The Influence of Lyophilized EmuGel Silica Microspheres on the Physicomechanical Properties, In Vitro Bioactivity and Biodegradation of a Novel Ciprofloxacin-Loaded PCL/PAA Scaffold
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of the Silica Microspheres
2.3. Preparation of the PCL/PAA Composite Scaffold
2.4. Morphological and Microstructure Characterization of the PCL/PAA Scaffold
2.5. Characterization of the Thermal Behavior of the PCL/PAA Scaffolds
2.6. Physicochemical Integrity Analysis of PCL/PAA Scaffolds
2.7. Determination of the Physicomechanical Properties of the PCL/PAA Scaffolds
2.8. In Vitro Bioactivity, Biodegradation and Micro-Environmental pH Variation Analysis
2.9. In Vitro Analysis of Ciprofloxacin Release
3. Results and Discussion
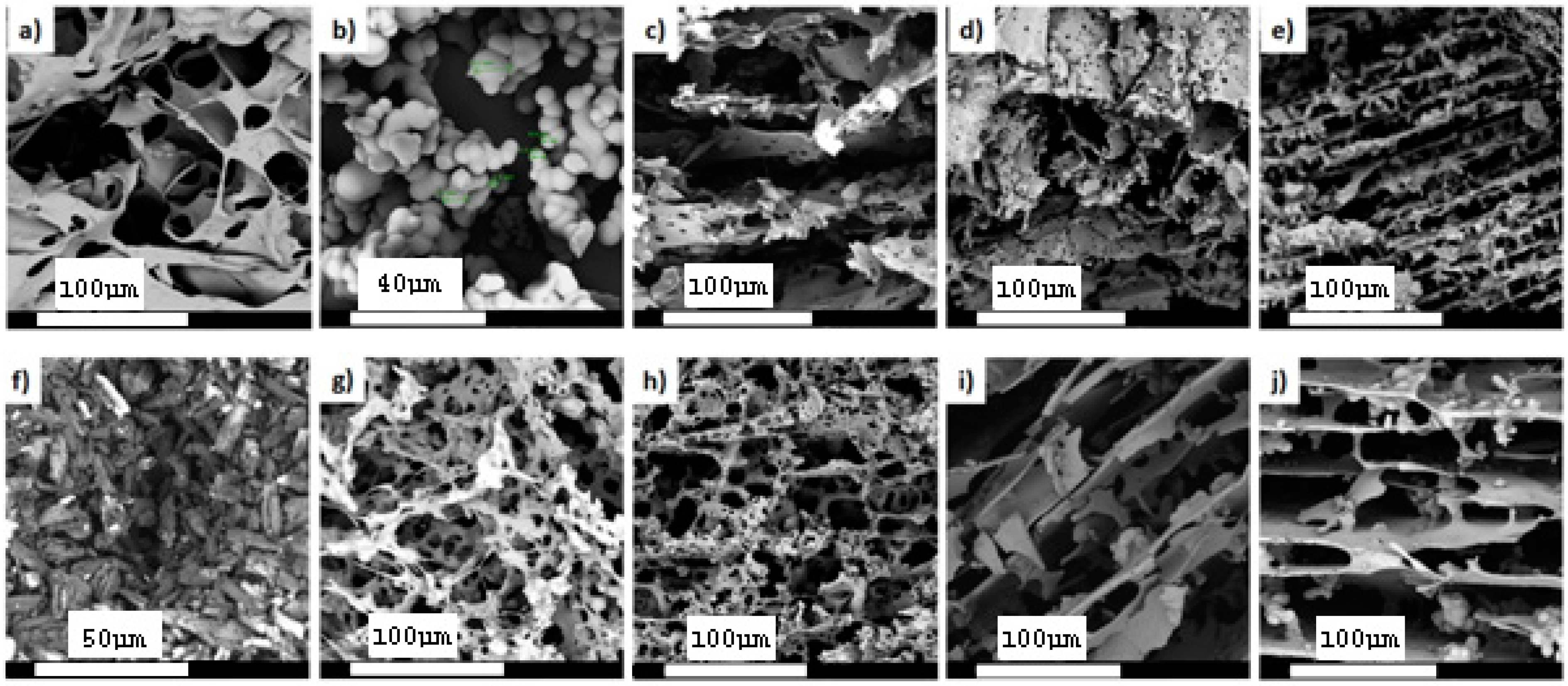
3.1. Morphological and Microstructure Property Assessment
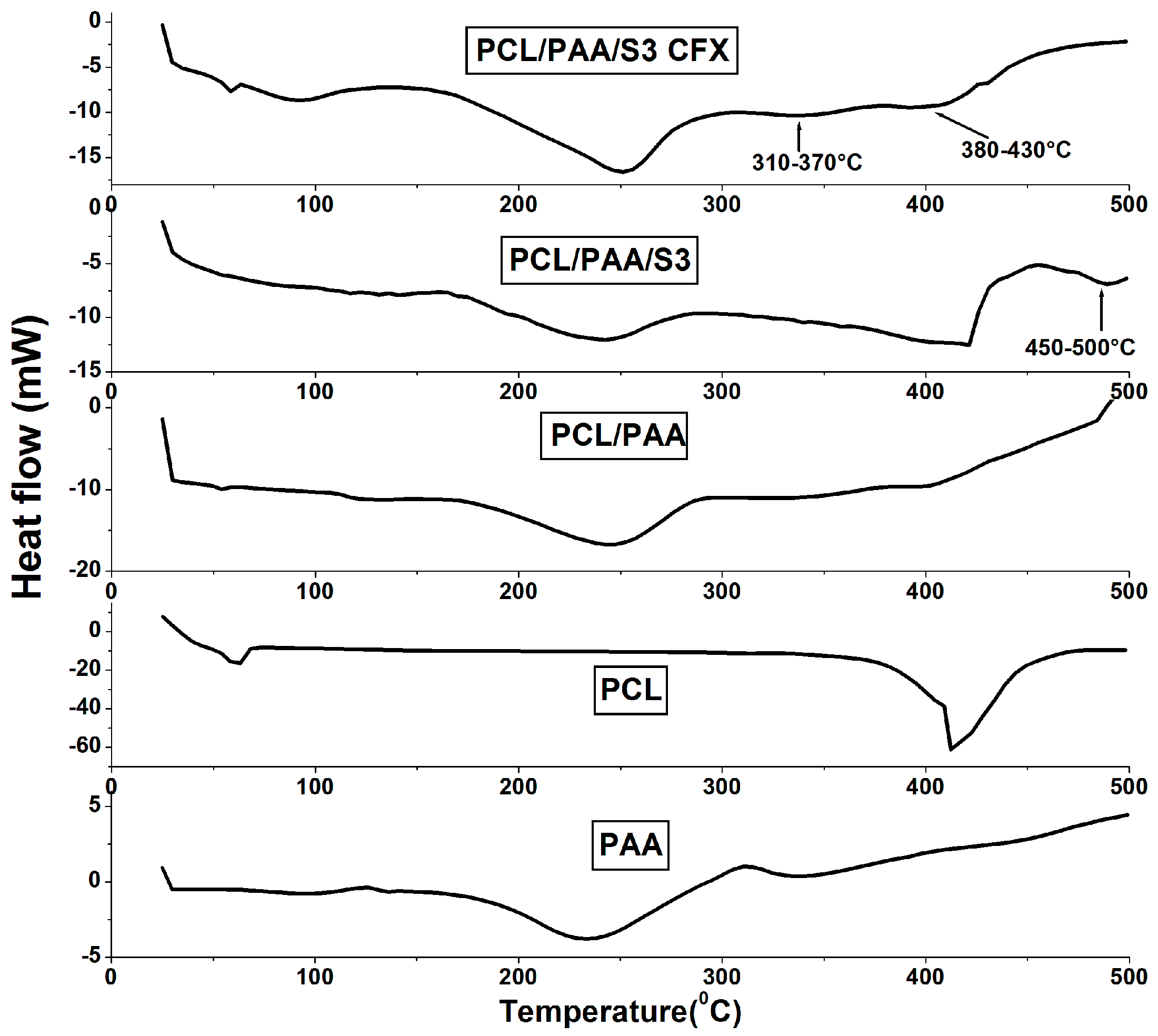
3.2. Thermal Behavior of the PCL/PAA Scaffolds
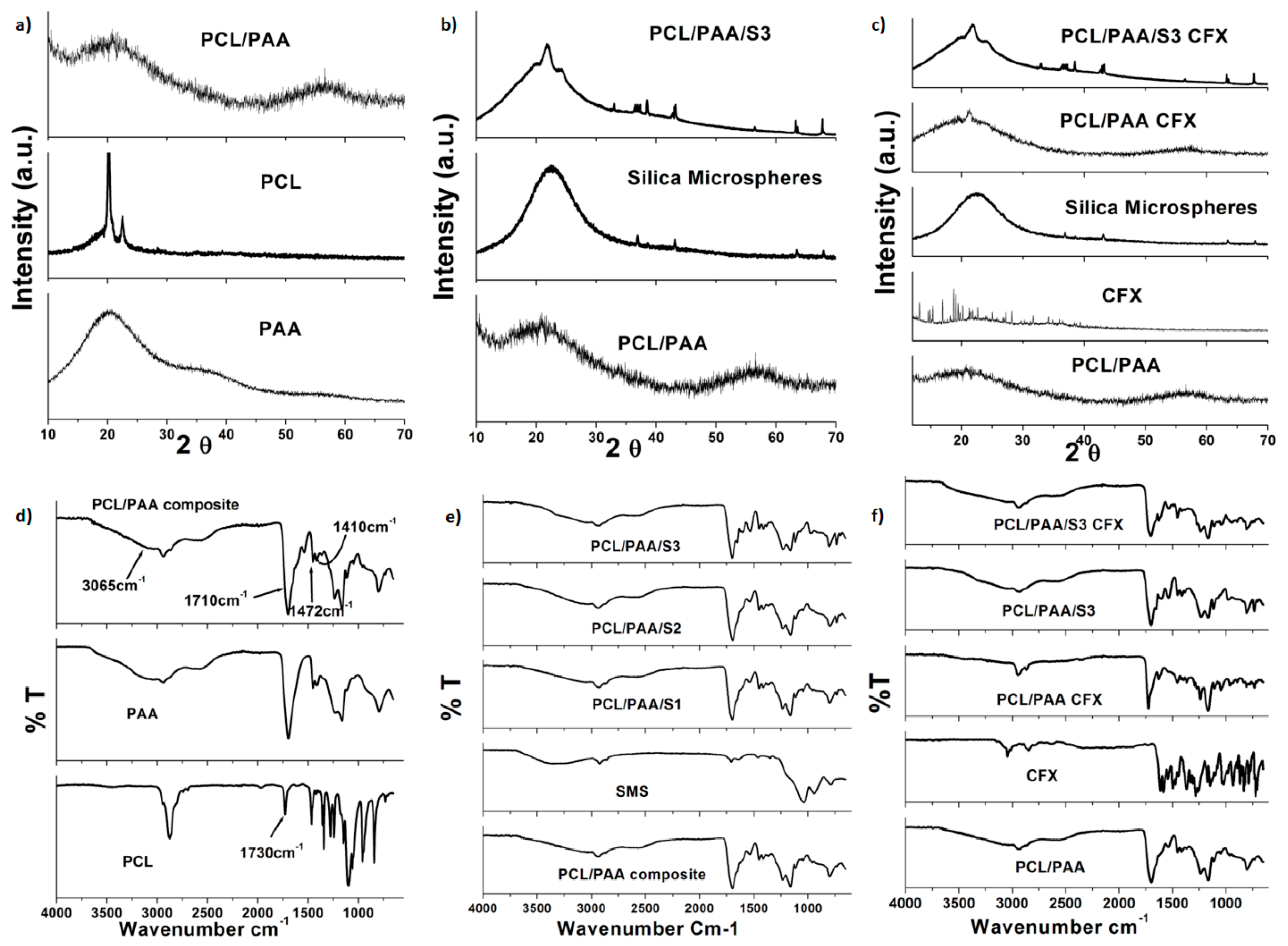
3.3. Assessment of the Physicochemical Structure Stability
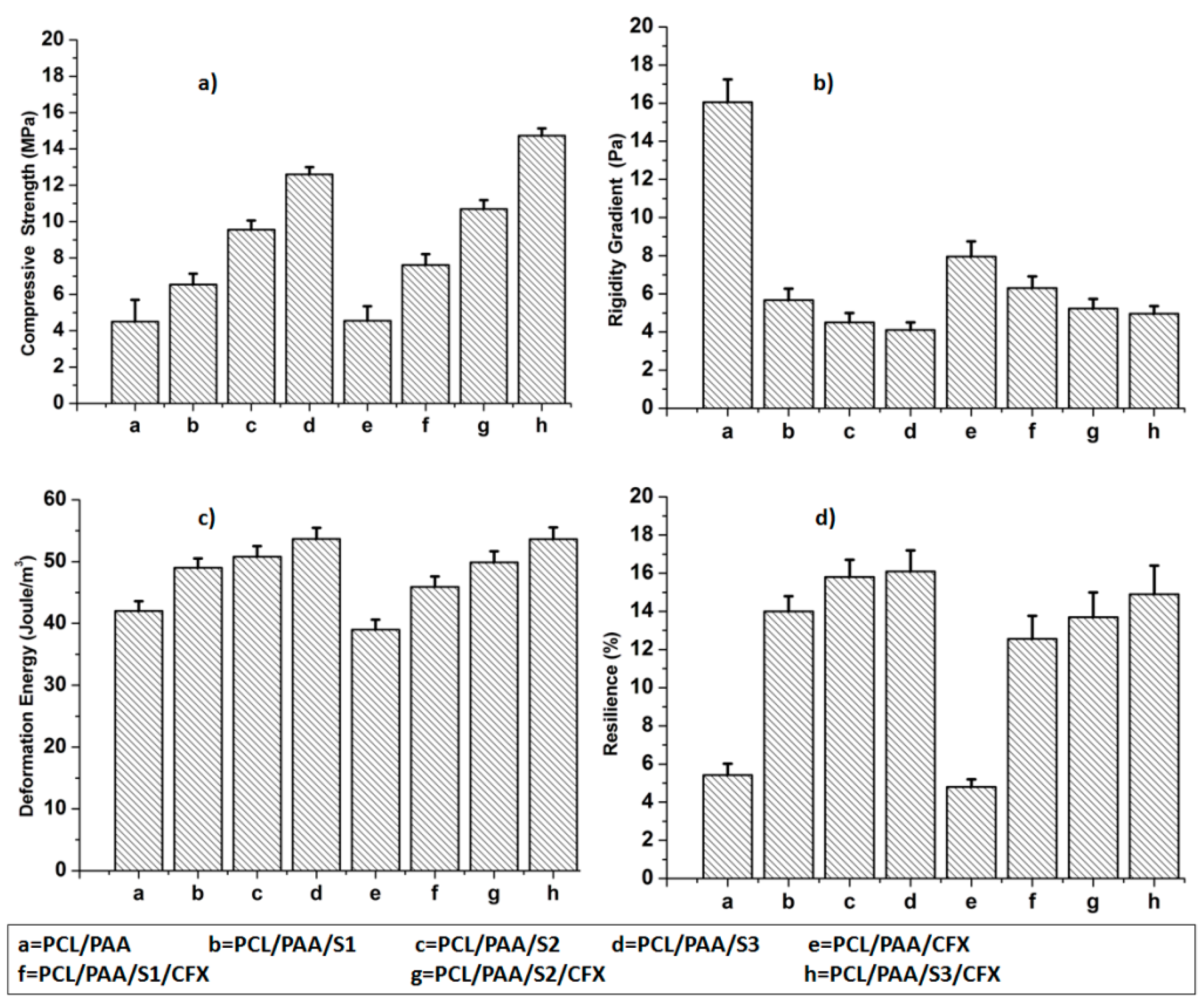
3.4. Assessment of the Mechanical Properties of the Scaffold
3.5. In Vitro Bioactivity, Biodegradation and SBF pH Variations
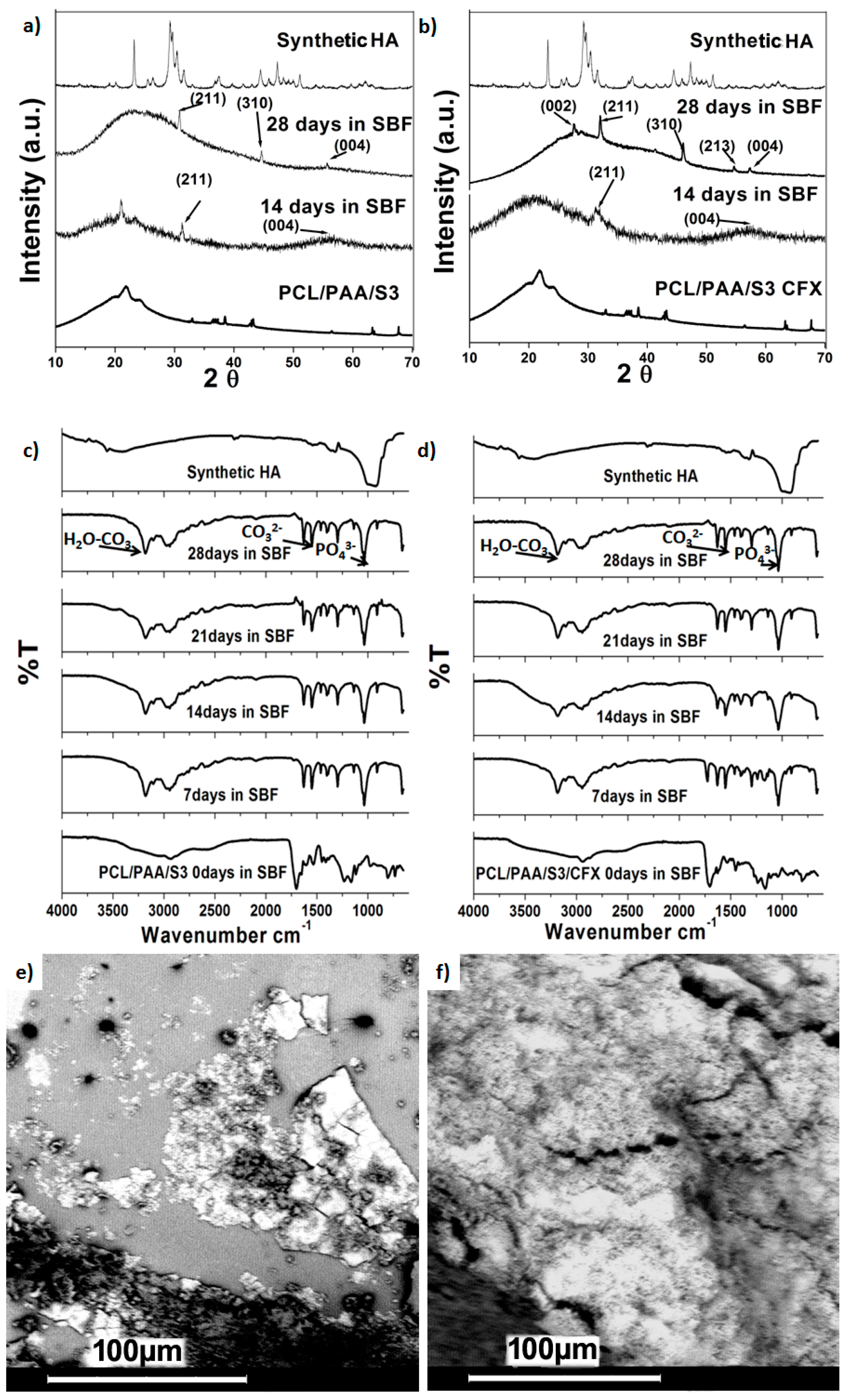
3.5.1. In Vitro Bioactivity
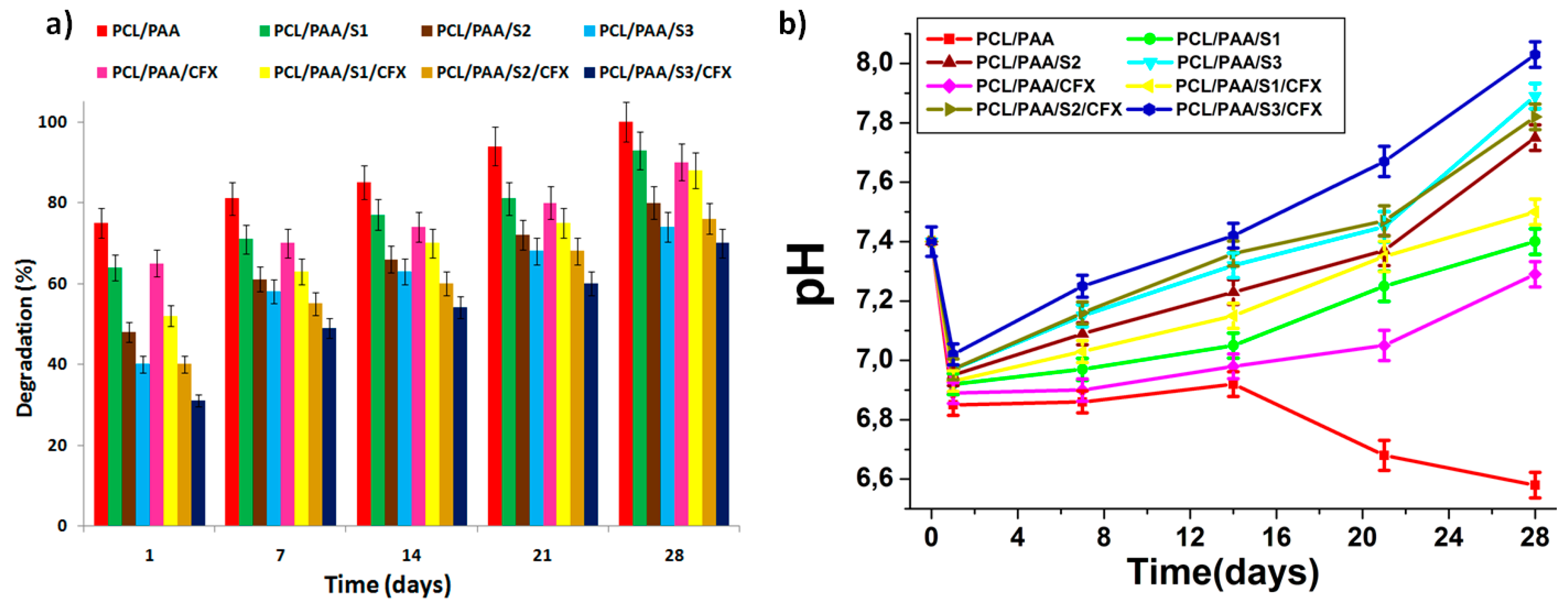
3.5.2. Biodegradation and SBF pH Variations
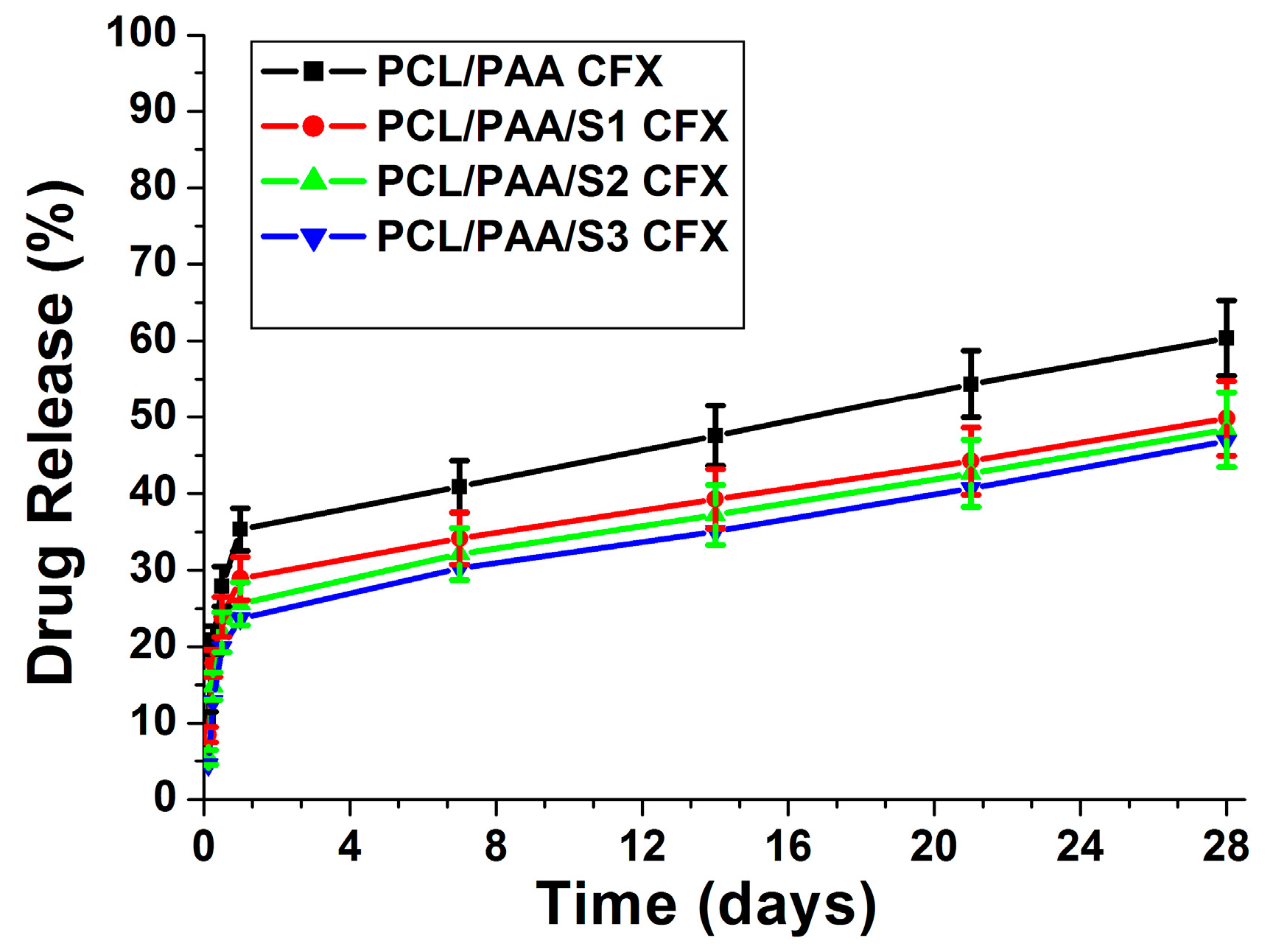
3.6. Assessment of the Ciprofloxacin Release Behavior from the PCL/PAA Scaffolds
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Napoli, A.; Sebok, D.; Senti, A.; Meier, W. Block Copolymers in Nanoscience; Lazzari, M., Liu, G., Lecommandoux, S., Eds.; WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; pp. 39–71. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.Q.; Sun, Y.X.; Xu, X.D.; Cheng, S.X.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zhuo, R.X. Biodegradable and pH-sensitive hydrogels for cell encapsulation and controlled drug release. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Kim, M.; Kim, G.H. A hybrid PCL/collagen scaffold consisting of solid freeform-fabricated, struts and EHD-direct-jet-processed fibrous threads for tissue. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 450, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghavimi, S.A.A.; Ebrahimzadeh, M.H.; Shokrgozar, M.A.; Solati-Hashjin, M.; Abu Osman, N.A. Effect of starch content on the biodegradation of polycaprolactone/starch composite for fabricating in situ pore-forming scaffolds. Polym. Test. 2015, 43, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, N.; Horiuchi, N.; Nakamura, M.; Hiyama, T.; Nagai, A.; Yamashita, K. Effect of poly(acrylicacid) and polarization on the controlled crystallization of calcium carbonate on single-phase calcite substrates. Cryst. Growth Des. 2013, 13, 2928–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; He, D.; Wang, G.S.; Yu, S.H. Bioinspired crystallization of CaCO3 coatings on electrospun cellulose acetate fiber scaffolds and corresponding CaCO3 micro tube networks. Langmuir 2011, 27, 7199–7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, R.; Mastai, Y.; Gedanken, A. Acoustic cavitation leading to the morpho synthesis of mesoporous silica vesicles. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1414–1418. [Google Scholar]
- Melvin, A.; Vijay, R.; Chaudhari, V.; Gupta, B.; Prakash, R.; Haram, S.; Baskar, G.; Khushalani, D. A facile methodology for the design of functionalized hollow silica-spheres. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 346, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabrouk, M.; Mostafa, A.A.; Oudadesse, H.; Mahmoud, A.A.; El-Gohary, M.I. Effect of ciprofloxacin incorporation in PVA and PVA bioactive glass composites scaffolds. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 4833–4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokubo, T.; Takadama, H. How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity? Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2907–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, S.; Jayasree, R.; Chennazhi, K.P.; Nair, S.V.; Jayakumar, R. Biocompatible alginate/nano bioactive glass ceramic composite scaffolds for periodontal tissue regeneration. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrouk, M.; Mostafa, A.A.; Oudadesse, H.; Wers, E.; Lucas-Girot, A.; El-Gohary, M.I. Comparative study of nanobioactive glass quaternary system 46S6. Bioceram. Dev. Appl. 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Tan, F.; Zhao, L.; Li, J. The synthesis, characterization and application of ciprofloxacin complexes and its coordination with copper, manganese and zirconium ions. J. Cryst. Process Technol. 2012, 2, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu-Li, L.; Yijun, L.; Hong-Ru, L. Evaluation of epirubicin in thermogelling and bioadhesive liquid and solid suppository formulations for rectal administration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 342–360. [Google Scholar]
- Perumal, S.; Ramadass, S.K.; Madhan, B. Sol–gel processed mupirocin silica microspheres loaded collagen scaffold: A synergistic bio-composite for wound healing. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 52, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninan, N.; Grohens, Y.; Elain, A.; Kalarikkal, N.; Thomas, S. Synthesis and characterisation of gelatin/zeolite porous scaffold. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 2433–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulou, A.; Efthimiadou, E.K.; Kordas, G. A new approach to fabricate bioactive silica binary and ternary hybrid microspheres. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 53, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.; Hearn, J.; Abdelmagid, W.; Zhang, H. Dual-tuned drug release by nanofibrous scaffolds of chitosan and mesoporous silica microspheres. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 25027–25035. [Google Scholar]
- Hollister, S.J. Porous scaffold design for tissue engineering. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indermun, S.; Choonara, Y.E.; Kumar, P.; Toit, L.C.; du Modi, G.; Luttge, R.; Pillay, V. An interfacially plasticized electro-responsive hydrogel for transdermal electro-activated and modulated (TEAM) drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 462, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, T.; Franco, R.A.; Lee, B. Preparation and characterization of a novel 3D scaffold from poly(ε-caprolactone)/biphasic calcium phosphate hybrid composite microspheres adhesion. Biochem. Eng. J. 2012, 64, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, A.; Zeppetelli, S.; Maio, E.D.; Iannace, S.; Netti, P.A. Novel 3D porous multi-phase composite scaffolds based on PCL, thermoplastic zein and ha prepared via supercritical CO2 foaming for bone regeneration. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 1838–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrouk, M.; Mostafa, A.A.; Oudadesse, H.; Mahmoud, A.A.; Gaafar, A.M.; El-Gohary, M.I. Fabrication, characterization and drug release of ciprofloxacin loaded porous polyvinyl alcohol/bioactive glass scaffold for controlled drug delivery. Bioceram. Dev. Appl. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczak-Kupiec, A.; Malina, D.; Tyliszczak, B.; Piatkowski, M.; Bialik-Was, K.; Wzorek, Z. Evaluation of bioactivity of poly(acrylic acid)-hydroxyapatite-nanogold composites in in vitro conditions. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2012, 7, 459–467. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Lui, Y.S.; Choo, C.K.C.; Sow, W.T.; Huang, C.L.; Ng, K.W.; Tan, L.P.; Loo, J.S. Calcium phosphate coated Keratin–PCL scaffolds for potential bone tissue regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 49, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basile, M.A.; Ayala, G.G.; Malinconico, M.; Laurienzo, P.; Coudane, J.; Nottelet, B.; Ragione, F.D.; Oliva, A. Functionalized PCL/HA nanocomposites as microporous membranes for bone regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 48, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.R.; Sepulveda, P.; Hench, L.L. Dose-dependent behavior of bioactive glass dissolution. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 58, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.K.; Kothiyal, G.P.; Srinivasan, A. In vitro evaluation of bioactivity of CaO–SiO2–P2O5–Na2O–Fe2O3 glasses. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 6827–6831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunatillake, P.A.; Adhikari, R. Biodegradable synthetic polymers for tissue engineering. Eur. Cell Mater. 2003, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wolf, M.T.; Dearth, C.L.; Sonnenberg, S.B.; Loboa, E.G.; Badylak, S.F. Naturally derived and synthetic scaffolds for skeletal muscle reconstruction. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 84, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manas, A.; Pocquet, M.; Biscans, B.; Sperandio, M.; Sperandio, M. Parameters influencing calcium phosphate precipitation in granular sludge sequencing batch reactor. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 77, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armentano, I.; Dottori, M.; Fortunati, E.; Mattioli, S.; Kenny, J.M. Biodegradable polymer matrix nanocomposites for tissue engineering: A review. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 2126–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.N.; Ekenseair, A.K.; Spicer, P.P.; Watson, B.M.; Tzouanas, S.N.; Roh, T.T.; Mikos, A.G. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of self-mineralization and biocompatibility of injectable, dual-gelling hydrogels for bone tissue engineering. J. Control. Release 2015, 205, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, Z.; Ma, P.; Li, C.; Kang, X.; Yang, D.; Lin, J. pH-responsive drug delivery system based on luminescent CaF2:Ce3+/Tb3+-poly(acrylic acid) hybrid microspheres. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 2583–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florczyk, S.J.; Leung, M.; Jana, S.; Li, Z.S.; Bhattarai, N.; Huang, J.I.; Hopper, R.A.; Zhang, M. Enhanced bone tissue formation by alginate gel-assisted cell seeding in porous ceramic scaffolds and sustained release of growth factor. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2012, 100A, 3408–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joddar, B.; Albayrak, A.; Kang, J.; Nishihara, M.; Abe, H.; Ito, Y. Sustained delivery of siRNA from dopamine-coated stainless steel surfaces. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6753–6761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.K.; Ferreira, J.M.F.; Kannan, S. Mechanically stable antimicrobial chitosan–PVA–silver nanocomposite coatings deposited on titanium implants. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 121, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.H.; Parka, D.H.; Yang, J.H.; Choy, Y.B.; Choy, J.H. Drug-inorganic-polymer nanohybrid for transdermal delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 444, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chennamaneni, S.R.; Mamalis, C.; Archer, B.; Oakey, Z.; Ambati, B.K. Development of a novel bioerodible dexamethasone implant for uveitis and postoperative cataract inflammation. J. Control. Release 2013, 167, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sample | PCL/PAA (wt %) | Silica microspheres (wt %) | CFX (wt %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCL/PAA | 100 | - | - |
| PCL/PAA/S1 | 90 | 10 | - |
| PCL/PAA/S2 | 80 | 20 | - |
| PCL/PAA/S3 | 70 | 30 | - |
| PCL/PAA/CFX | 90 | - | 10 |
| PCL/PAA/S1/CFX | 80 | 10 | 10 |
| PCL/PAA/S2/CFX | 70 | 20 | 10 |
| PCL/PAA/S3/CFX | 60 | 30 | 10 |
| Sample | BET Surface area | Porosity (%) by liquid displacement method |
|---|---|---|
| PCL/PAA | 3.87± 0.108 m2/g | 87.10 ± 2.50 |
| PCL/PAA/S1 | 19.31 ± 0.20 m2/g | 81.35 ± 2.18 |
| PCL/PAA/S2 | 26.51 ± 0.25 m2/g | 77.45 ± 1.90 |
| PCL/PAA/S3 | 45.37 ± 0.39 m2/g | 51.74 ± 1.68 |
| PCL/PAA/CFX | 3.99 ± 0.07 m2/g | 81.83 ± 2.70 |
| PCL/PAA/S1/CFX | 6.28 ± 0.11 m2/g | 76.13 ± 2.11 |
| PCL/PAA/S2/CFX | 9.87 ± 0.19 m2/g | 63.10 ± 1.87 |
| PCL/PAA/S3/CFX | 25.92 ± 0.33 m2/g | 58.06 ± 1.63 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mabrouk, M.; Choonara, Y.E.; Kumar, P.; Du Toit, L.C.; Pillay, V. The Influence of Lyophilized EmuGel Silica Microspheres on the Physicomechanical Properties, In Vitro Bioactivity and Biodegradation of a Novel Ciprofloxacin-Loaded PCL/PAA Scaffold. Polymers 2016, 8, 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8060232
Mabrouk M, Choonara YE, Kumar P, Du Toit LC, Pillay V. The Influence of Lyophilized EmuGel Silica Microspheres on the Physicomechanical Properties, In Vitro Bioactivity and Biodegradation of a Novel Ciprofloxacin-Loaded PCL/PAA Scaffold. Polymers. 2016; 8(6):232. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8060232
Chicago/Turabian StyleMabrouk, Mostafa, Yahya Essop Choonara, Pradeep Kumar, Lisa Claire Du Toit, and Viness Pillay. 2016. "The Influence of Lyophilized EmuGel Silica Microspheres on the Physicomechanical Properties, In Vitro Bioactivity and Biodegradation of a Novel Ciprofloxacin-Loaded PCL/PAA Scaffold" Polymers 8, no. 6: 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8060232
APA StyleMabrouk, M., Choonara, Y. E., Kumar, P., Du Toit, L. C., & Pillay, V. (2016). The Influence of Lyophilized EmuGel Silica Microspheres on the Physicomechanical Properties, In Vitro Bioactivity and Biodegradation of a Novel Ciprofloxacin-Loaded PCL/PAA Scaffold. Polymers, 8(6), 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8060232