Engineering Porous Poly(lactic acid) Scaffolds with High Mechanical Performance via a Solid State Extrusion/Porogen Leaching Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
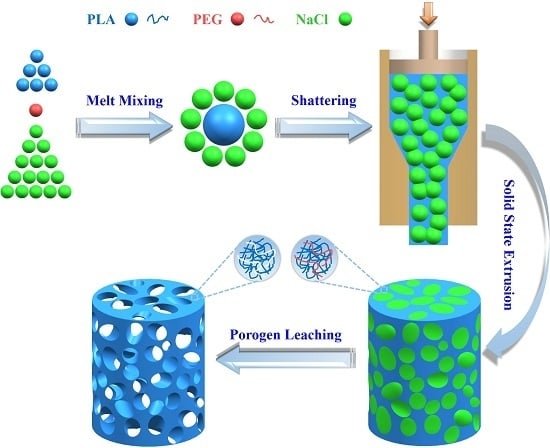
2.2. Preparation of PLA/PEG/NaCl Mixtures
2.3. Preparation of Porous PLA Scaffolds
2.4. Residual Mass, Connectivity, and Porosity Measurement
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.6. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.7. Mechanical Properties
2.8. Water Contact Angle Analysis
2.9. Cytotoxicity Test
2.10. Cell Adhesion
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
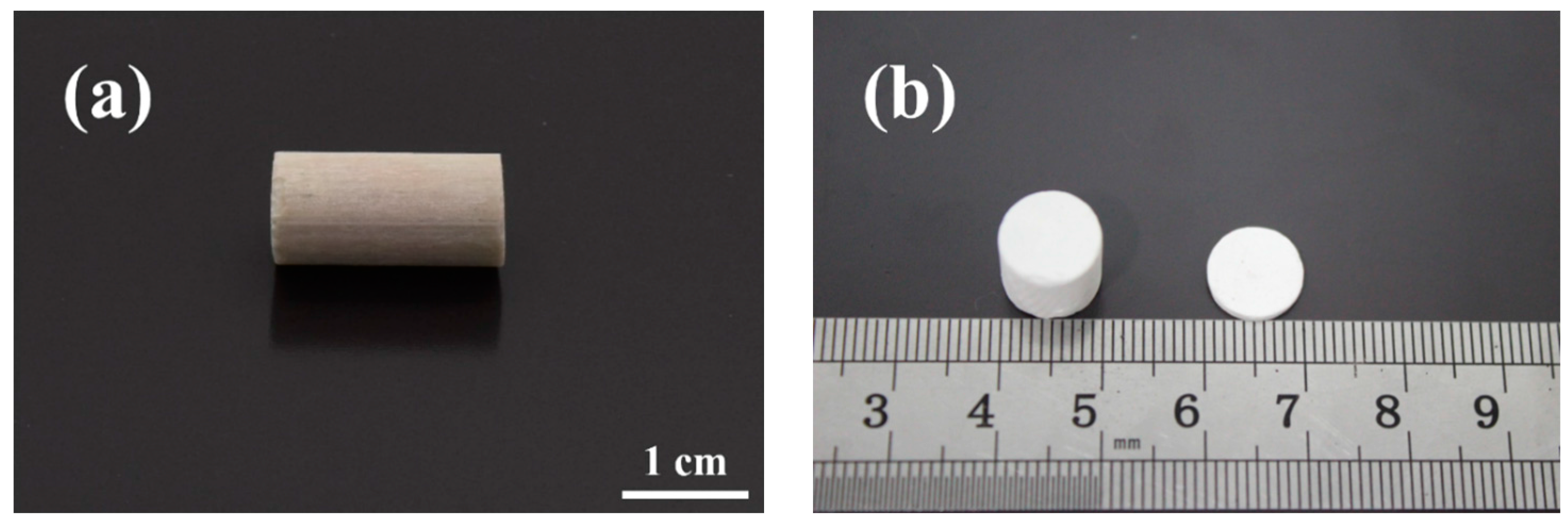
3.1. Structural Integrity
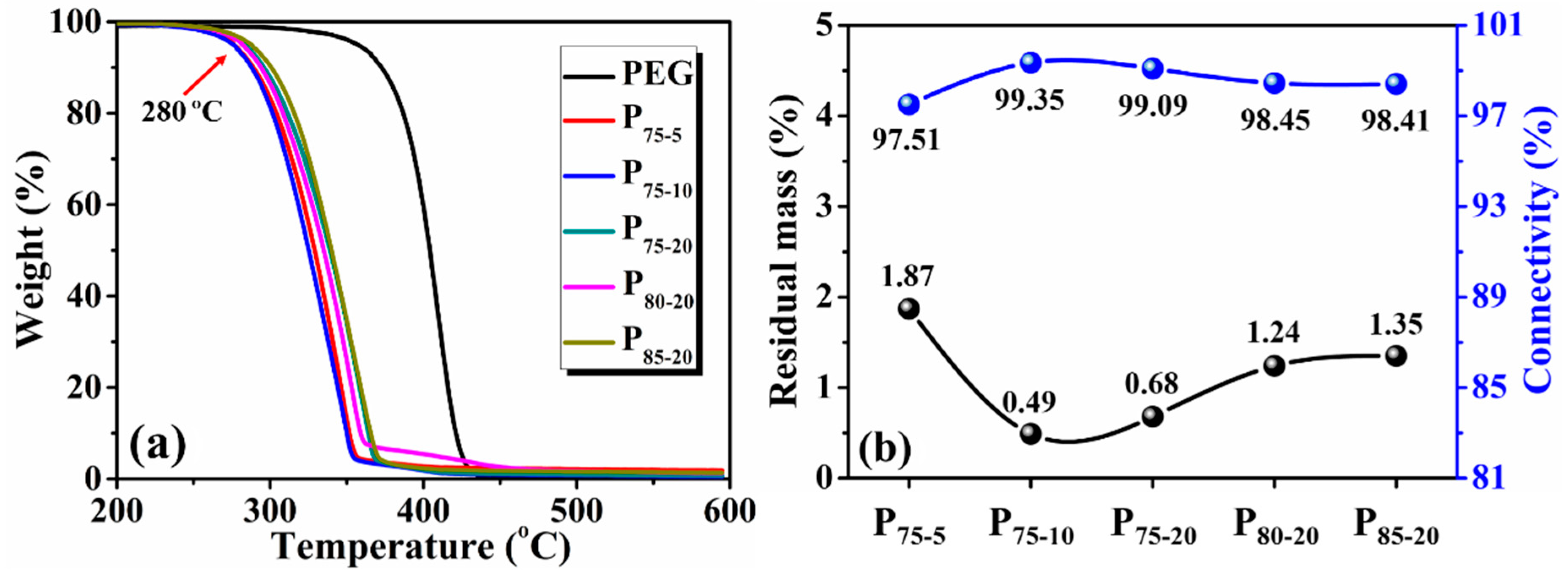
3.2. Residual Mass and Connectivity
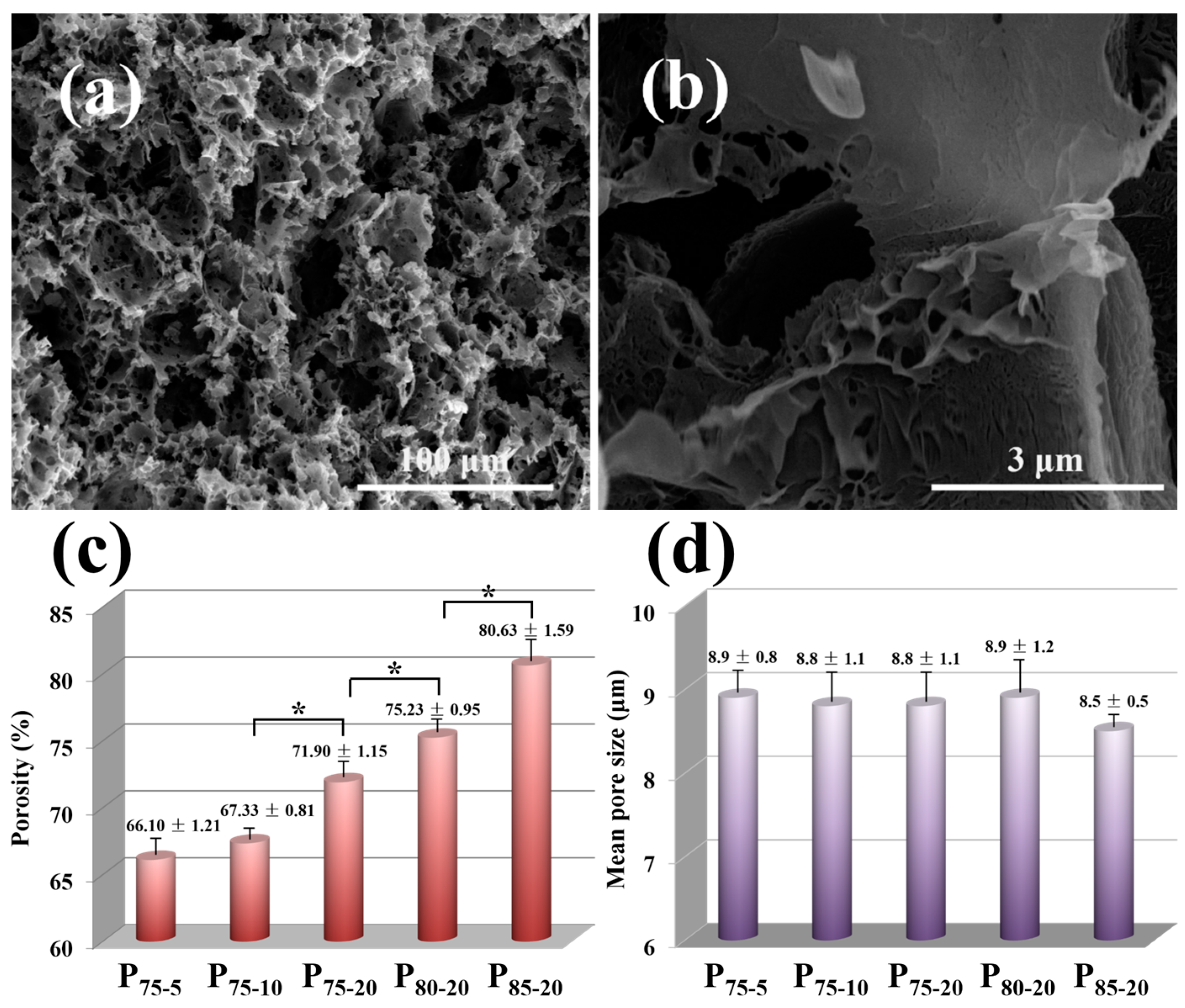
3.3. Morphology and Structure
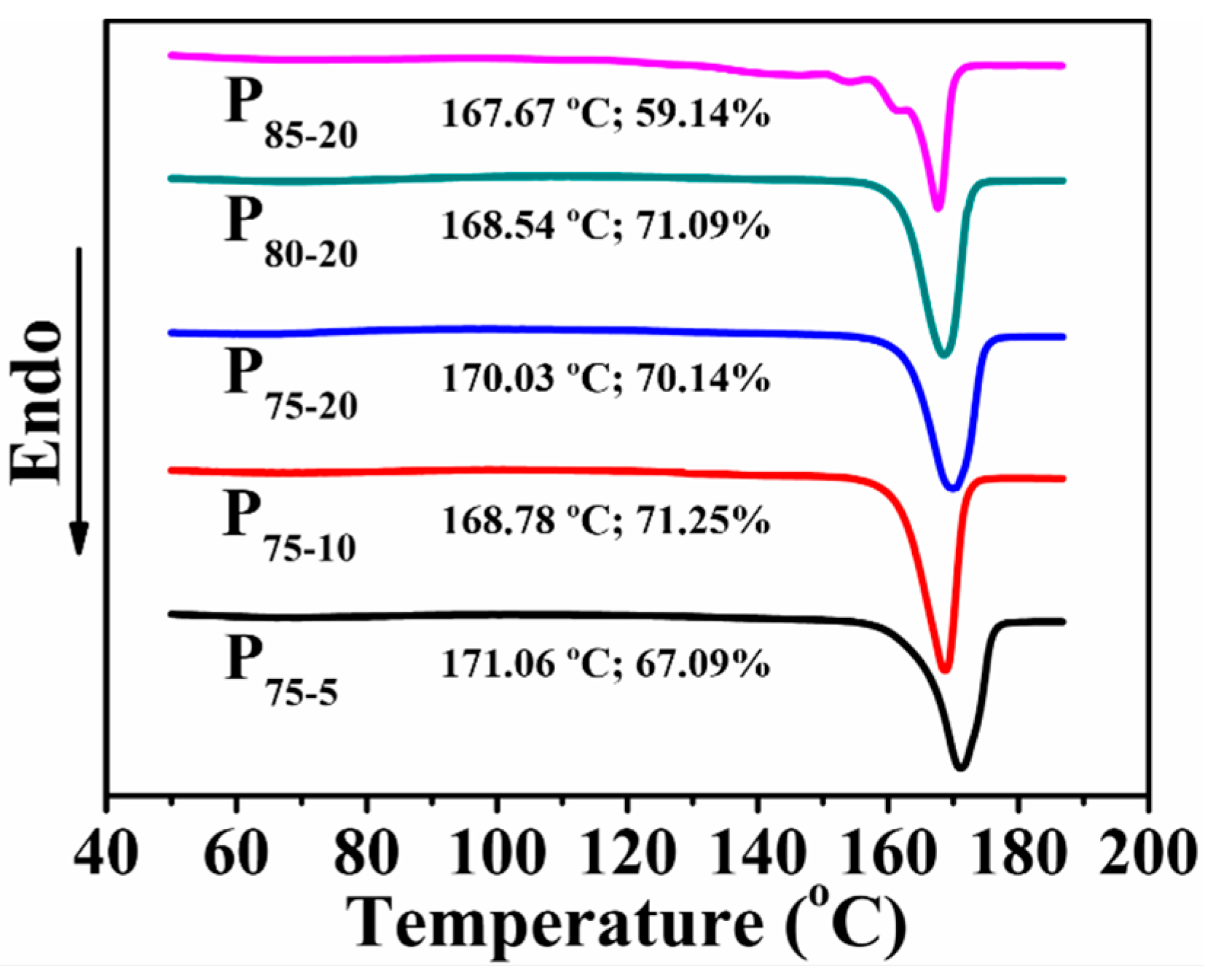
3.4. Thermal Behavior
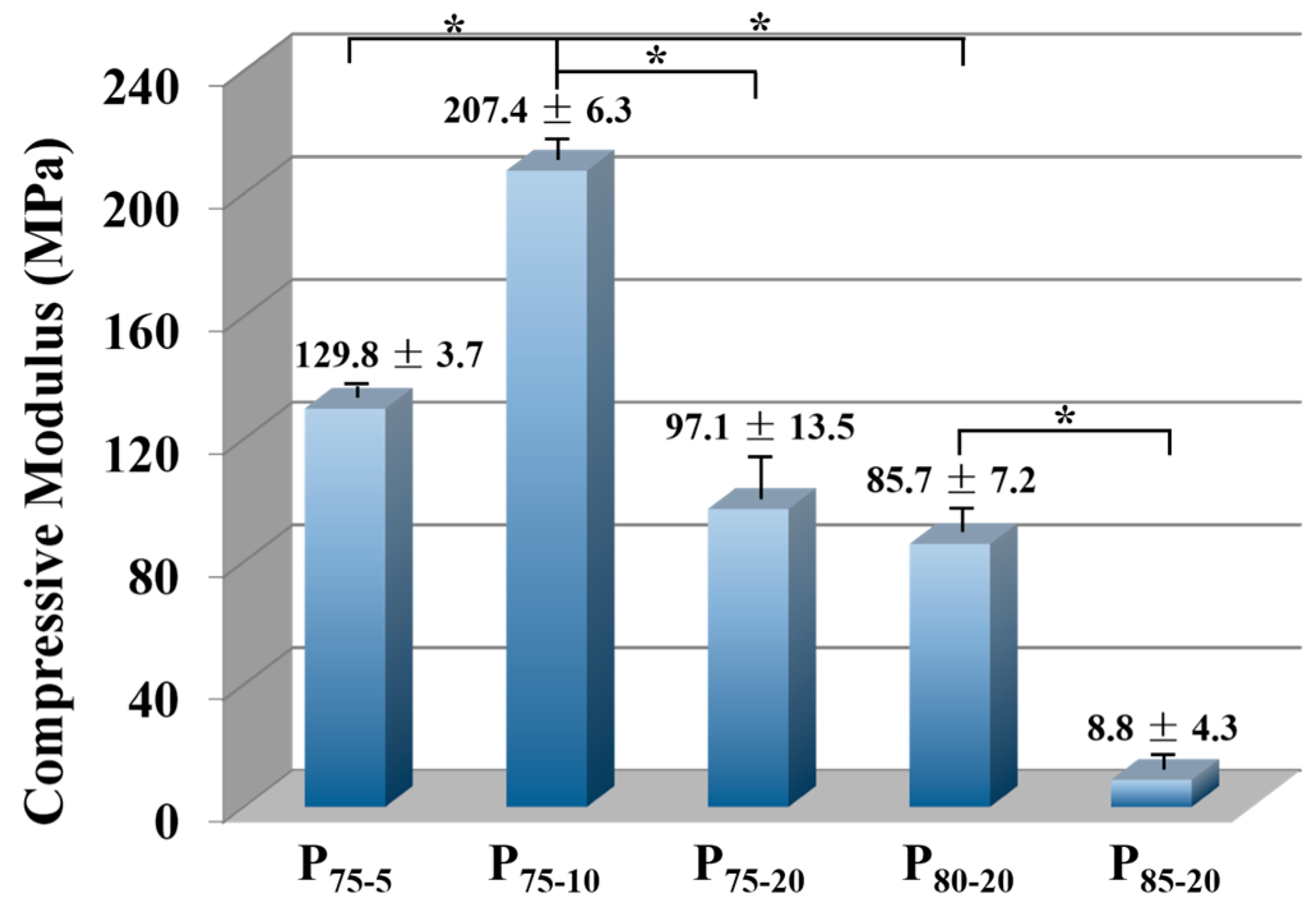
3.5. Compressive Properties
3.6. Surface Wettability
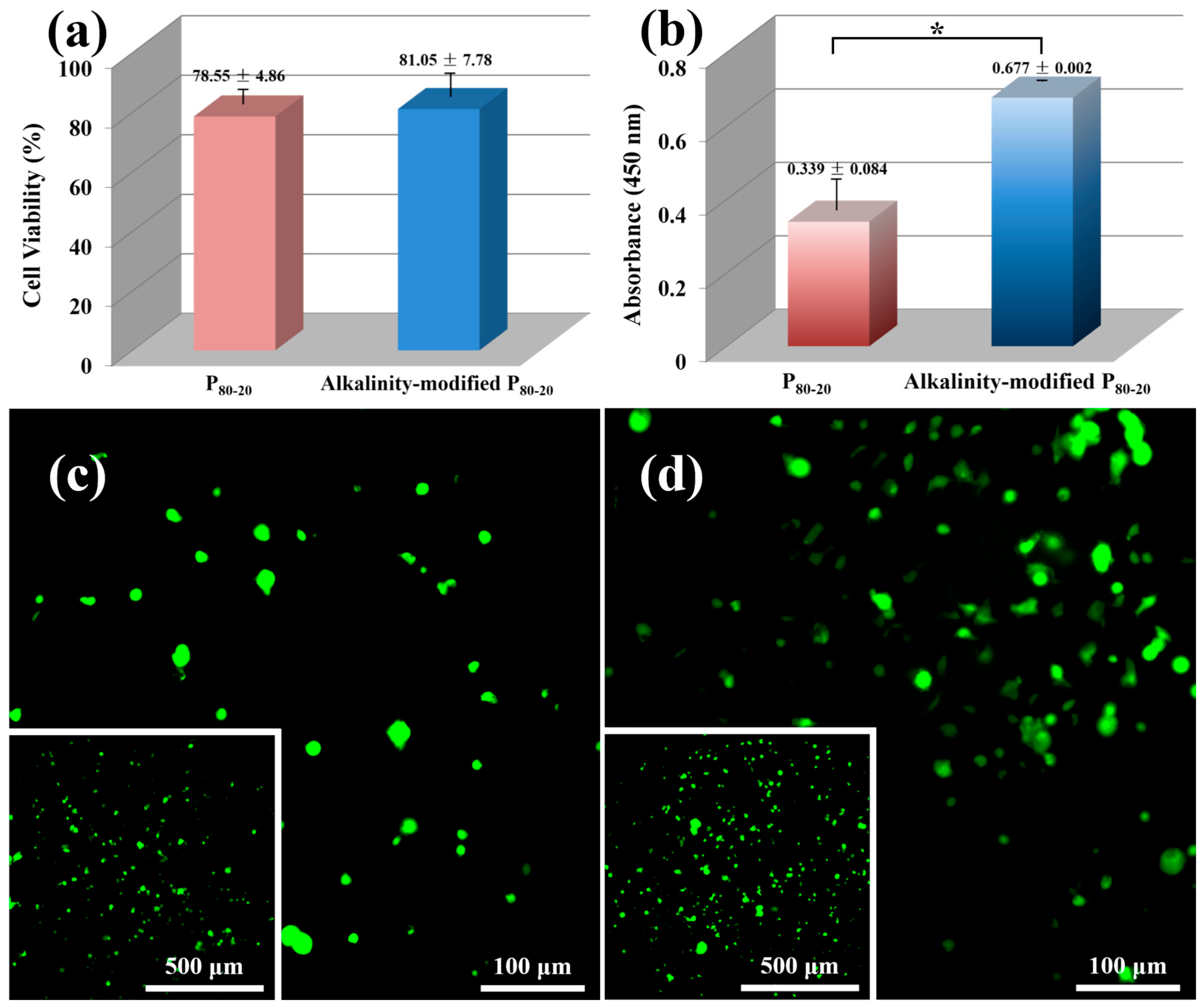
3.7. Cytotoxicity Test and Cell Adhesion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, J.; Cuddihy, M.J.; Kotov, N.A. Three-dimensional cell culture matrices: State of the art. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2008, 14, 61–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzwarth, J.M.; Ma, P.X. Biomimetic nanofibrous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9622–9629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarino, V.; Causa, F.; Taddei, P.; Di Foggia, M.; Ciapetti, G.; Martini, D.; Fagnano, C.; Baldini, N.; Ambrosio, L. Polylactic acid fibre-reinforced polycaprolactone scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 3662–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, G.; Ma, P.X. Partially nanofibrous architecture of 3D tissue engineering scaffolds. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 6426–6434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronca, A.; Ambrosio, L.; Grijpma, D.W. Preparation of designed poly(d,l-lactide)/nanosized hydroxyapatite composite structures by stereolithography. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 5989–5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.F.; Wang, K.; Mei, J.J.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.M.; Zheng, W.T.; An, D.; Xiao, N.N.; Zhao, Q.; Kong, D.L.; et al. Fabrication of highly interconnected porous silk fibroin scaffolds for potential use as vascular grafts. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 2014–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.S.; Mooney, D.J. Engineering smooth muscle tissue with a predefined structure. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1998, 41, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, R.C.; Wake, M.C.; Yaszemski, M.J.; Mikos, A.G. Biodegradable polymer scaffolds to regenerate organs. Adv. Polym. Sci. 1995, 122, 245–274. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, P.X.; Choi, J.W. Biodegradable polymer scaffolds with well-defined interconnected spherical pore network. Tissue Eng. 2001, 7, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Q.P.; Grijpma, D.W.; Feijen, J. Porous polymeric structures for tissue engineering prepared by a coagulation, compression moulding and salt leaching technique. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 1937–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, S.; Choi, C.Y.; Kim, S.H. A poly(lactic acid)/calcium metaphosphate composite for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6314–6322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Vianac, J.C.; Reis, R.L.; Mano, J.F. Development of porous lamellar poly(l-lactic acid) scaffolds by conventional injection molding process. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virgilio, N.; Sarazin, P.; Favis, B.D. Towards ultraporous poly(l-lactide) scaffolds from quaternary immiscible polymer blends. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 5719–5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yin, H.M.; Hsiao, B.S.; Zhong, G.J.; Li, Z.M. Biodegradable poly(lactic acid)/hydroxyl apatite 3D porous scaffolds using high-pressure molding and salt leaching. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 1648–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whang, K.; Thomas, C.H.; Healy, K.E.; Nuber, G. A novel method to fabricate bioabsorbable scaffolds. Polymer 1995, 36, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.C.; Ma, L.; Li, W.; Yao, D.G. Fabrication of tissue engineering scaffolds through solid-state foaming of immiscible polymer blends. Biofabrication 2011, 3, 045003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vissers, C.A.B.; Harvestine, J.N.; Leach, J.K. Pore size regulates mesenchymal stem cell response to Bioglass-loaded composite scaffolds. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 8650–8658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, Y.S.; Park, T.G. Biodegradable polymeric microcellular foams by modified thermally induced phase separation method. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 1783–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Jiang, X.J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.C.; Li, Y.F.; You, Q.Z.; Long, Y.Z. Electrospun anisotropic architectures and porous structures for tissue engineering. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 5389–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, Q.P.; Sharma, U.; Mikos, A.G. Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for tissue engineering applications: A review. Tissue Eng. 2006, 12, 1197–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colosi, C.; Costantini, M.; Latini, R.; Ciccarelli, S.; Stampella, A.; Barbetta, A.; Massimi, M.; Devirgiliis, L.C.; Dentini, M. Rapid prototyping of chitosan-coated alginate scaffolds through the use of a 3D fiber deposition technique. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 6779–6791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, S.; Kas, J.; Fini, F.; Steinberg, M.; Ruml, T. The effect of different solvents on the ATP/ADP content and growth properties of HeLa cells. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 1999, 13, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmer, M.S.; Gupta, P.K.; Lu, L.C.; Meszlenyi, R.K.; Evans, G.R.D.; Brandt, K.; Savel, T.; Gurlek, A.; Patrick, C.W.; Mikos, A.G. Manufacture of porous biodegradable polymer conduits by an extrusion process for guided tissue regeneration. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 1945–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.X.; Nelson, B.; Peng, Y.Y.; Li, K.; Pilla, S.; Li, W.J.; Turng, L.S.; Shen, C.Y. Fabrication and characterization of injection molded poly(ε-caprolactone) and poly(ε-caprolactone)/hydroxyapatite scaffolds for tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 1674–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Huang, W.; Rahaman, M.N.; Day, D.E. Bone regeneration in rat calvarial defects implanted with fibrous scaffolds composed of a mixture of silicate and borate bioactive glasses. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 9126–9136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, C.J.; Keller, A. Direct ram extrusion of polyethylene; a correlation between chain-folding and tensile modulus. J. Mater. Sci. 1977, 12, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, W.G.; Porter, R.S. Solid-state deformation of polyethylene and nylon and its effects on their structure and morphology. J. Mater. Sci. 1977, 12, 2355–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, P.D.; Gibson, A.G.; Ward, I.M. Analysis of the mechanics of solid-phase extrusion of polymers. J. Mater. Sci. 1980, 15, 359–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachariades, A.E.; Mead, W.T.; Porter, R.S. Recent developments in ultra-orientation of polyethylene by solid-state extrusion. Chem. Rev. 1980, 80, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Lim, S.; Kim, Y.H. Improvement of flexural strengths of poly(l-lactic acid) by solid-state extrusion. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2001, 202, 2447–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, S.; Wahl, D.; Gogolewski, S. Enhancement of the mechanical properties of polylactides by solid-state extrusion. II. Poly(l-lactide), poly(l/d-lactide), and poly(l/dl-lactide). J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1996, 30, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakinoki, S.; Yamaoka, T. Thermoresponsive elastin/laminin mimicking artificial protein for modifying PLLA scaffolds in nerve regeneration. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 5061–5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasal, R.M.; Janorkar, A.V.; Hirt, D.E. Poly(lactic acid) modifications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 338–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiebe, J.; Hamm, C.W.; Nef, H.M. Bioresorbable scaffolds in daily clinical routine: A practical review of all-comers results. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2015, 30, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasal, R.M.; Hirt, D.E. Toughness decrease of PLA-PHBHHx blend films upon surface-confined photopolymerization. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2009, 88A, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.H.; Chen, B.Y.; Zhao, H.B.; Yu, P.; Fu, D.J.; Wen, J.S.; Peng, X.F. Processing and characterization of supercritical CO2 batch foamed poly(lactic acid)/poly(ethylene glycol) scaffold for tissue engineering application. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 3066–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens, E.; Del Valle, L.J.; Ferrán, R.; Rodríguez-Galán, A.; Puiggalí, J. Scaffolds with tuneable hydrophilicity from electrospun microfibers of polylactide and poly(ethylene glycol) mixtures: Morphology, drug release behavior, and biocompatibility. J. Polym. Res. 2014, 21, 360–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcelik, B.; Blencowe, A.; Palmer, J.; Ladewig, K.; Stevens, G.W.; Abberton, K.M.; Morrison, W.A.; Qiao, G.G. Highly porous and mechanically robust polyester poly(ethylene glycol) sponges as implantable scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 2769–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, T.; Ortiz-Hernandez, M.; Engel, E.; Planell, J.A.; Navarro, M. Relevance of PEG in PLA-based blends for tissue engineering 3D-printed scaffolds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 38, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Mi, H.Y.; Yu, P.; Kuang, T.R.; Peng, X.F.; Wen, J.S. Effect of poly(ethylene glycol) on the properties and foaming behavior of macroporous poly(lactic acid)/sodium chloride scaffold. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, E.W.; Sterzel, H.J.; Wegner, G. Investigation of structure of solution grown crystals of lactide copolymers by means of chemical-reactions. Kolloid Z. Z. Polym. 1973, 251, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.B.; Jing, D.Y.; Ding, J.D. A “room-temperature” injection molding/particulate leaching approach for fabrication of biodegradable three-dimensional porous scaffolds. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reignier, J.; Huneault, M.A. Preparation of interconnected poly(ε-caprolactone) porous scaffolds by a combination of polymer and salt particulate leaching. Polymer 2006, 47, 4703–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Liu, X.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Liu, C.; Yang, X. Biomimetic porous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2014, 80, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.M.; Qu, X.; Han, B.X.; Bei, J.Z.; Wang, S.G. Adhesion and proliferation of OCT-1 osteoblast-like cells on micro-and nano-scale topography structured poly(l-lactide). Biomaterials 2005, 26, 4453–4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Viana, J.C.; Reis, R.L.; Mano, J.F. The double porogen approach as a new technique for the fabrication of interconnected poly(l-lactic acid) and starch based biodegradable scaffolds. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2007, 18, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.H.; Ma, P.X. Polymeric scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 32, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yan, D.X.; Lei, J.; Xu, J.Z.; Hsiao, B.S.; Li, Z.M. Ultraporous poly(lactic acid) scaffolds with improved mechanical performance using high-pressure molding and salt leaching. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 3509–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrossamay, M.R.; Balachandran, K.; Capulli, A.K.; Golecki, H.M.; Agarwal, A.; Goss, J.A.; Kim, H.; Shin, K.; Parker, K.K. Engineering hybrid polymer-protein super-aligned nanofibers via rotary jet spinning. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 3188–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.M.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.B.; Lei, J.; Xu, J.Z.; Li, Z.M. Effects of extrusion draw ratio on the morphology, structure and mechanical properties of poly(l-lactic acid) fabricated using solid state ram extrusion. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 69016–69023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Todo, M. Characterization of compressive deformation behavior and biocompatibility of bioabsorbable layered PLLA scaffolds. IFMBE Proc. 2010, 31, 1230–1233. [Google Scholar]
- Acosta Santamaría, V.; Deplaine, H.; Mariggió, D.; Villanueva-Molines, A.R.; García-Aznar, J.M.; Gómez Ribelles, J.L.; Doblaré, M.; Gallego Ferrer, G.; Ochoa, I. Influence of the macro and micro-porous structure on the mechanical behavior of poly(l-lactic acid) scaffolds. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2012, 358, 3141–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzati, P.; Ghasemi, I.; Karrabi, M.; Azizi, H.; Fortelny, I. Preparation of porous PLLA/PCL blend by a combination of PEO phase and NaCl particulate leaching in PLLA/PCL/PEO/NaCl blend. Iran. Polym. J. 2014, 23, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.S.P.; Barrows, T.H.; Cartmell, S.H.; Guldberg, R.E. Microarchitectural and mechanical characterization of oriented porous polymer scaffolds. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.H.; Kang, S.G.; Kim, E.S.; Cho, S.H.; Lee, J.H. Fabrication and characterization of hydrophilic poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)/poly(vinyl alcohol) blend cell scaffolds by melt-molding particulate-leaching method. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4011–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| P75-5 | P75-10 | P75-20 | P80-20 | P85-20 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaCl (wt %) | 75.00 | 75.00 | 75.00 | 80.00 | 85.00 |
| PEG (wt %) | 1.25 | 2.50 | 5.00 | 4.00 | 3.00 |
| PLA (wt %) | 23.75 | 22.50 | 20.00 | 16.00 | 12.00 |
| MR (wt %) 1 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Theoretical porosity (%) | 65.66 | 67.55 | 71.29 | 76.28 | 81.62 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, H.-M.; Qian, J.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Z.-F.; Li, J.-S.; Xu, J.-Z.; Li, Z.-M. Engineering Porous Poly(lactic acid) Scaffolds with High Mechanical Performance via a Solid State Extrusion/Porogen Leaching Approach. Polymers 2016, 8, 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8060213
Yin H-M, Qian J, Zhang J, Lin Z-F, Li J-S, Xu J-Z, Li Z-M. Engineering Porous Poly(lactic acid) Scaffolds with High Mechanical Performance via a Solid State Extrusion/Porogen Leaching Approach. Polymers. 2016; 8(6):213. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8060213
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Hua-Mo, Jing Qian, Jin Zhang, Zai-Fu Lin, Jian-Shu Li, Jia-Zhuang Xu, and Zhong-Ming Li. 2016. "Engineering Porous Poly(lactic acid) Scaffolds with High Mechanical Performance via a Solid State Extrusion/Porogen Leaching Approach" Polymers 8, no. 6: 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8060213
APA StyleYin, H.-M., Qian, J., Zhang, J., Lin, Z.-F., Li, J.-S., Xu, J.-Z., & Li, Z.-M. (2016). Engineering Porous Poly(lactic acid) Scaffolds with High Mechanical Performance via a Solid State Extrusion/Porogen Leaching Approach. Polymers, 8(6), 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8060213