Investigation of a New Stacking Pattern of Laminates with Approximately Constant Bending Stiffness
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Normalized Direction Factor of Bending Stiffness (NDFBS)
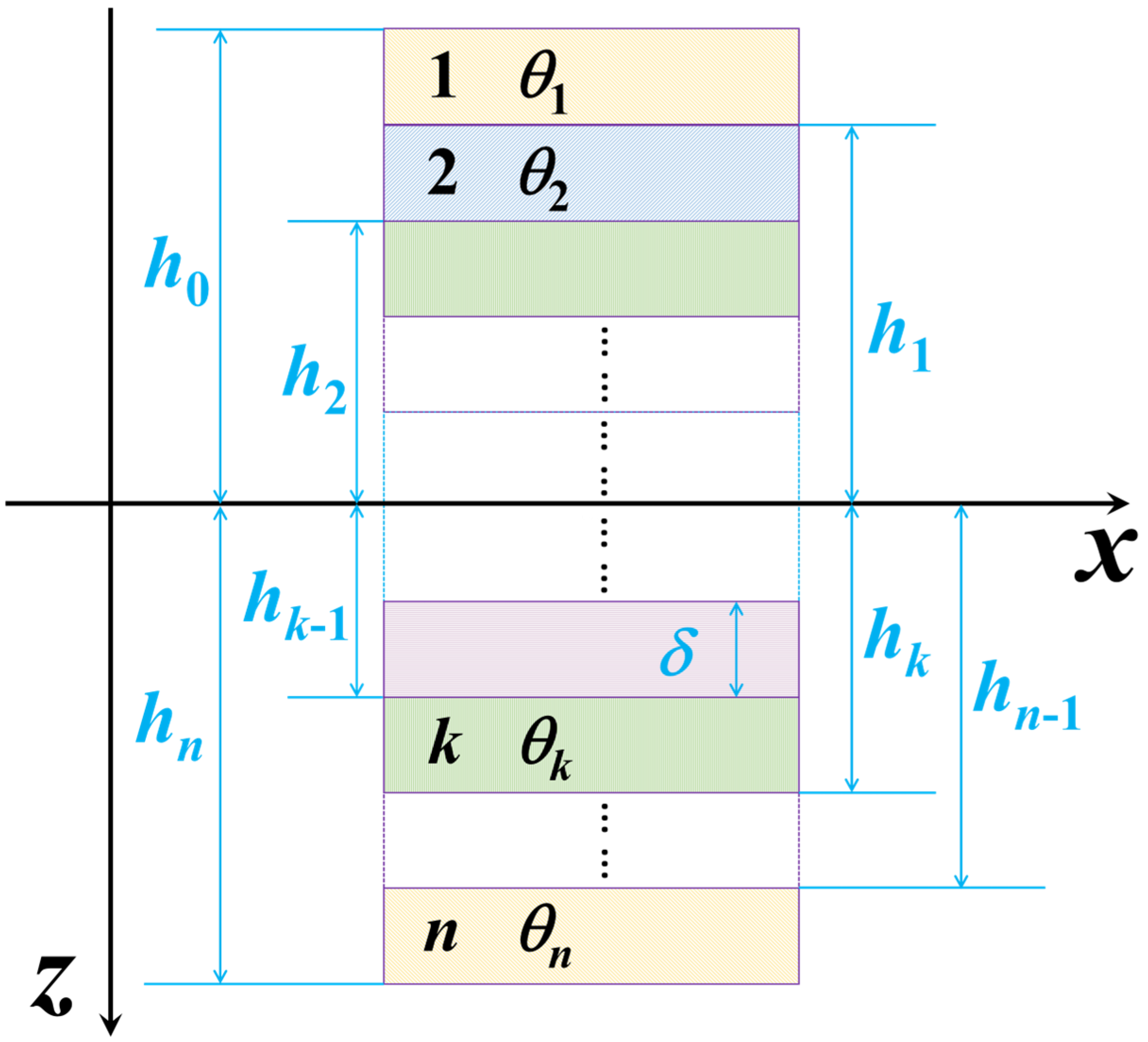
2.1. Normalized Stiffness Matrix
2.2. Definition of NDFBS
- ()3 − ()3 ≡ Const. This condition is too hard to follow since the ply thickness within a laminate is generally constant or varies only slightly [39].
- The sum of the cubic difference with the same ply orientation is constant, named the normalized direction factors of bending stiffness (NDFBS), η*(j), that is,
2.3. NDFBSs for Three Stacking Patterns
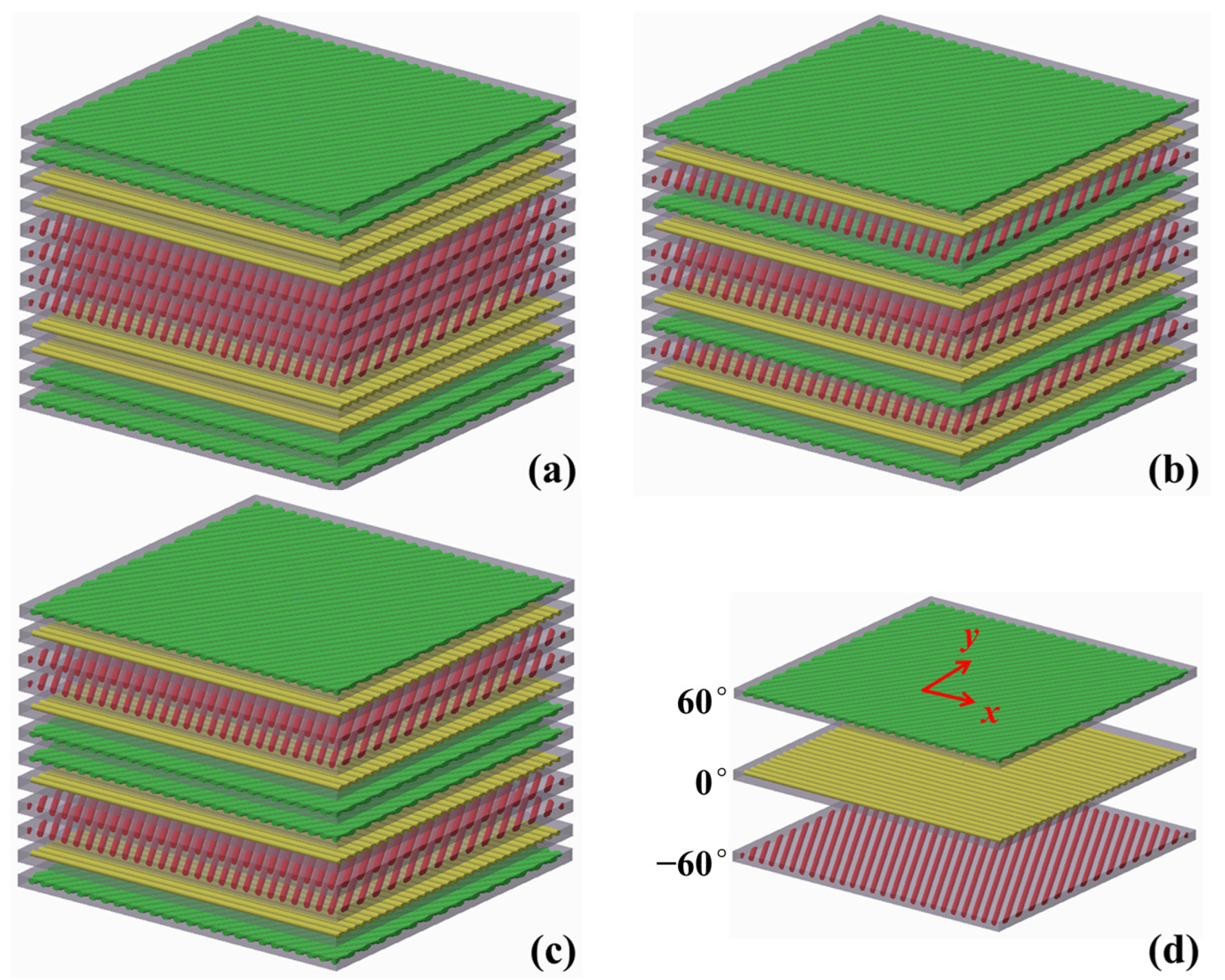
2.3.1. Laminates with Symmetry After Each Ply Cycle
2.3.2. Laminates with Symmetry After Cycle
2.3.3. Laminates with Symmetry Before Cycle
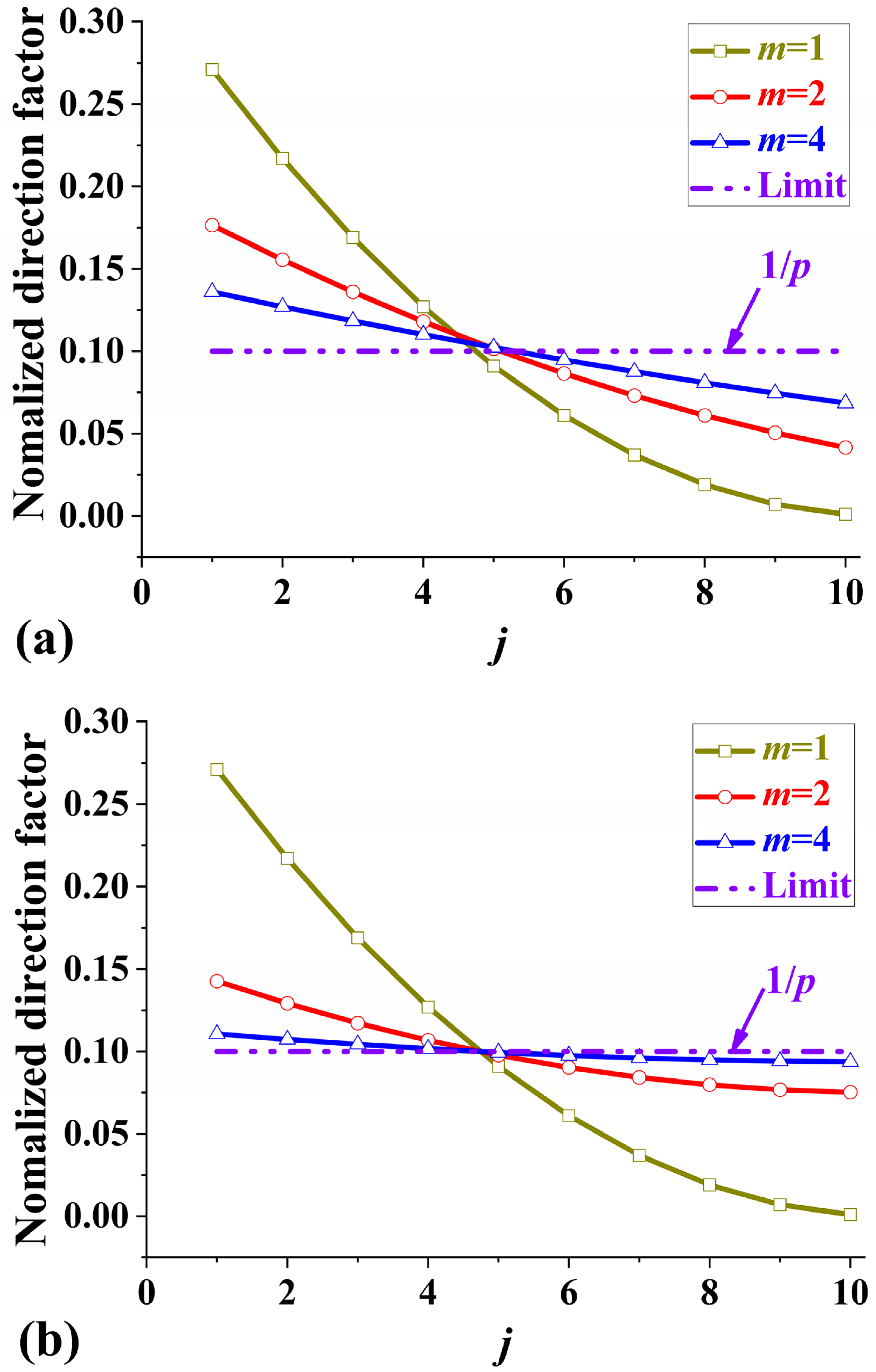
2.4. Comparing Three NDFBSs
2.5. Variance of the Normalized Direction Factors of Bending Stiffness (VNDFBS)
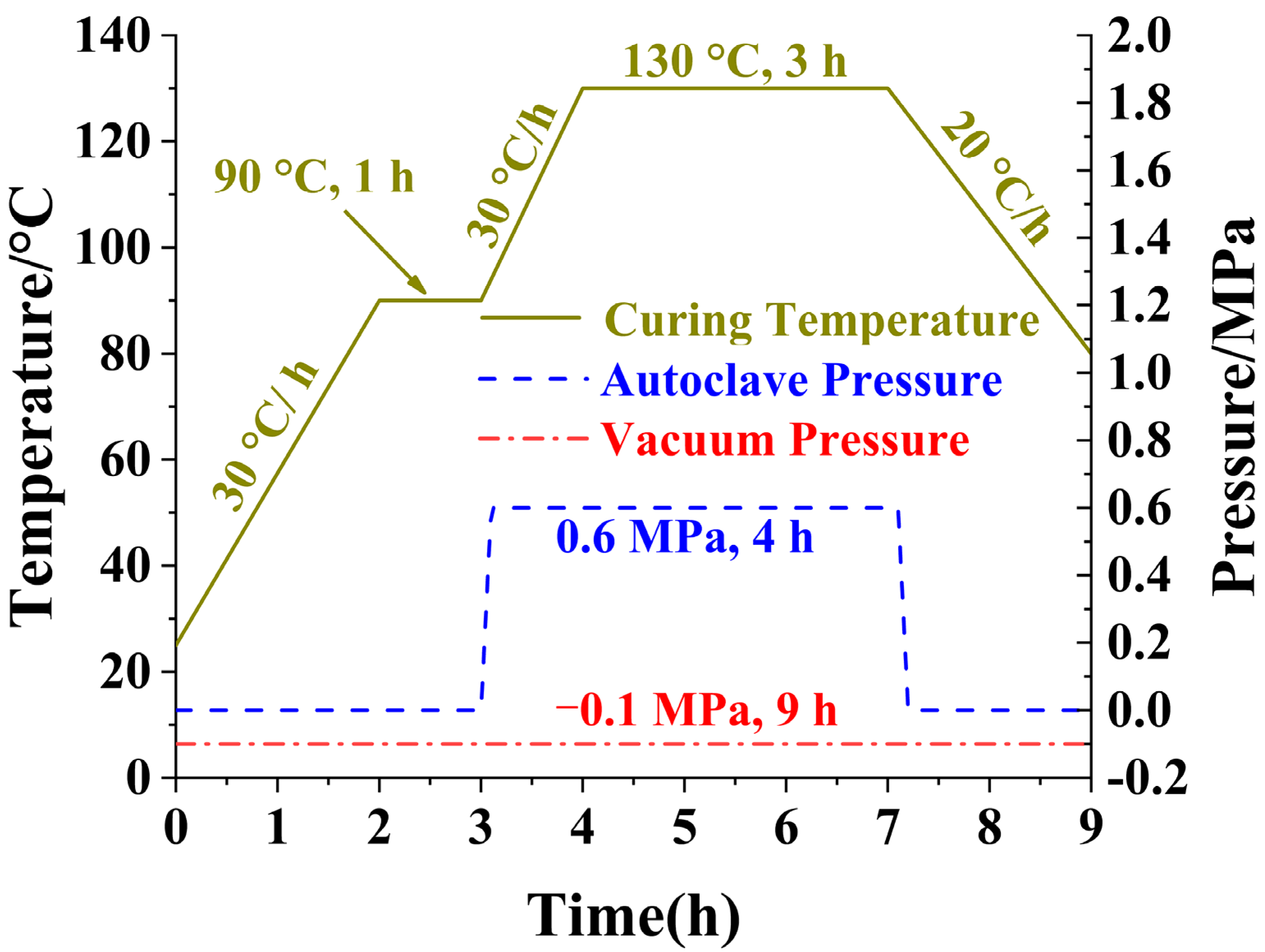
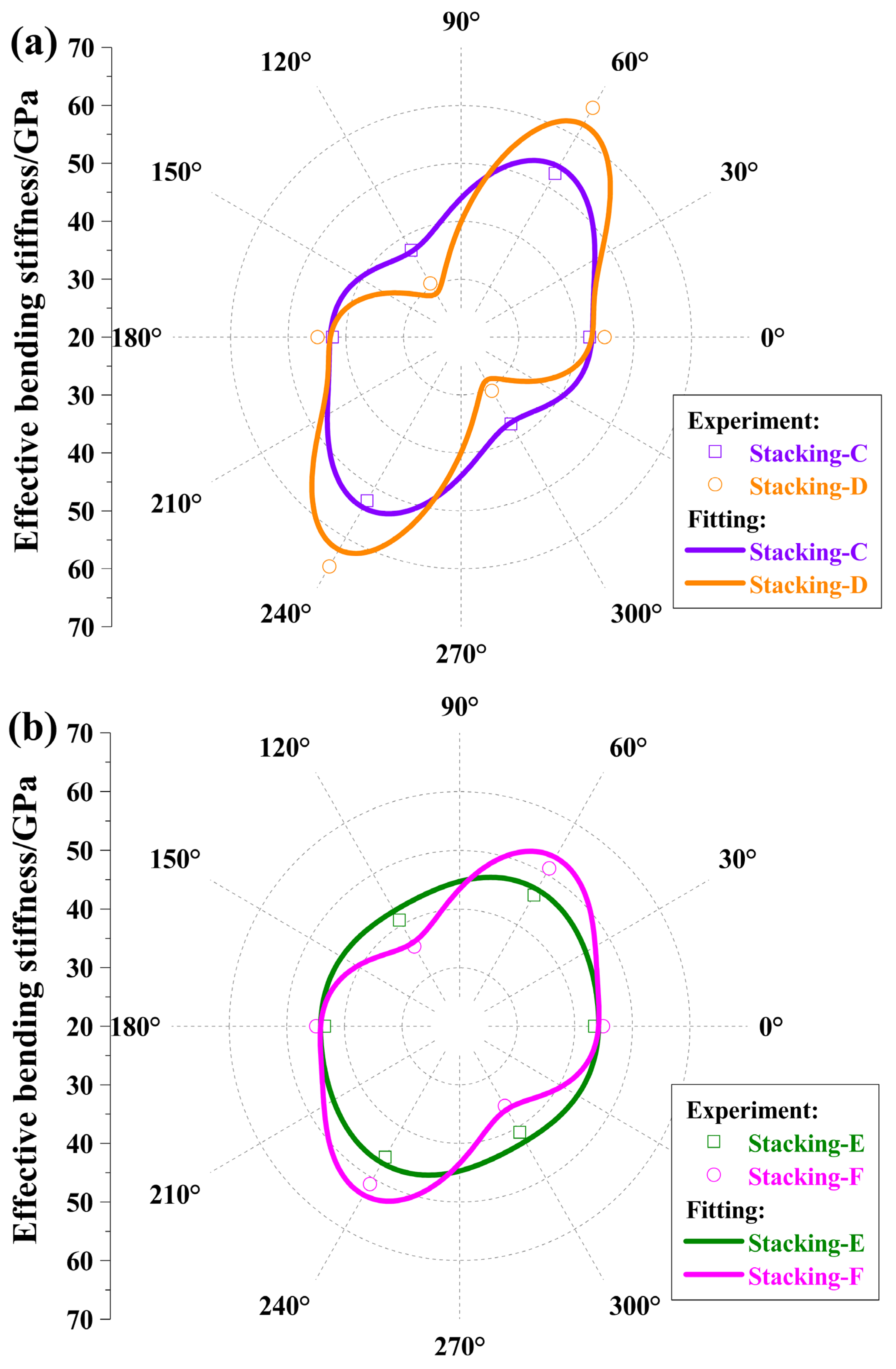
3. Experiment Results and Discussion
3.1. Four-Angle Ply
3.2. Three-Angle Ply
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, L.; Gong, P.; Wang, Q.; Zou, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. Effects of ply thickness deviation and ply angle misalignment on the surface accuracy of CFRP laminates. Compos. Struct. 2021, 270, 114073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Sun, Q.; Fan, Z.; Mu, X.; Wang, F. A novel layup process for reducing surface thermal distortion of CFRP laminate reflector. Compos. Struct. 2025, 351, 118517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arao, Y.; Koyanagi, J.; Utsunomiya, S.; Kawada, H. Effect of ply angle misalignment on out-of-plane deformation of symmetrical cross-ply CFRP laminates: Accuracy of the ply angle alignment. Compos. Struct. 2011, 93, 1225–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qingnian, L.; Yingfeng, S.; Long, L.; Yong, C.; Fan, S. Uniformity Prediction of Bending Stiffness of Composite Space Mirrors With Ply Angle Misalignments by Deflection Angle. Front. Mech. Eng. 2022, 8, 888350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Moya, M.Á.; García-Martínez, E.; Miguel, V.; Coello, J.; Martínez-Martínez, A. Experimental Analysis and Application of a Multivariable Regression Technique to Define the Optimal Drilling Conditions for Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) Composites. Polymers 2023, 15, 3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, M.; Boccarusso, L.; De Fazio, D.; Formisano, A.; Langella, A. Investigation on the Mechanical Recycling of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Polymers by Peripheral Down-Milling. Polymers 2023, 15, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, M.; Radjef, R.; Eisenbart, B.; Wartzack, S. Effects of Ply Misalignment in Material Characterization of Composite Laminates. Fibers 2024, 12, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, B.; Xu, L.; Tang, Z.; Xie, Y. Influence of layup sequence on the surface accuracy of carbon fiber composite space mirrors. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2019, 26, 219–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Du, S.; Zhang, L. Fundamentals of Composite Materials; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2018; Volume 1, p. 786. [Google Scholar]
- Pryor, M.K. Hygrothermal Stability of Curved Fiber-Reinforced Laminates; University of California: Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Pryor, M.K. Hygrothermal stability of laminated CFRP composite mirrors. In UV, Optical, and IR Space Telescopes and Instruments; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2000; pp. 655–662. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X. Study on Non-Spherical Active Shaping of Quasi-Isotropic CFRP Mirror; Suzhou University: Suzhou, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, C.; Yu, X.; Guo, P. Active deformation and engineering analysis of CFRP mirror of various lay-up sequences within quasi-isotropic laminates. In Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Advanced Optical Manufacturing and Testing Technologies (AOMATT 2014), Harbin, China, 26–29 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Chunmei, Z.; Peiji, G. Lay-up design of quasi-isotropic CFRP mirror for active forming. Infrared Laser Eng. 2012, 41, 1885–1892. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Tang, Z.; Xie, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhang, B.; Guo, H. Effect of Lamina Thickness of Prepreg on the Surface Accuracy of Carbon Fiber Composite Space Mirrors. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2018, 25, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Cai, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Leng, S. Influence of the ply angle deviation on the out-of-plane deformation of the composite space mirror. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2019, 26, 897–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.M.; Avery, B.L. Fully Isotropic Laminates and Quasi-Homogeneous Anisotropic Laminates. J. Compos. Mater. 1992, 26, 2107–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werren, F.; Norris, C.B. Mechanical Properties of a Laminate Designed to be Isotropic; US Forest Prod. Lab.: Madison, WI, USA, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Hinckley, M. Statistical evaluation of the variation in laminated composite properties resulting from ply misalignment. In Proceedings of the Advances in Optical Structure Systems, Orlando, FL, USA, 16–19 April 1990; pp. 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q. Handbook of Advanced Composite Materials; China Machinery Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2003; p. 1906. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, S.J.; Bichon, S.; Grant, R.J. Influence of ply misalignment on form error in the manufacturing of CFRP mirrors. Opt. Mater. Express 2014, 4, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-P.; Hale, R.D. Composite mirror surface deformation due to lay-up sequences within quasi-isotropic laminates. Opt. Eng. 2010, 49, 063002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.P.; Lou, M.C.; Rapp, D. Thermal-mechanical behavior of high precision composite mirrors. In Proceedings of the Aiaa/asme/asce/ahs/asc Structures, Structural Dynamics, & Materials Conference, La Jolla, CA, USA, 19–22 April 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, W.T.; Hong, T.H. Introduction to Composite Materials; Technomic Publishing Company, Inc.: Lancaster, PA, USA, 1980; p. 466. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Wang, X. The Base of Construction Design of Composites; Wuhan University of Industry Press: Wuhan, China, 1993; p. 296. [Google Scholar]
- Caprino, G.; Visconti, I.C. A note on specially orthotropic laminates. J. Compos. Mater. 1982, 16, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Cai, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, Z. Investigation of the quasi-homogenous laminate by means of the direction factor of the bending stiffness. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2019, 26, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, H. On isotropic laminate configurations. J. Compos. Mater. 1990, 24, 519–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, H.; Vanderplaats, G.N. Stiffness optimization of orthotropic laminated composites using lamination parameters. Aiaa J. 1991, 29, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, M. Design of laminated fibrous composite plates with required flexural stiffness. In Recent Advances in Composites in the United States and Japan; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1985; pp. 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, M.; Sugiyama, Y. Optimum design of laminated composite plates using lamination parameters. Aiaa J. 1993, 31, 921–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setoodeh, S.; Abdalla, M.M.; Gürdal, Z. Design of variable–stiffness laminates using lamination parameters. Compos. Part B Eng. 2006, 37, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradies, R. Designing quasi-isotropic laminates with respect to bending. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1996, 56, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grédiac, M. A procedure for designing laminated plates with required stiffness properties. Application to thin quasi-isotropic quasi-homogeneous uncoupled laminates. J. Compos. Mater. 1999, 33, 1939–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verchery, G. Design rules for the laminate stiffness. Mech. Compos. Mater. 2011, 47, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemurro, M.; Vincenti, A.; Vannucci, P. Design of the elastic properties of laminates with a minimum number of plies. Mech. Compos. Mater. 2012, 48, 369–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannucci, P.; Verchery, G. A special class of uncoupled and quasi-homogeneous laminates. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2001, 61, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannucci, P.; Verchery, G. A new method for generating fully isotropic laminates. Compos. Struct. 2002, 58, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q. Composite materials bend isotropic laminated plates. J. South China Univ. Technol. 1989, 17, 123–127. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D 7264-2015; Standard Test Method for Flexural Properties of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- Kaw, A.K. Mechanics of Composite Materials; CRC press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; p. 473. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, D.E. Genetic Algorithms in Search, Optimization, and Machine Learning; Addison-Wesley Pub. Co.: Boston, MA, USA, 1989; p. 372. [Google Scholar]


| Material | E1/GPa | E2/GPa | G12/GPa | ν12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T700/602 | 115 | 8.36 | 4.56 | 0.30 |
| Serial Number | Pattern | Stacking Pattern | Specimen Size/mm | Number of Plies | Angle /° | Ef/GPa | σf/MPa | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Std | Mean | Std | ||||||
| Stacking-A | III | [(45/−45/0/90)S]2 | 100 × 12.5 × 2.4 | 16 | 0 | 41.1 | 1.5 | 788 | 25.4 |
| 45 | 48.2 | 1.7 | 691 | 67.0 | |||||
| 90 | 35.4 | 1.9 | 791 | 30.9 | |||||
| −45 | 40.9 | 1.4 | 738 | 37.1 | |||||
| Stacking-B | II | [45/−45/0/90]2S | 100 × 12.5 × 2.4 | 16 | 0 | 36.1 | 2.0 | 805 | 34.8 |
| 45 | 53.2 | 2.6 | 798 | 76.6 | |||||
| 90 | 30.9 | 1.5 | 650 | 22.4 | |||||
| −45 | 44.6 | 2.0 | 760 | 58.4 | |||||
| Serial Number | Pattern | Stacking Pattern | Specimen Size/mm | Number of Plies | Angle /° | Ef/GPa | σf/MPa | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Std | Mean | Std | ||||||
| Stacking-C | III | [(60/0/−60)S]2 | 85 × 12.5 × 1.8 | 12 | 0 | 42.3 | 1.0 | 997 | 45.9 |
| 60 | 52.6 | 2.5 | 766 | 77.3 | |||||
| −60 | 37.3 | 1.6 | 968 | 68.2 | |||||
| Stacking-D | II | [60/0/−60]2S | 85 × 12.5 × 1.8 | 12 | 0 | 44.9 | 2.5 | 1087 | 86.7 |
| 60 | 65.7 | 4.0 | 920 | 59.4 | |||||
| −60 | 30.7 | 1.8 | 806 | 27.8 | |||||
| Stacking-E | III | [(60/0/−60)S]4 | 150 × 12.5 × 3.6 | 24 | 0 | 43.4 | 0.7 | 927 | 93.9 |
| 60 | 45.8 | 1.0 | 730 | 46.6 | |||||
| −60 | 40.9 | 1.4 | 948 | 39.5 | |||||
| Stacking-F | II | [60/0/−60]4S | 150 × 12.5 × 3.6 | 24 | 0 | 44.9 | 5.1 | 883 | 113.8 |
| 60 | 51.1 | 1.7 | 810 | 117.0 | |||||
| −60 | 35.7 | 2.4 | 692 | 61.4 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Shao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Li, L.; Song, F. Investigation of a New Stacking Pattern of Laminates with Approximately Constant Bending Stiffness. Polymers 2025, 17, 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17081098
Liu Q, Shao Y, Cai Y, Li L, Song F. Investigation of a New Stacking Pattern of Laminates with Approximately Constant Bending Stiffness. Polymers. 2025; 17(8):1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17081098
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qingnian, Yingfeng Shao, Yong Cai, Long Li, and Fan Song. 2025. "Investigation of a New Stacking Pattern of Laminates with Approximately Constant Bending Stiffness" Polymers 17, no. 8: 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17081098
APA StyleLiu, Q., Shao, Y., Cai, Y., Li, L., & Song, F. (2025). Investigation of a New Stacking Pattern of Laminates with Approximately Constant Bending Stiffness. Polymers, 17(8), 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17081098







