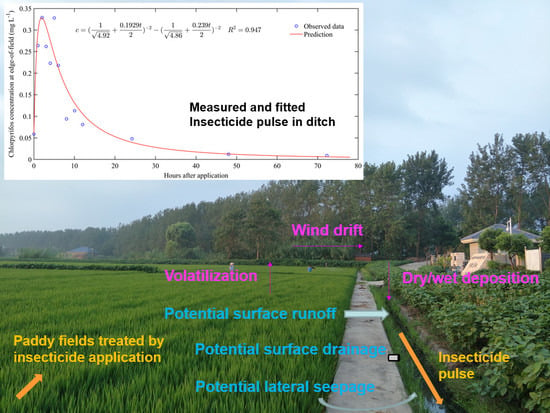
New Approach to the Assessment of Insecticide Losses from Paddy Fields Based on Frequent Sampling Post Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- capture the dynamic features of drainage and insecticide pulses in the field drainage ditch of paddy fields shortly after application,
- (2)
- identify the key factors that affect insecticide behavior and establish a kinetic model that can better describe the edge-of-field insecticide concentration variations, and
- (3)
- analyze the influence of sampling strategies on monitoring results and propose drainage control strategies after insecticide application in rice growing areas.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Insecticide Application and Sampling Procedure
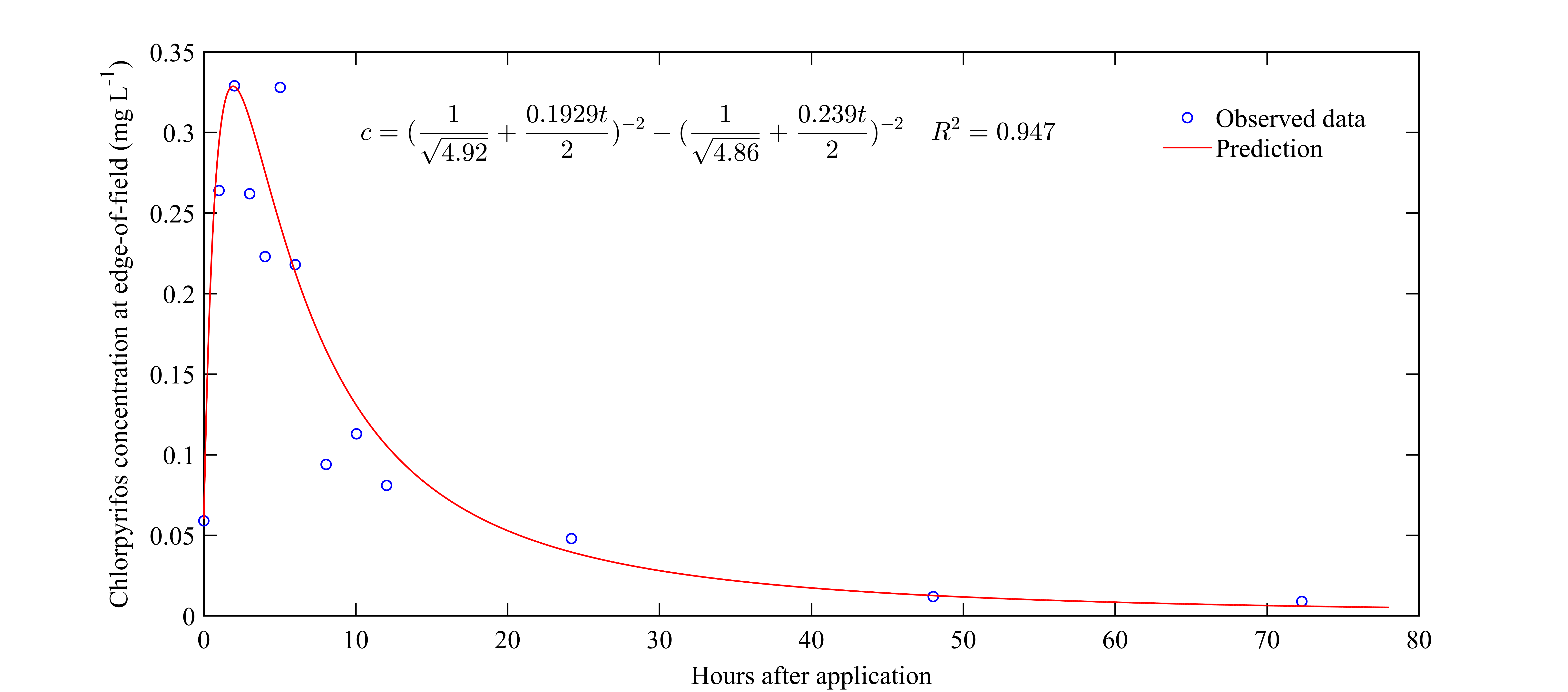
2.3. Estimation of Insecticide Load and Concentration Kinetics
3. Results
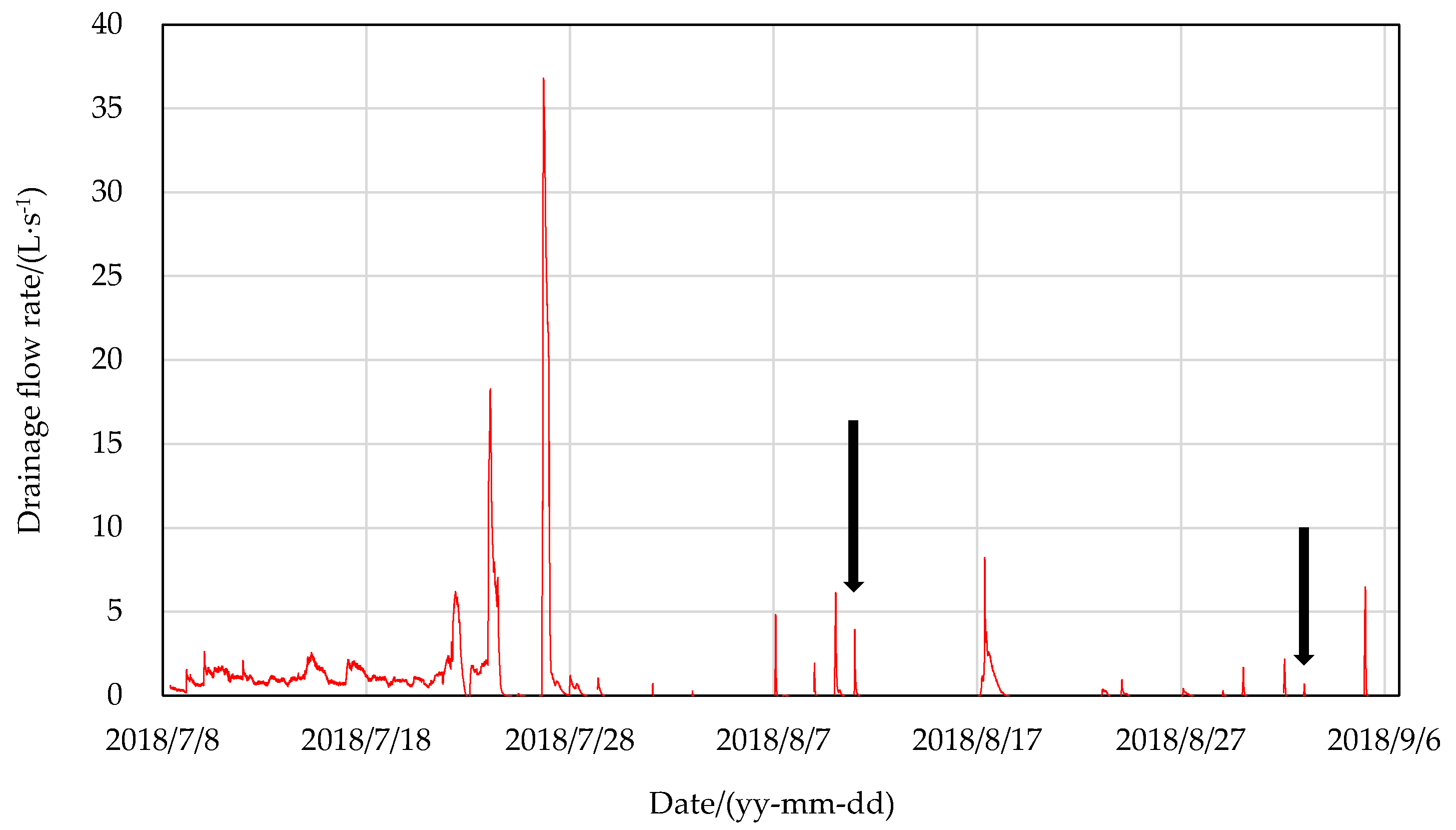
3.1. Drainage Process at the Field Edge during the Rice Growing Season
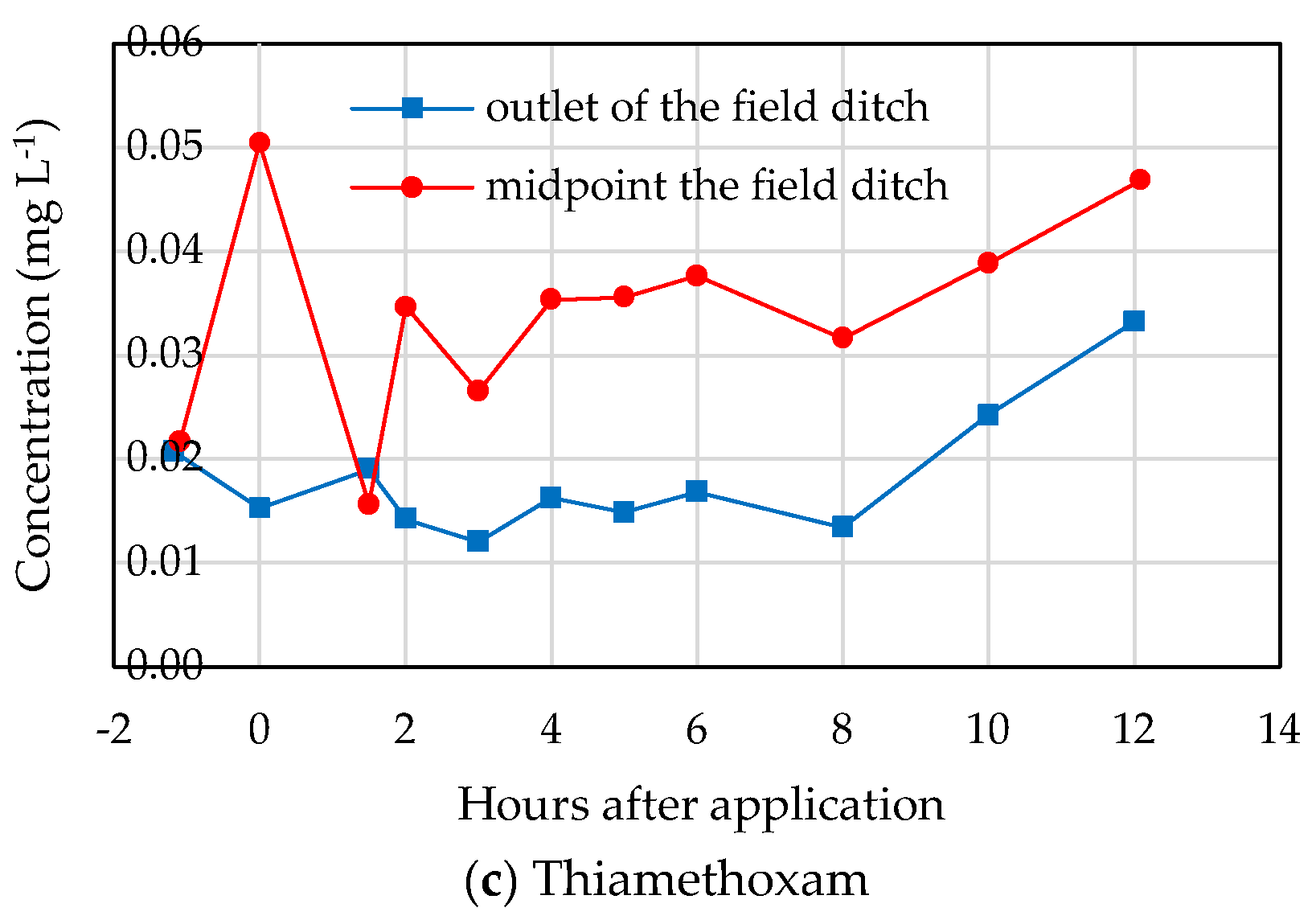
3.2. Insecticide Concentration Variations in Different Waters
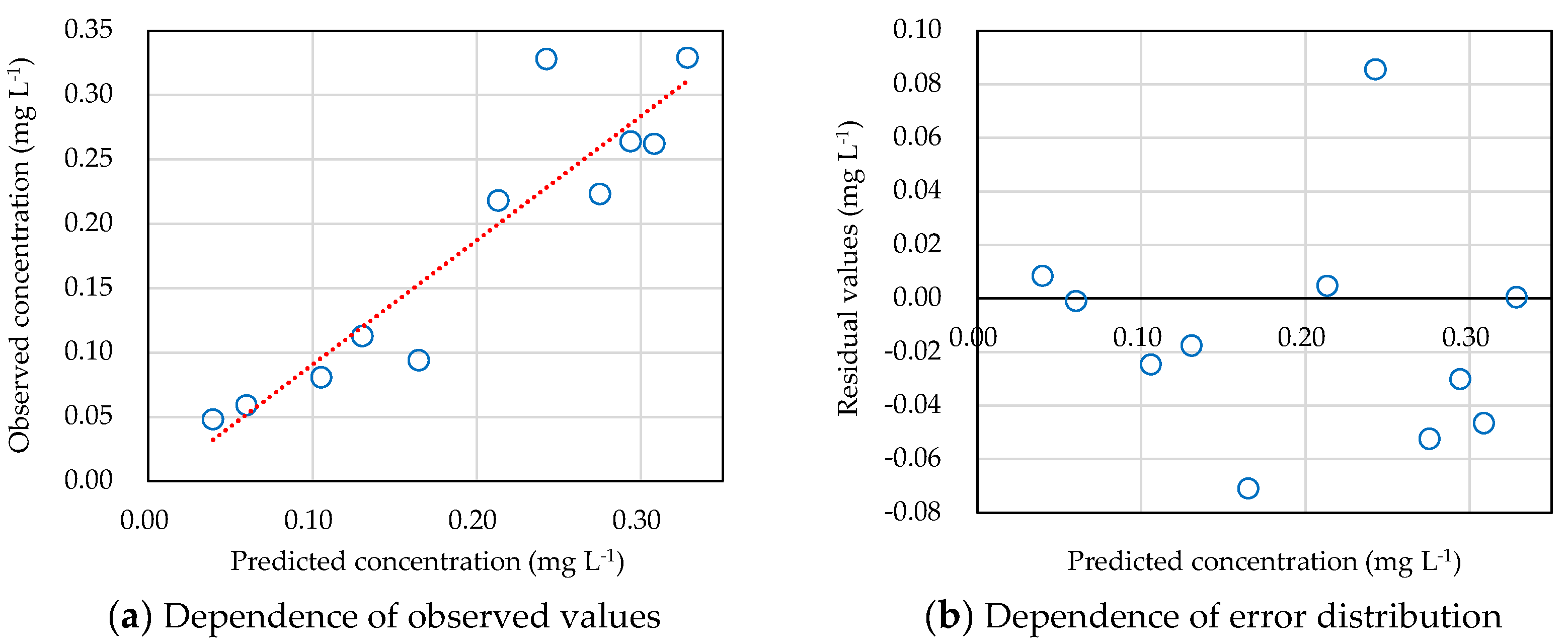
3.3. Kinetic Model to Predict Insecticide Concentration Variations
3.4. Estimated Insecticide Loads
4. Discussion
4.1. Drainage Feature during the Pest-Control Irrigation Period
4.2. Factors Affecting the Field-Scale Insecticide Behavior
4.2.1. Effect of Physico-Chemical Properties of Insecticides
4.2.2. Effect of the Primary and Secondary Drift
4.2.3. Deposition and Volatilization at the Air–Water Interface
4.3. Insights from High-Frequency Monitoring of Insecticides
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Astaykina, A.; Streletskii, R.; Maslov, M.; Kazantseva, S.; Karavanova, E.; Gorbatov, V. Novel pesticide risk indicators for aquatic organisms and earthworms. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosamu, I.; Kaonga, C.; Utembe, W. A critical review of the status of pesticide exposure management in Malawi. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Chen, L.; Zhai, L.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, K.; Jiao, C.; Shen, Z. National assessment of spatiotemporal loss in agricultural pesticides and related potential exposure risks to water quality in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 677, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, M.A.Z.; Banik, S.; Uddin, B.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Karim, N.; Gan, S.H. Organophosphorus and carbamate pesticide residues detected in water samples collected from paddy and vegetable fields of the Savar and Dhamrai Upazilas in Bangladesh. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 3318–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furihata, S.; Kasai, A.; Hidaka, K.; Ikegami, M.; Ohnishi, H.; Goka, K. Ecological risks of insecticide contamination in water and sediment around off-farm irrigated rice paddy fields. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 251, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehle, S.; Knäbel, A.; Schulz, R. Probabilistic risk assessment of insecticide concentrations in agricultural surface waters: A critical appraisal. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 6295–6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashauer, R.; Brown, C.D. Highly time-variable exposure to chemicals—Toward an assessment strategy. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2013, 9, e27–e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, J.J.; Wiberg-Larsen, P.; Kristensen, E.A.; Cedergreen, N.; Friberg, N. Pyrethroid effects on freshwater invertebrates: A meta-analysis of pulse exposures. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 182, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wieczorek, M.V.; Bakanov, N.; Bilancia, D.; Szöcs, E.; Stehle, S.; Bundschuh, M.; Schulz, R. Structural and functional effects of a short-term pyrethroid pulse exposure on invertebrates in outdoor stream mesocosms. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothstein, E.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Peverly, J.H.; Geohring, L.D. Atrazine fate on a tile drained field in northern New York: A case study. Agric. Water Manag. 1996, 31, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyusheva, M.; Lamers, M.; La, N.; Nguyen, V.V.; Streck, T. Fate of pesticides in combined paddy rice-fish pond farming systems in Northern Vietnam. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 41, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phong, T.K.; Yoshino, K.; Hiramatsu, K.; Harada, M.; Inoue, T. Pesticide discharge and water management in a paddy catchment in Japan. Paddy Water Environ. 2010, 8, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangchan, W.; Hugenschmidt, C.; Ingwersen, J.; Schwadorf, K.; Thavornyutikarn, P.; Pansombat, K.; Streck, T. Short-term dynamics of pesticide concentrations and loads in a river of an agricultural watershed in the outer tropics. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 158, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Nguyen, M.H.T.; Souphasay, K.; Vu, S.H.; Phong, T.K.; Tournebize, J.; Ishihara, S. Effect of water management practice on pesticide behavior in paddy water. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 88, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, Y.; Yu, X.Y.; Liu, X.J. Dissipation of chlorpyrifos and residue analysis in rice, soil and water under paddy field conditions. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 78, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuyet, D.Q.; Watanabe, H.; Motobayashi, T.; Ok, J. Behavior of nursery-box-applied fipronil and its sulfone metabolite in rice paddy fields. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 179, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, G. Distribution of chlorpyrifos in rice paddy environment and its potential dietary risk. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 35, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsochatzis, E.D.; Tzimou-Tsitouridou, R.; Menkissoglu-Spiroudi, U.; Karpouzas, D.G.; Katsantonis, D. Laboratory and field dissipation of penoxsulam, tricyclazole and profoxydim in rice paddy systems. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.Y.; Yang, Y.; McBride, M.B.; Tao, R.; Dai, Y.N.; Zhang, X.M. Removal of chlorpyrifos in recirculating vertical flow constructed wetlands with five wetland plant species. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefrancq, M.; Jadas-Hécart, A.; La Jeunesse, I.; Landry, D.; Payraudeau, S. High frequency monitoring of pesticides in runoff water to improve understanding of their transport and environmental impacts. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 587, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joseph, A.; Ort, C.; Brien, D.S.O.; Lewis, S.E.; Davis, A.M.; Mueller, J.F. Understanding the uncertainty of estimating herbicide and nutrient mass loads in a flood event with guidance on estimator selection. Water Res. 2018, 132, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fantke, P.; Juraske, R. Variability of pesticide dissipation half-lives in plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 3548–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akan, A.O. Open Channel Hydraulics, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2006; ISBN 9780750668576. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z.; Chen, C.; Luo, W.; Zou, J.; Wu, W.; Xu, M.; Tang, Y. Hydraulic conditions affect pollutant removal efficiency in distributed ditches and ponds in agricultural landscapes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Jia, Z.; Luo, W.; Hong, J.; Yin, X. Efficiency of different monitoring units in representing pollutant removals in distributed ditches and ponds in agricultural landscapes. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 108, 105677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.A.; Tzilivakis, J.; Warner, D.J.; Green, A. An international database for pesticide risk assessments and management. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2016, 22, 1050–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joo, M.; Raymond, M.A.A.; McNeil, V.H.; Huggins, R.; Turner, R.D.R.; Choy, S. Estimates of sediment and nutrient loads in 10 major catchments draining to the Great Barrier Reef during 2006–2009. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 65, 150–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonmatin, J.M.; Giorio, C.; Girolami, V.; Goulson, D.; Kreutzweiser, D.P.; Krupke, C.; Liess, M.; Long, E.; Marzaro, M.; Mitchell, E.A.; et al. Environmental fate and exposure; neonicotinoids and fipronil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 35–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akay Demir, A.E.; Dilek, F.B.; Yetis, U. A new screening index for pesticides leachability to groundwater. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 1193–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Hageman, K.J.; Taylor, M.; Michelsen-Heath, S.; Stewart, I. Fate of the organophosphate insecticide, chlorpyrifos, in leaves, soil, and air following application. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivan, O.; Segal-Rosenheimer, M.; Dubowski, Y. Airborne organophosphate pesticides drift in Mediterranean climate: The importance of secondary drift. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 127, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazanti, L.; Rice, C.; Bialek, K.; Sparling, D.; Stevenson, C.; Johnson, W.E.; Kangas, P.; Rheinstein, J. Aqueous-phase disappearance of atrazine, metolachlor, and chlorpyrifos in laboratory aquaria and outdoor macrocosms. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2003, 44, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giesy, J.P.; Solomon, K.R. Ecological Risk Assessment for Chlorpyrifos in Terrestrial and Aquatic Systems in the United States. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 35–76. [Google Scholar]
- Zivan, O.; Bohbot-Raviv, Y.; Dubowski, Y. Primary and secondary pesticide drift profiles from a peach orchard. Chemosphere 2017, 177, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, T.L.; Coffin, A.W. Assessing pesticide wet deposition risk within a small agricultural watershed in the Southeastern Coastal Plain (USA). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pereira, A.S.; José Cerejeira, M.; Daam, M.A. Ecological risk assessment of imidacloprid applied to experimental rice fields: Accurateness of the RICEWQ model and effects on ecosystem structure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 142, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teló, G.M.; Marchesan, E.; Zanella, R.; De Oliveira, M.L.; Coelho, L.L.; Martins, M.L. Residues of fungicides and insecticides in rice field. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffner, A.; Ingwersen, J.; Hugenschmidt, C.; Streck, T. Pesticide transport pathways from a sloped litchi orchard to an adjacent tropical stream as identified by hydrograph separation. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 41, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Chunmei, X.; Weijian, Z.; Xiufu, Z.; Fengbo, L.; Jianping, C.; Danying, W. Effects of rhizosphere dissolved oxygen content and nitrogen form on root traits and nitrogen accumulation in rice. Rice Sci. 2011, 18, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 boundary of the stud y area,
boundary of the stud y area,  position and angle of view of Figure 1b,
position and angle of view of Figure 1b,  field ditch,
field ditch,  weather station.
weather station.  sampling point at the midpoint of the field ditch,
sampling point at the midpoint of the field ditch,  v-notch weir (sampling point at the outlet of the field ditch),
v-notch weir (sampling point at the outlet of the field ditch),  sampling point of the paddy surface water,
sampling point of the paddy surface water,  90-cm depth well (sampling point of the paddy groundwater).
90-cm depth well (sampling point of the paddy groundwater).
 boundary of the stud y area,
boundary of the stud y area,  position and angle of view of Figure 1b,
position and angle of view of Figure 1b,  field ditch,
field ditch,  weather station.
weather station.  sampling point at the midpoint of the field ditch,
sampling point at the midpoint of the field ditch,  v-notch weir (sampling point at the outlet of the field ditch),
v-notch weir (sampling point at the outlet of the field ditch),  sampling point of the paddy surface water,
sampling point of the paddy surface water,  90-cm depth well (sampling point of the paddy groundwater).
90-cm depth well (sampling point of the paddy groundwater).


| Insecticide | Substance Group | Solubility in Water (20 °C) (mg L−1) | Henry’s Constant (25 °C) (Pa m3 mol−1) | Vapor Pressure (25 °C) (mPa) | Koc/Kfoc 3 (mL g−1) | Kow (log P) (20 °C, pH 7) | Aqueous Hydrolysis DT50 (20 °C, pH 7) (d) | Aqueous Photolysis DT50 (pH 7) (d) | Soil Degradation DT50 (field) (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPF 1 | Organophosphate | 1.05 | 0.478 | 1.43 | 5509/3954 | 4.7 | 53.5 | 29.6 | 27.6 |
| ABM 2 | Micro-organism derived | 0.020 | 2.70 × 10−3 | 0.0037 | NA 4/6631 | 4.4 | Stable | 1.5 | 1 |
| THM 1 | Neonicotinoid | 4100 | 4.70 × 10−10 | 6.60 × 10−6 | 56.2/NA 4 | −0.13 | Stable | 2.7 | 39 |
| Hours after Application (h) | 36 | 48 | 72 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Outlet of the field ditch (mg L−1) | 0.0072 | 0.012 | 0.0090 |
| Midpoint of the field ditch (mg L−1) | 0.020 | 0.011 | 0.0066 |
| Paddy surface water (mg L−1) | 0.011 | 0.0096 | 0.0038 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.; Luo, W.; Zou, J.; Jia, Z. New Approach to the Assessment of Insecticide Losses from Paddy Fields Based on Frequent Sampling Post Application. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101615
Chen C, Luo W, Zou J, Jia Z. New Approach to the Assessment of Insecticide Losses from Paddy Fields Based on Frequent Sampling Post Application. Agronomy. 2020; 10(10):1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101615
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Cheng, Wan Luo, Jiarong Zou, and Zhonghua Jia. 2020. "New Approach to the Assessment of Insecticide Losses from Paddy Fields Based on Frequent Sampling Post Application" Agronomy 10, no. 10: 1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101615
APA StyleChen, C., Luo, W., Zou, J., & Jia, Z. (2020). New Approach to the Assessment of Insecticide Losses from Paddy Fields Based on Frequent Sampling Post Application. Agronomy, 10(10), 1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101615