Integrating Cover Crops as a Source of Carbon for Anaerobic Soil Disinfestation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Location and Set up
2.2. Cover Crops Plant Material and Growing System
2.3. Biometric Assessment
2.4. Plant Tissue Total Carbon, Total Nitrogen, and Mineral Analysis
2.5. Simulation of ASD Treatment
2.6. Soil Monitoring and Laboratory Analysis
2.7. Lettuce Cultivation, Sampling, and Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Cover Crop Fresh and Dry Biomass Production
3.2. Cover Crop and Molasses Total C, N, C:N Ratio, and Total C Applied
3.3. Cover Crop Mineral Concentration and Potential Mineral Return to the Soil
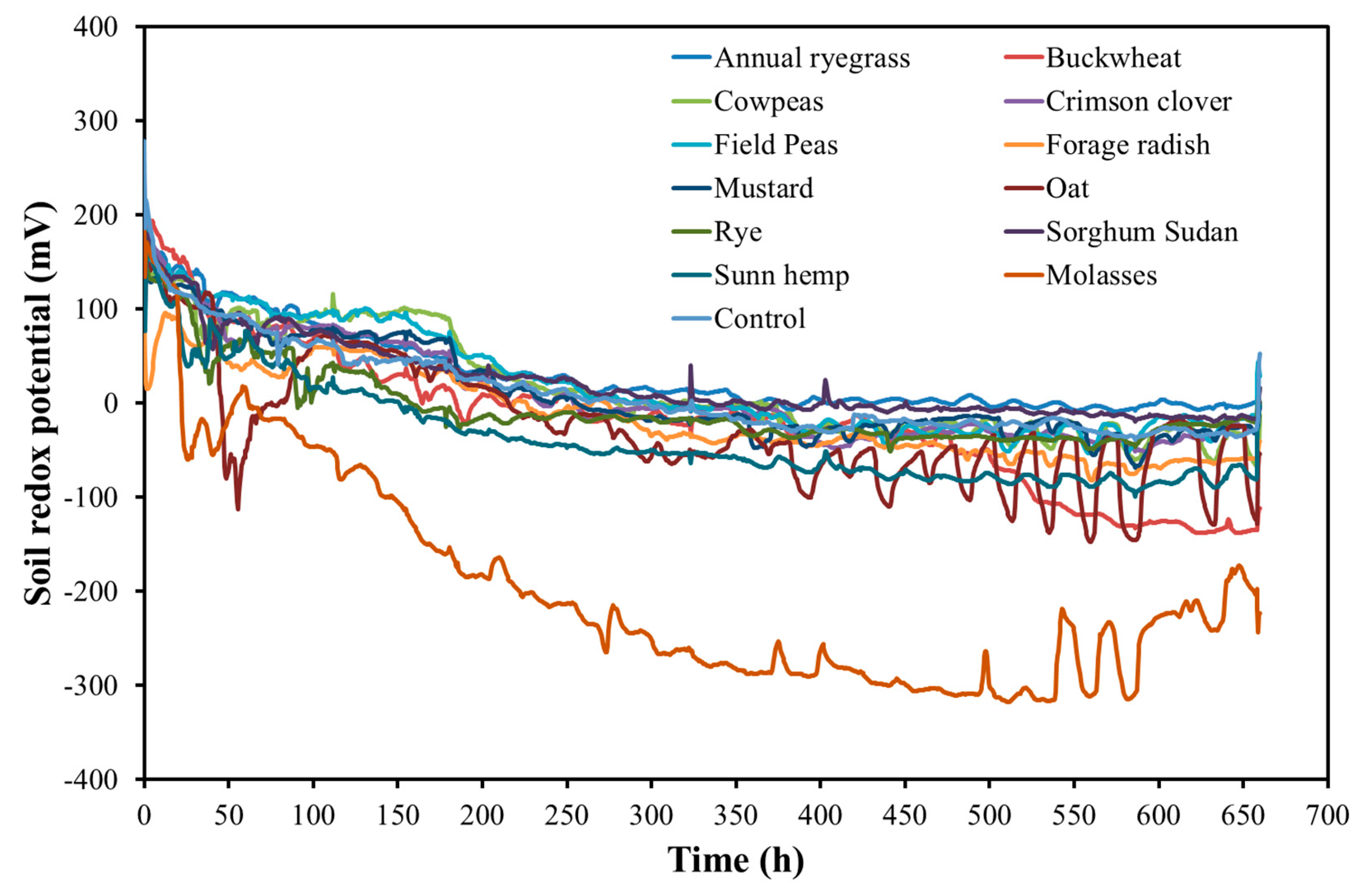
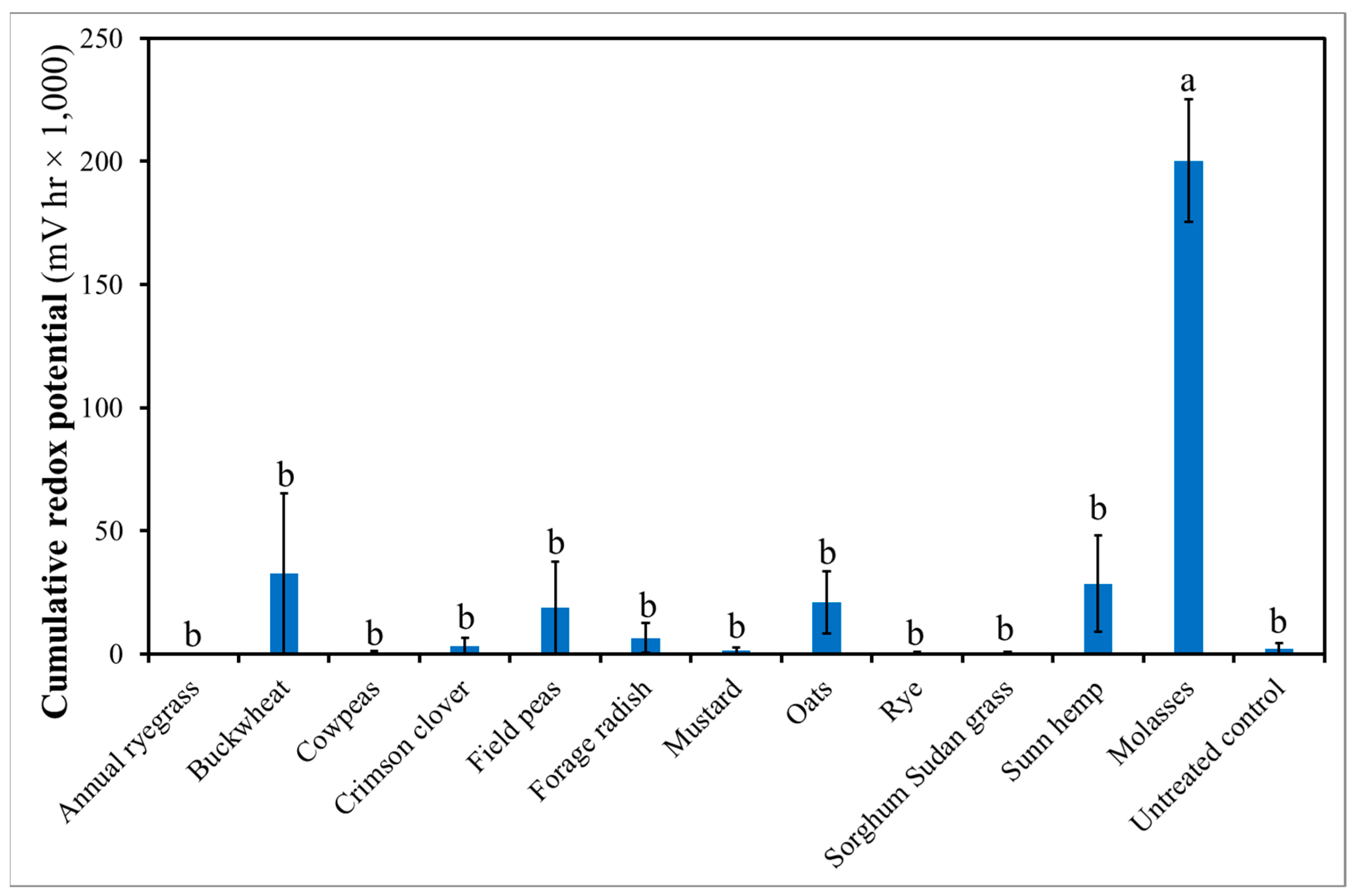
3.4. Treatment Effect on Soil Redox Potential, Temperature, pH and Electrical Conductivity (EC)
3.5. Treatment Effect on Soil Mineral Content
3.6. Treatment Effect on Lettuce Growth and Mineral Profile
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Brien, P.A. Biological control of plant diseases. Australas Plant Pathol. 2017, 46, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosskopf, E.; Di Gioia, F.; Hong, J.C.; Pisani, C.; Kokalis-burelle, N. Organic amendments for pathogen and nematode control. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2020, 58, 277–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosskopf, E.N.; Chellemi, D.O.; Kokalis-Burelle, N.; Church, G.T. Alternatives to methyl bromide: A florida perspective. Plant Health Prog. 2005, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexeeff, G.V.; Kilgore, W.W. Methyl bromide. Residue Rev. 1983, 88, 101–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, F.N. Development of alternative strategies for management of soilborne pathogens currently controlled with methyl bromide. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2003, 41, 325–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shennan, C.; Muramoto, J.; Koike, S.; Baird, G.; Fennimore, S.; Samtani, J.; Bolda, M.; Dara, S.; Daugovish, O.; Lazarovits, G.; et al. Anaerobic soil disinfestation is an alternative to soil fumigation for control of some soilborne pathogens in strawberry production. Plant Pathol. 2018, 67, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosskopf, E.N.; Di Gioia, F.; Hong, J.; Ozores-Hampton, M.; Zhao, X.; Black, Z.; Gao, Z.; Wilson, C.; Thomas, J.; Jones, J.; et al. Anaerobic soil disinfestation: Areawide project on obstacles and adoption. Acta Hortic. 2020, 1270, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosskopf, E.N.; Serrano-Pérez, P.; Hong, J.; Shrestha, U.; Del, M.; Rodríguez-Molina, C.; Martin, K.; Kokalis-Burelle, N.; Shennan, C.; Muramoto, J.; et al. Anaerobic soil disinfestation and soilborne pest management. In Organic Amendments and Soil Suppressiveness in Plant Disease Management; Meghvansi, M.K., Varma, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 277–305. ISBN 9783319230757. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J.; Di Gioia, F.; Jones, J.; Turechek, W.; Kokalis-Burelle, N.; Johns, C.W.; Finley, N.; Ozores-Hampton, M.; McCollum, G.; Rosskopf, E.N. Defining anaerobic soil disinfestation through changes in the microbiome. Acta Hortic. 2020, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhao, X.; Rosskopf, E.N.; Di Gioia, F.; Hong, J.C.; McNear, D.H. Impacts of anaerobic soil disinfestation and chemical fumigation on soil microbial communities in field tomato production system. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 126, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momma, N. Biological soil disinfestation (BSD) of soilborne pathogens and its possible mechanisms. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 2008, 42, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butler, D.M.; Kokalis-Burelle, N.; Muramoto, J.; Shennan, C.; McCollum, T.G.; Rosskopf, E.N. Impact of anaerobic soil disinfestation combined with soil solarization on plant-parasitic nematodes and introduced inoculum of soilborne plant pathogens in raised-bed vegetable production. Crop Prot. 2012, 39, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gioia, F.; Ozores-Hampton, M.; Hong, J.; Kokalis-Burelle, N.; Albano, J.; Zhao, X.; Black, Z.; Gao, Z.; Moore, K.; Swisher, M.; et al. The effects of anaerobic soil disinfestation on weed and nematode control, fruit yield, and quality of florida fresh-market tomato. HortScience 2016, 51, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ueki, A.; Kaku, N.; Ueki, K. Role of anaerobic bacteria in biological soil disinfestation for elimination of soil-borne plant pathogens in agriculture. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 6309–6318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewavitharana, S.S.; Klarer, E.; Reed, A.J.; Leisso, R.; Poirier, B.; Honaas, L.; Rudell, D.R.; Mazzola, M. Temporal dynamics of the soil metabolome and microbiome during simulated anaerobic soil disinfestation. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Di Gioia, F.; Hwang, J.; Hong, J.; Ozores-Hampton, M.; Zhao, X.; Pisani, C.; Rosskopf, E.; Wilson, P.C. Dissipation of fomesafen in fumigated, anaerobic soil disinfestation-treated, and organic-amended soil in Florida tomato production systems. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 76, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Di Gioia, F.; Zhao, X.; Ozores-Hampton, M.; Swisher, M.E.; Hong, J.; Kokalis-Burelle, N.; DeLong, A.N.; Rosskopf, E.N. Optimizing anaerobic soil disinfestation for fresh market tomato production: Nematode and weed control, yield, and fruit quality. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 218, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Gioia, F.; Hong, J.; Ozores-Hampton, M.; Zhao, X.; Wilson, C.; Thomas, J.; Li, Z.; Pisani, C.; Guo, H.; Paudel, B.R.; et al. Anaerobic soil disinfestation: Nutrient cycling and potential environmental impact. Acta Hortic. 2020, 1270, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shennana, C.; Muramoto, J.; Mazzola, M.; Momma, N.; Kobara, Y.; Lamers, J.; Rosskopf, E.N.; Kokalis-Burelle, N.; Butler, D.M. Anaerobic soil disinfestation for soil borne disease control in strawberry and vegetable systems: Current knowledge and future directions. Acta Hortic. 2014, 1044, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, D.M.; Rosskopf, E.N.; Kokalis-Burelle, N.; Albano, J.P.; Muramoto, J.; Shennan, C. Exploring warm-season cover crops as carbon sources for anaerobic soil disinfestation (ASD). Plant Soil 2012, 355, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, B.R.; Di Gioia, F.; Zhao, X.; Ozores-Hampton, M.; Hong, J.C.; Kokalis-Burelle, N.; Pisani, C.; Rosskopf, E.N. Evaluating anaerobic soil disinfestation and other biological soil management strategies for open-field tomato production in Florida. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2018, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Wang, J.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, X.; Di Gioia, F.; Guo, H.; Hong, J.; Ozores-Hampton, M.; Rosskopf, E. Economic analysis of anaerobic soil disinfestation for open-field fresh-market tomato production in southwest and North Florida. Horttechnology 2019, 29, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muramoto, J.; Shennan, C.; Zavatta, M.; Baird, G.; Toyama, L.; Mazzola, M. Effect of anaerobic soil disinfestation and mustard seed meal for control of charcoal rot in California strawberries. Int. J. Fruit Sci. 2016, 16, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Kong, J.; Cui, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, F.; Cai, Z.; Huang, X. Relationships of decomposability and C/N ratio in different types of organic matter with suppression of Fusarium oxysporum and microbial communities during reductive soil disinfestation. Biol. Control 2016, 101, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipanski, M.E.; Barbercheck, M.; Douglas, M.R.; Finney, D.M.; Haider, K.; Kaye, J.P.; Kemanian, A.R.; Mortensen, D.A.; Ryan, M.R.; Tooker, J.; et al. A framework for evaluating ecosystem services provided by cover crops in agroecosystems. Agric. Syst. 2013, 125, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blok, W.J.; Lamers, J.G.; Termorshuizen, J.; Bollen, G.J. Control of soilborne plant pathogens by incorporating fresh organic amendments followed by tarping. Phytopathology 2000, 90, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCarty, D.G.; Eichler Inwood, S.E.; Ownley, B.H.; Sams, C.E.; Wszelaki, A.L.; Butler, D.M. Field evaluation of carbon sources for anaerobic soil disinfestation in tomato and bell pepper production in Tennessee. HortScience 2014, 49, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goud, J.-K.K.C.; Termorshuizen, A.J.; Blok, W.J.; Van Bruggen, A.H.C.C. Long-term effect of biological soil disinfestation on verticillium wilt. Plant Dis. 2004, 88, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snapp, S.S.; Swinton, S.M.; Labarta, R.; Mutch, D.; Black, J.R.; Leep, R.; Nyiraneza, J.; O’Neil, K. Evaluating cover crops for benefits, costs and performance within cropping system niches. Agron. J. 2005, 97, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finney, D.M.; White, C.M.; Kaye, J.P. Biomass Production and carbon/nitrogen ratio influence ecosystem services from cover crop mixtures. Agron. J. 2016, 108, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jose, S. Agroforestry for ecosystem services and environmental benefits: An overview. Agrofor. Syst. 2009, 76, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrell, E.G.; Schipanski, M.E.; Finney, D.M.; Hunter, M.C.; Burgess, M.; LaChance, J.C.; Baraibar, B.; White, C.M.; Mortensen, D.A.; Kaye, J.P. Achieving diverse cover crop mixtures: Effects of planting date and seeding rate. Agron. J. 2017, 109, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.M.; Finney, D.M.; Kemanian, A.R.; Kaye, J.P. A model-data fusion approach for predicting cover crop nitrogen supply to corn. Agron. J. 2016, 108, 2527–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabriel, J.L.; Garrido, A.; Quemada, M. Cover crops effect on farm benefits and nitrate leaching: Linking economic and environmental analysis. Agric. Syst. 2013, 121, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gioia, F.; Ozores-Hampton, M.; Zhao, X.; Thomas, J.; Wilson, P.; Li, Z.; Hong, J.; Albano, J.; Swisher, M.; Rosskopf, E. Anaerobic soil disinfestation impact on soil nutrients dynamics and nitrous oxide emissions in fresh-market tomato. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 240, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kokalis-Burelle, N.; Butler, D.M.; Rosskopf, E.N. Evaluation of cover crops with potential for use in anaerobic soil disinfestation (ASD) for susceptibility to three species of Meloidogyne. J. Nematol. 2013, 45, 272–278. [Google Scholar]
- Sarwar, M.; Kirkegaard, J.A. Biofumigation potential of brassicas II. Effect of environment and ontogeny on glucosinolate production and implications for screening. Plant Soil 1998, 201, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesh, R.; Suryanarayana, M.A.; Nair, A.K.; Ghoshal Chaudhuri, S. Leguminous cover crop effects on nitrogen mineralization rates and kinetics in soils. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2001, 187, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A. Managing Cover Crops Profitably; Sustainable Agriculture Research and Education (SARE): College Park, MD, USA, 2008; ISBN 1437903797. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Method 3052: Microwave Assisted Acid Digestion of Siliceous and Organically Based Matrices; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1996.
- Di Gioia, F.; Gonnella, M.; Buono, V.; Ayala, O.; Santamaria, P. Agronomic, physiological and quality response of romaine and red oak-leaf lettuce to nitrogen input. Ital. J. Agron. 2017, 12, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Gioia, F.; Gonnella, M.; Buono, V.; Ayala, O.; Cacchiarelli, J.; Santamaria, P. Calcium cyanamide effects on nitrogen use efficiency, yield, nitrates, and dry matter content of lettuce. Agron. J. 2017, 109, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gioia, F.; Ozores-Hampton, M.; Hong, J.C.; McCollum, G.; Rosskopf, E.N. ASD: Carbon rate effects on tomato plant growth and organic acid production. In Proceedings of the 2016 Annual International Research Conference on Methyl Bromide Alternatives and Emissions Reductions, Maitland, FL, USA, 8–10 November 2016; pp. 58-1–58-3. [Google Scholar]
- Momma, N.; Yamamoto, K.; Simandi, P.; Shishido, M. Role of organic acids in the mechanisms of biological soil disinfestation (BSD). J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2006, 72, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Botanical Family | Common Name | Scientific Name | Broadcast Seed Rate (kg ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leguminosae | Berseem clover | Trifolium alexandrinum L. | 22 |
| Cowpea | Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp. | 135 | |
| Crimson clover | Trifolium incarnatum L. | 34 | |
| Field pea | Pisum sativum L. | 132 | |
| Sunn hemp | Crotalaria juncea L. | 56 | |
| Brassicaceae | Forage radish | Raphanus sativus L. var. longipinnatus | 22 |
| Mustard | Brassica juncea L. Czern. | 17 | |
| Polygonaceae | Buckwheat | Fagopyrum esculentum Möench | 101 |
| Graminaceae | Annual Ryegrass | Lolium multiflorum Lam | 34 |
| Oat | Avena sativa L. | 157 | |
| Rye | Secale cereale L. | 179 | |
| Sorghum-sudangrass hybrid | S. bicolor × S. vulgare var. sudanense | 56 |
| Cover Crop Species | 32 DAS | 46 DAS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Root Dry Biomass | Above-Ground Dry Biomass | Total Plant Dry Biomass | Root Dry Biomass | Above-Ground Dry Biomass | Total Plant Dry Biomass | |
| kg ha−1 | ||||||
| Annual ryegrass | 299.1 bc | 1325.7 d | 1624.8 c | 1192.6 a | 3059.2 e | 4251.8 d |
| Buckwheat | 287.0 bc | 2894.3 a | 3181.2 a | 627.6 bc | 8312.7 a | 8940.2 a |
| Cowpeas | 165.9 c | 1100.8 d | 1266.7 cd | 485.5 c | 3279.1 e | 3764.5 de |
| Crimson clover | 175.8 c | 1014.1 de | 1189.9 cd | 501.5 c | 2974.0 e | 3475.5 def |
| Field peas | 127.7 c | 962.4 de | 1090.1 cde | 331.7 c | 2643.0 e | 2974.8 ef |
| Forage radish | 182.5 c | 2569.6 ab | 2752.1 ab | 1183.2 a | 5121.1 c | 6304.3 b |
| Mustard | 227.8 c | 2478.0 b | 2705.8 ab | 614.8 bc | 5944.6 b | 6559.4 b |
| Oats | 420.2 ab | 1822.1 c | 2242.3 b | 986.4 ab | 5243.3 c | 6229.7 b |
| Rye | 547.9 a | 2412.7 b | 2960.6 a | 1163.9 a | 4079.5 d | 5243.3 c |
| Sorghum Sudan grass | 158.7 c | 623.1 ef | 781.8 de | 706.6 bc | 1957.3 f | 2663.9 fg |
| Sunn hemp | 89.7 c | 476.6 f | 566.2 e | 443.4 c | 1633.3 f | 2076.7 g |
| p-value | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 |
| Cover Crop Species | 32 Days After Sowing | 46 Days After Sowing | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total N (%) | Total C (%) | C:N | TCA (kg ha−1) | Total N (%) | Total C (%) | C:N | TCA (kg ha−1) | |
| Annual ryegrass | 4.64 b | 38.26 c | 8.35 cde | 507.3 e | 2.21 b | 39.51 c | 18.04 c | 1209.1 g |
| Buckwheat | 3.18 e | 39.55 b | 13.18 b | 1146.3 b | 1.27 f | 41.19 b | 33.45 a | 3424.8 b |
| Cowpea | 5.04 a | 38.33 c | 7.62 e | 421.3 ef | 1.70 de | 40.71 b | 24.45 b | 1333.2 g |
| Crimson clover | 4.47 bc | 39.74 b | 8.91 cde | 402.6 ef | 2.02 bc | 39.65 c | 19.82 c | 1178.6 g |
| Field peas | 4.83 ab | 40.25 ab | 8.36 cde | 386.7 ef | 1.90 cd | 42.39 a | 23.39 b | 1118.7 g |
| Forage radish | 3.90 d | 34.72 e | 9.08 cde | 892.2 c | 1.99 bc | 36.69 d | 18.62 c | 1879.0 f |
| Mustard | 4.46 bc | 35.28 e | 7.98 de | 877.3 c | 1.56 e | 40.99 b | 26.86 b | 2436.5 c |
| Oat | 4.60 b | 38.31 c | 8.33 cde | 696.3 d | 1.58 e | 41.32 b | 26.33 b | 2168.0 d |
| Rye | 4.07 d | 40.52 ab | 10.15 c | 978.8 c | 2.41 a | 41.64 b | 17.65 c | 1699.7 f |
| Sorghum Sudangrass | 4.16 cd | 40.54 ab | 9.75 cd | 250.3 fg | 1.69 de | 41.50 b | 24.94 b | 811.3 h |
| Sunn hemp | 5.09 a | 41.07 a | 8.09 cde | 195.8 g | 2.09 bc | 40.62 b | 19.51 c | 662.0 h |
| Molasses | 1.05 f | 36.54 d | 35.42 a | 7161.8 a | 1.05 g | 36.54 d | 35.42 a | 7161.8 a |
| p-value | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 |
| Cover Crop Species | N | NO3-N | P | K | Ca | Mg | S | Na | Fe | Mn | Zn | Bo | Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kg ha−1 | g ha−1 | ||||||||||||
| Annual ryegrass | 31.0 c | 13.4 ab | 10.7 cd | 96.3 c | 7.4 ef | 6.8 d | 4.9 cde | 3.7 c | 425.7 | 229.9 de | 94.2 ef | 12.1 d | 26.6 bc |
| Buckwheat | 30.8 c | 18.2 ab | 26.2 a | 166.8 a | 24.7 c | 32.0 a | 8.1 c | 1.5 d | 866.5 | 688.5 a | 273.2 a | 119.2 a | 29.6 ab |
| Cowpea | 28.4 c | 5.3 b | 13.8 c | 56.9 d | 20.0 cd | 10.1 d | 6.7 cd | 0.3 d | 366.4 | 444.4 bc | 79.3 f | 47.2 c | 7.9 e |
| Crimson clover | 31.0 c | 4.1 b | 7.1 de | 53.8 d | 14.7 de | 7.1 d | 5.1 cde | 4.1 c | 150.5 | 170.5 e | 65.0 f | 47.5 c | 9.4 e |
| Field peas | 33.3 c | 4.0 b | 9.5 de | 53.2 d | 13.3 e | 5.4 d | 3.5 de | 1.4 d | 233.9 | 156.6 e | 78.6 f | 17.5 d | 8.4 e |
| Forage radish | 56.9 a | 18.5 ab | 22.9 ab | 174.9 a | 52.4 a | 26.3 b | 24.5 b | 22.6 a | 406.1 | 490.9 bc | 178.4 c | 95.3 b | 21.3 d |
| Mustard | 48.3 ab | 33.5 a | 19.0 b | 186.0 a | 46.6 b | 20.4 c | 30.8 a | 10.4 b | 499.4 | 564.0 b | 232.1 b | 95.0 b | 24.2 cd |
| Oat | 43.8 b | 25.0 ab | 20.6 b | 135.0 b | 8.5 ef | 9.6 d | 8.4 c | 1.9 d | 275.2 | 365.4 cd | 138.6 d | 18.3 d | 25.5 bcd |
| Rye | 52.8 ab | 19.9 ab | 21.5 b | 160.2 a | 11.7 e | 11.0 d | 8.8 c | 1.0 d | 492.5 | 295.9 de | 120.4 de | 15.1 d | 32.9 a |
| Sorghum Sudan | 16.2 d | 2.3 b | 7.5 de | 36.8 de | 3.2 f | 3.8 d | 2.0 e | 0.2 d | 164.1 | 151.7 e | 57.2 f | 5.0 d | 10.5 e |
| Sunn hemp | 14.2 d | 2.2 b | 5.7 e | 18.2 e | 7.5 ef | 4.9 d | 2.5 de | 0.6 d | 95.1 | 212.4 de | 28.4 g | 22.2 d | 3.6 f |
| p-value | 0.0001 | 0.005 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.23 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 |
| Cover Crop Species | N | NO3-N | P | K | Ca | Mg | S | Na | Fe | Mn | Zn | Bo | Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kg ha−1 | g ha−1 | ||||||||||||
| Annual ryegrass | 30.7 c | 5.9 ab | 16.7 cd | 139.9 b | 17.8 e | 13.6 f | 9.1 def | 30.2 c | 299.1 cd | 663.2 c | 163.4 d | 26.1 g | 41.4 b |
| Buckwheat | 67.7 a | 6.3 ab | 38.2 a | 213.9 a | 78.1 b | 82.5 a | 15.0 cd | 3.3 e | 1226.2 a | 1192.9 a | 475.6 a | 226.3 a | 76.9 a |
| Cowpea | 50.5 b | 0.7 b | 19.0 c | 101.3 cd | 48.1 c | 27.4 d | 10.9 cdef | 0.9 e | 569.2 bcd | 769.4 bc | 143.8 d | 110.0 d | 20.7 c |
| Crimson clover | 50.8 b | 0.5 b | 14.4 de | 117.3 c | 47.8 c | 19.4 ef | 11.0 cdef | 15.8 d | 687.7 abcd | 353.2 d | 142.2 d | 123.2 d | 23.2 c |
| Field peas | 53.7 b | 1.2 b | 12.4 e | 89.7 d | 34.4 d | 12.6 f | 7.1 efg | 2.9 e | 426.5 cd | 262.3 d | 146.5 d | 46.5 f | 21.7 c |
| Forage radish | 70.7 a | 9.9 a | 28.1 b | 206.6 a | 110.1 a | 56.6 b | 33.1 b | 72.2 a | 1142.2 ab | 868.5 bc | 303.0 b | 179.3 b | 40.1 b |
| Mustard | 52.1 b | 9.0 ab | 28.5 b | 207.0 a | 79.2 b | 34.8 c | 43.0 a | 25.9 c | 831.2 abc | 916.2 b | 333.2 b | 155.7 c | 49.0 b |
| Oat | 42.3 b | 3.1 ab | 28.7 b | 205.2 a | 20.3 e | 21.6 de | 15.8 c | 59.5 b | 459.8 cd | 1156.5 a | 244.1 c | 47.2 f | 48.2 b |
| Rye | 48.0 b | 10.2 a | 25.4 b | 199.1 a | 24.3 e | 23.7 de | 11.5 cde | 2.0 e | 397.7 cd | 853.1 bc | 155.4 d | 30.7 fg | 48.9 b |
| Sorghum Sudan | 18.8 d | 0.2 b | 10.4 e | 81.2 d | 10.0 f | 12.6 f | 2.9 g | 0.4 e | 198.0 cd | 342.9 d | 109.9 de | 13.7 g | 21.9 c |
| Sunn hemp | 22.8 cd | 0.2 b | 10.2 e | 48.1 e | 26.8 de | 16.8 ef | 4.8 fg | 1.3 e | 165.1 d | 385.8 d | 77.4 e | 75.1 e | 9.5 d |
| p-value | 0.0001 | 0.0005 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.02 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 |
| DAT | Carbon Source | NO3-N | P | K | Ca | Mg | S | Na | Fe | Mn | Zn | Cu | B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Annual ryegrass | 27.67 | 72.67 | 220.7 b | 2811.70 | 225.00 | 37.0 b | 46.67 b | 290.33 | 176.67 b | 5.73 | 4.43 | 0.70 |
| Buckwheat | 36.67 | 82.33 | 267.3 b | 2964.00 | 244.33 | 40.0 b | 43.67 b | 306.00 | 180.67 b | 6.33 | 4.67 | 0.77 | |
| Cowpeas | 17.00 | 74.33 | 200.0 b | 2837.30 | 196.67 | 31.0 b | 36.00 b | 287.00 | 162.00 b | 5.73 | 4.23 | 0.70 | |
| Crimson clover | 33.00 | 72.33 | 227.0 b | 2849.70 | 215.67 | 34.7 b | 44.33 b | 292.00 | 176.67 b | 6.00 | 4.50 | 0.73 | |
| Field peas | 36.67 | 73.00 | 194.0 b | 2889.00 | 197.00 | 31.3 b | 37.00 b | 294.00 | 182.33 b | 6.00 | 4.27 | 0.67 | |
| Forage radish | 16.67 | 83.00 | 270.0 b | 2705.30 | 231.33 | 49.0 b | 77.67 a | 303.67 | 180.00 b | 6.33 | 4.50 | 0.77 | |
| Mustard | 26.67 | 78.00 | 263.0 b | 2942.00 | 219.00 | 48.0 b | 60.00 ab | 289.67 | 192.00 b | 6.03 | 4.00 | 0.80 | |
| Oats | 8.00 | 81.67 | 262.0 b | 2710.00 | 211.00 | 33.3 b | 61.33 ab | 303.00 | 182.67 b | 6.20 | 4.53 | 0.73 | |
| Rye | 38.33 | 82.33 | 248.0 b | 2668.30 | 207.00 | 36.7 b | 39.33 b | 302.67 | 165.00 b | 6.03 | 4.23 | 0.70 | |
| Sorghum Sudan grass | 47.67 | 80.33 | 254.0 b | 2762.70 | 215.33 | 35.7 b | 51.33 b | 301.00 | 174.67 b | 6.60 | 4.33 | 0.73 | |
| Sunn hemp | 75.33 | 76.33 | 203.0 b | 2786.30 | 214.33 | 38.0 b | 42.00 b | 308.33 | 180.67 b | 6.07 | 4.70 | 0.70 | |
| Molasses | 32.00 | 77.00 | 528.7 a | 3071.00 | 262.00 | 100.0 a | 58.33 ab | 308.00 | 229.33 a | 7.03 | 4.53 | 0.77 | |
| Untreated control | 46.33 | 75.33 | 180.0 b | 2750.00 | 203.67 | 32.7 b | 34.67 b | 304.33 | 177.00 b | 5.97 | 4.47 | 0.70 | |
| p-value | 0.08 | 0.29 | 0.0001 | 0.98 | 0.06 | 0.0001 | 0.002 | 0.42 | 0.0001 | 0.49 | 0.93 | 0.77 | |
| 7 | Annual ryegrass | 15.33 b | 75.00 | 233.3 bc | 2717.70 | 206.7 b | 32.7 b | 49.7 ab | 297.67 | 196.0 b | 6.17 | 4.23 | 0.63 bc |
| Buckwheat | 13.00 b | 78.67 | 255.7 bc | 2781.30 | 229.0 b | 35.0 b | 45.0 ab | 294.67 | 209.3 b | 6.03 | 4.40 | 0.77 a | |
| Cowpeas | 21.00 b | 72.00 | 216.7 bc | 2718.00 | 215.7 bc | 30.0 b | 33.3 b | 313.00 | 192.3 b | 6.87 | 4.10 | 0.60 c | |
| Crimson clover | 23.33 b | 74.67 | 216.7 bc | 2624.30 | 213.0 b | 35.3 b | 46.0 ab | 300.67 | 186.3 b | 6.30 | 4.23 | 0.67 abc | |
| Field peas | 10.67 b | 78.00 | 216.7 bc | 2633.30 | 208.7 b | 33.0 b | 40.3 ab | 304.00 | 191.3 b | 6.40 | 4.50 | 0.73 ab | |
| Forage radish | 11.67 b | 77.00 | 287.0 b | 2802.70 | 248.7 ab | 42.3 b | 68.3 a | 323.67 | 224.0 b | 6.40 | 4.83 | 0.77 a | |
| Mustard | 19.00 b | 76.00 | 234.3 bc | 2686.30 | 207.7 b | 37.0 b | 49.0 ab | 321.00 | 201.0 b | 6.27 | 3.93 | 0.67 abc | |
| Oats | 17.33 b | 79.00 | 256.7 bc | 2820.70 | 210.3 b | 34.3 b | 64.0 ab | 308.00 | 215.3 b | 6.33 | 4.30 | 0.73 ab | |
| Rye | 18.33 b | 76.00 | 306.7 b | 3303.00 | 231.7 abc | 40.7 b | 52.7 ab | 298.33 | 215.0 b | 6.03 | 4.37 | 0.77 a | |
| Sorghum Sudan grass | 31.67 b | 80.67 | 260.7 bc | 3025.70 | 226.3 abc | 38.0 b | 56.0 ab | 311.33 | 176.7 b | 6.17 | 4.37 | 0.77 a | |
| Sunn hemp | 30.33 b | 76.67 | 235.0 bc | 2681.30 | 212.3 b | 33.0 b | 41.0 ab | 306.67 | 174.0 b | 6.03 | 4.37 | 0.67 abc | |
| Molasses | 6.67 b | 81.00 | 468.7 a | 2961.00 | 258.3 a | 81.0 a | 54.7 ab | 356.67 | 304.0 a | 6.90 | 4.60 | 0.77 a | |
| Untreated control | 75.00 a | 73.33 | 176.3 c | 2673.30 | 204.3 b | 30.3 b | 32.0 b | 315.00 | 163.7 b | 6.00 | 4.13 | 0.60 c | |
| p-value | 0.001 | 0.63 | 0.0001 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.0001 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.0001 | 0.89 | 0.24 | 0.005 | |
| 28 | Annual ryegrass | 17.0 b | 75.3 abc | 264.3 bc | 2841.70 | 224.3 ab | 44.0 b | 64.3 abc | 306.3 b | 186.7 b | 6.13 | 4.13 | 0.73 b |
| Buckwheat | 8.3 b | 77.0 abc | 281.3 bc | 2933.30 | 246.7 ab | 39.7 b | 50.3 bc | 335.3 b | 206.3 b | 6.50 | 4.67 | 0.83 ab | |
| Cowpeas | 13.3 b | 77.3 abc | 259.0 bc | 2943.30 | 233.3 ab | 42.3 b | 40.7 c | 321.7 b | 193.7 b | 6.63 | 4.60 | 0.77 b | |
| Crimson clover | 19.7 b | 73.7 bc | 269.0 bc | 3101.30 | 229.3 ab | 42.0 b | 53.0 bc | 311.3 b | 197.7 b | 6.47 | 4.33 | 0.83 ab | |
| Field peas | 28.7 b | 70.0 c | 213.7 c | 2575.00 | 202.0 b | 35.3 b | 40.0 c | 286.3 b | 167.3 b | 6.07 | 4.00 | 0.70 b | |
| Forage radish | 11.0 b | 78.3 abc | 299.3 ab | 2896.30 | 235.3 ab | 45.3 b | 76.0 ab | 315.7 b | 206.7 b | 6.43 | 4.47 | 0.80 ab | |
| Mustard | 9.3 b | 82.7 ab | 360.7 b | 3388.00 | 281.3 a | 64.3 a | 85.3 a | 335.3 b | 218.3 b | 7.67 | 4.67 | 0.97 a | |
| Oats | 6.7 b | 73.0 bc | 303.3 ab | 2851.30 | 231.3 ab | 41.7 b | 76.7 ab | 301.3 b | 210.7 b | 6.43 | 4.63 | 0.77 b | |
| Rye | 12.3 b | 70.0 c | 266.3 bc | 2659.00 | 209.3 b | 38.0 b | 41.0 c | 302.7 b | 184.0 b | 5.73 | 4.07 | 0.70 b | |
| Sorghum Sudan grass | 24.0 b | 81.0 ab | 288.0 bc | 3202.30 | 256.3 ab | 42.7 b | 54.7 bc | 315.7 b | 201.7 b | 7.37 | 4.77 | 0.83 ab | |
| Sunn hemp | 26.0 b | 81.7 ab | 254.3 bc | 3066.70 | 227.3 ab | 44.7 b | 56.3 bc | 305.7 b | 177.7 b | 6.57 | 4.07 | 0.80 ab | |
| Molasses | 4.0 b | 83.7 a | 507.0 a | 2704.70 | 255.0 ab | 70.3 a | 51.0 bc | 419.3 a | 288.7 a | 6.93 | 4.43 | 0.80 ab | |
| Untreated control | 87.3 a | 76.7 abc | 236.0 c | 3184.70 | 249.3 ab | 40.3 b | 42.0 c | 329.7 b | 190.7 b | 6.73 | 4.70 | 0.80 ab | |
| p-value | 0.0001 | 0.03 | 0.0001 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.0006 | 0.0003 | 0.0003 | 0.0003 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.01 | |
| Carbon Source | Leaf Number | Plant Fresh Weight | Plant Dry Weight | Leaf Area | Specific Leaf Area | Leaf dry Mass Per Unit Area | Dry Matter Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g Plant−1 | g Plant−1 | cm2 Plant−1 | cm2 g−1 | g m−2 | g kg−1 | ||
| Annual ryegrass | 65.0 | 142.4 | 4.64 | 2450 b | 527.21 ab | 19.04 ab | 33.17 |
| Buckwheat | 66.7 | 145.1 | 4.84 | 2578 ab | 533.50 ab | 18.82 ab | 32.73 |
| Cowpea | 71.8 | 143.5 | 4.71 | 2515 b | 534.19 ab | 18.83 ab | 32.76 |
| Crimson clover | 70.6 | 150.1 | 4.76 | 2589 ab | 544.17 ab | 18.39 ab | 31.55 |
| Field peas | 71.7 | 152.0 | 4.91 | 2529 b | 514.63 ab | 19.51 ab | 32.34 |
| Forage radish | 65.4 | 146.1 | 4.82 | 2593 ab | 538.45 ab | 18.62 ab | 32.74 |
| Mustard | 66.8 | 144.8 | 4.77 | 2615 ab | 548.56 ab | 18.29 ab | 33.04 |
| Oat | 66.2 | 146.6 | 4.80 | 2689 ab | 558.71 a | 18.00 b | 33.16 |
| Rye | 63.1 | 148.0 | 4.79 | 2541 ab | 531.02 ab | 18.89 ab | 32.45 |
| Sorghum sudangrass | 66.2 | 143.2 | 4.59 | 2372 b | 515.75 ab | 19.47 ab | 32.62 |
| Sunn hemp | 69.3 | 145.6 | 4.92 | 2472 b | 503.41 b | 20.05 a | 33.71 |
| Molasses | 69.8 | 149.8 | 5.11 | 2838 a | 554.36 ab | 18.12 b | 33.75 |
| Untreated control | 64.3 | 148.5 | 4.83 | 2570 ab | 531.82 ab | 18.84 ab | 33.11 |
| p-value | 0.20 | 0.68 | 0.14 | 0.002 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.57 |
| Carbon Source | Total C (%) | Total N (%) | C:N |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annual ryegrass | 33.85 ab | 5.11 ab | 6.62 abc |
| Buckwheat | 33.08 b | 5.30 a | 6.26 b |
| Cowpea | 33.88 ab | 5.10 ab | 6.65 abc |
| Crimson clover | 33.40 ab | 4.94 b | 6.76 ab |
| Field peas | 34.42 a | 5.08 ab | 6.79 ab |
| Forage radish | 33.38 ab | 4.92 b | 6.79 ab |
| Mustard | 32.91 b | 5.13 ab | 6.42 bc |
| Oat | 33.68 ab | 4.98 b | 6.77 ab |
| Rye | 33.13 b | 5.03 b | 6.60 abc |
| Sorghum sudangrass | 33.40 ab | 5.12 ab | 6.53 abc |
| Sunn hemp | 33.45 ab | 5.00 b | 6.73 ab |
| Molasses | 34.28 a | 4.95 b | 6.93 a |
| Untreated control | 33.05 b | 5.16 ab | 6.41 bc |
| p-value | 0.04 | 0.0001 | 0.0006 |
| Carbon Source | NO3-N | P | K | Ca | Mg | S | Na | Fe | Mn | Zn | Bo | Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg kg−1 | % | % | % | % | % | % | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | |
| Annual ryegrass | 15,067 | 0.55 | 9.26 | 1.60 | 0.37 | 0.36 | 0.30 ab | 208.67 | 74.00 b | 42.00 c | 33.00 | 11.67 |
| Buckwheat | 17,867 | 0.55 | 9.16 | 1.61 | 0.39 | 0.35 | 0.25 b | 193.00 | 75.67 b | 45.67 bc | 31.33 | 11.67 |
| Cowpea | 13,167 | 0.63 | 9.99 | 1.73 | 0.44 | 0.38 | 0.28 b | 253.33 | 83.00 b | 45.67 bc | 35.33 | 12.33 |
| Crimson clover | 13,267 | 0.69 | 10.85 | 1.80 | 0.46 | 0.41 | 0.32 ab | 206.67 | 84.00 b | 46.00 bc | 37.67 | 12.67 |
| Field peas | 17,100 | 0.60 | 9.25 | 1.86 | 0.41 | 0.37 | 0.26 b | 274.33 | 81.67 b | 45.00 bc | 33.33 | 11.67 |
| Forage radish | 15,033 | 0.61 | 10.24 | 1.70 | 0.41 | 0.38 | 0.41 a | 296.33 | 88.00 b | 54.67 ab | 35.00 | 12.00 |
| Mustard | 14,833 | 0.58 | 9.58 | 1.64 | 0.42 | 0.36 | 0.33 ab | 266.67 | 85.00 b | 51.33 abc | 32.67 | 12.33 |
| Oat | 15,267 | 0.56 | 9.38 | 1.77 | 0.38 | 0.36 | 0.36 ab | 215.00 | 79.67 b | 46.67 bc | 33.33 | 11.67 |
| Rye | 16,800 | 0.58 | 9.65 | 1.77 | 0.41 | 0.38 | 0.26 b | 367.33 | 83.00 b | 47.00 bc | 33.33 | 12.33 |
| Sorghum sudangrass | 14,667 | 0.58 | 9.34 | 1.76 | 0.40 | 0.36 | 0.28 b | 158.67 | 71.00 b | 46.00 bc | 32.33 | 10.67 |
| Sunn hemp | 15,100 | 0.58 | 9.12 | 1.71 | 0.38 | 0.35 | 0.25 b | 207.00 | 70.33 b | 43.00 bc | 31.67 | 10.33 |
| Molasses | 12,500 | 0.53 | 9.28 | 1.63 | 0.40 | 0.38 | 0.23 b | 194.00 | 120.67 a | 59.67 a | 32.00 | 12.67 |
| Untreated control | 15,700 | 0.66 | 10.34 | 1.94 | 0.49 | 0.38 | 0.30 ab | 206.67 | 78.67 b | 47.00 bc | 35.00 | 12.00 |
| p-value | 0.32 | 0.26 | 0.46 | 0.54 | 0.19 | 0.51 | 0.01 | 0.40 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.36 | 0.75 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vecchia, L.; Di Gioia, F.; Ferrante, A.; Hong, J.C.; White, C.; Rosskopf, E.N. Integrating Cover Crops as a Source of Carbon for Anaerobic Soil Disinfestation. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101614
Vecchia L, Di Gioia F, Ferrante A, Hong JC, White C, Rosskopf EN. Integrating Cover Crops as a Source of Carbon for Anaerobic Soil Disinfestation. Agronomy. 2020; 10(10):1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101614
Chicago/Turabian StyleVecchia, Luca, Francesco Di Gioia, Antonio Ferrante, Jason C. Hong, Charles White, and Erin N. Rosskopf. 2020. "Integrating Cover Crops as a Source of Carbon for Anaerobic Soil Disinfestation" Agronomy 10, no. 10: 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101614
APA StyleVecchia, L., Di Gioia, F., Ferrante, A., Hong, J. C., White, C., & Rosskopf, E. N. (2020). Integrating Cover Crops as a Source of Carbon for Anaerobic Soil Disinfestation. Agronomy, 10(10), 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101614







