Inulin as a Biopolymer; Chemical Structure, Anticancer Effects, Nutraceutical Potential and Industrial Applications: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
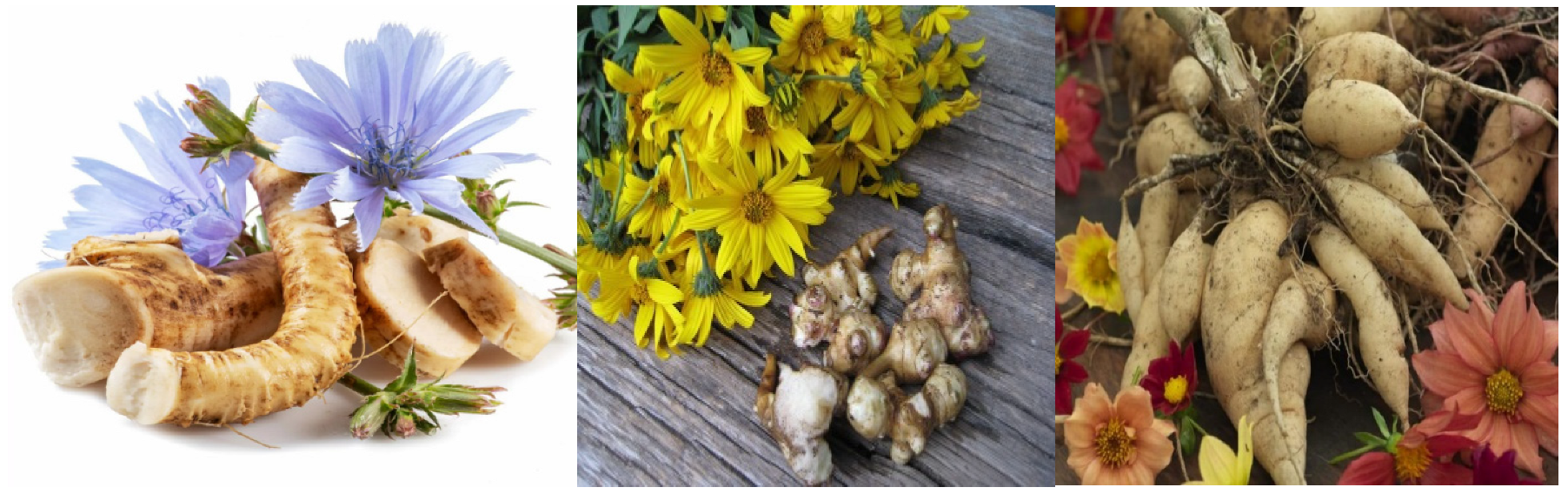
1. Introduction
2. Methodology of Literature Review
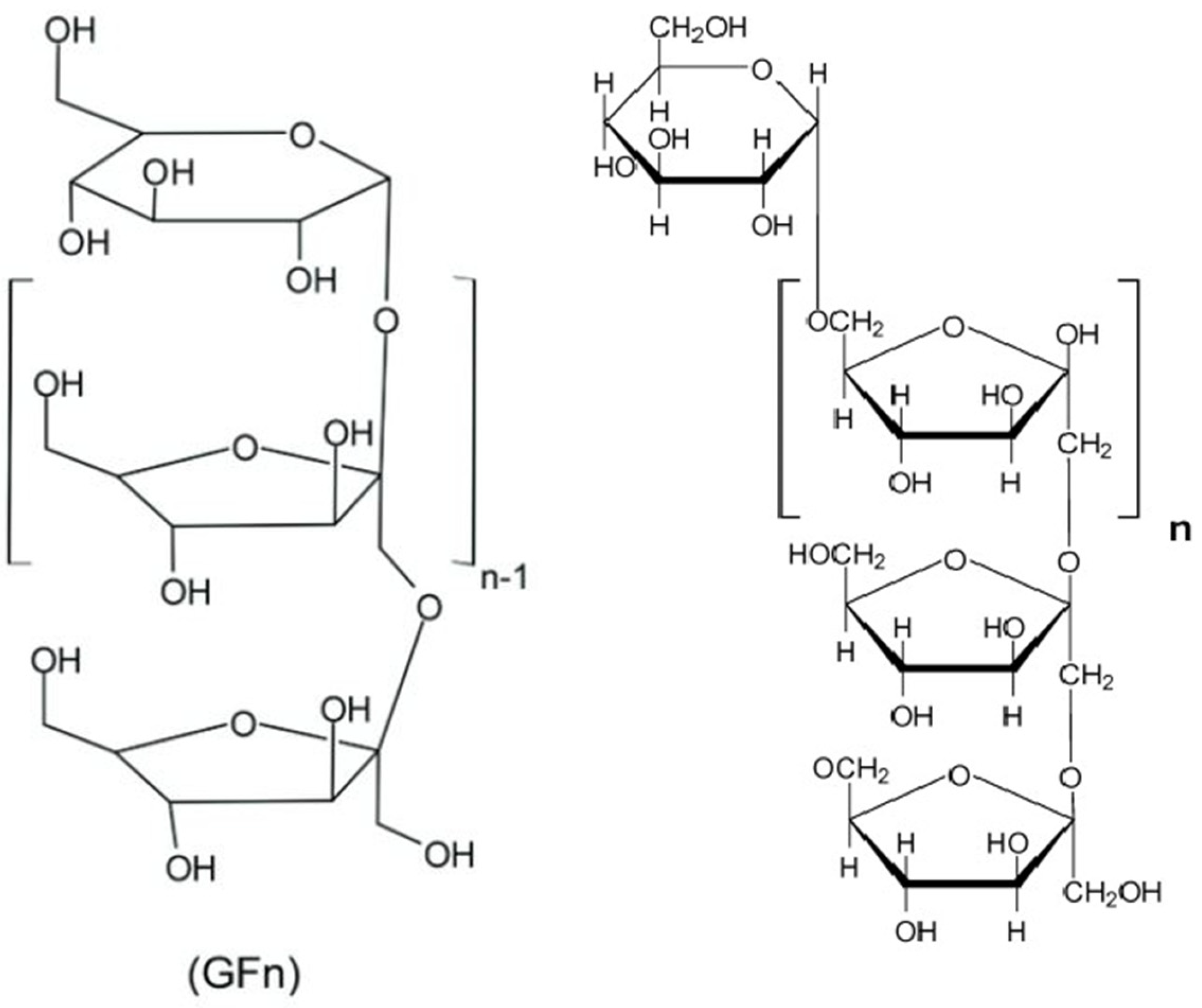
3. Chemical Structure
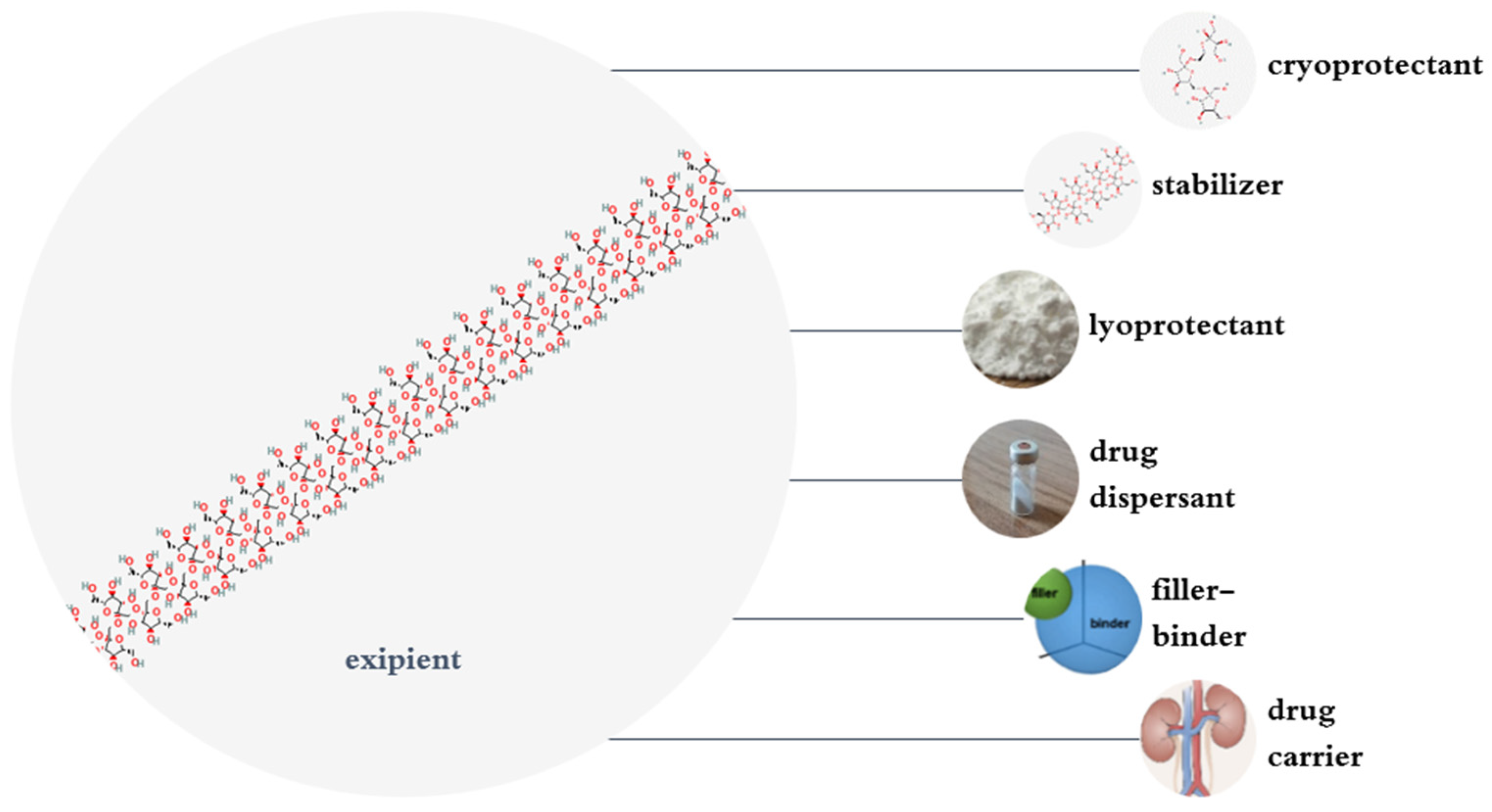
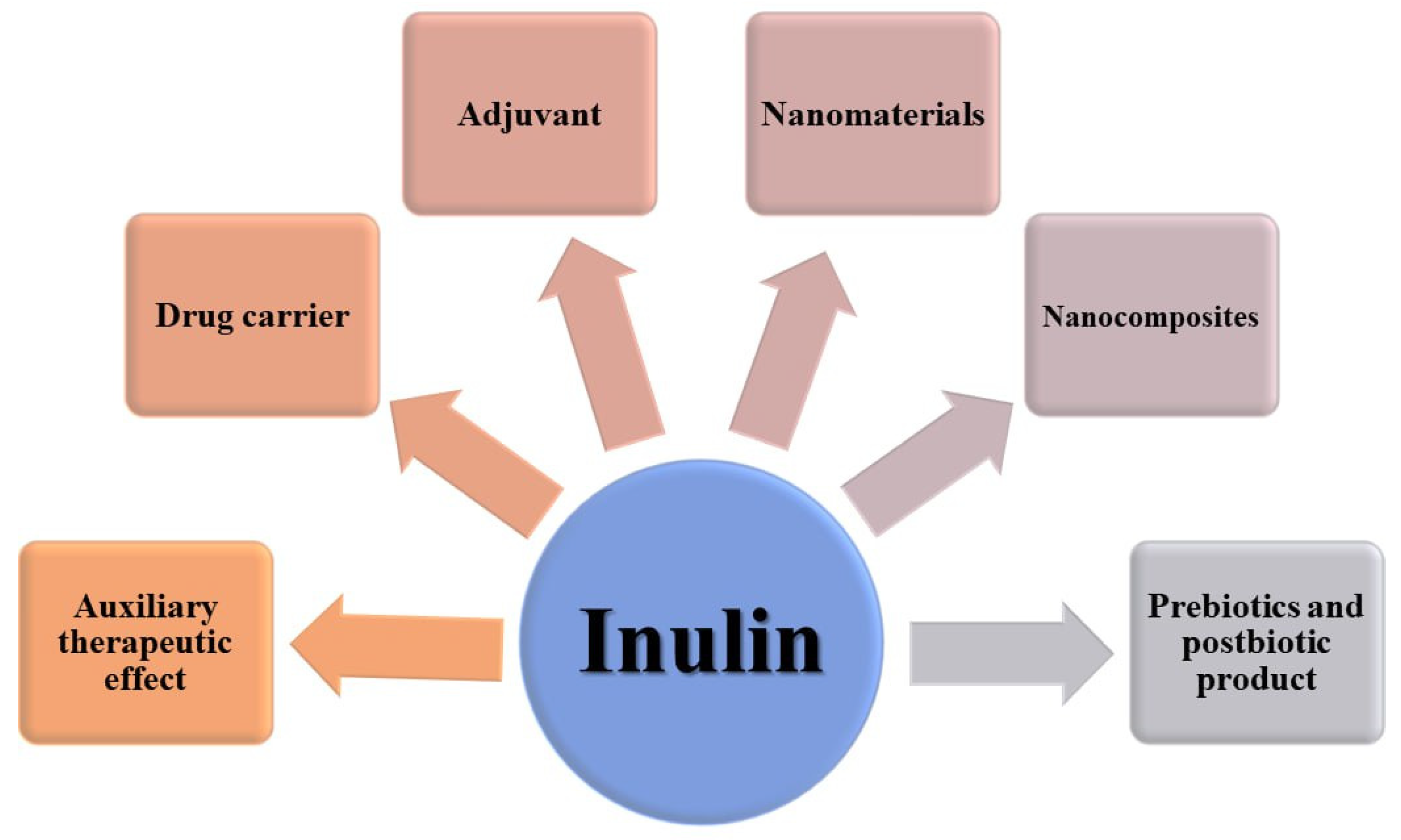
4. Pharmaceutical and Pharmacological Applications of Inulin
5. Anticancer Effects of Inulin
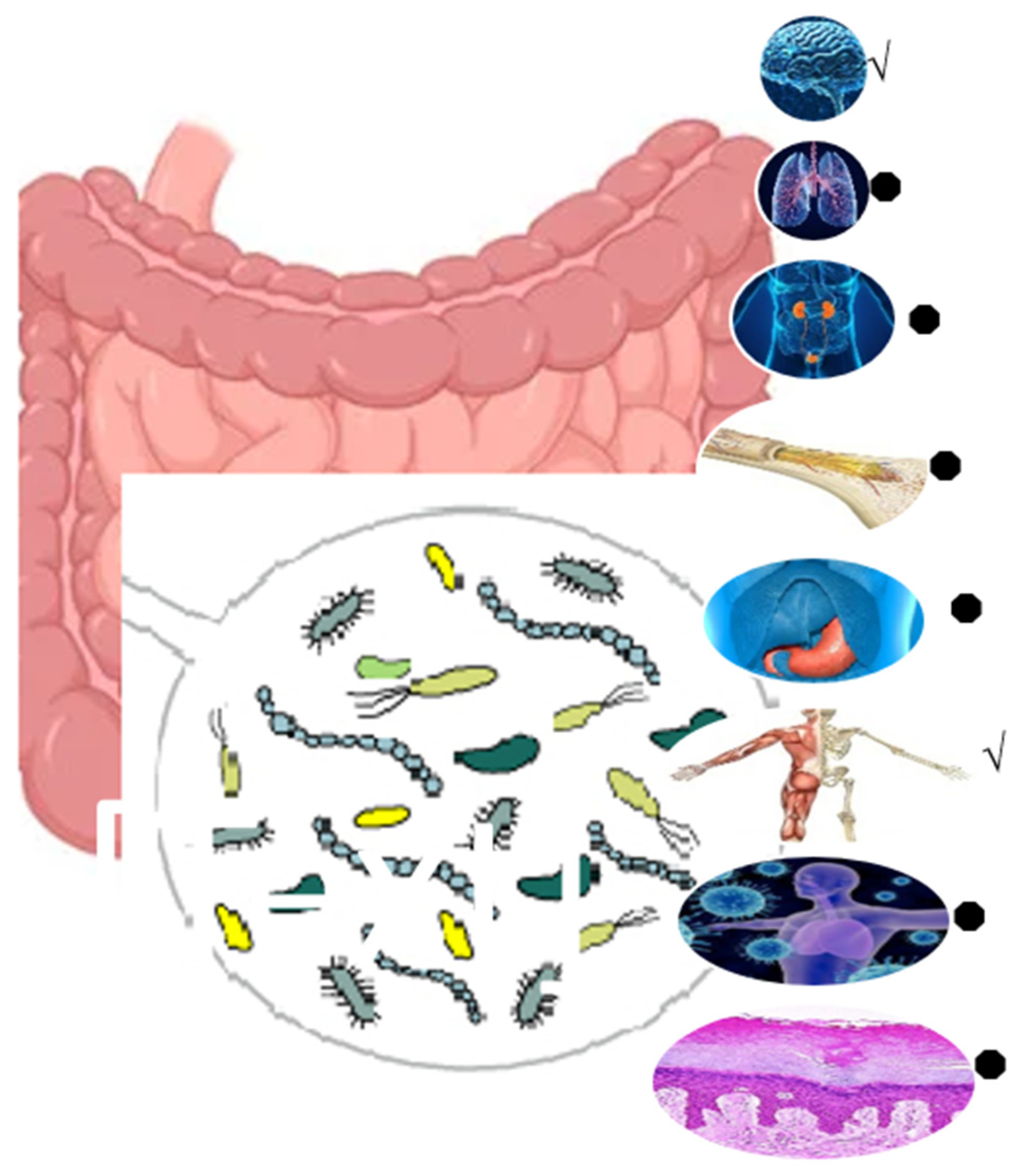
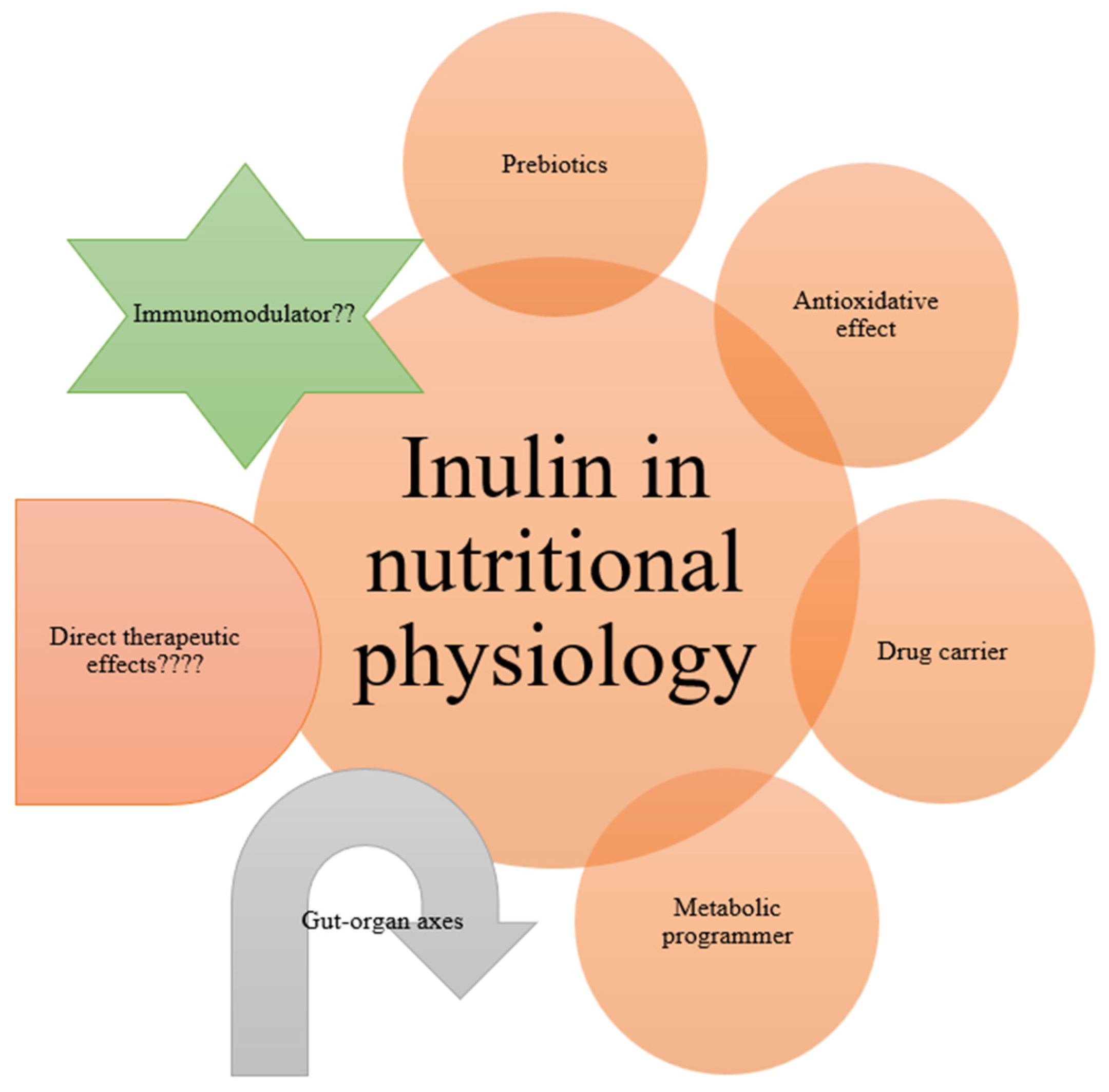
6. Nutraceutical Potentials of Inulin
7. Conclusions and Remark
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boeckner, L.S.; Schnepf, M.I.; Tungland, B.C. Inulin: A review of nutritional and health implications. 2001. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2001, 43, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, R. Enzymatic preparation of high fructose syrup from inulin. In Bioprocessing of Foods; Asiatech Publishing Inc.: New Delhi, India, 2011; pp. 77–98. [Google Scholar]
- Delzenne, N.M.; Kok, N.N. Nutritional and health benefits of inulin and oligofructose. J. Nutr. 1999, 129, 1402S–1406S. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, G.R.; Probert, H.M.; Van Loo, J.; Rastall, R.A.; Roberfroid, M.B. Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: Updating the concept of prebiotics. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2004, 17, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, R.; Sethi, P.; Rudrangi, S.R.S.; Padarthi, P.K.; Kumar, V.; Rudrangi, S.; Vaghela, K. Inulin: A multifaceted ingredient in pharmaceutical sciences. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2024, 35, 2570–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barclay, T.; Ginic-Markovic, M.; Johnston, M.R.; Cooper, P.D.; Petrovsky, N. Analysis of the hydrolysis of inulin using real time 1H NMR spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Res. 2012, 352, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, D.; Xu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, T.; Guang, C.; Mu, W. Inulin and its enzymatic production by inulosucrase: Characteristics, structural features, molecular modifications and applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavin, J. Fiber and prebiotics: Mechanisms and health benefits. Nutrients 2013, 5, 1417–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandracchia, D.; Tripodo, G.; Latrofa, A.; Dorati, R. Amphiphilic inulin-d-α-tocopherol succinate (INVITE) bioconjugates for biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 103, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Gupta, A.K. Applications of inulin and oligofructose in health and nutrition. J. Biosci. 2002, 27, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banguela, A.; Hernández, L. Fructans: From natural sources to transgenic plants. Biotecnol. Apl. 2006, 23, 202–210. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, D.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, W.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, T.; Mu, W. Biosynthesis of inulin from sucrose using inulosucrase from Lactobacillus gasseri DSM 20604. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peshev, D.; Van den Ende, W. Fructans: Prebiotics and immunomodulators. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 8, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nester, K.; Plazinski, W. Conformational properties of inulin, levan and arabinan studied by molecular dynamics simulations. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 240, 116266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akram, W.; Pandey, V.; Sharma, R.; Joshi, R.; Mishra, N.; Garud, N.; Haider, T. Inulin: Unveiling its potential as a multifaceted biopolymer in prebiotics, drug delivery, and therapeutics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, A.; Kaiser, I.; Trebstein, A.; Henle, T. Heat-induced degradation of inulin. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2005, 220, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibowski, P.; Bukowska, A. The effect of pH, temperature and heating time on inulin chemical stability. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2011, 10, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Du, M.; Cheng, X.; Qian, L.; Huo, A.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y. Extraction, physicochemical properties, functional activities and applications of inulin polysaccharide: A review. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2023, 78, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfick, M.M.; Xie, H.; Zhao, C.; Shao, P.; Farag, M.A. Inulin fructans in diet: Role in gut homeostasis, immunity, health outcomes and potential therapeutics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 208, 948–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensink, M.A.; Frijlink, H.W.; van der Voort Maarschalk, K.; Hinrichs, W.L. Inulin, a flexible oligosaccharide I: Review of its physicochemical characteristics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 130, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensink, M.A.; Frijlink, H.W.; van der Voort Maarschalk, K.; Hinrichs, W.L. Inulin, a flexible oligosaccharide. II: Review of its pharmaceutical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 134, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinrichs, W.; Prinsen, M.; Frijlink, H. Inulin glasses for the stabilization of therapeutic proteins. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 215, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furlán, L.T.R.; Padilla, A.P.; Campderrós, M.E. Inulin like lyoprotectant of bovine plasma proteins concentrated by ultrafiltration. Int. Food Res. 2010, 43, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlán, L.T.R.; Lecot, J.; Padilla, A.P.; Campderrós, M.E.; Zaritzky, N. Effect of saccharides on glass transition temperatures of frozen and freeze dried bovine plasma protein. J. Food Eng. 2011, 106, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayen, W.Y.; Kumar, N. A systematic study on lyophilization process of polymersomes for long-term storage using doxorubicin-loaded (PEG) 3–PLA nanopolymersomes. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 46, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jonge, J.; Amorij, J.-P.; Hinrichs, W.L.; Wilschut, J.; Huckriede, A.; Frijlink, H.W. Inulin sugar glasses preserve the structural integrity and biological activity of influenza virosomes during freeze-drying and storage. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 32, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorij, J.; Meulenaar, J.; Hinrichs, W.; Stegmann, T.; Huckriede, A.; Coenen, F.; Frijlink, H. Rational design of an influenza subunit vaccine powder with sugar glass technology: Preventing conformational changes of haemagglutinin during freezing and freeze-drying. Vaccine 2007, 25, 6447–6457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Drooge, D.; Hinrichs, W.; Frijlink, H. Anomalous dissolution behaviour of tablets prepared from sugar glass-based solid dispersions. J. Control. Release 2004, 97, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Drooge, D.-J.; Hinrichs, W.L.; Dickhoff, B.H.; Elli, M.N.; Visser, M.R.; Zijlstra, G.S.; Frijlink, H.W. Spray freeze drying to produce a stable Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol containing inulin-based solid dispersion powder suitable for inhalation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 26, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinarong, P.; Hämäläinen, S.; Visser, M.R.; Hinrichs, W.L.; Ketolainen, J.; Frijlink, H.W. Surface-active derivative of inulin (Inutec® SP1) is a superior carrier for solid dispersions with a high drug load. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 2333–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinarong, P.; Faber, J.; Visser, M.; Hinrichs, W.; Frijlink, H. Strongly enhanced dissolution rate of fenofibrate solid dispersion tablets by incorporation of superdisintegrants. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 73, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M.R.; Baert, L.; van’t Klooster, G.; Schueller, L.; Geldof, M.; Vanwelkenhuysen, I.; De Kock, H.; De Meyer, S.; Frijlink, H.W.; Rosier, J. Inulin solid dispersion technology to improve the absorption of the BCS Class IV drug TMC240. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 74, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Drooge, D.; Hinrichs, W.; Wegman, K.; Visser, M.; Eissens, A.; Frijlink, H. Solid dispersions based on inulin for the stabilisation and formulation of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 21, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.; Guo, H.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Liu, Z.; Li, K.; Niu, F.; Zhai, X.; Wang, L. The physiological functions and pharmaceutical applications of inulin: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 246, 116589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coombes, A.; Rizzi, S.; Williamson, M.; Barralet, J.; Downes, S.; Wallace, W. Precipitation casting of polycaprolactone for applications in tissue engineering and drug delivery. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhgari, A.; Farahmand, F.; Garekani, H.A.; Sadeghi, F.; Vandamme, T.F. Permeability and swelling studies on free films containing inulin in combination with different polymethacrylates aimed for colonic drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 28, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitarresi, G.; Tripodo, G.; Calabrese, R.; Craparo, E.F.; Licciardi, M.; Giammona, G. Hydrogels for Potential Colon Drug Release by Thiol-ene Conjugate Addition of a New Inulin Derivative. Macromol. Biosci. 2008, 8, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Lin, D.; Zhang, W.; Chen, S.; Ding, H.; Zhong, H.-J. Progress in the Preparation and Application of Inulin-Based Hydrogels. Polymers 2024, 16, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licciardi, M.; Scialabba, C.; Sardo, C.; Cavallaro, G.; Giammona, G. Amphiphilic inulin graft co-polymers as self-assembling micelles for doxorubicin delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 4262–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Niu, C.; Liang, S.; Guo, J.; Li, K.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Jin, Y.; Bai, J.; Dai, J. An inulin-based glycovesicle for pathogen-targeted drug delivery to ameliorate salmonellosis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 267, 131656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz-Ahrens, K.E.; Schrezenmeir, J. Inulin and oligofructose and mineral metabolism: The evidence from animal trials. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 2513S–2523S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunshea, F.; Pluske, J.; Ponnampalam, E. Dietary iron or inulin supplementation alters iron status, growth performance, intramuscular fat and meat quality in finisher pigs. Meat Sci. 2024, 213, 109496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakirhan, H.; Karabudak, E. Effects of inulin on calcium metabolism and bone health. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2023, 93, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Zhao, X.; Leng, Y.; Xia, Z. Dietary supplementation with inulin improves burn-induced skeletal muscle atrophy by regulating gut microbiota disorders. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, S.A.; Griffin, I.J.; Hawthorne, K.M.; Liang, L.; Gunn, S.K.; Darlington, G.; Ellis, K.J. A combination of prebiotic short-and long-chain inulin-type fructans enhances calcium absorption and bone mineralization in young adolescents. T. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiyar, A.C.; Norman, A.W. Effects of sodium butyrate on 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor activity in primary chick kidney cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1992, 84, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coudray, C.; Rambeau, M.; Feillet-Coudray, C.; Tressol, J.C.; Demigne, C.; Gueux, E.; Mazur, A.; Rayssiguier, Y. Dietary inulin intake and age can significantly affect intestinal absorption of calcium and magnesium in rats: A stable isotope approach. Nutr. J. 2005, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coudray, C.; Feillet-Coudray, C.; Gueux, E.; Mazur, A.; Rayssiguier, Y. Dietary inulin intake and age can affect intestinal absorption of zinc and copper in rats. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahara, S.; Morohashi, T.; Sano, T.; Ohta, A.; Yamada, S.; Sasa, R. Fructooligosaccharide consumption enhances femoral bone volume and mineral concentrations in rats. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1792–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ROOT, H.F.; BAKER, M.L. Inulin and artichokes in the treatment of diabetes. Arch. Intern. Med. 1925, 36, 126–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, G.T.; Guimarães, S.B.; Sampaio, H.A.d.C. Fructo-oligosaccharide effects on blood glucose: An overview. Acta Cir. Bras. 2012, 27, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberfroid, M. Dietary fiber, inulin, and oligofructose: A review comparing their physiological effects. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1993, 33, 103–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Prabhakar, M.; Ju, J.; Long, H.; Zhou, H. Effect of inulin-type fructans on blood lipid profile and glucose level: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.M. Effects of inulin on lipid parameters in humans. J. Nutr. 1999, 129, 1471S–1473S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delzenne, N.M.; Kok, N.; Fiordaliso, M.-F.; Deboyser, D.M.; Goethals, F.M.; Roberfroid, M.B. Dietary fructooligosaccharides modify lipid metabolism in rats. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1993, 57, 820S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiordaliso, M.; Kok, N.; Desager, J.P.; Goethals, F.; Deboyser, D.; Roberfroid, M.; Delzenne, N. Dietary oligofructose lowers triglycerides, phospholipids and cholesterol in serum and very low density lipoproteins of rats. Lipids 1995, 30, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, A.; Sandström, B.; Van Amelsvoort, J.M. The effect of ingestion of inulin on blood lipids and gastrointestinal symptoms in healthy females. Br. J. Nutr. 1997, 78, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, M.H.; Maki, K.C.; Synecki, C.; Torri, S.A.; Drennan, K.B. Effects of dietary inulin on serum lipids in men and women with hypercholesterolemia. Nutr. Res. 1998, 18, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, H.; Hu, J. Lipid metabolism regulation by dietary polysaccharides with different structural properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 270, 132253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, S.; Chouinard-Castonguay, S.; Gagnon, C.; Rudkowska, I. Prebiotics in the management of components of the metabolic syndrome. Maturitas 2017, 104, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, P.; Xu, L. Assessing the effects of inulin-type fructan intake on body weight, blood glucose, and lipid profile: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 4598–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, F.; Shiri, A.; Tahmouzi, S.; Mollakhalili-Meybodi, N.; Nematollahi, A. Application of inulin in bread: A review of technological properties and factors affecting its stability. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Nashar, H.A.; Taleb, M.; EL-Shazly, M.; Zhao, C.; Farag, M.A. Polysaccharides (pectin, mucilage, and fructan inulin) and their fermented products: A critical analysis of their biochemical, gut interactions, and biological functions as antidiabetic agents. Br. J. Nutr. 2024, 38, 662–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, I.F.d.; Bragante, W.R.; Junior, R.C.M.; Laurindo, L.F.; Guiguer, E.L.; Araújo, A.C.; Fiorini, A.M.; Nicolau, C.C.; Oshiiwa, M.; Lima, E.P.d. Effects of Smallanthus sonchifolius Flour on Metabolic Parameters: A Systematic Review. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, W.; Ji, G.; Zhang, L. Immunomodulatory effects of inulin and its intestinal metabolites. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1224092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Allende, J.; Milagro, F.I.; Aranaz, P. Health Effects and Mechanisms of Inulin Action in Human Metabolism. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bartolomeo, F.; Startek, J.; Van den Ende, W. Prebiotics to fight diseases: Reality or fiction? Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 1457–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadha, S.; Kumar, A.; Srivastava, S.A.; Behl, T.; Ranjan, R. Inulin as a delivery vehicle for targeting colon-specific cancer. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 651–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illippangama, A.U.; Jayasena, D.D.; Jo, C.; Mudannayake, D.C. Inulin as a functional ingredient and their applications in meat products. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 275, 118706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghali, E.N.H.K.; Chauhan, S.C.; Yallapu, M.M. Inulin-based formulations as an emerging therapeutic strategy for cancer: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Jangid, A.K.; Pooja, D.; Kulhari, H. Inulin: A novel and stretchy polysaccharide tool for biomedical and nutritional applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 132, 852–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.-M.; Zhou, H.-Z.; Yang, J.-Y.; Li, R.; Song, H.; Wu, H.-X. In vitro and in vivo antioxidant activities of inulin. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasqualetti, V.; Altomare, A.; Guarino, M.P.L.; Locato, V.; Cocca, S.; Cimini, S.; Palma, R.; Alloni, R.; De Gara, L.; Cicala, M. Antioxidant activity of inulin and its role in the prevention of human colonic muscle cell impairment induced by lipopolysaccharide mucosal exposure. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, G.; He, Y.; Wan, H.; Hui, Y.; Li, H. Effects of prebiotics on antioxidant activity of goat milk fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum L60. Acta Univ. Cibiniensis-Ser. E Food Technol. 2017, 21, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kleniewska, P.; Hoffmann, A.; Pniewska, E.; Pawliczak, R. The influence of probiotic Lactobacillus casei in combination with prebiotic inulin on the antioxidant capacity of human plasma. Oxidative Med. Cell Longev. 2016, 2016, 1340903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Q.; Mi, Y.; Guo, Z. Synthesis and characterization of novel carboxymethyl inulin derivatives bearing cationic Schiff bases with antioxidant potential. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 275, 133761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanja, A.; Sutar, P.P.; Mishra, M. Inulin-A polysaccharide: Review on its functional and prebiotic efficacy. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Zhang, C.; Patil, P.J.; Mehmood, A.; Li, X.; Bilal, M.; Haider, J.; Ahmad, S. Potential applications of hydrophobically modified inulin as an active ingredient in functional foods and drugs-A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 252, 117176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, W.; Garud, N.; Joshi, R. Role of inulin as prebiotics on inflammatory bowel disease. Drug Discov. Ther. 2019, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.L.; Hedin, C.R.; Benjamin, J.L.; Koutsoumpas, A.; Ng, S.C.; Hart, A.L.; Forbes, A.; Stagg, A.J.; Lindsay, J.O.; Whelan, K. Dietary intake of inulin-type fructans in active and inactive Crohn’s disease and healthy controls: A case–control study. J. Crohns Colitis 2015, 9, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Jung, S.-C.; Kwak, K.; Kim, J.-S. The Role of Prebiotics in Modulating Gut Microbiota: Implications for Human Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, E.E.; Le Danh Tuyen, P.D.; Chongviriyaphan, N.; Wang, W.; Dillon, D.H.; Meyer, D.; Bindels, J.; Hautvast, J.; Ong, S.; Khan, N.C. Fructans in the first 1000 days of life and beyond, and for pregnancy. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 25, 652–675. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; He, J.; Zheng, P.; Mao, X.; Huang, Z.; Yan, H.; Luo, Y.; Yu, J.; Luo, J.; Yu, B. Prebiotic inulin as a treatment of obesity related nonalcoholic fatty liver disease through gut microbiota: A critical review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, B.; Whelan, K. Prebiotic inulin-type fructans and galacto-oligosaccharides: Definition, specificity, function, and application in gastrointestinal disorders. Asia. Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 32, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, S.; Liu, T.; Yao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Ma, L.; Lu, F. Friend or foe? The roles of inulin-type fructans. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 252, 117155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, R.L.; Alvarado, D.A.; Swanson, K.S.; Holscher, H.D. The prebiotic potential of inulin-type fructans: A systematic review. Adv. nutr. 2022, 13, 492–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, K.; De Vos, W.; Martens, E.; Gilbert, J.; Menon, R.; Soto-Vaca, A.; Hautvast, J.; Meyer, P.; Borewicz, K.; Vaughan, E. Effect of fructans, prebiotics and fibres on the human gut microbiome assessed by 16S rRNA-based approaches: A review. Benef. Microbes. 2020, 11, 101–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Yu, L.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.; Chen, W.; Zhai, Q. Effect of inulin, galacto-oligosaccharides, and polyphenols on the gut microbiota, with a focus on Akkermansia muciniphila. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 4763–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Fan, Z.; Yan, Q.; Pan, T.; Luo, J.; Wei, Y.; Li, B.; Fang, Z.; Lu, W. Gut microbiota determines the fate of dietary fiber-targeted interventions in host health. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2416915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, S.-K.; Ooi, L.-G.; Lim, T.-J.; Liong, M.-T. Antihypertensive properties of plant-based prebiotics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 3517–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apolinário, A.C.; de Lima Damasceno, B.P.G.; de Macêdo Beltrão, N.E.; Pessoa, A.; Converti, A.; da Silva, J.A. Inulin-type fructans: A review on different aspects of biochemical and pharmaceutical technology. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buriti, F.C.; Saad, S.M. Chilled milk-based desserts as emerging probiotic and prebiotic products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisha Rakhesh, N.R.; Fellows, C.; Sissons, M. Evaluation of the technological and sensory properties of durum wheat spaghetti enriched with different dietary fibres. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 95, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar Singh, P.; Kumar, V.; Yadav, R.; Shukla, P. Bioengineering for microbial inulinases: Trends and applications. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2017, 18, 966–972. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz, A.; Irshad, S.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Xiong, H. The functionality of prebiotics as immunostimulant: Evidences from trials on terrestrial and aquatic animals. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2018, 76, 272–278. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, M.R.; Welch, R.; Rush, E.C.; Xiang, X.; Wang, X. A sustainable wholesome foodstuff; health effects and potential dietotherapy applications of yacon. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.A.; Jomaa, S.A.; Abd El-Wahed, A.; El-Seedi, H.R. The many faces of kefir fermented dairy products: Quality characteristics, flavour chemistry, nutritional value, health benefits, and safety. Nutrients 2020, 12, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho Correa, A.; Lopes, M.S.; Perna, R.F.; Silva, E.K. Fructan-type prebiotic dietary fibers: Clinical studies reporting health impacts and recent advances in their technological application in bakery, dairy, meat products and beverages. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 323, 121396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Name/PubChem CID | Molecular Weight g/mol | XLogP3-AA | Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | Rotatable Bond Count | Topological Polar Surface Area Å | Canonicalized | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
C228H382O191 | Inulin [USP: BAN]/18772499] | 6179 | −70.2 | 116 | 191 | 149 | 3040 | Yes |
C24H42O21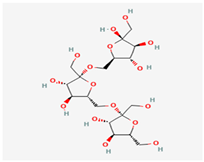 | Inulin—chicory Inulin—Jerusalem artichoke/132932783 | 666.6 | −7.4 | 14 | 21 | 13 | 384 | Yes |
C18H32O16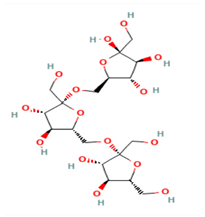 | Levan—Erwinia herbicola 440946 | 504.4 | −6 | 11 | 16 | 10 | 296 | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karimi, I.; Ghowsi, M.; Mohammed, L.J.; Haidari, Z.; Nazari, K.; Schiöth, H.B. Inulin as a Biopolymer; Chemical Structure, Anticancer Effects, Nutraceutical Potential and Industrial Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Polymers 2025, 17, 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17030412
Karimi I, Ghowsi M, Mohammed LJ, Haidari Z, Nazari K, Schiöth HB. Inulin as a Biopolymer; Chemical Structure, Anticancer Effects, Nutraceutical Potential and Industrial Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Polymers. 2025; 17(3):412. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17030412
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarimi, Isaac, Mahnaz Ghowsi, Layth Jasim Mohammed, Zohreh Haidari, Kosar Nazari, and Helgi B. Schiöth. 2025. "Inulin as a Biopolymer; Chemical Structure, Anticancer Effects, Nutraceutical Potential and Industrial Applications: A Comprehensive Review" Polymers 17, no. 3: 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17030412
APA StyleKarimi, I., Ghowsi, M., Mohammed, L. J., Haidari, Z., Nazari, K., & Schiöth, H. B. (2025). Inulin as a Biopolymer; Chemical Structure, Anticancer Effects, Nutraceutical Potential and Industrial Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Polymers, 17(3), 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17030412






