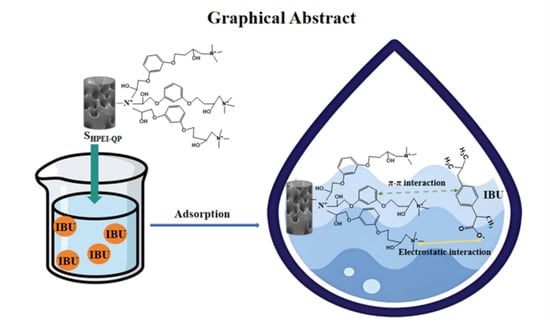
Bifunctionalized Polyethyleneimine-Based Sponge for Adsorption of Ibuprofen from Aqueous Solution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
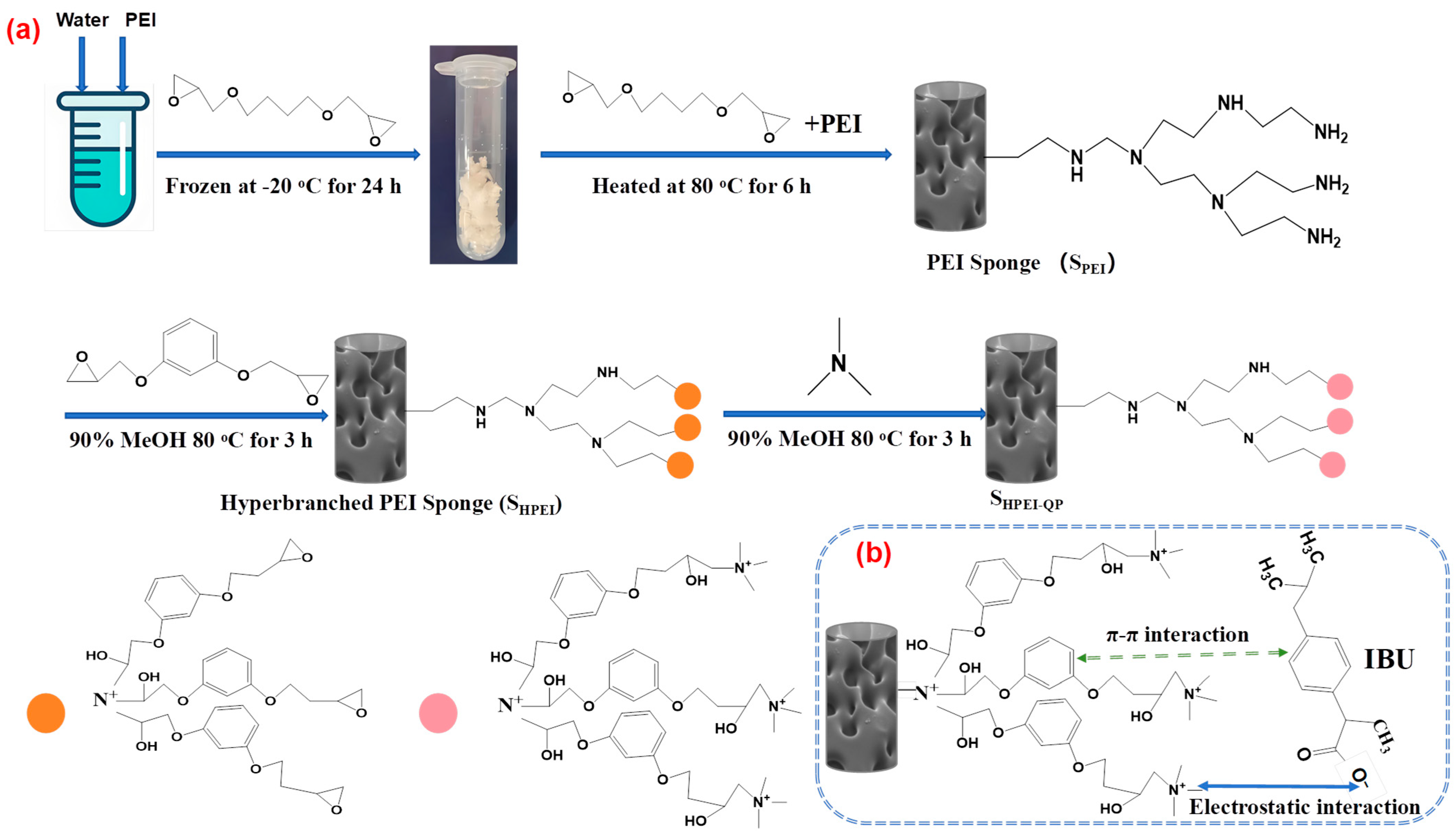
2.2. Preparation of Quaternized and Phenyl-Functionalized Hyperbranched PEI Sponge (SHPEI-QP)
2.3. Characterizations and Instruments
2.4. Batch Sorption Experiments
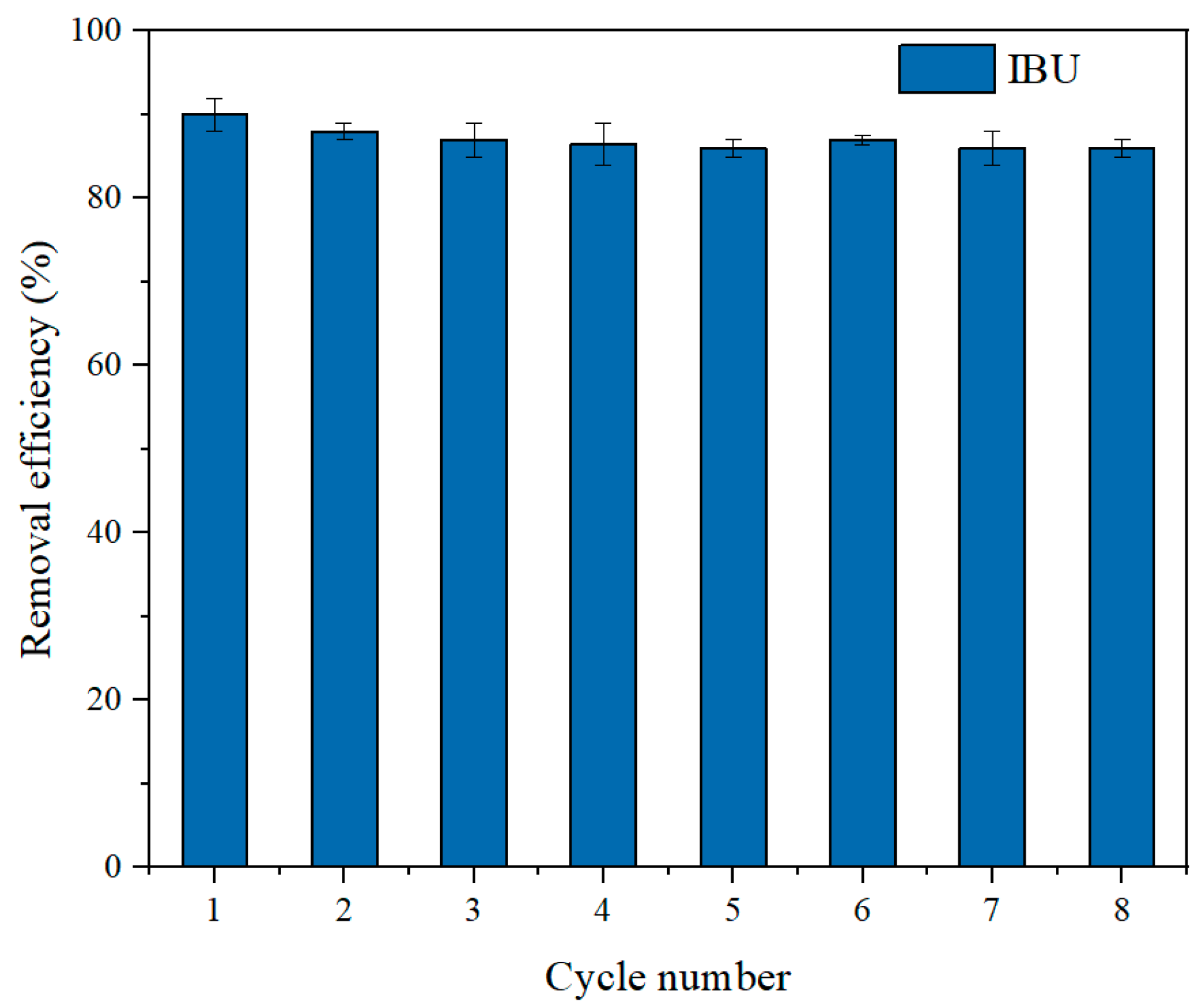
2.5. Regeneration and Recycling Studies
3. Results and Discussion
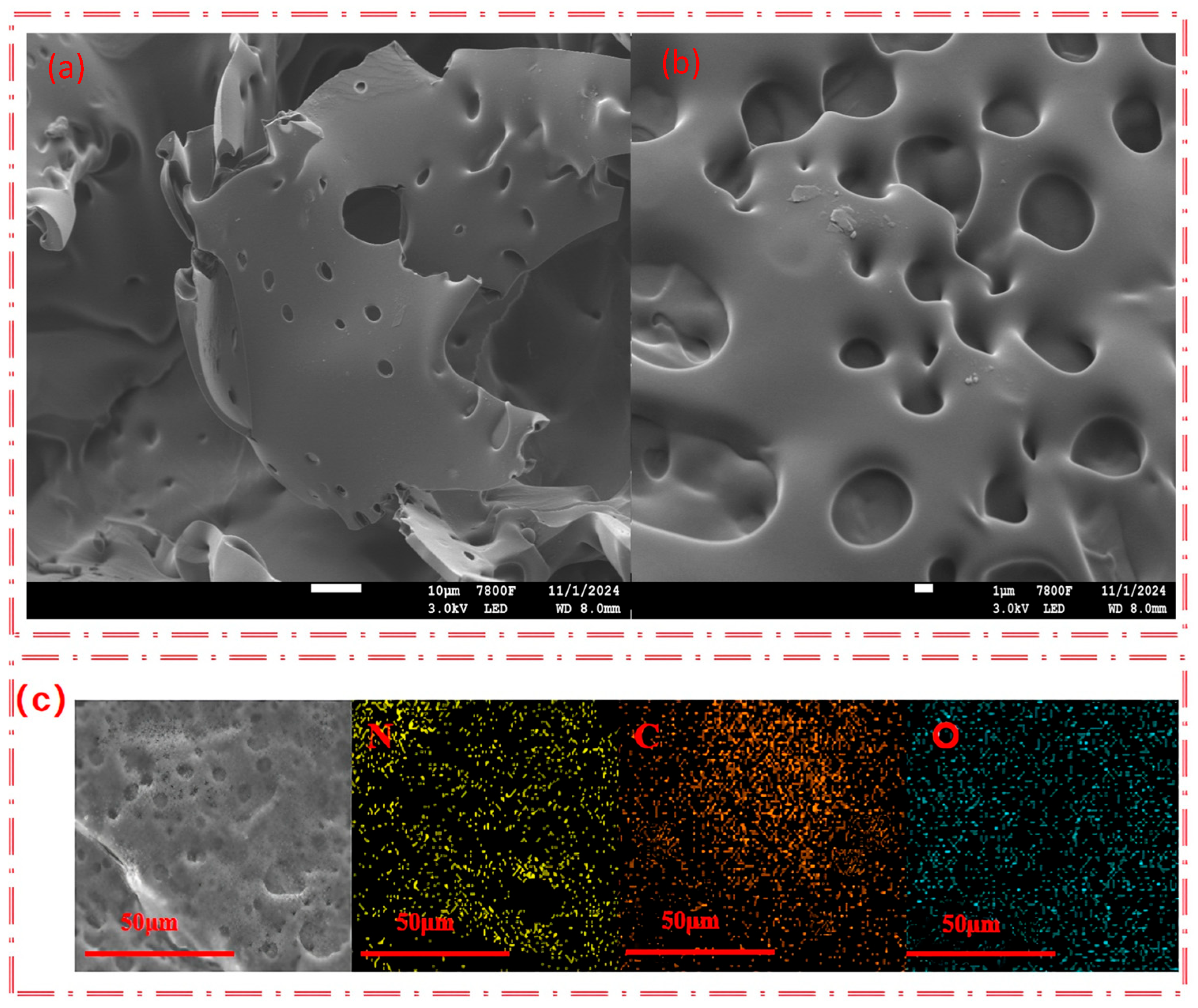
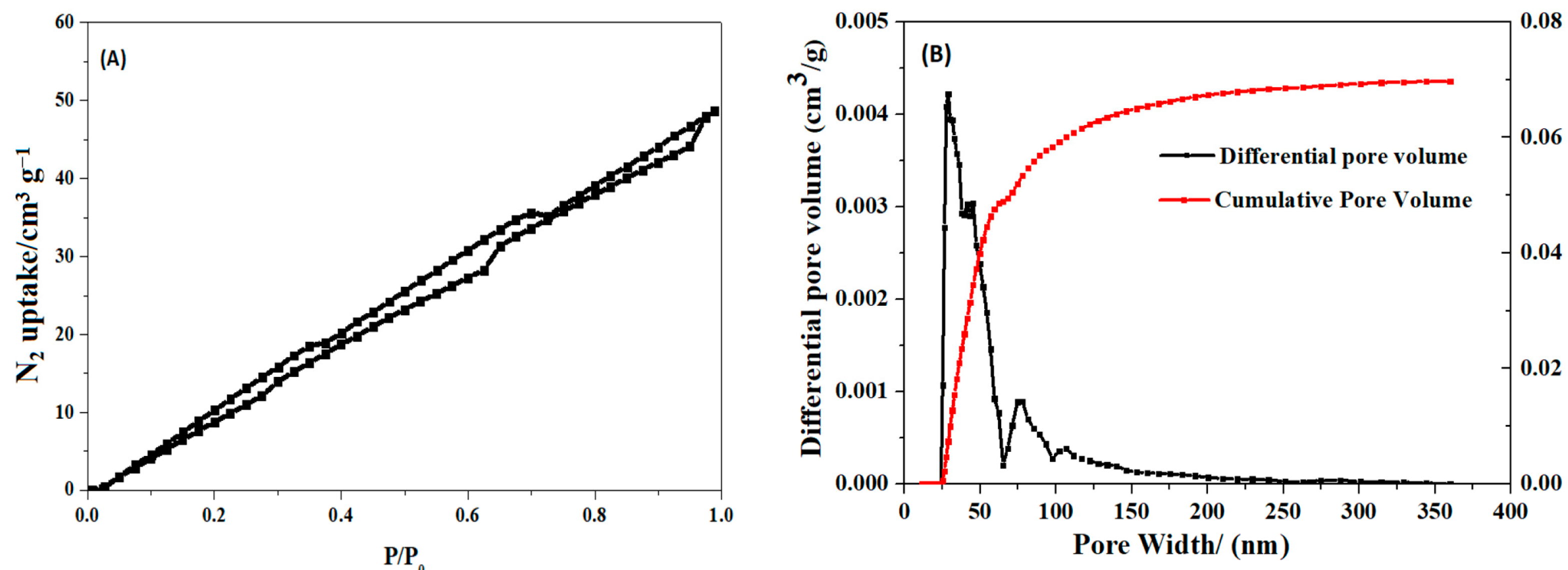
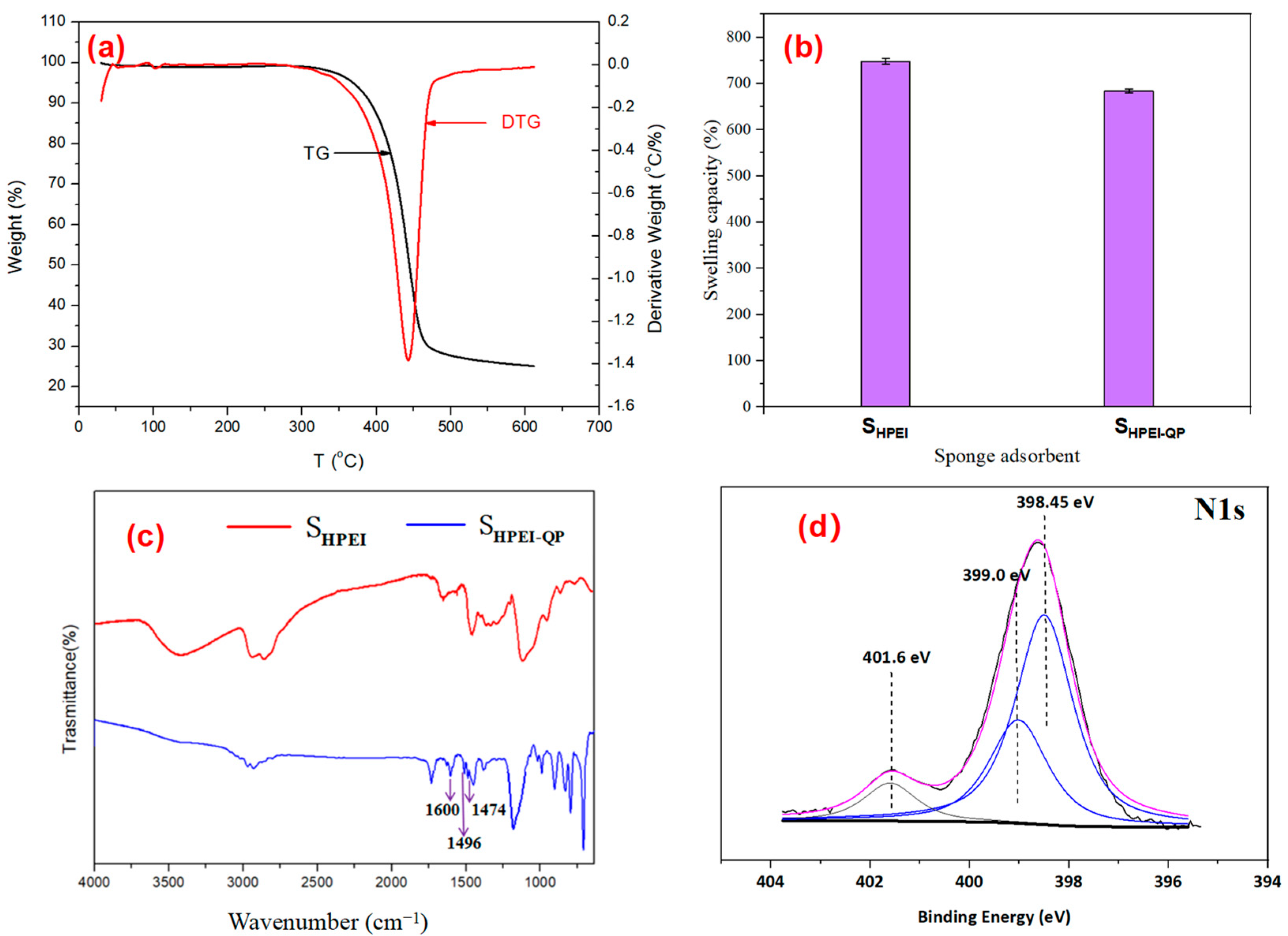
3.1. Characterizations of SHPEI-QP
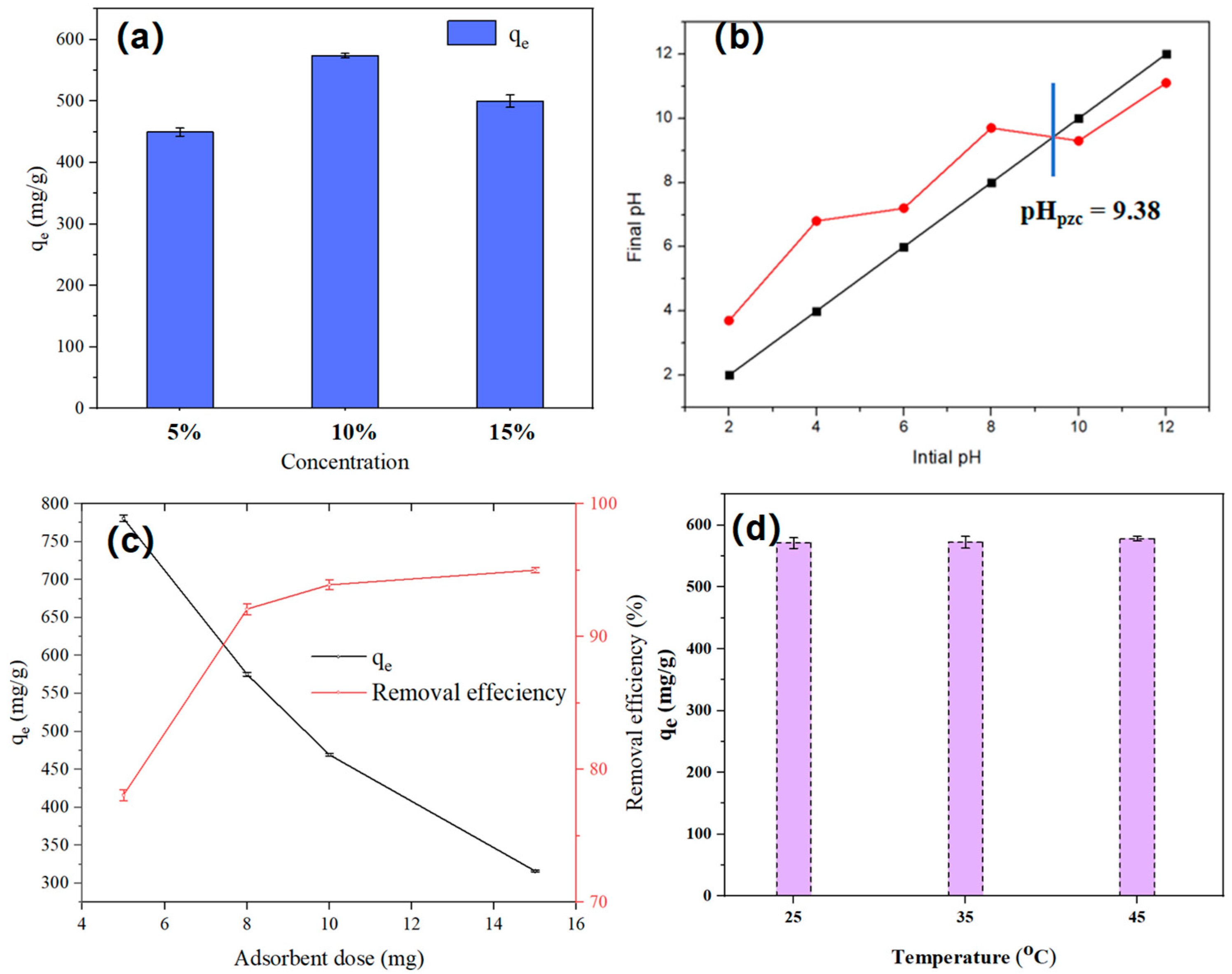
3.2. Adsorption Properties of SHPEI-QP for IBU
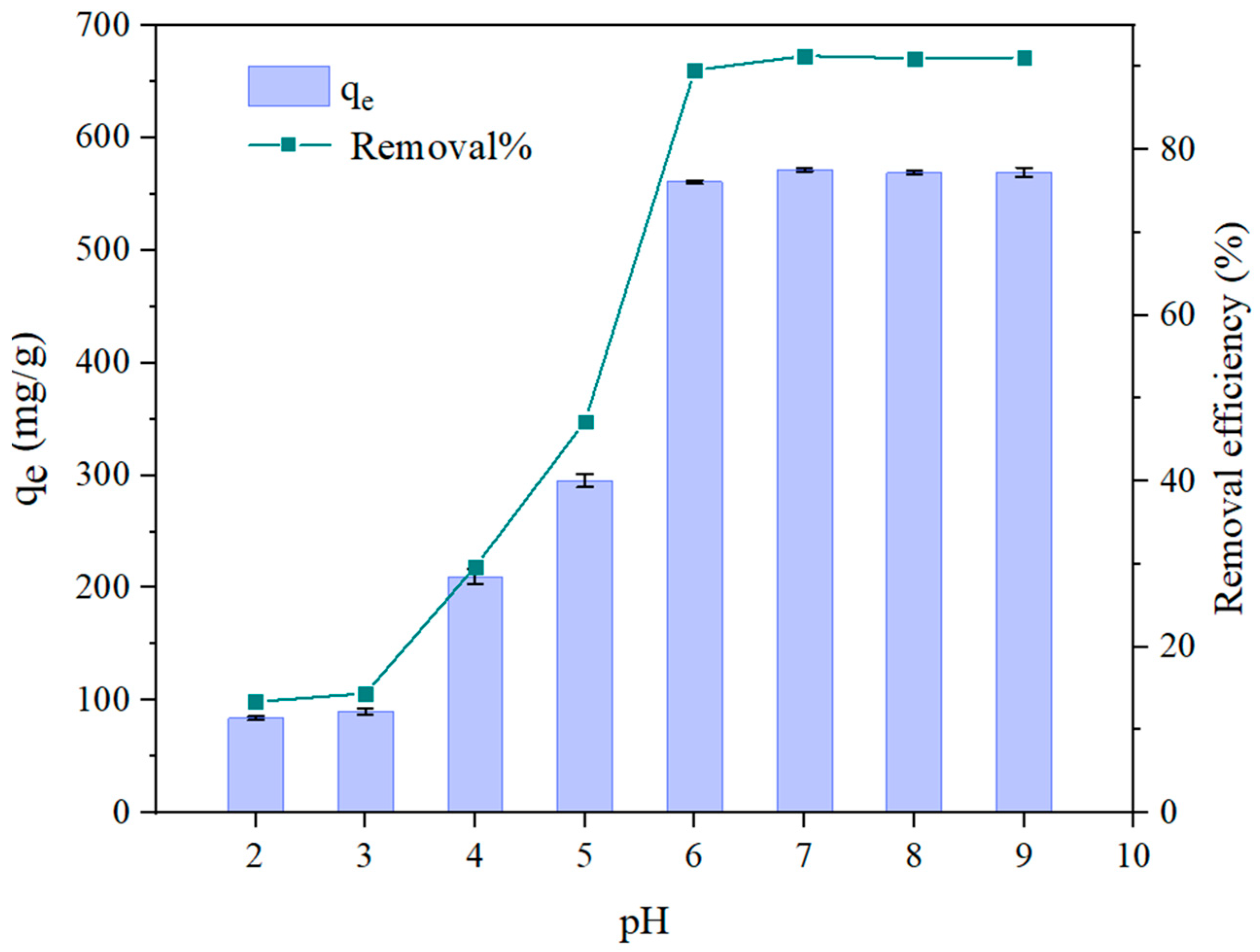
3.2.1. Effect of Solution pH
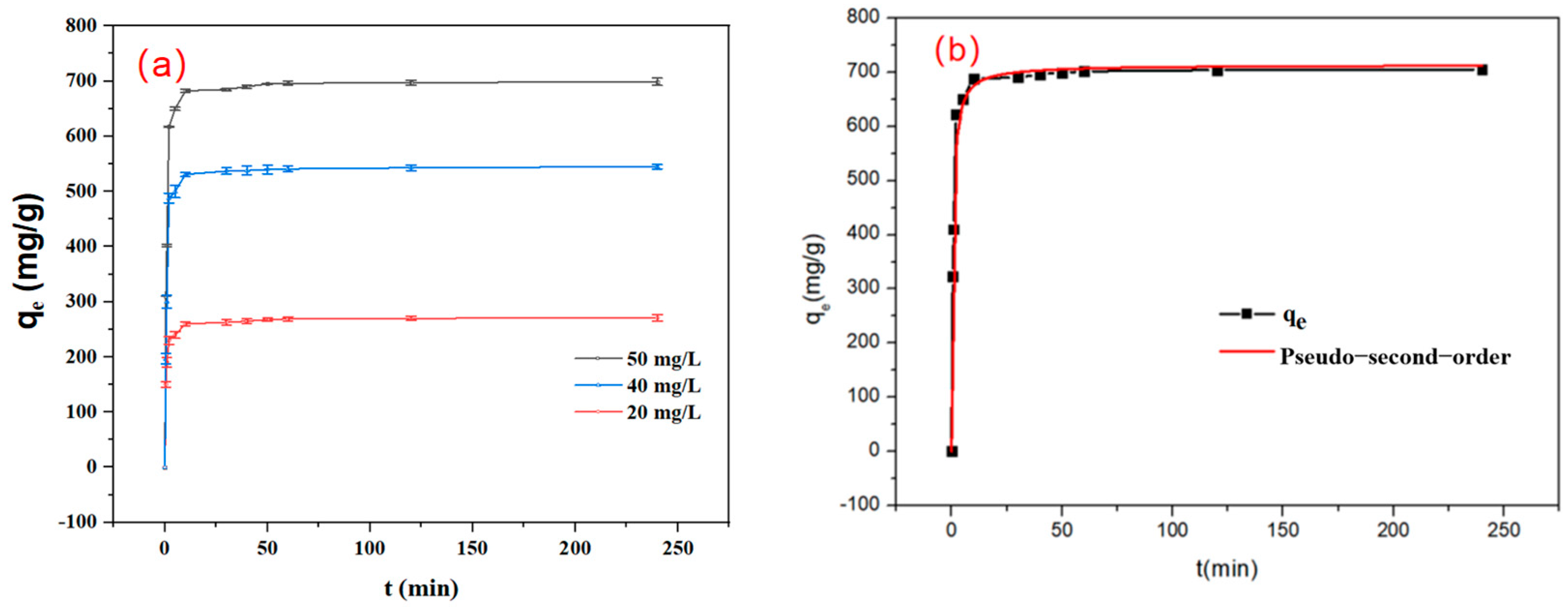
3.2.2. Adsorption Kinetic Study
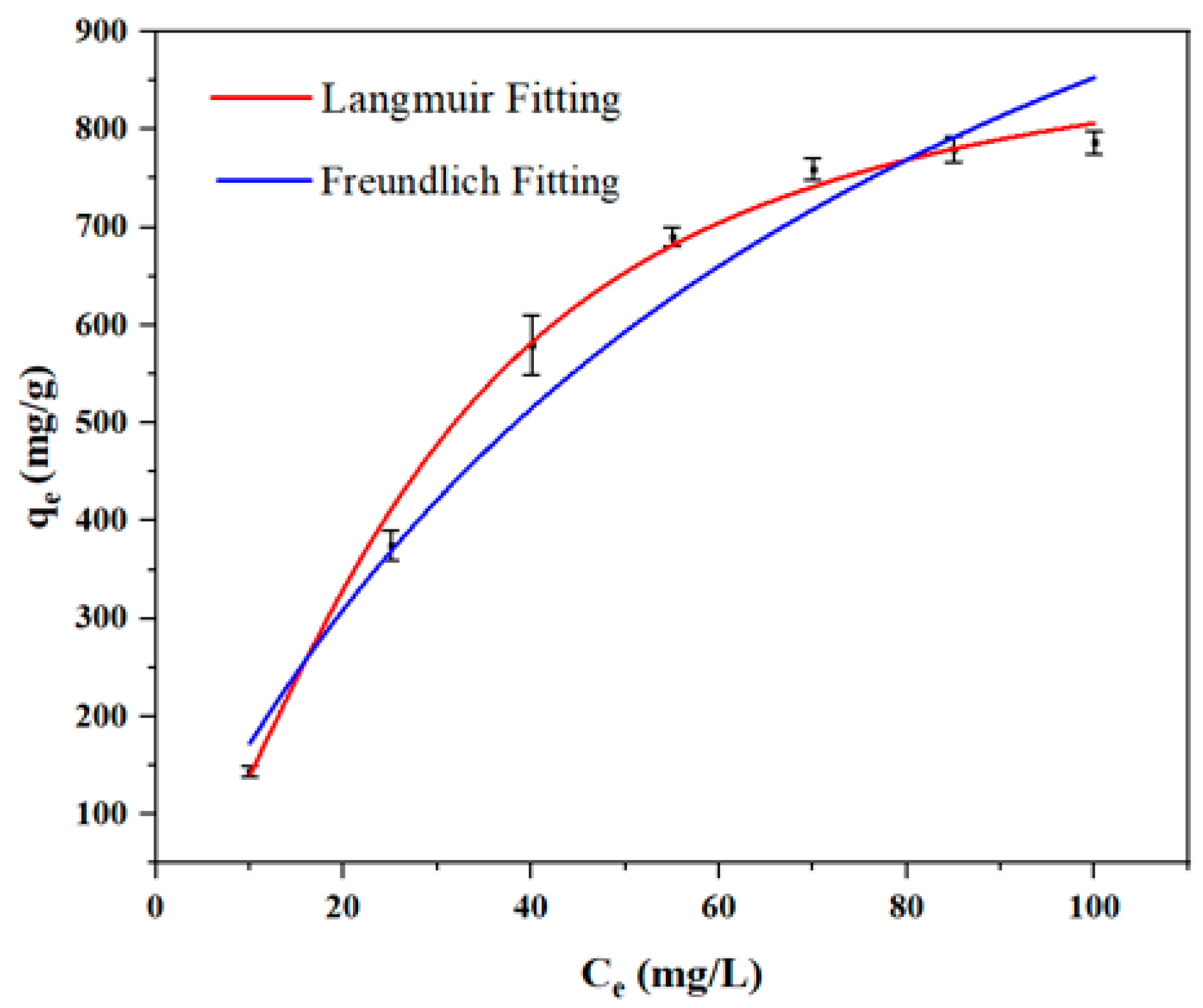
3.2.3. Adsorption Isotherm Study
3.3. Regeneration and Reusability
| Adsorbents | Optimum pH | Dosage (g L−1) | SBET (m2 g−1) | Qmax (mg g−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SHPEI-QP | 5–9 | 0.08 | 77.2 | 905.73 for IBU | This study |
| Carbon nanospheres (CNS) | 6 | 0.8 | 359 | 356.89 for IBU | [35] |
| Magnetic anion exchange resin | 6–8 | 1.0 | 3.62 | 47.4 for IBU | [38] |
| UiO-66(Zr) | 3 | 0.25 | 1139.2 | 729.92 for IBU | [39] |
| SBA-15 | 3 | 10 | 879 | 0.41 for IBU | [40] |
| Mesoporous silver impregnated granules of aluminum mineral | 5–7 | 1.33 | 268 | 8.24 for IBU | [41] |
| Iron-incorporated pomegranate husk carbon (NPH) | 8 | 0.05 | 190 | 39.77 for IBU | [42] |
| Magnetic carboxylic multiwalled carbon nanotube | 1–10 | 0.0125 | 2.38 | 370.52 for IBU | [43] |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- González-González, R.B.; Sharma, A.; Parra-Saldívar, R.; Ramirez-Mendoza, R.A.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Decontamination of Emerging Pharmaceutical Pollutants Using Carbon-Dots as Robust Materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, S.K.; Singh, R. Bioelectrochemical Treatment of Emerging Contaminants and Molecular Characterization of Transformation Products in Landfill Leachate. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2025, 30, 102153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Rana, A.; Sharma, G.; Naushad, M.; Dhiman, P.; Kumari, A.; Stadler, F.J. Recent Advances in Nano-Fenton Catalytic Degradation of Emerging Pharmaceutical Contaminants. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Iqbal, J.; Deng, C.; Wenjing, X.; Galstyan, H. Innovative Desalination Strategies for the Removal of Emerging Pollutants in Aquatic Systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 360, 131241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verlicchi, P.; Al Aukidy, M.; Galletti, A.; Petrovic, M.; Barceló, D. Hospital Effluent: Investigation of the Concentrations and Distribution of Pharmaceuticals and Environmental Risk Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 430, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, S.; Jindal, R.; Kho, Y.L.; Eo, S.; Choi, K. Major Pharmaceutical Residues in Wastewater Treatment Plants and Receiving Waters in Bangkok, Thailand, and Associated Ecological Risks. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Flowers, R.C.; Weinberg, H.S.; Singer, P.C. Occurrence and Removal of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCPs) in an Advanced Wastewater Reclamation Plant. Water Res. 2011, 45, 521–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, I.; Kawakami, T.; Onodera, S. Monitoring the Concentrations of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Cyclooxygenase-Inhibiting Activities in the Surface Waters of the Tone Canal and Edo River Basin. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2015, 50, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paíga, P.; Santos, L.H.M.L.M.; Amorim, C.G.; Araújo, A.N.; Montenegro, M.C.B.S.M.; Pena, A.; Delerue-Matos, C. Pilot Monitoring Study of Ibuprofen in Surface Waters of North of Portugal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 20, 2410–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginebreda, A.; Muñoz, I.; de Alda, M.L.; Brix, R.; López-Doval, J.; Barceló, D. Environmental Risk Assessment of Pharmaceuticals in Rivers: Relationships between Hazard Indexes and Aquatic Macroinvertebrate Diversity Indexes in the Llobregat River (NE Spain). Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vom Hofe, I.; Stricker, B.H.; Ikram, M.K.; Wolters, F.J.; Ikram, M.A. Long-Term Exposure to Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Medication in Relation to Dementia Risk. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2025, 73, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Bian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Du, R.; Li, M.; Tan, Y.; Feng, X. Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) in the Environment: Recent Updates on the Occurrence, Fate, Hazards and Removal Technologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, C.; Pereira, M.I.P.; Valério, P.; Barroso, J.B.; Mendes, T.; Pereira, J.G. Incidence of Kidney Toxicity of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs in Critically Ill Patients. J. Crit. Care 2025, 90, 155202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, S.; Coimbra, A.M.; Herath, L.A.; Alves, N.; Pinheiro, M.; Ribeiro, M.; Morais, H.; Branco, R.; Martinez, O.; Santos, H.G.; et al. Are Environmental Levels of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs a Reason for Concern? Chronic Life-Cycle Effects of Naproxen in Zebrafish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 19627–19638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Geng, J.; Hu, H.; Ma, H.; Gao, X.; Ren, H. Impact of Selected Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Pharmaceuticals on Microbial Community Assembly and Activity in Sequencing Batch Reactors. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Adhikary, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Dutta, S.; CHATTERJEE, S.D.; Banerjee, D.; Ganguly, A.; Rajak, P. Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products as Emerging Environmental Contaminants: Prevalence, Toxicity, and Remedial Approaches. J. Chem. Health Saf. 2023, 30, 362–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlunguza, N.Y.; Ncube, S.; Nokwethemba Mahlambi, P.; Chimuka, L.; Madikizela, L.M. Adsorbents and Removal Strategies of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs from Contaminated Water Bodies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco-Urrea, E.; Pérez-Trujillo, M.; Cruz-Morató, C.; Caminal, G.; Vicent, T. Degradation of the Drug Sodium Diclofenac by Trametes Versicolor Pellets and Identification of Some Intermediates by NMR. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 176, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco-Urrea, E.; Pérez-Trujillo, M.; Cruz-Morató, C.; Caminal, G.; Vicent, T. White-Rot Fungus-Mediated Degradation of the Analgesic Ketoprofen and Identification of Intermediates by HPLC–DAD–MS and NMR. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Q.; Dai, L.; Dang, Z. Occurrence, Removal and Risk Evaluation of Ibuprofen and Acetaminophen in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants: A Critical Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 891, 164600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rimawi, L.N.; Al-Jabari, M.H.; Sulaiman, S.M.; Nazal, M.K.; Idrees, A.S. Pencil Graphite Synergistic Improvement of Zero-Valent Iron Composite for the Removal of Diclofenac Sodium in Aqueous Solutions: Kinetics and Comparative Study. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, T.S.; Crestani, L.; Marchezi, G.; Melara, F.; de Mello, J.R.; Dotto, G.L.; Piccin, J.S. Synthesis of Glutaraldehyde-Modified Silica/Chitosan Composites for the Removal of Water-Soluble Diclofenac Sodium. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 277, 118868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, C.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Ding, W.; Zheng, H. Degradation of Diclofenac Sodium with Low Concentration from Aqueous Milieu through Polydopamine-Chitosan Modified Magnetic Adsorbent-Assisted Photo-Fenton Process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 289, 120771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Deng, S.; Huang, Q.; Nie, Y.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Yu, G. Regenerable Granular Carbon Nanotubes/Alumina Hybrid Adsorbents for Diclofenac Sodium and Carbamazepine Removal from Aqueous Solution. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4139–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Fan, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Shen, X.; Wu, C.; Huang, Y.; Huang, G.; Huang, H.; Zheng, M. A 3D Stable Metal–Organic Framework for Highly Efficient Adsorption and Removal of Drug Contaminants from Water. Polymers 2018, 10, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Cheng, G.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Zhu, G. Highly Efficient and Rapid Removal of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs from Environmental Samples Based on an Eco-Friendly ZIF-67-Molecularly Imprinted Composite. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 443, 136396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Tong, J.; Lan, H.; Pan, D. Fabrication of Polyethyleneimine-Functionalized Magnetic Cellulose Nanocrystals for the Adsorption of Diclofenac Sodium from Aqueous Solutions. Polymers 2022, 14, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, S.; Saikia, A.; Purkait, M.K.; Mohanty, K. Chitosan Based Ceramic Ultrafiltration Membrane: Preparation, Characterization and Application to Remove Hg(II) and As(III) Using Polymer Enhanced Ultrafiltration. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 170, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Huang, X.; Peng, K.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lu, L.; Liu, J.; Li, S. PDA-PEI Copolymerized Highly Hydrophobic Sponge for Oil-In-Water Emulsion Separation via Oil Adsorption and Water Filtration. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 406, 126743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, C.; Gou, X.; Fan, Y.; Chen, J. Underwater Suspended Bifunctionalized Polyethyleneimine-Based Sponge for Selective Removal of Anionic Pollutants from Aqueous Solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjan, A.M.; Premakshi, H.G.; Kariduraganavar, M.Y. Synthesis and Characterization of GTMAC Grafted Chitosan Membranes for the Dehydration of Low Water Content Isopropanol by Pervaporation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 25, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godiya, C.B.; Kumar, S.; Xiao, Y. Amine Functionalized Egg Albumin Hydrogel with Enhanced Adsorption Potential for Diclofenac Sodium in Water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Gou, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z. Dendritic Bifunctional Nanotraps inside SBA-15 for Highly Efficient Removal of Selected Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs from Wastewater. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2024, 43, e14347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Liang, R.; Sun, G. Super-Adsorbent Hydrogel for Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Aqueous Solution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 17612–17624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alluhaybi, A.A.; Hameed, A.M.; Alotaibi, M.T.; Alharbi, A.; Shahat, A. Synthesis and Characterization of Carbon Nanospheres for Adsorption of Ibuprofen from Aqueous Solution: Optimization by Box–Behnken Design. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 383, 122059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.I.; Ayati, A.; Farghali, M.; Krivoshapkin, P.V.; Tanhaei, B.; Karimi-Maleh, H.; Krivoshapkina, E.F.; Taheri, P.; Tracey, C.; Al-Fatesh, A.S.; et al. Advanced Adsorbents for Ibuprofen Removal from Aquatic Environments: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 22, 373–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, L.; Białoszewska, M.; Malinowski, S.; Franus, W. Adsorptive Performance of Fly Ash-Derived Zeolite Modified by β-Cyclodextrin for Ibuprofen, Bisphenol a and Caffeine Removal from Aqueous Solutions—Equilibrium and Kinetic Study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 562, 150160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, H.; Shuang, C.; Li, A.; Wang, C.; Huang, Y. Effect of Pore Structure on Adsorption Behavior of Ibuprofen by Magnetic Anion Exchange Resins. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 210, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Sharma, S.; Umar, A.; Jha, M.; Mehta, S.K.; Kansal, S.K. Nanocuboidal-Shaped Zirconium Based Metal Organic Framework for the Enhanced Adsorptive Removal of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug, Ketorolac Tromethamine, from Aqueous Phase. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 1921–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, H.; Ma, D.; Chen, Y.; Bao, X.; Klein-Hoffmann, A.; Pfänder, N.; Su, D.S. Alkanes-Assisted Low Temperature Formation of Highly Ordered SBA-15 with Large Cylindrical Mesopores. Chem. Commun. 2005, 42, 5343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, A.D.; Gopal, K.; Jain, R. Strengthening Adsorption Characteristics of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug onto Microwave-Assisted Mesoporous Material: Process Design, Mechanism and Characterization. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shooto, N.D. Shooto Application of Carbon from Pomegranate Husk for the Removal of Ibuprofen, Cadmium and Methylene Blue from Water. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, C.; Wang, R.; Han, R. Remediation of Ibuprofen and Naproxen in Water by a Green Composite Material of Magnetic Carbon Nanotube–Metal–Organic Framework. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Pharmaceutical | pKa | CAS Number | Log P | Water Solubility (mg L−1) | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IBU | 4.91 | 15687-27-1 | 3.97 | 21 | 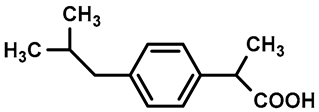 |
| SBET (m2 g−1) | Pore Volume (cm3 g−1) | Pore Size (nm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SHPEI-QP | 77.2 | 0.05 | 25–100 |
| Model | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||||
| Material | qe,exp (mg/g) | qe (mg/g) | K1 (min−1) | R2 | qe (mg/g) | K2 (g/mg·min) | R2 |
| SHPEI-QP | 705.11 | 592.54 | 0.08 | 0.889 | 713.44 | 0.0024 | 0.997 |
| Model | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | |||||||
| Material | qe,exp (mg/g) | qm (mg/g) | KL (L mg−1) | RL | R2 | Kf (L mg−1) | n | R2 |
| SHPEI-QP | 786.66 | 905.73 | 0.156 | 0.0791 | 0.991 | 53.1 | 1.43 | 0.977 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gou, X.; Ahmad, Z.; You, Z.; Ren, Z. Bifunctionalized Polyethyleneimine-Based Sponge for Adsorption of Ibuprofen from Aqueous Solution. Polymers 2025, 17, 3221. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17233221
Gou X, Ahmad Z, You Z, Ren Z. Bifunctionalized Polyethyleneimine-Based Sponge for Adsorption of Ibuprofen from Aqueous Solution. Polymers. 2025; 17(23):3221. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17233221
Chicago/Turabian StyleGou, Xiaoyi, Zia Ahmad, Zaijin You, and Zhou Ren. 2025. "Bifunctionalized Polyethyleneimine-Based Sponge for Adsorption of Ibuprofen from Aqueous Solution" Polymers 17, no. 23: 3221. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17233221
APA StyleGou, X., Ahmad, Z., You, Z., & Ren, Z. (2025). Bifunctionalized Polyethyleneimine-Based Sponge for Adsorption of Ibuprofen from Aqueous Solution. Polymers, 17(23), 3221. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17233221