Smart Bacterial Cellulose–Methylacrylated Chitosan Composite Hydrogel: Multifunctional Characterization for Real-Time pH Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
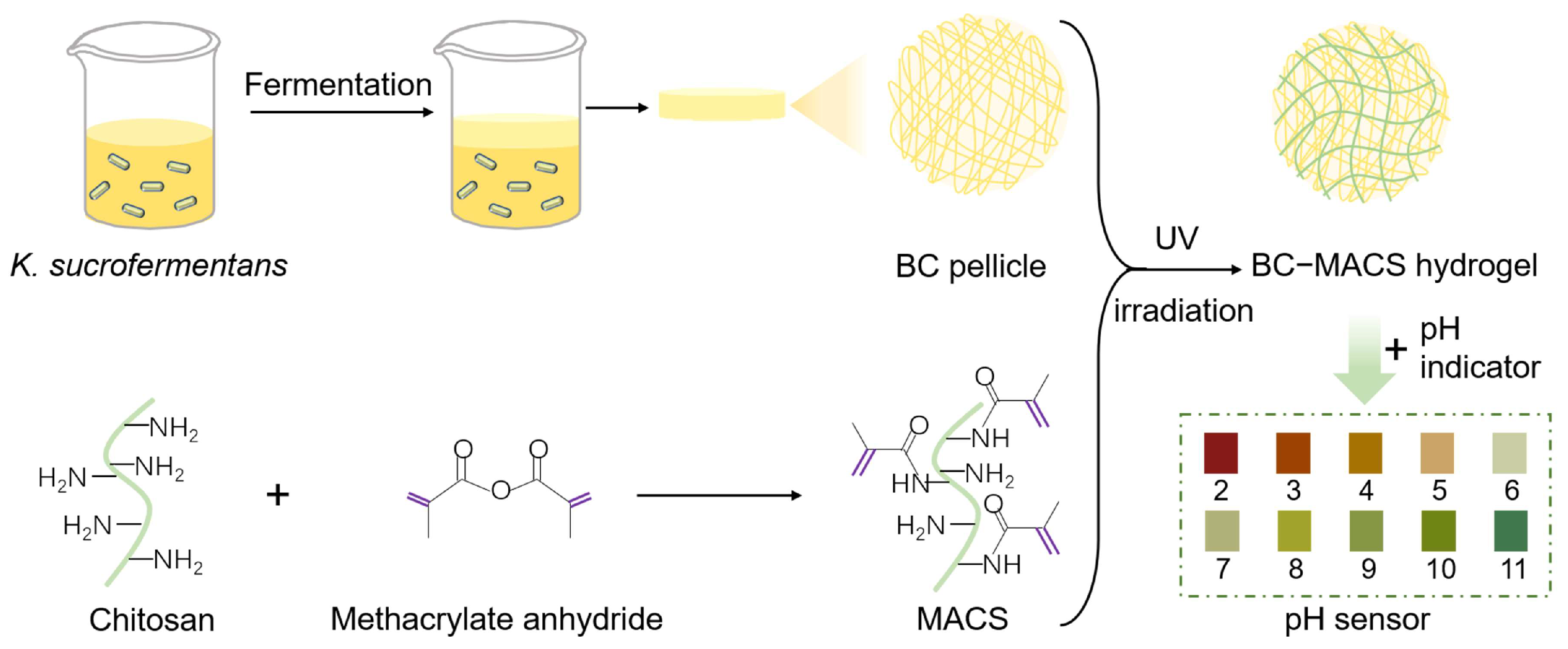
2.2. Synthesis of MACS and BC
2.2.1. Synthesis of MACS
2.2.2. Synthesis of BC Pellicles
2.3. Preparation of MACS and BC-MACS Hydrogels
2.4. Characterization of BC-MACS Hydrogel
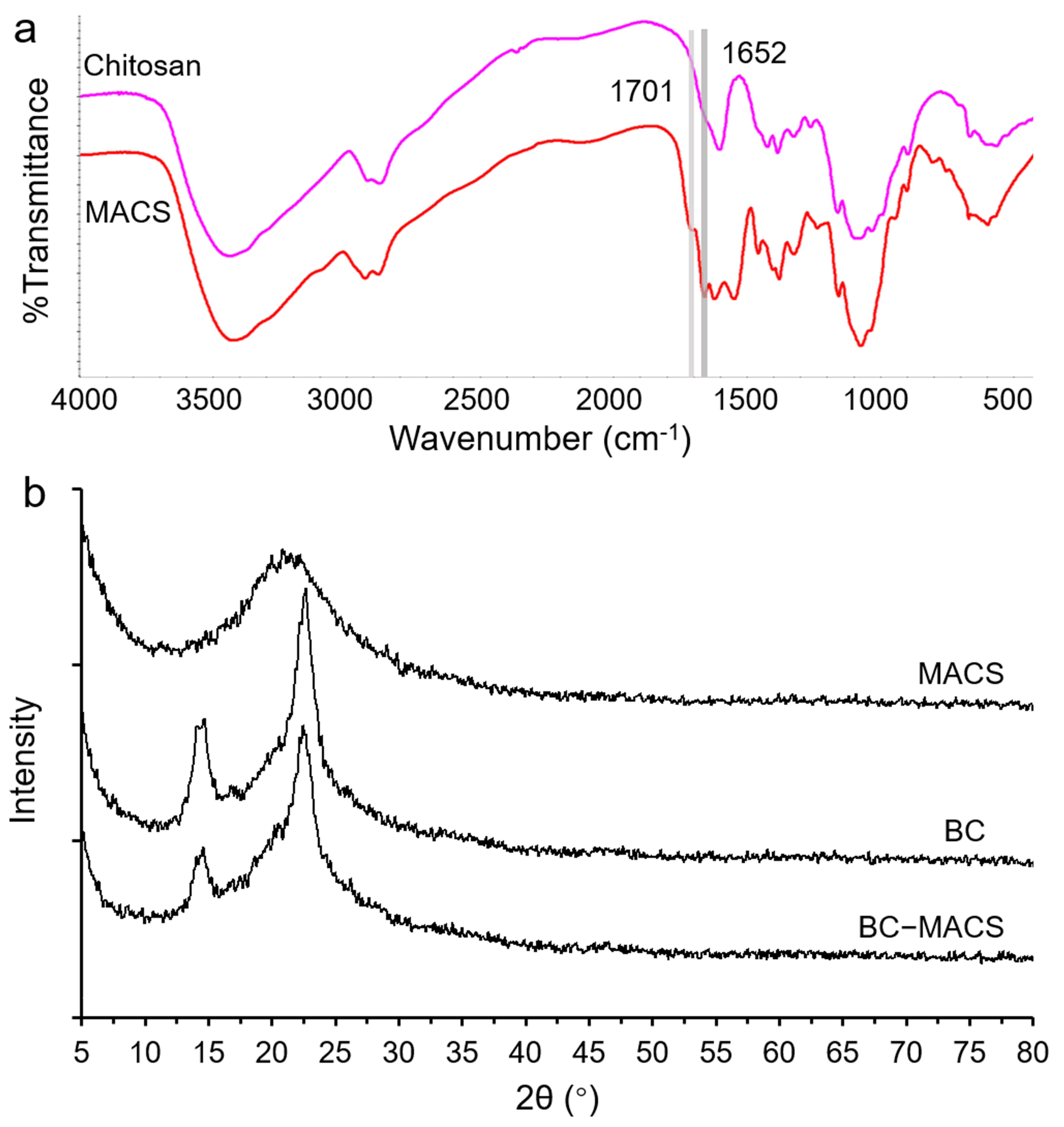
2.4.1. FTIR Analysis
2.4.2. XRD Analysis
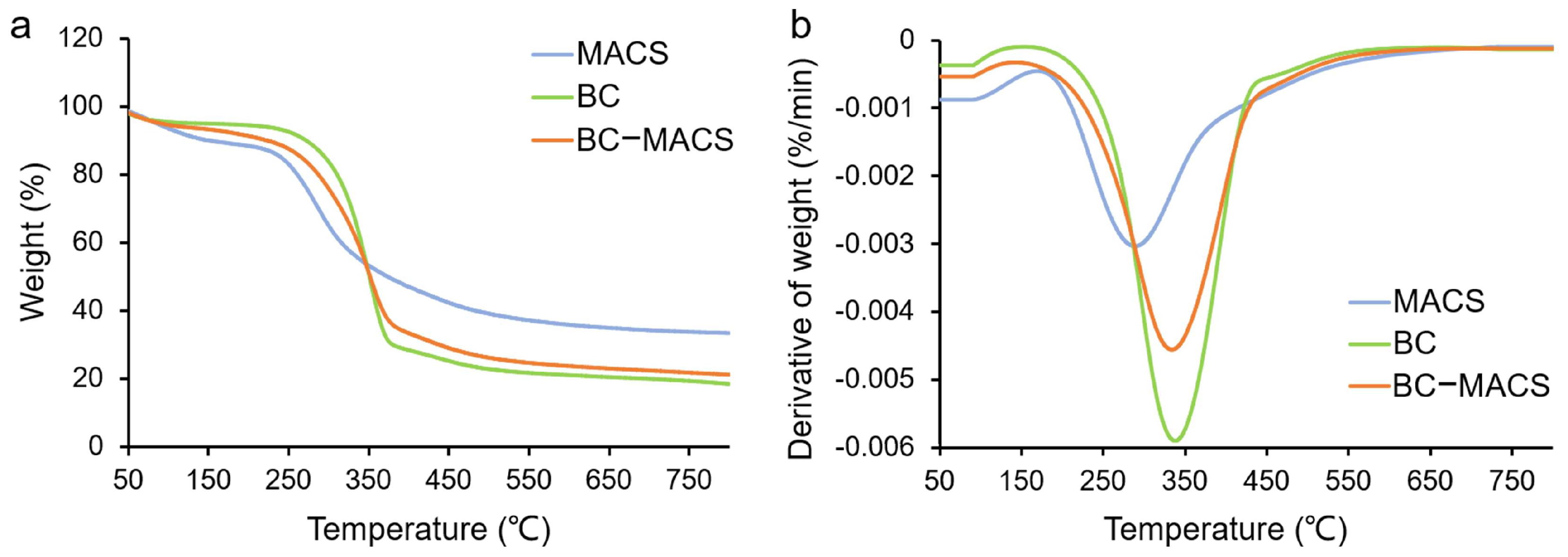
2.4.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
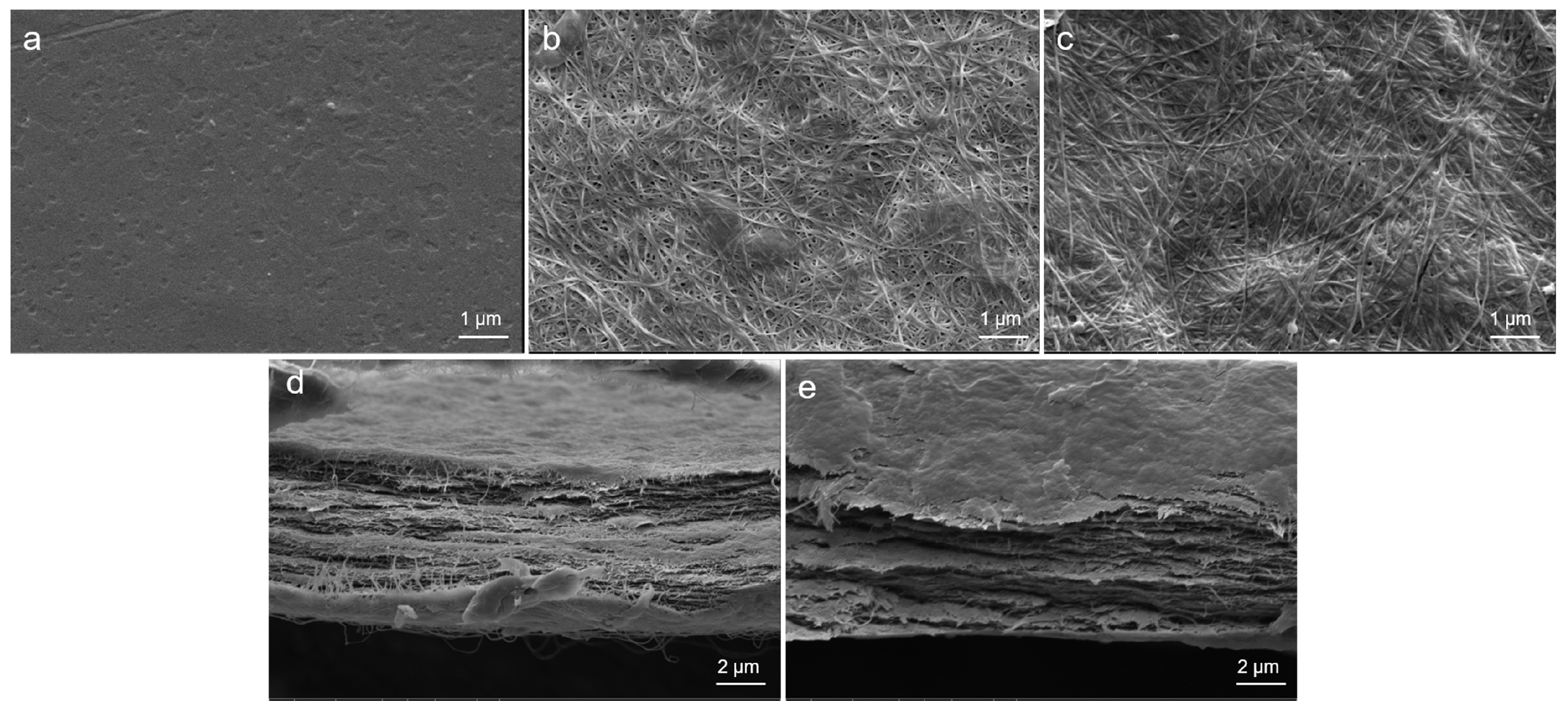
2.4.4. SEM
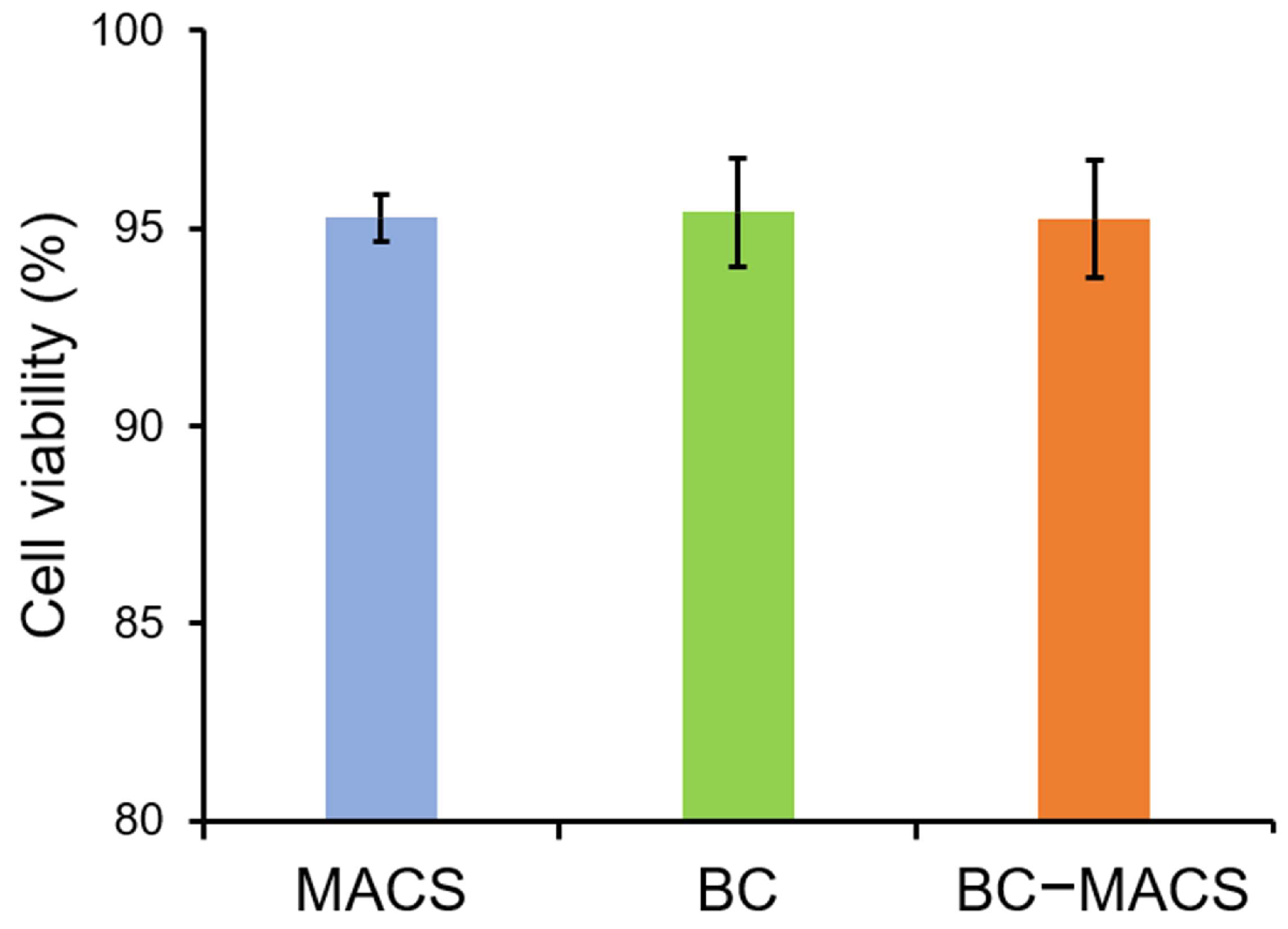
2.4.5. Cytocompatibility
2.5. Swelling Behavior
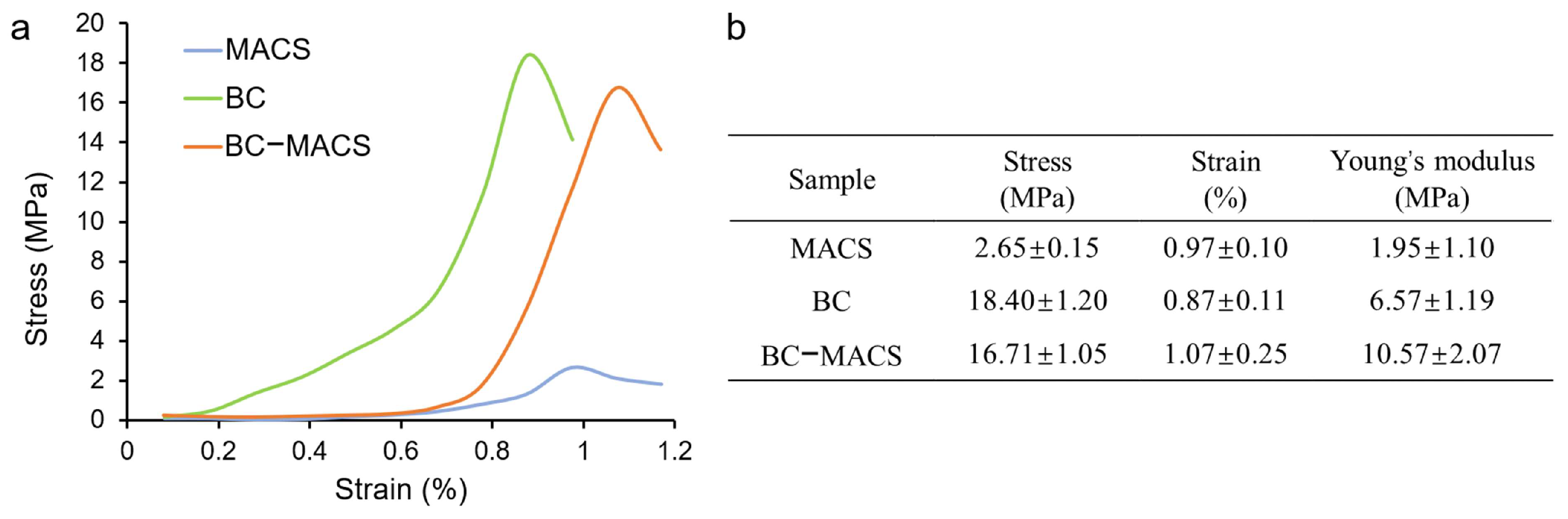
2.6. Mechanical Properties
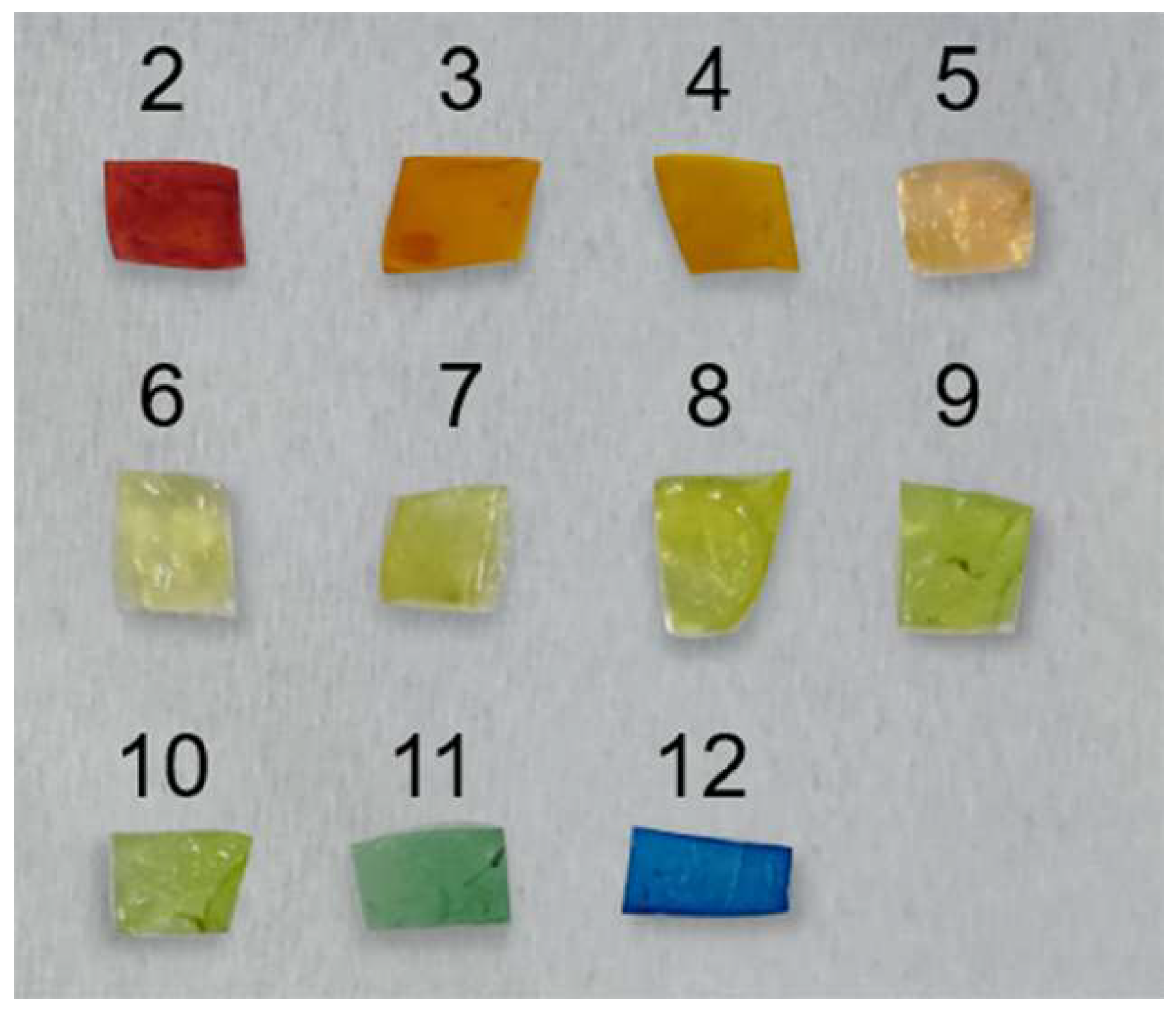
2.7. Preparation of BC-MACS pH Sensor
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of BC-MACS Hydrogel
3.2. Swelling Behavior
3.3. Mechanical Properties
3.4. BC-MACS-Based Colorimetric pH Sensor
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Avolio, R.; Grozdanov, A.; Avella, M.; Barton, J.; Cocca, M.; De Falco, F.; Dimitrov, A.T.; Errico, M.E.; Fanjul-Bolado, P.; Gentile, G.; et al. Review of pH sensing materials from macro- to nano-scale: Recent developments and examples of seawater applications. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 52, 979–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Li, J.; Ma, N.; Ma, X.; Gao, M. Bacterial cellulose hydrogel for sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 461, 142062. [Google Scholar]
- Han, F.; Wang, T.; Liu, G.; Liu, H.; Xie, X.; Wei, Z.; Li, J.; Jiang, C.; He, Y.; Xu, F. Materials with tunable optical properties for wearable epidermal sensing in health monitoring. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2109055. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Su, R.; Teng, L.; Tian, Q.; Han, F.; Li, H.; Cao, Z.; Xie, R.; Li, G.; Liu, X.; et al. Recent advances in flexible and wearable sensors for monitoring chemical molecules. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 1653–1669. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vivaldi, F.; Santalucia, D.; Poma, N.; Bonini, A.; Salvo, P.; Del Noce, L.; Melai, B.; Kirchhain, A.; Kolivoška, V.; Sokolova, R.; et al. A voltammetric pH sensor for food and biological matrices. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 322, 128650. [Google Scholar]
- Waimin, J.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Heredia-Rivera, U.; Kerr, N.A.; Nejati, S.; Gallina, N.L.F.; Bhunia, A.K.; Rahimi, R. Low-Cost nonreversible electronic-free wireless pH sensor for spoilage detection in packaged meat products. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 45752–45764. [Google Scholar]
- Briggs, E.M.; Sandoval, S.; Erten, A.; Takeshita, Y.; Kummel, A.C.; Martz, T.R. Solid state sensor for simultaneous measurement of total alkalinity and pH of seawater. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pourjavaher, S.; Almasi, H.; Meshkini, S.; Pirsa, S.; Parandi, E. Development of a colorimetric pH indicator based on bacterial cellulose nanofibers and red cabbage (Brassica oleraceae) extract. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 156, 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, N.; Yusufu, D.; Mills, A. Colourimetric plastic film indicator for the detection of the volatile basic nitrogen compounds associated with fish spoilage. Talanta 2019, 194, 830–836. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, C.M.; Maciel, V.B.V.; Mendonça, M.E.D.; Franco, T.T. Chitosan biobased and intelligent films: Monitoring pH variations. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 55, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, S.; Chen, X.J.S.; Chemical, A.B. A visual pH sensing film using natural dyes from Bauhinia blakeana Dunn. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 198, 268–273. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, X.; Shi, J.; Zou, X.; Wang, S.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Zhang, W.; Holmes, M. Novel colorimetric films based on starch/polyvinyl alcohol incorporated with roselle anthocyanins for fish freshness monitoring. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 69, 308–317. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, V.A., Jr.; de Arruda, I.N.Q.; Stefani, R. Active chitosan/PVA films with anthocyanins from Brassica oleraceae (Red Cabbage) as Time–Temperature Indicators for application in intelligent food packaging. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 180–188. [Google Scholar]
- Rukchon, C.; Nopwinyuwong, A.; Trevanich, S.; Jinkarn, T.; Suppakul, P. Development of a food spoilage indicator for monitoring freshness of skinless chicken breast. Talanta 2014, 130, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.; Ul-Islam, M.; Khattak, W.A.; Park, J.K. Overview of bacterial cellulose composites: A multipurpose advanced material. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 1585–1598. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Li, J.; Bao, Z.; Hu, M.; Nian, R.; Feng, D.; An, D.; Li, X.; Xian, M.; Zhang, H. A natural in situ fabrication method of functional bacterial cellulose using a microorganism. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 437. [Google Scholar]
- Siripongpreda, T.; Somchob, B.; Rodthongkum, N.; Hoven, V.P. Bacterial cellulose-based re-swellable hydrogel: Facile preparation and its potential application as colorimetric sensor of sweat pH and glucose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 256, 117506. [Google Scholar]
- Moradi, M.; Tajik, H.; Almasi, H.; Forough, M.; Ezati, P.J. A novel pH-sensing indicator based on bacterial cellulose nanofibers and black carrot anthocyanins for monitoring fish freshness. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 222, 115030. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.; Han, J.; Sun, X.; Guo, Y.; Yang, X.; Jia, Z. An intelligent colorimetric film based on complex anthocyanins and bacterial cellulose nanofibers for tilapia freshness detection in an actual cold chain. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 221, 183–192. [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen, J.T.; Hiekkataipale, P.; Malm, J.; Karppinen, M.; Ikkala, O.; Ras, R.H.A. Inorganic hollow nanotube aerogels by atomic layer deposition onto native nanocellulose templates. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1967–1974. [Google Scholar]
- Osi, A.R.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, R.; Fu, J.; Müller-Buschbaum, P.; Zhong, Q. Three-Dimensional-printable thermo/photo-cross-linked methacrylated chitosan–gelatin hydrogel composites for tissue engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 22902–22913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Bratlie, K.M. pH sensitive methacrylated chitosan hydrogels with tunable physical and chemical properties. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 132, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liang, K.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, X.; Yin, X.; Chen, D.; Xu, W.; Xiao, P. Photocrosslinked methacrylated chitosan-based nanofibrous scaffolds as potential skin substitute. Cellulose 2017, 24, 4253–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wang, K.; Yang, D.; Nie, J. Photopolymerization of methacrylated chitosan/PNIPAAm hybrid dual-sensitive hydrogels as carrier for drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2009, 44, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolawole, O.M.; Lau, W.M.; Khutoryanskiy, V. Methacrylated chitosan as a polymer with enhanced mucoadhesive properties for transmucosal drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 550, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, W.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Li, N.; Jian, X. Apatite formation induced by chitosan/gelatin hydrogel coating anchored on poly(aryl ether nitrile ketone) substrates to promote osteoblastic differentiation. Macromol. Biosci. 2021, 21, 2100262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Hakkarainen, M.; Grützmacher, H.; Chiappone, A.; Sangermano, M. Photocrosslinked chitosan hydrogels reinforced with chitosan-derived nano-graphene oxide. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2019, 220, 1900174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, X.; Wu, W.; Zhang, A.; Lu, B.; Zhang, T.; Kong, M. Dual cure (thermal/photo) composite hydrogel derived from chitosan/collagen for in situ 3D bioprinting. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 182, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, J.; Du, H.; Chai, N.; Sha, Z.; Geng, M.; Zhou, X.; He, C. Tannic acid-reinforced methacrylated chitosan/methacrylated silk fibroin hydrogels with multifunctionality for accelerating wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 116689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Cui, Y.; Chen, J.; Gao, C.; Yang, Y.; Yu, W.; Rai, K.; Zhang, M.; Nian, R.; Bao, Z.; et al. High-Strength collagen-based composite films regulated by water-soluble recombinant spider silk proteins and water annealing. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 3341–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, I.M.S.; Silva, R.R.; Pacheco, G.; Lustri, W.R.; Tercjak, A.; Gutierrez, J.; Júnior, J.R.S.; Azevedo, F.H.C.; Figuêredo, G.S.; Vega, M.L.; et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of bacterial cellulose–copper oxide nanocomposites and evaluation of their antimicrobial activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 179, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lima Fontes, M.; Meneguin, A.B.; Tercjak, A.; Gutierrez, J.; Cury, B.S.F.; dos Santos, A.M.; Ribeiro, S.J.L.; Barud, H.S. Effect of in situ modification of bacterial cellulose with carboxymethylcellulose on its nano/microstructure and methotrexate release properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 179, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, J.; Jia, Z.; Yang, X. Preparation and characterization of intelligent packaging film for visual inspection of tilapia fillets freshness using cyanidin and bacterial cellulose. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 205, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Ma, H.; Dai, Z.; Wang, J.; Dong, S.; Shen, J.; Dong, J. Improved thermal and mechanical properties of bacterial cellulose with the introduction of collagen. Cellulose 2017, 24, 3777–3787. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, K.; Zhang, X.-L.; Zhao, Y.-L.; Wu, Z.-L. Removal of color from textile dyeing wastewater by foam separation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Promphet, N.; Rattanawaleedirojn, P.; Siralertmukul, K.; Soatthiyanon, N.; Potiyaraj, P.; Thanawattano, C.; Hinestroza, J.P.; Rodthongkum, N. Non-Invasive textile based colorimetric sensor for the simultaneous detection of sweat pH and lactate. Talanta 2019, 192, 424–430. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Yao, J.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yang, Y. Bacterial cellulose incorporating multicolor fluorescent probes for visual acidity detection in paper-based cultural relics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 60902–60911. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bao, Z.; Liu, J.; Bi, Y.; Zhao, G. Smart Bacterial Cellulose–Methylacrylated Chitosan Composite Hydrogel: Multifunctional Characterization for Real-Time pH Monitoring. Polymers 2025, 17, 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070914
Bao Z, Liu J, Bi Y, Zhao G. Smart Bacterial Cellulose–Methylacrylated Chitosan Composite Hydrogel: Multifunctional Characterization for Real-Time pH Monitoring. Polymers. 2025; 17(7):914. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070914
Chicago/Turabian StyleBao, Zixian, Jiezheng Liu, Yujia Bi, and Guang Zhao. 2025. "Smart Bacterial Cellulose–Methylacrylated Chitosan Composite Hydrogel: Multifunctional Characterization for Real-Time pH Monitoring" Polymers 17, no. 7: 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070914
APA StyleBao, Z., Liu, J., Bi, Y., & Zhao, G. (2025). Smart Bacterial Cellulose–Methylacrylated Chitosan Composite Hydrogel: Multifunctional Characterization for Real-Time pH Monitoring. Polymers, 17(7), 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070914








