Comparative Physicochemical Characterization of Polylactic Acid-Based Dermal Fillers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis
2.3. Morphology Observation
2.4. Reconstitution Test
2.5. Osmotic Pressure Measurement
2.6. Rheological Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
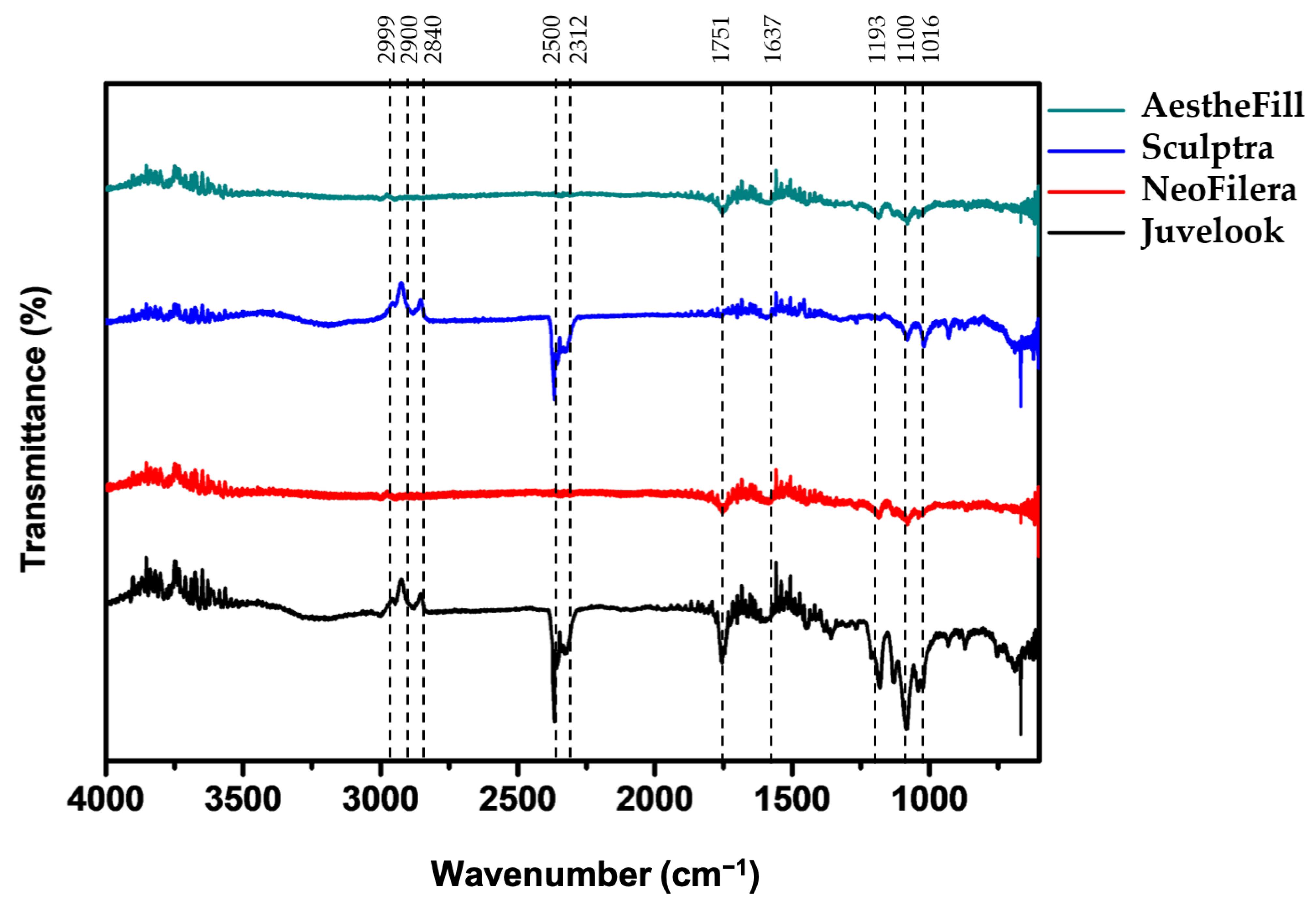
3.1. Functional Group Profiles of All Dermal Fillers Are Largely Similar
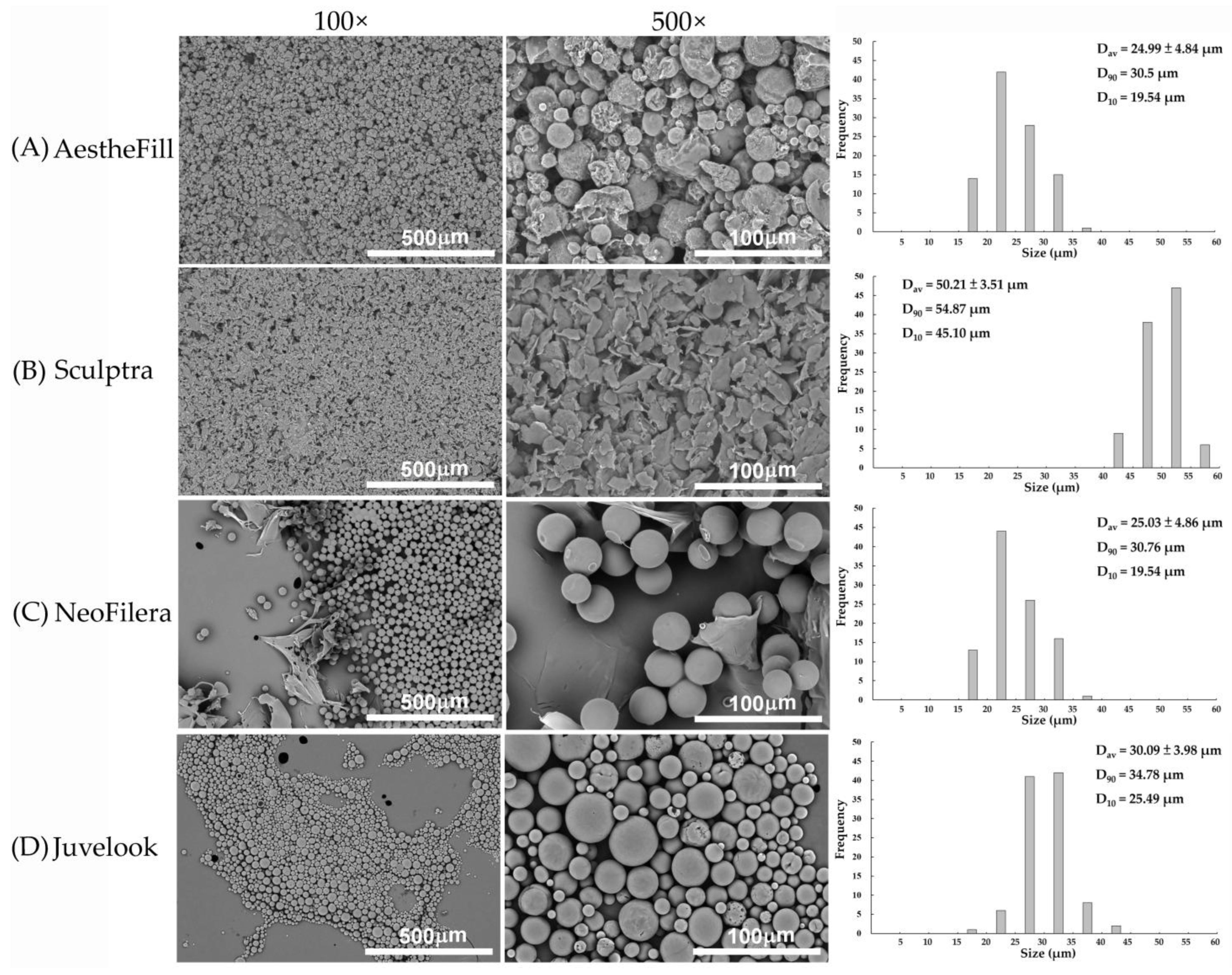
3.2. Microparticle Morphology Differs Markedly Among Dermal Fillers
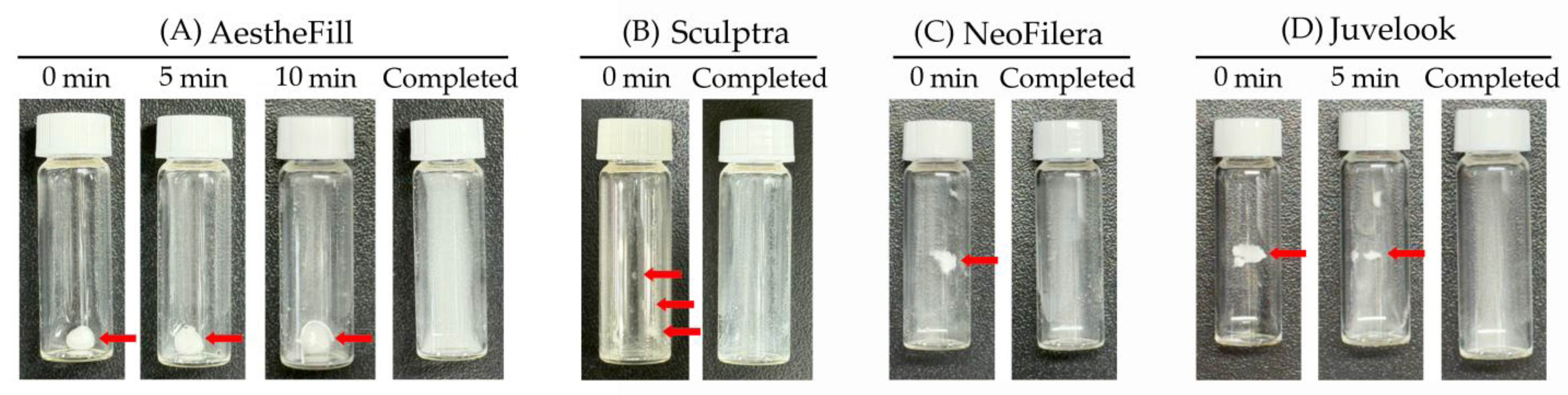
3.3. NeoFilera Exhibits the Shortest Reconstitution Time
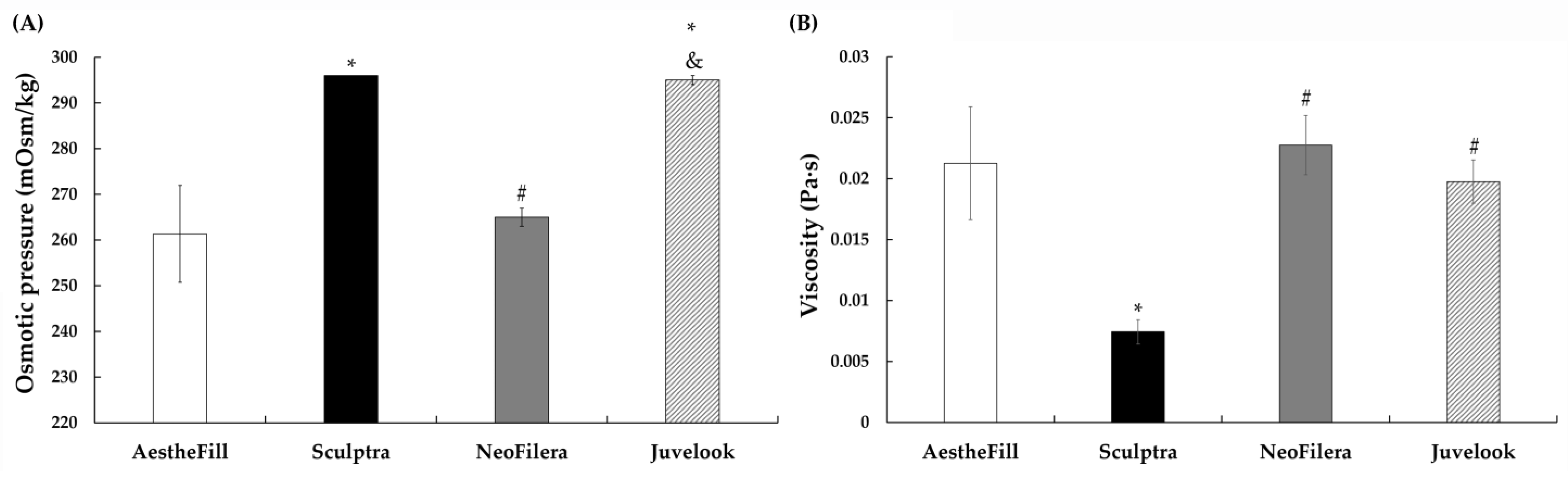
3.4. Viscosity Reveals Distinct Physicochemical Characteristics Among Dermal Fillers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PLA | Polylactic acid |
| PDLLA | Poly(D,L-lactic acid) |
| PLLA | Poly(L-lactic acid) |
| CMC | Carboxymethylcellulose |
| HA | Hyaluronic acid |
| FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared spectroscope |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| SWFI | Sterile water for injection |
References
- Guo, J.; Fang, W.; Wang, F. Injectable fillers: Current status, physicochemical properties, function mechanism, and perspectives. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 23841–23858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, R.; Graivier, M.H.; Kane, M.; Lorenc, Z.P.; Vleggaar, D.; Werschler, W.P.; Kenkel, J.M. Update on facial aging. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2010, 30, 11S–24S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemperle, G.; Morhenn, V.; Charrier, U. Human histology and persistence of various injectable filler substances for soft tissue augmentation. Aesthetic. Plast. Surg. 2003, 27, 354–366, discussion 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemperle, G.; Romano, J.J.; Busso, M. Soft tissue augmentation with artecoll: 10-year history, indications, techniques, and complications. Dermatol. Surg. 2003, 29, 573–587. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chan, L.; Li, A.; Schlesinger, T. Permanent fillers—What is their role. Dermatol. Rev. 2023, 4, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedush, N.G.; Kalinin, K.T.; Azarkevich, P.N.; Gorskaya, A.A. Physicochemical characteristics and hydrolytic degradation of polylactic acid dermal fillers: A comparative study. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.B.; Wan, J.; Yi, K.H. Energy-based device management of nodular reaction following poly-d, l-lactic acid injection for tear trough rejuvenation. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2025, 24, e16575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.Y.; Chang, Y.C.; Lu, B.R.; Fang, H.W. Investigating the relationship between the emulsification parameters and physical-chemical properties of poly(d,l-lactic acid) particles for dermal fillers. Polymers 2024, 16, 3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, A.D.; Hartmann, C.; Durkin, A.; Shahriar, S.; Khalifian, S.; Xie, J. A morphological analysis of calcium hydroxylapatite and poly-l-lactic acid biostimulator particles. Skin Res. Technol. 2024, 30, e13764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.B.; Wan, J.; Thulesen, J.; Jalali, A.; Vitale, M.; Kim, S.B.; Yi, K.H. Poly-d,l-lactic acid via transdermal microjet drug delivery for treating rosacea in asian patients. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2024, 23, 3993–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.W.; Wan, J.; Park, Y.; Chang, K.; Chan, L.K.W.; Lee, K.W.A.; Yi, K.H. Rheological characteristics of hyaluronic acid fillers as viscoelastic substances. Polymers 2024, 16, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, G.W.; Wan, J.; Yoon, S.E.; Wong, S.; Yi, K.H. Conditions to consider when choosing fillers. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2025, 24, e70075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apikian, M.; Roberts, S.; Goodman, G.J. Adverse reactions to polylactic acid injections in the periorbital area. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2007, 6, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, A.; Long, T.; Zarraga, M.; Aguilera, S.B. Nodules on the anterior neck following poly-l-lactic acid injection. Cutis 2022, 109, E15–E17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Chen, S.T.; Lin, J.Y.; Lin, C.Y. Reconstitution of injectable poly-d,l-lactic acid: Efficacy of different diluents and a new accelerating method. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2020, 8, e2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.Y.; Lin, C.Y. Hydration and dispersion: Two key steps in six aesthefill reconstitution methods. Aesthetic. Plast. Surg. 2025, 49, 5037–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathania, D.; Sood, S.; Saini, A.K.; Kumari, S.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.K. Studies on anticancerious and photocatalytic activity of carboxymethyl cellulose-cl-poly(lactic acid-co-itaconic acid)/zno-ag nanocomposite. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 6966–6976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilli, R.; Kacurakova, M.; Mathlouthi, M.; Navarini, L.; Paoletti, S. Ftir studies of sodium hyaluronate and its oligomers in the amorphous solid phase and in aqueous solution. Carbohydr. Res. 1994, 263, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalid, M.; Gustiraharjo, G.; Pangesty, A.I.; Adyandra, A.; Whulanza, Y.; Supriadi, S. Effect of peg incorporation on physicochemical and in vitro degradation of plla/pdlla blends: Application in biodegradable implants. J. Renew. Mater. 2023, 11, 3043–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maduka, C.V.; Alhaj, M.; Ural, E.; Kuhnert, M.M.; Habeeb, O.M.; Schilmiller, A.L.; Hankenson, K.D.; Goodman, S.B.; Narayan, R.; Contag, C.H. Stereochemistry determines immune cellular responses to polylactide implants. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 932–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.W.A.; Chan, L.K.W.; Lee, A.W.K.; Lee, C.H.; Wong, S.T.H.; Yi, K.H. Poly-d,l-lactic acid (pdlla) application in dermatology: A literature review. Polymers 2024, 16, 2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, Y.J.; Yi, Y.; Wu, G.H. Application of plla (poly-l-lactic acid) for rejuvenation and reproduction of facial cutaneous tissue in aesthetics: A review. Medicine 2024, 103, e37506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Ko, K.; Choo, M.S.; Lee, W.K.; Jeong, H.C.; Cho, S.T.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.; Kang, W.H.; Kim, G.P.; et al. The effect and safety of polylactic acid and adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction cell as an injectable bulking agent in urologic field: A 24-week follow-up study. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2015, 103, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.Y.; Lin, C.Y. Adjusting thickness before injection: A new trend for preparing collagen-stimulating fillers. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2021, 9, e3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, K.W.A.; Chan, L.K.W. New method to immediate reconstitute sculptra to create a more homogenous mixture for immediate use in year 2023. J. Cosmet. Med. 2023, 7, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VAIM Co., Ltd. Juvelook® Instructions for Use (Manufacturer’s Manual). Available online: https://easyfairsassets.com/sites/188/2024/05/Juvelook-Lenisna-brochure-web.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Chen, S.Y.; Lin, J.Y.; Lin, C.Y. Micro-fisheyes of carboxymethyl cellulose: The cause of micro-clumps in the suspension of injectable poly-l-lactic acid. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2020, 40, NP409–NP411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.Y.; Peng, X.; Lin, C.Y. The differences between sculptra and aesthefill reconstitution processes. Aesthetic. Plast. Surg. 2025, 49, 3337–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berska, J.; Bugajska, J.; Sztefko, K. The accuracy of serum osmolarity calculation in small children. J. Med. Biochem. 2023, 42, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.Y.; Lin, J.Y.; Lin, C.Y. Compositions of injectable poly-d,l-lactic acid and injectable poly-l-lactic acid. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 45, 347–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Kunduru, K.R.; Basu, A.; Mizrahi, B.; Domb, A.J.; Khan, W. Injectable formulations of poly(lactic acid) and its copolymers in clinical use. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- No, Y.A.; Seok, J.; Hyun, M.Y.; Kwon, T.R.; Oh, C.T.; Choi, E.J.; Kim, B.J. Long-term (24-month) safety evaluation of poly-dl-lactic acid filler injection for the nasolabial fold: A multicenter, open, randomized, evaluator-blind, active-controlled design. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 135, 1074e–1075e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotunda, A.M.; Narins, R.S. Poly-l-lactic acid: A new dimension in soft tissue augmentation. Dermatol. Ther. 2006, 19, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vleggaar, D.; Bauer, U. Facial enhancement and the european experience with sculptra (poly-l-lactic acid). J. Drugs Dermatol. 2004, 3, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.C. A Prospective, Split-Face, Randomized Study of the Poly-d, l Lactic Acid (Pdlla) for Photoaged Skin. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05913102 (accessed on 5 November 2025).
| Dermal Fillers | AestheFill | Sculptra | NeoFilera | Juvelook |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reconstitution (seconds) | 966.3 ± 37.6 | 250.0 ± 41.3 | 140.7 ± 32.9 | 450.7 ± 36.7 * |
| p value when comparing against reconstitution time of AestheFill | N.A. | 2.6 × 10−5 * | 1.0 × 10−5 * | 7.0 × 10−5 * |
| p value when comparing against reconstitution time of Sculptra | N.A. | N.A. | 0.025 | 0.0034 * |
| p value when comparing against reconstitution time of NeoFilera | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | 0.0004 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Su, C.-Y.; Chang, Y.-C.; Cheng, P.-J.; Fang, H.-W. Comparative Physicochemical Characterization of Polylactic Acid-Based Dermal Fillers. Polymers 2026, 18, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym18010084
Su C-Y, Chang Y-C, Cheng P-J, Fang H-W. Comparative Physicochemical Characterization of Polylactic Acid-Based Dermal Fillers. Polymers. 2026; 18(1):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym18010084
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Chen-Ying, You-Cheng Chang, Pei-Ju Cheng, and Hsu-Wei Fang. 2026. "Comparative Physicochemical Characterization of Polylactic Acid-Based Dermal Fillers" Polymers 18, no. 1: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym18010084
APA StyleSu, C.-Y., Chang, Y.-C., Cheng, P.-J., & Fang, H.-W. (2026). Comparative Physicochemical Characterization of Polylactic Acid-Based Dermal Fillers. Polymers, 18(1), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym18010084







