Abstract
Soil salinization typically inhibits the ability of decomposer organisms to utilize soil organic matter, and an increase in soil clay content can mediate the negative effect of salinity on carbon (C) mineralization. However, the interactive effects of soil salt concentrations and properties on C mineralization remain uncertain. In this study, a laboratory experiment was performed to investigate the interactive effects of soil salt content (0.1%, 0.3%, 0.6% and 1.0%) and texture (sandy loam, sandy clay loam and silty clay soil with 6.0%, 23.9% and 40.6% clay content, respectively) on C mineralization and microbial community composition after cotton straw addition. With increasing soil salinity, carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from the three soils decreased, but the effect of soil salinity on the decomposition of soil organic carbon varied with soil texture. Cumulative CO2 emissions in the coarse-textured (sandy loam and sandy clay loam) soils were more affected by salinity than those in the fine-textured (silty clay) soil. This difference was probably due to the differing responses of labile and resistant organic compounds to salinity across different soil texture. Increased salinity decreased the decomposition of the stable C pool in the coarse-textured soil, by reducing the proportion of fungi to bacteria, whereas it decreased the mineralization of the active C pool in the fine-textured soil through decreasing the Gram-positive bacterial population. Overall, our results suggest that soil texture controlled the negative effect of salinity on C mineralization through regulating the soil microbial community composition.
1. Introduction
In the desert-oasis ecotone of China, the transformation of native desert soils to farmlands generally benefits the formation of soil aggregation by increasing soil clay or organic matter contents [1]. Soil texture determines the accessibility of soil organic matter (SOM) to decomposer organisms, and a high clay content generally inhibits the ability of soil microorganisms to decompose soil organic matter [2]. In a meta-analysis, Xu et al. [2] found a negative relationship between clay content and the decomposition of the active (fast-turnover) carbon (C) pool, whereas soil texture did not affect the decomposition of the stable (slow-turnover) C pool. Furthermore, in this region, most of the salt in the irrigation water stores in the field due to high evaporation rather than leaching to the groundwater [3,4]. This accumulation not only threatens agricultural productivity but also affects the turnover of soil organic matter.
The effect of salinity on soil organic carbon (SOC) mineralization has been widely investigated in laboratory or field experiments. Rath and Rousk [5] reviewed previous studies and concluded that salinization inhibited the ability of soil microorganisms to utilize soil organic matter by reducing osmotic potential in the soil solution. However, few studies have focused on the interactive effects of soil salinity and texture on the process of SOC mineralization [6,7]. In an incubation experiment, Setia et al. [6] found that the decomposition of the labile C pool was more affected by salinity than that of the stable C pool across different soil textures, but that the rate of active C mineralization was more affected by salinity in a loamy sand soil than in a clay soil. This inconsistency was probably attributed to the different responses of the soil microbial community to salinity among different soil textures, which most likely controlled the decomposition process of various C pools.
In general, bacteria and fungi primarily use labile and resistant organic compounds, respectively [8,9]. Compared with fungi, bacteria are more affected by high salinity at low water potential [5,10]. A previous study found that at a given soil water content, the osmotic potential of a soil solution was higher in a fine-textured soil than in a coarse-textured soil, which reduced the influence of salinity on the active C pool in the fine-textured soil [6]. Therefore, we speculate that an increased clay content can mediate the negative effects of salt stress on bacteria, and thereby inhibit the process of C mineralization. However, few studies have investigated the associations between the mineralization of labile and resistant C pools and soil microbial community structure across different soil texture and salinity levels.
In this study, a laboratory experiment was performed to estimate the effects of soil salinity and texture on the decomposition of active and stable C pools following straw addition, using a two-compartment kinetic model. Phospholipid fatty acid (PLFA) analysis was used to identify associations between soil microorganisms and the decomposition rates of various C pools. In this study, the objective was to assess the impact of soil salinity on C mineralization across different soil textures, and we hypothesize that a high clay content can mediate the negative effect of soil salinization on bacteria, thereby reducing the sensitivity of the decomposition of the active C pool to salinity in soils with a high clay content.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
In the Manas oasis farmland of Northwest China, three non-salinized (salt content <0.1%) soils in the 0–20 cm horizon were sampled, sieved (<2 mm), and then air-dried in a dark environment. A conductivity meter (DDS-307, Shanghai, China) and a pH meter (PHS-2C, Shanghai, China) were used to detect the electrical conductivity and pH of soil (soil:water ratio of 1:5), respectively. The ash method and hydrometer method were conducted to analyze the soil salt content and particle sizes, respectively. Information (including sampling position and soil properties) on the collected soils is presented in Table 1. Cotton (Gossypium herbaceum L.) straw was sampled, oven-dried (65 °C) for >2 days and then ground (<0.3 mm). The preprocessed soil and cotton residue (with C and nitrogen (N) contents of 396.5 g kg−1 and 10.8 g kg−1, respectively) were then stored at room temperature.

Table 1.
Information on the sampled soils in this study. SL, SCL and SC indicate sandy loam soil, sandy clay loam soil and silty clay soil, respectively. CEC, SOC and TN represent cation exchange capacity, soil organic carbon content and total nitrogen content, respectively.
A total of 12 treatments with two factors (soil texture and salinity) and three replicates were established in a microcosm experiment with three soil textures (sandy clay loam (SCL), sandy loam (SL) and silty clay (SC)) and four salt levels (0.1%, 0.3%, 0.6% and 1.0%, produced by adding sodium chloride (NaCl) to achieve 1, 3, 6 and 10 g kg−1). The four salinity levels of 0.1%, 0.3%, 0.6% and 1.0% represent the weight ratio of NaCl to air-dried soil. In this study, in order to achieve 0.1%, 0.3% and 0.6% and 1.0% salinity, the salt contents were 75, 225, 450 and 750 mg NaCl per 75 g air-dried soil, respectively. The four salt levels represented the thresholds of non (0.1%), slightly (0.3%), moderately (0.6%) and heavy (1.0%) saline soils in the oasis field of Northwest China [11], and Na+ is the dominant cation and Cl¯ is the secondary anion in the Manas oasis farmland [12]. Cotton residue at a typical rate (5.4 g per 1 kg dry soil, equivalent to 7500 kg per hectare in this region) was added to each treatment.
2.2. Carbon Mineralization Measurements
The microcosm experiment was designed to observe C mineralization throughout the entire experiment. Briefly, 75 g air-dried soil was added to a transparent jar (550 mL). A reshaped plastic cap with a 10 mm diameter columniform silicone stopper was installed in each jar, and a 0.9 mm inner diameter puncture needle was injected into the midpoint of the silicone cap and used to gather gas in the jar. Under dark conditions, we added distilled water to the soils to achieve 60% water-holding capacity, which then were preincubated at 25 °C for 14 days, to allow soil microbes to reactivate under the different salt conditions [13].
During the experimental period (56 days), the jars were sealed and then incubated for approximately 1 day to accumulate gas. Before sealing, the headspace of the jar was flushed by air fan for 30 s, and then opened for 15 min to equilibrate with the atmospheric CO2 contents of the surrounding room. Three jars without soil were used to represent the initial CO2 concentrations. On days 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 12, 17, 23, 30, 38, 47 and 56, a syringe was connected to the spinal needle and used to collect the gas. We pumped the syringe three times to mix the air in the headspace before sampling. A hydrogen flame ionization detector of a gas chromatograph (Agilent 7890A, Agilent, Palo Alto, CA, USA) was used to determine the CO2 concentrations of the sampled gas. The linear interpolation method was used to calculate the total CO2 emissions over the entire experimental period.
2.3. Measurement of Dissolved Organic Carbon (DOC) Contents
On day 56, 3 g of incubated soils were destructively sampled, extracted (1:5 for soil and 0.5 mol L−1 K2SO4 solution), shaken for 60 min, and leached through a quantitative filter. The DOC of the leached solution was detected by a TOC analyzer (Vario TOC select, Elementar Company, Hanau, Germany).
2.4. Analysis of Phospholipid Fatty Acids (PLFAs) and the Microbial Metabolic Quotient (qCO2)
Subsamples of soil were freeze-dried (−80 °C) for more than two days for the soil PLFA analysis. Soil PLFAs were extracted and analyzed by the following process [14,15,16]. First, 2.0 g of freeze-dried soil was extracted with a buffer solution (4 mL of methanol, 2 mL of chloroform and 1.6 mL of 0.15 M citrate); second, the extracts were methylated to their fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs), dried under nitrogen gas and then the phospholipid concentrations were quantified by an internal standard methyl nonadecanoate fatty acid [17,18]. The extracts were then analyzed by a flame ionization detector of a gas chromatograph (Agilent 7890B, Agilent, Palo Alto, CA, USA) equipped with a microbial identification system (MIDI Inc., Newark, DE, USA). Lastly, nineteen main PLFAs, accounting for approximately 90% of the total PLFA biomass, were considered in the following analysis [15,19]. The nomenclature of the PLFAs in this study is presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
The nomenclature of the phospholipid fatty acids (PLFAs) in this study.
2.5. Data Analysis
A two-compartment kinetic model was used to estimate the decay of active and stable C pools after straw addition [20,21]:
where Rt, Ra and Rs are the total decomposition rate (mg C kg−1 day−1) at day t, the initial decomposition rate (mg C kg−1 day−1) of the active C pool, and the decomposition rate (mg C kg−1 day−1) of stable C pool, respectively, and k is the decay rate constant (day−1) of the active C pool. Meanwhile, Akaike’s information criterion (AIC) value was used to evaluate the performance of this model in describing the daily microbial respiration rate after straw addition [22]. The sizes (mg C) of the active (Ca) and stable (Cs) C pools were evaluated using the equations Ca = Ra/k and Cs = Rs · t, respectively. The sensitivity index (SI, with a higher absolute SI value indicating a greater influence of salt on soil CO2 emissions) was used to quantify the sensitivity of cumulative CO2 emissions to salinity [23]:
where Smax, Smin and Savg are the maximum, minimum and average values, respectively, of salinity; and Cmax, Cmin and Cavg are the cumulative CO2 emissions corresponding to Smax, Smin and Savg, respectively. Positive or negative values indicate a positive or negative effect, respectively, of salinity on C mineralization.
Regression was performed with SPSS 16.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) to fit the relationships among soil salinity and CO2 emissions (including total CO2 emissions and CO2 emissions from active and stable C pools), DOC, PLFA indexes (including total PLFA biomass, the biomasses of PLFA-distinguishable bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-positive bacteria, and fungi and the ratio of fungi to bacteria) and qCO2. qCO2 was computed as the ratio of total CO2 emissions to the total biomass of PLFAs [24]. Redundancy analysis (RDA) was applied with CANOCO 4.5 (Microcomputer Power, Ithaca, New York, NY, USA) to analyze the correlations between environmental factors (DOC, clay content and salinity) and PLFA-distinguishable bacteria, Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria and fungi. The main and interaction effects of soil texture and salt on the cumulative CO2 emissions and qCO2 were analyzed by multi-factor ANOVA.
3. Results
3.1. Soil CO2 Emissions
Across different soil salinity conditions, cotton straw addition largely increased daily microbial respiration rate, and the peaks of microbial respiration for the SL, SCL and SC soils were 48.0–55.7, 56.2–63.1 and 32.0–38.5 mg C kg−1 day−1, respectively (Figure 1). After two weeks, these emissions had decreased to basal values (Figure 1). Over the entire period, the cumulative CO2 emissions from SL, SCL and SC soils were 558.2–856.0, 437.6–653.6 and 420.5–563.3 mg C kg−1, respectively, and the emissions from the three soils decreased with increasing salinity (Figure 2a). Overall, the cumulative CO2 emissions were significantly (p < 0.05) affected by soil texture, salt and their interactions (Table 3). The sensitivity analysis showed that the total CO2 emissions from the SL and SCL soils were more affected by salinity than those from the SC soil were. In addition, no significant difference in the sensitivity index of these emissions to salinity was found between the SL and SCL soils (Table 4).
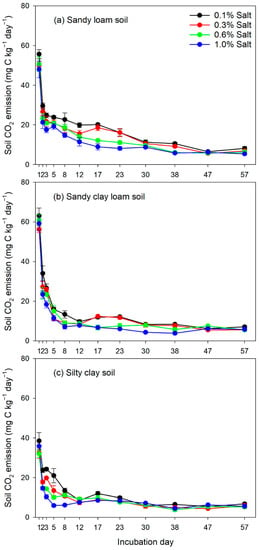
Figure 1.
Soil CO2 emissions from the sandy loam soil (a), sandy clay loam soil (b) and silty clay soil (c) at different salt levels. Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean (n = 3).
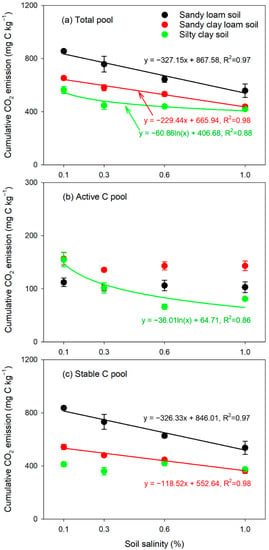
Figure 2.
Relationships between cumulative CO2 emissions from total (a), active (b) and stable (c) carbon pools and salinity in the sandy loam soil, sandy clay loam soil and silty clay soil. Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean (n = 3).

Table 3.
Main and interaction effects of soil texture and salinity on cumulative CO2 emissions and qCO2.

Table 4.
Indexes of sensitivity of cumulative CO2 emissions and microbial metabolic quotient (cumulative CO2 emissions per PLFA) to salinity in the three soils. Different letters indicate statistically significant differences.
The two-compartment kinetic model performed well (R2 > 0.83 and AIC ranged from 37.5 to 73.5) in simulating the temporal variation of C mineralization (Table 5). The simulated sizes of the active C pool (ranging from 66.2 to 156.5 mg C kg−1) in the three soils were lower than those of the stable C pool (ranging from 359.7 to 836.5 mg C kg−1), and the simulated sizes of the labile and stable C pools varied with soil texture (Figure 2b,c). In the SL and SCL soils, the size of the stable C pool decreased linearly with increasing salinity, whereas the size of the labile C pool did not vary with salinity. In contrast, in the SC soil, the size of the labile C pool declined logarithmically with increasing salt content, whereas the size of the stable C pool did not.

Table 5.
The simulated values of initial decomposition rate (Ra) and decay rate constant (k) of the active carbon pool and decomposition rate of stable carbon pool (Rs) based on the two-compartment kinetic model for the three soils. AIC denote Akaike’s information criterion value.
3.2. Soil DOC Contents
In the SCL soil, DOC contents increased logarithmically with increasing salinity (Figure 3), and DOC contents were 77.5, 84.2, 93.7 and 97.8 mg C kg−1 for the 0.1%, 0.3%, 0.6% and 1.0% salinity levels, respectively. However, in the other (SL and SC) soils, there were no significant trends of DOC with increasing salt levels (Figure 3).
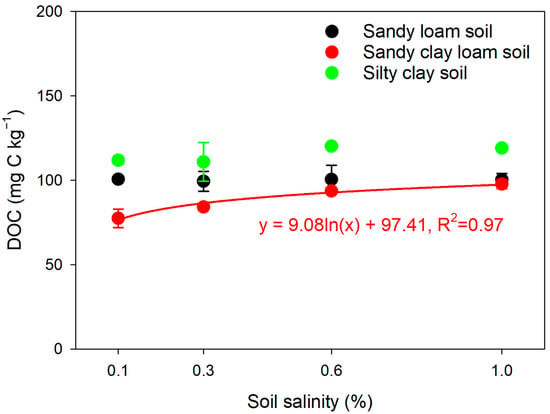
Figure 3.
Relationships between dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and salinity in the sandy loam soil, sandy clay loam soil and silty clay soil. Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean (n = 3).
3.3. Soil Microbial Biomass, Metabolic Quotient and Community Structure
There were no significant trends of soil total PLFA contents or of the biomasses of PLFA-distinguishable bacteria, Gram-positive bacteria or fungi with increasing salinity in the SL and SCL soils (Figure 4a–c,e). However, the biomass of Gram-negative bacteria increased linearly with increasing salinity in these two soils (Figure 4d). In the SC soil, total PLFA contents and the biomasses of PLFA-distinguishable bacteria and Gram-positive bacteria decreased logarithmically with increasing salinity (Figure 4a–c). The effect of salinity on the fungi-to-bacteria ratio varied with soil texture. The fungi-to-bacteria ratio decreased linearly with increasing soil salinity in the SL and SCL soils, whereas no significant relationship between this ratio and salt content was observed in the SC soil (Figure 5a). The microbial metabolic quotient (expressed as cumulative CO2 emissions per PLFA) decreased with increasing salinity (Figure 5b), and the sensitivity analysis showed that the microbial metabolic quotients in the SL and SCL soils were more affected by salinity than those in the SC soil were (Table 4).
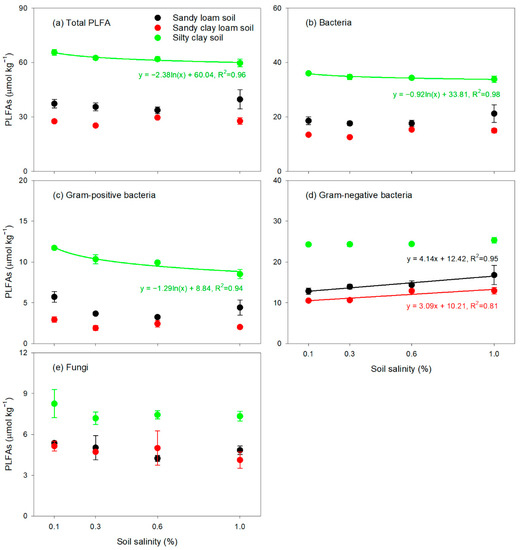
Figure 4.
Relationships of total PLFAs (a), PLFA-distinguishable bacteria (b), Gram-positive bacteria (c), Gram-negative bacteria (d) and fungi (e) with salinity in the sandy loam soil, sandy clay loam soil and silty clay soil. Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean (n = 3).
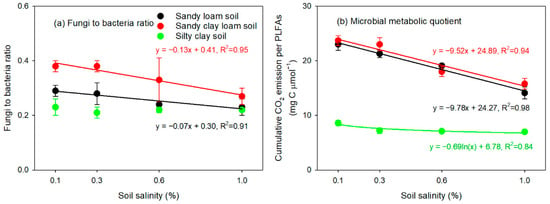
Figure 5.
Relationships of the PLFA-distinguishable fungi-to-bacteria ratio (a) and microbial metabolic quotient (b) with salinity in the sandy loam soil, sandy clay loam soil and silty clay soil. Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean (n = 3).
The RDA results showed that soil texture (clay content), salt and treatment-induced change in DOC content together explained 64.2% of the variation in the PLFA-distinguishable soil microbial community composition (Figure 6). The relationships between both DOC content and clay content and soil microbial community structure were closely related to the first redundancy analysis axis. DOC content and clay content were positively correlated with the relative abundances of bacteria and Gram-positive bacteria but negatively associated with fungi. Salinity was related to the soil microbial community composition on the second redundancy analysis axis, and this factor was positively correlated with the relative abundance of Gram-negative bacteria.
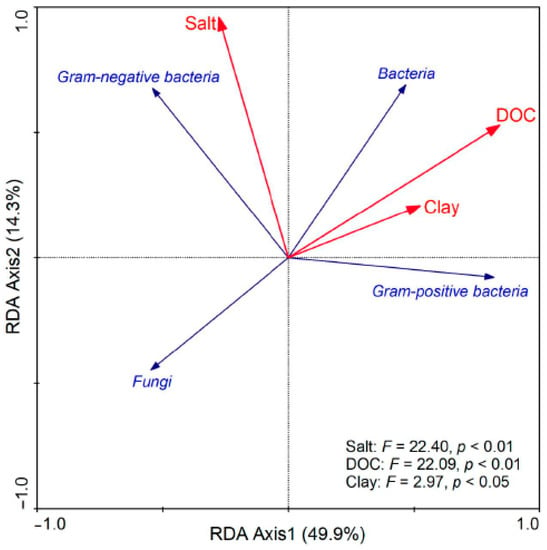
Figure 6.
Ordination diagram from the redundancy analysis (RDA) of the PLFA-distinguishable bacteria, Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria and fungi. Explanatory environmental variables were dissolved organic carbon (DOC), salt and clay content.
4. Discussion
In the present study, CO2 emissions decreased with increasing soil salt concentrations in the three soils. This result is consistent with previous studies [25,26,27,28]. In general, soil salinization inhibits microbial activity and then reduces the ability of soil microorganisms (e.g., bacteria and fungi) to decompose soil organic matter [5,10,29,30]. In this study, the microbial metabolic quotient (expressed as cumulative CO2 emissions per PLFA) decreased with increasing salinity, whereas total microbial biomass (expressed as total PLFAs) slightly decreased or did not change with increasing salt content. This latter result was probably because the soil microbes could survive in the salt stress condition, but their activities were extremely inhibited under this environment, [29,31,32], which inhibited decomposition of SOM. In addition, we observed a significant increase in DOC content with increasing salinity only in the SCL soil. This result disagreed with that of Yang et al. [33], who found a positive correlation between soil microbial respiration and DOC concentrations in estuary wetlands. This difference indicated that the ability of salt-stressed microorganisms to utilize labile available organic matter depends on ecosystems [34] or the incubation period [35,36]. The sensitivity tests indicated that the effect of soil salinity on the decomposition of SOM varied with soil texture. Chowdhury et al. [29] also found that microbial respiration in sandy clay loam and clay soils (with clay percentages of 23% and 42%, respectively) was less affected by increasing salinity than it was in a loamy sand soil (with a clay percentage of 6%). Our result is partly consistent with that presented by Chowdhury et al. [29], and we found that C mineralization was more affected by soil salinization with low clay content (6–24%) than in the high clay content (41%). The results of the two-compartment model revealed that this greater sensitivity in the lower-clay soils was mainly attributed to the interaction of soil salinity and texture on the active and stable C pools. Increasing salinity mainly decreased the size of the stable C pool in the SL and SCL soils, and the size of the labile C pool in the SC soil. These differences were mainly because soil clay content controlled the impact of soil salinization on microbial community composition. In addition, due to the release of CO2 originating from both SOC and crop residue, C isotope labeling method should be conducted to precisely estimate the effect of salinity on the decomposition rate of organic residues in future.
In general, after crop residue amendment, the labile organic matter is mainly decomposed by bacteria, and the stable organic compounds (such as cellulose and lignin) are mostly utilized by fungi [8]; furthermore, fungi are more resistant to high salt stress conditions than soil bacteria are [5]. In this study, the soil microbial communities became less fungi-dominated with increasing salinity in the coarse-textured (SL and SCL) soils, which was the major reason for the decrease in the decomposition of the stable C pool (Figure 7). This reduction in fungal abundance in the coarse-textured soils occurred because the salt stress of the soil solution is higher in fine-textured soil than in coarse-textured soil [6]. The results of the RDA confirmed the negative correlation between fungal biomass and the clay content. However, this negative correlation is inconsistent with previous studies reporting that with increasing soil salinity, the fungi-to-bacteria ratio slightly increased in a soil amended with maize straw [37], or fungal abundance significantly increased in a soil with pea residues over a certain range of soil salinity [38]. These differences among studies indicate that the effect of salinity on C mineralization mediated through fungi probably varied with soil- or crop-residue specifically. In the fine-textured (SC) soil, the decrease in the size of active C pool was mainly attributed to the decrease in biomass of Gram-positive bacteria with increasing salinity (Figure 7). Similarly, Setia et al. [6] observed that the decomposition of the labile C pool was more affected by salinity than that of the stable C pool across different soil textures following wheat residue amendment. Therefore, our results suggest that soil texture alters the negative effect of salinity on C mineralization by regulating the composition of the soil microbial community.
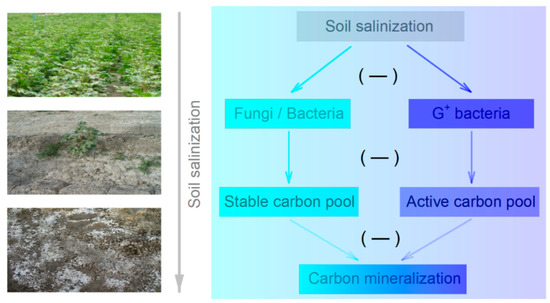
Figure 7.
A conceptual model of the impact of soil salinity on microbial community composition and carbon mineralization after straw addition in coarse-textured soil (cyan) and fine-textured soil (blue).
5. Conclusions
Our results suggested that the negative effect of soil salinity on the decomposition of soil organic carbon varied with soil texture, and the negative effect of salinity on C mineralization was higher in coarse-textured soils than in fine-textured soil. In the coarse-textured soil, increased salinity inhibited the ability of fungi to utilize the stable C pool. In the fine-textured soil, increased salt decreased the stable C mineralization rate by inhibiting the Gram-positive bacterial population. Our results suggest that changes in soil texture alter the effect of soil salinization on the microbial community, thereby affecting the decomposition of various organic C pools. Compared with the labile C pool, the resistant C pool has greater potential to impact soil C storage over a long-term period; therefore, our results suggest that soil texture changed the soil carbon sequestration potential in the salt-affected soils. However, this suggestion should be confirmed by C isotope labeling to distinguish the interaction of soil salinity and property on the decomposition of various C pools.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.S., Y.Y., C.G. and H.Y.; methodology, R.S., Y.Y., C.G. and H.Y.; formal analysis, R.S., Y.Y., C.G. and H.Y.; data curation, R.S., Y.Y., C.G. and H.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, R.S.; writing—review and editing, R.S., Y.Y., C.G. and H.Y.; visualization, R.S. and Y.Y.; supervision, C.G. and H.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation (41807040, 41525002, 41761134085).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Fu, L. Soil macropore characteristics following conversion of native desert soils to irrigated croplands in a desert-oasis ecotone, Northwest China. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 168, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Shi, Z.; Li, D.; Rey, A.; Ruan, H.; Craine, J.M.; Liang, J.; Zhou, J.; Luo, Y. Soil properties control decomposition of soil organic carbon: Results from data-assimilation analysis. Geoderma 2016, 262, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Hou, Z.; Wu, L.; Liang, Y.; Wei, C. Evaluating salinity distribution in soil irrigated with saline water in arid regions of northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 2001–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Othmanli, H.; Schiller, T.; Zhao, C.; Sheng, Y.; Zia, S.; Mueller, J.; Stahr, K. Water use efficiency in saline soils under cotton cultivation in the Tarim River Basin. Water 2015, 7, 3103–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, K.M.; Rousk, J. Salt effects on the soil microbial decomposer community and their role in organic carbon cycling: A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 81, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setia, R.; Marschner, P.; Baldock, J.; Chittleborough, D.; Smith, P.; Smith, J. Salinity effects on carbon mineralization in soils of varying texture. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1908–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setia, R.; Marschner, P.; Baldock, J.; Chittleborough, D.; Verma, V. Relationships between carbon dioxide emission and soil properties in salt-affected landscapes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, W.; Folman, L.B.; Summerbell, R.C.; Boddy, L. Living in a fungal world: Impact of fungi on soil bacterial niche development. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 795–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.P.; Shen, W.J.; Li, Y.E.; Hui, D.F. Interactive effects of temperature and moisture on composition of the soil microbial community. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 68, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, K.M.; Maheshwari, A.; Rousk, J. The impact of salinity on the microbial response to drying and rewetting in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 108, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zheng, N.; Jia, H.; Yao, H. Interactive effects of soil texture and salinity on nitrous oxide emissions following crop residue amendment. Geoderma 2019, 337, 1146–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilili, A.; Ayiguli, M.; Tang, Y. Soil salinization in the manas river basin in spring. AZRC 2013, 30, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, B.M.; Chambers, L.; White, J.R. Effect of fluctuating salinity on potential denitrification in coastal wetland soil and sediments. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2016, 80, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bligh, E.; Dyer, W. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 378, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frostegard, A.; Tunlid, A.; Baath, E. Phospholipid fatty acid composition, biomass, and activity of microbial communities from two soil types experimentally exposed to different heavy metals. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 3605–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Chapman, S.J.; Thornton, B.; Paterson, E. 13C PLFAs: A key to open the soil microbial black box? Plant. Soil 2014, 392, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chapman, S.J.; Yao, H. Incorporation of 13C-labelled rice rhizodeposition into soil microbial communities under different fertilizer applications. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 101, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, N.; Wang, J.; Yao, H.; Qiu, Q.; Chapman, S.J. High turnover rate of free phospholipids in soil confirms the classic hypothesis of PLFA methodology. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frostegard, A.; Tunlid, A.; Baath, E. Use and misuse of PLFA measurements in soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1621–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonde, T.A.; Rosswall, T. Seasonal-variation of potentially mineralizable nitrogen in 4 cropping systems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1987, 51, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, Y.; Pendall, E.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Morgan, J.A.; Newcomb, J.M. Response of soil organic matter pools to elevated CO2 and warming in a semi-arid grassland. Plant. Soil 2011, 347, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Multimodel inference: Understanding AIC and BIC in model selection. Sociol. Methods Res. 2004, 33, 261–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, M.A.; Deer-Ascough, L.M.; Laflen, J. Sensitivity analysis of the WEEP hillslope profile erosion model. Trans. ASABE 1990, 33, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willers, C.; van Rensburg, P.J.J.; Claassens, S. Phospholipid fatty acid profiling of microbial communities–a review of interpretations and recent applications. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 1207–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasbullah, H.; Marschner, P. Residue properties influence the impact of salinity on soil respiration. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2015, 51, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, M.; Zhao, W.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, D.; Zhan, C.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lv, Z.; et al. Different effects of NaCl and Na2SO4 on the carbon mineralization of an estuarine wetland soil. Geoderma 2019, 344, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setia, R.; Marschner, P.; Baldock, J.; Chittleborough, D. Is CO2 evolution in saline soils affected by an osmotic effect and calcium carbonate? Biol. Fertil. Soils 2010, 46, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Song, L.; Wang, B.; Shao, H.; Zhang, L.; Qin, X. Co-effects of salinity and moisture on CO2 and N2O emissions of laboratory-incubated salt-affected soils from different vegetation types. Geoderma 2018, 332, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, N.; Marschner, P.; Burns, R.G. Soil microbial activity and community composition: Impact of changes in matric and osmotic potential. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K. Microbial and enzyme activities of saline and sodic soils. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 706–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.T.; Joergensen, R.G.; Knoblauch, C.; Lucassen, R.; Singh, Y.; Watson, C.; Wichern, F. Rice straw addition does not substantially alter microbial properties under hypersaline soil conditions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2016, 52, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Gao, M.; Zhang, Y. Microbial biomass and activity in salt affected soils under arid conditions. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2007, 35, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhan, C.; Li, Y.; Zhou, D.; Yu, Y.; Yu, J. Effect of salinity on soil respiration in relation to dissolved organic carbon and microbial characteristics of a wetland in the Liaohe River estuary, Northeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavi, M.S.; Marschner, P.; Chittleborough, D.J.; Cox, J.W.; Sanderman, J. Salinity and sodicity affect soil respiration and dissolved organic matter dynamics differentially in soils varying in texture. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 45, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, F.; Bhupinderpal, S.; Cui, Z.; Rengel, Z. Decomposition of maize straw in saline soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2006, 42, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Li, J.; Han, G.; Wu, H.; Song, W.; Zhang, X. Effect of salinity on the decomposition of soil organic carbon in a tidal wetland. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichern, J.; Wichern, F.; Joergensen, R.G. Impact of salinity on soil microbial communities and the decomposition of maize in acidic soils. Geoderma 2006, 137, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmajdoub, B.; Marschner, P. Responses of soil microbial activity and biomass to salinity after repeated additions of plant residues. Pedosphere 2015, 25, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).