Multi-Scale Synergistic Mechanism of Damping Performance in Crumb Rubber-Modified Asphalt
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Specimens
2.3. Experimental Section
2.3.1. Dynamic Shear Rheometer (DSR) Test
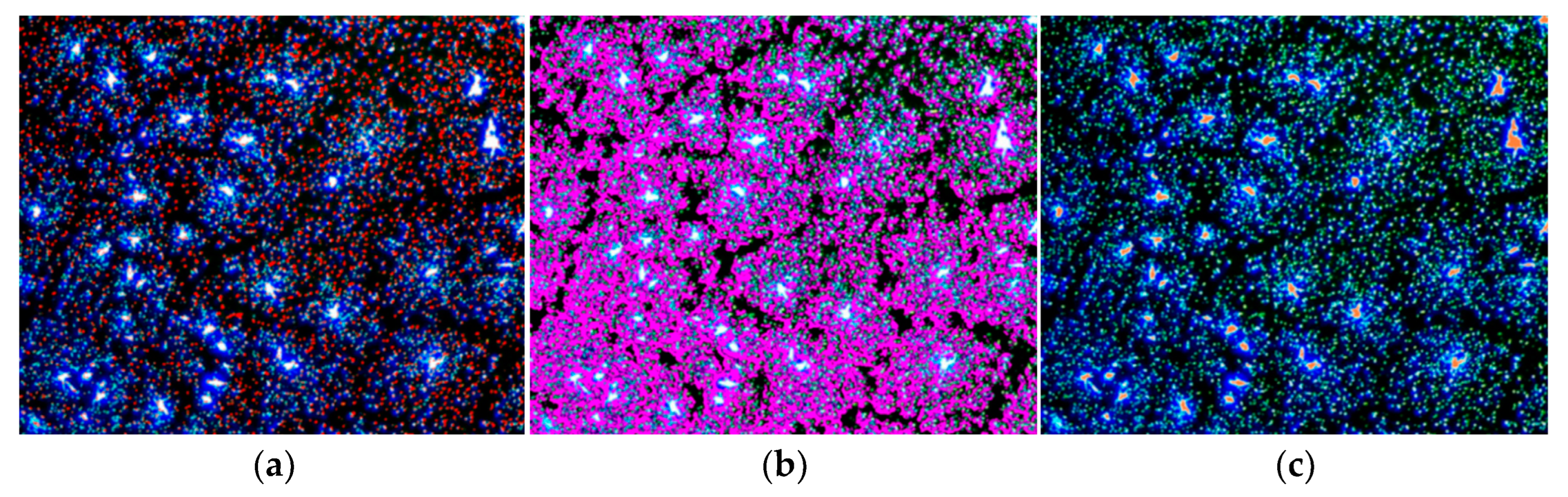
2.3.2. Fluorescence Microscopy (FM) Test
2.4. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulation
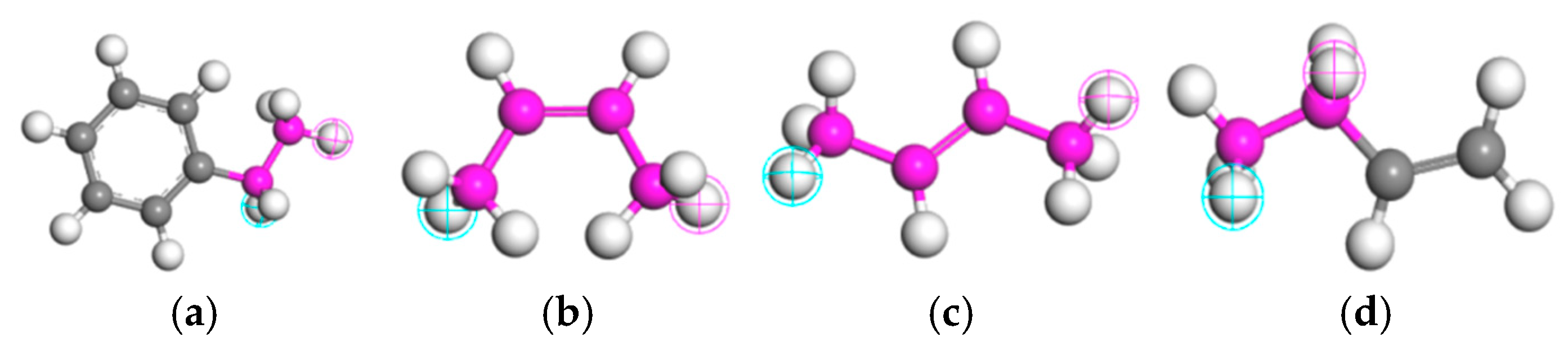
2.4.1. Molecular Composition of Base Asphalt
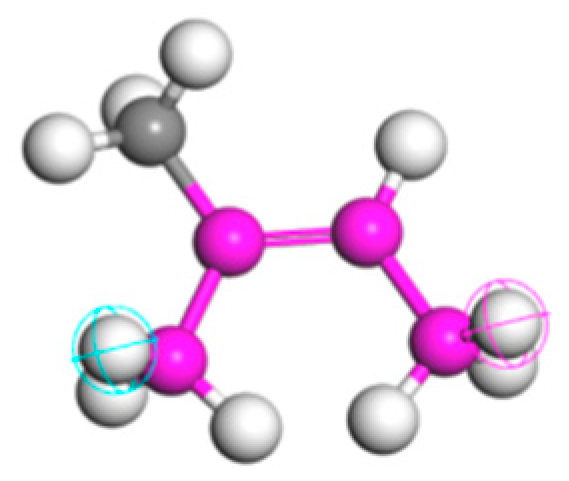
2.4.2. Molecular Composition of Crumb Rubber
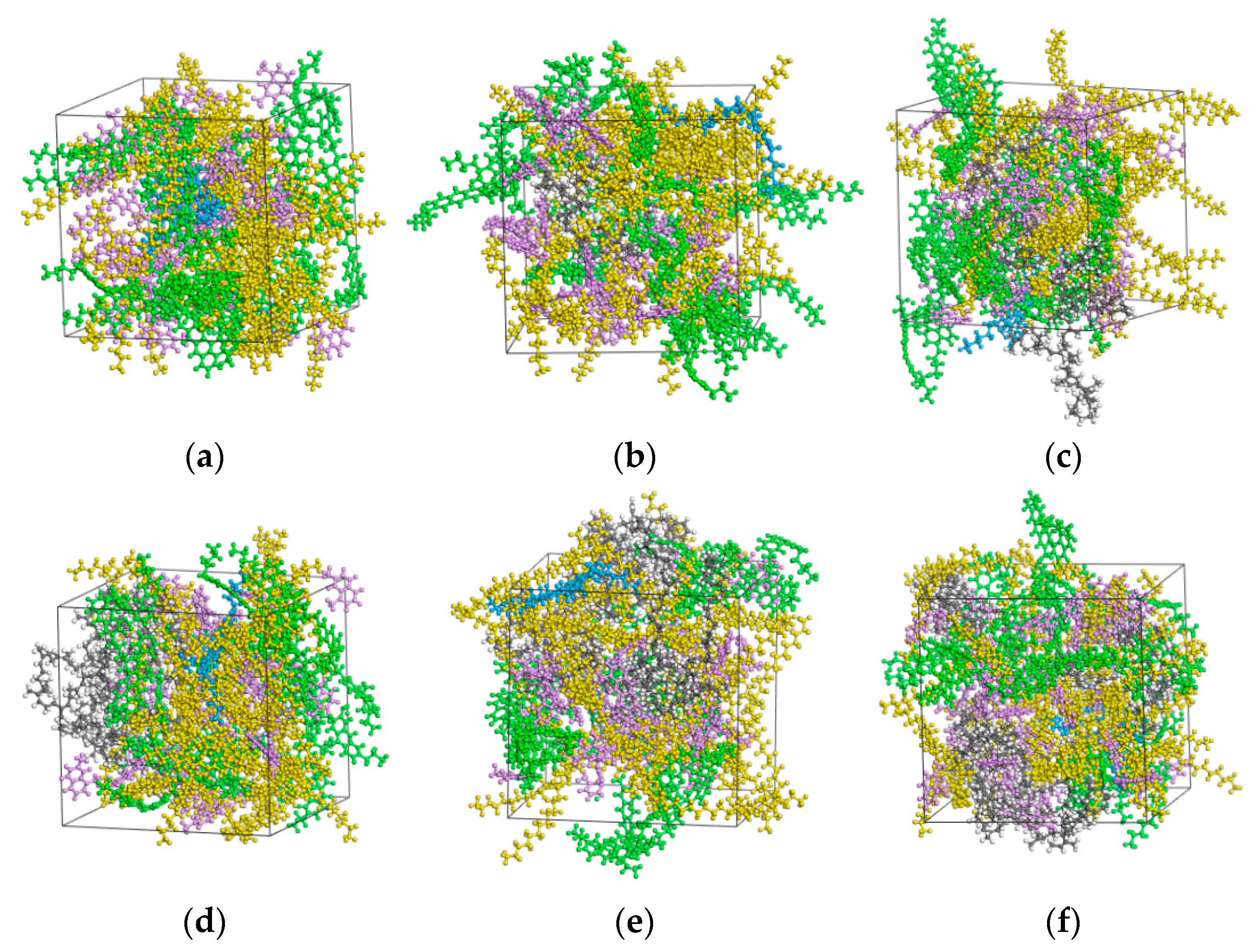
2.4.3. Construction of MD Models
3. Results and Discussion
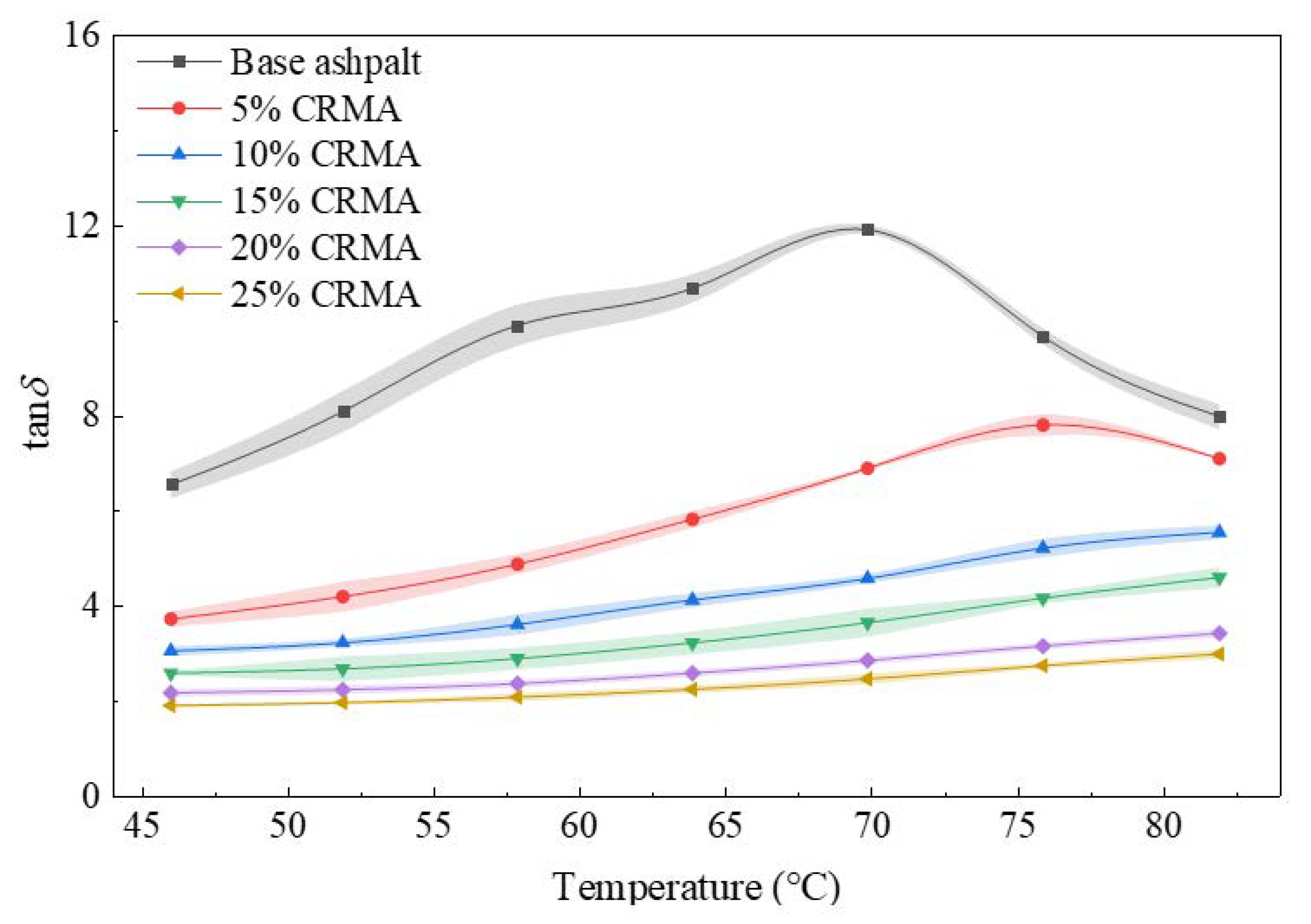
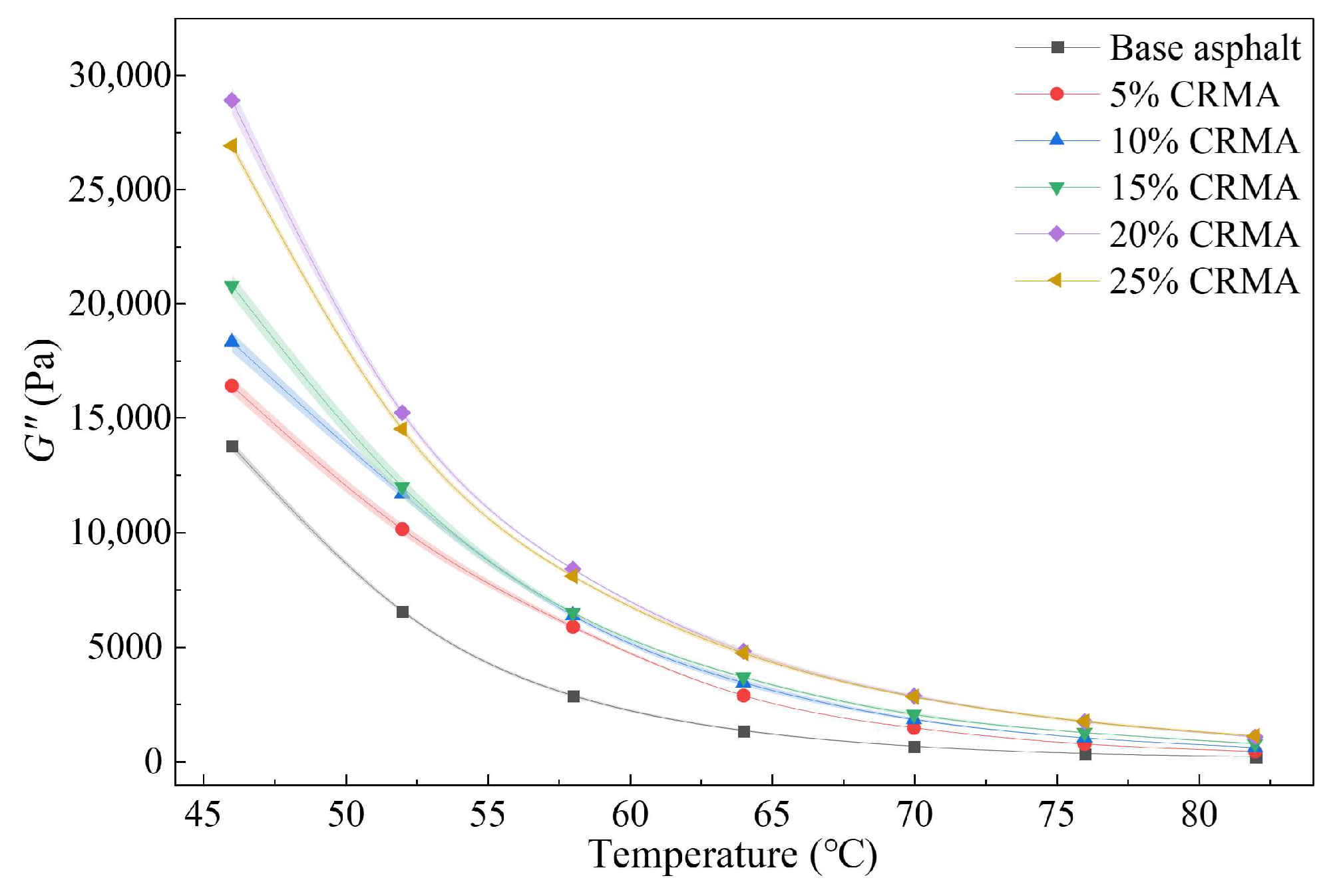
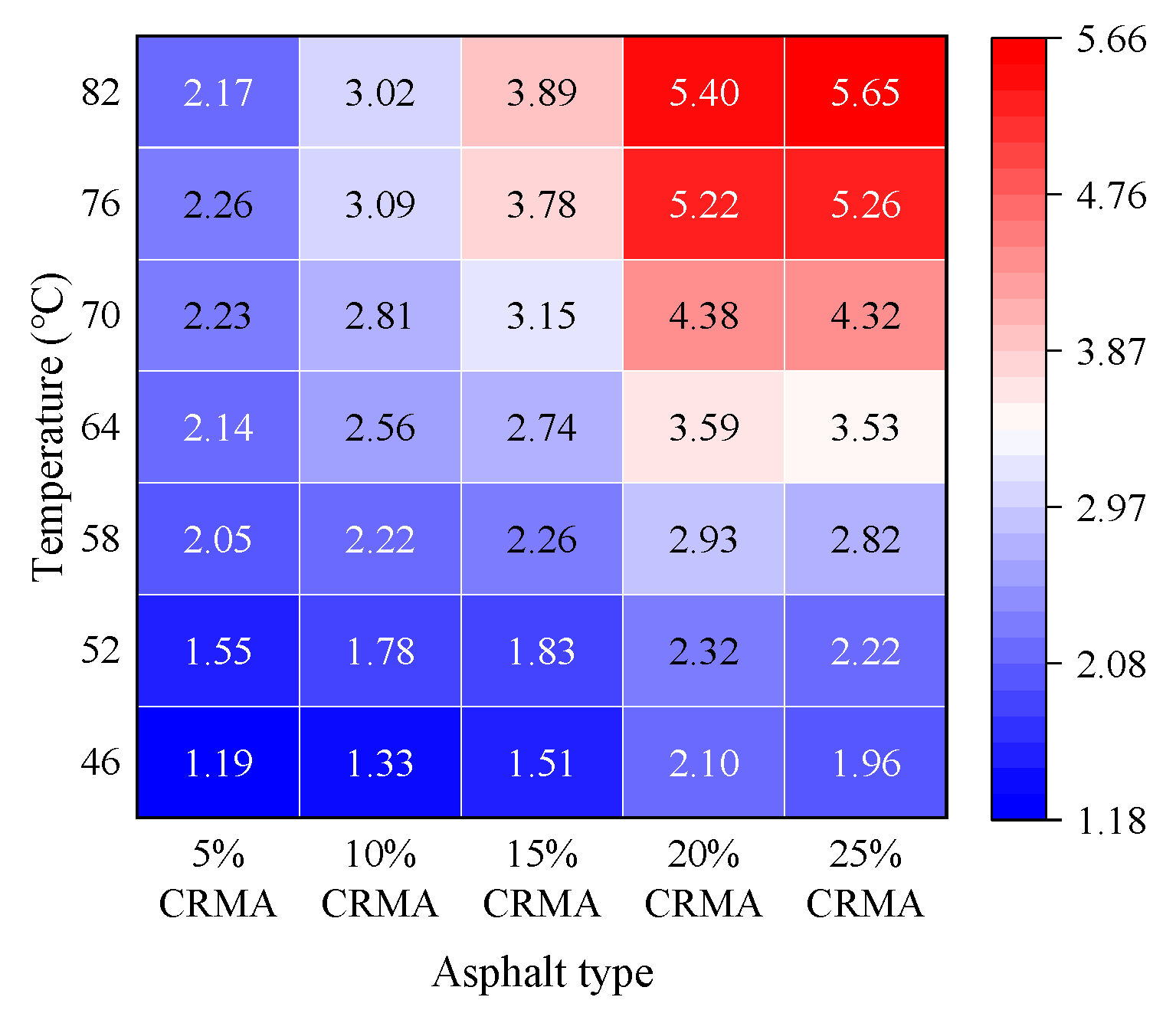
3.1. DSR Test Results
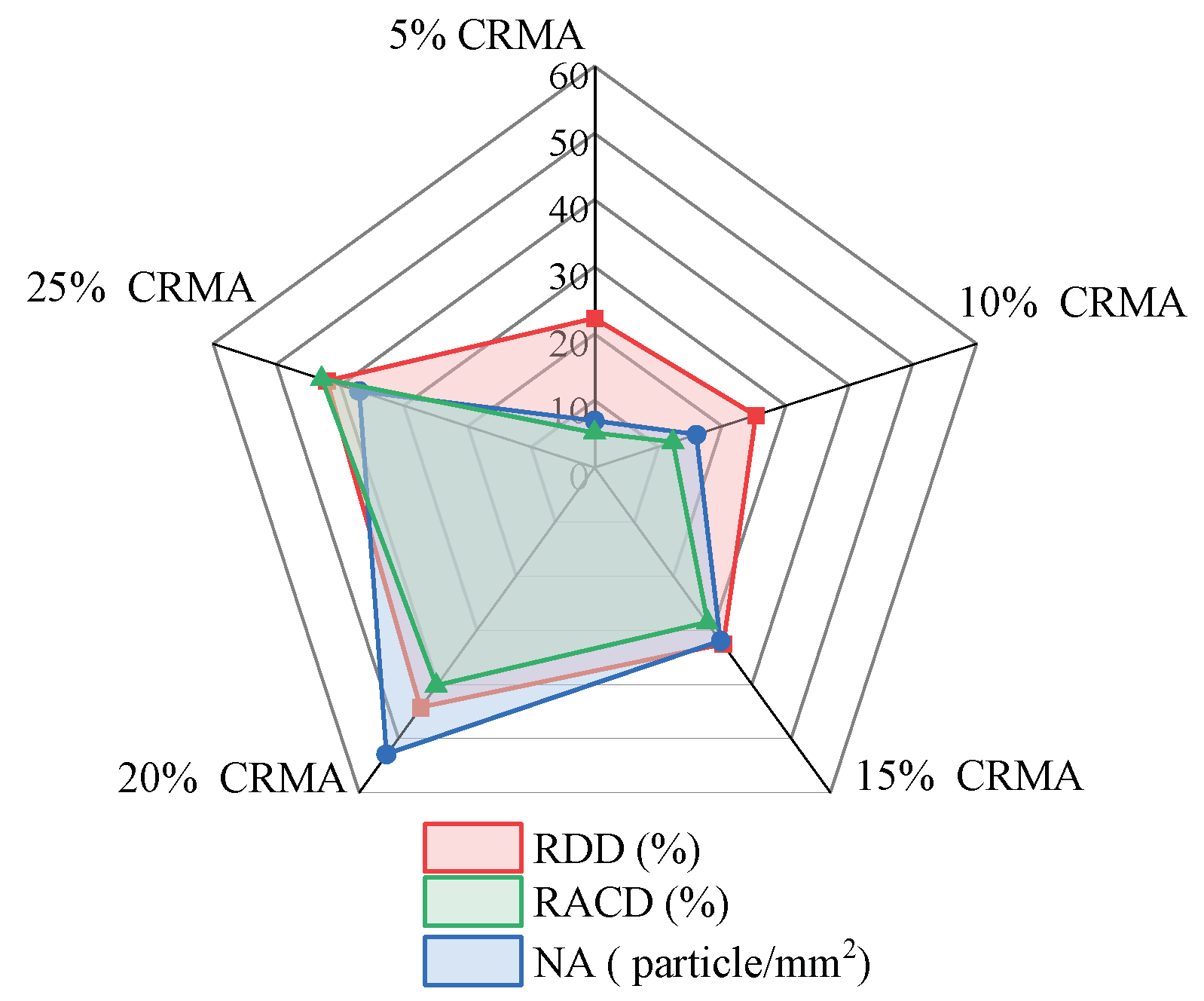
3.2. FM Test Results
3.3. MD Simulation Results
3.3.1. Solubility Parameter
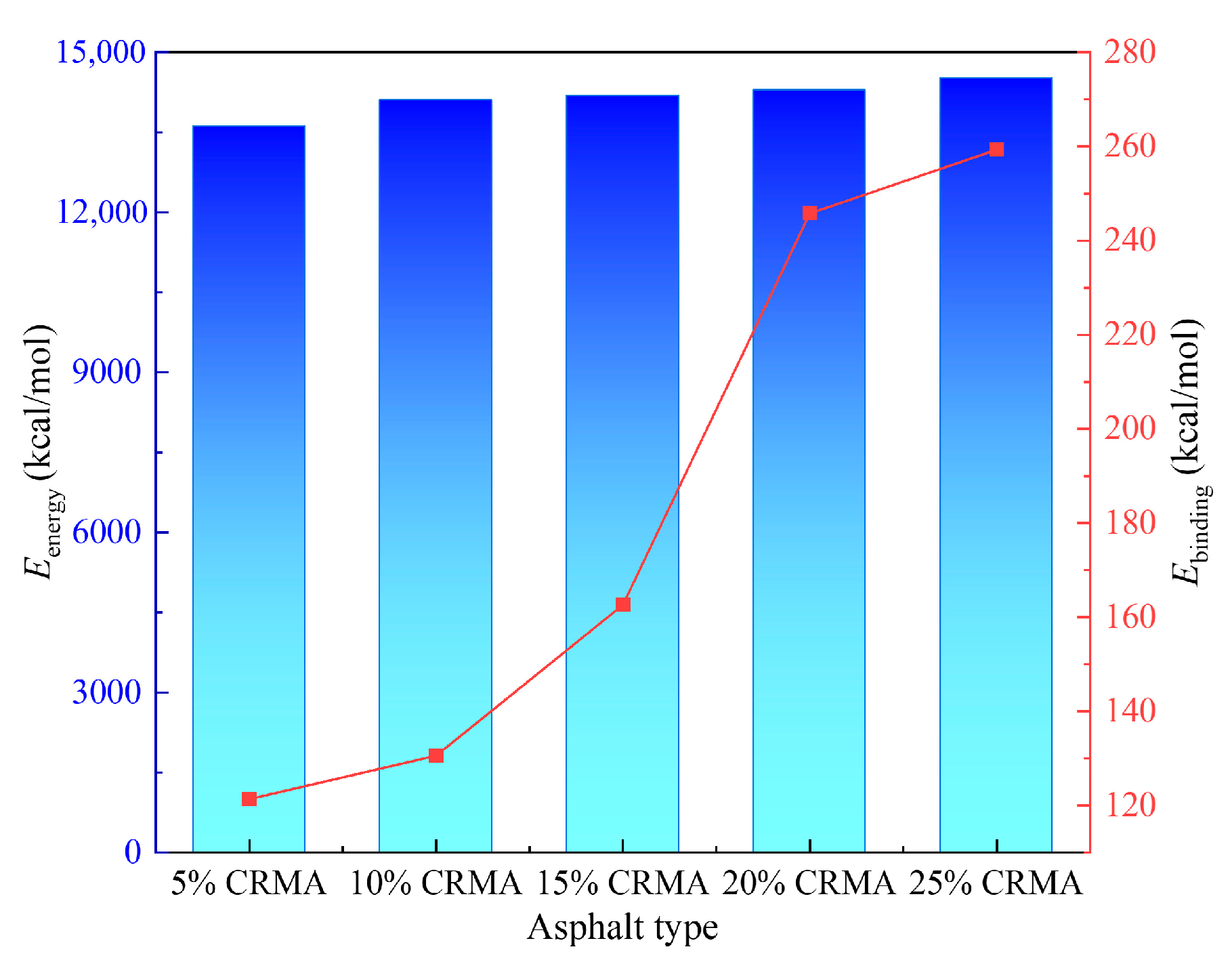
3.3.2. Binding Energy
3.4. Quantitative Integration of Multi-Scale Parameters Using Gray Relational and Ridge Regression Analyses
3.4.1. Gray Relational Analysis
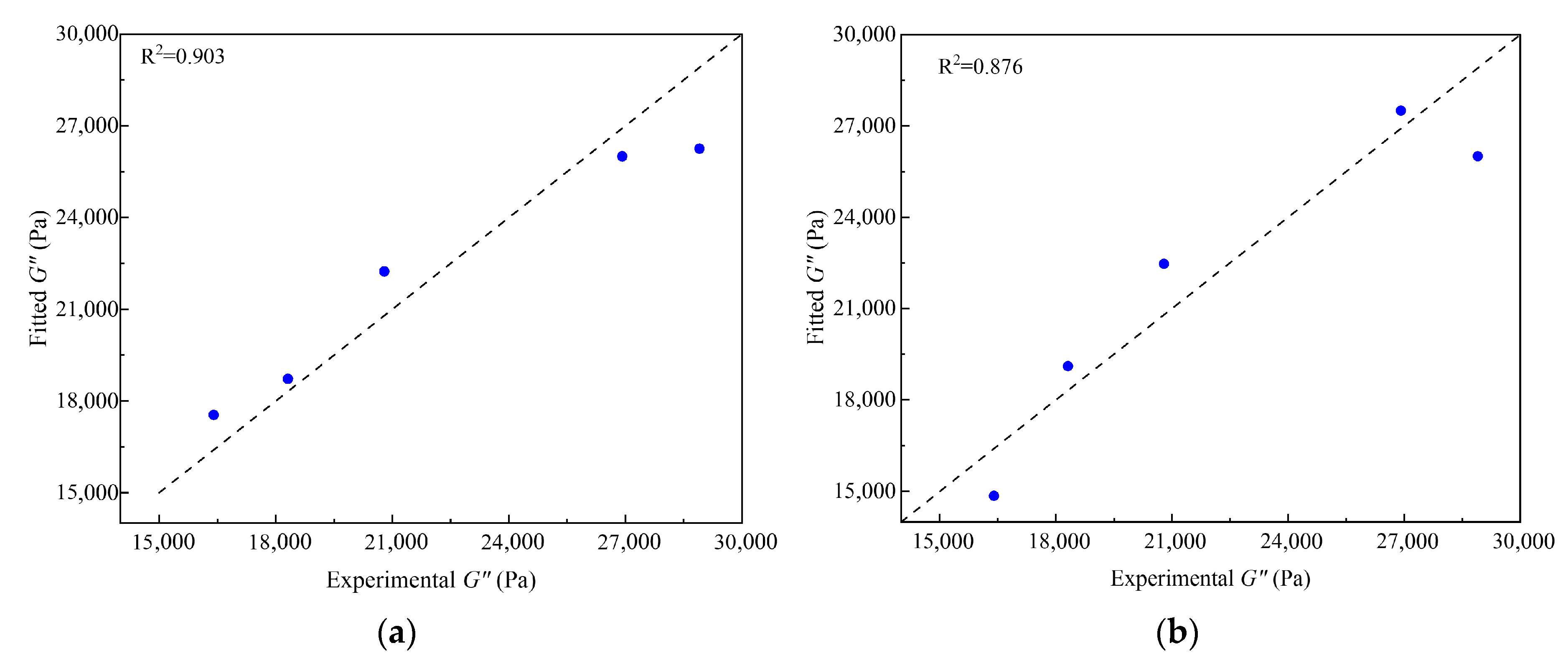
3.4.2. Ridge Regression Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CRMA | Crumb rubber-modified asphalt |
| DSR | Dynamic shear rheometer |
| FM | Fluorescence microscopy |
| MD | Molecular dynamics |
| Tan δ | Loss factor |
| G” | Loss modulus |
| NR | Natural rubber |
| SBR | Styrene-butadiene rubber |
| RDD | Rubber dispersion degree |
| RACD | Relative area of colloidal domains |
| NA | Number of agglomerates per unit area |
| CED | Cohesive energy density |
| ΔE | Cohesive energy |
| V | Volume |
| δs | Solubility parameter |
| Ebinding | binding energy |
| ECRMA | Total energy of the CRMA in its equilibrium state |
| Easphalt | Total energy of asphalt in its equilibrium state |
| Erubber | Total energy of crumb rubber in its equilibrium state |
References
- Yang, Z.N.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, W.; Lv, J.H.; Lu, Z.C.; Ling, X.Z. Advances in Properties of Rubber Reinforced Soil. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 6629757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, Z.T. Remanufactured waste tire by-product valorization: Quantitative-qualitative sustainability-based assessment. Results Eng. 2024, 22, 102229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Shen, A.; Cui, H.; Dai, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, J. Effect of Crumb Rubber Particles on Antisliding and Noise-Reduction Performance of Asphalt Pavement. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2023, 35, 04023118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.T.; Mendes, F.G. City noise-air: An environmental quality index for cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2012, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.O.; Ghosh, S. Urban cities and road traffic noise: Reduction through vegetation. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 120, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.L.; Easa, S.M.; Hu, C.B.; Zheng, X.Y. Understanding damping performance and mechanism of crumb rubber andstyrene-butadiene-styrene compound modified asphalts. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 206, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biligiri, K.P.; Way, G.B. Noise-damping characteristics of different pavement surface wearing courses. Road. Mater. Pavement. Des. 2014, 15, 925–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boodihal, M.A.; Chethan, A.; Swamy, R.; Sahu, R.; Biligiri, K.P. Case study development of tyre/road noise assessment methodology in India. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2014, 1, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Hu, C.; Easa, S.; Zheng, X.; Halim, A. Identifying optimal polymer type of modified asphalt based on damping characteristics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 173, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.Y.; Tong, Z.L.; Ren, Q.B.; Li, Z.G.; Wang, J.L. Modification of the Crumb Rubber Asphalt by Eucommia Ulmoides Gum under a High-Temperature Mixing Process. Coatings 2024, 14, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Zhao, H.S.; Zhang, D.F.; Zhang, P.Y.; Ding, Y.P.; Liu, Y.P.; Su, C.; Han, Q.J.; Li, Y.R. Study on the Volatile Organic Compound Emission Characteristics of Crumb Rubber-Modified Asphalt. Coatings 2025, 15, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.K.; Wang, R.H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, B.; Fan, Y.H.; Yu, W.W.; Zheng, Q.; Zhu, F.B. Hybrid Devulcanized/Vulcanized Crumb Rubber Strategy for High-Performance Asphalt with over 40% Recycled Tire Rubber Content. Polymers 2025, 17, 2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkenzheyeva, A.; Haritonovs, V.; Bussurmanova, A.; Merijs-meri, R. The Use of Rubber-Polymer Composites in Bitumen Modification for the Disposal of Rubber and Polymer Waste. Polymers 2024, 16, 3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biligiri, K.P.; Kalman, B.; Samuelsson, A. Understanding the fundamental material properties of low-noise poroelastic road surfaces. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2013, 14, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, E.; Xu, H.K.; Sun, Z.Y. Composition optimization and damping performance evaluation of porous asphalt mixture containing recycled crumb rubber. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavridou, S.; Kehagia, F. Noise Reduction in Pavement Made of Rubberized Bituminous Top Layer. Open J. Civ. Eng. 2014, 4, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Ge, D.; Wang, J.; Malburg, L.; You, Z. Reconstruction of Asphalt Pavements with Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt Mixture in Cold Region: Material Characterization, Construction, and Performance. Materials 2023, 16, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Deng, Y.; Ni, H.T.; Sun, D.Q.; Ling, S.L.; Tian, Y.F. Effect of aging on damping properties of rubberized asphalt binder and rubberized porous asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Chen, T.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Xie, J.; Wu, S.; Xu, H.; Zhao, P.; et al. Diffusion mechanism of waste crumb rubber composite modified asphalt based on molecular dynamics simulation. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 482, 144155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, H.; Ye, Q. Effects of biological desulfurization on storage stability of crumb rubber modified asphalt: Experimental analysis and molecular simulation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 482, 141728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, Y.; Lei, L.; Zhao, Y.; Li, F.; Xue, Y. Viscosity reduction mechanism and rheological properties of ethylene-bis-stearamide and crumb rubber modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 412, 134830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, L. Modification and Aging Mechanism of Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt Based on Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Materials 2025, 18, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.W.; Gao, S.J.; He, Y.H.; Liu, Q.T.; Zhuang, R.H.; Zeng, S.H.; Duan, H.; Yu, J.Y. Effect of Dynamic Disulfide Bonds on Microstructure, Storage Stability, and Self-Healing Performance of Desulfurized Waste Crumb Rubber-Modified Asphalt. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2025, 37, 04025122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG E20-2011; Standard Test Methods of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway Engineering. Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- JT/T 797-2019; Ground Vulcanized Rubber of Scrap Tires for Highway Engineering. Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- JT/T 798-2019; Crumb Rubber Asphalt for Highway Engineering. Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Gao, M.X.; Fan, C.H.; Chen, X.X.; Li, M.J. Study on Ultraviolet Aging Performance of Composite Modified Asphalt Based on Rheological Properties and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 2022, 7894190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, J.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Huang, W.; Wang, X.; Xie, J. Investigation on microstructure characteristics of crumb rubber compound modified asphalt at preparation process. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2024, 25, 1756–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.J. A comprehensive study on the rheological properties of desulfurized rubberized asphalt and establishment of micro-scale mechanical models. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Xia, T.; Xu, J.H.; Li, Y.B.; Wang, M. Effect of polyurethane addition on the dynamic mechanical properties of cement emulsified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 401, 132693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AASHTO T 315-20; Standard Method of Test for Determining the Rheological Properties of Asphalt Binder Using a Dynamic Shear Rheometer (DSR). American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2020.
- AASHTO M 320-22; Standard Specification for Performance-Graded Asphalt Binder. American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2022.
- Hu, Y.; Yu, J.; Cui, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Guo, W.; Zhao, C.; Chen, X.; Meng, M.; Li, Y.; et al. Combination Usage of AdipoCount and Image-Pro Plus/ImageJ Software for Quantification of Adipocyte Sizes. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 642000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.Y.; Yang, K.D.; Wang, X. Quick measurement of all filaments’ diameters in E-glass yarn by Image-Pro Plus. J. Ind. Text. 2022, 51, 1376–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storm, D.A.; Edwards, J.C.; Decanio, S.J.; Sheu, E.Y. Molecular representations of Ratawi and Alaska north slope asphaltenes based on liquid-and solid-state NMR. Energy Fuels 1994, 8, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Q.; Greenfield, M.L. Analyzing properties of model asphalts using molecular simulation. Energy Fuels 2007, 21, 1712–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Dong, Z.J.; Tan, Y.Q.; Liu, Z.Y. Investigating the interactions of the saturate, aromatic, resin, and asphaltene four fractions in asphalt binders by molecular simulations. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.X.; Chen, Y.L.; Fan, C.H.; Li, M.J. Molecular dynamics study on the compatibility of asphalt and crumb rubber with different component contents. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 36157–36164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.C.; Zhang, J.P.; Pei, J.Z.; Ma, W.S.; Hu, Z.; Guan, Y.S. Evaluation of the compatibility between rubber and asphalt based on molecular dynamics simulation. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 2020, 14, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; You, Z.; Jin, D. Adhesion Performance of Rubber Modified Asphalt in Chip Seal: A Molecular Dynamic Study. Materials 2023, 16, 6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Liu, J.; Xu, M.; Ji, J.; Dai, Q.; You, Z. Discussion on molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of the asphalt materials. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 299, 102565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, B.Z.; Pan, B.F.; Che, T.K. Evaluating impacts of desulfurization and depolymerization on thermodynamics properties of crumb rubber modified asphalt through molecular dynamics simulation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 323, 126360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.S.; Chakravorty, A.; Kalayan, J.; de Visser, S.P.; Henchman, R.H. Energy-entropy method using multiscale cell correlation to calculate binding free energies in the SAMPL8 host–guest challenge. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2021, 35, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Zeng, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Dai, Q.; You, Z. Perspectives on the Application of Waste Materials in Asphalt Based on Molecular Dynamics Simulations: A Review. Energy Fuels 2024, 38, 14839–14865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Xu, Z.-D.; Xu, Y.; Guo, Y.-Q.; Huang, X.-H.; Dong, Y.-R.; Shah, A. Mechanical and Damping Properties Analyses of Small Molecular Modifiers/Nitrile-Butadiene Rubber Composite: Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Macromol. Theory Simul. 2023, 32, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, B.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Guo, R.; Yu, X. Functionalised Conductive Elastomers for Strain Monitoring of Seismic Isolation Bearings: Experiments and Molecular Simulations. Eng. Sci. 2025, 34, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ni, H.T.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, D.Q.; Zheng, Y.P.; Hu, M.J. Porous asphalt mixture use asphalt rubber binders: Preparation and noise reduction evaluation. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 376, 134119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

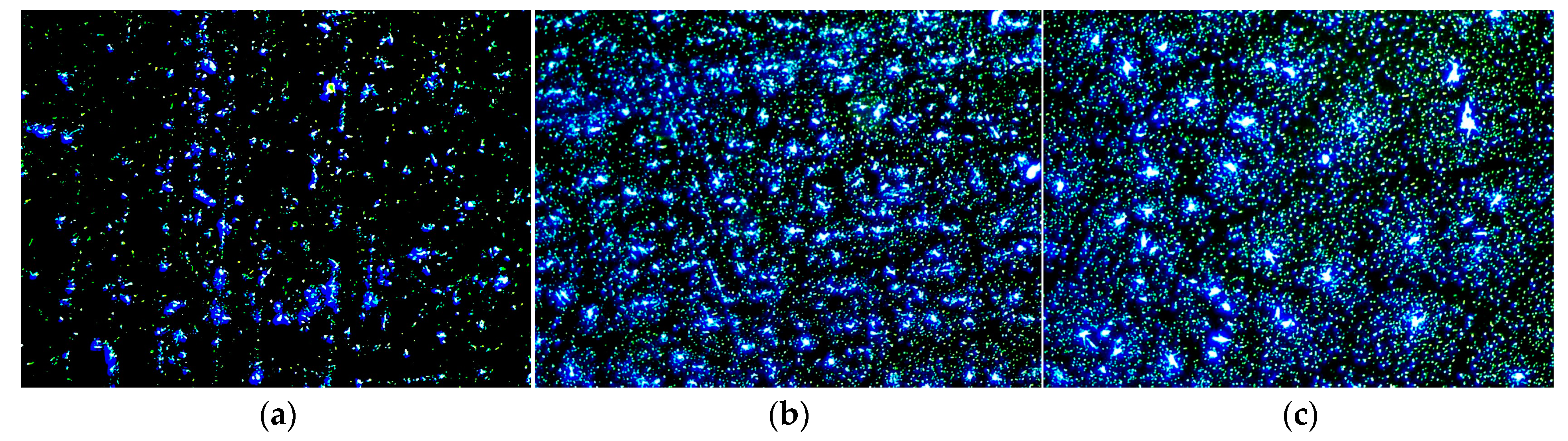
| Type of Material | Trial Items | Unit | Technical Requirements | Experimental Results | Specifications [24,25] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90# karamay base asphalt | Penetration | 0.1 mm | 80–100 | 81 | JTG E20-2011 T0604 |
| Softening point | °C | ≥44 | 45.5 | JTG E20-2011 T0606 | |
| Ductility 15 °C | cm | ≥100 | >100 | JTG E20-2011 T0605 | |
| Flash point | °C | ≥245 | 309 | JTG E20-2011 T0611 | |
| Solubility | % | ≥99.5 | 99.84 | JTG E20-2011 T0607 | |
| 80-mesh desulfurized crumb rubber | Relative density | g/cm3 | 1.10–1.30 | 1.17 | JT/T 797-2019 |
| Moisture | % | <1 | 0.74 | JT/T 797-2019 | |
| Metal content | % | <0.05 | 0.041 | JT/T 797-2019 | |
| Fiber content | % | <1 | 0.71 | JT/T 797-2019 |
| Component of Asphalt | Molecular Number | Simulated Mass Fraction (%) | Experimental Mass Fraction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| asphaltenes | 1 | 2.91 | 3.00 |
| aromatics | 38 | 22.74 | 22.47 |
| resins | 7 | 35.36 | 35.96 |
| saturates | 33 | 38.99 | 38.57 |
| Type | Number of NR Molecules | Number of SBR Molecules | Total Crumb Rubber Mass (g/mol) | Weight (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRMA with a 5% crumb rubber content (5% CRMA) | 2 | 1 | 1320.13 | 5.07 |
| CRMA with a 10% crumb rubber content (10% CRMA) | 4 | 2 | 2640.26 | 10.13 |
| CRMA with a 15% crumb rubber content (15% CRMA) | 6 | 3 | 3960.39 | 15.20 |
| CRMA with a 20% crumb rubber content (20% CRMA) | 8 | 4 | 5280.52 | 20.27 |
| CRMA with a 25% crumb rubber content (25% CRMA) | 10 | 5 | 6600.65 | 25.33 |
| Asphalt Type | CED (J/m3) | δs ((J/cm3)0.5) | |∆δs| ((J/cm3)0.5) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base asphalt | 3.56 × 108 | 18.87 | |
| 5% CRMA | 3.64 × 108 | 19.08 | 0.21 |
| 10% CRMA | 3.61 × 108 | 18.99 | 0.12 |
| 15% CRMA | 3.58 × 108 | 18.92 | 0.05 |
| 20% CRMA | 3.55 × 108 | 18.85 | 0.02 |
| 25% CRMA | 3.57 × 108 | 18.89 | 0.02 |
| Parameters | FM Test | MD Simulation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RDD | RACD | NA | Ebinding | δs | |
| ri | 0.7214 | 0.6483 | 0.6725 | 0.5729 | 0.5540 |
| Parameters | FM Test | MD Simulation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RDD | RACD | NA | Ebinding | δs | |
| VIF | 15.49 | 32.22 | 33.57 | 10.86 | 10.86 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Kou, W.; Gao, M.; Zhao, T.; Li, D.; Li, H. Multi-Scale Synergistic Mechanism of Damping Performance in Crumb Rubber-Modified Asphalt. Polymers 2026, 18, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym18010090
Kou W, Gao M, Zhao T, Li D, Li H. Multi-Scale Synergistic Mechanism of Damping Performance in Crumb Rubber-Modified Asphalt. Polymers. 2026; 18(1):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym18010090
Chicago/Turabian StyleKou, Wenqi, Mingxing Gao, Ting Zhao, Danlan Li, and Hangtian Li. 2026. "Multi-Scale Synergistic Mechanism of Damping Performance in Crumb Rubber-Modified Asphalt" Polymers 18, no. 1: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym18010090
APA StyleKou, W., Gao, M., Zhao, T., Li, D., & Li, H. (2026). Multi-Scale Synergistic Mechanism of Damping Performance in Crumb Rubber-Modified Asphalt. Polymers, 18(1), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym18010090





