Calcium Ion-Induced Self-Assembly of Carboxylated Polyallylamine-graft-Poly(Ethylene Glycol) in an Aqueous Medium
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
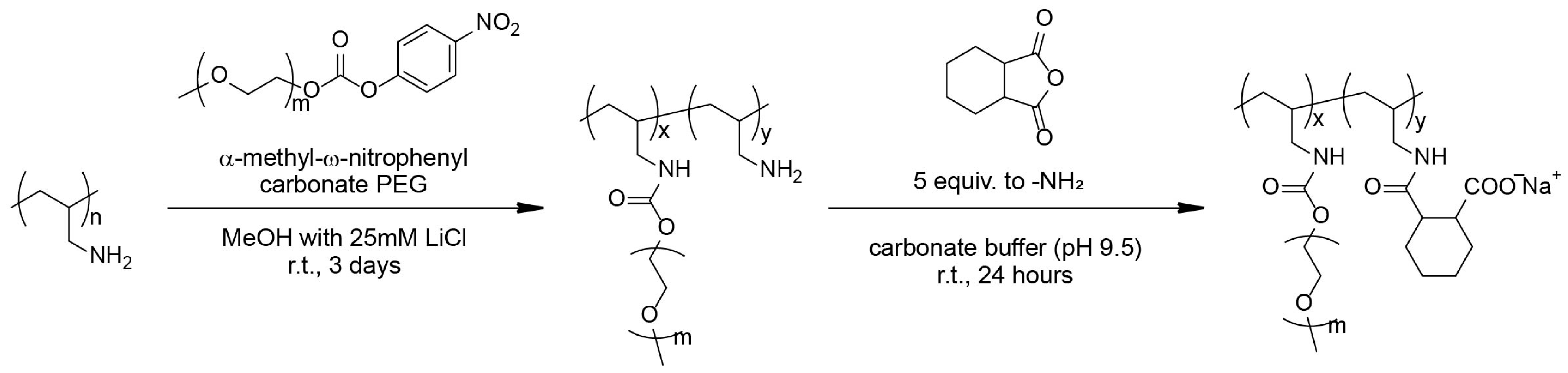
2.2. Synthesis of Carboxylated PAA-g-PEG
2.2.1. Synthesis of α-methyl-ω-nitrophenyl Carbonate PEG
2.2.2. Synthesis of PAA-g-PEG
2.2.3. Carboxylation of Primary Amines in PAA-g-PEG
2.3. Characterization of the Carboxylated PAA-g-PEG Self-Assembly
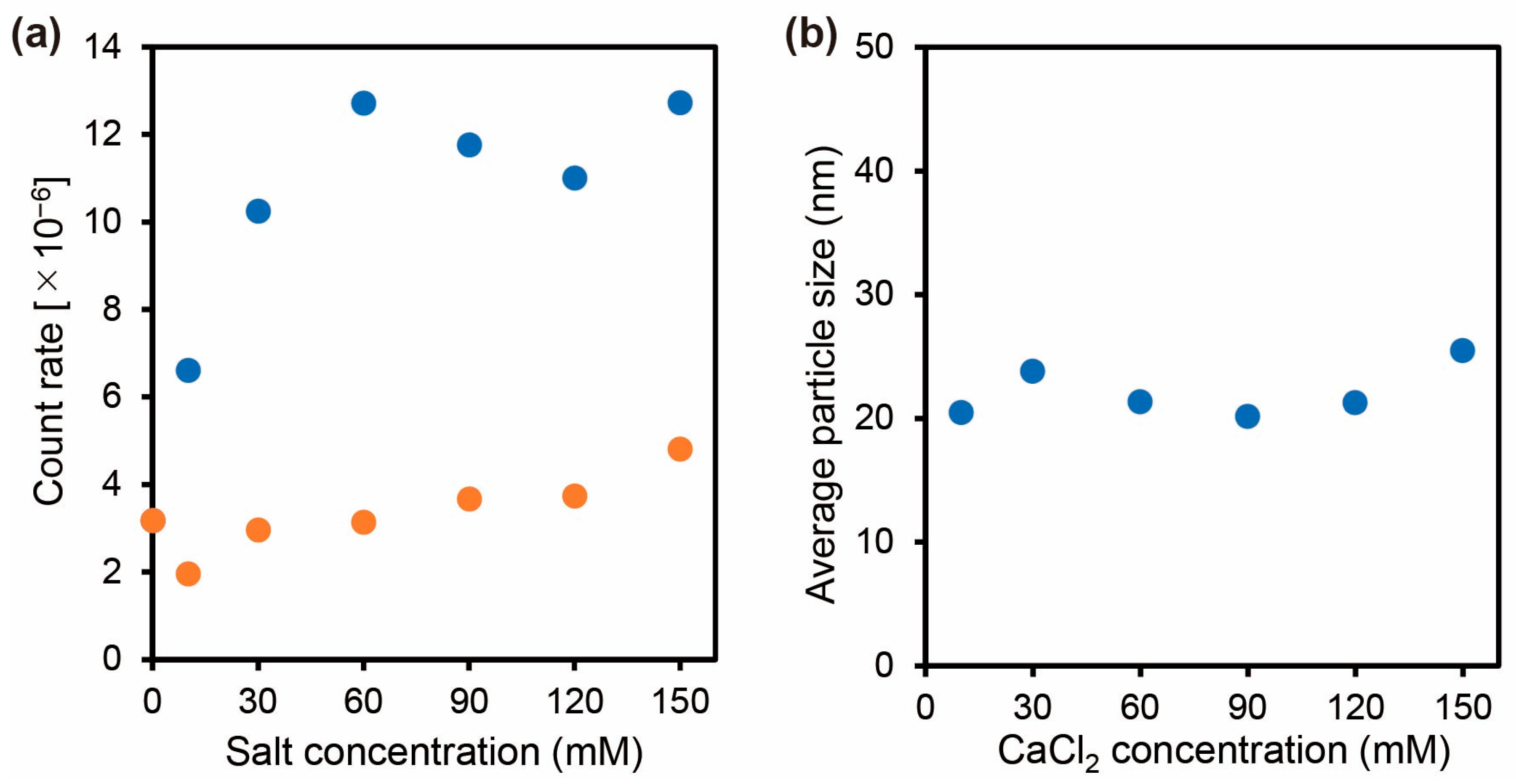
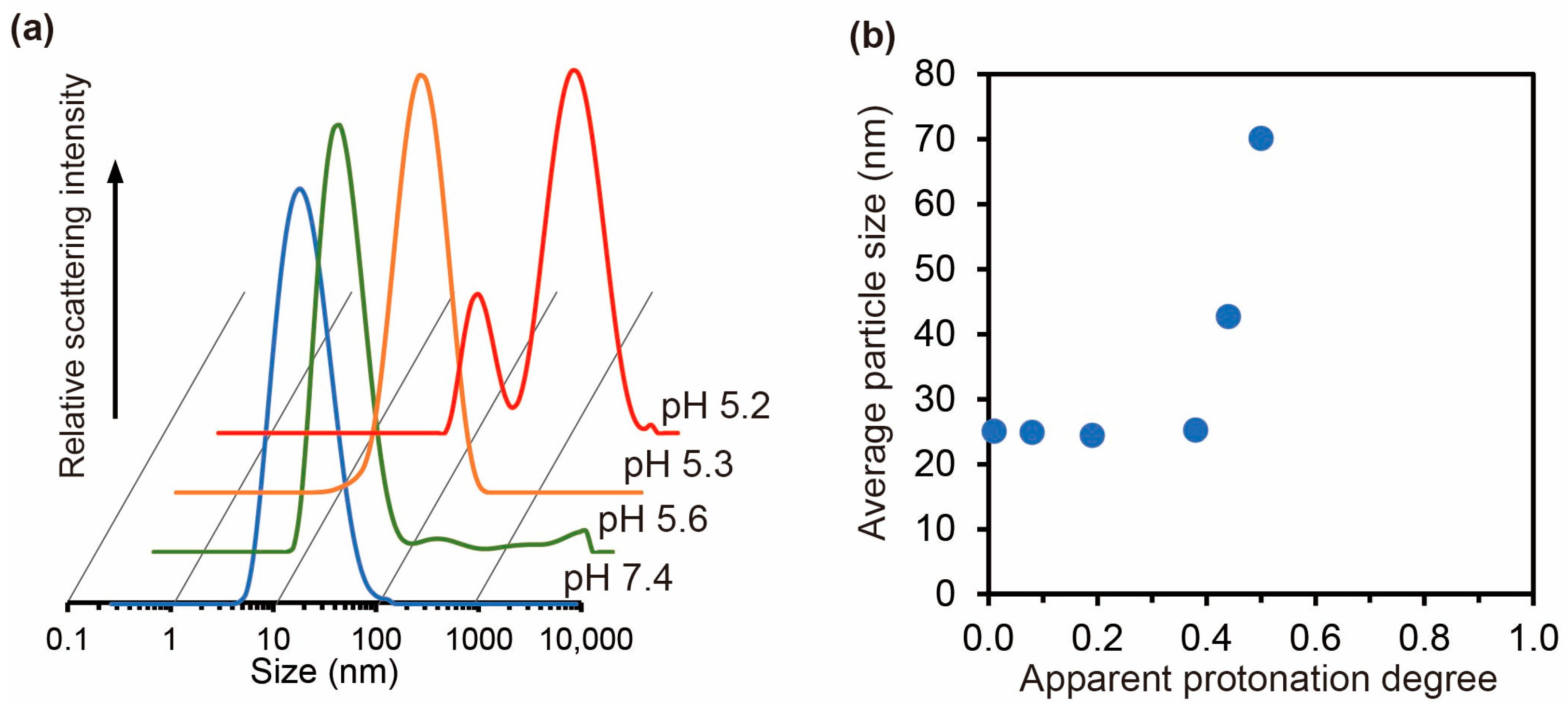
2.3.1. Effect of Salt on Self-Assembly of Carboxylated PAA-g-PEG
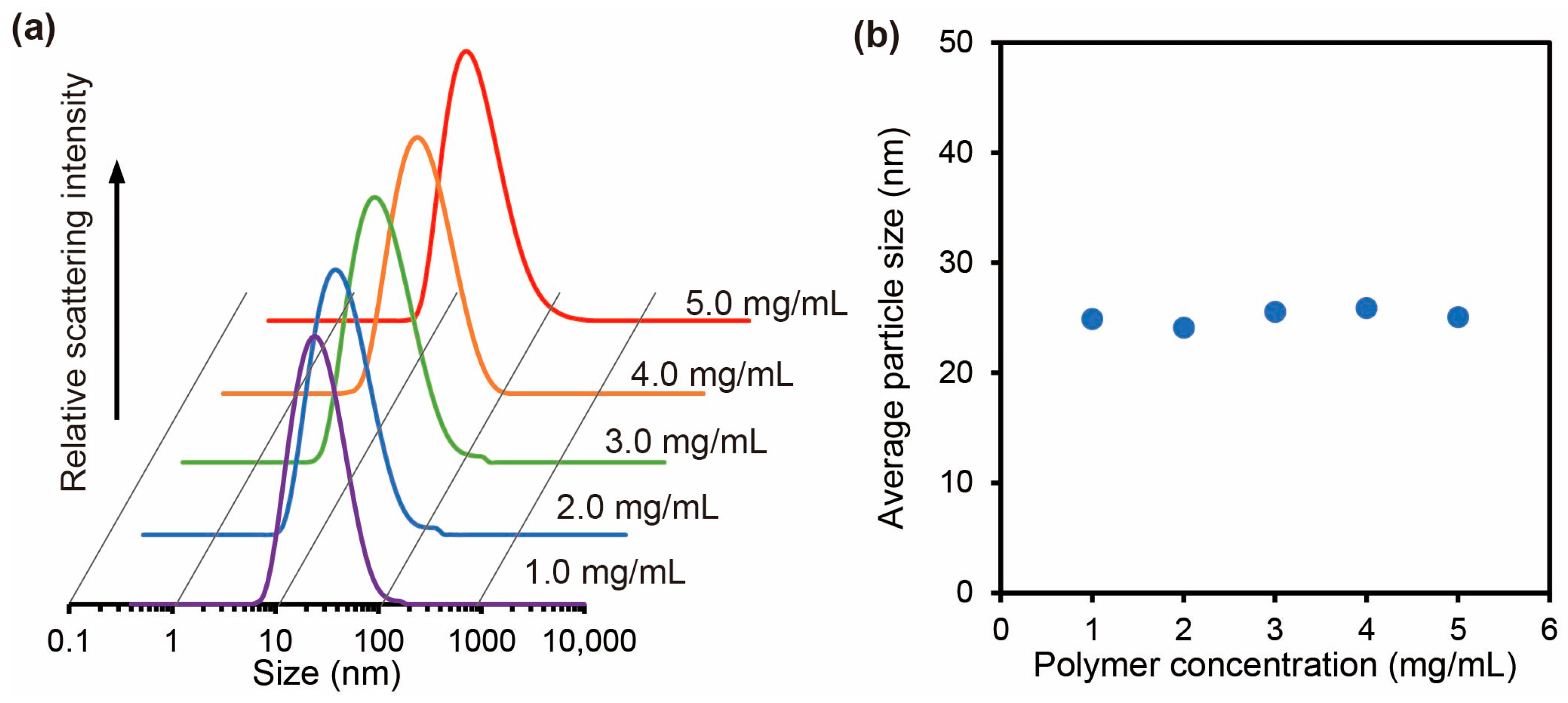
2.3.2. Effect of the Polymer Concentration on Self-Assembly of Carboxylated PAA-g-PEG
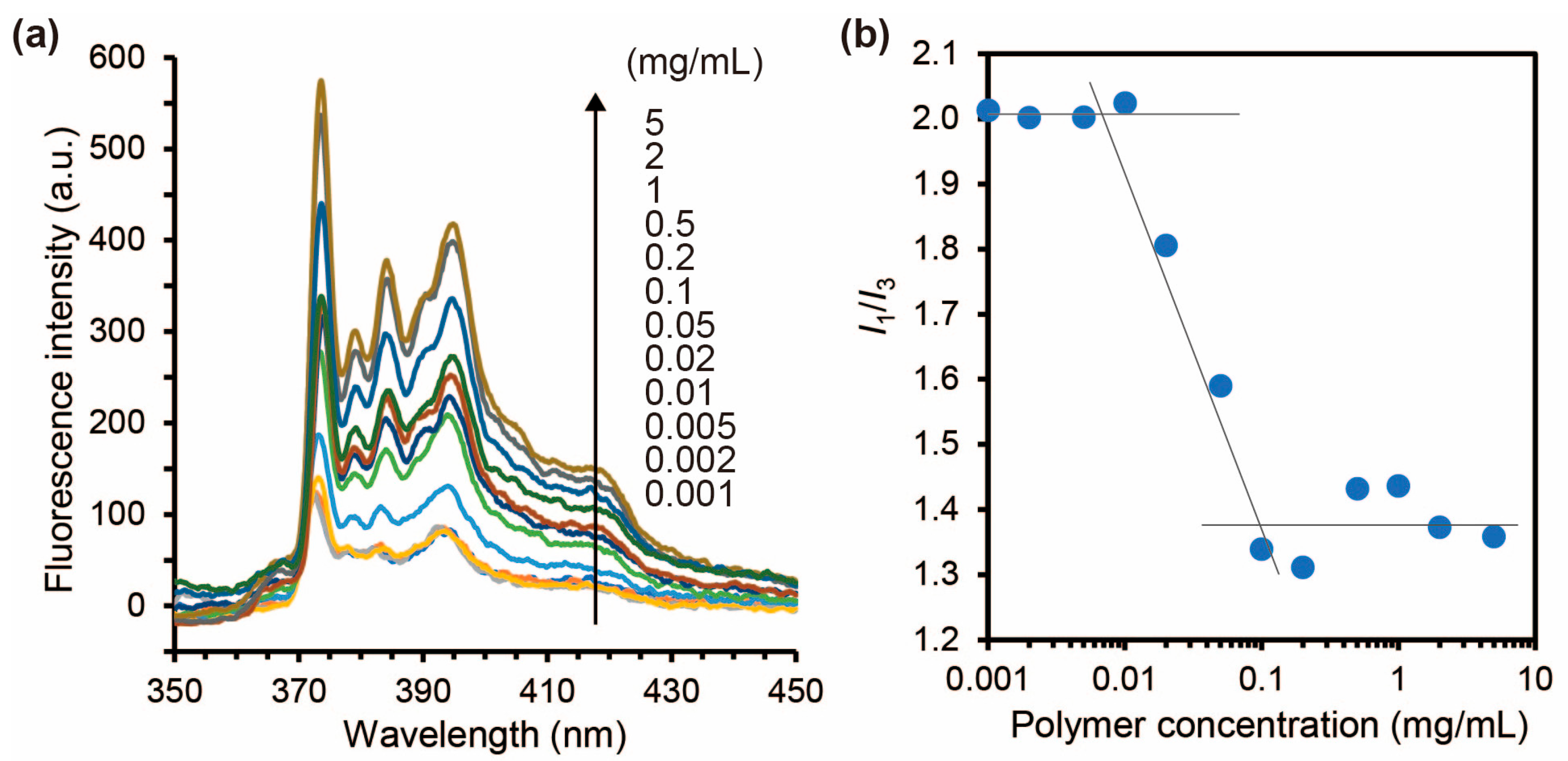
2.3.3. Determination of the Critical Micelle Concentration of the Carboxylated PAA-g-PEG Self-Assemblies
2.3.4. Acid–Base Titration of Carboxylated PAA-g-PEG
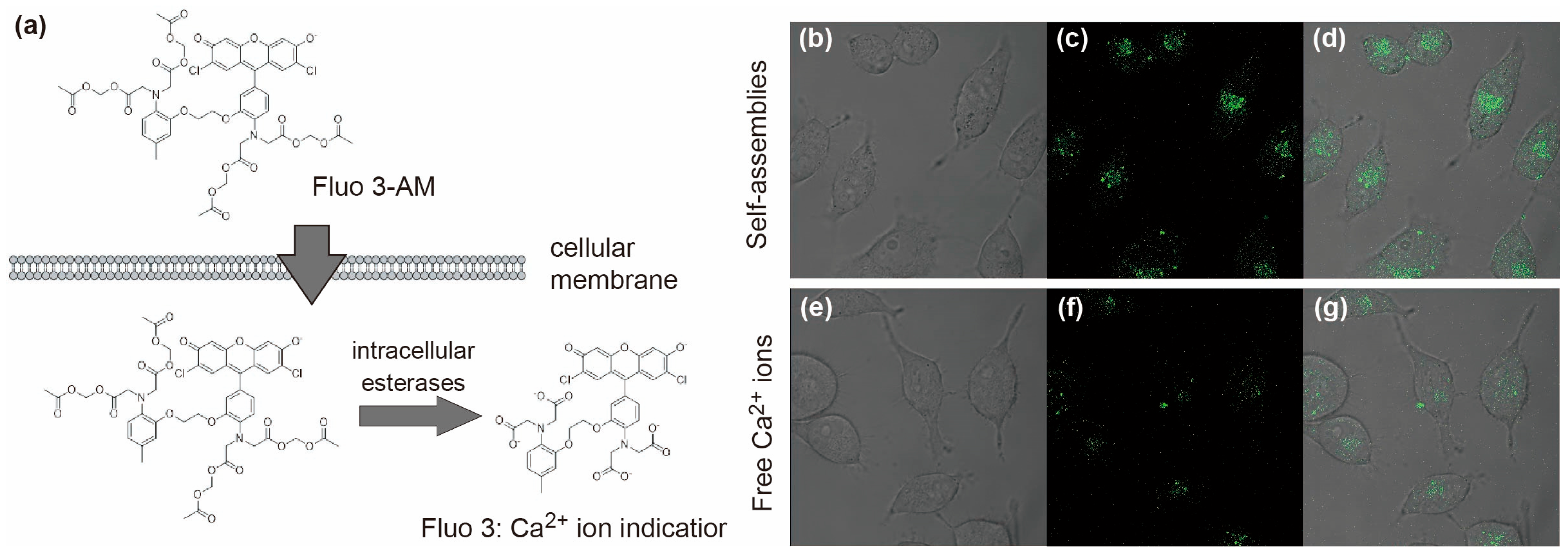
2.3.5. Intracellular Delivery of Ca2+ Ions by the Carboxylated PAA-g-PEG Self-Assembly
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Carboxylated PAA-g-PEG
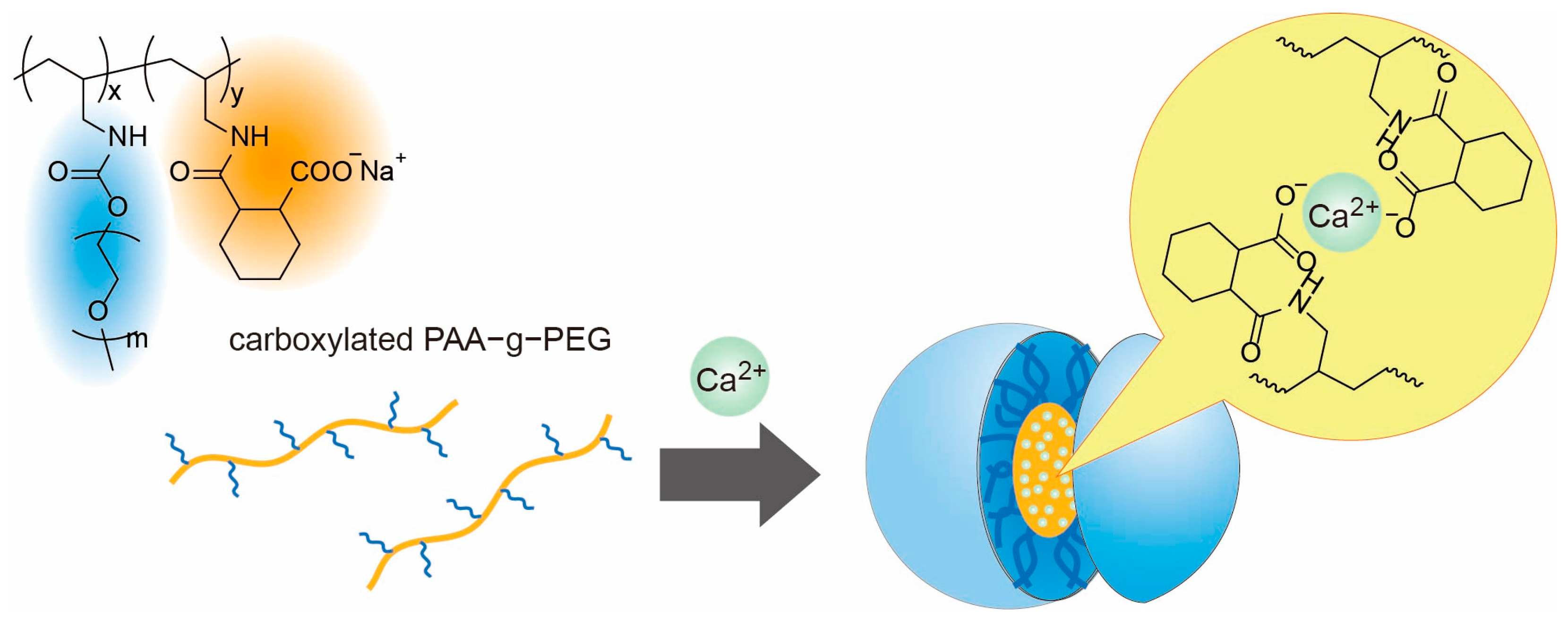
3.2. Ca2+ Ion-Induced Self-Assembly of Carboxylated PAA-g-PEG
3.3. Characterization of the Carboxylated PAA-g-PEG Self-Assemblies
3.4. Intracellular Delivery of Ca2+ Ions by the Carboxylated PAA-g-PEG Self-Assembly
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Willersinn, J.; Schmidt, V.B. Self-Assembly of Double Hydrophilic Poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)-b-poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone) Block Copolymers in Aqueous Solution. Polymers 2017, 9, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willersinn, J.; Schmidt, V.B. Aqueous self-assembly of pullulan-b-poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) double hydrophilic block copolymers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 55, 3757–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohy, J.; Creutz, S.; Garcia, M.; Mahltig, B.; Stamm, M.; Jérôme, R. Aggregates Formed by Amphoteric Diblock Copolymers in Water. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 6378–6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.T.; Procházka, K.; Munk, P.; Webber, E.S. pH-Dependent Micellization of Poly(2-vinylpyridine)-block-poly(ethylene oxide). Macromolecules 1996, 29, 6071–6073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arotçaréna, M.; Heise, B.; Ishaya, S.; Laschewsky, A. Switching the Inside and the Outside of Aggregates of Water-Soluble Block Copolymers with Double Thermoresponsivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 3787–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, Y.; Mochiduki, H.; Ikeda, I. Hydration Changes during Thermosensitive Association of a Block Copolymer Consisting of LCST and UCST Blocks. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2004, 25, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakrishna, K.; Jewrajka, K.S.; Ruiz, A.; Marcilla, R.; Pomposo, A.J.; Mecerreyes, D.; Taton, D.; Gnanou, Y. Synthesis by RAFT and Ionic Responsiveness of Double Hydrophilic Block Copolymers Based on Ionic Liquid Monomer Units. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 6299–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosnan, M.S.; Schlaad, H.; Antonietti, M. Aqueous Self-Assembly of Purely Hydrophilic Block Copolymers into Giant Vesicles. Angew. Chem. 2015, 54, 9715–9718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Tang, Y.; Armes, P.S. Direct Synthesis and Stimulus-Responsive Micellization of Y-Shaped Hydrophilic Block Copolymers. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 9728–9737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ge, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Luo, S.; Liu, H.; Liu, S. Synthesis and Micellization Properties of Double Hydrophilic A2BA2 and A4BA4 Non-Linear Block Copolymers. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 8178–8185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Lei, X.; Yuan, W. Synthesis and self-assembly of double-hydrophilic pentablock copolymer with pH and temperature responses via sequential atom transfer radical polymerization. Mater. Lett. 2012, 67, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, T.; Nagao, M.; Hoshino, Y.; Miura, Y. Self-Assembly of a Double Hydrophilic Block Glycopolymer and the Investigation of Its Mechanism. Langmuir 2018, 34, 8591–8598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wu, J.; Duan, J. Synthesis and self-assembly of thermo/pH-responsive double hydrophilic brush-coil copolymer with poly(L-glutamic acid) side chains. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 397, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Z.; Cai, Y.; Yin, J.; Zhu, Z.; Rao, J.; Liu, S. Synthesis and ‘Schizophrenic’ Micellization of Double Hydrophilic AB4 Miktoarm Star and AB Diblock Copolymers: Structure and Kinetics of Micellization. Langmuir 2007, 23, 1114–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Shen, Z.; Gu, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Lu, G.; Huang, X. Synthesis and characterization of PNIPAM-b-(PEA-g-PDEA) double hydrophilic graft copolymer. Polym. Chem. 2008, 46, 5638–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; He, P.; Xiao, C.; Gao, X.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, X. Synthesis of temperature and pH-responsive crosslinked micelles from polypeptide-based graft copolymer. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 359, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaive, A.; Amiel, C.; Volet, G. Synthesis and thermoresponsive behavior of double hydrophilic graft copolymer based on poly(2-methyl-2-oxazoline) and poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline). Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 179, 111504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gong, Y.; Nakashima, K.; Murata, Y. Nanoaggregate Formation of Poly(ethylene oxide)-b-polymethacrylate Copolymer Induced by Alkaline Earth Metal Ion Binding. Langmuir 2002, 18, 6727–6729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronich, K.T.; Keifer, A.P.; Shlyakhtenko, S.L.; Kabanov, V.A. Polymer Micelle with Cross-Linked Ionic Core. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 8236–8237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjandra, W.; Yao, J.; Ravi, P.; Tam, C.K.; Alamsjah, A. Nanotemplating of Calcium Phosphate Using a Double-Hydrophilic Block Copolymer. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 4865–4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondjaja, R.H.; Hatton, A.T.; Tam, C.K. Self-Assembly of Poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(acrylic acid) Induced by CaCl2: Mechanistic Study. Langmuir 2008, 24, 8501–8506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandino, A.; Macías, M.; Cantero, D. Formation of calcium alginate gel capsules: Influence of sodium alginate and CaCl2 concentration on gelation kinetics. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 1999, 88, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, A.; Kojima, C.; Iijima, M.; Harada, A.; Kono, K. Polyion Complex Micelles Formed From Glucose Oxidase and Comb-Type Polyelectrolyte with Poly(ethylene glycol) Grafts. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2008, 46, 3459–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugaboopathy, S.; Matsuoka, H. Surface Active to Non-Surface Active Transition and Micellization Behaviour of Zwit-terionic Amphiphilic Diblock Copolymers: Hydrophobicity and Salt Dependency. Polymers 2017, 9, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, G.B.; Chakraborty, I.; Moulik, S.P. Pyrene absorption can be a convenient method for probing critical micellar concentration (cmc) and indexing micellar polarity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 294, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñeiro, L.; Novo, M.; Al-Soufi, W. Fluorescence emission of pyrene in surfactant solutions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 215, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsionis, A.I.; Vaimakis, T.C. Estimation of AOT and SDS CMC in a methanol using conductometry, viscometry and pyrene fluorescence spectroscopy methods. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2012, 547, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.C.; Winnik, M.A. The Py scale of solvent polarities. Can. J. Chem. 1984, 62, 2560–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khutoryanskiy, V.V.; Dubolazov, V.A.; Nurkeeva, S.Z.; Mun, A.G. pH Effects in the Complex Formation and Blending of Poly(acrylic acid) with Poly(ethylene oxide). Langmuir 2004, 20, 3785–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohy, J.F.; Varshney, S.K.; Jérôme, R. Water-Soluble Complexes Formed by Poly(2-vinylpyridinium)-block-poly(ethylene oxide) and Poly(sodium methacrylate)-block-poly(ethylene oxide) Copolymers. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 3361–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Peng, Z.; Liu, X.; Tong, Z. Synthesis and pH-sensitive micellization of doubly hydrophilic poly(acrylic acid)-b-poly(ethylene oxide)-b-poly(acrylic acid) triblock copolymer in aqueous solutions. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2010, 288, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolsover, S.R. Calcium signaling in growth cone migration. Cell Calcium 2005, 37, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konur, S.; Ghosh, A. Calcium signaling and the control of dendritic development. Neuron 2005, 46, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeno, S.; Niki, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; Morioka, H.; Yatabe, T.; Funayama, A.; Toyama, Y.; Taguchi, T.; Tanaka, J. The effect of calcium ion concentration on osteoblast viability, proliferation and differentiation in monolayer and 3D culture. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 4847–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, J.P. The calcium-sensing receptor in bone cells: A potential therapeutic target in osteoporosis. Bone 2010, 46, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarn, D.; Xue, M.; Zink, I.J. pH-Responsive Dual Cargo Delivery from Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with a Metal-Latched Nanogate. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 2044–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteith, R.G.; McAndrew, D.; Faddy, M.H.; Roberts-Thomson, J.S. Calcium and cancer: Targeting Ca2+ transport. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarn, D.; Yu, C.; Lu, J.; Hartz, A.; Tamanoi, F.; Zink, I.J. In vitro delivery of calcium ions by nanogated mesoporous silica nanoparticles to induce cancer cellular apoptosis. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2017, 2, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Emoto, J.; Kitayama, Y.; Harada, A. Calcium Ion-Induced Self-Assembly of Carboxylated Polyallylamine-graft-Poly(Ethylene Glycol) in an Aqueous Medium. Polymers 2025, 17, 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17233129
Emoto J, Kitayama Y, Harada A. Calcium Ion-Induced Self-Assembly of Carboxylated Polyallylamine-graft-Poly(Ethylene Glycol) in an Aqueous Medium. Polymers. 2025; 17(23):3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17233129
Chicago/Turabian StyleEmoto, Junya, Yukiya Kitayama, and Atsushi Harada. 2025. "Calcium Ion-Induced Self-Assembly of Carboxylated Polyallylamine-graft-Poly(Ethylene Glycol) in an Aqueous Medium" Polymers 17, no. 23: 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17233129
APA StyleEmoto, J., Kitayama, Y., & Harada, A. (2025). Calcium Ion-Induced Self-Assembly of Carboxylated Polyallylamine-graft-Poly(Ethylene Glycol) in an Aqueous Medium. Polymers, 17(23), 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17233129







