Mitigating Potassium Leaching from Muriate of Potash in a Tropical Peat Soil Using Clinoptilolite Zeolite, Forest Litter Compost, and Chicken Litter Biochar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Peat Soil Sampling
2.2. Selected Properties of Clinoptilolite Zeolite, Forest Litter Compost, and Chicken Litter Biochar
2.3. Initial Characterization of Tropical Peat Soil
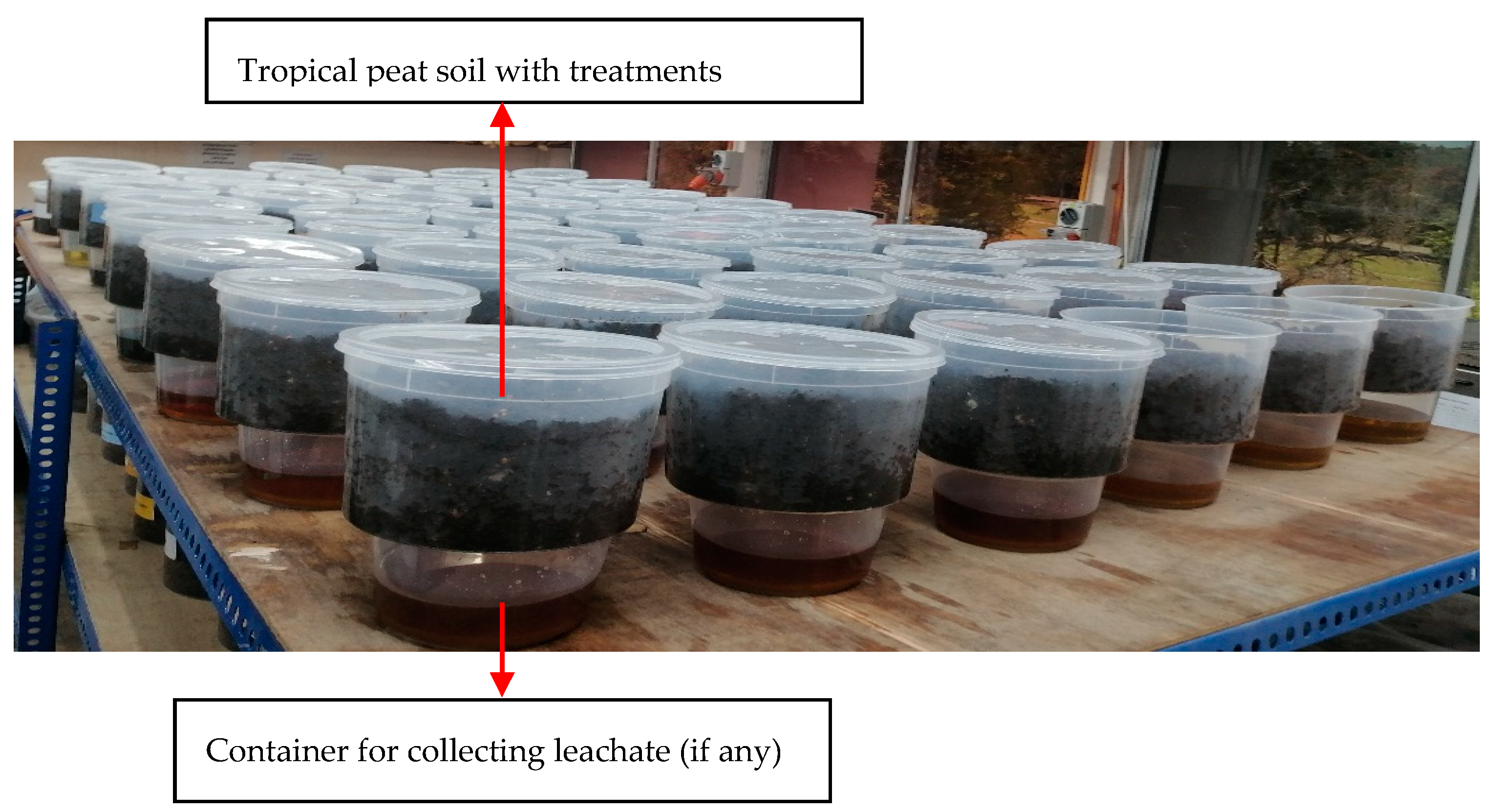
2.4. Leaching Study
2.5. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Selected Physico-Chemical Properties of Tropical Peat Soil
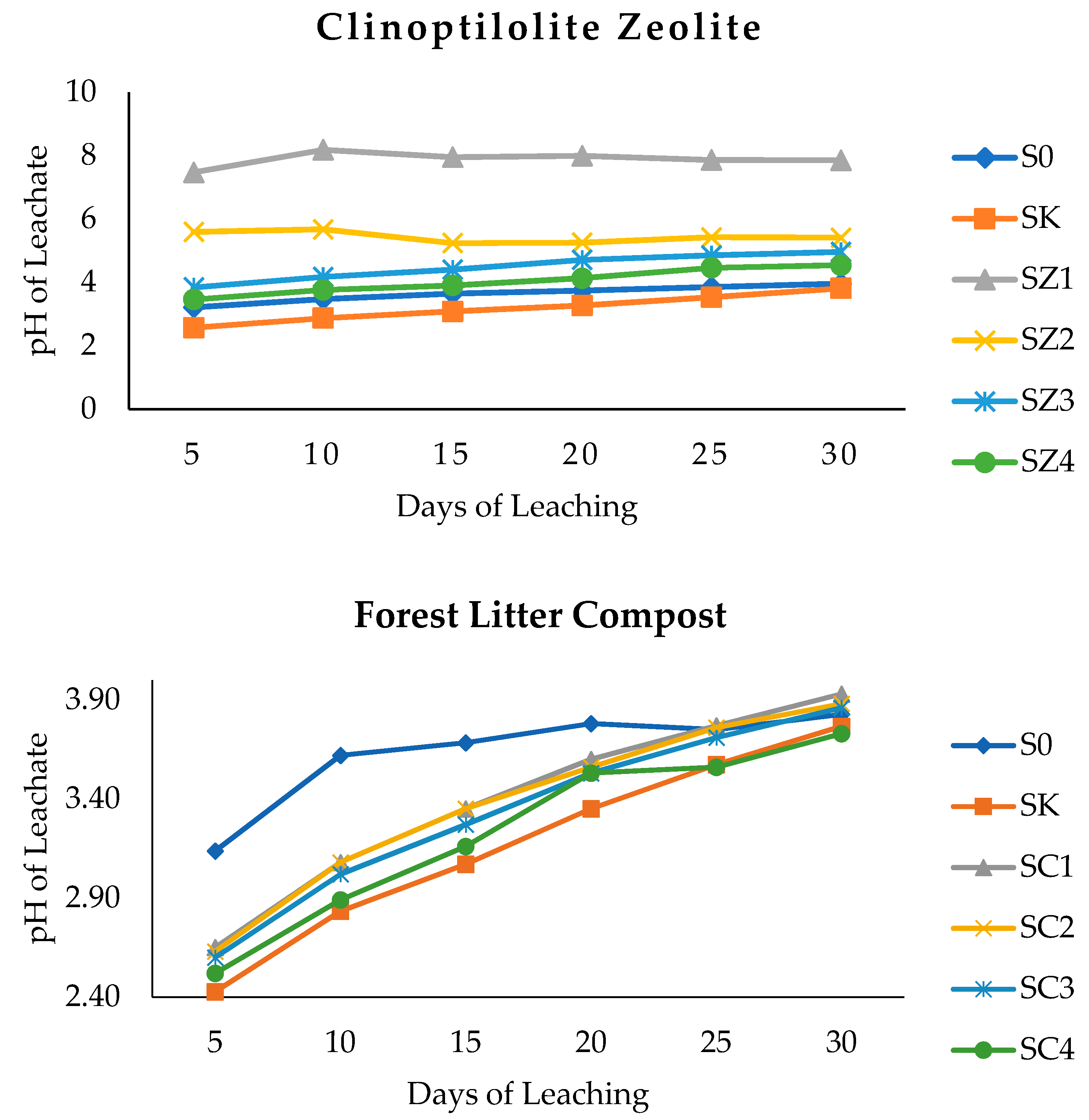
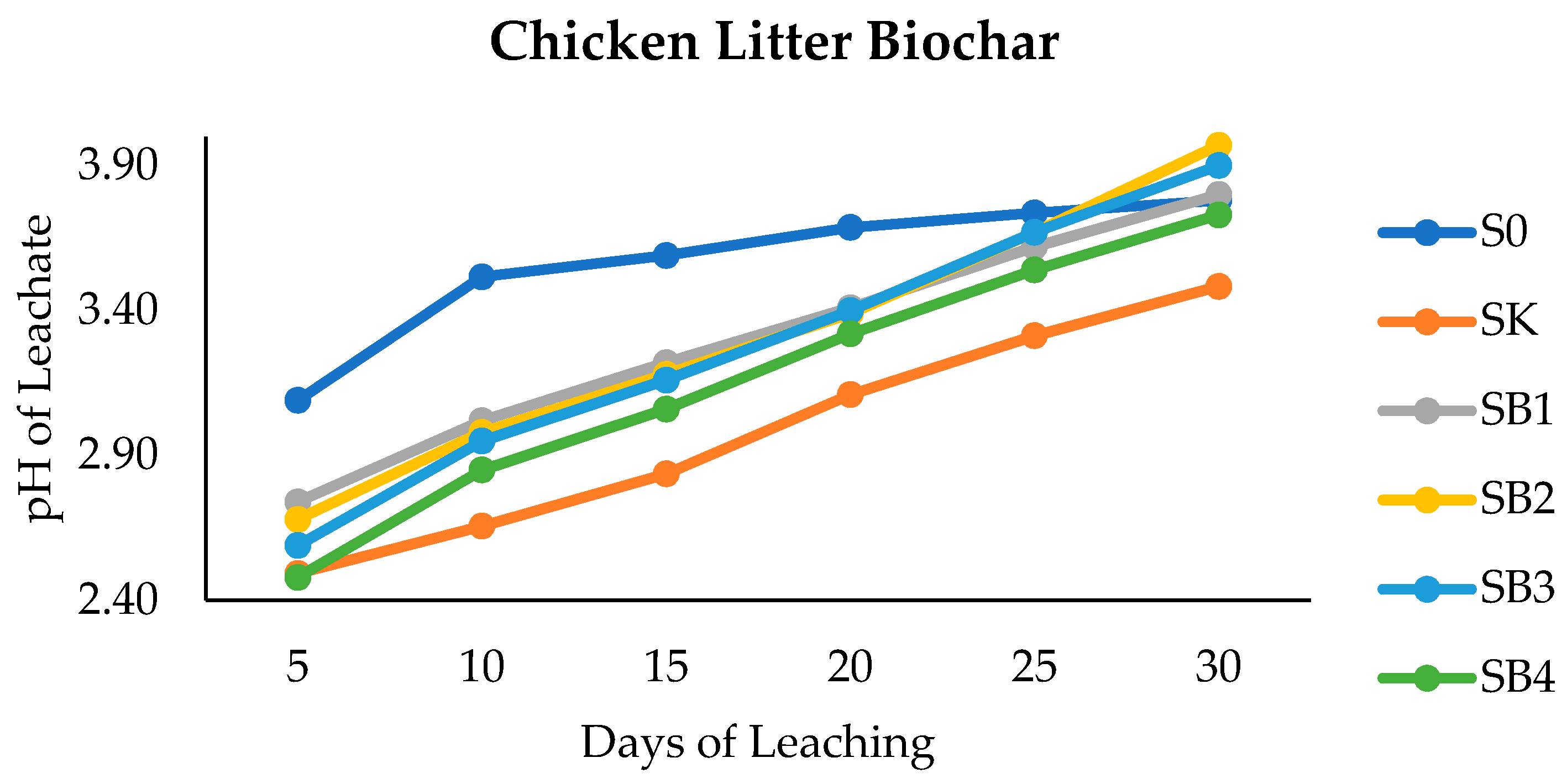
3.2. Clinoptilolite Zeolite, Forest Litter Compost, and Chicken Litter Biochar on pH of Leachate and Peat Soil after Thirty Days of Leaching
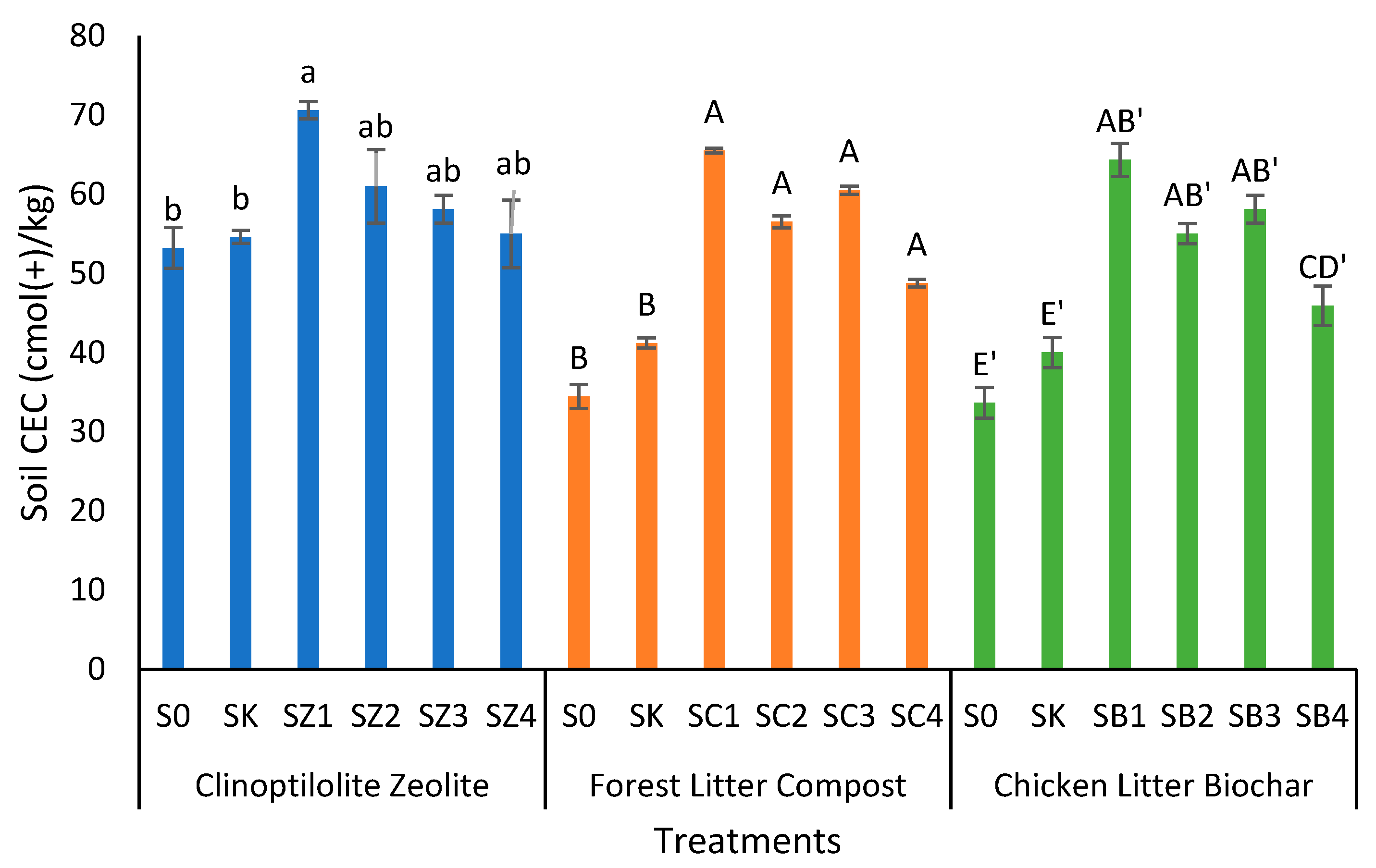
3.3. Clinoptilolite Zeolite, Forest Litter Compost, and Chicken Litter Biochar on Cation Exchange Capacity of Peat Soil after Thirty Days of Leaching
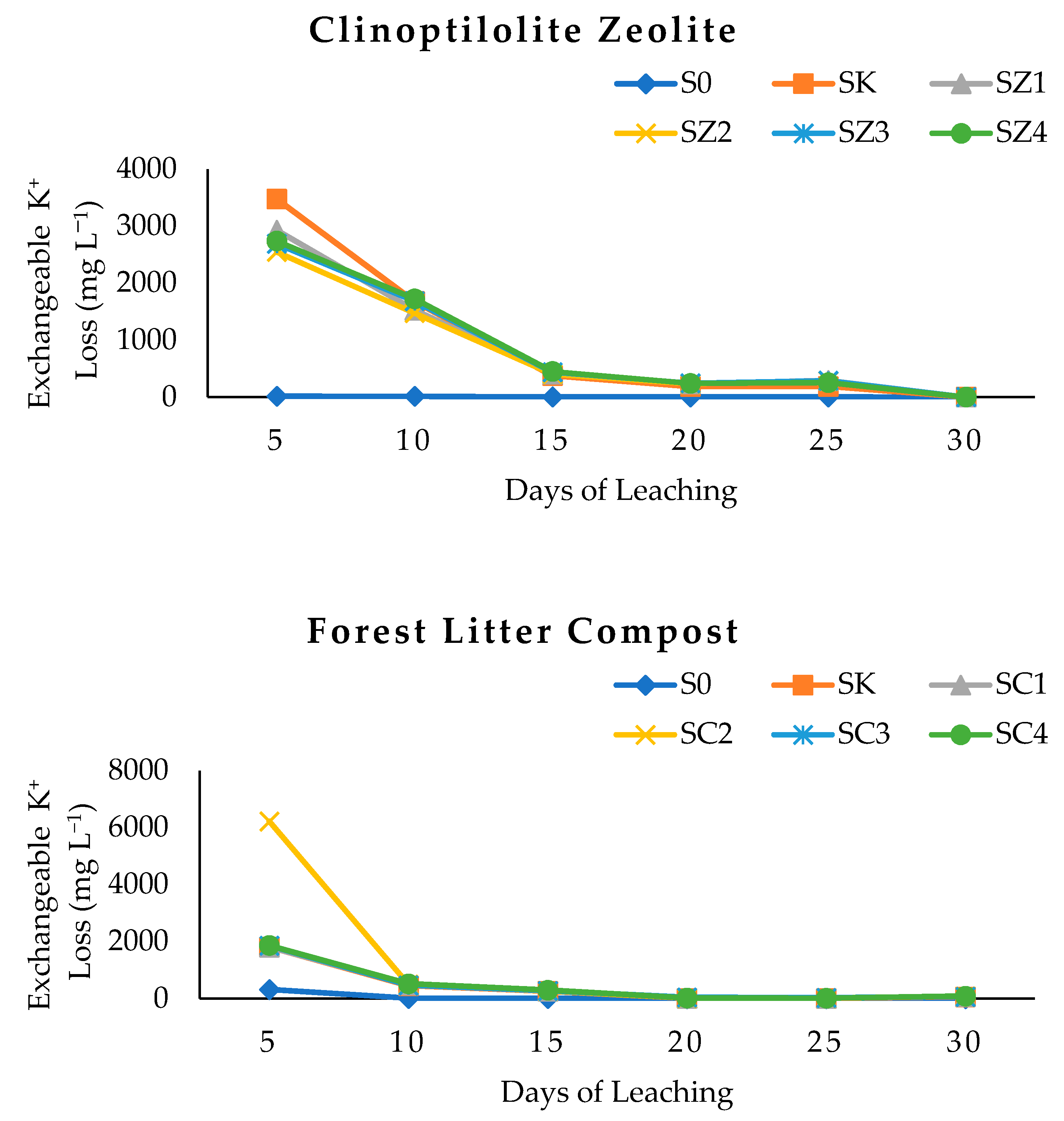
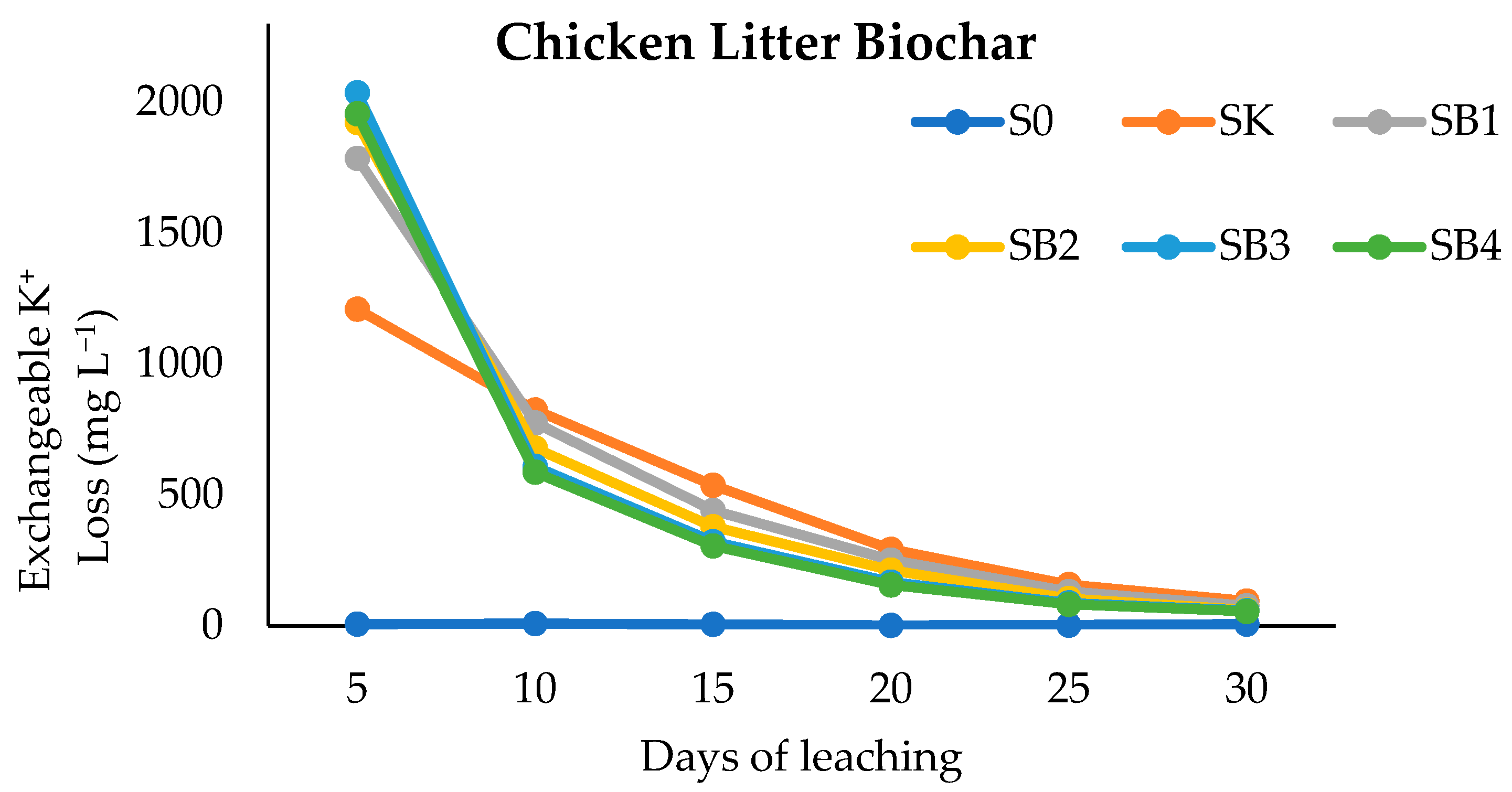
3.4. Clinoptilolite Zeolite, Forest Litter Compost, and Chicken Litter Biochar on Exchangeable K of Leachate after Thirty Days of Leaching
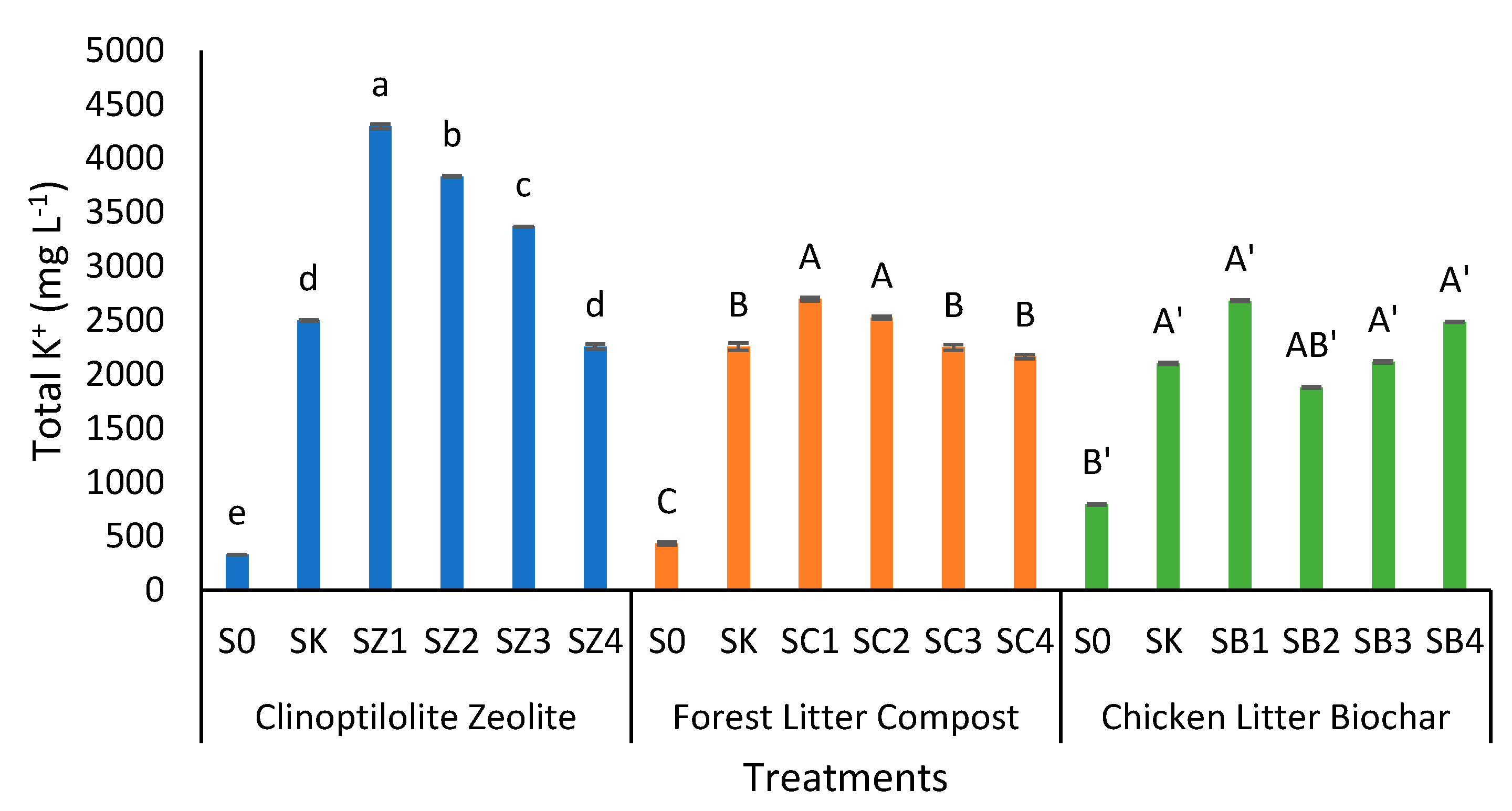
3.5. Clinoptilolite Zeolite, Forest Litter Compost, and Chicken Litter Biochar on Exchangeable and Total Potassium of Peat Soil after Thirty Days of Leaching
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MOP | Muriate of potash | Ca | Calcium |
| K | Potassium | Mg | Magnesium |
| CZ | Clinoptilolite zeolite | Na | Sodium |
| FLC | Forest litter compost | N | Nitrogen |
| CLB | Chicken litter biochar | P | Phosphorus |
| CEC | Cation exchange capacity | AAS | Atomic absorption spectrophotometry |
References
- Osman, K.T. Peat Soils; Management of Soil Problems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 145–183. ISBN 9783319755274. [Google Scholar]
- Murtedza, M.; Padmanabhan, E.; Mei, B.L.H.; Siong, W.B. The Peat Soils of Sarawak; Strapeat Status Report; STRAPEAT: Gelugor, Malaysia, 2002; pp. 2–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, O.H.; Ahmad, H.M.H.; Musa, H.M.; Rahim, A.A.; Rastan, S.O.S. Applied K fertilizer use efficiency in pineapples grown on a tropical peat soil under residues removal. Sci. World J. 2005, 5, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brady, N.C.; Weil, R.R. The Nature and Properties of Soils, 13th ed.; Pearson Education Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2002; ISBN 9780130167637. [Google Scholar]
- Zoerb, C.; Senbayram, M.; Peiter, E. Potassium in agriculture—Status and perspectives. J. Plant Physiol. 2014, 171, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahoor, R.; Dong, H.; Abid, M.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z. Potassium fertilizer improves drought stress alleviation potential in cotton by enhancing photosynthesis and carbohydrate metabolism. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2017, 137, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Xu, Q.W.; Zou, Y.G.; Ma, S.M.; Zhang, X.D.; Xie, X.Y.; Wang, L.C. Effect of potassium deficiency on growth, antioxidants, ionome and metabolism in rapeseed under drought stress. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 90, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, R. Essential nutrients for plant growth: Nutrient functions and deficiency, symptoms. In Plant Nutrient Management in Hawaii’s Soils; College of Tropical; Agriculture and Human Resources; University of Hawaii at Manoa: Honolulu, HI, USA, 2000; pp. 31–55. [Google Scholar]
- Torabian, S.; Farhangi-Abriz, S.; Qin, R.; Noulas, C.; Sathuvalli, V.; Charlton, B.; Loka, D.A. Potassium: A Vital Macronutrient in Potato Production—A Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, R.; Garivait, H.; Pongsatorn, P.A. Impacts of precipitation on leaching behavior of plant nutrients in agricultural soils of the tropics. In Proceedings of the 2010 2nd International Conference on Chemical, Biological and Environmental Engineering, Cairo, Egypt, 2–4 November 2010; pp. 336–340. [Google Scholar]
- Goulding, K.; Jarvis, S.; Whitmore, A. Optimizing nutrient management for farm systems. Philos Trans. R. Soc. B. 2008, 363, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timilsena, Y.P.; Adhikari, R.; Casey, P.; Muster, T.; Gill, H.; Adhikari, B. Enhanced efficiency fertilisers: A review of formulation and nutrient release patterns. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsintskaladze, G.; Eprikashvili, L.; Urushadze, T.; Kordzakhia, T.; Sharashenidze, T.; Zautashvili, M.; Burjanadze, M. Nanomodified natural zeolite as a fertilizer of prolonged activity. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2016, 14, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbahce, A.; Tari, A.F.; Gönülal, E.; Simsekli, N.; Padem, H. The effect of zeolite applications on yield components and nutrient uptake of common bean under water stress. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2015, 61, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltys, L.; Myronyuk, I.; Tatarchuk, T.; Tsinurchyn, V. Zeolite-based composites as slow-release fertilizers. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2020, 21, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashman, M.; Puri, G. Essential Soil Science: A Clear and Concise Introduction to Soil Science; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-0-632-04885-4. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Caballero, R.; Gil, J.; Benitez, C.; Gonzalez, J.L. The effect of adding zeolite to soils in order to improve the NK nutrition of olive trees. Preliminary results. Am. J. Agric. Bio. Sci. 2008, 2, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Purakayastha, T.J.; Bera, T.; Bhaduri, D.; Sarkar, B.; Mandal, S.; Wade, P.; Kumari, S.; Biswas, S.; Menon, M.; Pathak, H.; et al. A review on biochar modulated soil condition improvements and nutrient dynamics concerning crop yields: Pathways to climate change mitigation and global food security. Chemosphere 2019, 227, 345–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malyan, S.K.; Kumar, S.S.; Fagodiya, R.K.; Ghosh, P.; Kumar, A.; Singh, R.; Singh, L. Biochar for environmental sustainability in the energy-water-agroecosystem nexus. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanivell, P.; Susilawati, K.; Ahmed, O.H.; Majid, N.M. Compost and crude humic substances produced from selected wastes and their effects on Zea mays L. nutrient uptake and growth. Sci. World J. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.A.; Agarwal, S.P.; Rahman, M.A.; Rauf, A.; Ahmad, N.; Alam, A.; Iqbal, Z. Role of humic acid on oral drug delivery of an antiepileptic drug. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2011, 37, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maru, A.; Haruna, O.A.; Charles Primus, W. Co-application of chicken litter biochar and urea only to improve nutrients use efficiency and yield of Oryza sativa L. cultivation on a tropical acid soil. Sci. World J. 2015, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Haruna, A.O.; Majid, N.M.A.; Primus, W.C.; Asap, A.; Maikol, N.; Jeffray, A.V. Mitigating Ammonia Volatilization from Waterlogged Acids Soils Using Organic Amendments. Sustain. Agric. Res 2019, 8, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, K.; Tomlinson, T. Poultry Litter Biochar-A US Perspective. International Biochar Initiative (IBI). Available online: http://www.biocharinternational.org/sites/default/files/Poultry_litter_final_2012.pdf (accessed on 25 February 2020).
- Song, W.; Guo, M. Quality variations of poultry litter biochar generated at different pyrolysis temperatures. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2012, 94, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Shen, Y.; He, Z. Poultry litter-based biochar: Preparation, characterization, and utilization. In Applied Research of Animal Manure: Challenges and Opportunities beyond the Adverse Environmental Concerns; He, Z., Ed.; Nova Science: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 169–202. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, O.H.; Palanivell, P.; Majid, N.M.A. Enhancing Rice Yield Using Organic and Inorganic Amendments; Universiti Putra Malaysia Press: Serdang, Malaysia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Palanivell, P.; Ahmed, O.H.; Latifah, O.; Abdul Majid, N.M. Adsorption and desorption of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and soil buffering capacity following application of chicken litter biochar to an acid soil. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peech, H.M. Hydrogen-ion Activity. In Methods of Soil Analysis Chemical and Microbiological Properties; Black, C.A., Evans, D.D., White, J.L., Ensminger, L.E., Clark, F.E., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1965; pp. 914–926. ISBN 0891180729. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, J.M. Total Nitrogen. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2; Black, C.A., Evans, D.D., Ensminger, L.E., White, J.L., Clark, F.F., Dinauer, R.C., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1965; pp. 1149–1178. [Google Scholar]
- Mehlich, A. Determination of P, Ca, Mg, K, Na, and NH4. In North Carolina Soil Test Division (Mimeo 1953); North Carolina Department of Agriculture: Raleigh, NC, USA, 1953; pp. 23–89. Available online: http://www.ncagr.gov/AGRONOMI/pdffiles/mehlich53.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2020).
- Jones, J.B., Jr. Laboratory Guide for Conducting Soil Tests and Plant Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001; ISBN 0-8493-0206-4. [Google Scholar]
- Chefetz, B.; Hatcher, P.H.; Hadar, Y.; Chen, Y. Chemical and biological characterization of organic matter during composting of municipal solid waste. J. Environ. Qual. 1996, 25, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloo, R.; Paramananthan, S.; Van Ranst, E. Classification of tropical lowland peats revisited: The case of Sarawak. Catena 2014, 118, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikmatullah, H.; Sukarman, S. Physical and chemical properties of cultivated peat soils in four trial sites of ICCTF in Kalimantan and Sumatra, Indonesia. J. Trop. Soils 2014, 19, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afip, I.A.; Jusoff, K. Properties of a Tropical Sapric Peat Soil in Sarawak. Malays. J. Soil Sci. 2019, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Melling, L.; Goh, K.J.; Hatano, R.; Uyo, L.J.; Sayok, A.; Nik, A.R. Characteristics of natural tropical peatland and their influence on C flux in Loagan Bunut National Park, Sarawak, Malaysia. In After Wise Use–The Future of Peatlands; EPA: Frankfurt, Germany, 2008; pp. 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Filcheva, E.G.; Tsadilas, C.D. Influence of clinoptilolite and compost on soil properties. Comm Soil Sci Plant Anal 2002, 33, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, E.; Karaca, M.; Demir, H.; Onus, A.N. Use of natural zeolite (clinoptilolite) in agriculture. J. Fruit Ornam. Plant Res. 2004, 12, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, D.W.; Boettinger, J.L. Zeolites in soil environments. In Natural Zeolites: Occurrence, Properties, Applications; Bish, D.L., Ming, D.W., Eds.; Mineralogical Society of America and Geochemical Society: McLean, VA, USA, 2001; Volume 45, pp. 323–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, O.H.; Sumalatha, G.; Nik Muhamad, A.M. Use of zeolite in maize (Zea mays) cultivation on nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus uptake and use efficiency. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2010, 5, 2393–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Nobili, M.D.; Aviad, T. Stimulatory effects of humic substances on plant growth. Soil Organic Matter in Sustainable Agriculture; Magdoff, F., Weil, R.R., Eds.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 103–129. ISBN 9780429209758. [Google Scholar]
- Zaidun, S.W.; Jalloh, M.B.; Awang, A.; Sam, L.M.; Besar, N.A.; Musta, B.; Ahmed, O.H.; Latifah, O. Biochar and clinoptilolite zeolite on selected chemical properties of soil cultivated with maize (Zea mays L.). Eurasian J. Soil Sci 2019, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jien, S.H.; Wang, C.S. Effects of biochar on soil properties and erosion potential in a highly weathered soil. Catena 2013, 110, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, O.H.; Liza Nuriati, L.K.C. Greenhouse Gas Emission and Carbon Leaching in Pineapple Cultivation on Tropical Peat Soil; Universiti Putra Malaysia Press: Serdang, Malaysia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Römheld, V.; Kirkby, E.A. Research on potassium in agriculture: Needs and prospects. Plant Soil 2010, 335, 155–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, S.; Zubaidah, S.R.I.; Shamsuddin, J.; Husni, M.H.A. Ammonium and Potassium Exchange in Acid Tropical Soil Treated with Zeolites. Malaysian J. Soil Sci. 2001, 5, 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Hoskins, B.R. Soil Testing Handbook for Professionals in Agriculture, Horticulture, Nutrient, and Residual Management, 3rd ed; University of Maine: Maine, UK, 1997; p. 119. [Google Scholar]
- Rabai, K.A.; Ahmed, O.H.; Kasim, S. Use of formulated nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium compound fertilizer using clinoptilolite zeolite in maize (Zea mays L.) Cultivation. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2013, 25, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakkula, V.S.; Wani, S.P. Zeolites: Potential soil amendments for improving nutrient and water use efficiency and agriculture productivity. Sci. Revs. Chem. Commun. 2018, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Dao, T.H. Competitive anion sorption effects on dairy wastewater dissolved phosphorus extraction with zeolite-based sorbents. J. Food. Agric. Environ. 2003, 1, 263–269. [Google Scholar]
- Adani, F.; Genevini, P.; Tambone, F.; Montoneri, E. Compost effect on soil humic acid: A NMR study. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 1414–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, T.E.; Sohi, S.P. Establishing release dynamics for plant nutrients from biochar. GCB Bioenergy 2013, 5, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Property | Clinoptilolite Zeolite | Forest Litter Compost | Chicken Litter Biochar |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.20 | 8.52 | 9.54 |
| EC (mS cm−1) | 0.13 | nd | 3.50 |
| CEC (cmol(+) kg−1) | 71 | 79.33 | 59.27 |
| (%) | |||
| Total N | 0.22 | 0.27 | 2.39 |
| Total P | 0.01 | 0.75 | 4.52 |
| Total K | 0.37 | 2.67 | 6.05 |
| Total Ca | 0.67 | nd | 4.80 |
| Total Mg | 0.10 | 1.24 | 1.77 |
| Total Na | 0.76 | nd | 1.75 |
| Total Fe | 0.11 | nd | 0.49 |
| Organic Matter | nd | 89.00 | 71.67 |
| (mg kg−1) | |||
| Total Zn | 15 | nd | 772 |
| Total Mn | 17 | nd | 1479 |
| Total Cu | 125 | nd | 264 |
| Treatment Codes | Peat Soil (g) | Clinoptilolite Zeolite (g) | Forest Litter Compost (g) | Chicken Litter Biochar (g) | MOP (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | 300 | - | - | - | - |
| SK | 300 | - | - | - | 1.78 |
| SZ1 | 300 | 7.7 | - | - | 1.78 |
| SZ2 | 300 | 5.8 | - | - | 1.78 |
| SZ3 | 300 | 3.9 | - | - | 1.78 |
| SZ4 | 300 | 1.9 | - | - | 1.78 |
| SC1 | 300 | - | 4.82 | - | 1.78 |
| SC2 | 300 | - | 3.62 | - | 1.78 |
| SC3 | 300 | - | 2.41 | - | 1.78 |
| SC4 | 300 | - | 1.21 | - | 1.78 |
| SB1 | 300 | - | - | 4.82 | 1.78 |
| SB2 | 300 | - | - | 3.62 | 1.78 |
| SB3 | 300 | - | - | 2.41 | 1.78 |
| SB4 | 300 | - | - | 1.21 | 1.78 |
| Variable | Data Obtained (0–25 cm) | Standard Data Range * |
|---|---|---|
| pH in water | 3.82 ± 0.09 | 3.6 |
| Electrical conductivity (µS/cm) | 160.47 ± 0.3 | 159.8–358 |
| Cation exchange capacity (cmol (+)/kg) | 55.33 ± 3.6 | 68 |
| (cmol kg−1) | ||
| Total soil K | 0.53 ± 0.005 | nd |
| Exchangeable K | 0.12 ± 0.007 | 0.12 |
| Total soil Ca | 3.7 ± 0.05 | nd |
| Exchangeable Ca | 1.11 ± 0.02 | 2.55 |
| Total soil Mg | 5.72 ± 0.13 | nd |
| Exchangeable Mg | 1.06 ± 0.03 | 1.24 |
| (%) | ||
| Organic matter | 94.27 ± 3.7 | nd |
| Total organic carbon | 54.68 ± 2.1 | nd |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krishnan, K.; Ngerong, A.A.; Ahim, K.; Ahmed, O.H.; Ali, M.; Omar, L.; Musah, A.A. Mitigating Potassium Leaching from Muriate of Potash in a Tropical Peat Soil Using Clinoptilolite Zeolite, Forest Litter Compost, and Chicken Litter Biochar. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1900. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11101900
Krishnan K, Ngerong AA, Ahim K, Ahmed OH, Ali M, Omar L, Musah AA. Mitigating Potassium Leaching from Muriate of Potash in a Tropical Peat Soil Using Clinoptilolite Zeolite, Forest Litter Compost, and Chicken Litter Biochar. Agronomy. 2021; 11(10):1900. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11101900
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrishnan, Kavinraj, Audrey Awing Ngerong, Karen Ahim, Osumanu Haruna Ahmed, Maru Ali, Latifah Omar, and Adiza Alhassan Musah. 2021. "Mitigating Potassium Leaching from Muriate of Potash in a Tropical Peat Soil Using Clinoptilolite Zeolite, Forest Litter Compost, and Chicken Litter Biochar" Agronomy 11, no. 10: 1900. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11101900
APA StyleKrishnan, K., Ngerong, A. A., Ahim, K., Ahmed, O. H., Ali, M., Omar, L., & Musah, A. A. (2021). Mitigating Potassium Leaching from Muriate of Potash in a Tropical Peat Soil Using Clinoptilolite Zeolite, Forest Litter Compost, and Chicken Litter Biochar. Agronomy, 11(10), 1900. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11101900






