Optimizing β-Phase Content in PVDF Membranes via Modification of Dope Solution with Citric Acid/Nano-TiO2 Using Nonsolvent-Induced Phase Separation Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of PVDF Dope Solutions
2.3. Fabrication of PVDF Membrane Films
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of TiO2 Nanoparticles
3.2. Characterization of Commercial PVDF Powder
3.3. Effect of Citric Acid in Dope Solution on Morphology of PVDF (TONx Series) Membranes
3.3.1. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis of TONx Series PVDF Membranes
3.3.2. FTIR Analysis of TONx Series PVDF Membranes
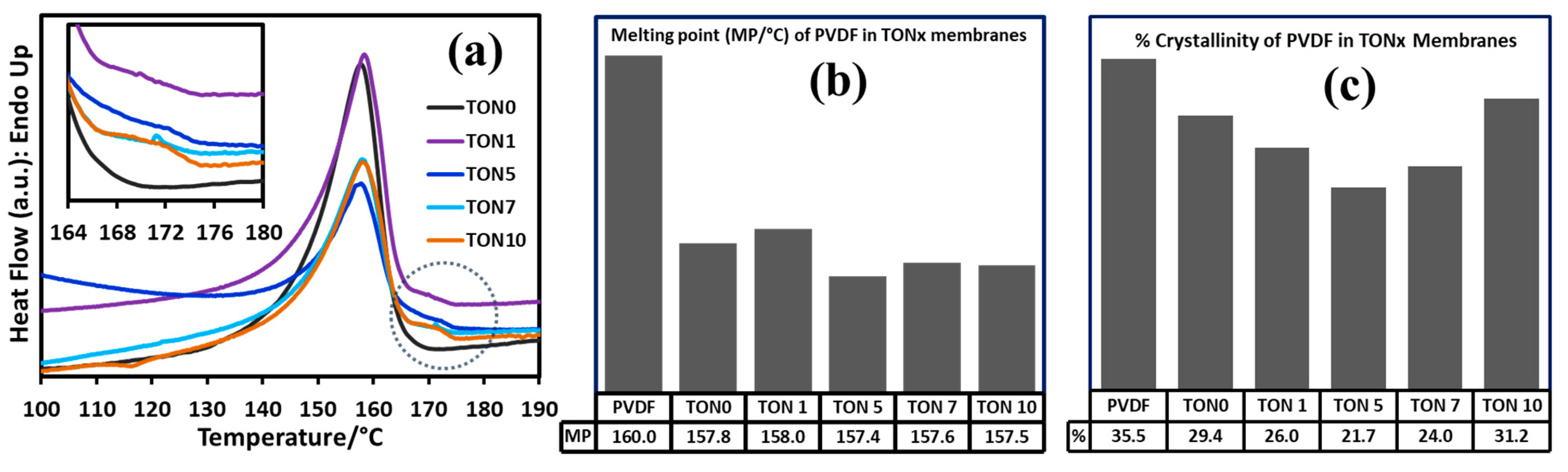
3.3.3. Thermal Analysis of PVDF Membranes of TONx Series
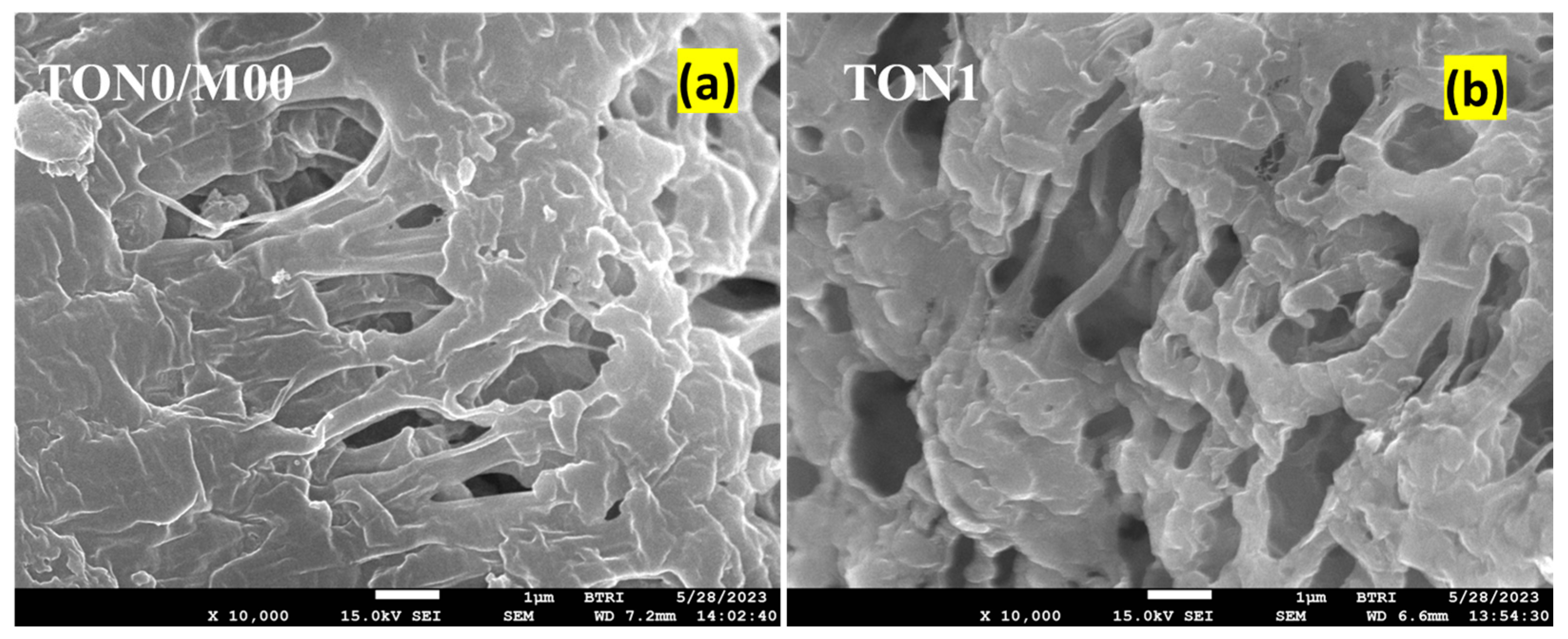
3.3.4. FESEM of PVDF Membranes of TONx Series
3.3.5. Porosity Analysis of PVDF Membranes of TONx Series
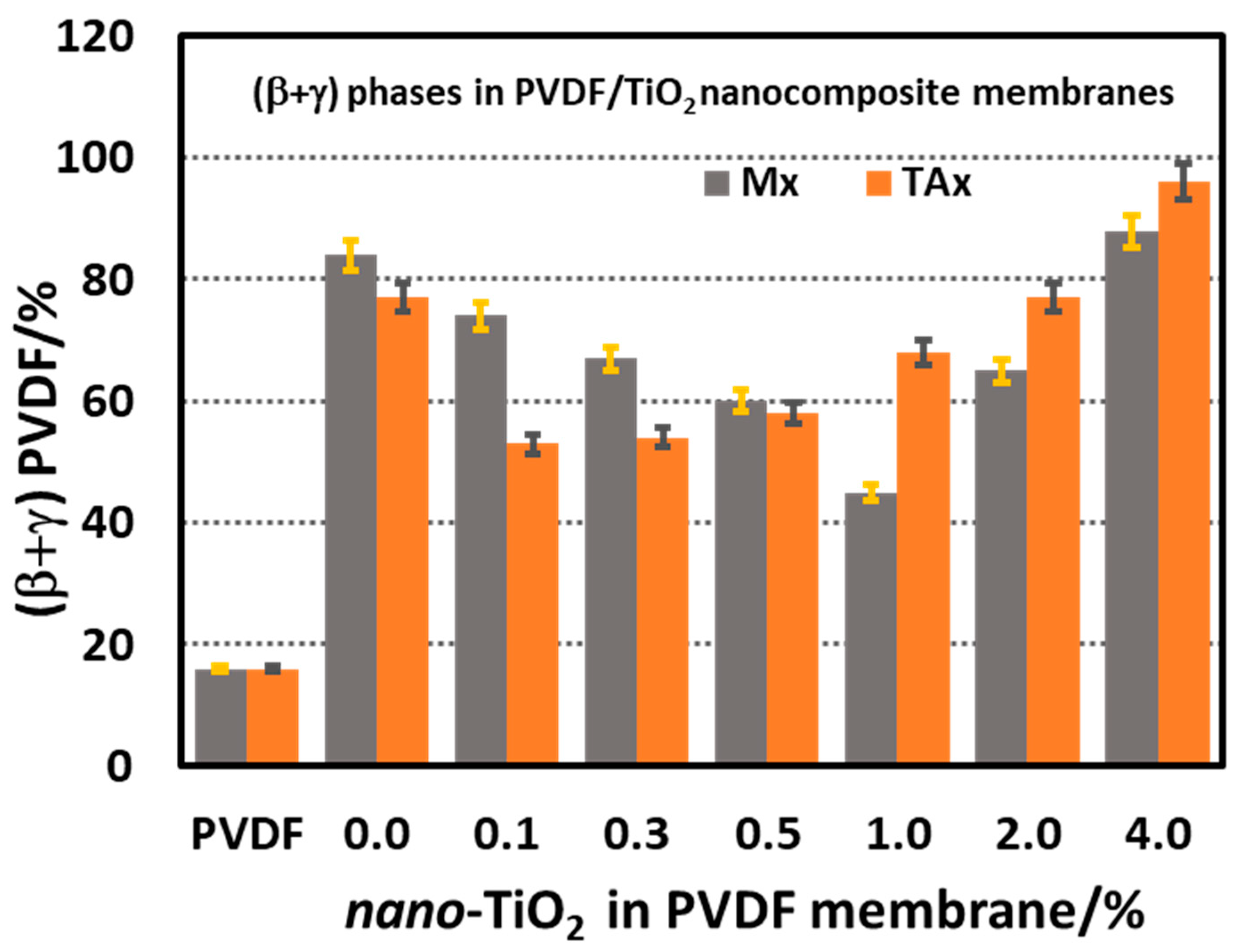
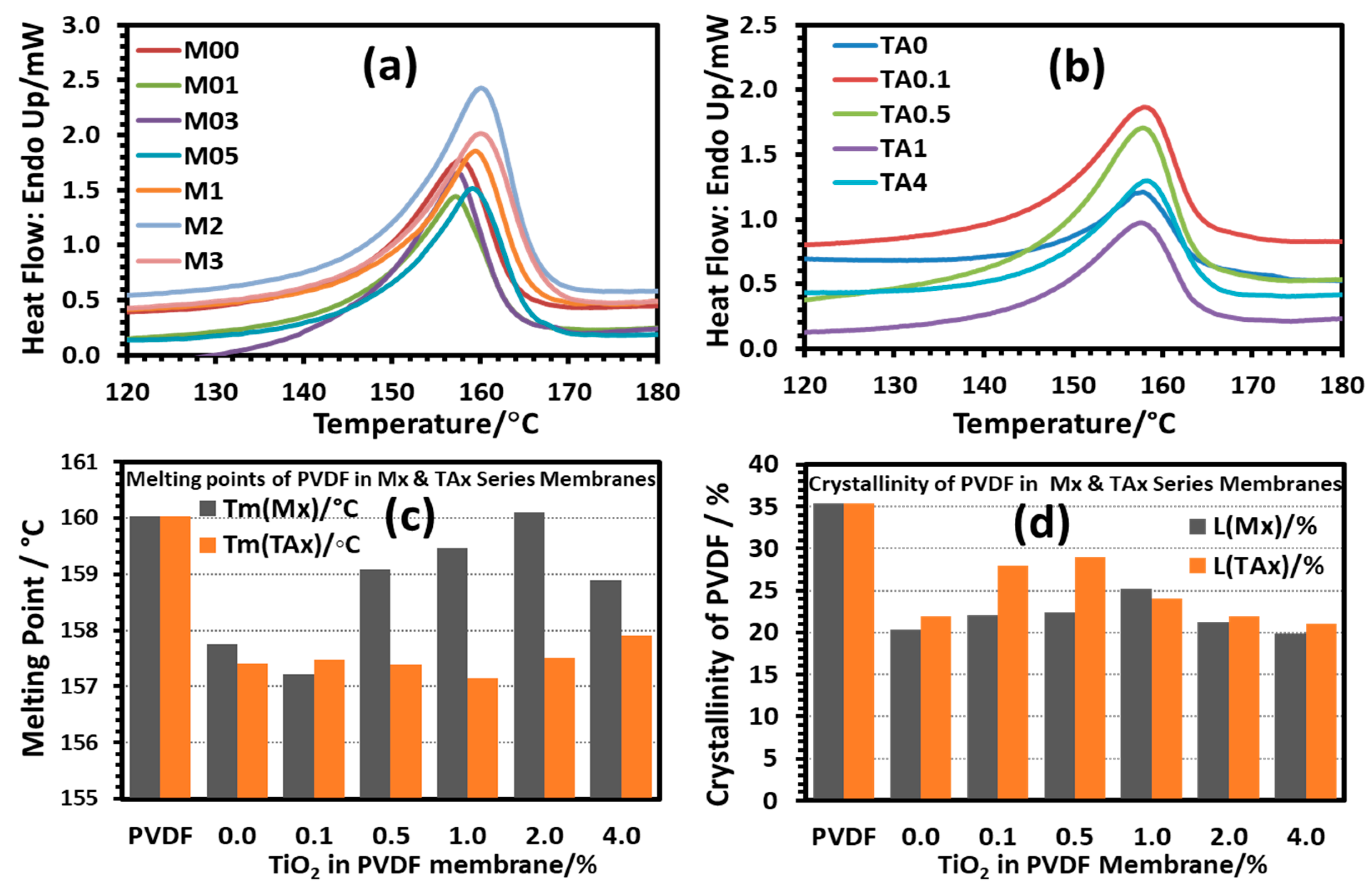
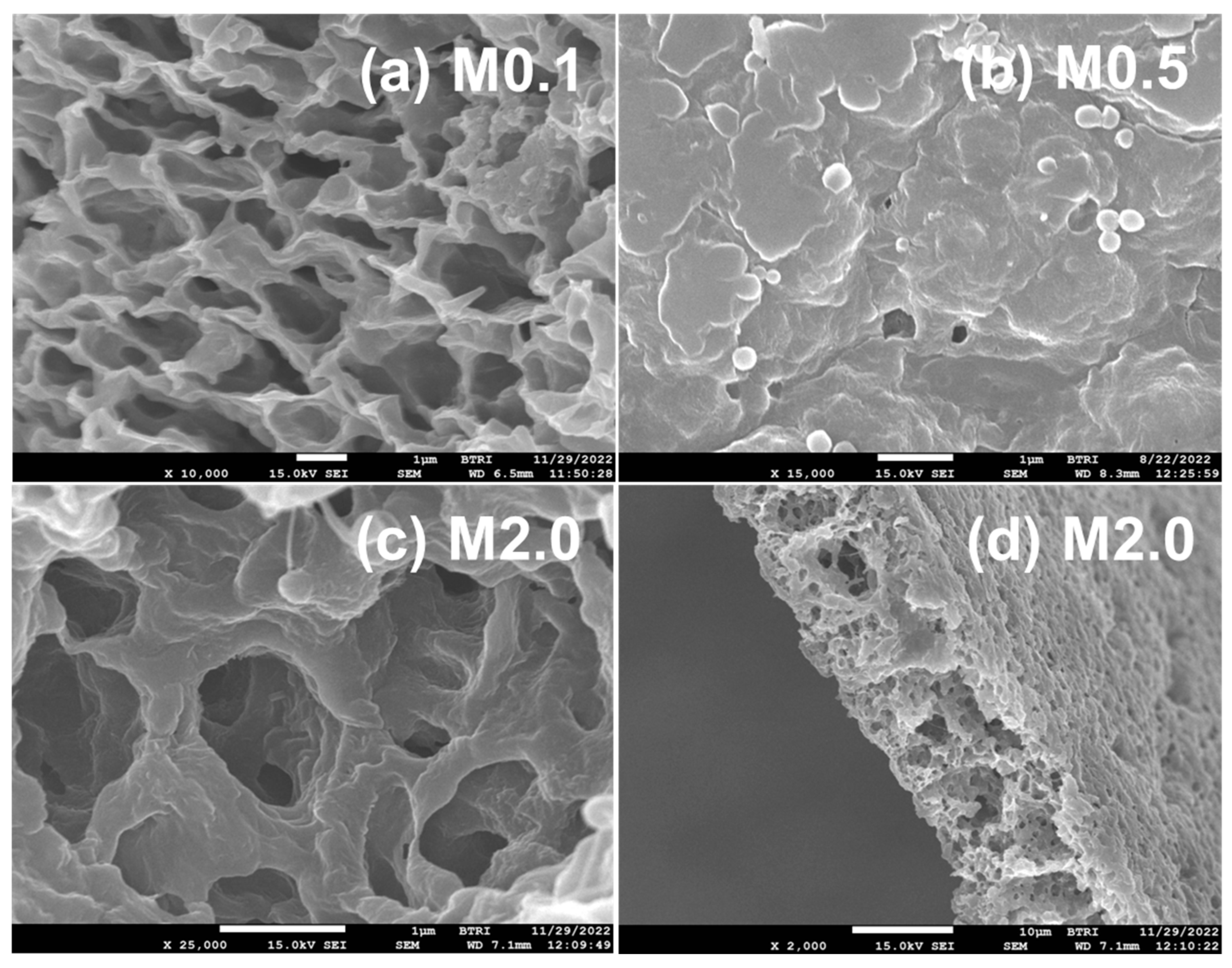
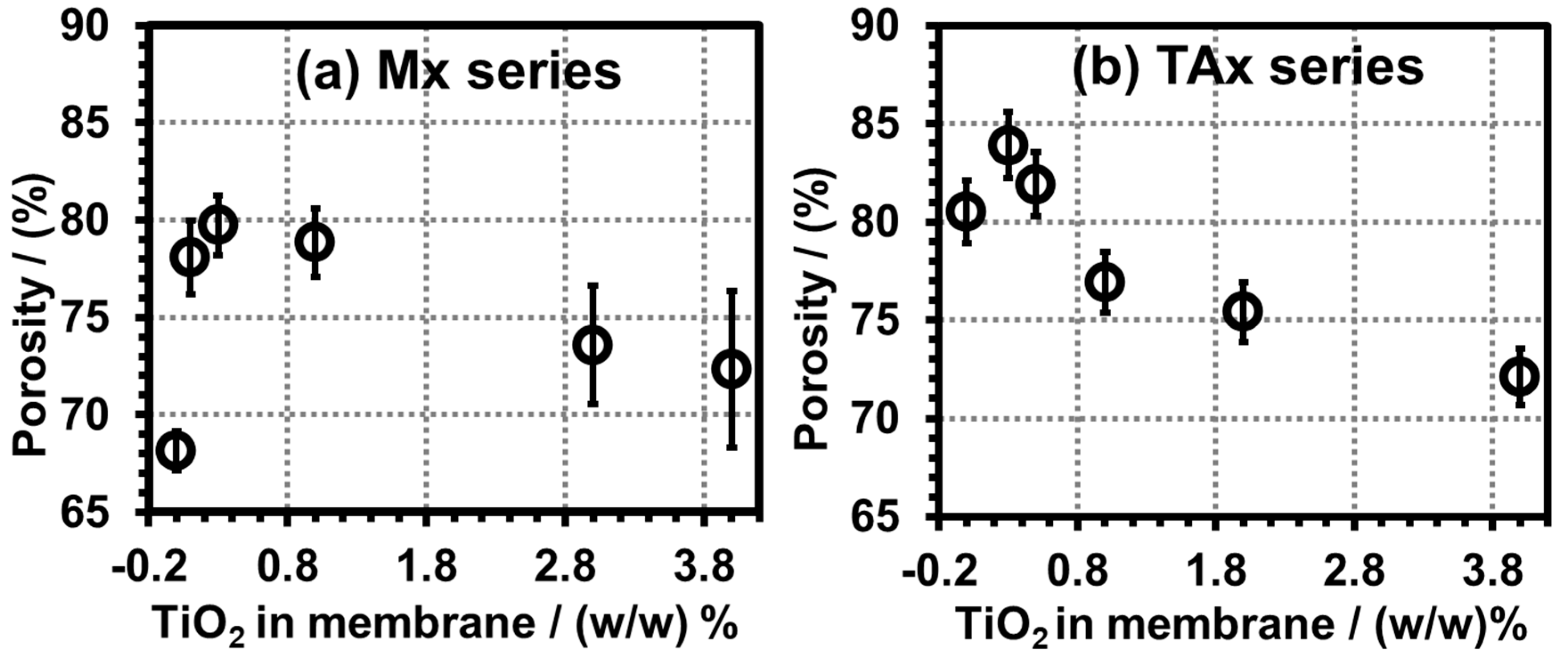
3.4. Morphology and Thermal Stability of PVDF/TiO2 (Mx Series) and PVDF/TiO2/CA (TAx Series) Membranes
3.4.1. X-Ray Diffraction Study of PVDF-TiO2 Nanocomposite Membranes of Mx and TAx Series
3.4.2. FTIR Spectroscopic Study of PVDF-TiO2 Nanocomposite Membranes of Mx and TAx Series
3.4.3. Thermal Analysis of PVDF-TiO2 Nanocomposite Membranes of Mx and TAx Series
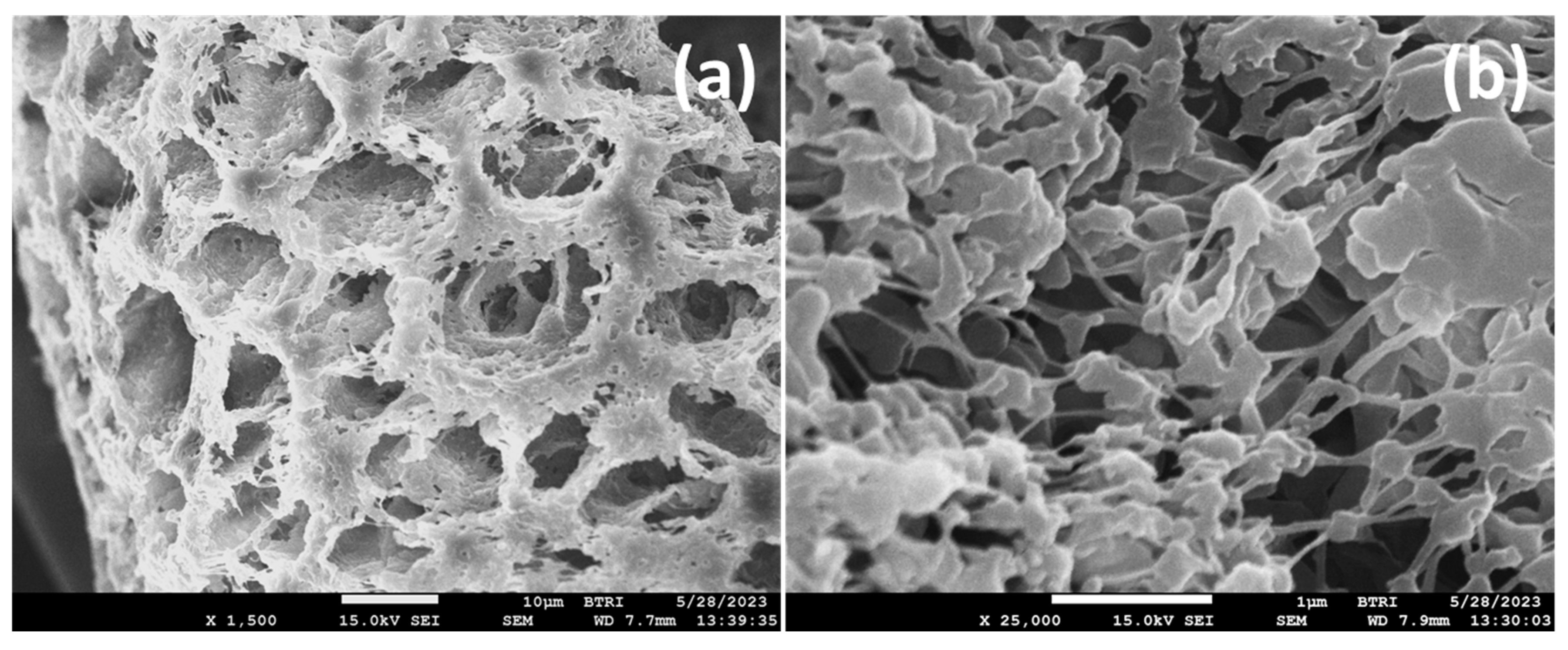
3.4.4. FESEM Study of PVDF-TiO2 Nanocomposite Membranes of Mx and TAx Series
3.4.5. Porosity Analysis of PVDF Membranes of Mx and TAx Series
4. Conclusions
- Structurally, citric acid significantly enhances pore opening, while nano-TiO2 transforms sponge-like porous structures into compact, honeycomb-like architectures. The porosity of the membranes increases as a function of additives, reaching 84% with an optimal CA concentration of 5% and low nano-TiO2 levels.
- Morphologically, the analysis reveals a significant enhancement in electroactive (β + γ)-phase content due to the presence of additives. In the TAx series membranes, the relative amount of this phase reaches 96%, with the β-phase being the dominant crystalline structure. This enhancement can be attributed to the nucleation of the electroactive PVDF phases from domains of aligned segments formed in the dope solution and a yet unknown interplay of CA and nano-TiO2 with the nucleating PVDF domains in the dope solution.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karki, S.; Hazarika, G.; Yadav, D.; Ingole, P.G. Polymeric Membranes for Industrial Applications: Recent Progress, Challenges and Perspectives. Desalination 2024, 573, 117200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrekrstos, A.; Muzata, T.S.; Ray, S.S. Nanoparticle-Enhanced β-Phase Formation in Electroactive PVDF Composites: A Review of Systems for Applications in Energy Harvesting, EMI Shielding, and Membrane Technology. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 7632–7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.W. Research Needs in the Membrane Separation Industry: Looking Back, Looking Forward. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 362, 134–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Martinez, A.R. Advanced Functional Membranes for Sensor Technologies. In Materials Research Foundations; Materials Research Forum LLC.: Millersville, PA, USA, 2022; Volume 120, pp. 315–333. ISBN 978-1-64490-181-6. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, C.M.; Cardoso, V.F.; Martins, P.; Correia, D.M.; Gonçalves, R.; Costa, P.; Correia, V.; Ribeiro, C.; Fernandes, M.M.; Martins, P.M.; et al. Smart and Multifunctional Materials Based on Electroactive Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride): Recent Advances and Opportunities in Sensors, Actuators, Energy, Environmental, and Biomedical Applications. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 11392–11487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, A.; Saeed, B.; AlMohamadi, H.; Lee, M.; Gilani, M.A.; Nawaz, R.; Khan, A.L.; Yasin, M. Sustainable and Green Membranes for Chemical Separations: A Review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 336, 126271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Du, L.; Meng, Z.; Gao, J.; Tan, A.; Jin, X.; Zhu, X. Ingenious Structure Engineering to Enhance Piezoelectricity in Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) for Biomedical Applications. Biomacromolecules 2024, 25, 5541–5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimkin, A.V.; Dayyoub, T.; Telyshev, D.V.; Gerasimenko, A.Y. Electroactive Polymer-Based Composites for Artificial Muscle-like Actuators: A Review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Kim, S.; Park, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, M. Recent Progress in Development and Applications of Ionic Polymer–Metal Composite. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallaev, R.; Pisarenko, T.; Sobola, D.; Orudzhev, F.; Ramazanov, S.; Trčka, T. Brief Review of PVDF Properties and Applications Potential. Polymers 2022, 14, 4793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, N.D.; Kumari, P. Development of Highly Flexible PVDF-TiO2 Nanocomposites for Piezoelectric Nanogenerator Applications. Mater. Res. Bull. 2023, 157, 112039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concha, V.O.C.; Timóteo, L.; Duarte, L.A.N.; Bahú, J.O.; Munoz, F.L.; Silva, A.P.; Lodi, L.; Severino, P.; León-Pulido, J.; Souto, E.B. Properties, Characterization and Biomedical Applications of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF): A Review. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 14185–14204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liao, C.; Tjong, S.C. Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride-Based Fibrous Scaffolds with Piezoelectric Characteristics for Bone and Neural Tissue Engineering. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrada, M.L.; Arranz-Andrés, J.; Caballero-González, A.; Blázquez-Blázquez, E.; Pérez, E. The β Form in PVDF Nanocomposites with Carbon Nanotubes: Structural Features and Properties. Polymers 2023, 15, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atif, R.; Khaliq, J.; Combrinck, M.; Hassanin, A.H.; Shehata, N.; Elnabawy, E.; Shyha, I. Solution Blow Spinning of Polyvinylidene Fluoride Based Fibers for Energy Harvesting Applications: A Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Zhai, S.; Zhang, C.; Xue, Y.; Yang, W.; Lin, J. Effect of Sulfonation Degree and PVDF Content on the Structure and Transport Properties of SPEEK/PVDF Blend Membranes. Polymers 2019, 11, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, W.; Tan, B.; Zhu, C.; Ni, Y.; Fang, L.; Lu, C.; Xu, Z. Crystallinity and β Phase Fraction of PVDF in Biaxially Stretched PVDF/PMMA Films. Polymers 2021, 13, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, L.; Yao, X.; Chang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Qin, G.; Zhang, X. Properties and Applications of the β Phase Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride). Polymers 2018, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basko, A.; Lebedeva, T.; Yurov, M.; Ilyasova, A.; Elyashevich, G.; Lavrentyev, V.; Kalmykov, D.; Volkov, A.; Pochivalov, K. Mechanism of PVDF Membrane Formation by NIPS Revisited: Effect of Precipitation Bath Nature and Polymer–Solvent Affinity. Polymers 2023, 15, 4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Hassankiadeh, N.T.; Zhuang, Y.; Drioli, E.; Lee, Y.M. Crystalline Polymorphism in Poly(Vinylidenefluoride) Membranes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 51, 94–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Ma, W.; Wang, X. A Review on Microporous Polyvinylidene Fluoride Membranes Fabricated via Thermally Induced Phase Separation for MF/UF Application. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 639, 119759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Hashim, N.A.; Liu, Y.; Abed, M.R.M.; Li, K. Progress in the Production and Modification of PVDF Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 375, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, S.; Li, J. Preparation and Modification of PVDF Membrane via VIPS Method for Membrane Distillation. Appl. Water Sci. 2024, 14, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Lu, D.; Harris, T.A.L.; Escobar, I.C. Polymers and Solvents Used in Membrane Fabrication: A Review Focusing on Sustainable Membrane Development. Membranes 2021, 11, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.-Y.; Li, C.-L.; Wang, D.-M.; Lai, J.-Y. Formation of Porous Structures and Crystalline Phases in Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) Membranes Prepared with Nonsolvent-Induced Phase Separation—Roles of Solvent Polarity. Polymers 2023, 15, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Sun, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xing, W. Preparation of PVDF Membrane via Synergistically Vapor and Non-Solvent-Induced Phase Separation. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Rault, F.; Lewandowski, M.; Mohsenzadeh, E.; Salaün, F. Electrospun PVDF Nanofibers for Piezoelectric Applications: A Review of the Influence of Electrospinning Parameters on the β Phase and Crystallinity Enhancement. Polymers 2021, 13, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Tian, B.; Zhu, Q.; Duan, C. Characterization and Application of PVDF and Its Copolymer Films Prepared by Spin-Coating and Langmuir–Blodgett Method. Polymers 2019, 11, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasar, M.; Hassett, P.; Murphy, N.; Ivankovic, A. β Phase Optimization of Solvent Cast PVDF as a Function of the Processing Method and Additive Content. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 26020–26029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janićijević, A.; Filipović, S.; Sknepnek, A.; Vlahović, B.; Đorđević, N.; Kovacević, D.; Mirković, M.; Petronijević, I.; Zivković, P.; Rogan, J.; et al. Dielectric and Structural Properties of the Hybrid Material Polyvinylidene Fluoride-Bacterial Nanocellulose-Based Composite. Polymers 2023, 15, 4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaglan, N.; Uniyal, P. On the Structural, Dielectric, Piezoelectric, and Energy Storage Behavior of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Thick Film: Role of Annealing Temperature. J. Appl. Phys. 2022, 132, 224109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-M.; Lai, J.-Y. Recent Advances in Preparation and Morphology Control of Polymeric Membranes Formed by Nonsolvent Induced Phase Separation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2013, 2, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, R.; Li, H.; Guo, Y.; Mu, R.; Zhao, Y. Microstructures and Properties of PVDF Membranes: Effect of the Solvent. Ferroelectrics 2022, 595, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.-Y.; Boaretti, C.; Lorenzetti, A.; Martucci, A.; Roso, M.; Modesti, M. Effects of Solvent and Electrospinning Parameters on the Morphology and Piezoelectric Properties of PVDF Nanofibrous Membrane. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhao, J.; He, B.; Hu, Z. Solution Processable Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride)-Based Ferroelectric Polymers for Flexible Electronics. APL Mater. 2021, 9, 010902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.E.; Zhenova, A.; Roberts, S.; Petchey, T.; Zhu, P.; Dancer, C.E.J.; McElroy, C.R.; Kendrick, E.; Goodship, V. On the Solubility and Stability of Polyvinylidene Fluoride. Polymers 2021, 13, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.-T.; Méricq, J.-P.; Mendret, J.; Brosillon, S.; Faur, C. Influence of Preparation Temperature on the Properties and Performance of Composite PVDF-TiO2 Membranes. Membranes 2021, 11, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-M.; Chou, M.-H.; Zeng, W.-Y. Piezoelectric Response of Aligned Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride/Carbon Nanotube Nanofibrous Membranes. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; Yang, S.; Xu, J.; Huang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; et al. Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride-Trifluoroethylene)/Cobalt Ferrite Composite Films with a Self-Biased Magnetoelectric Effect for Flexible AC Magnetic Sensors. J. Mater. Sci 2021, 56, 9728–9740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, T.; D’Souza, N.; Berman, D. Electrospun Fe3O4-PVDF Nanofiber Composite Mats for Cryogenic Magnetic Sensor Applications. Textiles 2021, 1, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, P.; Costa, C.M.; Benelmekki, M.; Botelho, G.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. On the Origin of the Electroactive Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) β-Phase Nucleation by Ferrite Nanoparticles via Surface Electrostatic Interactions. CrystEngComm 2012, 14, 2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zheng, J.; Xu, C. Silver Nanowire Dopant Enhancing Piezoelectricity of Electrospun PVDF Nanofiber Web. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Smart Materials and Nanotechnology in Engineering, Gold Coast, Australia, 10–12 July 2013; Epaarachchi, J.A., Lau, A.K., Leng, J., Eds.; p. 879314. [Google Scholar]
- Garain, S.; Jana, S.; Sinha, T.K.; Mandal, D. Design of In Situ Poled Ce3+ -Doped Electrospun PVDF/Graphene Composite Nanofibers for Fabrication of Nanopressure Sensor and Ultrasensitive Acoustic Nanogenerator. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 4532–4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baji, A.; Mai, Y.-W.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y. Electrospinning Induced Ferroelectricity in Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) Fibers. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, A.C.; Silva, M.P.; Gonçalves, R.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Botelho, G.; Fonseca, A.M.; Lanceros-Mendez, S.; Neves, I.C. Enhancement of the Dielectric Constant and Thermal Properties of α-Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride)/Zeolite Nanocomposites. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 14446–14452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, F.; Shamshirsaz, M.; Latifi, M. Investigation of β Phase Formation in Piezoelectric Response of Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride Nanofibers: LiCl Additive and Increasing Fibers Tension. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2016, 56, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.Z.Y.; Nursam, N.M.; Xia, F.; Truong, Y.B.; Kyratzis, I.L.; Wang, X.; Caruso, R.A. Electrospun PVDF–TiO2 with Tuneable TiO2 Crystal Phases: Synthesis and Application in Photocatalytic Redox Reactions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorayani Bafqi, M.S.; Bagherzadeh, R.; Latifi, M. Fabrication of Composite PVDF-ZnO Nanofiber Mats by Electrospinning for Energy Scavenging Application with Enhanced Efficiency. J. Polym. Res. 2015, 22, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairagi, S.; Ali, S.W. Flexible Lead-Free PVDF/SM-KNN Electrospun Nanocomposite Based Piezoelectric Materials: Significant Enhancement of Energy Harvesting Efficiency of the Nanogenerator. Energy 2020, 198, 117385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobola, D.; Kaspar, P.; Částková, K.; Dallaev, R.; Papež, N.; Sedlák, P.; Trčka, T.; Orudzhev, F.; Kaštyl, J.; Weiser, A.; et al. PVDF Fibers Modification by Nitrate Salts Doping. Polymers 2021, 13, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.L.; Li, B.; Zhang, Z.G.; Zhong, W.H. Achieving Very High Fraction of β-Crystal PVDF and PVDF/CNF Composites and Their Effect on AC Conductivity and Microstructure through a Stretching Process. Eur. Polym. J. 2010, 46, 2112–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ke, W.; Chang, T.; Hu, Z. A Molecular Ferroelectrics Induced Electroactive β-Phase in Solution Processed PVDF Films for Flexible Piezoelectric Sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 1532–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, A.M.; Varun, S.; Mural, P.K.S. Development of Self-Poled PVDF/MWNT Flexible Nanocomposites with a Boosted Electroactive β-Phase. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 14578–14591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Song, R.; Hao, Y. Facile and Effective Promotion of β Crystalline Phase in Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) via the Incorporation of Imidazolium Ionic Liquids. Polym. Int. 2013, 62, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greeshma, T.; Balaji, R.; Jayakumar, S. PVDF Phase Formation and Its Influence on Electrical and Structural Properties of PZT-PVDF Composites. Ferroelectr. Lett. Sect. 2013, 40, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.H.; Singh, S.; Khare, N. Enhanced β-phase in PVDF Polymer Nanocomposite and Its Application for Nanogenerator. Polym. Adv. Techs 2018, 29, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, J.R.; Samal, S.K.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)/Ag@TiO2 Nanocomposite Membrane with Enhanced Fouling Resistance and Antibacterial Performance. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 268, 124723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodar, R.A.; You, S.-J.; Chou, H.-H. Study the Self Cleaning, Antibacterial and Photocatalytic Properties of TiO2 Entrapped PVDF Membranes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto Pozo, I.; Olmos, D.; Orgaz, B.; Božanić, D.K.; González-Benito, J. Titania Nanoparticles Prevent Development of Pseudomonas Fluorescens Biofilms on Polystyrene Surfaces. Mater. Lett. 2014, 127, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahloul, W.; Mélis, F.; Bounor-Legaré, V.; Cassagnau, P. Structural Characterisation and Antibacterial Activity of PP/TiO2 Nanocomposites Prepared by an in Situ Sol–Gel Method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 134, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, J.M.; Olmos, D.; Orgaz, B.; Puga, C.H.; San José, C.; González-Benito, J. Effect of the Presence of Titania Nanoparticles in the Development of Pseudomonas Fluorescens Biofilms on LDPE. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 51451–51458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Benito, J.; Teno, J.; González-Gaitano, G.; Xu, S.; Chiang, M.Y. PVDF/TiO2 Nanocomposites Prepared by Solution Blow Spinning: Surface Properties and Their Relation with S. Mutans Adhesion. Polym. Test. 2017, 58, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-C.; Guo, C.-G.; Lv, J.-L. Tributyl Citrate as Diluent for Preparation of Pvdf Porous Membrane via Thermally Induced Phase Separation. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2015, 23, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo, L.L.; Soleimani, H.; Yahya, N.; Abbas, Z.; Ridwan, A.T.; Wahaab, F.A. Investigation of the Broadband Microwave Absorption of Citric Acid Coated Fe3O4/PVDF Composite Using Finite Element Method. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Roni, M.N.P.; Ali, M.Y.; Islam, M.R.; Hossan, M.S.; Rahman, M.H.; Zahid, A.A.S.M.; Alam, M.N.E.; Hanif, M.A.; Akhtar, M.S. Selectivity of Sol-Gel and Hydrothermal TiO2 Nanoparticles towards Photocatalytic Degradation of Cationic and Anionic Dyes. Molecules 2023, 28, 6834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Shen, F.; Chen, X.; Luo, J.; Su, Y.; Wu, H.; Wan, Y. A Novel Plasma-Induced Surface Hydrophobization Strategy for Membrane Distillation: Etching, Dipping and Grafting. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 499, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, P.; Lopes, A.C.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Electroactive Phases of Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride): Determination, Processing and Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 683–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Lei, T.; Sun, D.; Lin, L. A Critical Analysis of the α, β and γ Phases in Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) Using FTIR. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 15382–15389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorio, R. Determination of the α, β, and γ Crystalline Phases of Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) Films Prepared at Different Conditions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 100, 3272–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathiowitz, E.; Ron, E.; Mathiowitz, G.; Amato, C.; Langer, R. Morphological Characterization of Bioerodible Polymers. 1. Crystallinity of Polyanhydride Copolymers. Macromolecules 1990, 23, 3212–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Jin, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J. Multiple Melting and Partial Miscibility of Ethylene-vinyl Acetate Copolymer/Low Density Polyethylene Blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 2863–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, X. Crystallization Behavior of PVDF/PMMA Blends Prepared by in Situ Polymerization from DMF and Ethanol. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 3720–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradys, A.; Sajkiewicz, P. Determination of the Melting Enthalpy of β Phase of Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride). e-Polymers 2013, 13, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, R.G.; Diab, M.; De Caro, T.; Al-Shemy, M.; Adel, A.; Caschera, D. Study of the Effect of Titanium Dioxide Hydrosol on the Photocatalytic and Mechanical Properties of Paper Sheets. Materials 2020, 13, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Duklan, N.; Singh, P.; Sharma, J. Synthesis and Photocatalytic Activity of Anatase TiO2 Nanoparticles for Degradation of Methyl Orange. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Condensed Matter and Applied Physics (ICC 2017), Bikaner, India, 24–25 November 2017; p. 030075. [Google Scholar]
- Devesa, S.; Rooney, A.P.; Graça, M.P.; Cooper, D.; Costa, L.C. Williamson-Hall Analysis in Estimation of Crystallite Size and Lattice Strain in Bi1.34Fe0.66Nb1.34O6.35 Prepared by the Sol-Gel Method. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 263, 114830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, S.; Ndamitso, M.M.; Abdulkareem, A.S.; Tijani, J.O.; Shuaib, D.T.; Mohammed, A.K.; Sumaila, A. Comparative Study of Crystallite Size Using Williamson-Hall and Debye-Scherrer Plots for ZnO Nanoparticles. Adv. Nat. Sci Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 045013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottino, A.; Capannelli, G.; Munari, S.; Turturro, A. Solubility Parameters of Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride). J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 1988, 26, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Cheng, S.; Li, H.; Zuo, D. Effect of Different Concentrations of Spraying Chitosan Solution on Structure and Properties of PVDF Porous Membrane. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2021, 299, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anousheh, N.; Soldera, A. Influence of Regio-Irregular Structures on Thermal Behaviour of PVDF. Polymer 2017, 125, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, G.; Lanceros-Mendez, S.; Gonçalves, A.M.; Sencadas, V.; Rocha, J.G. Relationship between Processing Conditions, Defects and Thermal Degradation of Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) in the β-Phase. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2008, 354, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurczuk, K.; Galeski, A.; Mackey, M.; Hiltner, A.; Baer, E. Orientation of PVDF α and γ Crystals in Nanolayered Films. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2015, 293, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, S.; Nabiyeva, T.; Biniek, L.; Gowd, E.B. Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) Aerogels with α, β, and γ Crystalline Forms: Correlating Physicochemical Properties with Polymorphic Structures. ACS Polym. Au 2024, 4, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okabe, M.; Wada, R.; Tazaki, M.; Homma, T. The Flory-Huggins Interaction Parameter and Thermoreversible Gelation of Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) in Organic Solvents. Polym. J. 2003, 35, 798–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.H.; Chen, C.-Y.; Liao, S.-C.; Chen, H.-L.; Tsao, C.-S.; Chen, J.-H.; Liao, J.-L.; Ivanov, V.A.; Chen, S.-A. Segmental Alignment in the Aggregate Domains of Poly(9,9-Dioctylfluorene) in Semidilute Solution. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 6572–6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.H.; Nandi, A.K. Supramolecular Organization of Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride)−Camphor Sulfonic Acid Blends: Giant Spherulites. Langmuir 2003, 19, 7056–7060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakhchaoui, N.; Farhan, R.; Eddiai, A.; Meddad, M.; Cherkaoui, O.; Mazroui, M.; Boughaleb, Y.; Van Langenhove, L. Improvement of the Electroactive β -Phase Nucleation and Piezoelectric Properties of PVDF-HFP Thin Films Influenced by TiO2 Nanoparticles. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 39, 1148–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

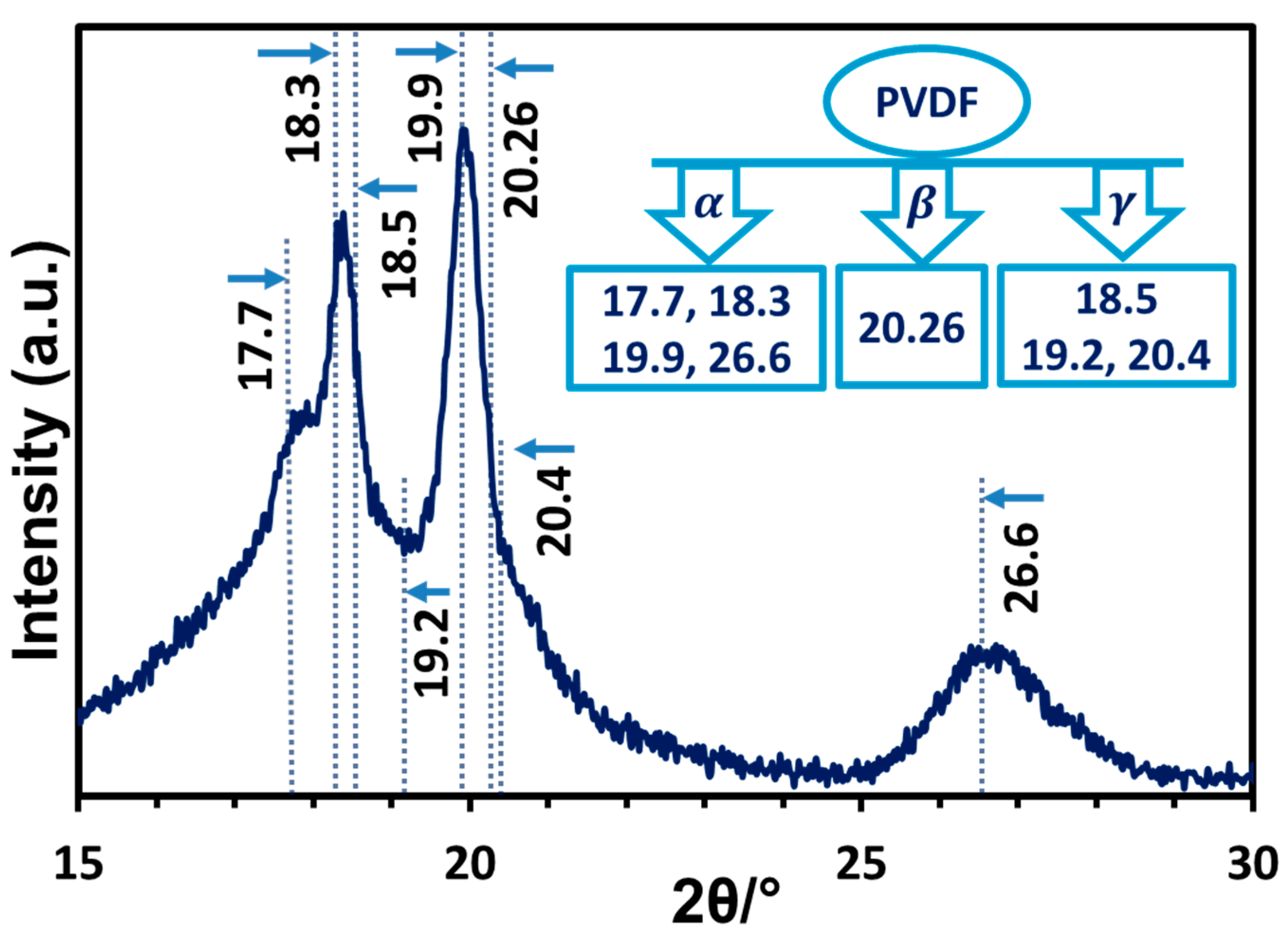


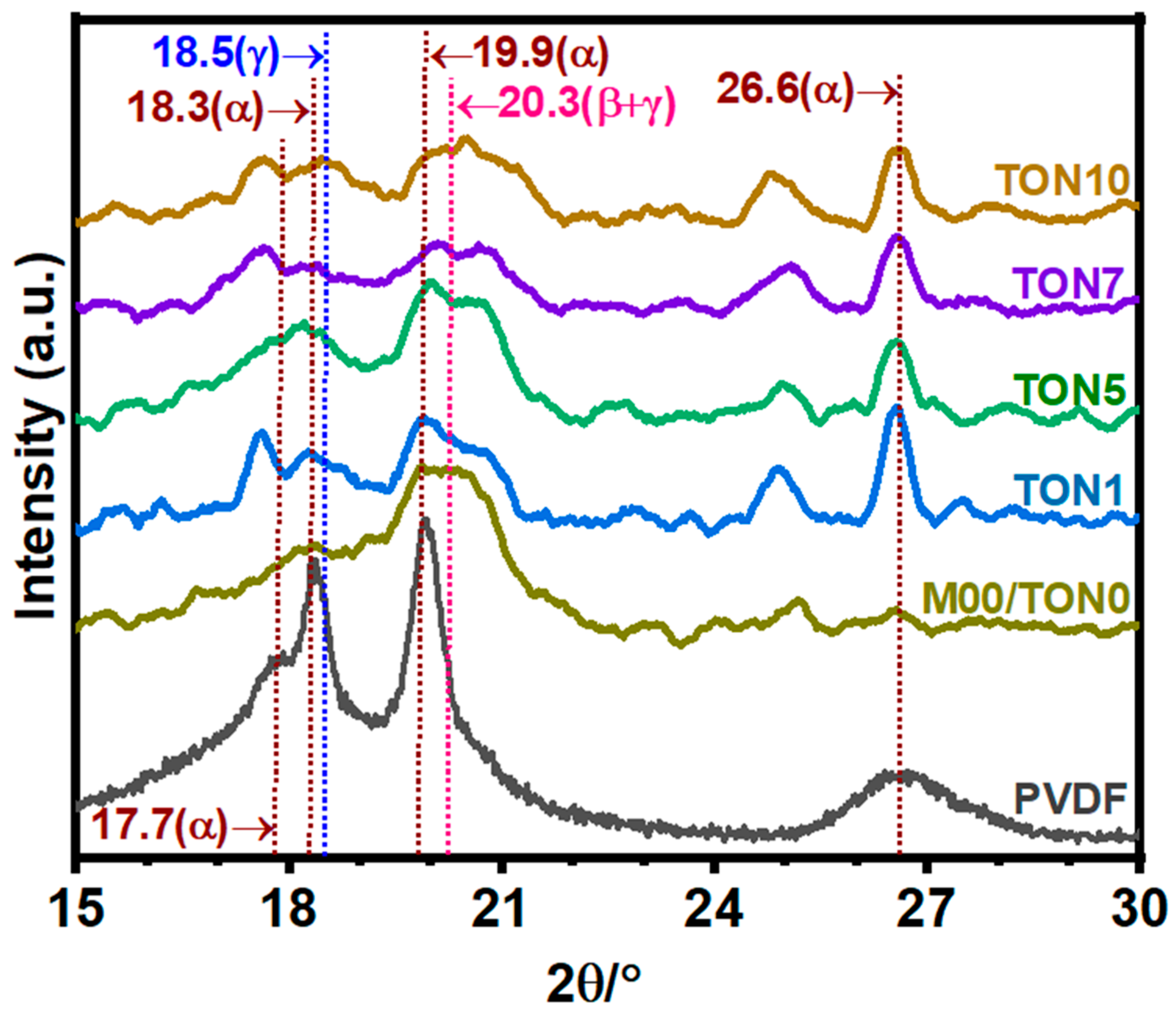




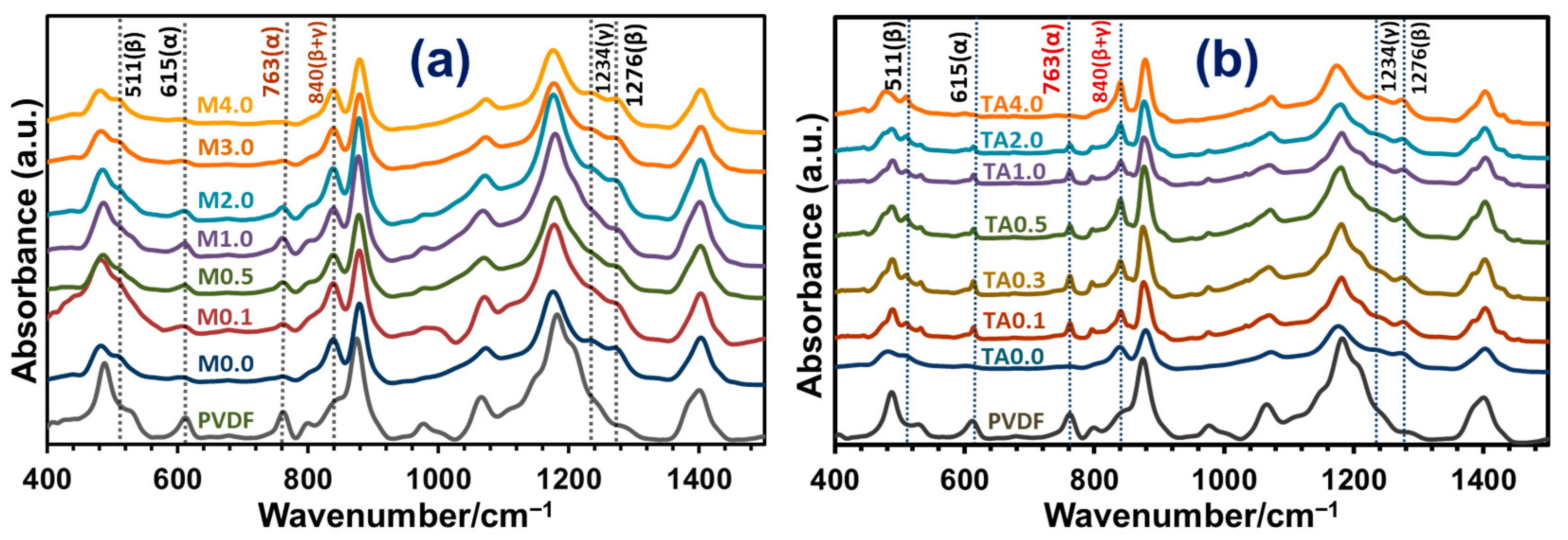


| Additive | Solvent | Method | % of β-Phase | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNFs | DMF and Acetone | Solution Casting Followed by Stretching | >96 | [51] |
| PMMA | Dimethicone | Solution Casting Followed by Stretching | 93 | [17] |
| dabcoHReO4 | DMF and Acetone | Solution Casting | 95 | [52] |
| MWCNTs | DMF and Acetone | Solution Casting | 93.8 | [53] |
| (bmim)[PF6] | DMF | Solution Casting and Annealing | 92.6 | [54] |
| PZT | - | Solution Casting | 57 | [55] |
| ZnO | DMF | Solution Casting | 76.1 | [56] |
| TiO2/CA | DMAc | NIPS (no post-treatment) | 96 | This work |
| Dope Solution: DS-1 | Dope Solution: DS-2 | Dope Solution: DS-3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Designation of Membranes | % Nano-TiO2 (w/v) | Designation of Membranes | % Nano-TiO2 (w/v) | % CA (w/v) | Designation of Membranes | % CA (w/v) |
| M0.0 | 0.00 | TA0.0 | 0.00 | 5.0 | TON0/M0.0 | 0.0 |
| M0.1 | 0.01 | TA0.1 | 0.01 | 5.0 | TON1 | 1.0 |
| M0.3 | 0.03 | TA0.3 | 0.03 | 5.0 | TON5/TA0.0 | 5.0 |
| M0.5 | 0.05 | TA0.5 | 0.05 | 5.0 | TON7 | 7.0 |
| M1.0 | 0.10 | TA0.7 | 0.07 | 5.0 | TON10 | 10.0 |
| M2.0 | 0.20 | TA1.0 | 0.10 | 5.0 | ||
| M3.0 | 0.30 | TA2.0 | 0.20 | 5.0 | ||
| M4.0 | 0.40 | TA4.0 | 0.40 | 5.0 | ||
| Sample ID | PVDF 1 | TON0 | TON1 | TON5 | TON7 | TON10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TD (±0.1)/°C | 449.1 | 447.7 | 441.3 | 442.6 | 447.6 | 442.9 |
| MP (±0.1)/°C | 160.0 | 157.8 | 158.0 | 157.4 | 157.6 | 157.5 |
| λ (DSC) 2/% | 35.5 | 29.4 | 26.0 | 21.7 | 24.0 | 31.2 |
| λ (XRD) 2/% | 34 | 28 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 |
| Porosity 2/% | -- | 67 | 79 | 81 | 82 | 83 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roni, M.N.P.; Neshath, T.A.; Hakim, M.A.; Hasan, M.M.; Rahman, M.H.; Hossan, M.S.; Zahid, A.A.S.M.; Alam, M.N.E.; Khatun, M.H. Optimizing β-Phase Content in PVDF Membranes via Modification of Dope Solution with Citric Acid/Nano-TiO2 Using Nonsolvent-Induced Phase Separation Method. Polymers 2025, 17, 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17040481
Roni MNP, Neshath TA, Hakim MA, Hasan MM, Rahman MH, Hossan MS, Zahid AASM, Alam MNE, Khatun MH. Optimizing β-Phase Content in PVDF Membranes via Modification of Dope Solution with Citric Acid/Nano-TiO2 Using Nonsolvent-Induced Phase Separation Method. Polymers. 2025; 17(4):481. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17040481
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoni, Md. Nahid Parvez, Tanvir Ahmed Neshath, Md. Azizul Hakim, Md. Mahadi Hasan, M. Habibur Rahman, Md. Shamim Hossan, A. A. S. Mostofa Zahid, Md. Nur E Alam, and Most. Halima Khatun. 2025. "Optimizing β-Phase Content in PVDF Membranes via Modification of Dope Solution with Citric Acid/Nano-TiO2 Using Nonsolvent-Induced Phase Separation Method" Polymers 17, no. 4: 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17040481
APA StyleRoni, M. N. P., Neshath, T. A., Hakim, M. A., Hasan, M. M., Rahman, M. H., Hossan, M. S., Zahid, A. A. S. M., Alam, M. N. E., & Khatun, M. H. (2025). Optimizing β-Phase Content in PVDF Membranes via Modification of Dope Solution with Citric Acid/Nano-TiO2 Using Nonsolvent-Induced Phase Separation Method. Polymers, 17(4), 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17040481






