurea steppe. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2018, 42, 95–104. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.G.; Yang, S.; Fu, M.M.; Cai, J.P.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, R.Z.; Xu, Z.W.; Bai, Y.F.; Jiang, Y. Sheep manure application increases soil exchangeable base cations in a semi-arid steppe of Inner Mongolia. J. Arid Land 2015, 7, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gondar, D.; López, R.; Antelo, J.; Fiol, S.; Arce, F. Adsorption of paraquat on soil organic matter: Effect of exchangeable cations and dissolved organic carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 235–236, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanya, D.; Amadji, L. Application of cow manure and inorganic fertilizer in one season and carryover of effects in sesame on tropical ferruginous soils. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2018, 13, 2207–2223. [Google Scholar]
- Malhi, S.J.; Nyborg, M.; Harapiak, J.K. Effects of long-term N fertilizer-induced acidification and liming on micronutrients in soil and in brome grass hay. Soil Till. Res. 1998, 48, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.J.; Wang, B.R.; Xu, M.G.; Zhang, H.M.; He, X.H.; Zhang, L.; Gao, S.D. Intensified soil acidification from chemical n fertilization and prevention by manure in an 18-year field experiment in the red soil of southern China. J. Soil. Sediments 2015, 15, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.T.F.; Swif, R.S.T. Role of organic matter in alleviating soil acidity. In Handbook of Soil Acidity; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; pp. 337–358. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Cai, Z.C.; Xu, Z.H. Does ammonium-based N addition in fluence nitrification and acidification in humid subtropical soils of China? Plant Soil 2007, 297, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coca-Salazar, A.; Richaume, A.; Florio, A.; Florio, A.; Carnol, M. Response of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea abundance and activity to land use changes in agricultural systems of the Central Andes. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2021, 102, 103263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dai, S.Y.; Huang, X.Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Cai, Z.C.; Zhang, J.B. pH-induced changes in fungal abundance and composition affects soil heterotrophic nitrification after 30 days of artificial pH manipulation. Geoderma 2020, 366, 114255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhao, C.; Cao, W.C.; Huang, T.; Wang, J.G.; Dong, Z.R. Changing roles of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in a continuously acidifying soil caused by over-fertilization with nitrogen. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 11964–11974. [Google Scholar]
- Chathurika, J.A.S.; Kumaragamage, D.; Indraratne, S.P.; Dandeniya, W.S. Improving soil carbon pool, soil fertility and yield of maize (Zea mays L.) in low-fertile tropical Alfisols by combining fertilizers with slow-decomposing organic amendments. J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 157, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holík, L.; Hlisnikovský, L.; Honzík, R.; Trögl, J.; Burdová, H.; Popelka, J. Soil Microbial Communities and Enzyme Activities after Long-Term Application of Inorganic and Organic Fertilizers at Different Depths of the Soil Profile. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Ni, T.; Li, Y.; Xiong, W.; Ran, W.; Shen, B.; Shen, Q.R.; Zhang, R.F. Response of bacterial communities in arable soils in a rice–wheat cropping system to different fertilizer regimes and sampling times. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85301. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.X.; Xu, J.L.; Liu, X.J.; Sheng, L.X.; Zhang, D.; Li, L.W.; Wang, A.X. Study on the pollution status and control measures for the livestock and poultry breeding industry in northeastern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 4435–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Treatments | N (kg ha−1) | P2O5 (kg ha−1) | K2O (kg ha−1) | Organic Carbon (kg ha−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Fertilizer | Organic Fertilizer | Chemical Fertilizer | Organic Fertilizer | Chemical Fertilizer | Organic Fertilizer | Chemical Fertilizer | Organic Fertilizer | |
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CF | 82.20 | 0 | 83.25 | 0 | 249.75 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| OCF | 82.20 | 165.00 | 83.25 | 167.25 | 249.75 | 384.00 | 0 | 3019.05 |
| OF | 0 | 247.50 | 0 | 250.87 | 0 | 576.00 | 0 | 4528.57 |
| Treatments | pH | Ec | Exchangeable Acidity (mmol kg−1) | Exchangeable H (mmol kg−1) | Exchangeable Al (mmol kg−1) | Al Saturatio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 5.41 ± 0.04 b | 62.27 ± 0.74 b | 9.10 ± 0.10 a | 2.30 ± 0.07 a | 6.40 ± 0.04 b | 5.29 ± 0.89 bc |
| CF | 4.50 ± 0.12 c | 70.03 ± 0.51 a | 10.90 ± 0.10 a | 2.30 ± 0.03 a | 9.00 ± 0.06 a | 9.17 ± 0.21 a |
| OCF | 5.51 ± 0.08 ab | 60.63 ± 0.49 b | 6.70 ± 0.07 b | 2.00 ± 0.06 a | 5.40 ± 0.04 bc | 6.56 ± 0.66 b |
| OF | 5.79 ± 0.11 a | 55.40 ± 0.59 c | 5.10 ± 0.07 b | 2.00 ± 0.06 a | 4.00 ± 0.07 c | 4.36 ± 0.50 c |
| Treatments | Exchangeable K (cmol kg−1) | Exchangeable Na (cmol kg−1) | Exchangeable Ca (cmol kg−1) | Exchangeable Mg (cmol kg−1) | EBC (cmol kg−1) | ECEC (cmol kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.27 ± 0.05 a | 0.07 ± 0.01 a | 6.13 ± 0.38 a | 3.13 ± 0.47 a | 9.10 ± 0.87 ab | 9.37 ± 0.94 a |
| CF | 0.25 ± 0.02 a | 0.09 ± 0.01 a | 6.07 ± 0.22 a | 2.83 ± 0.19 a | 7.69 ± 0.40 b | 11.35 ± 0.99 a |
| OCF | 0.28 ± 0.04 a | 0.09 ± 0.02 a | 6.20 ± 0.32 a | 3.37 ± 0.28 a | 10.55 ± 0.45 a | 10.6 ± 0.70 a |
| OF | 0.31 ± 0.02 a | 0.11 ± 0.02 a | 6.70 ± 0.11 a | 3.80 ± 0.31 a | 10.92 ± 0.38 a | 10.17 ± 0.68 a |
| Treatments | NH4+-N (mg kg−1) | NO3−-N (mg kg−1) | NP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NP Value (mg kg−1 h−1) | R2 (n = 4) | |||
| CK | 4.53 ± 0.82 b | 6.87 ± 0.41 c | 0.07 | 0.9996 |
| CF | 18.49 ± 1.74 a | 13.75 ± 0.95 a | 1.67 | 0.9989 |
| OCF | 4.97 ± 0.27 b | 10.99 ± 0.44 b | 0.04 | 0.9997 |
| OF | 4.59 ± 0.20 b | 12.73 ± 0.88 ab | 0.09 | 0.9754 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, P.; Cong, P.; Wang, P.; Dong, J.; Dong, Z.; Song, W. Alleviating Soil Acidification and Increasing the Organic Carbon Pool by Long-Term Organic Fertilizer on Tobacco Planting Soil. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2135. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112135
Dai P, Cong P, Wang P, Dong J, Dong Z, Song W. Alleviating Soil Acidification and Increasing the Organic Carbon Pool by Long-Term Organic Fertilizer on Tobacco Planting Soil. Agronomy. 2021; 11(11):2135. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112135
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Peigang, Ping Cong, Peng Wang, Jianxin Dong, Zhaorong Dong, and Wenjing Song. 2021. "Alleviating Soil Acidification and Increasing the Organic Carbon Pool by Long-Term Organic Fertilizer on Tobacco Planting Soil" Agronomy 11, no. 11: 2135. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112135
APA StyleDai, P., Cong, P., Wang, P., Dong, J., Dong, Z., & Song, W. (2021). Alleviating Soil Acidification and Increasing the Organic Carbon Pool by Long-Term Organic Fertilizer on Tobacco Planting Soil. Agronomy, 11(11), 2135. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112135





