Biomimetic Prussian Blue Sensor for Ultrasensitive Direct Detection of Myoglobin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Solutions
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Synthesis of the PBNCs
2.4. Electrochemical Measurements
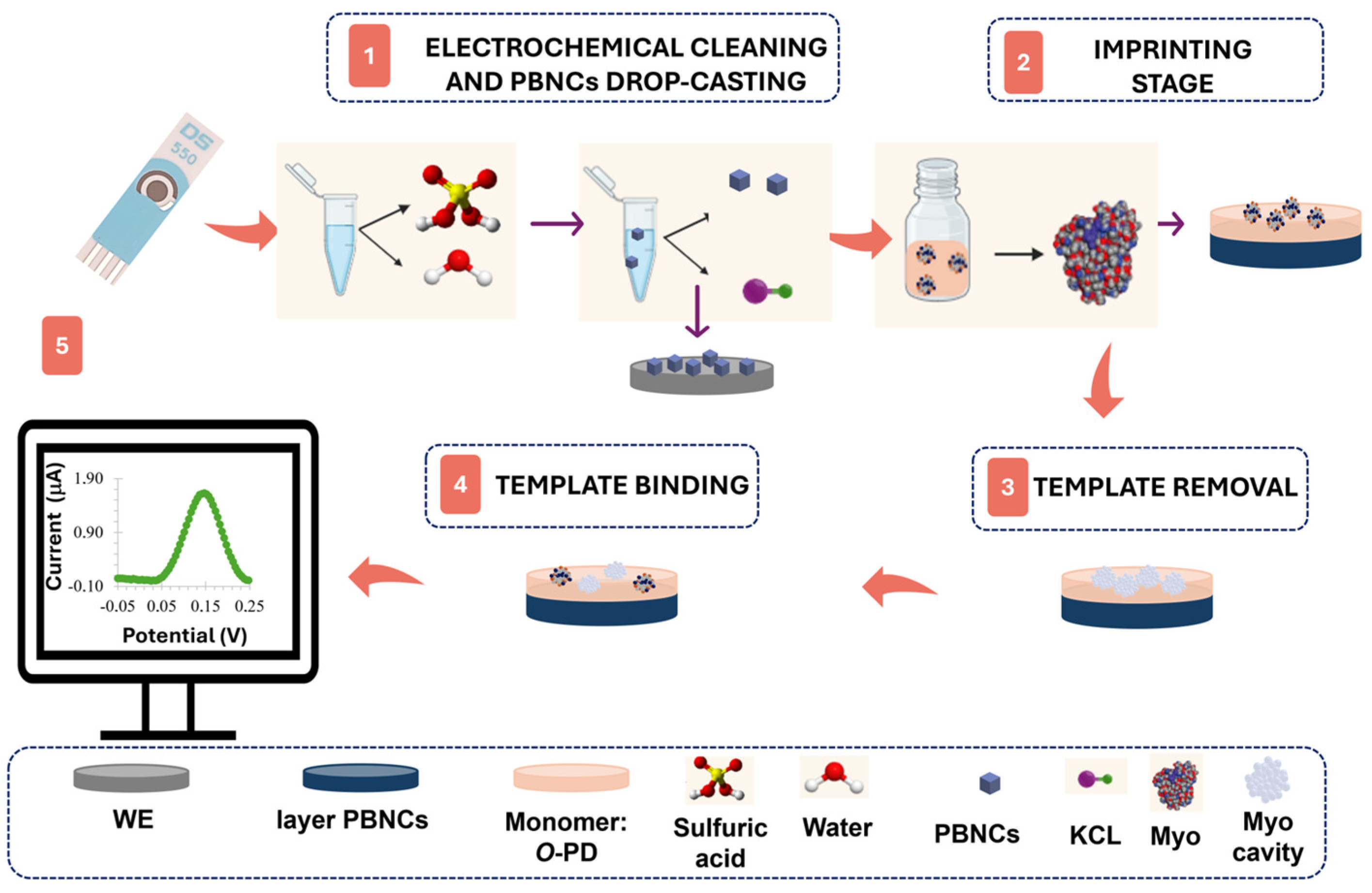
2.5. Design of the Plastic Antibody on the Pt-SPE
2.6. Analytical Performance Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
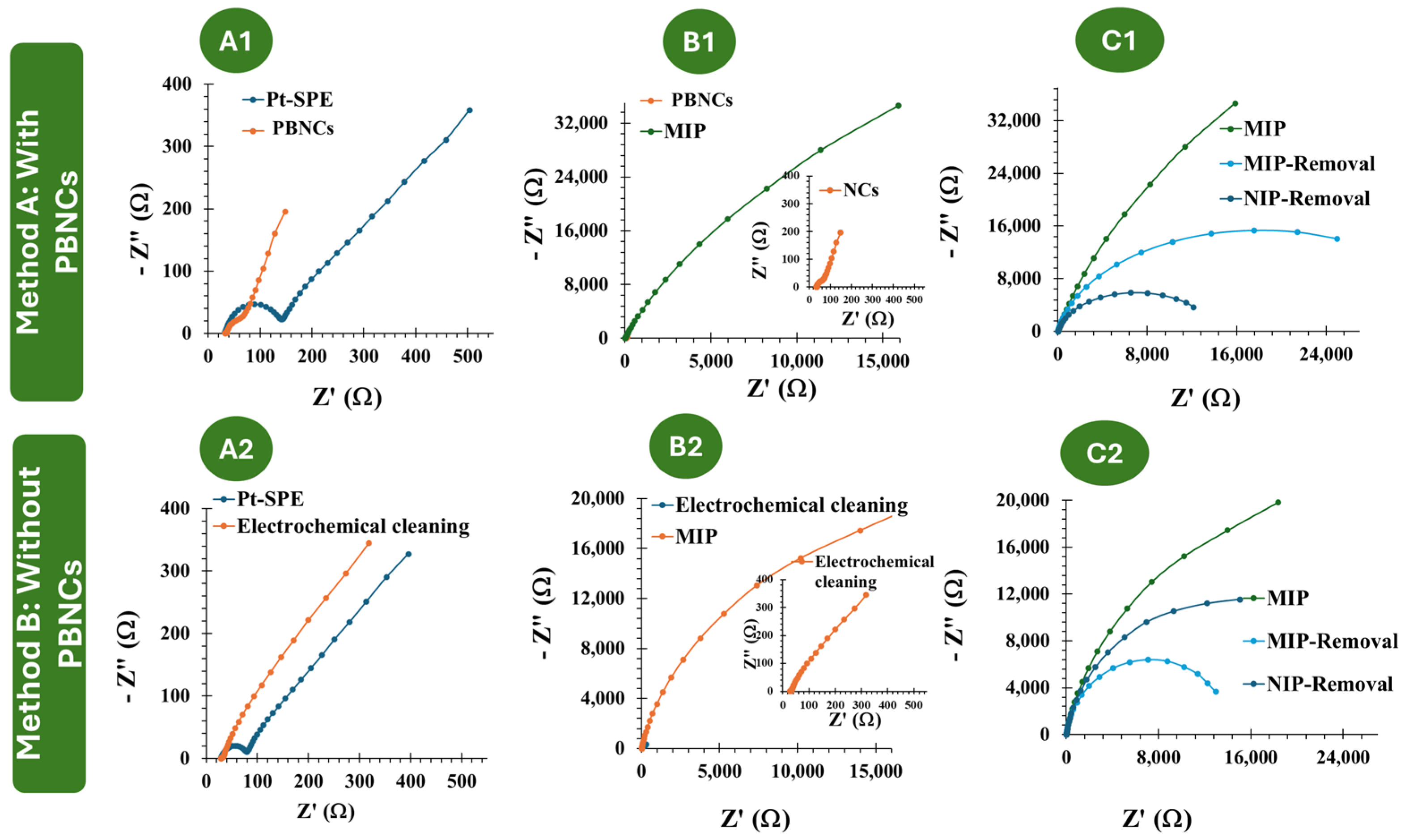
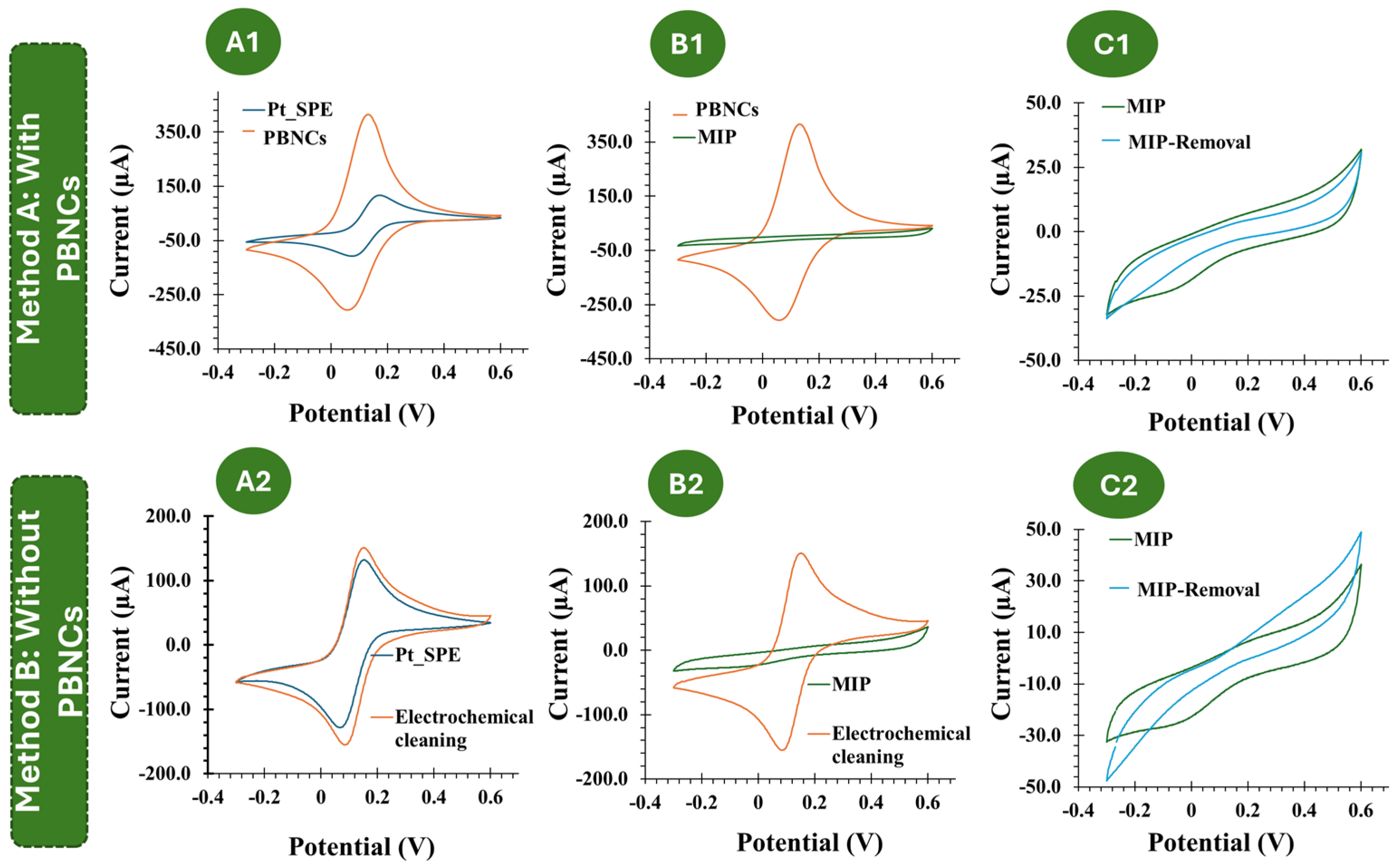
3.1. Electrochemical Follow-Up of the Biosensor Assembling
3.2. Morphological and Chemical Characterization of the Biosensor Surfaces
3.2.1. SEM
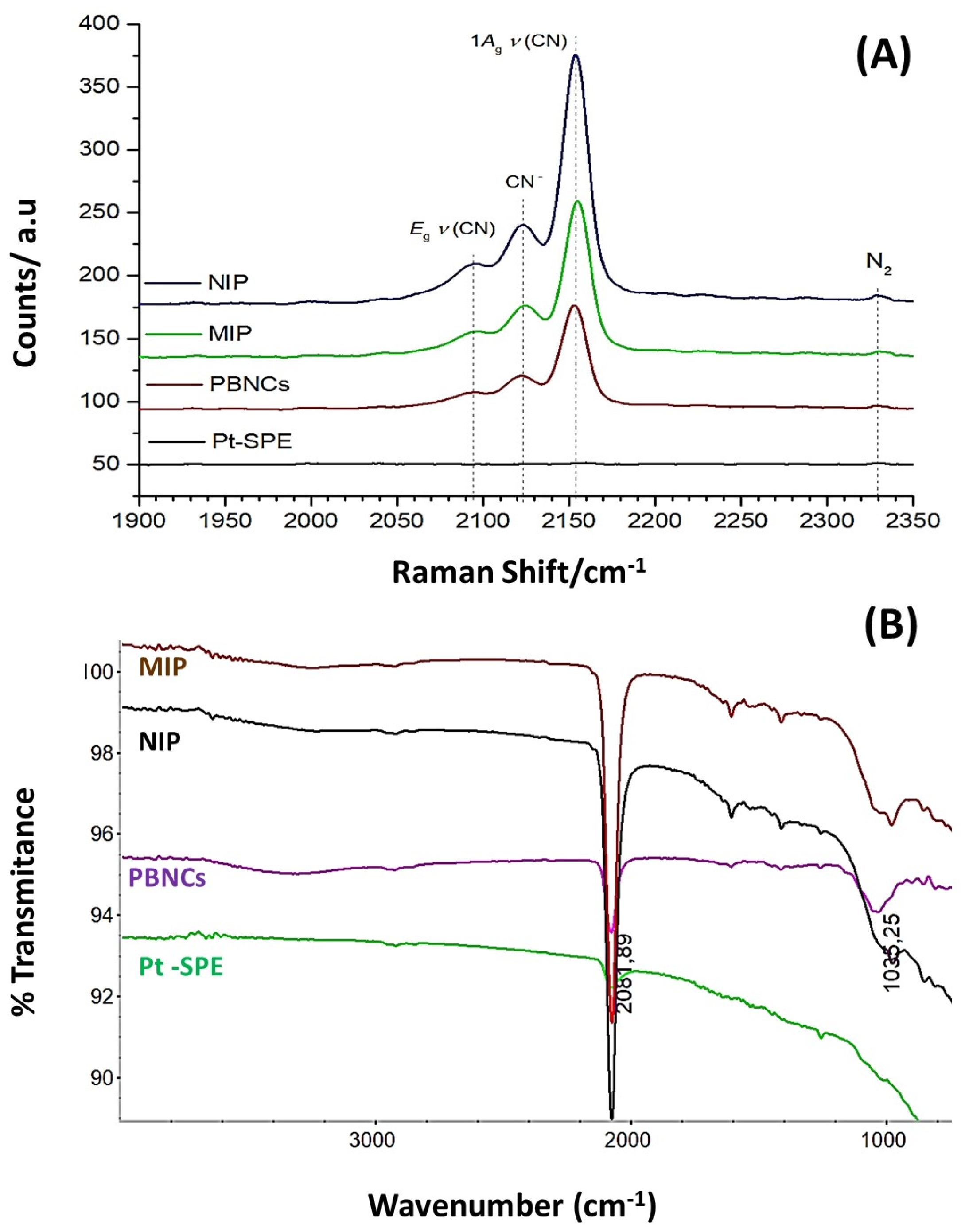
3.2.2. Chemical Characterization
3.3. Performance of the Biosensor in Buffer
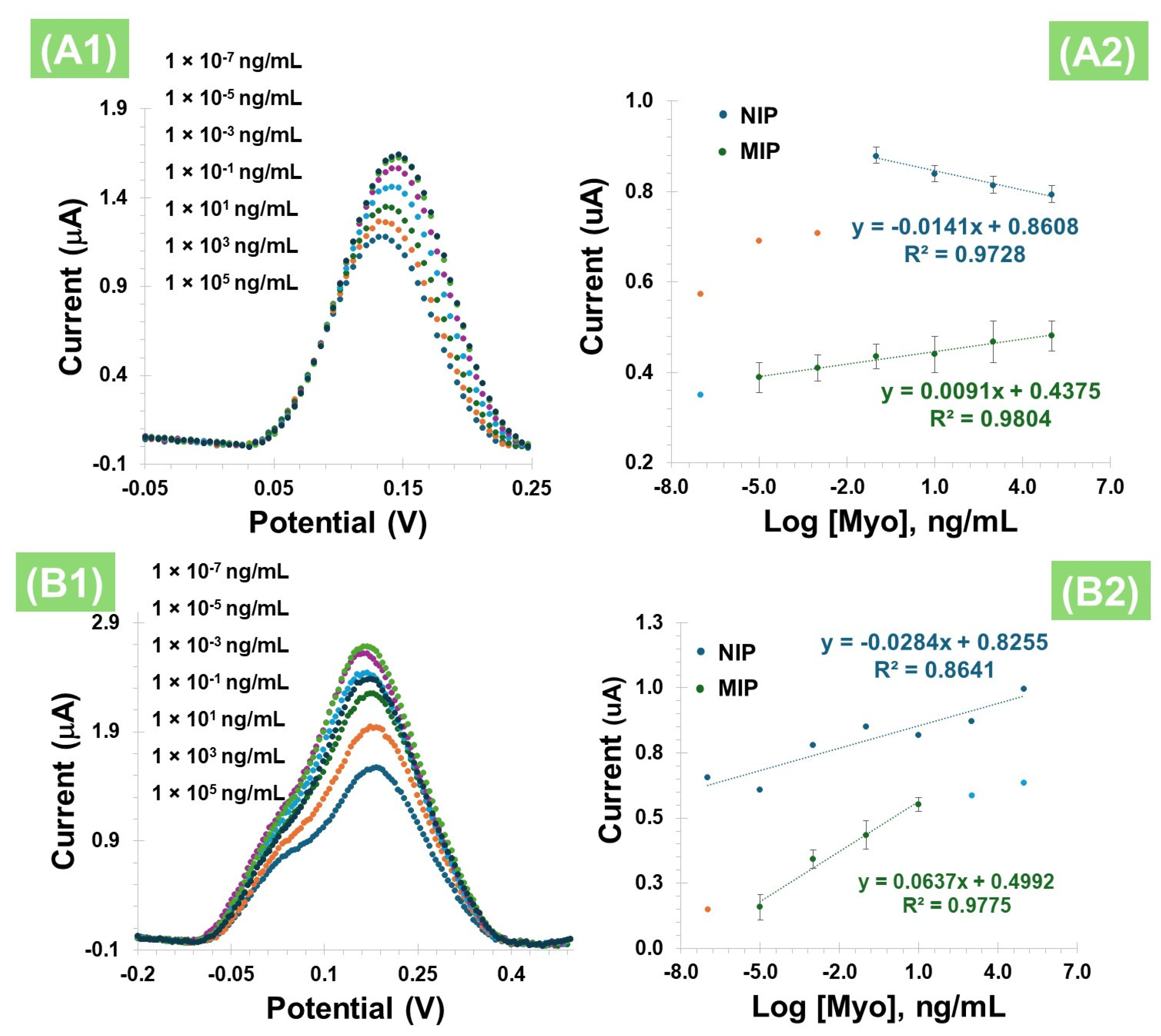
3.3.1. Calibration Curve Without PBNCs
3.3.2. Calibration Curve with PBNCs
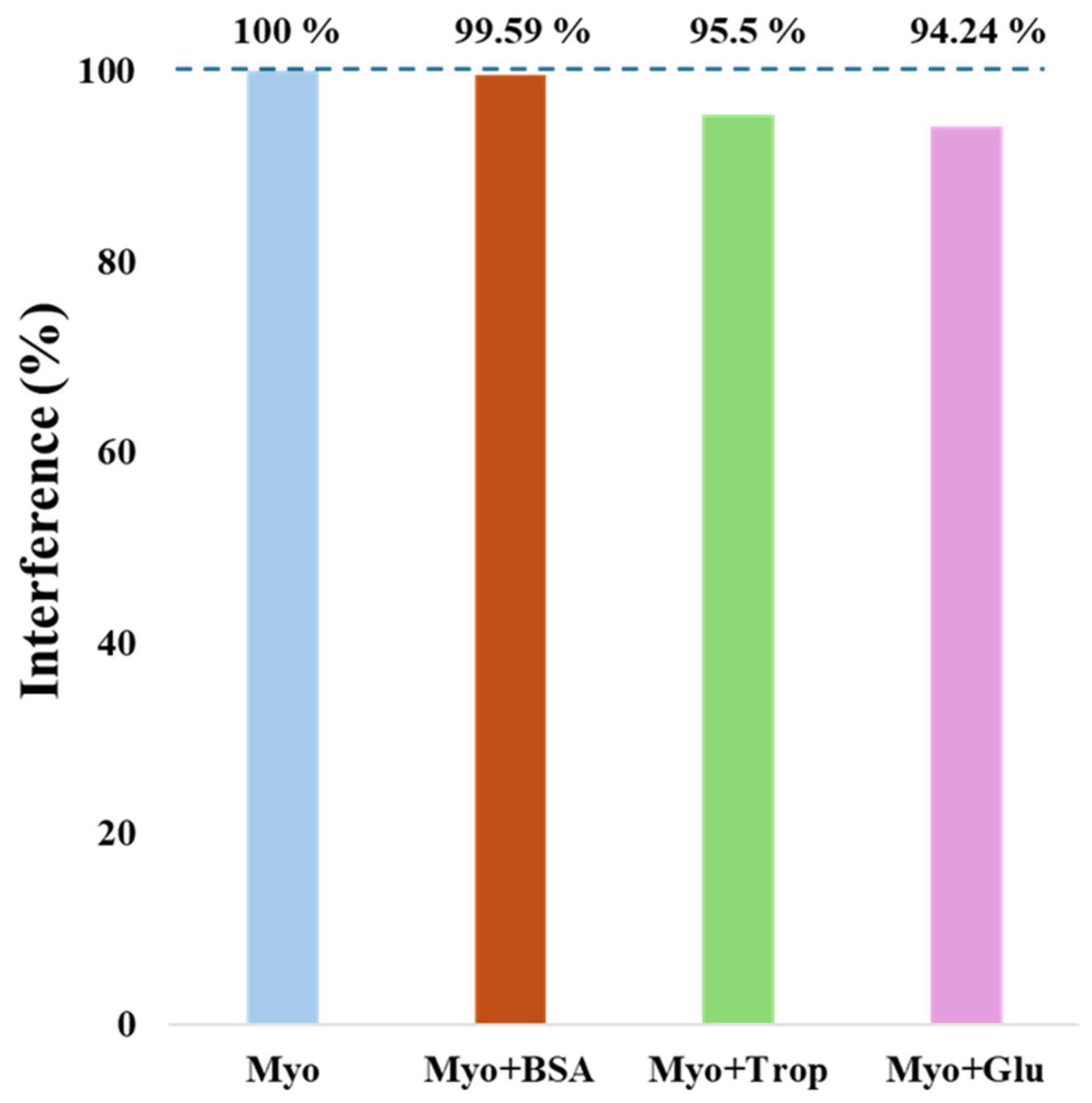
3.3.3. Selectivity Study
3.4. Direct Calibration of the Biosensor in Serum
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Donald, T.G.; Cloonan, M.J.; Neale, C.; Wilcken, D.E.L. Excretion of myoglobin in urine after acute myocardial-infarction. Br. Heart J. 1977, 39, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamm, C.W. Acute coronary syndromes—The diagnostic role of troponins. Thromb. Res. 2001, 103, S63–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matveeva, E.G.; Gryczynski, Z.; Lakowicz, J.R. Myoglobin immunoassay based on metal particle-enhanced fluorescence. J. Immunol. Methods 2005, 302, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaldo, A.M.; Ercolini, P.; Forino, F.; Basevi, A.; Vrenna, L.; Castaldo, P.; Ambrosio, V.D.; Castaldo, A. Plasma myoglobin in the early diagnosis of acute myocardial-infarction. Eur. J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem. 1994, 32, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Woo, J.; Lacbawan, F.L.; Sunheimer, R.; Lefever, D.; McCabe, J.B. Is myoglobin useful in the diagnosis of acute myocardial-infarction in the emergency department setting. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1995, 103, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, M.J.; Waterman, M.R.; Harimoto, D.; Murray, G.; Willson, N.; Platt, M.R.; Blomqvist, G.; Willerson, J.T. Serum myoglobin level as diagnostic test in patients with acute myocardial-infarction. Br. Heart J. 1977, 39, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloonan, M.J.; Bishop, G.A.; Wiltonsmith, P.D.; Carter, I.W.; Allan, R.M.; Wilcken, D.E.L. Enzyme-immunoassay for myoglobin in human-serum and urine—Method development, normal values and application to acute myocardial-infarction. Pathology 1979, 11, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.J.; Tang, Y.C.; Liu, W.P.; Yu, S.X.; Lan, X.P.; Xu, B.; Wu, Y.S.; Li, L.; Zhu, Z.Y. Qualitative bedside assay of increased human serum myoglobin by sandwich dot-immunogold filtration for the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Clin. Chim. Acta 1998, 273, 119–130. [Google Scholar]
- Nishida, Y.; Kawai, H.; Nishino, H. A sensitive sandwich enzyme-immunoassay for human myoglobin using fab-horseradish peroxidase conjugate—Methods and results in normal subjects and patients with various diseases. Clin. Chim. Acta 1985, 153, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogan, G.X.; Friedman, S.; McCuskey, C.; Cooling, D.S.; Berrutti, L.; Thode, H.C.; Bock, J.L. Evaluation of a new rapid quantitative immunoassay for serum myoglobin versus ck-mb for ruling out acute myocardial-infarction in the emergency department. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1994, 24, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuerle, J.R.; Azzazy, H.M.E.; Apple, F.S.; Duh, S.H.; Tan, A.; Christenson, R.H. Performance characteristics of a new myoglobin microparticle enzyme immunoassay: A multicenter evaluation. Clin. Biochem. 2000, 33, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.; Gurbuz, Y.; Niazi, J.H. Biosensors for cardiac biomarkers detection: A review. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2012, 171, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, M.J.; Willerson, J.T.; Gomezsanchez, C.E.; Waterman, M.R. Radioimmunoassay of myoglobin in human-serum—Results in patients with acute myocardial-infarction. J. Clin. Investig. 1975, 56, 1334–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilkeson, G.; Stone, M.J.; Waterman, M.; Ting, R.; Gomezsanchez, C.E.; Hull, A.; Willerson, J.T. Detection of myoglobin by radioimmunoassay in human sera—Its usefulness and limitations as an emergency room screening-test for acute myocardial-infarction. Am. Heart J. 1978, 95, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friess, U.; Stark, M. Cardiac markers: A clear cause for point-of-care testing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 393, 1453–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straface, A.L.; Myers, J.H.; Kirchick, H.J.; Blick, K.E. A rapid point-of-care cardiac marker testing strategy facilitates the rapid diagnosis and management of chest pain patients in the emergency department. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2008, 129, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-Y.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Thomas, J.L.; Wang, S.-E.; Chen, H.-C.; Chou, T.-C. The microcontact imprinting of proteins: The effect of cross-linking monomers for lysozyme, ribonuclease A and myoglobin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 22, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, F.T.C.; Dutra, R.A.F.; Noronha, J.P.C.; Sales, M.G.F. Myoglobin-biomimetic electroactive materials made by surface molecular imprinting on silica beads and their use as ionophores in polymeric membranes for potentiometric transduction. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 4760–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirhagl, R.; Latif, U.; Podlipna, D.; Blumenstock, H.; Dickert, F.L. Natural and Biomimetic Materials for the Detection of Insulin. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 3908–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.-C.; Rick, J.; Weng, Y.-C. Nanocavity Protein Biosensor—Fabricated by Molecular Imprinting. In Proceedings of the 2007 7th IEEE Conference on Nanotechnology, Hong Kong, China, 2–5 August 2007; Volumes 1–3, pp. 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasco, M.; Truta, L.; Sales, M.; Moreira, F. Imprinting Technology in Electrochemical Biomimetic Sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malitesta, C.; Losito, I.; Zambonin, P.G. Molecularly imprinted electrosynthesized polymers: New materials for biomimetic sensors. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 1366–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algieri, C.; Drioli, E.; Guzzo, L.; Donato, L. Bio-Mimetic Sensors Based on Molecularly Imprinted Membranes. Sensors 2014, 14, 13863–13912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cieplak, M.; Kutner, W. Artificial Biosensors: How Can Molecular Imprinting Mimic Biorecognition? Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 922–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzun, L.; Turner, A.P.F. Molecularly-imprinted polymer sensors: Realising their potential. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 76, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, F.T.C.; Dutra, R.A.F.; Noronha, J.P.C.; Sales, M.G.F. Electrochemical biosensor based on biomimetic material for myoglobin detection. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 107, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, F.T.C.; Sharma, S.; Dutra, R.A.F.; Noronha, J.P.C.; Cass, A.E.G.; Sales, M.G.F. Protein-responsive polymers for point-of-care detection of cardiac biomarker. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2014, 196, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, W. Molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) based electrochemical sensors and their recent advances in health applications. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2023, 5, 100153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.; Gomes, R.; Rocha, S.; Barroca-Ferreira, J.; Maia, C.; Guillade, L.; Correa-Duarte, M.; Passarinha, L.; Moreira, F. Development of a novel electrochemical biosensor based on plastic antibodies for detection of STEAP1 biomarker in cancer. Bioelectrochemistry 2023, 152, 108461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarman, A.; Scheller, F.W. How Reliable Is the Electrochemical Readout of MIP Sensors? Sensors 2020, 20, 2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crapnell, R.D.; Dempsey-Hibbert, N.C.; Peeters, M.; Tridente, A.; Banks, C.E. Molecularly imprinted polymer based electrochemical biosensors: Overcoming the challenges of detecting vital biomarkers and speeding up diagnosis. Talanta Open 2020, 2, 100018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szunerits, S.; Mishyn, V.; Grabowska, I.; Boukherroub, R. Electrochemical cardiovascular platforms: Current state of the art and beyond. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 131, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Hassine, A.; Raouafi, N.; Moreira, F.T.C. Novel biomimetic Prussian blue nanocubes-based biosensor for Tau-441 protein detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 226, 115251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glória, J.; Oliveira, D.; Gandarilla, A.; Barcelay, Y.; Mariúba, L.; Nogueira, P.; Brito, W.; Moreira, F. Liquid Redox Probe-Free Plastic Antibody Development for Malaria Biomarker Recognition. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 33130–33139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grieshaber, D.; MacKenzie, R.; Voeroes, J.; Reimhult, E. Electrochemical biosensors—Sensor principles and architectures. Sensors 2008, 8, 1400–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, D.; Ren, L.; Zhao, H.; Xu, C.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Y.; Wang, H.; Lan, Y.; Roberts, M.F.; Chuang, J.H.; et al. A molecular-imprint nanosensor for ultrasensitive detection of proteins. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronkainen, N.J.; Halsall, H.B.; Heineman, W.R. Electrochemical biosensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1747–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadeh, Z.B.; Hosseini, S.M.; Mohammadnejad, J.; Tanhaei, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Label-Free Detection of Cardiac Biomarkers: A Review on Microfluidic Electrochemical Biosensors. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2023, 6, 2622–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, F.T.C.; Rodriguez, B.A.G.; Dutra, R.A.F.; Sales, M.G.F. Redox probe-free readings of a beta-amyloid-42 plastic antibody sensory material assembled on copper@carbon nanotubes. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2018, 264, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Zhang, B.H.; Lu, L.H. In situ Controllable Growth of Prussian Blue Nanocubes on Reduced Graphene Oxide: Facile Synthesis and Their Application as Enhanced Nanoelectrocatalyst for H2O2 Reduction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 2339–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billah, M.M.; Hodges, C.S.; Hays, H.C.W.; Millner, P.A. Directed immobilization of reduced antibody fragments onto a novel SAM on gold for myoglobin impedance immunosensing. Bioelectrochemistry 2010, 80, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, R.S.; Moreira, F.T.C.; Fernandes, R.; Sales, M.G.F. Sensing CA 15-3 in point-of-care by electropolymerizing O-phenylenediamine (oPDA) on Au-screen printed electrodes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, M.V.; Marques, A.C.; Oliveira, D.; Martins, R.; Moreira, F.T.C.; Sales, M.G.F.; Fortunato, E. Paper-Based Platform with an In Situ Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for beta-Amyloid. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 12057–12066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, G.; Gervais, C. Raman spectroscopy of the photosensitive pigment Prussian blue. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2018, 49, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, A.; Clark, R.; Ribeiro, M.; Duarte, M. Pigment study by Raman microscopy of 23 paintings by the Portuguese artist Henrique Pousao (1859–1884). J. Raman Spectrosc. 2007, 38, 1390–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muslu, E.; Eren, E.; Oksuz, A. Prussian Blue-Based Flexible Thin Film Nanoarchitectonics for Non-enzymatic Electrochemical Glucose Sensor. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2022, 32, 2843–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gervais, C.; Languille, M.; Réguer, S.; Gillet, M.; Pelletier, S.; Garnier, C.; Vicenzi, E.; Bertrand, L. Why does Prussian blue fade? Understanding the role(s) of the substrate. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2013, 28, 1600–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettle, S.; Diana, E.; Boccaleri, E.; Stanghellini, P. The vibrational spectra of the cyanide ligand revisited. Bridging cyanides. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 2409–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keçili, R. Selective Recognition of Myoglobin in Biological Samples Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Affinity Traps. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2018, 2018, 4359892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ricardo, J.; Duarte, A.; Chiussi, S.; Martins, G.V.; Moreira, F.T.C. Biomimetic Prussian Blue Sensor for Ultrasensitive Direct Detection of Myoglobin. Polymers 2025, 17, 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17050630
Ricardo J, Duarte A, Chiussi S, Martins GV, Moreira FTC. Biomimetic Prussian Blue Sensor for Ultrasensitive Direct Detection of Myoglobin. Polymers. 2025; 17(5):630. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17050630
Chicago/Turabian StyleRicardo, Jacinta, Abel Duarte, Stefano Chiussi, Gabriela V. Martins, and Felismina T. C. Moreira. 2025. "Biomimetic Prussian Blue Sensor for Ultrasensitive Direct Detection of Myoglobin" Polymers 17, no. 5: 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17050630
APA StyleRicardo, J., Duarte, A., Chiussi, S., Martins, G. V., & Moreira, F. T. C. (2025). Biomimetic Prussian Blue Sensor for Ultrasensitive Direct Detection of Myoglobin. Polymers, 17(5), 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17050630







